Abstract
Introduction: Non-communicable chronic diseases, such as overweight and obesity, are considered a high risk for type 2 diabetes. Globally, there are 536.6 million people with diabetes. Mexico has a high prevalence of these diseases. Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of a synbiotic beverage and a 12-week dietary intervention on body composition and biochemical parameters in women with T2D, overweight, or obesity as an additional strategy for treatment. Methods: This was a double-blind, randomized, and experimental study of a 12-week dietary intervention with a synbiotic fermented beverage with n = 51 women divided into four groups: G1 followed a moderate calorie-restricted diet, G2 followed the same moderate calorie-restricted diet and consumed a synbiotic beverage, G3 only consumed the synbiotic beverage, and G4 consumed a placebo beverage. Results: Significant changes were seen in BMI (p < 0.001) and fat mass (kg) (%) (p < 0.001) after the 12-week dietary intervention, proving that the synbiotic beverage had an effect on body composition. Conclusions: Significant decreases in different body composition and biochemical profiles were seen, showing the benefits of the beverage. A dietary intervention and the consumption of a fermented beverage could be an additional treatment for non-communicable diseases.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, overweight and obesity are considered detonating risk factors for type 2 diabetes (T2D) [1]. In 2021, the global prevalence of T2D in adults was approximately 536.6 million people. It is estimated that this number will increase to 783.2 million by 2045 [2]. Mexico is not an exception, ranking seventh in the world for T2D prevalence. According to the National Survey of Health and Nutrition (ENSANUT), this represents 12.4 million people with diabetes [3].
As is well known, there are proven ways to treat T2D, overweight, and obesity. However, in recent years, new alternatives to these treatments have emerged. The nutritional aspects of diets have revealed important benefits for improving human health, such as the intake of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. These are associated with weight loss, a low glycemic index, and lower cholesterol levels, among others [4].
Probiotics are living beneficial microorganisms, while prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that stimulate the growth and activity of gut bacteria [5,6]. In this study, a synbiotic was developed using a traditional Mexican fermented beverage called “aguamiel”, which was tasted in a previous study [7]. It is defined as a fresh drink made from various species of Agave, and it was used to improve biochemical profiles and body composition. Dysbiosis, an alteration in gut microbiota homeostasis, has been associated with chronic diseases [8,9]. Aguamiel works by reducing the concentration of soluble carbohydrates, contributing to decreasing the glycemic index by delaying gastric emptying and reducing starch availability [10].
From early life, synbiotics (a combination of prebiotics and probiotics) have shown beneficial effects on obesity and T2D and other metabolic diseases [11]. Recent studies have demonstrated promising results, especially when given to individuals with T2D and obesity [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. However, although probiotics and synbiotics have shown positive effects on glycemic control and other metabolic parameters, some studies have failed to confirm these effects. Therefore, further research is needed to provide a comprehensive conclusion on their impact [35]. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of a synbiotic beverage and a 12-week dietary intervention on body composition and biochemical profiles in women with T2D, overweight, or obesity as an additional strategy for treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
This was a longitudinal, prospective, double-blinded, randomized, and experimental clinical trial study. The sample was randomized by identifying similar factors between the groups, ensuring equal representation. Thus, we intentionally generated homogeneous groups. This dietary intervention was approved by the ethics committee of the university [CEIUPAEP18/2021], the Declaration of Helsinki, and the Mexican Health Law [36]. The protocol was approved under the ID code CON-BIOETICA21CEI00620131021. All participants provided written informed consent.
The inclusion criteria were women between 30 and 50 years old with overweight (BMI > 25), obesity (BMI > 30), or T2D, diagnosed for at least three years according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) criteria. Participants were undergoing their prescribed medical treatments. Those who did not meet these criteria were excluded. Initially, the sample included 62 women, with an attrition of 11 women (n = 51). Women who did not complete the dietary intervention were excluded due to lack of participation, missing blood samples, lack of interest, or other reasons. The study flowchart and enrollment are illustrated in Figure 1.
