Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids During Zaolajiao Fermentation: Correlation with Physicochemical Properties and CAZymes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. E-Nose Analysis
2.3. Total Acid and Amino Acid Nitrogen Assays
2.4. Soluble Sugar and CAZymes Assay
2.5. Targeted Quantification of Organic Acids (OAs)
2.5.1. Sample Handling
2.5.2. Organic Acid Detection
2.5.3. The Calculation of Taste Activity Value (TAV)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of E-Nose
3.2. Physical and Chemical Properties Profiling of the Samples
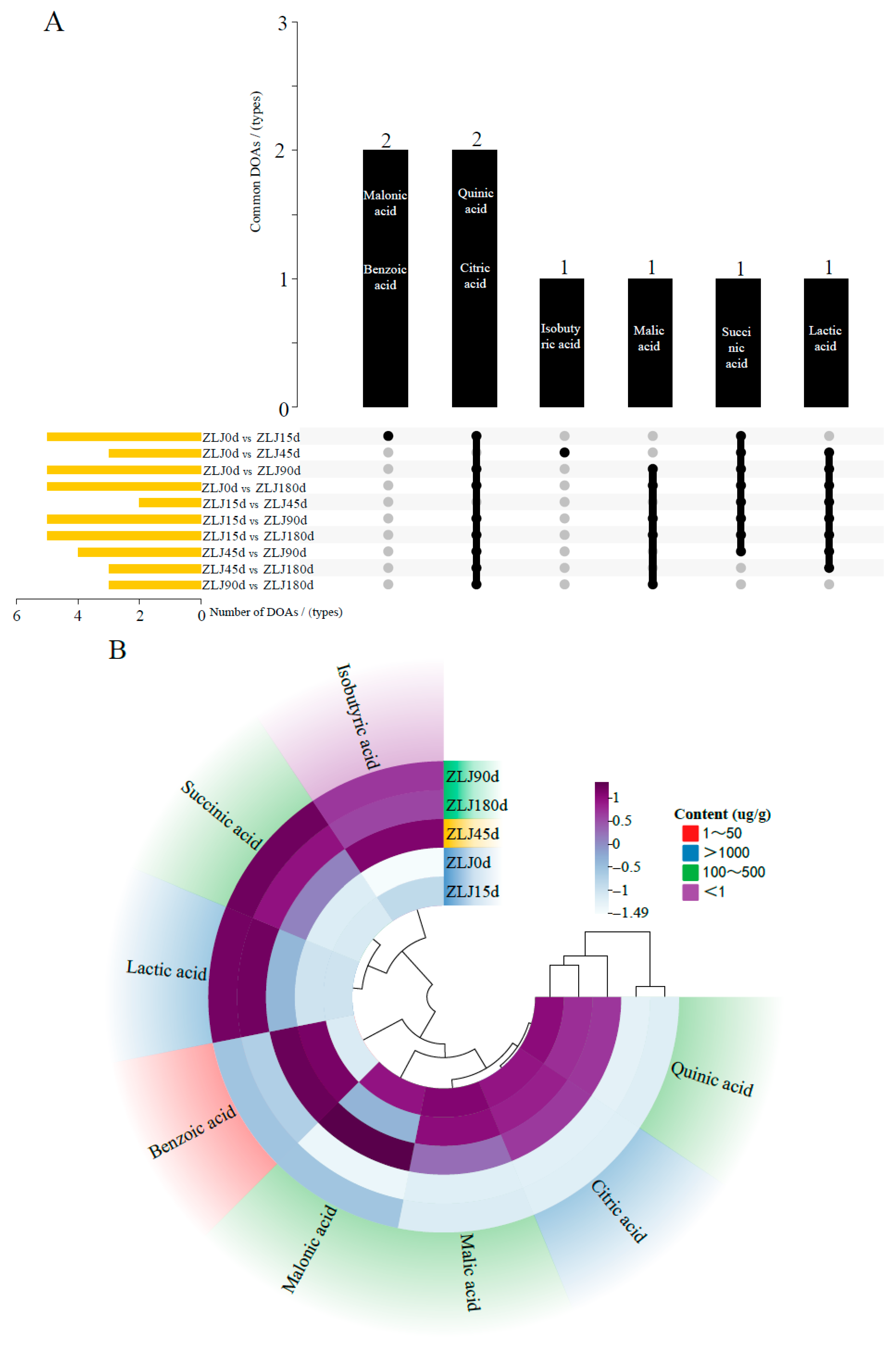
3.3. Analysis of Changes in Organic Acids During Fermentation of Zaolajiao
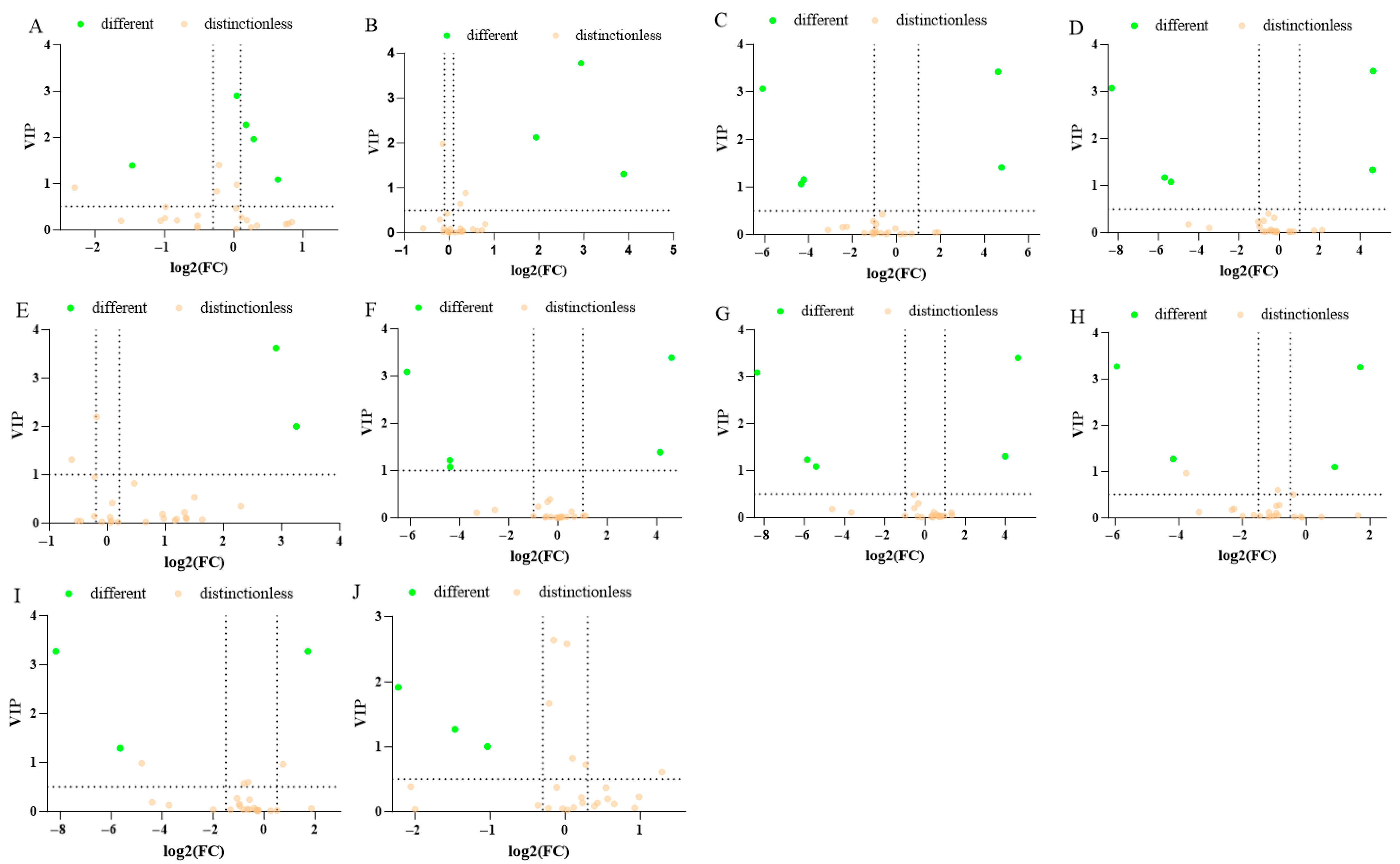
3.4. Analysis of DOAs in the Fermentation Process of Zaolajiao
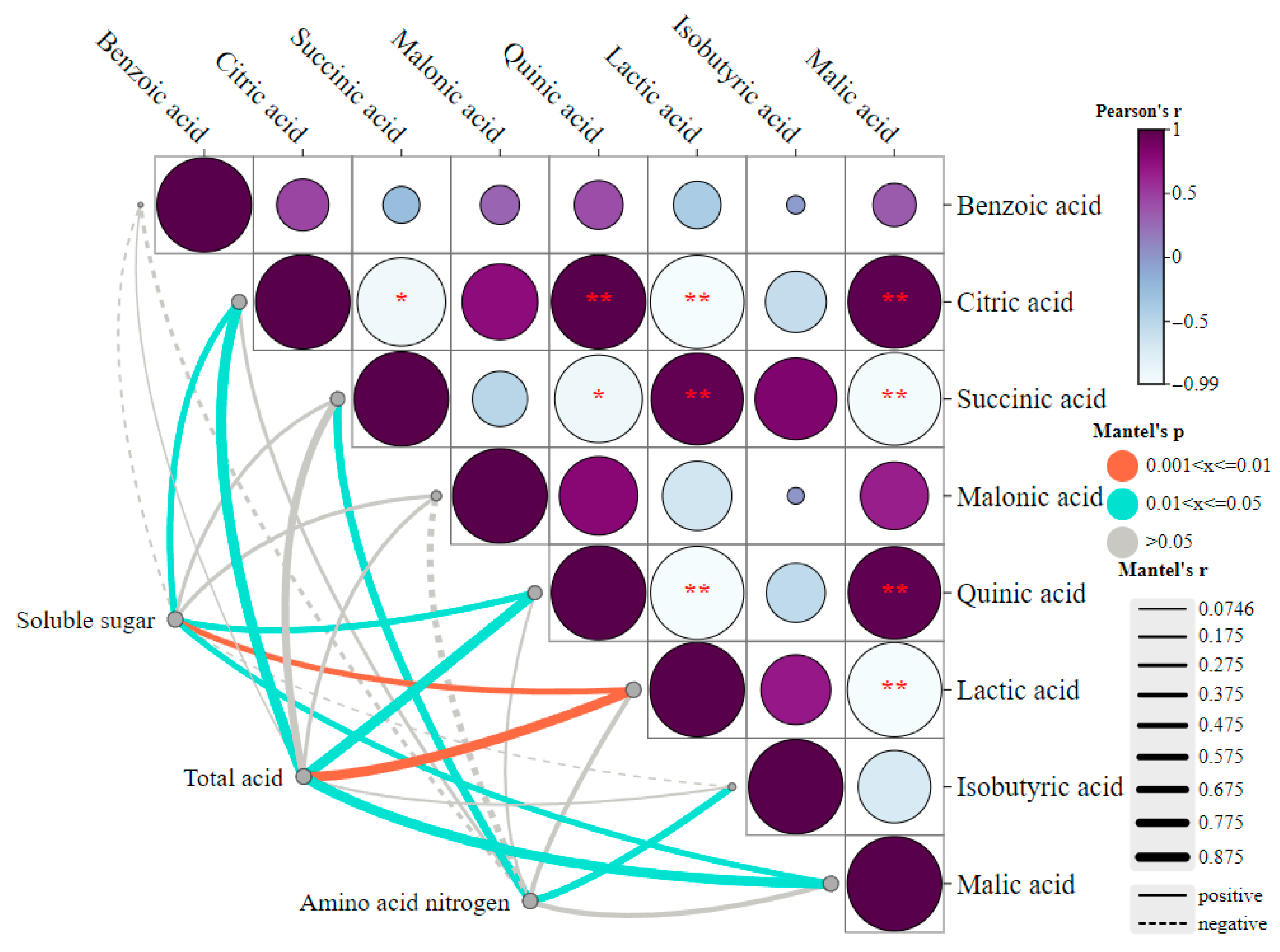
3.5. Analysis of the Relationship Between Physical and Chemical Indicators and DOAs
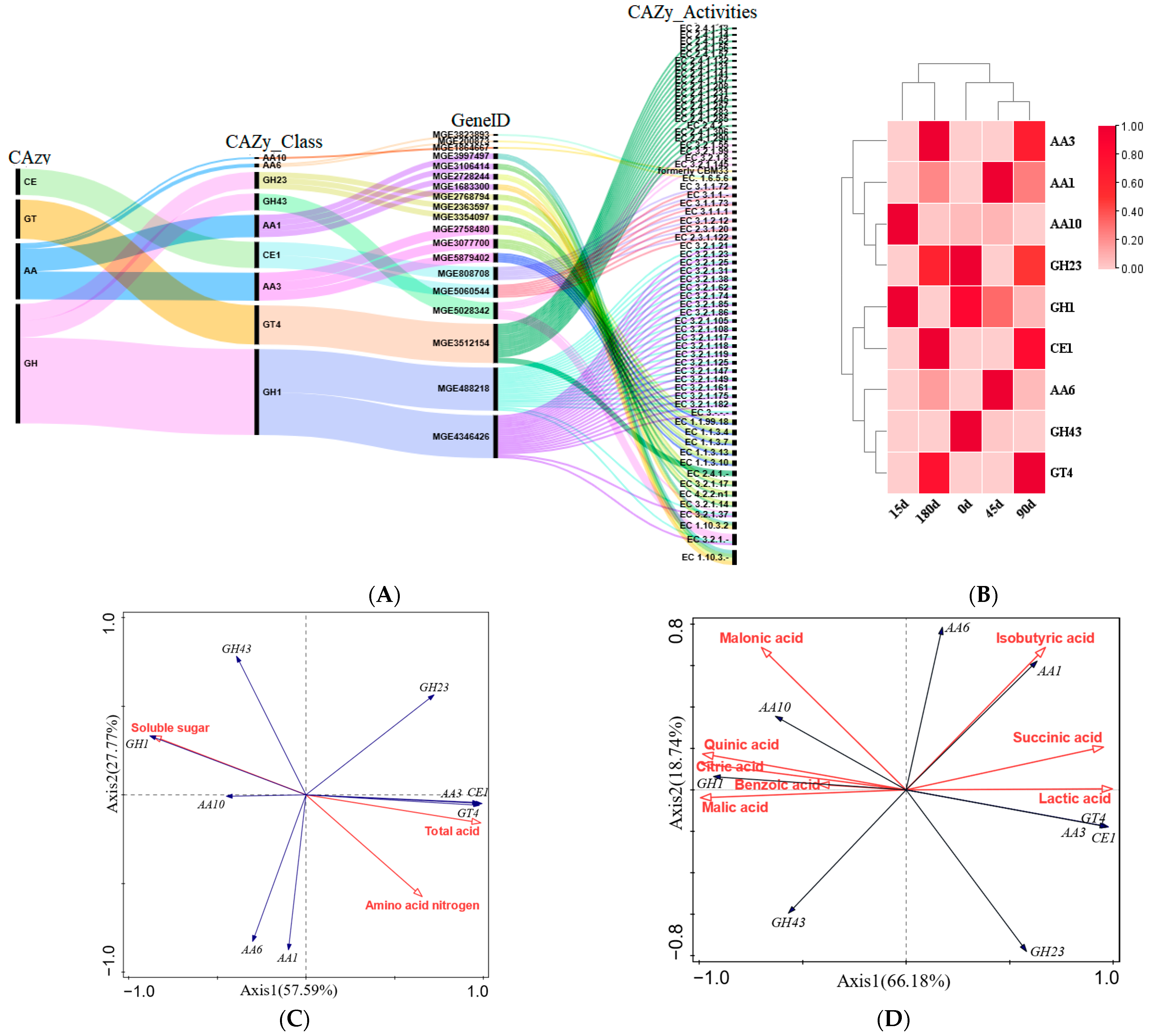
3.6. Analysis of the Relationship Between CAZymes, DOAs, and Physicochemical Indicators During Fermentation of Zaolajiao
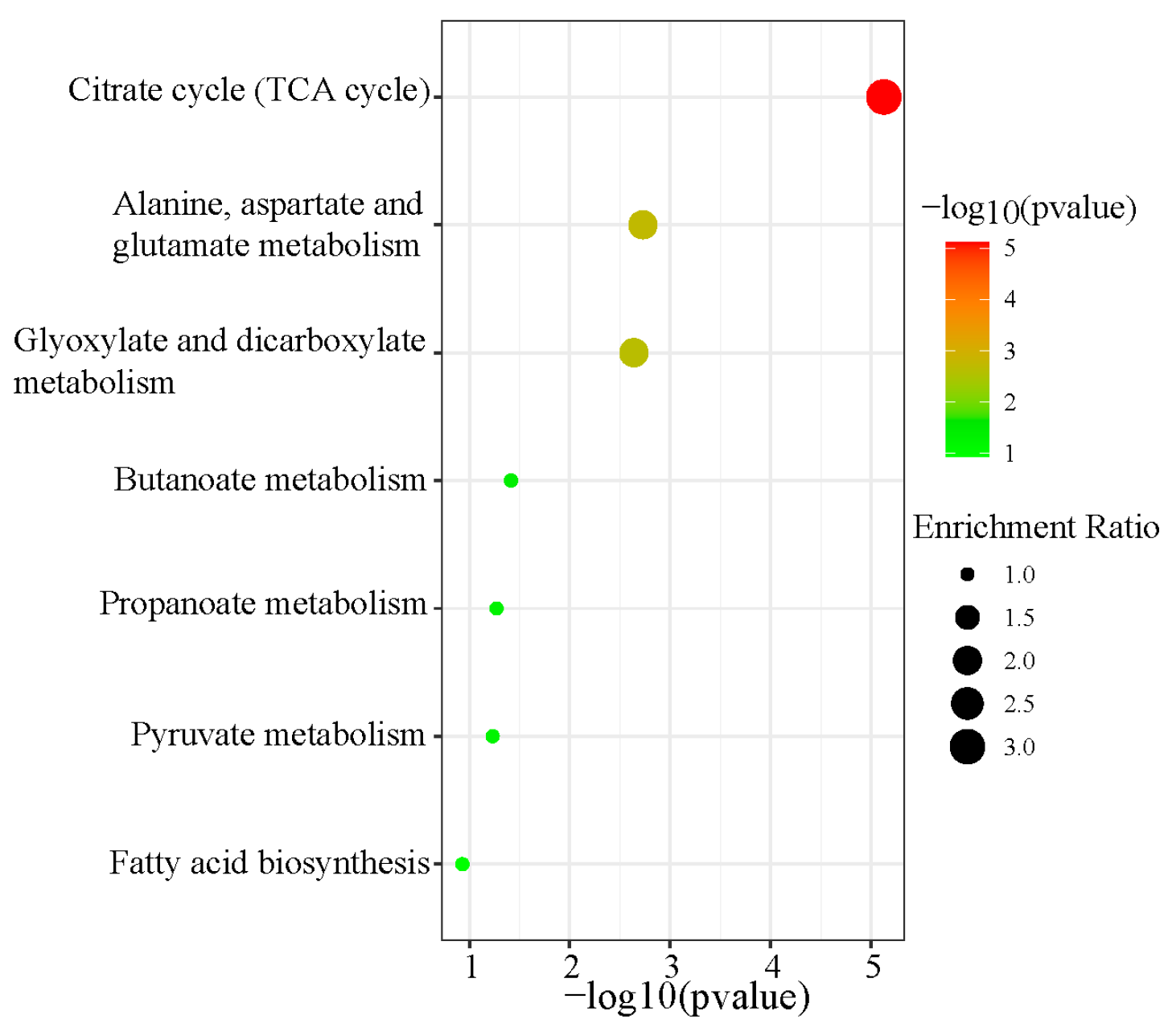
3.7. Metabolic Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Differential Organic Acids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subhash, K.; Longvah, T. Capsaicinoids, amino acid and fatty acid profiles in different fruit components of the world hottest Naga king chilli (Capsicum chinense Jacq). Food Chem. 2018, 238, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Geng, Y.; Wang, M.; Lv, D.; Huang, S.; Guan, Y.; Hu, Y. Relationship between microbial community and flavor profile during the fermentation of chopped red chili (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, B.; Zhao, W.; Lao, F.; Chen, F.; Liao, X.; Wu, J. Shifts in autochthonous microbial diversity and volatile metabolites during the fermentation of chili pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.). Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xu, X.; Du, T.; Liu, Q.; Huang, T.; Ren, H.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Organic acids drove the microbiota succession and consequently altered the flavor quality of Laotan Suancai across fermentation rounds: Insights from the microbiome and metabolome. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, C.; Shuang, Q. Novel insight into physicochemical and flavor formation in koumiss based on microbial metabolic network. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Physicochemical properties and flavour profile of fermented dry sausages with a reduction of sodium chloride. LWT 2020, 124, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Huang, E.; Xia, S.; He, C.; Ye, G. Bioturbation analysis of microbial community and organic acid metabolism in the enriched liquid of pit mud by Daqu, HuangShui, and ZaoPei. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 34, 1981–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-X.; Shi, W.; Huang, T.-C.; Mei, J.-L.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; et al. Overproduction of organic acids affects the microbial community succession and flavor metabolism during Baijiu fermentation. LWT 2024, 213, 117093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, N.; Hu, K.; Liu, S.; Blaiotta, G.; Zhou, J. Uncovering the microbial community dynamics and metabolic pathways of primary organic acids in Sichuan Baoning vinegar through metagenomics. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Xue, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, C.; Zheng, F.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Analysis of bacterial community dynamics in the manufacture process of lajiaojiang (red chili paste). LWT 2020, 122, 108976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, B.; Zhao, W.; Pang, X.; Wu, J. Correlation between autochthonous microbial communities and key odorants during the fermentation of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Li, W.; Lu, M.; Sun, X.; Yin, Y. Revealing core functional microorganisms in the fermentation process of Qicaipaojiao (Capsicum annuum L.) based on microbial metabolic network. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, X.; Bi, S.; Pan, X.; Lao, F.; Wu, J. Identification and validation of core microbes associated with key aroma formation in fermented pepper paste (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Effect of ripening and variety on the physiochemical quality and flavor of fermented Chinese chili pepper (Paojiao). Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, C.; Deng, F.; Zhou, H. SPME/GC-MS characterization of volatile compounds of Chinese traditional-chopped pepper during fermentation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, M. Effect of ageing time on the flavour compounds in Nanjing water-boiled salted duck detected by HS-GC-IMS. LWT 2022, 155, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, F.; Qu, D.; Wan, T.; Xi, L.; Hu, C.Y. Aroma characterization of Sichuan and Cantonese sausages using electronic nose, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, gas chromatography-olfactometry, odor activity values and metagenomic. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, M.; Zhao, N.; Tu, L.; Xue, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Metabolic profile of main organic acids and its regulatory mechanism in solid-state fermentation of Chinese cereal vinegar. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, Y.; Cui, M.; Ma, X.; Yin, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Gao, F. Characterization of differences in physicochemical properties, volatile organic compounds and non-volatile metabolites of prune wine by inoculation of different lactic acid bacteria during malolactic fermentation. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Jin, P.; Tang, S.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Xiong, F.; et al. Serum metabolite signatures in normal individuals and patients with colorectal adenoma or colorectal cancer using UPLC-MS/MS method. J. Proteomics 2023, 270, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Sun, B.; Fu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Li, X. Analysis of Physicochemical Indices, Volatile Flavor Components, and Microbial Community of a Light-Flavor Daqu. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 76, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.P.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Jinhua ham aroma profiles in specific to aging time by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Guan, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Hu, F.; Khan, M.R.; Wei, Z.J. Metabolomics and HS-SPME-GC-MS-based analysis of quality succession patterns and flavor characteristics changes during the fermentation of Lycium barbarum and Polygonatum cyrtonema compound wine. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandić, L.M.; Žulj, M.M.; Fruk, G.; Skendrovic, M.; Jeromel, A. The profile of organic acids and polyphenols in apple wines fermented with different yeast strains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yin, R.; Xie, Y.; Ma, X.; Cui, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Niu, J.; Cheng, W. Effects of cofermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and different lactic acid bacteria on the organic acid content, soluble sugar content, biogenic amines, phenol content, antioxidant activity and aroma of prune wine. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, C.; Devahastin, S.; Jiang, L.; Du, M.; Yi, J. Non-destructive determination of volatile compounds and prediction of amino acid nitrogen during sufu fermentation via electronic nose in combination with machine learning approaches. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 207, 116648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wan, F.; Cai, Z.; Zeng, R.; Tang, J.; Nie, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, C.; Laghi, L. Comprehensive comparison of flavor and metabolomic profiles in kiwi wine fermented by kiwifruit flesh with different colors. LWT 2024, 208, 116719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres Fabbri, L.; Cavallero, A.; Vidotto, F.; Gabriele, M. Bioactive Peptides from Fermented Foods: Production Approaches, Sources, and Potential Health Benefits. Foods 2024, 13, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Dumba, T.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, C.; Cai, C.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. Microbial diversity and chemical property analyses of sufu products with different producing regions and dressing flavors. LWT 2021, 144, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Du, H.; Chen, C.; Xue, Q.; Hu, Y. Effect of starter cultures on dynamics succession of microbial communities, physicochemical parameters, enzyme activities, tastes and volatile flavor compounds during sufu fermentation. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.A.K.; Ali, S.G.; Hassan, M.A.M.; Gabra, F.A.; Mawad, A.M.M. Optimization of citrulline production from a Bacillus subtilis BH-01 isolated from raw buffalo milk. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wang, H.; Suo, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Microbial composition and correlation between microbiota and quality-related physiochemical characteristics in chongqing radish paocai. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, C.O.; Dong, K.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J. Comparative genomics reveals the organic acid biosynthesis metabolic pathways among five lactic acid bacterial species isolated from fermented vegetables. New Biotechnol. 2022, 70, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Effects of enhanced fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WWPC on physicochemical characteristics and flavor profiles of radish paocai and dried-fermented radish. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Peng, Z.; Hardie, W.J.; Huang, T.; Xiong, T. Exploring the typical flavours formation by combined with metatranscriptomics and metabolomics during Chinese Sichuan paocai fermentation. LWT 2021, 153, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Q.; Zheng, M.; Dai, X.; Li, Y. Metagenomic characterization of the enhanced performance of anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge with CaO2 addition at ambient temperature: Fatty acid biosynthesis metabolic pathway and CAZymes. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kumar, A.; Singhal, B.; Kuhad, R.C.; Sharma, K.K. Fungal oxidoreductases and CAZymes effectively degrade lignocellulosic component of switchgrass for bioethanol production. Fuel 2022, 328, 125341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garron, M.-L.; Henrissat, B. The continuing expansion of CAZymes and their families. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 53, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, J.F.; Bains, R.K.; Rahfeld, P.; Withers, S.G. Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) in the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, S.; Nain, P.K.S.; Nain, L.; Shukla, P. Bioprospecting of novel thermostable beta-glucosidase from Bacillus subtilis RA10 and its application in biomass hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ma, Z.; Yin, J.; Shi, G.; Ding, Z. Biological strategies for oligo/polysaccharide synthesis: Biocatalyst and microbial cell factory. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.M.; Nascimento, A.S.; Polikarpov, I. Structural diversity of carbohydrate esterases. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2017, 1, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, S.W.; Thiel, Q.P.; Gastl, M.I.; Becker, T.M. Optimizing the fermentation parameters in the Lactic Acid Fermentation of Legume-based Beverages- a statistically based fermentation. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xin, F. Advances and prospects for lactic acid production from lignocellulose. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2025, 182, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britannica, E. Tricarboxylic acid cycle. In Encyclopedia Britannica; Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, B.-B.; Li, J.; Shan, J.-J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Wei, X.-T.; Zhu, R.-R.; Wang, J.-Y. Tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolites: New players in macrophage. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, N.; Su, S.; Zhao, M.; Du, H.; Sahoo, L.K.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gupta, N.; Xiao, L.; et al. Metabolic crosstalk between the mitochondrion and the nucleus is essential for Toxoplasma gondii infection. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
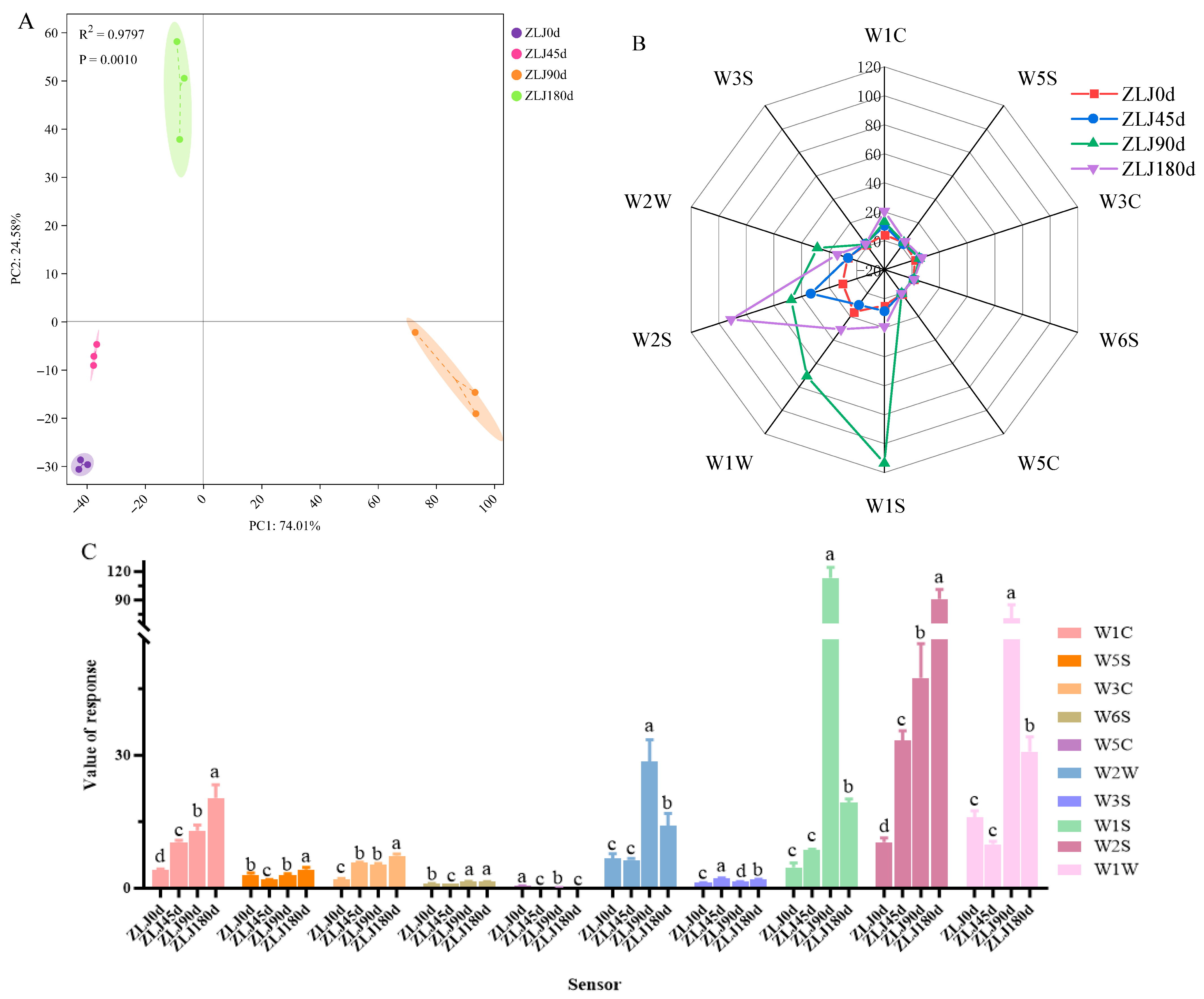



| Sensor Name | Performance Description | Representative Material Species |
|---|---|---|
