Enhancement of Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides: Designing Feeding Strategies Through Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metabolic Model for Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides
2.2. Designed Strains for Growth-Couple Lipid Production in R. toruloides
2.3. Simulation of Lipid Production by R. toruloides During Fed-Batch Cultivation Using DFBA
2.3.1. DFBA Implementation
2.3.2. Simulation of the Batch Phase
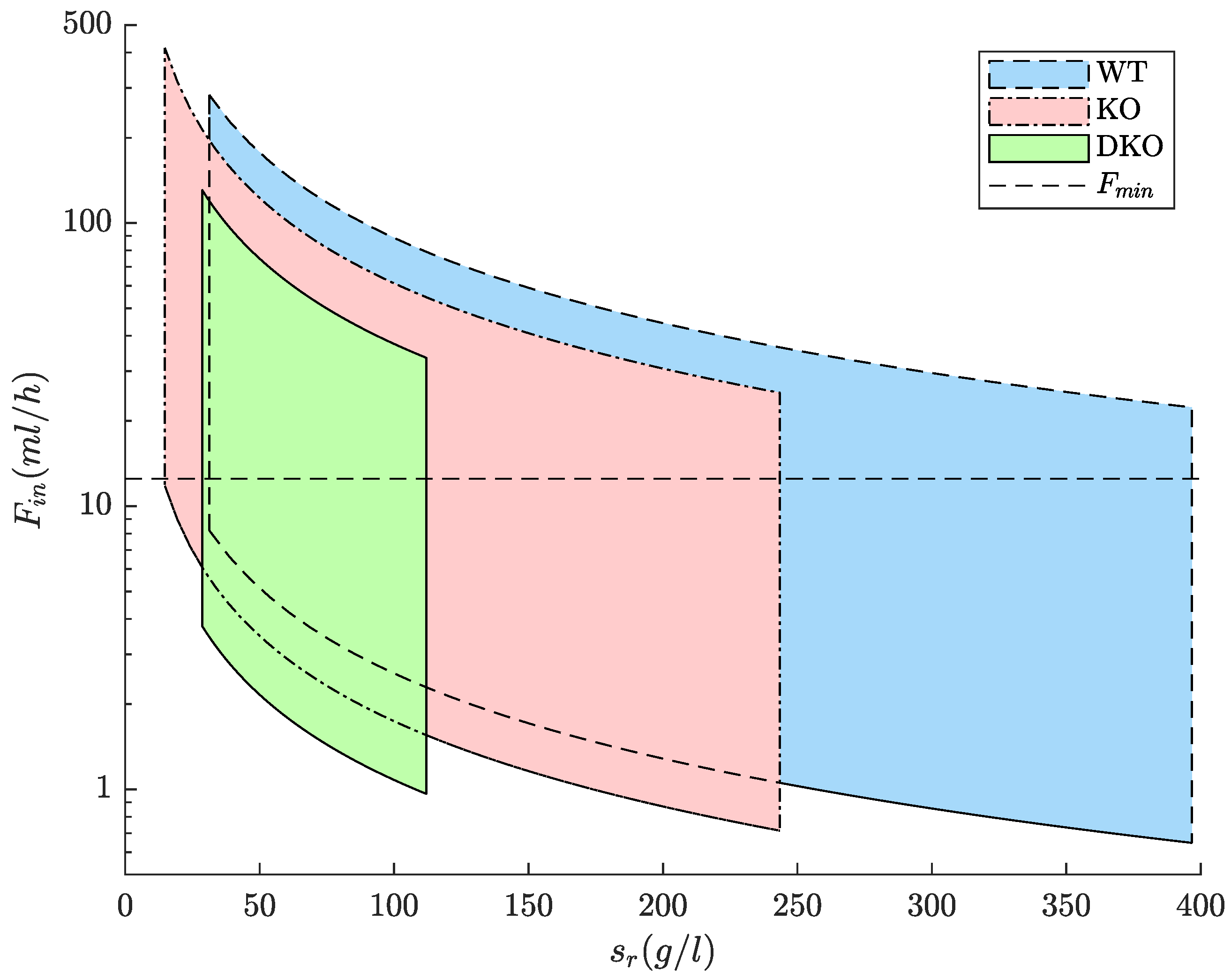
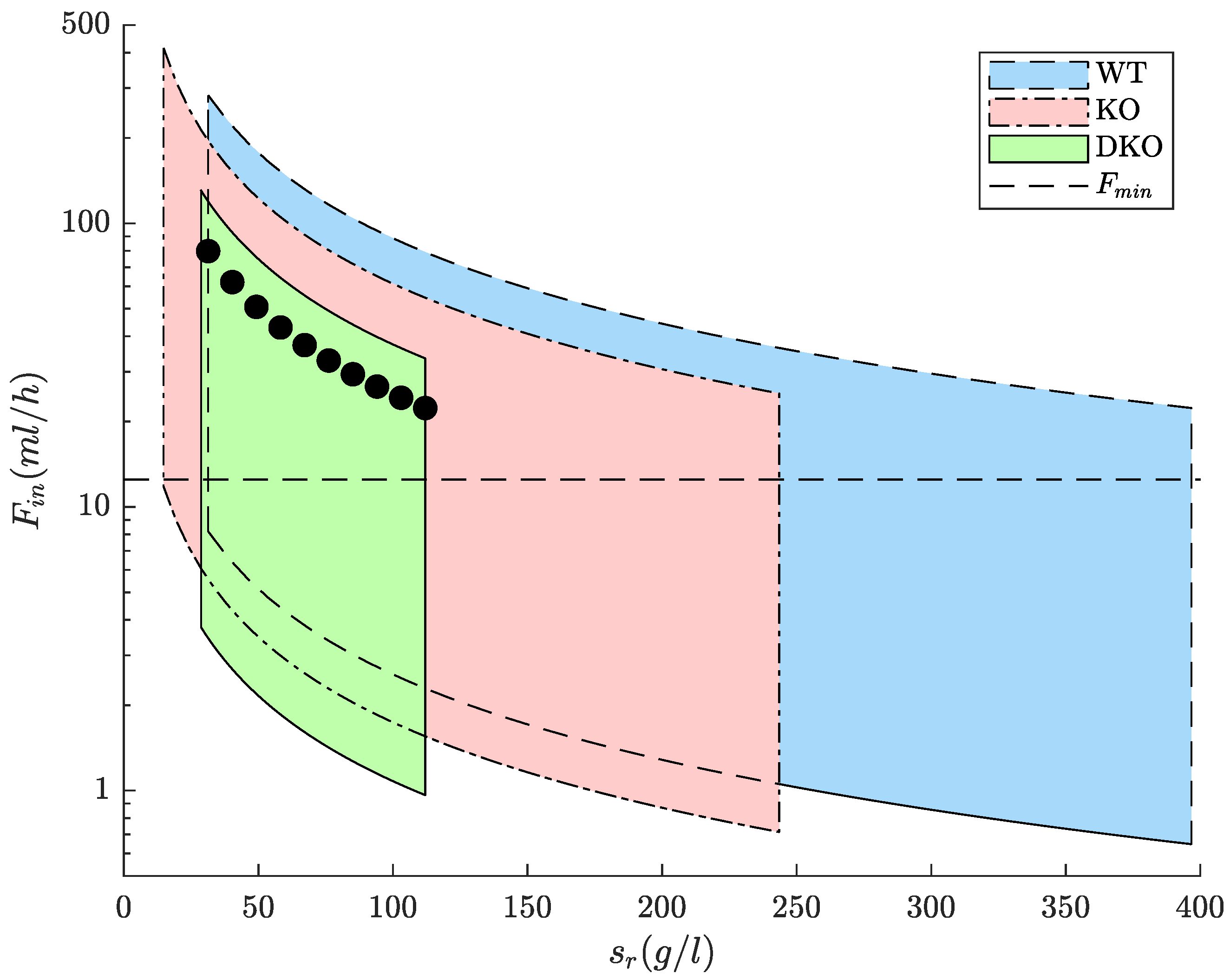
2.3.3. Design of Feeding Strategies
2.4. Bioprocess Efficiency Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Feeding Strategies for WT and Designed Strains Lipid Production
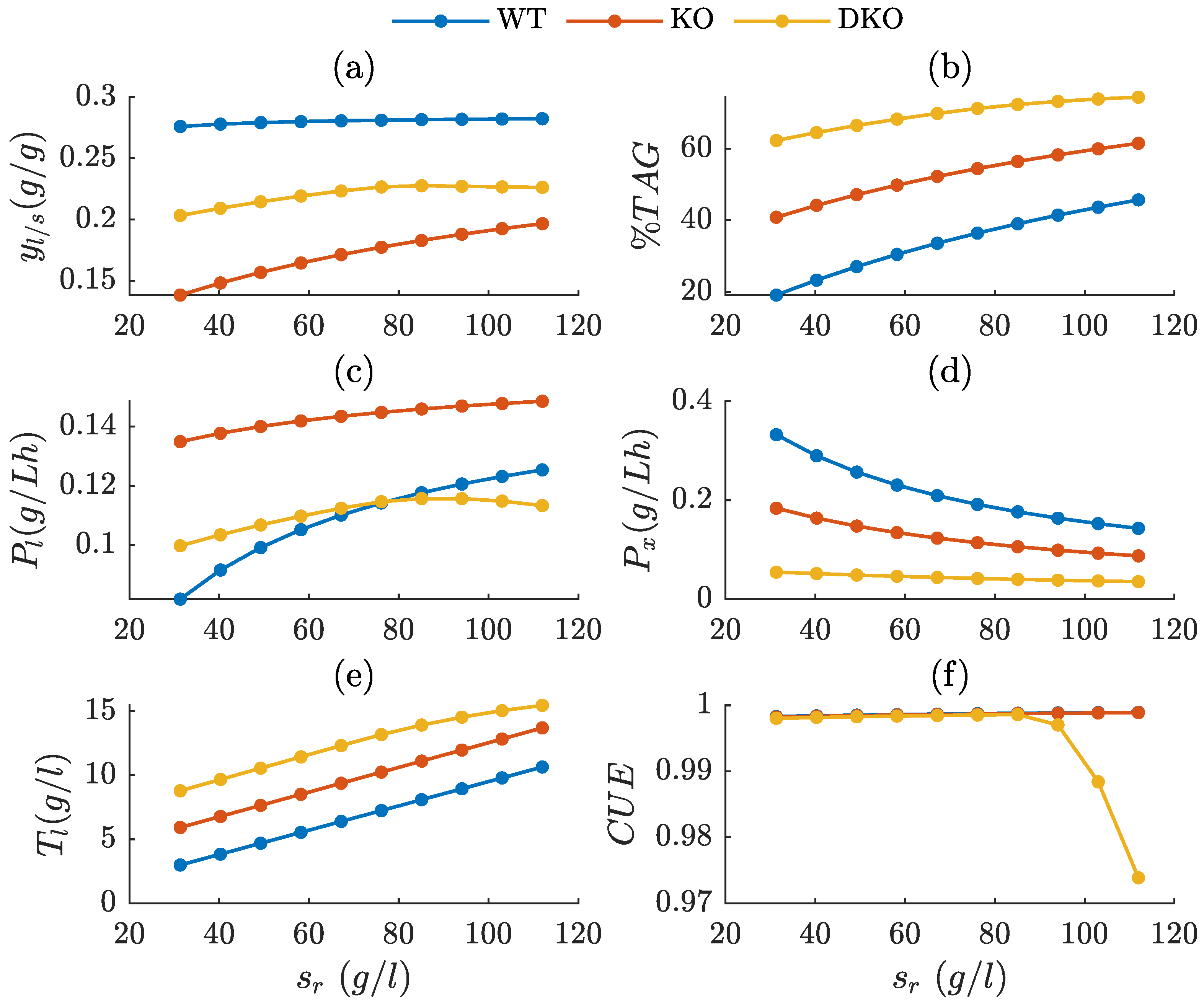
3.2. Growth and Lipid Production of R. toruloides Strains During Fed-Batch Cultivation
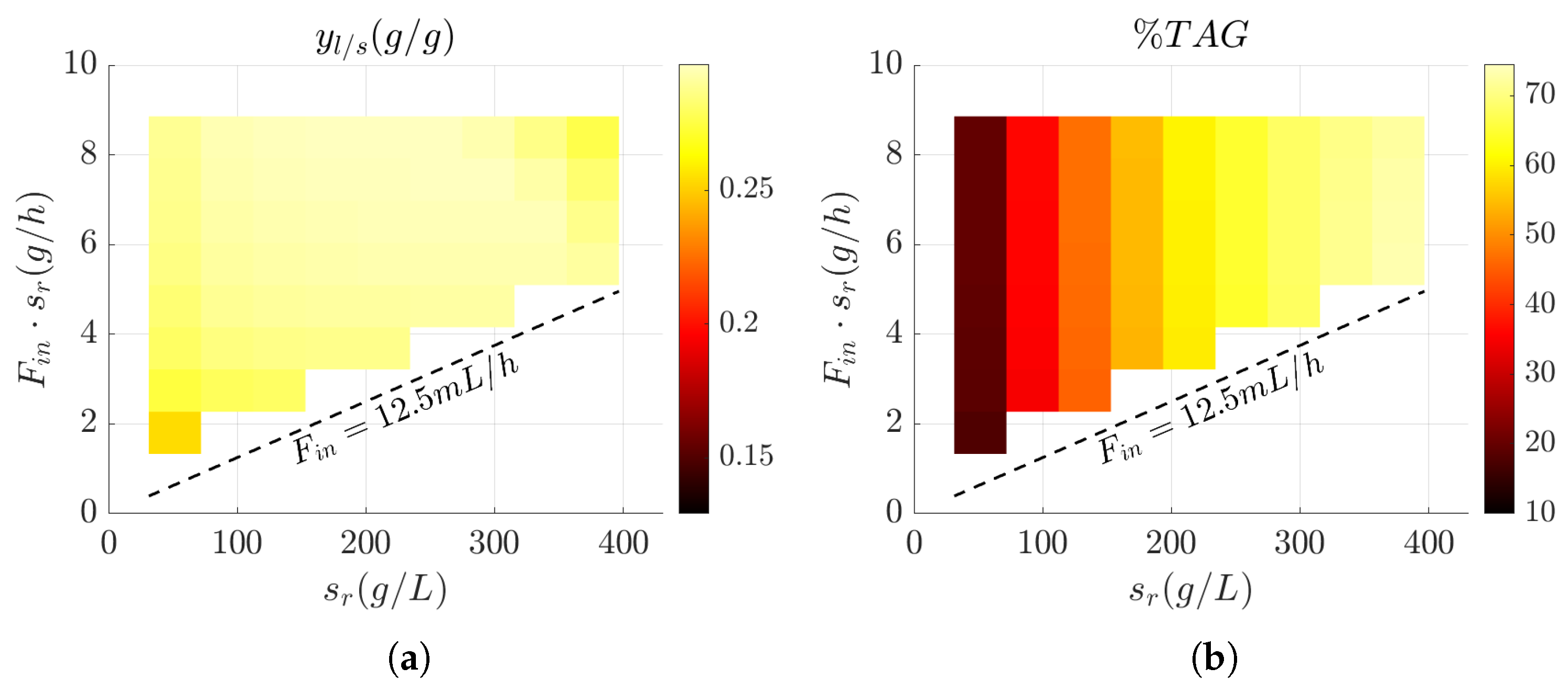
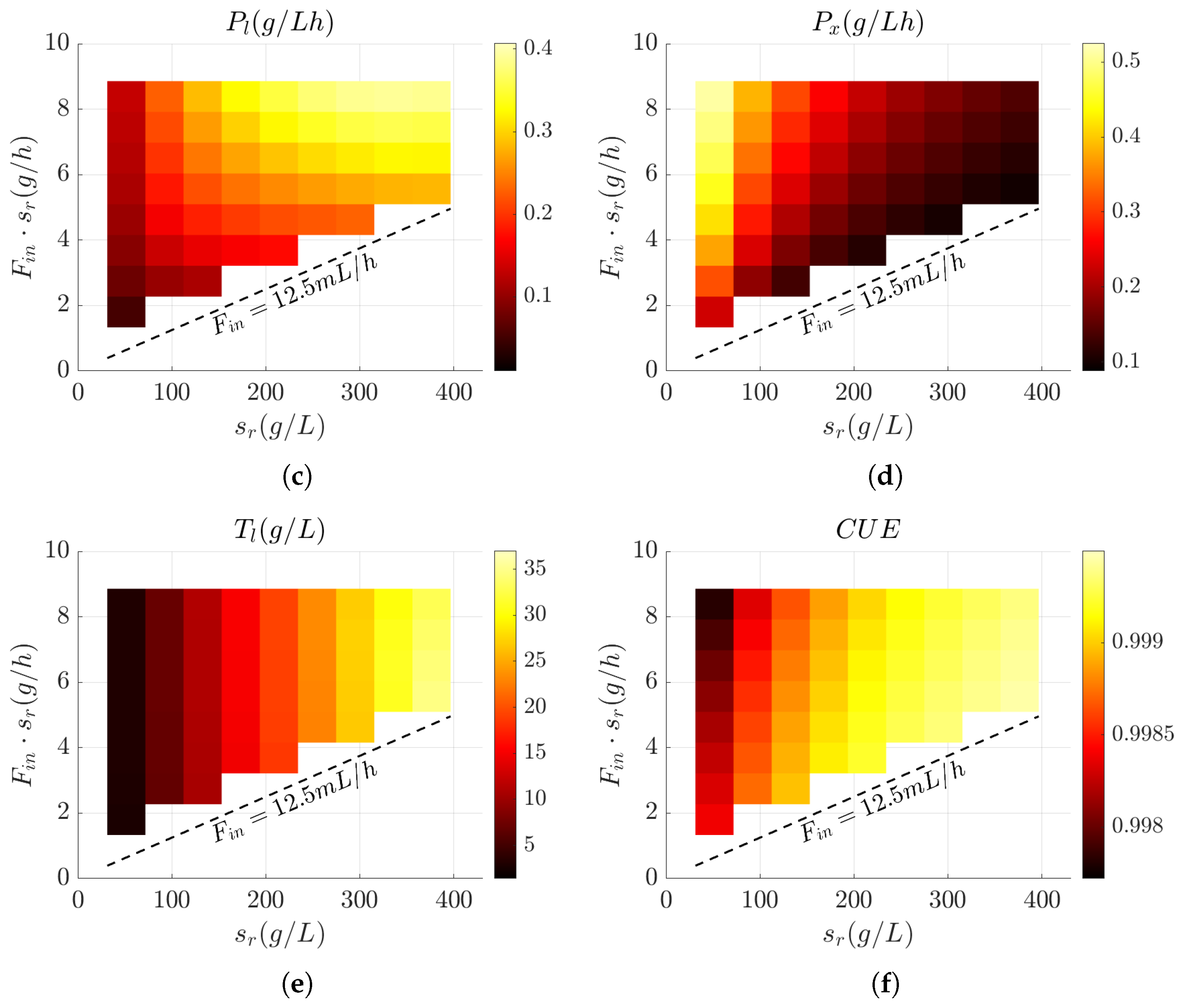
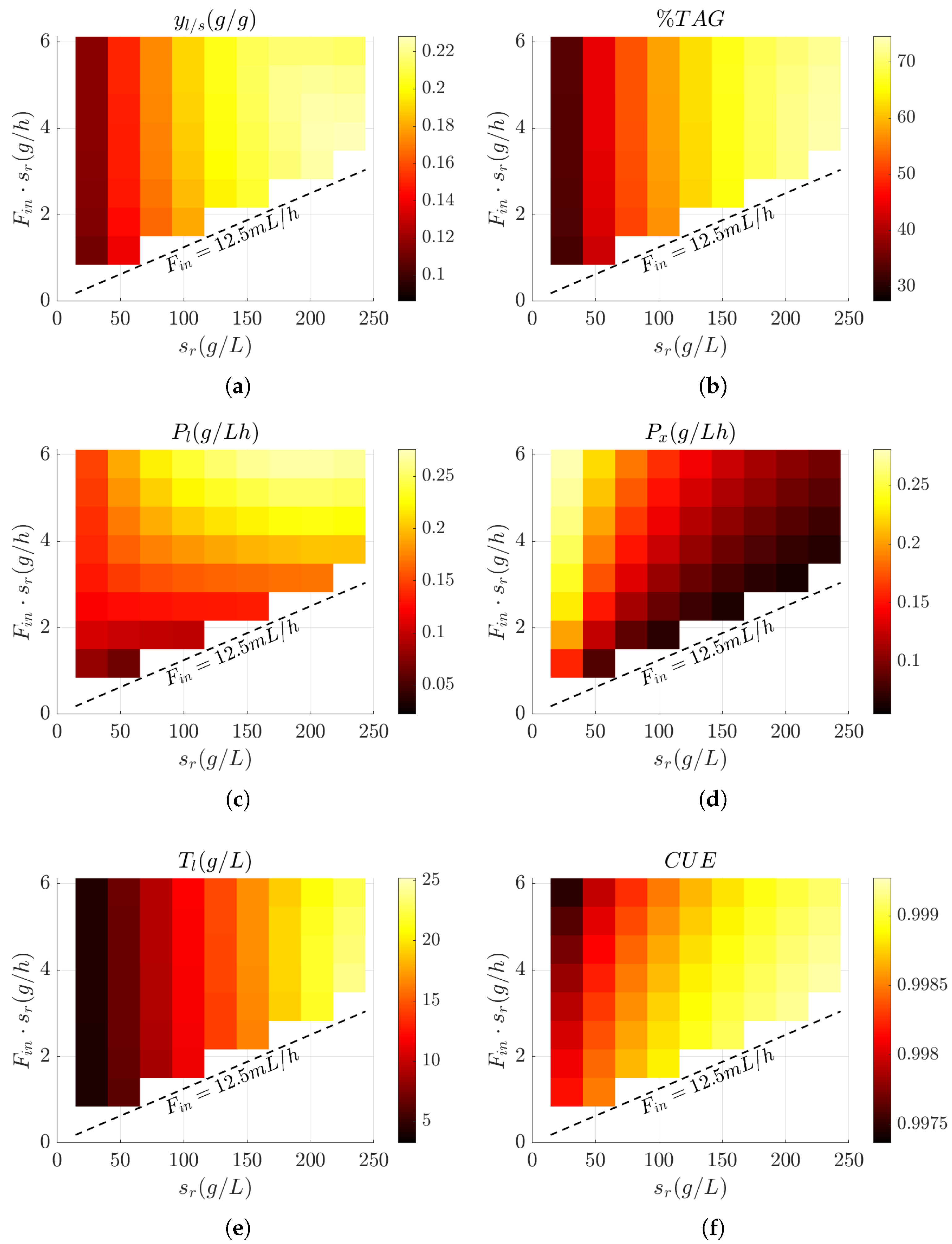
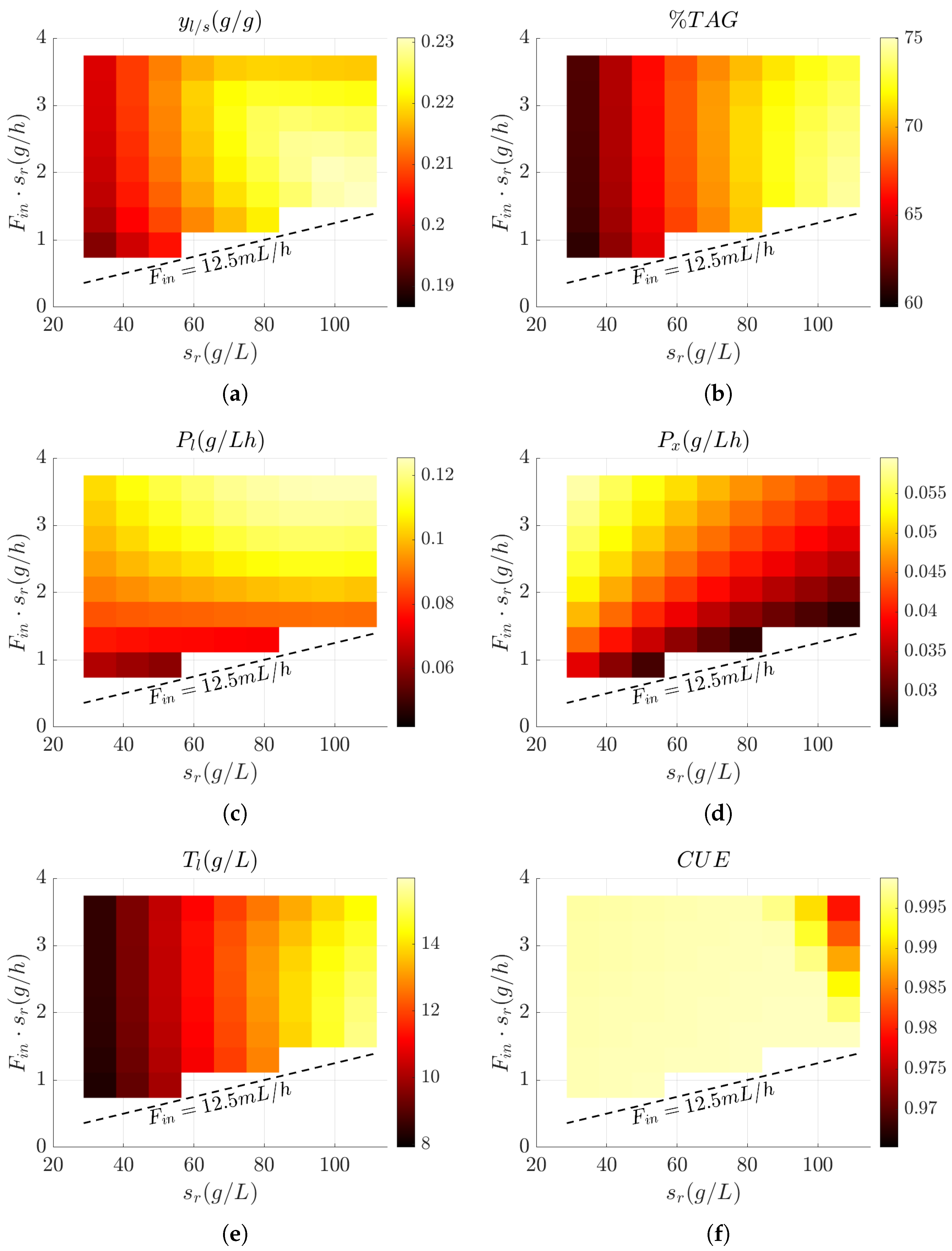
3.3. Influence of Feed Design on Key Bioprocess Performance Metrics
3.4. Evaluation of Bioprocess Efficiency in Wild-Type and Engineered Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Lipids of oleaginous yeasts. Part I: Biochemistry of single cell oil production. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes da Silva, T.; Fontes, A.; Reis, A.; Siva, C.; Gírio, F. Oleaginous Yeast Biorefinery: Feedstocks, Processes, Techniques, Bioproducts. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Dar, R.A.; Baganz, F.; Smoliński, A.; Rasmey, A.H.M.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L. Effects of Lignocellulosic Biomass-Derived Hydrolysate Inhibitors on Cell Growth and Lipid Production During Microbial Fermentation of Oleaginous Microorganisms—A Review. Fermentation 2025, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soccol, C.R.; Neto, C.J.D.; Soccol, V.T.; Sydney, E.B.; da Costa, E.S.F.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P. Pilot scale biodiesel production from microbial oil of Rhodosporidium toruloides DEBB 5533 using sugarcane juice: Performance in diesel engine and preliminary economic study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Sun, T.; Hao, H.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, M.; Chen, G. Optimising nutrients in the culture medium of Rhodosporidium toruloides enhances lipids production. Amb Express 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhede, L.; Bhardwaj, G.; Saini, R.; Osorio-Gonzalez, C.S.; Brar, S.K. Technological modes and processes to enhance the Rhodosporidium toruloides based lipid accumulation. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 287, 127840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-González, C.S.; Saini, R.; Hegde, K.; Brar, S.K.; Lefebvre, A.; Ramirez, A.A. Carbon/Nitrogen ratio as a tool to enhance the lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides-1588 using C5 and C6 wood hydrolysates. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, M.; Yaguchi, A.; Blenner, M. Oleaginous yeast for biofuel and oleochemical production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Odoh, C.K.; Jin, M.; Zhao, Z.K. Rhodosporidium toruloides-A potential red yeast chassis for lipids and beyond. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020, 20, foaa038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamerou, E.E.; Webb, C. Cultivation modes for microbial oil production using oleaginous yeasts—A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 151, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ito, M.; Skerker, J.M.; Arkin, A.P.; Rao, C.V. Metabolic engineering of the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides IFO0880 for lipid overproduction during high-density fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9393–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiznieks, R.; Dace, E.; Stalidzans, E. Integrated Sustainability Score Implementation as an Objective Function in Sustainable Metabolic Engineering. Fermentation 2023, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, M.T.; Nuñez, S.; Jamilis, M.; De Battista, H. Computational assessment of lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides in two-stage and one-stage batch bioprocesses. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2024, 121, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, M.T.; Nuñez, S.; Garelli, F.; Voget, C.; De Battista, H. Comprehensive analysis of a metabolic model for lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 280, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Palsson, B.O. Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3724–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Q.; O’Brien, M.; Nelson, R.; Chen, X.; Lowell, A.; Dowe, N. Enhanced lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides using different fed-batch feeding strategies with lignocellulosic hydrolysate as the sole carbon source. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolmanis, E.; Dubencovs, K.; Suleiko, A.; Vanags, J. Model predictive control—A stand out among competitors for fed-batch fermentation improvement. Fermentation 2023, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Gong, Z.; Yang, X.; Jin, G.; Bai, F.; Zhao, Z.K. Kinetics of continuous cultivation of the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, M.T.; Nuñez, S.; Voget, C.; De Battista, H. In silico optimization of lipid production in Rhodosporidium toruloides by gene knockout strategies. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgard, A.P.; Pharkya, P.; Maranas, C.D. OptKnock: A bilevel programming framework for identifying gene knockout strategies for microbial strain optimization. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 84, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Z.A.; Dräger, A.; Ebrahim, A.; Sonnenschein, N.; Lewis, N.E.; Palsson, B.O. Escher: A web application for building, sharing, and embedding data-rich visualizations of biological pathways. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.D.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.Ø. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.A.; Höffner, K.; Barton, P.I. DFBAlab: A fast and reliable MATLAB code for dynamic flux balance analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurobi Optimization, LLC. Gurobi Optimizer Reference Manual. 2025. Available online: https://www.gurobi.com (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Pirt, S.J. Maintenance energy: A general model for energy-limited and energy-sufficient growth. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 133, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heirendt, L.; Arreckx, S.; Pfau, T.; Mendoza, S.N.; Richelle, A.; Heinken, A.; Haraldsdóttir, H.S.; Wachowiak, J.; Keating, S.M.; Vlasov, V.; et al. Creation and analysis of biochemical constraint-based models using the COBRA Toolbox v. 3.0. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 639–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Z.B.; Bai, F.W. Optimization of Culture Conditions for Lipid Production by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, S.; Kotyk, A.; Tauchová, R. Monosaccharide transport systems in the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis. Arch. Microbiol. 1976, 111, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamerou, E. Bioprocessing Strategies for the Cultivation of Oleaginous Yeasts on Glycerol; The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mozumder, M.S.I.; Goormachtigh, L.