Research Progress of Fermented Functional Foods and Protein Factory-Microbial Fermentation Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Fermentation
4. Functional Foods
5. Health Promotion and Fermentation
6. The Method of Protein Mass Expression
7. Fermentation Technologies
7.1. Solid State Fermentation (SSF)
7.2. Submerged Fermentation (SmF)
8. Lactic Acid Fermentation and Protein
9. Alcoholic Fermentation and Protein
10. Acetic Acid Fermentation and Protein
11. Eukaryotic Microorganism Species and Fermentation Technology
12. Prokaryotic Microorganism Species and Fermentation Technology
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Erkmen, O.; Bozoglu, T.F. Basic principles of food fermentation. In Food Microbiology: Principles into Practice; Erkmen, O., Bozoglu, T.F., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016; Volume 2: Microorganisms in Food Preservation and Processing, pp. 228–252. [Google Scholar]
- Erkmen, O.; Bozoglu, T.F. Microbial metabolism of food components. In Food Microbiology: Principles into Practice; Erkmen, O., Bozoglu, T.F., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016; Volume 2: Microorganisms in Food Preservation and Processing, pp. 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig, C.; Rousta, N.; Wikandari, R.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Haggblom-Kronlof, G.; Bolton, K.; Rousta, K. Household fermentation of leftover bread to nutritious food. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.F.; Garcia-Bejar, B.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Hansen, E.B. Extracellular microbial proteases with specificity for plant proteins in food fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 381, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, K. Fermentation trip: Amazing microbes, amazing metabolisms. Ann Microbiol. 2018, 68, 7171–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, W. The importance of neglected and underutilized medicinal plants from South America in modern pharmaceutical sciences. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2022, 19, 7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, W. Wonderful natural drugs with surprising nutritional values, Rheum species, gifts of the nature. Lett Org Chem. 2022, 19, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Millan, J.-A.; Aznar, A.; Conesa, E.; Conesa-Bueno, A.; Aguayo, E. Functional food obtained from fermentation of broccoli by-products (stalk): Metagenomics profile and glucosinolte and phenolic compounds characterization by LC-ESI-QqQ-MS/MS. LWT 2022, 169, 113915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Health benefits of wolfberry (Gou Qi Zi) on the basis of ancient Chinese herbalism and western modern medicine. Avicenna. J. Phytomed. 2021, 11, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Barberry (Berberis vulgaris), a medicinal fruit and food with traditional and modern pharmaceutical uses. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2021, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q. Natural dietary and medicinal plants with anti-obesity therapeutics activities for treatment and prevention of obesity during lock down and in post-COVID-19 era. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.F.; Ng, K.R.; Samarasiri, M.; Chen, W.N. Precision fermentation to advance fungal food fermenations. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H. Medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory activities for natural and organic healing. Curr. Org. Chem. 2021, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W. Importance of thymoquinone, sulforaphane, phloretin, and epigallocatechin and their health benefits. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2022, 19, 10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, W. The most important medicinal herbs and plants in traditional Chinese and Iranian medicinal sciences with antioxidant activities. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2022, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. The importance of flavonoids and phytochemicals of medicinal plants with antiviral activities. Mini.-Rev. Org. Chem. 2022, 19, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, K.; Li, H. Nano iron materials enhance food waste fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.H.; Lubeck, M.; Moller, A.H.; Dalsgaard, T.K. Protein recovery and quality of alfalfa extracts obtained by acid precipitation and fermentation. Bioresour. Technolo. Rep. 2022, 19, 101190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cen, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y. Exploring the roles of microorganisms and metabolites in the fermentation sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) based on high-throughput sequencing and untargeted metabolomics. LWT 2022, 167, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pswarayi, F.; Ganzle, M. African cereal fermentations: A review on fermentation processes and microbial composition of non-alcoholic fermented cereal foods and beverages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 378, 109815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Vuyst, L.D. Lactic acid bacteria as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Carboune, Q.; Saucedo-Castaneda, G.; Cazares-Marinero, J.D.J. Biosurfactants: The green generation of speciality chemicals and potential production using Solid-State fermentation (SSF) technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H. High rejection rate of polysaccharides by microfiltration benefits Christensenella minuta and acetic acid production in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for sludge fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Liang, C.-H.; Qu, C.-H.; Liang, Z.-C. Zinc ion addition to grain media enhanced hispidin production during solid-state fermentation of Phellinus linteus. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 121, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.L.; Paufler, S.; Harms, H.; Maskow, T.; Schlosser, D. Applicability and information value of biocalorimetry for the monitoring of fungal solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic agricultural by-products. New Biotechnol. 2022, 66, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Xiang, L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Q. Solid-state fermentation with pretreated rice husk: Green technology for the distilled spirit (Baijiu) production. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrero-Lopez, A.M.; Valencia, C.; Dominguez, G.; Eugenio, M.E.; Franco, J.M. Rheology and adhesion performance of adhesives formulated with lignins from agricultural waste straws subjected to solid-state fermentation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 1771, 113876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes-Betancur, D.P.; Marquez-Cardozo, C.J.; Cadena-Chamorro, E.M.; Martinez-Saldarriaga, J.; Torres-Leon, C.; Ascacio-Valdes, A.; Aguilar, C.N. Solid-state fermentation-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from has avocado seeds. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda-Cejudo, N.D.; Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.J.; Sepulveda, L.; Torres-Leon, C.; Chavez-Gonzalez, M.L.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Aguilar, C.N. Recovery of ellagic acid from mexican rambutan peel by solid-state fermentation-assisted extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 134, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhao, H.; Edwards, N.; Peyer, L.; Tao, Y.; Arneborg, N. The effects of cell-cell contact between Pichia kluyveri and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on amino acids and volatiles in mixed culture alcoholic fermentations. Food Microbiol. 2022, 103, 103960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namboodiri, M.M.T.; Paul, T.; Medisetti, R.M.N.; Pakshirajan, K.; Narayanasamy, S.; Pugazhenthi, G. Solid state fermentation of rice straw using Penicillium citrinum for chitosan production and application as nanobiosorbent. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, L. The influence of protease hydrolysis of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation induced soybean protein gel: Protein molecule, peptides and amino acids. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Xia, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Lang, F.; Song, J.; Wang, M. Kinetics of predominant microorganisms in the multi-microorganisms solid-state fermentation of cereal vinegar. LWT 2022, 159, 113209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Leon, C.; Ramirez-Guzman, N.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.; Serna-Cock, L.; Correia, M.T.D.S.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Aguilar, C.N. Solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger to enhance the phenolic contents and antioxidative activity of Mexican mango seed: A promising source of natural antioxidants. LWT 2019, 112, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, S.A.; Rasit, N.; Ooi, C.K. Statistical analysis of xylanase production from solid state fermentation of rice husk associated fungus Aspergillus niger. Mater. Today Proceed. 2021, 39, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Vittone, S.; Barrena, R.; Sanchez, A.; Artola, A. Scanning agro-industrial wastes as substrates for fungal biopesticide production: Use of Beauveria bassiana and Trichoderma harzianum in solid-state fermentation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Sui, M.; Jiang, G.; Xiao, J.; Ning, Y.; Ma, C.; et al. Microbial community succession in the fermentation of Qingzhuan tea at various temperatures and their correlations with the quality formation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 382, 109937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, M.A.; Webb, C. Design aspects of solid state fermentation as applied to microbial bioprocessing. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 4, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, A.; Artola, A.; Barrena, R.; Font, X.; Gea, T.; Sanchez, A. Innovative production of bioproducts from organic waste through solid-state fermentation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpali-Tsigbe, N.D.K.; Ma, Y.; Ekumah, J.-N.; Osabutey, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, M.; Johnson, N.A.N.; Quaisie, J. Two-step optimization of solid-state fermentation conditions of heliong48 soybean variety for maximum chlorogenic acid extraction yield with improved antioxidant activity. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 168, 113565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; He, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Characteristics fingerprints and change of volatile organic compounds of dark teas during solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum by using HS-GC-IMS, HS-SPME-GC-MS, E-nose and sensory evaluation. LWT 2022, 169, 113925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, T.; Zhaong, X.-Z.; Chai, L.-J.; Lu, Z.-M.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Komagataeibacter europaeus improves community stability and function in solid-state cereal vinegar fermentation ecosystem: Non-abundant species plays important role. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Feng, K.; Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J. Promote lactic acid production from food waste fermentation using biogas slurry recirculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gui, R.; Li, N.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, Z.; Yang, S.-T.; Li, X. Production of soluble dietary fibers and red pigments from potato pomace in submerged fermentation by Monascus purpureus. Process. Biochem. 2021, 111, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Mazza, G.; Zhang, X. Taste-active indicators and their correlation with antioxidant ability during the Monascus rice vinegar solid-state fermentation process. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 104, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.E.; Tom-James, A.; Falowo, O.A.; Okoji, A.; Adeyi, O.; Olalere, A.O.; Eloka-Eboka, A. Techno-economic analysis of cellulase production of Trichoderma reesei in submerged fermentation processes using a process simulator. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 42, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Song, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, L.; Wan, S.; Wang, M. Unraveling the core functional bacteria and their succession throughout three fermentation stages of broad bean paste with chili. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, M.A.; Webb, C. Estimating fungal growth in submerged fermentation in the presence of solid particles based on colour development. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboyibor, C.; Kong, W.-B.; Zhang, A.-M.; Niu, S.-Q. Nutrition regulation for the production of Monascus red and yellow pigment with submerged fermentation by Monascus purpureus. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, L.; Laredo-Alcala, E.; Buenrostro-Figueroa, J.J.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Genisheva, Z.; Aguilar, C.; Teixeira, J. Ellagic acid production using polyphenols from orange peel waste by submerged fermentation. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.X.; Mok, W.K.; Chen, W.N. Potential novel nutritional beverage using submerged fermentation with Bacillus subtilis WX-17 on brewers spent grains. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Bai, R.; Yong, H.; Zong, S.; Jin, C.; Liu, J. Improving the digestive stability and prebiotic effect of carboxymethyl chitosan by grafting with gallic acid: In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gomez, J.A.; Giraldo-Estrada, C.; Haberych, D.; Baena, S. Evaluation of biological production of lactic acid in a synthetic medium and in Aloe vera (L.) Burm f. processing by-products. Univ. Sci. 2015, 20, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multari, S.; Guzzon, R.; Caruso, M.; Licciardello, C.; Martens, S. Alcoholic fermentation of citrus flavedo and albedo with pure and mixed yeast strains: Physicochemical characteristics and phytochemical profiles. LWT 2021, 144, 111133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.-G.; Zhu, W.-L.; Yu, W.-S.; Zou, B.; Xu, Y.-J.; Xiao, G.-S.; Wu, J.-J. The variation on structure and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharide during the longan pulp fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scariot, F.J.; Delamare, A.P.L.; Echeverrigaray, S. The effect of chlorothalonil on Saccharomyces cerevisiae under alcoholic fermentation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 182, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, L.; Guo, Q.; Shi, L.; Deng, X.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C. Effects of fermentation with lactic bacteria on the structural characteristics and physicochemical and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from prosomillet bran. LWT 2022, 154, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobys, D.; Johannis, W.; Juebner, M.; Drinhaus, H. A new kind of barrel chest: Alcoholic fermentation due to Candida albicans in a pleural effusion. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, e482–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Revealing the co-fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe on the quality of cider based on the metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis. LWT 2022, 168, 113943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicin, R.; Ozdemir, N.; Simsek, O.; Con, A.H. Production of volatiles relation to bread aroma in flour-based fermentation with yeast. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tashiro, Y.; Sonomoto, K. Construction and metabolic analysis of acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation using mixed acetic acid and lactic acid in wastewater. Indust. Crop. Prod. 2022, 187, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschaedler, A.; Iniguez-Munoz, L.E.; Flores-Flores, N.Y.; Kirchmayr, M.; Arellano-Plaza, M. Use of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in cider fermentation: Importance of the nutrients addition to obtain an efficient fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 347, 109169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Sarabia, V.L.; Ballinas-Cesatti, C.B.; Melgar-Lalanne, G.; Cristiani-Urbina, E.; Morales-Barrera, L. Isolation, identification, and kinetic and thermodynamic characterization of Pichia kudriavzevii yeast strain capable of fermentation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 131, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.M.M.; Alvarez, O.L.M.; Castaneda, M.P.A.; Medina, P.X.L. Bioprospecting of indigenous yeasts involved in cocoa fermentation using sensory and chemical strategies for selecting a starter inoculum. Food Microbiol. 2022, 101, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalis, H.; Cox, J.; Frank, D.; Zhao, J. The crucial role of yeasts in the wet fermentation of coffee beans and quality. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoud, S.; Aouf, C.; Devillers, H.; Sicard, D.; Segond, D. Sourdough yeast-bacteria interactions can change ferulic acid metabolism during fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Menchero, J.R.; Ogawa, M.; Mauricio, J.; Moreno, J.; Moreno-Garcia, J. Effect of calcium alginate coating on the cell retention and fermentation of a fungus-yeast immobilization system. LWT 2021, 144, 111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, N.; Ma, H. Increasing peptide yield of soybean meal solid-state fermentation of ultrasound-treated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 72, 1027704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyajaroenwong, P.; Laopaiboon, P.; Laopaiboon, L. Improvement of batch and continuous ethanol fermentations from sweet sorghum stem juice in a packed bed bioreactor by immobilized yeast cells under microaeration. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahule, C.E.; Martins, L.H.D.S.; Chauque, B.J.M.; Lopes, A.S. Metaproteomics as a tool to optimize the maize fermentation process. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voidarou, C.; Antoniadou, M.; Rozos, G.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Varzakas, T.; Lagiou, A.; Bezirtzoglou, F. Fermentative foods: Microbiology, biochemistry, potential human health benefits and public health issues. Foods 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdichon, F.; Casaregola, S.; Farrokh, C.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gerds, M.L.; Hammes, W.P.; Harnett, J.; Huys, G.; Laulund, S.; Ouwehand, A.; et al. Food fermentations: Microorganisms with technological beneficial use. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 154, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraffa, G. Studying the dynamics of microbial populations during food fermentation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, M.; Han, G.; Seo, Y.-S.; Park, I. Evolution of food fermentation processes and the use of multi-omics in deciphering the roles of the microbiota. Foods 2021, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Song, Z.; Zhang, M.; Nie, Y.; Xu, Y. The deletion of Schizosaccharomyces pombe decreased the production of flavor-related metabolites during traditional Baijiu fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ahluwalia, V.; Saran, S.; Kumar, J.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R. Recent developments on solid-state fermentation for production of microbial secondary metabolites: Challenges and solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafetto, L. Application of solid-state fermentation by microbial biotechnology for bioprocessing of agro-industrial wastes from 1970 to 2020: A review and bibliometric analysis. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubber, S.; Marti-Quijal, F.; Tomasevic, I.; Remize, F.; Barba, F.J. Lactic acid fermentation as a useful strategy to recover antimicrobial and antioxidant compounds from food and by-products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J. Lactic acid production from mesophilic and thermophilic fermentation of food waste at different pH. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Carg, P.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kulshrestha, S. Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, P.; Dantroliya, S.; Modi, A.; Shukla, A.; Patel, D.; Joshi, C.; Joshi, M. Enhanced production process of recombinant mature serratiopeptidase in Escherichia coli using Fed-Batch culture by self-proteolytic activity of fusion protein. Fermentation 2022, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermies, M.; Fickers, P. Bioreactor-Scale strategies for the production of recombinant protein in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Adhikari, B.; Fang, Z. Fermentation transforms the phenolic profiles and bioactivities of plant-based foods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 49, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, P. Sophisticated cloning, fermentation, and purification technologies for an enhanced therapeutic protein production: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-enabled wellness foods: A fresh perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lyu, X.; Liao, A.