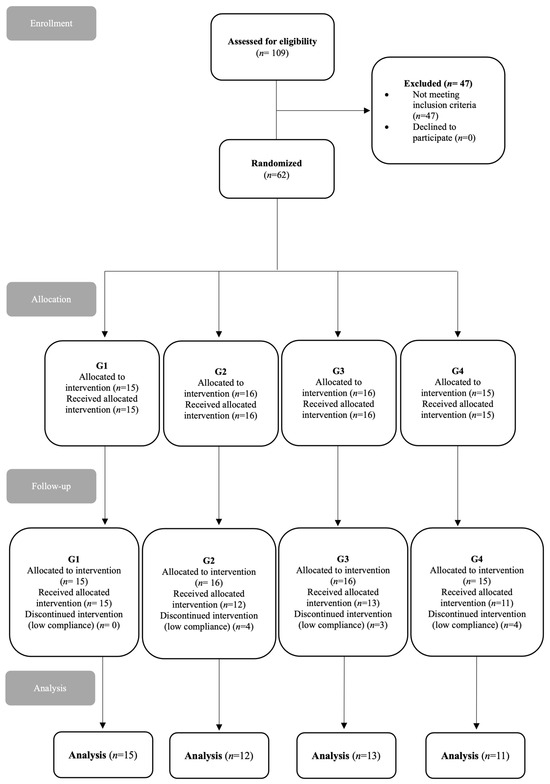
Figure 1.
Study flow chart and enrollment.
In this dietary intervention, a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage was developed by diluting aguamiel (1:1 ratio with water). It was pasteurized at 80 °C for 30 min in a 30 L fermenter (Grainfather G30v3®, Ningbo, China) and inoculated with 0.5% of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus paracasei with an optical density (OD) between 0.6 and 0.8. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. At the end of the incubation period, the concentration of bacteria in the symbiotic beverage was measured, yielding 1 × 1010 CFU/mL. This synbiotic beverage was used by a previous study conducted by the same university [7]. A placebo beverage was also developed using rice water, acid citric, and sweetener fermented using Grainfather G30v3® pasteurized at 80 °C for 30 min; it was then bottled and left to cool off, and after this process, the bottles were kept refrigerated (4 °C).
The measurements were taken at two different times, namely at the beginning of the study and then 12 weeks after. Body composition parameters were measured, including weight, height, BMI, waist/hip ratio, and bioimpedance (TANITA BC-418). Also, biochemical profiles were tested, including total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG), glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum insulin, and Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA) index.
The dietary intervention was carried out as follows: The participants were assigned to four different groups, including three experimental groups and a control group. Group one (G1) (n = 15) followed a moderate calorie-restricted diet of 1500 kcal with a distribution of 50% of carbohydrates, 30% of lipids, and 20% of proteins. Group two (G2) (n = 12) followed the same moderate calorie-restricted diet and consumed 120 mL of a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage, while group three (G3) (n = 13) consumed 120 mL of the synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage without a restricted diet or any other dietary intervention. Finally, group four (G4) (n = 11) consumed 120 mL of the placebo beverage with the same organoleptic characteristics without a restricted diet or any other dietary intervention, with this group being the control. All of the groups followed the same instructions for 12 weeks.
For this study, statistical inference was performed using IBM SPSS® Statistics 29 and MINITAB® Inc. 21.3. Additionally, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The results were statistically evaluated by means of Pearson correlation tests (r2), a t test, and average tests (ANOVA).
3. Results
Of the total of 62 women, 11 were excluded from the study for various reasons; 5 did not complete the treatment, 2 did not receive the fermented beverage on time, and 4 did not show up for the blood test. Therefore, 51 women (G1 = 15, G2 =12, G3 = 13, and G4 = 11) completed the study.
The following results are presented for the four groups, showing the body composition and biochemical profiles at the beginning and end of 12-week dietary intervention.
Table 1 shows the body composition parameters before and after the 12-week dietary intervention. For G1, changes were observed in waist circumference (M = 92.6, SD = 10.6), p = 0.017, and hip circumference (M = 105.5, SD = 9.6) (p = 0.029). For BMI, the results were M = 29.1, SD = 4.8, and p = 0.044, and for fat mass (kg), the results were M = 27.5, SD = 9.4, and p = 0.058. These results indicate the effectiveness of the moderate calorie-restricted diet alone.

Table 1.
