Combined Antimicrobial Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant and Supercritical CO2-Extracted Rosmarinus officinalis Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pathogenic Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
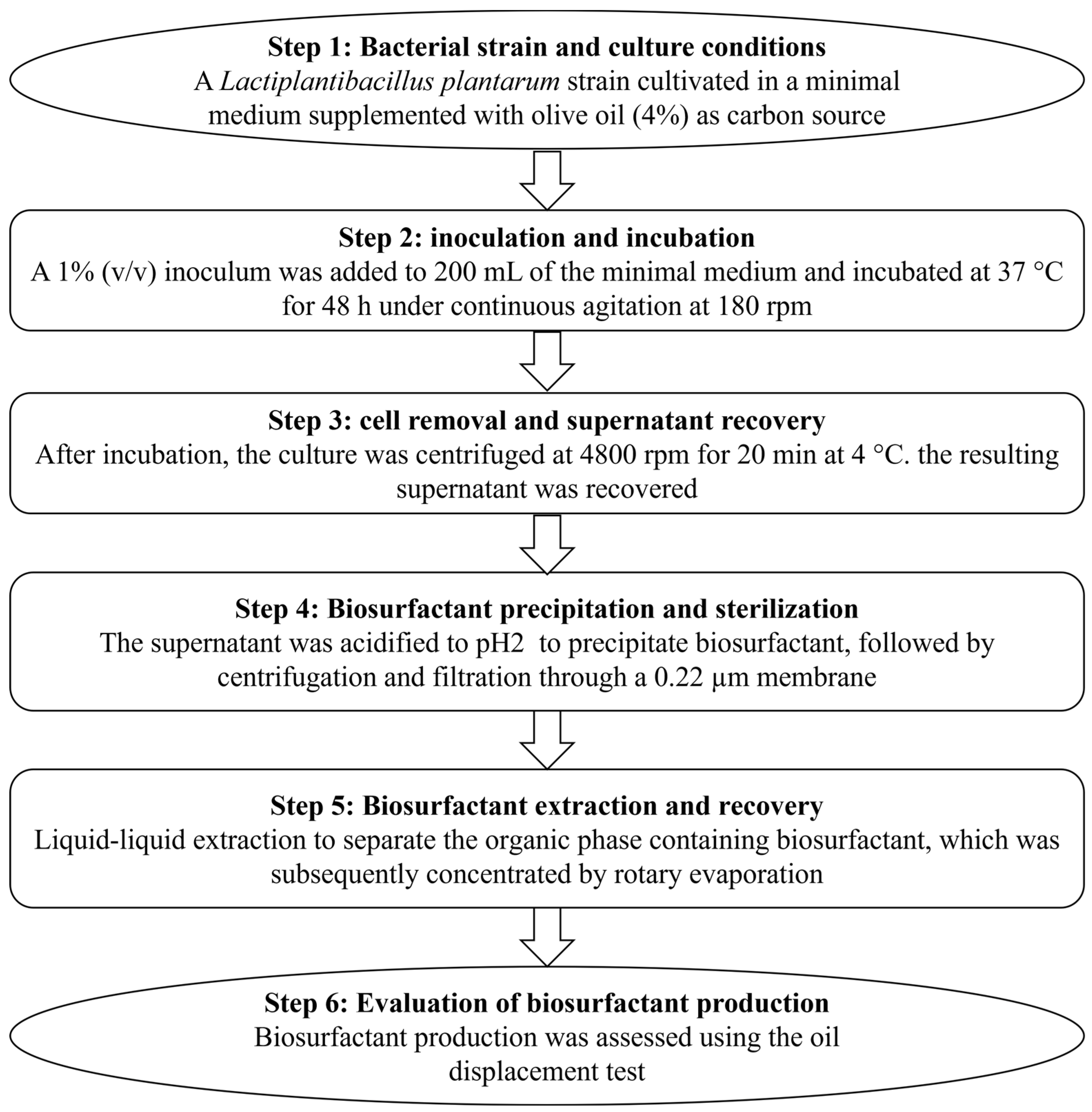
2.2. Production and Extraction of BS from L. plantarum
2.3. Oil Displacement Assay for BS Activity
2.4. Plant Material
2.5. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
2.6. Study of Antibacterial Activity
2.6.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assay
2.6.2. Determination of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Index (MAR) Index
2.6.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.6.4. Bacterial Cell Membrane Disintegration Test
2.7. RNA Extraction
2.8. RT-PCR Amplification
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Isolated S. aureus
3.2. Antibacterial Activity
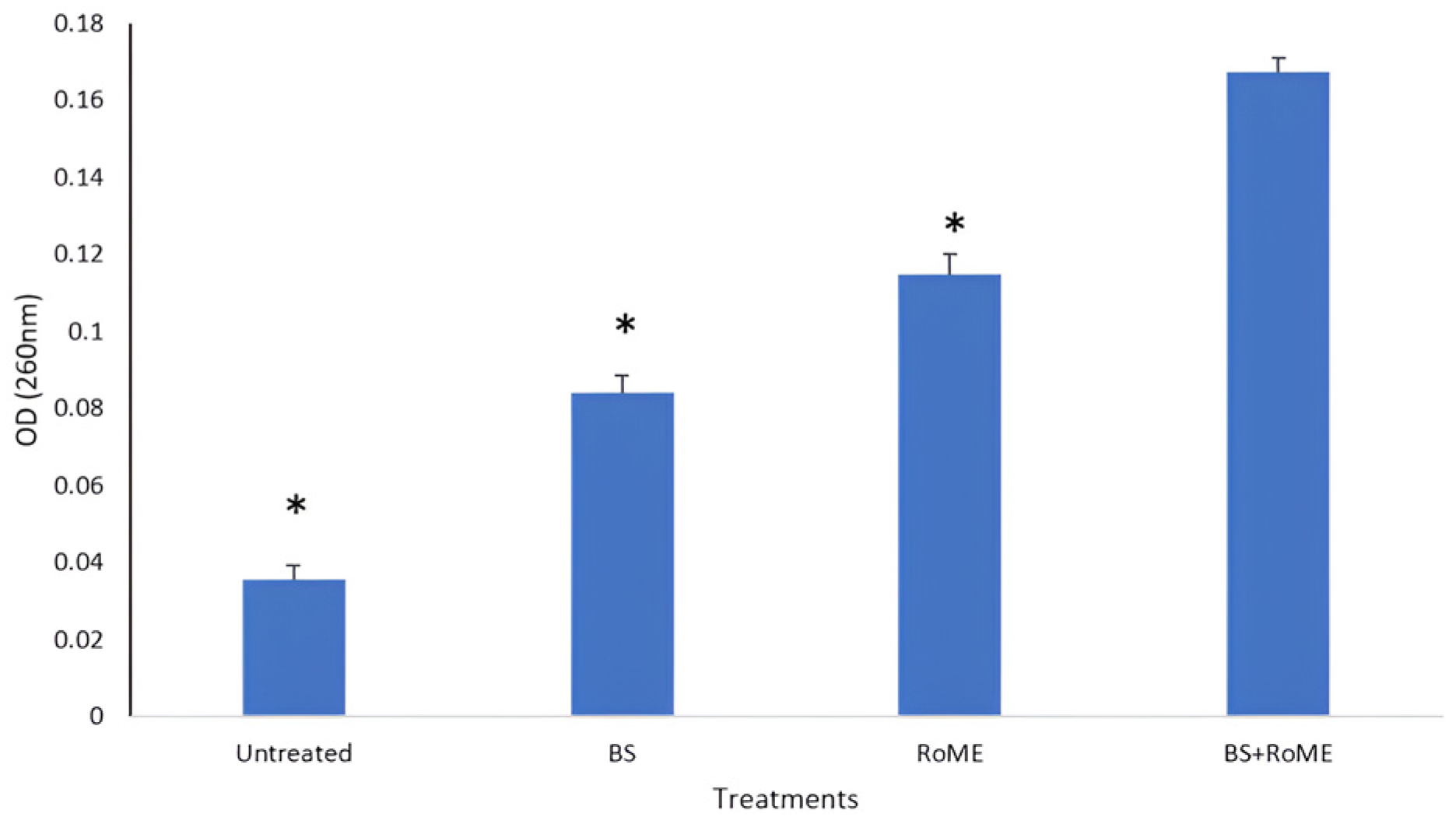
3.3. Bacterial Cell Membrane Disintegration Test
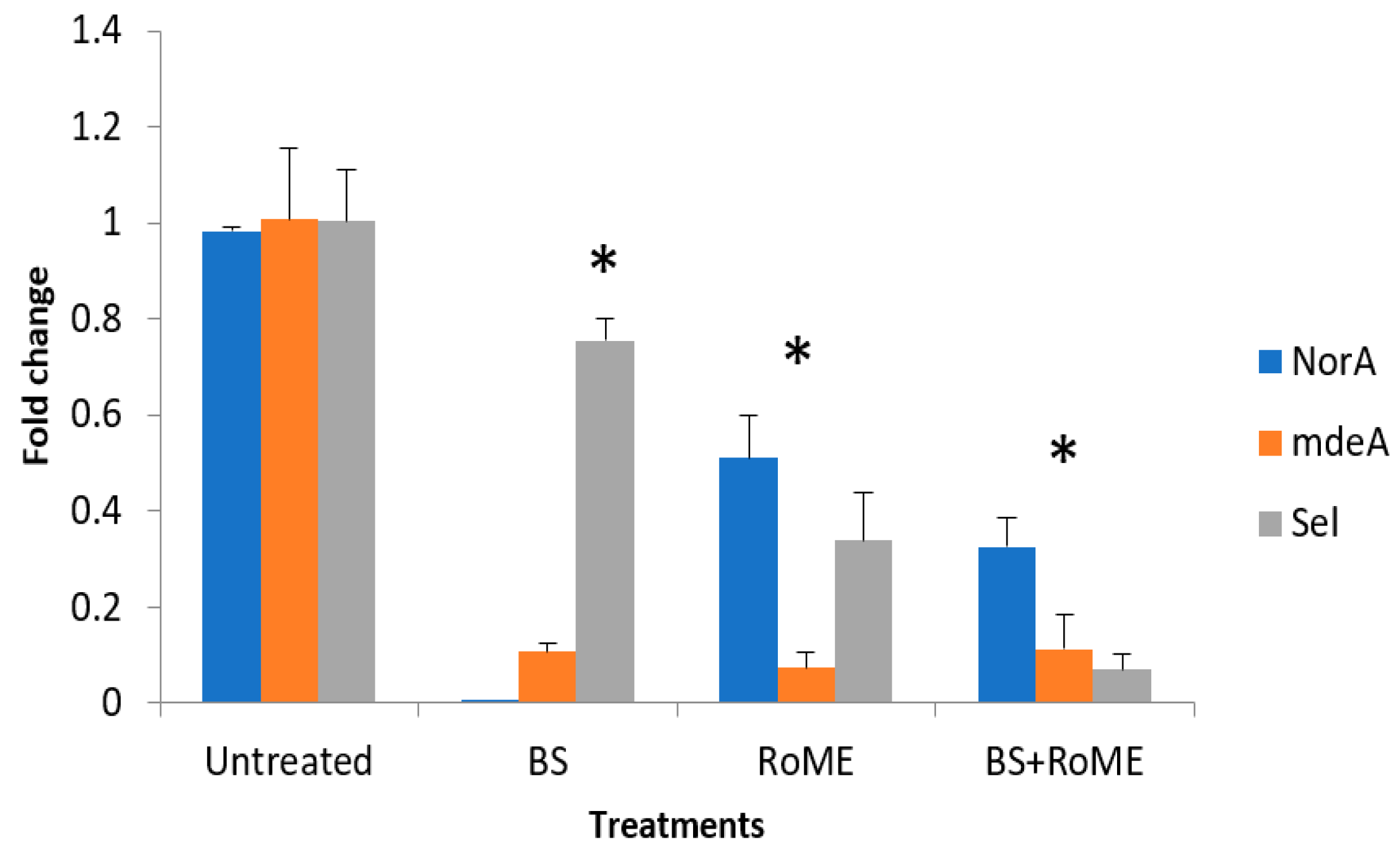
3.4. Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, S.Y.; Fowler, V.G.; Skalla, L.; Holland, T.L. Management of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A review. JAMA 2025, 334, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular characterization, evolution, and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21, Volume 3, Chapter 1. Part 182, Substances Generally Recognized as Safe, Subpart A, General Provision, Section 182.20, Essential Oils, Oleoresins (Solvent Free), and Natural Extractives (Including Distillates); Office of the Federal Register National Archives and Records: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mouafo, H.T.; Sokamte, A.T.; Manet, L.; Mbarga, A.J.M.; Nadezdha, S.; Devappa, S.; Mbawala, A. Biofilm inhibition, antibacterial and antiadhesive properties of a novel biosurfactant from Lactobacillus paracasei N2 against multi-antibiotics-resistant pathogens isolated from braised fish. Fermentation 2023, 9, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, A.N.; Prapulla, S.G. Evaluation and functional characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Lactobacillus plantarum CFR 2194. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Bioprospecting antimicrobials from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: Key factors underlying its probiotic action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdhi, A.; Leban, N.; Chakroun, I.; Bayar, S.; Mahdouani, K.; Majdoub, H.; Kouidhi, B. Use of extracellular polysaccharides, secreted by Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus spp., as reducing indole production agents to control biofilm formation and efflux pumps inhibitor in Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gu, S.; Cui, X.; Shi, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, H.; Ge, J. Antimicrobial, anti-adhesive and anti-biofilm potential of biosurfactants isolated from Pediococcus acidilactici and Lactobacillus plantarum against Staphylococcus aureus CMCC26003. