Streptomyces sp. ADR1, Strain Producing β- and γ-Rubromycin Antibiotics, Isolated from Algerian Sahara Desert
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Antibiotic-Producing Strain
2.2. Taxonomic Study of the Isolated Strain
2.3. Fermentation in 16 L Stirred-Tank Bioreactor and Ethyl Acetate (EtOAc) Extraction
2.4. Cytotoxic Activity of the Microbial EtOAc Extract
2.5. Physicochemical Analysis of the Microbial Extract and Identification of Antibiotics
3. Results
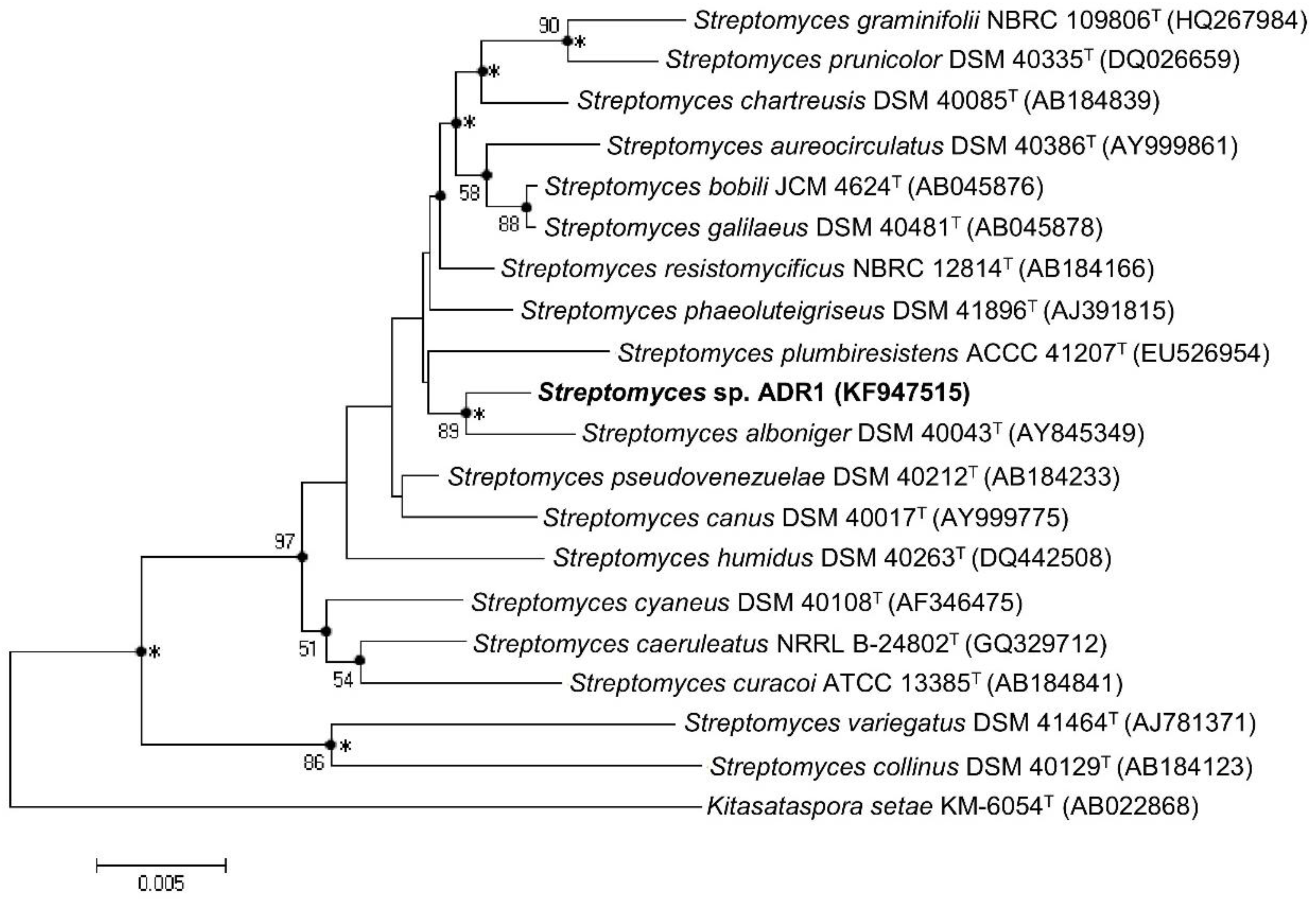
3.1. Isolation and Identification of ADR1 Strain
3.2. Cytotoxic Activity of the Microbial EtOAc Extract
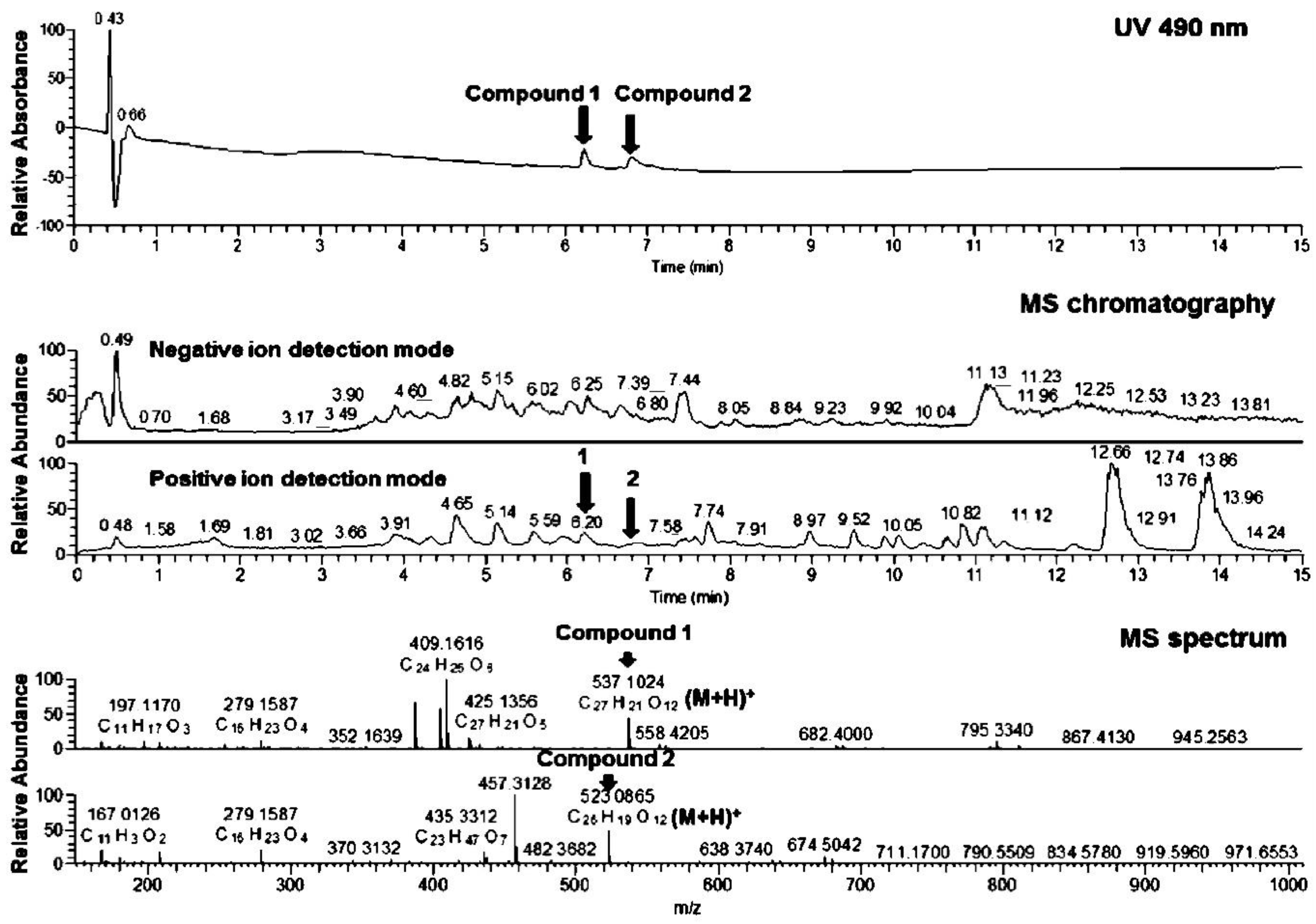
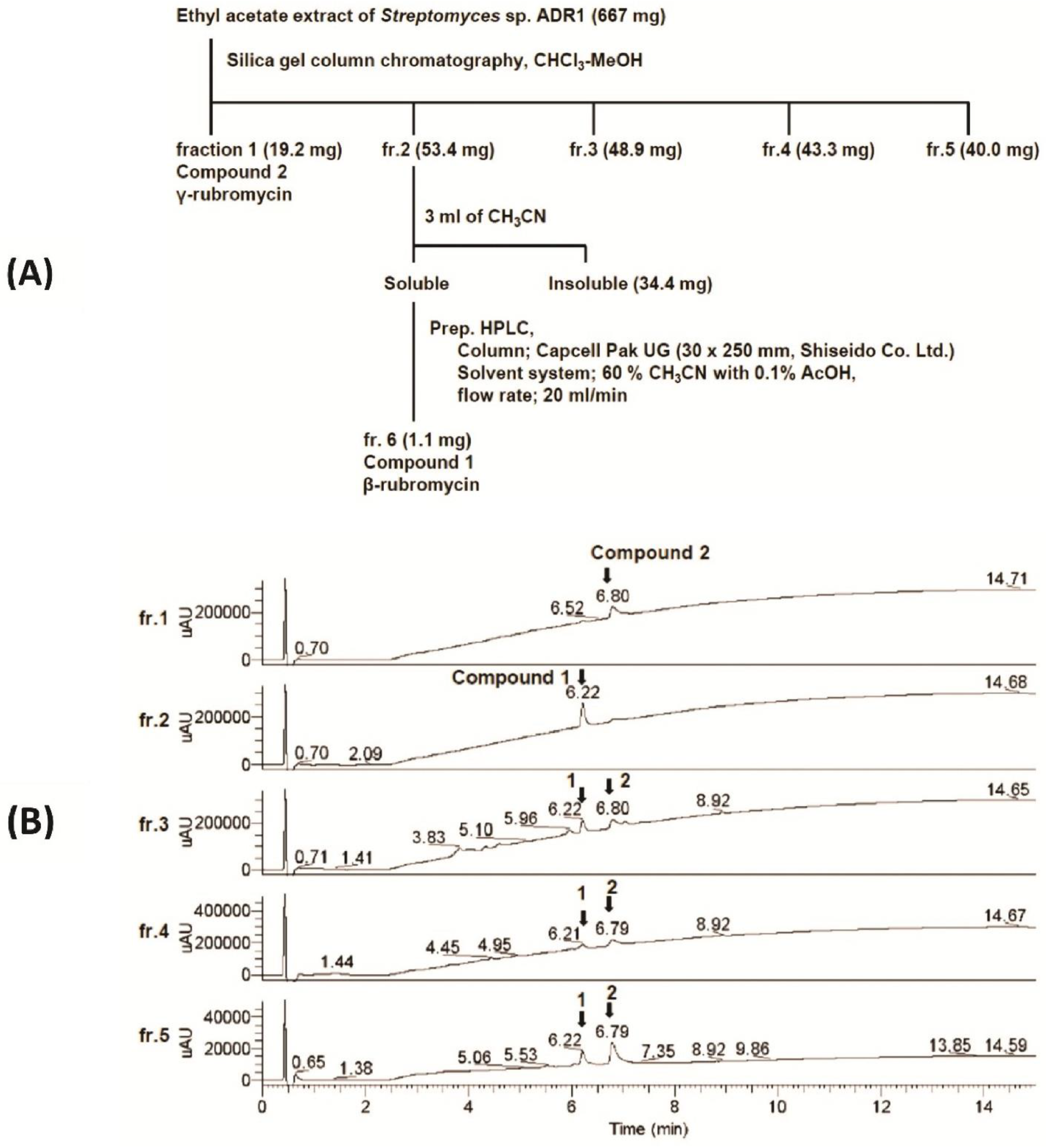
3.3. Physicochemical Analysis of the Microbial Extract and Isolation of β- and γ-Rubromycin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumehira, A.Z.; Akchiche, Y.F.; Chorfi, W.; Talhi, O.; Djidjik, R.; Dailin, J.D.; El Enshasy, H.A. Metabolomics approaches for early cancer diagnosis: A review. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2022, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, P.; Shi, L.; Garofalo, M. Role of microRNAs in chemoresistance. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.A.; Hunt, B.; Asirwa, F.C.; Adebamowo, C.; Lopes, G. Global Health Equity: Cancer Care Outcome Disparities in High-, Middle-, and Low-Income Countries. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Chen, E.; Lu, T. Anticancer drug development, a matter of money or a matter of idea. Metabolomics 2015, 5, e134. [Google Scholar]