Body composition parameters before and after the 12-week intervention in the different groups.
For G2, as predicted, the women experienced significant weight loss (M = 76.3, SD = 12.2) (p = 0.015), having followed a moderate calorie-restricted diet and consumed 120 mL of a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage. The fat mass (%) in G2 was significantly reduced (M = 39.1, SD = 5.5) (p = 0.003), showing the most statically significant change among the four groups. The BMI of G2 also showed a statically greater significance (M = 30.8, SD = 3.9) (p < 0.001) compared to G1 (M = 29.1, SD = 4.8) (p = 0.044). Additionally, the waist circumference of G2 showed greater statistical significance (M = 97, SD = 10) (p = 0.006) compared to G1 (M = 92.6, SD = 10.6) (p = 0.017).
In G3, the only significant change was seen in hip circumference (M = 104.3, SD = 12.2) (p = 0.051), likely due to the consumption of the synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage alone. For G4, no statistically significant changes were observed.
For the biochemical profiles, the following was reported (Table 2): TC showed a statistically significant change in G2 (M = 185.4, SD = 24.3) (p = 0.006). LDL-C showed the greatest statistically significant change (M = 94.2, SD = 19) (p = 0.054) compared to G1, G3, and G4.

Table 2.
Biochemical profiles before and after the 12-week dietary intervention in the different groups.
For Table 3, the correlation between the initial weight measurement and the weight measured after 12 weeks was significant (p < 0.005). The table shows that several variables had a significant impact, including BMI (p < 0.001), fat mass (%) (p < 0.001), and fat mass (kg) (p < 0.001). For the biochemical profiles, it was found that the serum insulin had a statistically significant correlation with weight after 12 weeks (p = 0.003) and with fat mass (kg) (p = 0.017). HbA1C (p = 0.008) and serum glucose (p = 0.049) were statistically significant when compared to the waist/hip ratio.

Table 3.
Pearson correlation coefficients (r2) of the relation between body composition parameters and biochemical profiles before and after the 12-week dietary intervention.
In the box and whiskers plots (Figure 2 and Figure 3), the horizontal line in the middle of each box represents the median value while the X indicates de mean value. The lower and upper ends of the box represent the 25 and 75th percentiles; and the peripheral lines extending to the outer fences indicates the minimum and maximum. Meanwhile, the dot extending the peripheral lines suggests the presence of distinct subgroups within the studied population.
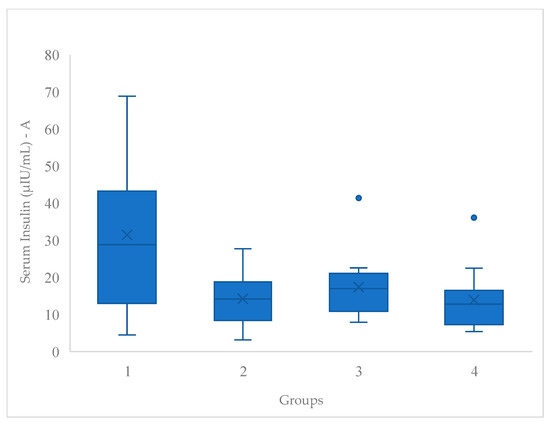
Figure 2.
Post-serum insulin (µIU/mL) box and whisker plot.
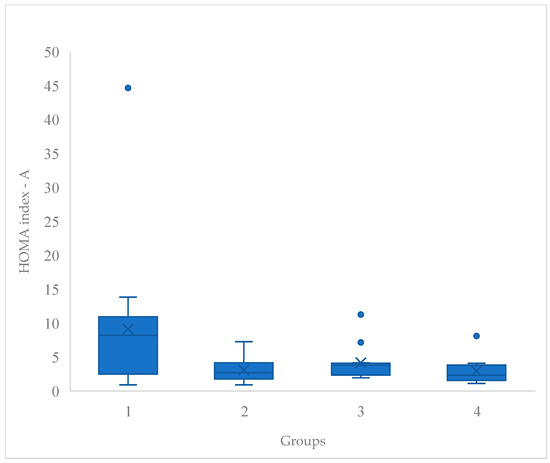
Figure 3.