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Savoia, D. Plant-derived antimicrobial compounds: Alternatives to antibiotics. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 979–990. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, G.; Ros, G.; Castillo, J. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis, L.): A review. Medicines 2018, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, M.; Junghanns, W. Rosmarinus officinalis L.: Rosemary. In Medicinal, Aromatic and Stimulant Plants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 501–521. [Google Scholar]
- Reverchon, E.; Della Porta, G.; Gorgoglione, D. Supercritical CO2 extraction of volatile oil from rose concrete. Flavour Fragr. J. 1997, 12, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Porto, C.; Decorti, D.; Natolino, A. Application of a supercritical CO2 extraction procedure to recover volatile compounds and polyphenols from Rosa damascena. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, Y.; Velamuri, R.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. Full-spectrum analysis of bioactive compounds in rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) as influenced by different extraction methods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, A.; Allahri, F.B.; Samian, P.; Najarkolaee, S.M.G.; Yusofvand, R.; Eslammanesh, T.; Hassanshahi, M. Investigating The Synergistic and Antimicrobial Effect of Glycolipid Biosurfactants Produced by Shewanella alga 12B and Bacillus pumilus SG Bacteria with Thyme Plant Extract on Some Pathogenic Bacteria. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2024, 26, e157556. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, W.; Meldrum, D.R. RT-qPCR based quantitative analysis of gene expression in single bacterial cells. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 85, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Ahn, J. Differential gene expression in planktonic and biofilm cells of multiple antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Slama, R.; Kouidhi, B.; Zmantar, T.; Chaieb, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Anti-listerial and anti-biofilm activities of potential Probiotic Lactobacillus strains isolated from Tunisian traditional fermented food. J. Food Saf. 2013, 33, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Haddaji, N.; Ncib, K.; Bahia, W.; Ghorbel, M.; Leban, N.; Bouali, N.; Bechambi, O.; Mzoughi, R.; Mahdhi, A. Control