- Amirkia, V.; Heinrich, M. Natural products and drug discovery: A survey of stakeholders in industry and academia. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive Microbial Metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, L.; Pipite, A.; Subramani, R.; Owen, J.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taufa, T. Streptomyces: Still the Biggest Producer of New Natural Secondary Metabolites, a Current Perspective. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirling, E.B.; Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1966, 16, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevalier, H.A. The actinomycetes III. A practical guide to generic identification of actinomycetes. In Bergey’s Manual Systematic Bacteriology; Williams, S.T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; Volume 4, pp. 2344–2347. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, J.M. Compendium of Actinobacteria; University of Braunschweig: Braunschweig, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nakeeb, M.A.; Lechevalier, H.A. Selective isolation of aerobic Actinomycetes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1963, 11, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locci, R. Actinomycete Spores. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schon, R.; Groth, I. Practical thin layer chromatography techniques for diaminopimelic acid and whole cell sugar analyses in the classification of environmental actinomycetes. J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.S.; Ruan, J.S. A proposal to transfer Microbispora bispora (Lechevalier 1965) to a new genus, Thermobispora gen. nov., as Thermobispora bispora comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1996, 46, 933–938. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, B.M.; Everest, G.J.; Meyers, P.R. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Kribbella based on the gyrB gene: Proposal of a gyrB-sequence threshold for species delineation in the genus Kribbella. Antoni van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 97, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.E.; Meyers, P.R. Rapid identification of filamentous actinomycetes to the genus level using genus-specific 16S rRNA gene restriction fragment patterns. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, W.M. Toward Defining the Course of Evolution: Minimum Change for a Specific Tree Topology. Syst. Biol. 1971, 20, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.K.; Lim, Y.-W. EzTaxon: A web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Woodruff, H.B. The Soil as a Source of Microorganisms Antagonistic to Disease-Producing Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1940, 40, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumehira, A.Z.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Hacène, H.; Elsayed, E.A.; Aziz, R.; Park, E.Y. Recent progress on the development of antibiotics from the genus Micromonospora. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2016, 21, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlop-Powers, Z.; Owen, J.G.; Reddy, B.V.B.; Ternei, M.A.; Brady, S.F. Chemical-biogeographic survey of secondary metabolism in soil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3757–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, H.; Renneberg, K.-H. Rubromycin, ein rotes Antibiotikum aus Actinomyceten. Naturwissenschaften 1953, 40, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumehira, A.Z.; Hacène, H.; El-Enshasy, H.A. Rubromycins: A Class of Telomerase Inhibitor Antibiotics Produced by Streptomyces spp. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Puder, C.; Loya, S.; Hizi, A.; Zeeck, A. Structural and biosynthetic investigations of the rubromycins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D.J.; Brimble, M.A. Isolation, biological activity, biosynthesis and synthetic studies towards the rubromycin family of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Takahashi, H.; Oda, M.; Mizunuma, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Goto, Y.; Mizushina, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Hayashi, H. Inhibition of human telomerase by rubromycins: Implication of spiroketal system of the compounds as an active moiety. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 5995–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buseman, C.M.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Is telomerase a viable target in cancer? Mutat. Res.-Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 2012, 730, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivancich, M.; Schrank, Z.; Wojdyla, L.; Leviskas, B.; Kuckovic, A.; Sanjali, A.; Puri, N. Treating Cancer by Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
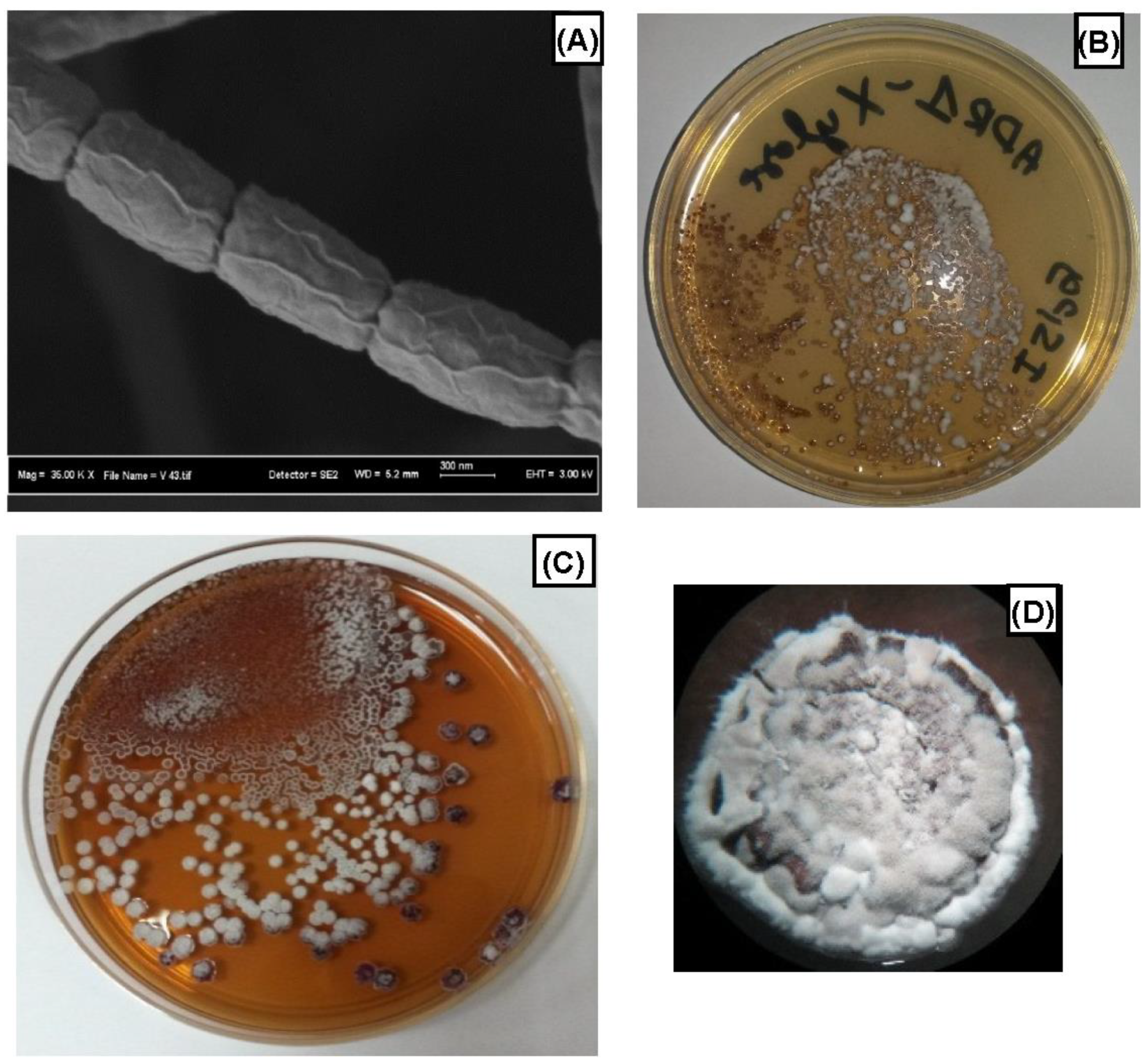

| Medium | Growth | Substrate | Soluble Pigment | Aerial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeast extract malt agar (ISP2) | Good | Purple-red | Brown-red | White |
| Oatmeal agar (ISP3) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Inorganic salt starch agar (ISP4) | Good | Purple-red | None | White |