Post-HOMA index serum box and whisker plot. Note. HOMA index, Homeostatic Model Assessment index.
Figure 2 shows that for serum insulin outcomes, G1 had a significantly higher mean than the other three groups. The G1 box is positioned in a higher range, indicating that both its median and quartiles are higher compared to those of the other groups.
Figure 3 demonstrates that regarding the post-HOMA index, G1 had higher mean and median values than the other groups. This group also had a wider interquartile range, suggesting greater variability in the results. G2 and G4 had ranges and distributions that were more similar to each other, both with lower means and medians compared to G1.
4. Discussion
The application of a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage has been proven to have effects on body composition parameters and biochemical profiles, as evidenced by several authors [5,36,37,38,39,40,41]. In previous studies, synbiotic fermented beverages were used as supplementations to assess body composition, glycemic indices, and lipid profiles, similar to the approach used in references [40,42]. The duration of the dietary intervention in this study was 12 weeks, consistent with references [38,39,42,43,44,45]. This contrasts with the study conducted by Darvishi et al. (2020), in which the dietary intervention lasted 8 weeks [46].
In our study, we found significant weight loss in only one group (G2), which followed a moderate calorie-restricted diet and consumed a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage. In contrast, G1 showed significant changes in body composition, such as waist circumference, hip circumference, BMI, and fat mass, which were attributed to the moderate calorie-restricted diet. For G3, the only change observed was related to the hip circumference, while G4 showed no significant changes. These findings suggest that the combination of a moderate calorie-restricted diet and a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage has synergistic effects [45,47] on individuals with overweight, obesity, and T2D compared to a moderate calorie-restricted diet without a synbiotic beverage. One of the most interesting aspects of our study was the impact of the body composition trend observed in G2 compared to the other groups (G1 and G3).
According to the findings of the present study, there were significant differences in weight loss, which contrasts with the results of Rabiei et al. (2019) and Othman et al. (2022). However, several other studies reported no significant differences [44,45,46,48]. Our results are consistent with those reported by Jamshidi et al. (2022), Rabiei et al. (2019), Chaiyasut et al. (2021), and Darvishi et al. (2020), which showed significant changes in BMI [42,44,46,49]. For fat mass, significant changes were reported, which contrasts with the findings of different previous studies.
On the other hand, the findings regarding the biochemical profile show significant changes in the HOMA index and serum insulin but only in one group, which is consistent with Othman et al. (2022) and Darvishi et al. (2020), who also reported significant differences. However, this group was not the one that received the synbiotic beverage. Additionally, anthropometric variables did not show significant differences in any of the groups. Moreover, BMI, fat mass, HOMA index, and serum insulin revealed significant differences due to the conditions under which the study was conducted.
Our data confirm the findings of studies conducted by several other authors, where promising associations with body composition were observed. In the present study, as described in the Results Section, the synbiotic fermented beverage contributed to considerable changes. It was also demonstrated that the dose and consumption duration of this beverage were adequate to positively influence body composition in our trial. As previously mentioned, Othman et al. (2022) found that anthropometric variables did not show any significant differences [47]. Our study also showed that when a weight loss diet is accompanied with a synbiotic fermented beverage, the reductions in several biochemical profiles, such as HOMA index and serum insulin, are significantly greater than when a weight loss diet is used alone. This could imply that the synbiotic beverage and associated changes in serum insulin levels could be linked to maintaining normal blood glucose levels in obesity [43].
There are controversial results regarding the efficacy of prebiotics and synbiotics on glucose levels as some studies, like ours, have not found these favorable effects [35]. Some studies showed no significant effects on glycemic and lipid profiles [50,51,52]. These controversial results may be attributed to factors such as the use of different probiotic strains and prebiotic types, the clinical characteristics of the participants, and the lack of appropriate instructions, among others [35,52,53].
No other studies are available regarding potential significant changes in the Mexican population, indicating that the effects of these types of beverages should be further explored in Latin populations given the high prevalence of non-communicable diseases in these populations [54,55,56]. There is a considerable need for clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of these Mexican fermented beverages due to their low cost and accessibility in our country [53,56].