of multidrug-resistant pathogenic staphylococci associated with vaginal infection using biosurfactants derived from potential probiotic Bacillus strain. Fermentation 2022, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, M.I.; Gayathiri, S.; Gnanaselvi, U.; Jenifer, P.S.; Raj, S.M.; Gurunathan, S. Novel lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by hydrocarbon degrading and heavy metal tolerant bacterium Escherichia fergusonii KLU01 as a potential tool for bioremediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9291–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.; Ahmad, S.A.; Wan Johari, W.L.; Abd Shukor, M.Y.; Alias, S.A.; Smykla, J.; Saruni, N.H.; Abdul Razak, N.S.; Yasid, N.A. Production of lipopeptide biosurfactant by a hydrocarbon-degrading Antarctic Rhodococcus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnif, S.; Chamkha, M.; Labat, M.; Sayadi, S. Simultaneous hydrocarbon biodegradation and biosurfactant production by oilfield-selected bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Soni, J.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, J. A study on biosurfactant production in Lactobacillus and Bacillus sp. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 723–733. [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan, C.N.; Cooper, D.G.; Neufeld, R.J. Selection of microbes producing biosurfactants in media without hydrocarbons. J. Ferment. Technol. 1984, 62, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Dhouibi, N.; Manuguerra, S.; Arena, R.; Mahdhi, A.; Messina, C.M.; Santulli, A.; Dhaouadi, H. Screening of antioxidant potentials and bioactive properties of the extracts obtained from two Centaurea L. Species (C. kroumirensis Coss. and C. sicula L. subsp sicula). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titilawo, Y.; Sibanda, T.; Obi, L.; Okoh, A. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of faecal contamination of water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10969–10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Rajeswari, P.; Kumar, B.S.; Saipriyanga, V.; Kalpana, M. Multi-drug resistant patterns of biofilm forming Aeromonas hydrophila from urine samples. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Sundheim, G.; Hagtvedt, T.; Dainty, R. Resistance of meat associated staphylococci to a quarternary ammonium compound. Food Microbiol. 