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, C. Proteomics-based analysis of functional proteins after fermentation of compound wheat embryo Chinese medicine. Grain. Oil. Sci. Technol. 2019, 2, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.G.R.; Gasga, V.M.Z.; Pescuma, M.; Nieuwenhove, C.V.; Mozzi, F.; Burgos, J.A.S. Fruits and fruit by-products as sources of bioactive compounds. Benefits and trends of lactic acid fermentation in the development of novel fruit-based functional beverages. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Li, N.; Wu, J.-L. Food-polysaccharide utilization via in vitro fermentation: Microbiota, structure and function. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 48, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, Y.R.; Thakur, R.; Thakur, P.; Mittal, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Siwal, S.S.; Thakur, V.K.; Saini, R.V.; Saini, A.K. Food fermentation-Significance to public health and sustainability challenges of modern diet and food systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 371, 109666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Flanagan, B.M.; Williams, B.A.; Mikkelsen, D.; Gidley, M.J. Particle size of dietary fibre has diverse effects on in vitro gt fermentation rate and end-products depending on food source. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboleira, J.; Silva, S.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Niranjan, K.; Lemos, M.F.L. Seaweed fermentation withing the fields of food and natural products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groof, V.D.; Coma, M.; Arnot, T.; Leak, D.J.; Lanham, A.B. Selecting fermentation products for food waste valorisation with HRT and OLR as the key operational parameters. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, T. Effect of solid-state fermentation with Bacilus subtilis 1wo on the proteolysis and the antioxidant properties of chickpeas. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 338, 108988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Xue, G. Copper (II) addition to accelerate lactic acid production from co-fermenation of food waste and waste activated sludge: Understanding of the corresponding metabolisms, microbial community and predictive functional profiling. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Whon, T.W.; Sung, H.; Bae, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-E.; Roh, S.W. Role of combinated lactic acid bacteria in bacterial, viral, and metabolite dynamics during fermentation of vegetable food, kimchi. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omay, D.; Guvenilir, Y. Lactic acid fermentation from refectory waste: Factorial design analysis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7693–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Othman, I.; Rambabu, K.; Bharath, G.; Taher, H.; Hasan, S.W.; Banat, F. Polymerization of lactic acid produced from food waste by metal oxide-assisted dark fermentation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhlmann, C.H.; Mickan, B.S.; Tait, S.; Batstone, D.J.; Mercer, G.D.; Bahri, P.A. Lactic acid from mixed food waste fermentation using and adapted inoculum: Influence of pH and temperature regulation on yield and product spectrum. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 373, 133716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, H.; Beresford, T.P.; Cotter, P.D. Health benefits of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S. Diversity of halophilic archaea in fermented foods and human intestines and their application. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-L.; Tong, S.-G.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-Q.; Lv, X.-C.; Weng, Q.; Yu, K.; Liu, G.-R.; Luo, X.-Q.; Wei, T.; et al. The dynamics of microbial community and flavor metabolites during the acetic acid fermentation of Hongqu aromatic vinegar. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Sriram, S.; Johnravindar, D.; Martin, T.L.P.; Wong, J.W.C.; Pradhan, N. Effect of inoculum pretreatment on the microbial and metabolic dynamics of food waste dark fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 358, 127404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Schlatter, D.C.; Glawe, D.A.; Edwards, C.G.; Weller, D.M.; Paulitz, T.C.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Okubara, P.A. Native yeast and non-yeast fungal communities of Cabernet Sauvignon berries from two Washington State vineyards, and persistence in spontaneous fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 350, 109225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutella, G.S.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Solieri, L. Survival an bioactivities of selected probiotic lactobacilli in yogurt fermentation and cold storage: New insights for developing a bi-functional dairy food. Food Microbiol. 2016, 60, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Lele, V.; Ruzauskas, M.; Bartkevics, V.; Bernatoniene, J.; Gallo, P.; Tenore, G.C.; Santini, A. Lactobacillus plantarum LUHS135 and paracasei LUHS244 as functional starter cultures for the food fermentation indutry: Characterization, mycotoxin-reducing properties, optimization of biomass growth an sustainable encapsulation by using dairy by-products. LWT 2018, 93, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Z.X.; Soh, E.Y.W.; Yong, P.H. The influence of fermentation and drying methods on the functional activities and sensory quality of Artemisia argyi H. Lev. & Vaniot herbal tea. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2022, 30, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayo-Omogie, H.N.; Jolayemi, O.S.; Chinma, C.E. Fermentation and blanching as adaptable strategies to improve nutritional and functional properties of unripe Cardaba banana flour. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 6, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klongklaew, A.; Banwo, K.; Soodsawaeng, P.; Christopher, A.; Khanongnuch, C.; Sarkar, D.; Shetty, K. Lactic acid bacteria based fermentation strategy to improve phenolic bioactive-linked functional qualities of select chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) varieties. NFS J. 2022, 27, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Tian, L.; Zhang, F.; Wei, H.; Tao, X. Effects of Lactiplantibacills plantarum WLPL01 fermentation on antioxidant activities, bioactive compounds, and flavor profile of Artemisia argyi. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ro, K.-S.; Du, L.; Tang, Y.-J.; Zhao, L.; Xie, J.; Wei, D. Genomics characteristics of a novel strain Lactiplantibacillus plantarum X7021 isolated from the brine of stinky tofu for the application in food fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 156, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, W.; Lei, P.; Xu, X.; Sun, D.; Wu, L.; Xu, H.; Li, S. Effect of surfactants on the production and biofunction of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide through submerged fermentation. LWT 2022, 163, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Munoz, C.; de Voorde, D.V.; Tuenter, E.; Lemarcq, V.; de Walle, D.V.; Maio, J.P.S.; Mencia, A.; Hernandez, C.E.; Comasio, A.; Sioriki, E.; et al. An in-depth multiphasic analysis of the chocolate production chain, from bean to bar, demonstrates the superiority of Saccharomyces cerevisiae over Hanseniaspora opuntiae as functional starter culture during cocoa fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2023, 109, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Ye, C.; Min, Y.; Li, L.; Ruan, L.; Yang, Z.; Wei, X. Production of a novel lycopene-rich soybean food by fermentation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Bhatt, S.; Agrawal, H.; Dadwal, V.; Gupta, M. Effect of fermentation conditions on nutritional and phytochemical constituents of pearl millet flour (Pennisetum glaucum) using response surface methodology. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, C.M.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, S.; Singh, B. Influence of alkaline fermentation time on in vitro nutrient digestibility, bio-& techno-functionality, secondary protein structure and macromolecular morphology of locust bean (Parkia biglobosa) flour. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 161, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Fu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, M. Effects of Lactobacillus kefiri fermentation supernatant on skin aging caused by oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 96, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Huang, W.; Tian, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, Z. Brewer’s spent grain fermentation improves its soluble sugar and protein as well as enzymatic activities using Bacillus velezensis. Process. Biochem. 2021, 111, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Sheng, F.; Hu, X.; Huang, Z.; Tian, X.; Wu, Z. Nutrition promotion of brewer’s spent grain by symbiotic fermentation adding Bacillus velezensis and Levilactobacillus brevis. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Yu, Q.; Ma, C.; Zou, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q. Enhancement of anti-inflammatory effect of cattle bile by fermentation and its inhibition of neuroinflammation on microglia by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 133, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Fang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Li, M. The anti-aging activity of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide extracted by yeast fermentation: In vivo and in vitro studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zhou, A.; Xie, P.; Azam, S.M.R.; Ma, H. Ultrasonic modification on fermentation characteristics of Bacillus varieties: Impact on protease activity, peptide content and its correlation coefficient. LWT 2022, 154, 112852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Mesa, H.; Delgado-Yuste, E.; Mas, A.; Torija, M.-J.; Beltran, G. Importance of micronutrients and organic nitrogen in fermentations with Torulaspora delbrueckii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 381, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-C.; Liu, L.-Y.; Yang, S.-S. Protein enrichment, cellulase production and in vitro digestion improvement of pangolagrass with solid state fermentation. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juodeikiene, G.; Trakselyte-Rupsiene, K.; Navickaite, B.; Zadeike, D.; Bendoraitiene, J.; Bartkiene, E.; Lele, V.; Rueller, L.; Robert, J.; Arnoldi, A.; et al. Functionalization of soya press cake (okara) by ultrasonication for enhancement of submerged fermentation with Lactobacillus paracasei LUHS244 for wheat bread production. LWT 2021, 152, 112337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Q.-W.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Tang, Z.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Xue, D.-Q.; Xu, M.-F.; Bai, X.-L.; Zhou, T.; Shi, L.-E. Initial purification of antimicrobial fermentation metabolites from Paecilomyces cicadae and its antimicrobial mechanism. LWT 2021, 148, 111785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Khan, R.A.A.; Wei, H.-Y.; Wang, R.; Hou, J.-M.; Liu, T. Rapid and mass production of biopesticide Trichoderma Brev T069 from cassava peels using newly established solid-state fermentation bioreactor system. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryachko, Y.; Batbayar, B.; Tanaka, T.; Nickerson, M.T.; Korber, D.R. Production of glycerol by Lactobacillus plantarum NRRL B-4496 and formation of hexamine during fermentation of pea protein enriched flour. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Perez, L.A.; Beltran-Barrientos, L.M.; Gonzalez-Cordova, A.F.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B. Artisanal cocoa bean fermentation: From cocoa bean proteins to bioactive peptides with potential health benefits. J. Funct. Foods. 2020, 73, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rosa-Sibakov, N.; Edelmann, M.; Sozer, N.; Katina, K.; Coda, R. Enhancing the utilization of rapeseed protein ingredients in bread making by tailored lactic acid fermentation. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Peng, Z.; Hardie, W.J.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Exploring the typical flavours formation by combined with metatranscriptomics and metabolomics during Chinese Sichuan paocai fermentation. LWT 2022, 153, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Xia, D.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Jia, J.; Yin, X. Metagenomic insight of corn straw conditioning on substrates metabolism during coal anaerobic fermentation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K.V.; Rochin-Medina, J.J. Fermentation of spent coffee grounds by Bacillus clausii induces release of potentially bioactive peptides. LWT 2021, 138, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeira, C.Z.; Silvello, M.A.D.C.; Remedi, R.D.; Feltrin, A.C.P.; Santos, L.O.; Garda-Buffon, J. Mitigation of nivalenol using alcoholic fermentation and magnetic field application. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.; Zhao, C.; Yang, S.; Zheng, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, M.; Yan, Y.; Lang, F.; Wang, M. Monitoring microbial succession and metabolic activity during manual and mechanical solid-state fermentation of Chinese cereal vinegar. LWT 2020, 133, 109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, O.; Kahala, M.; Marsol-Vall, A.; Blasco, L.; Jarvenpaa, E.; Rosenvald, S.; Virtanen, M.; Tarvainen, M.; Yang, B. Impact of lactic acid fermentation on sensory and chemical quality of dairy analogues prepared from lupine (Lupinus angustifolius L.) seeds. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.; Silva, K.T.D.; Carvalho, B.F.; Schwan, R.F.; Pereira, R.A.N.; Pereira, M.N.; Avila, C.L.D.S. Effect of amylases and storage length on losses, nutritional value, fermentation, and microbiology of silages of corn and sorghum kernels. Anim Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 285, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sadiq, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Abbas, A.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Xue, G.; Sobotka, D.; et al. Salinity enhances high optically active L-lactate prouction from co-fermentation of food waste and waste activated sludge: Unveiling the response of microbial community shift and functional profiling. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobani, S.; Latimer, C.; McDougall, G.J.; Allwood, J.W.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Ternan, N.G.; Pourshahidi, L.K.; Lawther, R.; Tuohy, K.M.; et al. Ex vivo fecal fermentation of human ileal fluid collected after raspberry consumption modifies (poly)phenolics and modulates genoprotective effects in colonic epithelial cells. Redox Biol. 2021, 40, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Shuai, L.; Lai, T.; Liao, L.; Li, J.; Duan, Z.; Xue, X.; Han, D.; Wu, Z. Up-regulated glycolysis, TCA, fermentation and energy metabolism promoted the sugar receding in Shixia longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) pulp. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Fan, D. Evaluation of Shandong pancake with sourdough fermentation on the alleviation of type 2 diabetes symptoms in mice. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 90, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, W.; Cai, H.; Guo, S.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z. Metabolomics analysis reveals differences in milk metabolism and fermentation rate between individual Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strains. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of autochthonous starter cultures on bacterial communities and metabolites during fermentation of Yu jiangsuan, a Chinese traditional fermented condiment. LWT 2022, 168, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, K.; Kang, J.S.; Kang, N.J.; Son, B.G.; Choi, Y.W. Strawberry fermentation with Cordyceps militaris has anti-adipogenesis activity. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikic-Pogacar, M.; Turk, D.M.; Fijan, S. Knowledge of fermentation and health benefits among general population in North-eastern Slovenia. BMC Public Health. 2022, 22, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, R.; Ray, M.; Halami, P.M. Preventive and therapeutic aspects of fermented foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3476–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanlier, N.; Gokcen, B.B.; Sezgin, A.C. Health benefits of fermented foods. 2019. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 506–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrete-Romero, B.; Valencia-Olivares, C.; Banos-Dossetti, G.A.; Perez-Armendariz, B.; Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A. Nutritional contributions and health associations of traditional fermented foods. Fermentation 2021, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrie, B.C.T.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The microbiota and health promoting characteristics of the fermented beverage Kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, F.; Melini, V.; Luziatelli, F.; Ficca, A.G.; Ruzzi, M. Health-promoting components in fermented foods: An up-to-date systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Battista, N.; Prete, R.; Corsetti, A. Health-promotion role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum isolated from fermented foods. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Hu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-T.; Chung, Y.-C. Submerged fermentation with Lactobacillus brevis significantly improved the physiological activities of Citrus aurantium flower extract. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Castro, A.P.; Zamora-Gasga, V.M.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Ruiz-Valdiviezo, V.M.; Venema, K.; Sayago-Ayerdi, S.G. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and husk tomato (Physalis ixocarpa Brot.): Phenolic compounds released and bioconverted by gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelak-Blaszczyk, K.; Czernecki, A.; Klewicki, R.; Grzegorzewska, M.; Klewicka, E. Lactic acid fermentation of osmo-dehydrated onion. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, E.A.E. Structural characterization and health benefits of a novel fructan produced by fermentation of an Asparagus sprengeri extract by Lactobacillus plantarum DMS 20174. Process. Biochem. 2022, 118, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Sun, Z.-H.; Zhang, H. Mesopic fermentation contributes more to the formation of important flavor compounds and increased growth of Lactobacillus casei Zhang than does high temperature during milk fermentation and storage. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4857–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiri, S.A.; Chitsaz, H.; Najdegerami, E.H.; Akrami, R.; Jalali, A.S. Influence of wheat and rice bran fermentation on water quality, growth performance, and health status of Common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) juveniles in a biofloc-based system. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, C.; Markou, G.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Arapoglou, D. Transformation of mixtures of olive mill stone waste and oat bran or Lathyrus clymenum pericarps into high added value products using solid state fermentation. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abesinghe, A.M.N.L.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Islam, N.; Karim, M.A. Effects of ultrasound on fermentation profile and metabolic activity of lactic acid bacteria in buffalo’s (Bubalus bubalis) milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 79, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Flanagan, B.M.; Mikkelsen, D.; Williams, B.A.; Gidley, M.J. In vitro fermentation of onion cell walls and model polysacharides using human faecal inoculum: Effects of molecular interactions and cell wall architecture. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Pan, X.; Lao, F.; Liao, X.; Shi, Y.; Wu, J. Improvement of antioxidant properties of jujube puree by biotransofrmation of polyphenols via Streptococcus thermophilus fermentation. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Tan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Teng, D.; Tian, J.; et al. Effects of L. plantarum dy-1 fermentation time on the characteristics structure and antioxidant activity of barley β-glucan in vitro. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Hao, Q.; Olsen, R.E.; Ringo, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Growth performance, hepatic enzymes, and gut health status of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in response to dietary Cetobacterium somerae fermentation products. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chai, Z.; Liu, M.; Battino, M.; Meng, X. Mixed fermentation of blueberry pomace with L. rhamnosus GG and L. plantarum-1: Enhance the active ingredient, antioxidant activity and health-promoting benefits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; Azzi, L.; Cavoski, I.; Vincentini, P.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M.; Cagno, R.D. Exploitation of the health-promoting and sensory properties of organic pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice through lactic acid fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.E.; Suarez, J.G.; Diaz, N.; Rodriguez, R.S.; Menendez, E.C.; Balaguer, H.D.; Lasa, A.M. Scaling-up fermentation of Escherichia coli for production of recombinant P64k protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 33, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diether, N.E.; Willing, B.P. Microbial fermentation of dietary protein: An important factor in diet-microbe-host interaction. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpela, K. Diet, microbiota, and metabolic health: Trade-off between saccharolytic and proteolytic fermentation. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Lee, C.-J.; Park, J.-S. Strategies for optimizing the production of proteins and peptides with multiple disulfide bonds. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solieri, L.; Valentini, M.; Cattivelli, A.; Sola, L.; Helal, A.; Martini, S.; Tagliazucchi, D. Fermentation of whey protein concentrate by Streptococcus thermophilus strains releases peptides with biological activities. Process. Biochem. 2022, 121, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Costa, A.; Nakayama, D.G.; Andrade, L.D.F.; Catelli, L.F.; Bassi, A.P.G.; Ceccato-Antonini, S.R.; Henrique-Silva, F. Industrial PE-2 strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: From alcoholic fermentation to the production of recombinant proteins. New Biotechnol. 2014, 31, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Hata, Y.; Kawato, A.; Abe, Y. Improvement of the glaB promoter expressed in solid-state fermentation (SSF) of Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meini, M.-R.; Cabezudo, I.; Galetto, C.S.; Romanini, D. Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.-X.; Liao, X.-Z.; Guo, H.; Li, C.-C.; Zhang, F.-F.; Liao, L.-S.; Luo, X.-M.; Feng, J.-X. Differential transcriptomic profiling of filamentous fungus during solid-state and submerged fermentation and identification of an essential regulatory gene PoxMBF1 that directly regulated cellulase and xylanase gene expression. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2019, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilakamarry, C.R.; Sakinah, A.M.M.; Zularisam, A.W.; Sirohi, R.; Khilji, I.A.; Ahmad, N.; Pandey, A. Advances in solid-state fermentation for bioconversion of agricultural wastes to value-added products: Opportunities and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, F.; Zhou, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, P. Biomass lignocellulolytic enzyme production and lignocellulose degradation patterns by Auricularia auricula during solid state fermentation of corn stalk residues under different pretreatments. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Cao, X.; Jia, J.; Ji, G.; Xiao, H. Solid state fermentation by Fomitopsis pinicola improves physicochemical and functional properties of wheat bran and the bran-containing products. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, P.; Belo, I.; Salgado, J.M. Co-management of agro-industrial wastes by solid-state fermentation for the production of bioactive compounds. Indu. Crop. Prod. 2021, 172, 113990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brison, A.; Rossi, P.; Gelb, A.; Derlon, N. The capture technology matters: Composition of municipal wastewater solids drives complexity of microbial community structure and volatile fatty acid profile during anaerobic fermentation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 815, 152762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, L.O.C.; Jacobo-Velazquez, A.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Amezquita, L.E.G.; Garcia-Cayuela, T. Solid-state fermentation for enhancing the nutraceutical content of agrifood by-products: Recent advances and its industrial feasibility. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, A.; Tomar, R.S.; Mishra, R.K. One step selection strategy for optimization of media to enhance arachidonic acid production under solid state fermentation. LWT 2021, 152, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Urrutia, C.; Volke-Sepulveda, T.; Figueroa-Martinez, F.; Favela-Torres, E. Solid-state fermentation enhances inulinase and invertase production by Aspergillus brasiliensis. Process. Biochem. 2021, 108, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Avila, O.; Llenas, L.; Ponsa, S. Sustainable polyhydroxyalkanoates production via solid-state fermentation: Influence of the operational parameters and scaling up of the process. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 132, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardi-Jimenez, M.A.; Hernandez-Martinez, R. Solid state fermentation (SSF): Diversity of applications to valorize waste and biomass. 3 Biotech. 2017, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.E.S.; Santiago, A.M.; Gusmao, T.A.S.; Oliveira, H.M.L.; Conrado, L.D.S.; Gusmao, R.P.D. Solid-state fermentation for single-cell protein enrichment of guava and cashew by-products and inclusion on cereal bars. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 25, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; El-Haroun, E.R.; Hassaan, M.S.; Bowyer, P.H. A Solid-State Fermentation (SSF) supplement improved performance, digestive function and gut ultrastrastructure of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed plant protein diets containing yellow lupin meal. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Sahu, N.P.; Deo, A.D.; Kumar, S. Solid state fermentation of de-oiled rice bran: Effect on in vitro protein digestibility, fatty acid profile and anti-nutritional factors. Food Res. Int. 2019, 199, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-K.; Liu, C.-P.; Liu, L.-Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Yang, S.-S. Protein enrichment and digestion improvement of napiergrass and pangolagrass with solid-state fermentation. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, A.; Ge, L.; He, J.; Zhao, M.; He, Q. Roles of water in improved production of mycelial biomass and lignocellulose-degrading enzymes by water-supply solid-state fermentation of Ganoderma lucidum. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 133, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.-H.; Cho, S.-J. Changes in allergenic and antinutritional protein profiles of soybean meal during solid-state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis. LWT 2016, 70, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qin, B. Solid state fermentation of aquatic macrophytes for crude protein extraction. Ecol. Engin. 2009, 35, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G. Monitoring of solid-state fermentation of protein feed by electronic nose and chemometric analysis. Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F.; Overland, M.; Hansen, J.O.; Mydland, L.T.; Urriola, P.R.; Chen, C.; Shurson, G.C.; Hu, B. Solid-state fermentation of Pleurotus ostreatus to improve the nutritional profile of mechanically-fractionated canola meal. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprayogi, W.P.S.; Ratriyanto, A.; Akhirini, N.; Hadi, R.F.; Setyono, W.; Irawan, A. Changes in nutritional and antinutritional aspects of soybean meals by mechanical and solid-state fermentation treatments with Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus oryzae. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacres, E.; Rosell, C.M. Kinetics of solid-state fermentation of lupin with Rhizophus oligosporus based on nitrogen compounds balance. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhomodi, A.F.; Gibbons, W.R.; Karki, B. Estimation of cellulase production by Aureobasidium pullulans, Neurospora crassa, and Trichoderma reesei during solid and submerged state fermentation for raw and processed canola meal. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, T.E. Production of value-added product from pineapple peels using solid state fermentation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 57, 102193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarruri, J.; Cebrian, M.; Hernandez, I. Valorisation of fruit and vegetable discards by fungal submerged and solid-state fermentation for alternative feed ingredients production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Waters, D.; Blanchard, C.; Tan, S.H. A study on Australian sorghum grain fermentation performance and the changes in Zaopei major composition during solid-state fermentation. J. Cereal. Sci. 2021, 98, 103160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Dai, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Impact of yeast fermentation on nutritional and biological properties of defatted adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L.). LWT 2021, 137, 110396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Improvement of the protein quality and degradation of allergens in soybean meal by combination fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis. LWT 2020, 128, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yang, E.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Zheng, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Dynamic changes in the chemical composition and metabolite profile of drumstick (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaf flour during fermentation. LWT 2022, 155, 112973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, J.; Yu, J.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Zheng, P.; Chen, D. Solid state fermentation of rapeseed cake with Aspergillus niger for degrading glucosinolates and upgrading nutritional value. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarruri, J.; Goiri, I.; Cebrian, M.; Garcia-Rodriguez, A. Solid state fermentation as a tool to stabilize and improve nutritive value of fruit and vegetable discards: Effect on nutritional composition, in vitro ruminal fermentation and organic matter digestibility. Animals 2021, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Kamal, M.; Correia, L.R. Kinetic modelling of continuous submerged fermentation of cheese whey for single cell protein production. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemeh, S.; Reihani, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Influencing factors on single-cell protein production by submerged fermentation: A review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Kamal, M.A. Submerged yeast fermentation of acid cheese whey for protein production and pollution potential reduction. Water Res. 2004, 38, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezekiel, O.O.; Aworh, O.C.; Blaschek, H.P.; Ezeji, T.C. Protein enrichment of cassava peel by submerged fermentation with Trichoderma viride (ATCC 36316). African. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, H. Comparative characterization of proteins secreted by Neurospora sitophila in solid-state and submerged fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmoser, R.; Sintca, C.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Lennartsson, P.R. Combining submerged and solid state fermentation to convert waste bread into protein and pigment using the edible filamentous fungus N. intermedia. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Nene, S.N.; Joshi, K.S. A comparative study of production of hydrophobin like proteins (HYD-LPs) in submerged liquid and solid state fermentation from white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeta-Salgado, C.; Cicatiello, P.; Lienqueo, M.E. Mycoprotein and hydrophobin like protein produced from marine fungi Paradendryphiella salina in submerged fermentation with green seaweed Ulva spp. Algal. Res. 2021, 56, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Effect of low-intensity magnetic field on the growth and metabolite of Grifola frondosa in submerged fermentation and its possible mechanisms. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aasar, S.A. Submerged fermentation of cheese whey and molasses for citric acid production by Aspergillus niger. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2006, 8, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Reihani, S.F.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Mycoprotein production from date waste using Fusarium venenatum in a submerged culture. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, B.; Xue, W.; Su, X.; Chen, X.; Dong, Z. Improving cellulase production in submerged fermentation by the expression of a Vitreoscilla hemoglobin in Trichoderma reesei. AMB Express. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, J.H. Microbiological production of lactic acid. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 42, 45–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, V.; Grieco, F. Editorial: Lactic acid fermentation and the colours of biotechnology 2.0. Fermentation 2021, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.D.; Twiddy, D.R.; Reilly, P.J.A. Lactic-acid fermentation as a low-cost means of food preservation in tropical countries. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1987, 46, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, N.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, C. Skin cell wall ripeness alters wine tannin profiles via modulating interaction with seed tannin during alcoholic fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, H.; Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. A new method for bio-degumming in less-water environment: Solid-state-fermentation progressive bio-degumming. Indust. Crop. Prod. 2022, 183, 114986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Singh, A.; Kitts, D.D.; Pratap-Singh, A. Lactic acid fermentation: A novel approach to eliminate unpleasant aroma in pea protein isolates. LWT 2021, 150, 111927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria-Fernandez, M.; Ytting, N.K.; Lubeck, M. Influence of the development stage of perennial forage crops for the recovery yields of extractable proteins using lactic acid fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Raikos, V. Lactic-acid bacteria fermentation-induced effects on microstructure and interfacial properties of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by goat-milk proteins. LWT 2019, 109, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ariyadasa, T.U.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Macroalgal biomass as a potential resource for lactic acid fermentation. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Koksel, F.; Du, Y.; Sun, L.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Pei, F. The effects of cooperative fermentation by yeast and lactic acid bacteria on the dough rheology, retention and stabilization of gas cells in a whole wheat flour dough system- A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 135, 108212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Xiong, D.; Jia, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X. Mechanism study on enhanced emulsifying properties of phosvitin and calcium-binding capacity of its phosphopeptides by lactic acid bacteria fermentation. LWT 2022, 155, 113002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupsaite, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Zadeike, D.; Bartkiene, E.; Maknickiene, Z.; Liutkute, G. The influence of lactic acid fermentation on functional properties of narrow-leaved lupine protein as functional additive for higher value wheat bread. LWT 2017, 75, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, K.; Pang, X.-N.; Huang, M. Metabolic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and interaction with yeast isolated from light-flavor Baijiu fermentation. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verni, M.; Mastro, G.D.; Cillis, F.D.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Lactic acid bacteria fermentation to exploit the nutritional potential of Mediterranean faba bean local biotypes. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ke, C.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Engin. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magala, M.; Kohajdova, Z.; Karovicova, J.; Greifova, M.; Hojerova, J. Application of lactic acid bacteria for production of fermented beverages based on rice flour. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2015, 33, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emkani, M.; Oliete, B.; Saurel, R. Effect of lactic acid fermentation on legume protein properties, a review. Fermentation 2022, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn-Garcia, D.; Cavaglia, J.; Giussani, B.; Busto, O.; Acena, L.; Mestres, M.; Boque, R. ART-MIR spectroscopy as a process analytical technology in wine alcoholic fermentation- A tutorial. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boura, K.; Kandylis, P.; Bekatorou, A.; Kolliopoulos, D.; Vasieleiou, D.; Panas, P.; Kanellaki, M.; Koutinas, A. New generation biofuel from whey: Successive acidogenesis and alcoholic fermentation using immobilized cultures on γ-alumina. Energy Convers Manag. 2017, 135, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando, T.; Mouret, J.-R.; Humbert-Goffard, A.; Aguera, E.; Sablayrolles, J.-M.; Farines, V. Comprehensive study of the dynamic interaction between SO2 and acetaldehyde during alcoholic fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Trinidad, A.S.; Lerena, M.C.; Alonso-del-Real, J.; Esteve-Zarzoso, B.; Mercado, L.A.; Mas, A.; Querol, A.; Combina, M. Effect of transient thermal shocks on alcoholic fermentation performance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 312, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, J.-Y.; Tan, S.J.; Liu, S.-Q. The impact of mixed amino acids supplementation of Torulaspora delbrueckii growth and volatile compound modulation in soy whey alcohol fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grijalva-Vallejos, N.; Aranda, A.; Matallana, E. Evaluation of yeasts from Ecuadorian chicha by their performance as starters for alcoholic fermentations in the food industry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 317, 108462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jiang, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, S. Comparison of fermentation behaviors and properties of raspberry wines by spontaneous and controlled alcoholic fermentations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.-L.; Ma, N.; Yin, J.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Tao, Y.-S. Fine tuning of medium chian fatty acids levels increases fruity ester production during alcoholic fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.; Tourdot-Marechal, R.; Sparrow, C.; Morge, C.; Alexandre, H. Influence of nitrogen status in wine alcoholic fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, F.; Fernandez-Pachon, M.-S.; Cerrillo, I.; Escudero-Lopez, B.; Ortega, A.; Rosi, A.; Bresciani, L.; Rio, D.D.; Mena, P. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of orange juice (poly) phenols in humans: The effect of a controlled alcoholic fermentation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.-L.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Tao, Y.-S. Spent yeast polysaccharides in mixed alcoholic fermentation between Pichia kluyveri, Pichia fermentans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae retarded wine fruity ester hydrolysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, M.; Zanicehlli, G.; Verzelloni, E.; Lemmetti, F.; Giudici, P. Feasible acetic acid fermentations of alcoholic and sugary substrates in combined operation mode. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karekar, S.C.; Srinivas, K.; Ahring, B.K. Continuous in-situ extraction of acetic acid produced by Acetobacterium woodii during fermentation of hydrogen and carbon dioxide using Amberlite FPA53 ion exchange resins. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 12, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Lv, N.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Pan, X. Compost-derived indole-3-acetic-acid-producing bacteria and their effects on enhancing the secondary fermentation of a swine manure-corn stalk composting. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Zhang, F.F.; Chen, F.S. Biodiversity of yeasts, lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria in the fermentaion of Shanxi aged vinegar, a traditional Chinese vinegar. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsutani, M.; Nishikura, M.; Saichana, N.; Hatano, T.; Masud-Tippayasak, U.; Theergool, G.; Yakushi, T.; Matsushita, K. Adaptive mutation of Acetobacter pasteurianus SKU1108 enhances acetic acid fermentation ability at high temperature. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 165, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Pretreatment of corn stover with diluted acetic acid for enhancement of acidogenic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabemanolontsoa, H.; Kawasaki, G.; Saka, S. Effects of decomposed products from Japanese cedar hydrolyzates on acetic acid fermentation by Clostridium thermocellum and Moorella thermoacetica (C. thermoaceticum). Process. Biochem. 2017, 57, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haosagul, S.; Vikromvarasiri, N.; Sawasdee, V.; Pisutpaisal, N. Impact of acetic acid in methane production from glycerol/acetic acid co-fermentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29568–29574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, S.-M.; Gong, G.; Oh, M.-K.; Um, Y. Butyric acid production with high selectivity coupled with acetic acid consumption in sugar-glycerol mixture fermentation by Clostridium tyrobutyricum ATCC25755. J. Indust. Engin. Chem. 2019, 75, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanino, T.; Nara, Y.; Tsujiguchi, T.; Ohshima, T. Coproduction of acetic acid and electricity by application of microbial fuel cell technology to vinegar fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.J.; Um, Y.; Lee, S.-M. Effect of manganese ions on ethanol fermentation by xylose isomerase expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae under acetic acid stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullo, M.; Verzelloni, E.; Canonico, M. Aerobic submerged fermentation by acetic acid bacteria for vinegar production: Process and biotechnological aspects. Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, V.T.T.; Fleet, G.H.; Zhao, J. Unravelling the contribution of lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria to cocoa fermentation using inoculated organisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 279, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, W. Kinetic modeling of lactic acid and acetic acid effects on butanol fermentation by Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum. Fuel 2018, 226, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evina, V.J.E.; Taeye, C.D.; Niemenak, N.; Youmbi, E.; Collin, S. Influence of acetic and lactic acids on cocoa flavan-3-ol degradation through fermentation-like incubations. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, M.; Shafiei, R.; Zarmehrkhorshid, R.; Hamouda, A.; Alaoui, M.I.; Thonart, P. Simultaneous production of acetic and gluconic acids by a thermotolerant Acetobacter strain during acetous fermentation in a bioreactor. J. Biosci Bioeng. 2016, 121, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Huang, J.H.; McMullen, J.G.; Newell, P.D.; Douglas, A.E. Physiological responses of insects to microbial fermentation products: Insights from the interactions between Drosophila and acetic acid. J. Insect. Physiol. 2018, 106, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Arriaga, C.; Cruz-Ramirez, A. Yeast and nonyeast fungi: The hidden allies in pulque fermentation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanprasartsuk, O.-O.; Prakitchaiwattana, C. Growth kinetics and fermentation properties of autochthonous yeasts in pineapple juice fermentation for starter culture development. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 371, 109636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguler, H.; Sener, S. Production of naturally flavoured and carbonated beverages using Williopsis saturnus yeast and cold fermentation process. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhan, X. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of an aminoglycan-rich exopolysaccharide from the submerged fermentation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernbach, S.; Kernbach, O.; Kuksin, I.; Kernbach, A.; Nepomnyashchiy, Y.; Dochow, T.; Bobrov, A.V. The biosensor based on electrochemical dynamics of fermentation in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozmuta, L.M.; Nicula, C.; Peter, A.; Apjok, R.; Jastrzebska, A.; Cozmuta, A.M. Insights into the fermentation process of fresh and frozen dough bread made with alginate-immobilized S. cerevisiae yeast cells. J. Cereal. Sci. 2022, 107, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveira-Pazos, C.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Accumulation of lipids by the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica grown on carboxylic acids simulating syngas and carbon dioxide. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Capone, D.L.; Roland, A.; Jeffery, D.W. Impact of accentuated cut edges, yeast strain, and malolactic fermentation on chemical and sensory profiles of Sauvignon blanc wine. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cui, J.; Shen, F.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Developing a sustainable process for cleaner production of baker’s yeast: An approach towards waste management by an integrated fermentation and membrane separation process. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wang, W.; Tong, J.; Fang, L.; He, X.; Xue, Q.; Li, Y. Changes of bioactive substances in lactic acid bacteria and yeasts fermented kiwifruit extract during the fermentation. LWT 2022, 164, 113629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraine, R.E.A.; Nickens, D.G.; Sun, D.J.; Leite, F.P.L.; Bochman, M.L. Isolation of wild yeasts from olympic national park and Moniliella megachiliensis ONP131 physiological characterization for beer fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2022, 104, 103974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H. Comparative metabolome and transcriptome analyses of the properties of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces yeasts in apple cider fermentation. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gomez, J.; Garcia-Martinez, T.; Varo, M.A.; Merida, J.; Serratosa, M.P. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and color in the fermentation of mixed blueberry and grape juice with different yeasts. LWT 2021, 146, 111661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, H.; Aoyagi, R.; Fujita, K.; Maekawa, Y.; Riya, S. Ethanol fermentation using macroporous monolithic hydrogels as yeast cell scaffolds. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 169, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Diaz, A.B.; Duran-Guerrero, E.; Lasanta, C. Influence of different fermentation conditions on the analytical and sensory properties craft beers: Hopping, fermentation temperature and yeast strain. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lee, Y.G.; Lee, D.-S.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Bae, H.-J. Utilization of bamboo biomass as a biofuels feedstocks: Process optimization with yeast immobilization and the sequential fermentation of glucose and xylose. Fuel 2022, 307, 121892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-M.; Jing, X.-J.; Li, Y.-Q.; Chai, Z.; Qiao, H.-P.; Zhao, W.-J.; Wang, Q. The community structure of eukaryotic microorganisms in nine kinds vegetable fermentation system. Sci. Technol. Food Indust. 2016, 37, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whon, T.W.; Ahn, S.W.; Yan, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.-M.; Jung, H.; Choi, Y.-E.; Lee, S.H.; et al. ODFM, an omics data resource from microorganisms associated with fermented foods. Sci. Data. 2021, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, Y.; Yang, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Jung, Y.H. Development of a post-processing method to reduce the unique off-flavor of Allomyrina dichotoma: Yeast fermentation. LWT 2021, 150, 111940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Gao, L.; Guo, Z.; Yang, N.; Liu, N.; Lei, H. Immobilization of larger yeast by hydrocolloids as supporting matrix for improving fermentation performance of high gravity brewing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 187, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Ye, D.; Zang, X.; Nan, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of low temperature on the shaping of yeast-derived metabolites compositions during wine fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zong, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, H. Potential yeast growth and fermentation promoting activity of wheat gluten hydrolysates and soy protein hydrolysates during high-gravity fermentation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 127, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Wang, X.; Caprioli, G.; Mi, S.; Sang, Y. Effect of fermentation by Lactobacillus acidophilus CH-2 on the enzymatic browning of pear juice. LWT 2021, 147, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinma, C.E.; Ilowefah, M.; Muhammad, K. Optimization of rice bran fermentation conditions enhanced by baker’s yeast for extraction of protein concentrate. Niger. Food J. 2014, 32, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, L.; Harford, A.J.; Hose, G.C.; Humphrey, C.L.; Chariton, A.; Greenfield, P.; Davis, J. Saline mine-water alters the structure and function of prokaryote communities in shallow groundwater below a tropical stream. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, X.A.G.; Garcia, F.C.; Rostad, A.; Silva, L.; Al-Otaibi, N.; Irigoien, X.; Calleja, M.L. Diel dynamics of dissolved organic matter and heterotrophic prokaryotes reveal enhanced growth at the ocean’s mesopelagic fish layer during daytime. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 804, 150098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Ishida, A.; Takahata, N.; Sano, Y.; Kakegawa, T. Evolutionary diversification of paleoproterozoic prokaryotes: New microfossil records in 1.88 Ga Gunflint formation. Precambrian. Res. 2022, 380, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. phoH-carrying virus communities responded to multiple factors and their correlation network with prokaryotes in sediments along Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 812, 152477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitman, W.B.; Chuvochina, M.; Hedlund, B.P.; Hugenholtz, P.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Murray, A.E.; Palmer, M.; Parks, D.H.; Probst, A.J.; Reysenbach, A.-L.; et al. Development of the SeqCode: A proposed nomenclatural code for uncultivated prokaryotes with DNA sequences as type. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 45, 126305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ling, T.C.; Croft, L.; Manickam, S.; Yap, Y.J.; Show, P.L. Description and detection of excludons as transcriptional regulators in gram-positive, gram-negative and archaeal strains of prokaryotes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; He, T.; Ren, M.; Xu, Y. Predicting essential genes of 37 prokaryotes by combining information-theoretic features. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2021, 188, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxsen, J.; Rutz, N.; Schmidt, S.I. Organic carbon and nutrients drive prokaryote and metazoan communities in a floodplain aquifer. Basic. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 51, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Bai, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X. Nutrient levels and prokaryotes affect viral communities in plateau lakes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 839, 156033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garel, M.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Boutrif, M.; Repeta, D.; Sempere, R.; Santinelli, C.; Charriere, B.; Nerini, D.; Poggiale, J.-C.; Tamburini, C. Contrasting degradation rates of natural dissolved organic carbon by deep-sea prokaryotes under stratified water masses and deep-water convection conditions in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Marine. Chem. 2021, 231, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylov, A.I.; Zabotkina, E.A.; Kosolapov, D.B.; Romanenko, A.V.; Sazhin, A.F. Viruses and viral infection of heterotrophic prokaryotes in shelf waters of the western part of the East Siberian Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 218, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Letona, M.; Aristegui, J.; Hernandez-Hernandez, N.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Alvarez, M.; Delgadillo, E.; Perez-Lorenzo, M.; Teira, E.; Hernandez-Leon, S.; Sebastian, M. Deep ocean prokaryotes and fluorescent dissolved organic matter reflect the history of the water masses across the Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 205, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, H.; Rezaei, S.; Darooneh, A.H.; Heshmati, E.; Khalifeh, K. A comparative analysis of dipeptides distribution in eukaryotes and prokaryotes by statistical mechanics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 555, 124567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Barral, A.; Teira, E.; Hernandez-Ruiz, M.; Fernandez, E. Response of prokaryote community composition to riverine and atmospheric nutrients in a coastal embayment: Role of organic matter on Vibrionales. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2021, 251, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailovsky, G.E.; Gordon, R. LUCA to LECA, the Lucacene: A model for the gigayear delay from the first prokaryote to eukaryogenesis. Biosystems 2021, 205, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, D.; Ribeiro, M.; Fonseca, L.; Regis, B.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Santos, H.F.D.; Jesus, H.E.D.; Schultz, J.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Archaea from the gut microbiota of humans: Could be linked to chronic diseases? Anaerobe 2022, 77, 102629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.; Park, T.; Kim, M.; Yu, Z. Rumen methanogens and mitigation of methane emission by anti-methanogenic compounds and substances. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.S.G.; Zhou, M.; Li, F.; Guan, L.L. Identifying active rumen epihelial associated bacteria and archaea in beef cattle divergent in feed efficiency using total RNA-seq. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, O.; Kumar, S.H.; Nayak, B.B. Relative abundance of halophilic archaea and bacteria in diverse salt-fermented fish products. LWT 2020, 117, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochier-Armanet, C.; Boussau, B.; Gribaldo, S.; Forterre, P. Mesophilic Crenarchaeota: Proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroun, B.; Bahreini, G.; Zaman, M.; Jang, E.; Okoye, F.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Santoro, D.; Walton, J.; Al-Omari, A.; Muller, C.; et al. Vacuum-enhanced anaerobic fermentation: Achieving process intensification, thickening and improved hydrolysis and VFA yields in a single treatment step. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.Y.; El-Assar, S.A.; Abdul-Gawad, S.M. Solid-state fermentation for the production of meroparamycin by Streptomyces sp. Strain MAR01. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Xiong, L.; Wang, M.; Peng, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Production of acetone-butanol-ethanol and lipids from sugarcane molasses via coupled fermentation by Clostridium acetobutylicum and oleaginous yeasts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 185, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, S.C.; Srinivas, K.; Ahring, B.K. Batch screening of weak base ion exchange resins for optimized extraction of acetic acid under fermentation conditions. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, S.; Gao, J.; Cheng, K.; Yuan, F. Changes of terpenoids and other volatiles during alcoholic fermentation of blueberry wines made from two southern highbush cultivars. LWT 2019, 109, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iu, S.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yan, G.; Li, J. Non-Saccharomyces yeasts highly contribute to characterisation of flavour profiles in greengage fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.H.A.; Najimudin, N.; Ismail, K.S.K. Transcriptomes analysis of Pichia kudriavzevii UniMAP 3-1 in response to acetic acid supplementation in glucose and xylose medium at elevated fermentation temperature. Process. Biochem. 2022, 118, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.S.D.; Mertz, C.; Morel, G.; Lacour, S.; Belleville, M.-P.; Durand, N.; Dornier, M. Alcoholic fermentation as a potential tool for coffee pulp detoxification and reuse: Analysis of phenolic composition and caffeine content by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Z. Combination of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of corn stover with consolidated biprocessing of cassava starch enhances lipid production by the amylolytic oleaginous yeast Lipomyces starkeyi. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lv, J.; Gu, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Zhou, Z. Mixed fermentation of Chinese bayberry pomace using yeast, lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria: Effects on color, phenolics and antioxidant ingredients. LWT 2022, 163, 113503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xie, C.-Y.; Yang, B.-X.; Gou, M.; Xia, Z.-Y.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Tang, Y.-Q. The response mechanisms of industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae to acetic acid and formic acid during mixed glucose and xylose fermentation. Process. Biochem. 2020, 91, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Du, W.; Meng, F.-B.; Rao, J.-W.; Liu, D.-Y.; Peng, L.-X. Tartary buckwheat protein hydrolysates enhance the salt tolerance of the soy sauce fermentation yeast Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Teng, Z.; Luo, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Bai, W. Pyruvic acid stress caused color attenuation by interfering with anthocyanins metabolism during alcoholic fermentation. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
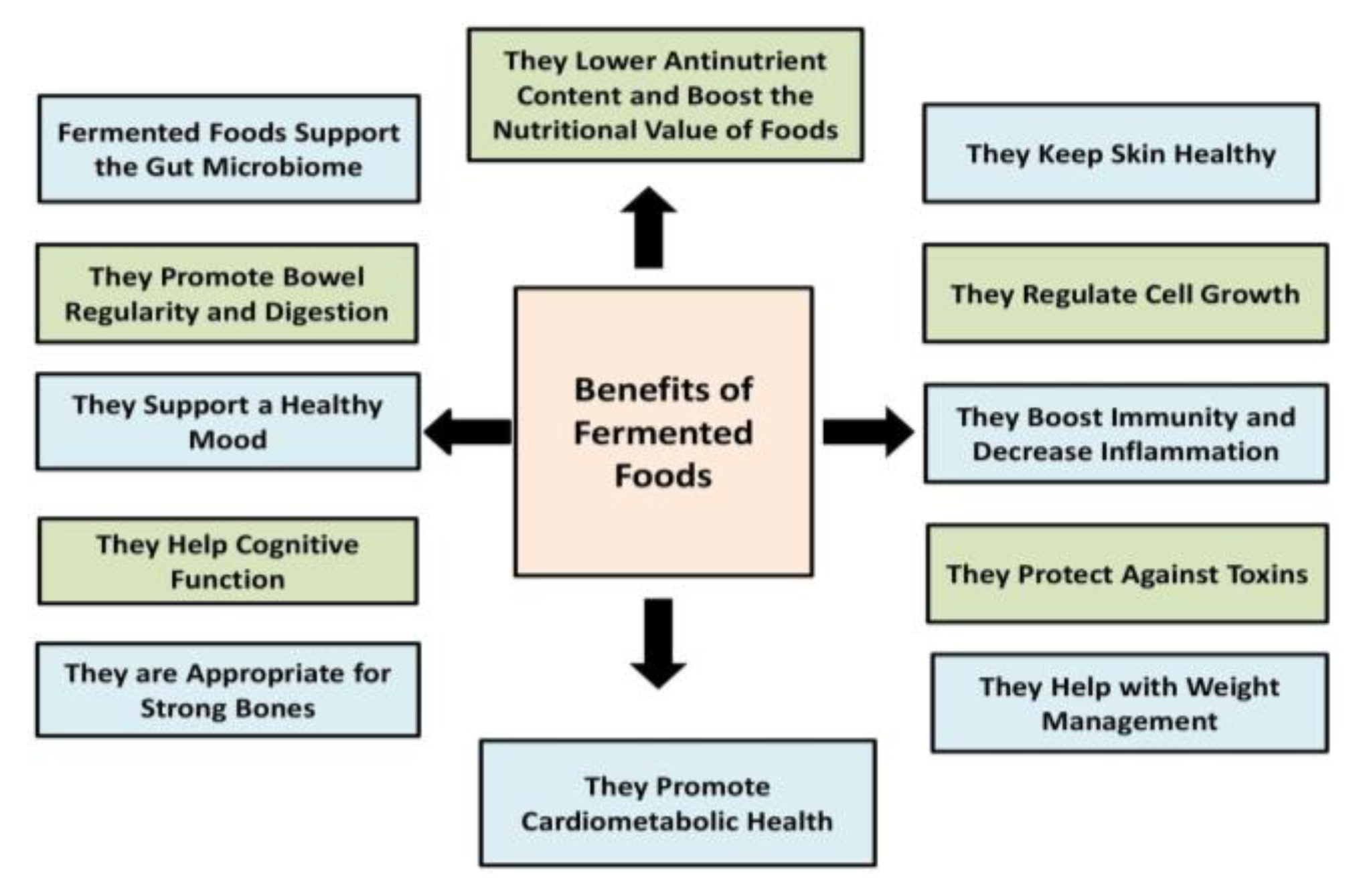
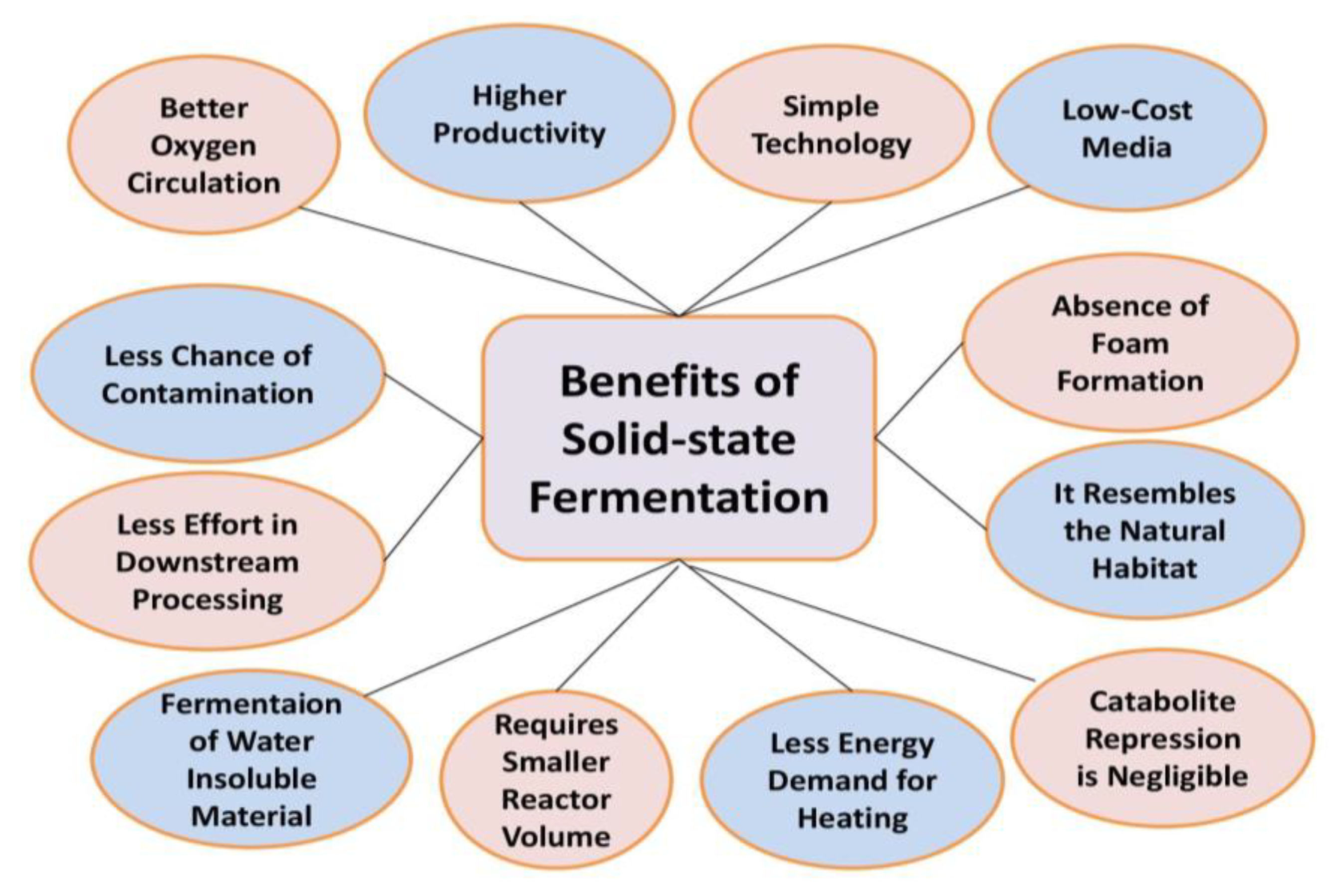
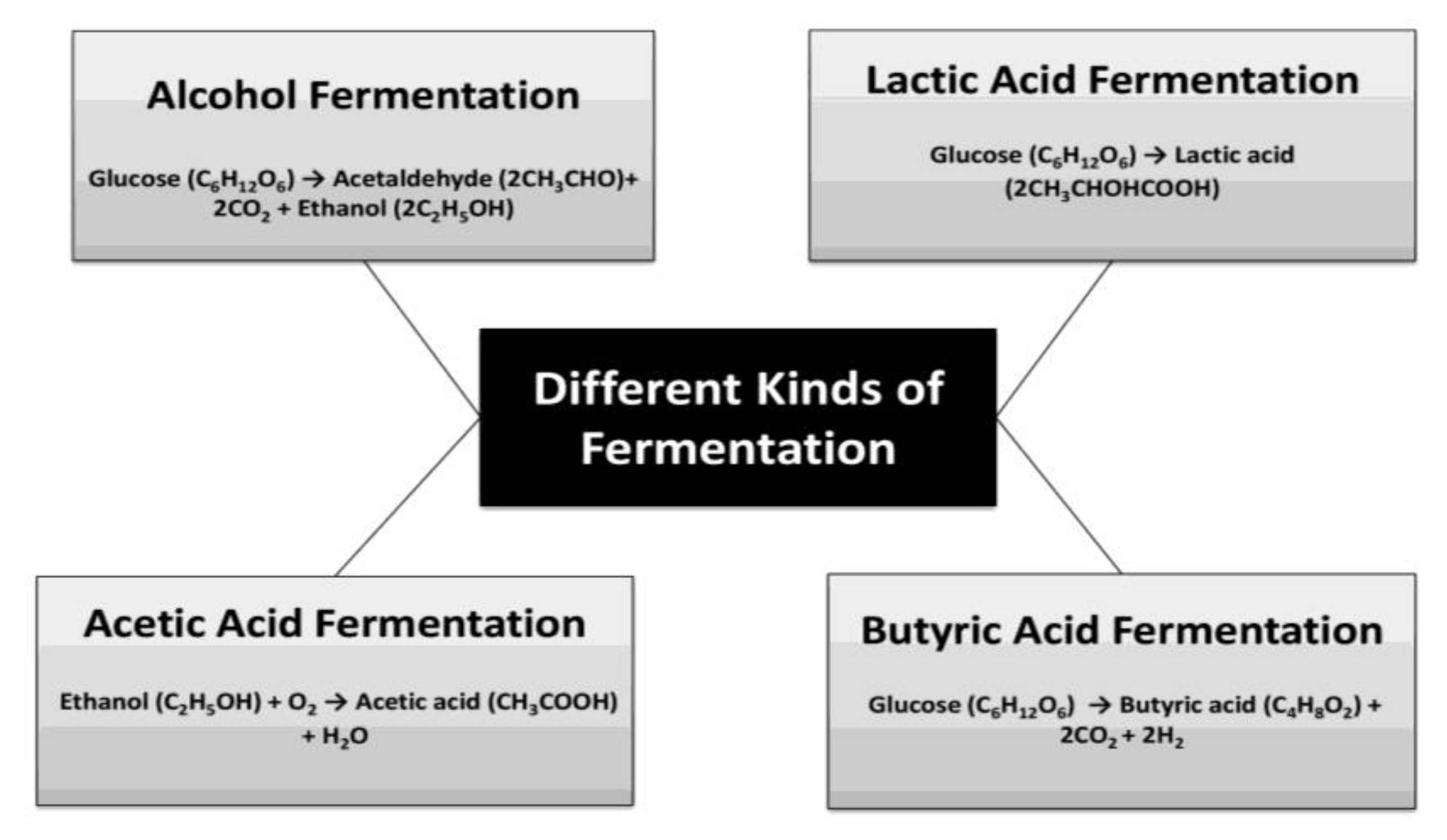
| Types | Commercial Enzymes Used in Fermentation Process | References |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Products | Lactobacillus bulgaricus | [80] |
| Lactococcus lactis | ||
| L. acidophilus | ||
| L. cremoris | ||
| L. thermophilus | ||
| L. casei | ||
| L. paracasei | ||
| L. kefiri | ||
| L. caucasicus | ||
| Penicillium camembreti | ||
| Acetobacter lovaniensis | ||
| P. roqueforti | ||
| Kluyveromyces lactis | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ||
| Cereals | L. pantheris | [80] |
| L. plantarum | ||
| Penicillium sp. | ||
| S. cerevisiae | ||
| L. mesenteroides | ||
| E. faecalis | ||
| Trichosporon pullulans | ||
| Pediococcus acidilactici | ||
| P. cerevisiae | ||
| Delbrueckii hansenii | ||
| Deb. tamari | ||
| Beverages | Aspergillus oryzae | [80] |
| Zygosaccharomyces bailii | ||
| S. cerevisiae | ||
| Acetobacter pasteurianus | ||
| Acetobacter xylinus | ||
| Gluconacetobacter | ||
| Komagataeibacter xylinus | ||
| Meat products | L. sakei | [80,82] |
| L. curvatus | ||
| L. plantarum | ||
| Leuconostoc carnosum | ||
| Leuconostoc gelidium | ||
| B. licheniformis | ||
| E. durans | ||
| E. hirae | ||
| Bacillus subtilis | ||
| L. divergens | ||
| L. carnis | ||
| E. cecorum | ||
| B. lentus | ||
| E. faecalis |
| Types | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Solid State Fermentation | Substrates need less pretreatment in comparison with liquid media | Low moisture level can restrict the growth of microorganisms |
| The medium is easily available, simple, and inexpensive | A problem in removing metabolic heat in large scale | |
| Forced aeration is usually easier | Problems and difficulties in monitoring the process parameters | |
| Contaminations are restricted since the moisture content is low | ||
| Simple fermentation equipment | ||
| Minimized and simplified downstream process and waste disposal | ||
| High volumetric productivity | ||
| Submerged Fermentation | Simplicity of measuring process parameters | Utilization of expensive equipment and costly media |
| Even distribution of microorganisms and nutrients | Expensive and complex downstream procedure and difficulty in the waste disposal | |
| Capability to control and monitor growth conditions | High power consumption | |
| Accessibility of high-water content for the growth of microbes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Lin, M. Research Progress of Fermented Functional Foods and Protein Factory-Microbial Fermentation Technology. Fermentation 2022, 8, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120688
Sun W, Shahrajabian MH, Lin M. Research Progress of Fermented Functional Foods and Protein Factory-Microbial Fermentation Technology. Fermentation. 2022; 8(12):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120688
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Wenli, Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian, and Min Lin. 2022. "Research Progress of Fermented Functional Foods and Protein Factory-Microbial Fermentation Technology" Fermentation 8, no. 12: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120688
APA StyleSun, W., Shahrajabian, M. H., & Lin, M. (2022). Research Progress of Fermented Functional Foods and Protein Factory-Microbial Fermentation Technology. Fermentation, 8(12), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120688