5. Conclusions
The present study revealed that a dietary intervention combined with the use of a Mexican fermented beverage can result in improvements in body composition in a group of women with type 2 diabetes, overweight, and obesity. However, the overall results of the biochemical profiles did not show the expected changes. Nonetheless, several authors have demonstrated that fermented beverages can lead to improvements in biochemical markers, highlighting that symbiotics can be effective tools for women with chronic diseases. Our study, however, faced limitations in proving this due to various factors, such as the conditions of the study and adherence to the instructions, among others.
These results may be influenced by lifestyle factors, adherence to medical treatments, dietary habits, stress, physical activity, hormonal variations, and other factors in the participants. The combination of a synbiotic Mexican fermented beverage and a moderate calorie-restricted diet showed significant potential benefits for these participants. It is also important to note that gut microbiota was not analyzed in our study, and further research should focus on this aspect. It is recommended that a follow-up be considered for participants to keep them motivated and ensure continued adherence to the treatment.
Further studies are needed to continue investigating the benefits of synbiotic fermented beverages. A dietary intervention combined with the use of a fermented beverage could serve as an additional treatment for diabetes, overweight, and obesity, offering a potential alternative treatment for non-communicable diseases and providing a low-cost option for healthcare professionals in Mexico.
Author Contributions
L.C.-G., P.R.-R. and E.L.-P.: Conceptualization, Investigation, and Writing—Original Draft. B.P.-A., M.d.L.M.-J., M.d.R.B.-L., D.S.Z.-M. and J.C.R.-E.: Main Idea, Project Administration, Funding Acquisition, Writing—Original Draft, Supervision, and Visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study protocol was reviewed and approved by Comité de Ética en Investigación del Decanato de Ciencias Médicas UPAEP [approval number CEIUPAEP18/2021]. Date: 5 November 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
For this study, an informed consent form was signed by all the women involved. The final data and these consent forms are kept safe by the main author.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to all the women that freely participated in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Nianogo, R.A.; Arah, O.A. Forecasting Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence and Burden: The ViLA-Obesity Simulation Model. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 818816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamah-Levy, T.R.-M.M.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Bautista-Arredondo, S.; Colchero, M.A.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Alpuche-Arana, C.; Rivera-Dommarco, J. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2021 Sobre Covid-19. Resultados Nacionales. 2021. Available online: https://ensanut.insp.mx/encuestas/ensanutcontinua2021/doctos/informes/220804_Ensa21_digital_4ago.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Robles-Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuamatzin-García, L.; Rodríguez-Rugarcía, P.; El-Kassis, E.G.; Galicia, G.; Meza-Jiménez, M.d.L.; Baños-Lara, M.d.R.; Zaragoza-Maldonado, D.S.; Pérez-Armendáriz, B. Traditional Fermented Foods and Beverages from around the World and Their Health Benefits. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probiotics in Food: Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria, Cordoba, Argentina, 1–4 October 2001 [and] Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Working Group on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food, London, Ontario, Canada, 30 April–1 May 2002. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/382476b3-4d54-4175-803f-2f26f3526256/content (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Marquez Morales, L.; El Kassis, E.; Cavazos-Arroyo, J.; Rocha Rocha, V.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, F.; Pérez-Armendáriz, B. Effect of the Intake of a Traditional Mexican Beverage Fermented with Lactic Acid Bacteria on Academic Stress in Medical Students. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devotee, D.; Contreras-Esquivel, J. Aguamiel and its fermentation: Science beyond tradition. Mex. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Díez-Sainz, E.; Milagro, F.I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Lorente-Cebrián, S. Effects of gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles on obesity and diabetes and their potential modulation through diet. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 78, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete-Romero, B.; Valencia-Olivares, C.; Baños-Dossetti, G.A.; Pérez-Armendáriz, B.; Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A. Nutritional Contributions and Health Associations of Traditional Fermented Foods. Fermentation 2021, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Zhou, D.-D.; Gan, R.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.; Angarita, L.; Morillo, V.; Navarro, C.; Martínez, M.S.; Chacín, M.; Torres, W.; Rajotia, A.; Rojas, M.; Cano, C.; et al. Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus: Role of Lipid Mediators. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Naya, I.