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; De Wever, H.; Volcke, E.I. Modeling pure culture heterotrophic production of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, R.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.; He, W.; Huang, L.; Lin, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Lipid and carotenoid production by the Rhodosporidium toruloides mutant in cane molasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Osorio-Gonzalez, C.S.; Hegde, K.; Brar, S.K.; Vezina, P. Effect of creating a fed-batch like condition using carbon to nitrogen ratios on lipid accumulation in Rhodosporidium toruloides-1588. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, M.G.; Koivuranta, K.; Penttilä, M.; Ruohonen, L. Lipid production in batch and fed-batch cultures of Rhodosporidium toruloides from 5 and 6 carbon carbohydrates. BMC Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, C.; Wu, S.; Shen, H.; Zhao, Z.K. Lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 using different substrate feeding strategies. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.K.; Bai, F. High-density cultivation of oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 in fed-batch culture. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouteu, S.S.; Kopsahelis, N.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Kalantzi, O.; Stoforos, N.G.; Koutinas, A.A.; Aggelis, G.; Papanikolaou, S. Rhodosporidium toruloides cultivated in NaCl-enriched glucose-based media: Adaptation dynamics and lipid production. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Batch phase volume | 3 L | |
| Final fed-batch volume | 4.5 L | |
| Initial biomass concentration (batch) | 0.5 g/L | |
| Initial glucose concentration (batch) | 30 g/L | |
| Initial lipid concentration (batch) | 0 g/L | |
| Final glucose concentration (batch) | 0.0054 g/L | |
| NGAM reaction flux | 0.422 mmol/g h † | |
| Maintenance coefficient | 0.0045 g/g h † | |
| Glucose maximum uptake rate | −3.07 mmol/g h † | |
| Ammonia maximum uptake rate | −1.95 mmol/g h † | |
| Lipid maximum production rate | 0.057 mmol/ g h † | |
| Glucose half-saturation constant | 0.47 mmol/L § | |
| Ammonia half-saturation constant | 3.571 mmol/L ‡ | |
| Max. lipid-to-residual biomass ratio | 3.1667 ¶ | |
| Min. lipid-to-residual biomass ratio | 0.25 ★ | |
| Lipid saturation power coefficient | 3.85 ≀ | |
| biomass to nitrogen source yield | 6.25 Cmol/Nmol ζ |
| Strain | (g/h) | (g/h) | (g/L) | (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 0.257 | 8.858 | 31.315 | 396.661 |
| KO | 0.174 | 6.123 | 14.747 | 243.476 |
| DKO | 0.108 | 3.742 | 28.671 | 111.977 |
| Strain | Method | (g/g) | (g/L h) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBS14 | Constant and intermittent feed | 0.22 | 75 | 0.21 | [33] |
| RT880 | Intermittent feed | 0.09 | 26 | 0.13 | [11] |
| Y4 | Constant and intermittent feed | 0.20–0.23 | 58.6–61.8 | 0.36–0.57 | [34] |
| Y4 | Intermittent feed | 0.23 | 67.5 | 0.54 | [35] |
| DSM 4444 | Intermittent feed | 0.21 | 64.5 | 0.088 | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castañeda, M.T.; Nuñez, S.; Jamilis, M.; De Battista, H. Enhancement of Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides: Designing Feeding Strategies Through Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis. Fermentation 2025, 11, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060354
Castañeda MT, Nuñez S, Jamilis M, De Battista H. Enhancement of Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides: Designing Feeding Strategies Through Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis. Fermentation. 2025; 11(6):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060354
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastañeda, María Teresita, Sebastián Nuñez, Martín Jamilis, and Hernán De Battista. 2025. "Enhancement of Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides: Designing Feeding Strategies Through Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis" Fermentation 11, no. 6: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060354
APA StyleCastañeda, M. T., Nuñez, S., Jamilis, M., & De Battista, H. (2025). Enhancement of Lipid Production in Rhodosporidium toruloides: Designing Feeding Strategies Through Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis. Fermentation, 11(6), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11060354