| Glycerol asparagine agar (ISP5) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Peptone yeast extract iron agar (ISP6) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Tyrosine agar (ISP7) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Glycerol Arginine Agar (GAA) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Sabouraud 4% Glucose Agar (SGA) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Nutrient Agar (NA) | Moderate | Brown-beige | None | None |
| Microscopic Aspect | |
|---|---|
| Gram staining | Positive |
| Spore morphology | Doliform |
| Spore surface ornamentation | Irregular rugose |
| Spore dimensions (μm) | (0.617 − 1.188) × (0.524 − 0.604) |
| Spore chain morphology | Rectiflexible |
| Spores per chain | 30–60 |
| Physiological Characteristics | |
| Temperature range for growth (°C) | 15–40 |
| Optimal temperature for growth (°C) | 25–30 |
| pH range of growth | 4–11 |
| Optimal pH for growth | 7–8 |
| NaCl range for growth (%) | 0–4 |
| Optimal NaCl for growth (%) | 0 |
| Biochemical Characteristics | |
| Melanin production (ISP6) | − |
| Catalase | + |
| β-galactosidase | + |
| Citrate utilization | − |
| H2S production | − |
| Gelatin liquefaction | + |
| Hydrolysis of starch in ISP4 | + |
| Utilization as sole carbon source | |
| D-glucose | + |
| D-xylose | + |
| L-rhamnose | + |
| L-arabinose | + |
| D-fructose | + |
| D-mannitol | + |
| Iso-inositol | − |
| D-sorbitol | − |
| Glycerol | + |
| D-galacturonic acid | − |
| D-sucrose | + |
| D-melibiose | + |
| Chitine | + |
| Pectin A | + |
| Amygdaline | + |
| Medium | Streptomyces sp. ADR1 | Streptomyces pseudovenezuelae NBRC 12904T | Streptomyces alboniger NBRC 12738T | Streptomyces collinus DSM 40129T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology on ISP2 | ||||
| Growth | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Colony color | Purple-red | Safran yellow | Black-grey | Dahlia yellow |
| Aerial mycelium | White | Sparse/cream | Black-grey | Cream |