1992, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y. Mode of action of pentocin 31-1: An antilisteria bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus pentosus from Chinese traditional ham. Food Control 2008, 19, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lee, H.; Ahn, J. Growth and virulence properties of biofilm-forming Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium under different acidic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7910–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latteef, N.S.; Salih, W.Y.; Abdulhassan, A.A.; Obeed, R.J. Evaluation of gene expression of norA and norB gene in ciproflaxin and levofloxacin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Arch. Razi Inst. 2022, 77, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Mahato, R.P.; Ch, S.; Kumbham, S. Current strategies against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and advances toward future therapy. Microbe 2025, 6, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Bonomo, R.A. Combination therapy for extreme drug–resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Ready for prime time? Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Kimera, Z.I.; Mshana, S.E.; Rweyemamu, M.M.; Mboera, L.E.; Matee, M.I. Antimicrobial use and resistance in food-producing animals and the environment: An African perspective. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saber, T.; Samir, M.; El-Mekkawy, R.M.; Ariny, E.; El-Sayed, S.R.; Enan, G.; Abdelatif, S.H.; Askora, A.; Merwad, A.M.; Tartor, Y.H. Methicillin-and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from humans and ready-to-eat meat: Characterization of antimicrobial resistance and biofilm formation ability. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 735494. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, B.; Gwida, M.; Sadat, A.; El-Toukhy, M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, M.S.; Elafify, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of virulent Listeria monocytogenes and Cronobacter sakazakii in dairy cattle, the environment, and dried milk with the in vitro application of natural alternative control. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Ashraf, S.A.; Surti, M.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Snoussi, M.; Hamadou, W.S.; Bardakci, F.; Jamal, A.; Jahan, S.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-derived biosurfactant attenuates quorum sensing-mediated virulence and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, B.; Kaur, S.; Dwibedi, V.; Albadrani, G.M.; Al-Ghadi, M.Q.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Unveiling the antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of biosurfactant produced by newly isolated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain 1625. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1459388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Makkar, R.S.; Cameotra, S.S. Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, M.; Costa, S. Biosurfactants in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, M.; Karygianni, L.; Argyropoulou, A.; Anderson, A.C.; Hellwig, E.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Wittmer, A.; Vach, K.; Al-Ahmad, A. The antimicrobial effect of Rosmarinus officinalis extracts on oral initial adhesion ex vivo. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 4369–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilal, A.; Sabu, K.R.; Woldemariam, M.; Aklilu, A.; Biresaw, G.; Yohanes, T.; Seid, M.; Merdekios, B. Antibacterial activity of Rosmarinus officinalis against multidrug-resistant clinical isolates and meat-borne pathogens. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6677420. [Google Scholar]
- Del Campo, J.; Amiot, M.; Nguyen-The, C. Antimicrobial effect of rosemary extracts. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camargo, A.d.P.; García-Cañas, V.; Herrero, M.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Comparative study of green sub- and supercritical processes to obtain carnosic acid and carnosol-enriched rosemary extracts with in vitro anti-proliferative activity on colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khashei, S.; Fazeli, H.; Rahimi, F.; Karbasizadeh, V. Antibiotic-potentiating efficacy of Rosmarinus officinalis L. to combat planktonic cells, biofilms, and efflux pump activities of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1558611. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-El Tawab, A.A.; El-Hofy, F.I.; Mobarez, E.A.; Taha, H.S.; Tawkol, N.Y. Synergistic effect between some antimicrobial agents and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) toward Staphylococcus aureus–in-vitro. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2015, 28, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourabiti, F.; Derdak, R.; El Amrani, A.; Momen, G.; Timinouni, M.; Soukri, A.; El Khalfi, B.; Zouheir, Y. The antimicrobial effectiveness of Rosmarinus officinalis, Lavandula angustifolia, and Salvia officinalis essential oils against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in silico. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 168, 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Smuts, J.P.; Dodbiba, E.; Rangarajan, R.; Lang, J.C.; Armstrong, D.W. Degradation study of carnosic acid, carnosol, rosmarinic acid, and rosemary extract (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) assessed using HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9305–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Mun, S.; Kim, Y. Influences of added surfactants on the water solubility and antibacterial activity of rosemary extract. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.Y.; Trucksis, M.; Hooper, D.C. Quinolone resistance mediated by norA: Physiologic characterization and relationship to flqB, a quinolone resistance locus on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussama, B.K.; Fatima, S.; Djilali, B.; Rym, B. The Combined effect of Rosmarinus officinalis L essential oil and Bacteriocin BacLP01 from Lactobacillus plantarum against Bacillus subtilis ATCC11778. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 7, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; O’Toole, P.W.; Shen, W.; Amrine-Madsen, H.; Jiang, X.; Lobo, N.; Palmer, L.M.; Voelker, L.; Fan, F.; Gwynn, M.N.; et al. Novel chromosomally encoded multidrug efflux transporter MdeA in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.; Abrantes, P.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Couto, I. Occurrence and variability of the efflux pump gene norA across the Staphylococcus genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Hillebrand, G.G.; Nunez, G. Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) extracts containing carnosic acid and carnosol are potent quorum sensing inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.A.M.; Abdelgalil, S.Y.; Khamis, T.; Abdelwahab, A.M.; Atwa, D.N.; Elmowalid, G.A. Thymoquinone’potent impairment of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump activity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16483. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, A.; Mooyottu, S.; Yin, H.; Nair, M.S.; Bhattaram, V.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Inhibiting microbial toxins using plant-derived compounds and plant extracts. Medicines 2015, 2, 186–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Onodera, Y.; Lee, J.C.; Hooper, D.C. NorB, an efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus strain MW2, contributes to bacterial fitness in abscesses. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7123–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, R.; Berry, V. Bacterial biofilm formation, pathogenicity, diagnostics and control: An overview. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2009, 63, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Darie-Niţă, R.N.; Vasile, C.; Stoleru, E.; Pamfil, D.; Zaharescu, T.; Tarţău, L.; Tudorachi, N.; Brebu, M.A.; Pricope, G.M.; Dumitriu, R.P.; et al. Evaluation of the rosemary extract effect on the properties of polylactic acid-based materials. Materials 2018, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Mendoza, L.; Guamba, E.; Miño, K.; Romero, M.P.; Levoyer, A.; Alvarez-Barreto, J.F.; Machado, A.; Alexis, F. Antimicrobial properties of plant fibers. Molecules 2022, 27, 7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotic | Tob | Gn | Kan | E | Cl | Nrfx | Lfx | Cpfx | Sxt | Lzd | Tec | Van | Tgc | Te | Fox | P G | Ox | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disc charge (µg) | 10 | 10 | 30 | 15 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 1.25–23.75 | 10 | 30 | 5 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 1U | 1 | 5 |