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Álvarez-Mon, M.; Buján, J.; Asúnsolo, Á.; de la Torre, B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Associated with Obesity (Diabesity). The Central Role of Gut Microbiota and Its Translational Applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscaini, S.; Leigh, S.J.; Lavelle, A.; García-Cabrerizo, R.; Lipuma, T.; Clarke, G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and body weight control: Weight watchers within? Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xiao, X. Effects of Oral Glucose-Lowering Agents on Gut Microbiota and Microbial Metabolites. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 905171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Yu, D.; Zhu, C. Gut Microbiota: An Important Player in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciun, C.-I.; Neag, M.-A.; Catinean, A.; Mitre, A.-O.; Rusu, A.; Bala, C.; Roman, G.; Buzoianu, A.-D.; Muntean, D.-M.; Craciun, A.-E. The Relationships between Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus, and Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Hu, F. Cross-Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Related Metabolic Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 908868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.; Ikram, A.; Dikareva, E.; Lahtinen, E.; Matharu, D.; Pajari, A.-M.; de Vos, W.M.; Hasan, F.; Salonen, A.; Jian, C. Unique Pakistani gut microbiota highlights population-specific microbiota signatures of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2142009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B. Gut Microbiota and Antidiabetic Drugs: Perspectives of Personalized Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 853771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Kim, M.; Bennett, B.J. Modulating the Microbiota as a Therapeutic Intervention for Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 632335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, V.; Ditu, L.-M.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Picu, A.; Petcu, L.; Cucu, N.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Gut Microbiota, Host Organism, and Diet Trialogue in Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Insights on Obesity and Diabetes from Gut Microbiome Alterations in Egyptian Adults. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2019, 23, 477–485. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Z.; Stirling, K.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, L. Gut microbiota and diabetes: From correlation to causality and mechanism. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, C.-S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hung, W.-W.; Hung, W.-C.; Tsai, H.-J.; Chang, C.-C.; Hwang, S.-J.; Dai, C.-Y.; Ho, W.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C. Interrelationship of Gut Microbiota, Obesity, Body Composition and Insulin Resistance in Asians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megur, A.; Daliri, E.B.-M.; Baltriukienė, D.; Burokas, A. Prebiotics as a Tool for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes: Classification and Ability to Modulate the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, M.; Śliżewska, K. Obesity as the 21st Century’s major disease: The role of probiotics and prebiotics in prevention and treatment. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; de Sousa, R.G.; Botelho, P.B.; Gomes, T.L.; Prada, P.O.; Mota, J.F. The additional effects of a probiotic mix on abdominal adiposity and antioxidant Status: A double-blind, randomized trial. Obesity 2017, 25, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yun, J.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, O.; Cho, B. Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 Supplementation Reduces the Visceral Fat Accumulation and Waist Circumference in Obese Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Yasom, S.; Tunapong, W.; Chunchai, T.; Wanchai, K.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Lungkaphin, A.; Sirilun, S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Chattipakorn, N.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, xylooligosaccharides, and synbiotics reduce gut disturbance in obese rats. Nutrition 2018, 54, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Javid, A.Z.; Dehghan, P. The effect of enriched chicory inulin on liver enzymes, calcium homeostasis and hematological parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Prim. Care Diabetes 2016, 10, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmpoosh, E.; Javadi, A.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Mirmiran, P.; Javadi, M.; Yousefinejad, A. The effect of probiotic supplementation on glycemic control and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized placebo controlled trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kyriienko, D.; Komissarenko, I. Effect of alive probiotic on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes patients: Randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi Zs Nasli-Esfahani, E.; Nadjarzade, A.; Mozaffari-khosravi, H. Effect of symbiotic supplementation on glycemic control, lipid profiles and microalbuminuria in patients with non-obese type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobi, S.; Rahimi, F.; Jafarnejad, S. Effects of Prebiotic and Synbiotic Supplementation on Glycaemia and Lipid Profile in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salud, S.d. Ley General de Salud. Artículo 54. “Reglamento Interno de Investigación en Salud”. 