| Soluble pigment | Brown-red | None | Umbra grey | None |
| Utilization as sole carbon source | ||||
| D-glucose | + | + | + | − |
| D-xylose | + | + | − | − |
| L-rhamnose | + | + | − | + |
| L-arabinose | + | + | + | − |
| D-fructose | + | + | − | − |
| Iso-inositol | − | + | + | + |
| D-sucrose | + | + | − | − |
| Production of rubromycins | + | − | − | + |
| 16S rRNA gene pairwise similarity with Streptomyces sp. ADR1 | 99.42% | 99.28% | 96.4% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boumehira, A.Z.; Kirby, B.; Trindade, M.; Hacène, H.; Park, E.Y.; El Enshasy, H.A. Streptomyces sp. ADR1, Strain Producing β- and γ-Rubromycin Antibiotics, Isolated from Algerian Sahara Desert. Fermentation 2022, 8, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100473
Boumehira AZ, Kirby B, Trindade M, Hacène H, Park EY, El Enshasy HA. Streptomyces sp. ADR1, Strain Producing β- and γ-Rubromycin Antibiotics, Isolated from Algerian Sahara Desert. Fermentation. 2022; 8(10):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100473
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoumehira, Ali Zineddine, Bronywn Kirby, Marla Trindade, Hocine Hacène, Enoch Y. Park, and Hesham A. El Enshasy. 2022. "Streptomyces sp. ADR1, Strain Producing β- and γ-Rubromycin Antibiotics, Isolated from Algerian Sahara Desert" Fermentation 8, no. 10: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100473
APA StyleBoumehira, A. Z., Kirby, B., Trindade, M., Hacène, H., Park, E. Y., & El Enshasy, H. A. (2022). Streptomyces sp. ADR1, Strain Producing β- and γ-Rubromycin Antibiotics, Isolated from Algerian Sahara Desert. Fermentation, 8(10), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100473