| S. aureus | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | R | S |
| Gene | Molecular Function | Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| mdeA | Multidrug efflux A | F: GTTTATGCGATTCGAATGGTTGGT R: AATTAATGCAGCTGTTCCGATAGA | [17] |
| norA | Efflux pumps | F: ATCGGTTTAGTAATACCAGTCTTGC R: GCGATATAATCATTTGAGATAACGC | [33] |
| sel | Enterotoxin | F: TAGATTCGCCAAGAATAATACC R: CTTTACCAGTATCATTGTGTCC | [17] |
| 16S rRNA | House Keeping gene | F: AGGCCTTCGGGTTGTAAAGT R: GTTAGCCGGTGCTTCTTCTG | [17] |
| Antibacterial Effect of BS and RoME Against S. aureus | ||
|---|---|---|
| MIC (mg/mL) | ||
| BS | RoME | |
| S. aureus | 0.125 | 0.5 |
| Oil displacement | ||
| BS | SDS | |
| Average clear zone (cm) | 3.8 ± 0.01 | 2.45 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Haddaji, N.; Leban, N.; Rouihem, W.; Almalg, A.S.; Alamoudi, M.O.; Majdoub, H.; Mahdhi, A. Combined Antimicrobial Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant and Supercritical CO2-Extracted Rosmarinus officinalis Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Fermentation 2026, 12, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation12010050
Haddaji N, Leban N, Rouihem W, Almalg AS, Alamoudi MO, Majdoub H, Mahdhi A. Combined Antimicrobial Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant and Supercritical CO2-Extracted Rosmarinus officinalis Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Fermentation. 2026; 12(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation12010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaddaji, Najla, Nadia Leban, Wissal Rouihem, Ali Saud Almalg, Muna O. Alamoudi, Hatem Majdoub, and Abdelkarim Mahdhi. 2026. "Combined Antimicrobial Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant and Supercritical CO2-Extracted Rosmarinus officinalis Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Fermentation 12, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation12010050
APA StyleHaddaji, N., Leban, N., Rouihem, W., Almalg, A. S., Alamoudi, M. O., Majdoub, H., & Mahdhi, A. (2026). Combined Antimicrobial Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant and Supercritical CO2-Extracted Rosmarinus officinalis Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Fermentation, 12(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation12010050