| W1C | Sensitive to aromatic constituents, benzene | Aromatic |
| W5S | Sensitive to nitrogen oxides | Broad range |
| W3C | Sensitive to aroma, ammonia | Aromatic compounds |
| W6S | Mainly selective for hydrides | Hydrogen |
| W5C | Short-chain alkane aromatic components | Arom-aliph |
| W1S | Broad-methane | Broad-methane |
| W1W | Sensitive to sulfides | Sulfur-organic |
| W2S | Sensitive to alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones | Broad -alcohol |
| W2W | Sensitive to aromatic ingredients and organic sulfides | Sulph-chlor |
| W3S | Sensitive to long-chain alkanes | Methane-aliph |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; He, J.; Yin, Y.; Lu, M.; Huang, Y. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids During Zaolajiao Fermentation: Correlation with Physicochemical Properties and CAZymes. Fermentation 2025, 11, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080479
Chen J, Wang X, Li W, He J, Yin Y, Lu M, Huang Y. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids During Zaolajiao Fermentation: Correlation with Physicochemical Properties and CAZymes. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080479
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ju, Xueya Wang, Wenxin Li, Jianwen He, Yong Yin, Min Lu, and Yubing Huang. 2025. "Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids During Zaolajiao Fermentation: Correlation with Physicochemical Properties and CAZymes" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080479
APA StyleChen, J., Wang, X., Li, W., He, J., Yin, Y., Lu, M., & Huang, Y. (2025). Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Dynamic Changes in Organic Acids During Zaolajiao Fermentation: Correlation with Physicochemical Properties and CAZymes. Fermentation, 11(8), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080479