2014. Available online: https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/regley/Reg_LGS_MIS.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Dimidi, E.; Cox, S.R.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, F.; Zarch, S.M.A.; Mehrjardi, M.Y.V.; Kalantar, S.M.; Jahan-Mihan, A.; Karimi-Nazari, E.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Hosseinzadeh-Shamsi-Anar, M.; Rahmanian, M.; Fazeli, M.R.; et al. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on gut microbiome, serum level of TNF-α, and expression of microRNA-126 and microRNA-146a in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Study protocol for a double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial. Trials 2020, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Heshmati, J.; Shirzad, N.; Vesali, S.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J.; Moini, A.; Sepidarkish, M. The effect of synbiotics supplementation on anthropometric indicators and lipid profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaei, N.; Heidari, M.; Esmaeili, F.; Khosravi, S.; Baeeri, M.; Tabatabaei-Malazy, O.; Emamgholipour, S. The effects of prebiotic, probiotic or synbiotic supplementation on overweight/obesity indicators: An umbrella review of the trials’ meta-analyses. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1277921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Arraño, V.; Martín-Peláez, S. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Khongtan, S.; Khampithum, N.; Thangaleela, S.; Peerajan, S.; Bumrungpert, A.; Chaiyasut, K.; Sirilun, S.; et al. Synbiotic Supplementation Improves Obesity Index and Metabolic Biomarkers in Thai Obese Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Foods 2021, 10, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, F.; Pasdar, Y.; Kaviani, M.; Abbasi, S.; Fry, H.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Nikpayam, O.; Sohrab, G.; Rezaei, M.; Nachvak, S.M.; et al. Efficacy of the Synbiotic Supplementation on the Metabolic Factors in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 2967977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, S.; Hedayati, M.; Rashidkhani, B.; Saadat, N.; Shakerhossini, R. The Effects of Synbiotic Supplementation on Body Mass Index, Metabolic and Inflammatory Biomarkers, and Appetite in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Triple-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2019, 16, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batu, Z.; Gök Balcı, U.; Akal Yıldız, E. The Effect of Using Synbiotic on Weight Loss, Body Fat Percentage and Anthropometric Measures in Obese Women. Prog. Nutr. 2021, 23, e2021116. [Google Scholar]
- Darvishi, S.; Rafraf, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Farzadi, L. Synbiotic Supplementation Improves Metabolic Factors and Obesity Values in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Independent of Affecting Apelin Levels: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo—Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 15, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben Othman, R.; Ben Amor, N.; Mahjoub, F.; Berriche, O.; El Ghali, C.; Gamoudi, A.; Jamoussi, H. A clinical trial about effects of prebiotic and probiotic supplementation on weight loss, psychological profile and metabolic parameters in obese subjects. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2023, 6, e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeev, I.N.; Aljutaily, T.; Walton, G.; Huarte, E. Effects of Synbiotic Supplement on Human Gut Microbiota, Body Composition and Weight Loss in Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, S.; Masoumi, S.J.; Abiri, B.; Vafa, M. The effects of synbiotic and/or vitamin D supplementation on gut-muscle axis in overweight and obese women: A study protocol for a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Trials 2022, 23, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greany, K.A.; Bonorden, M.J.L.; Hamilton-Reeves, J.M.; McMullen, M.H.; E Wangen, K.; Phipps, W.R.; Feirtag, J.; Thomas, W.; Kurzer, M.S. Probiotic capsules do not lower plasma lipids in young women and men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, C.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Xia, J.; Chen, B.; et al. Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Jiménez, C.; Martínez-Ramírez, M.J.; Gil, Á.; Gómez-Llorente, C. Effects of Probiotics on Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.G.; Liong, M.T. Cholesterol-lowering effects of probiotics and prebiotics: A review of in vivo and in vitro findings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Linares, C.; Álvarez-Ríos, G.D.; Figueredo-Urbina, C.J.; Islas, L.A.; Lappe-Oliveras, P.; Nabhan, G.P.; Torres-García, I.; Vallejo, M.; Casas, A. Traditional Fermented Beverages of Mexico: A Biocultural Unseen Foodscape. Foods 2021, 10, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Arce, Z.P.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Exploring the potentialities of the Mexican fermented beverage: Pulque. J. Ethn. Foods 2021, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Luna, H.E.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Dávila-Ortiz, G. Traditional fermented beverages from Mexico as a potential probiotic source. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).