Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Constipation Stress Modulation by a Heteropolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL75
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Fermentation and EPS Isolation
2.2. Partial Characterization
2.2.1. Molecular Weight and Monomer Composition
2.2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies
2.2.3. Refractive Index Increment (dn/dC) and Particle Size
2.2.4. Conformational Analysis: Congo Red Test
2.3. Chromatic Parameter Evaluation
2.4. Thermal Properties Analysis
2.5. Biological Properties
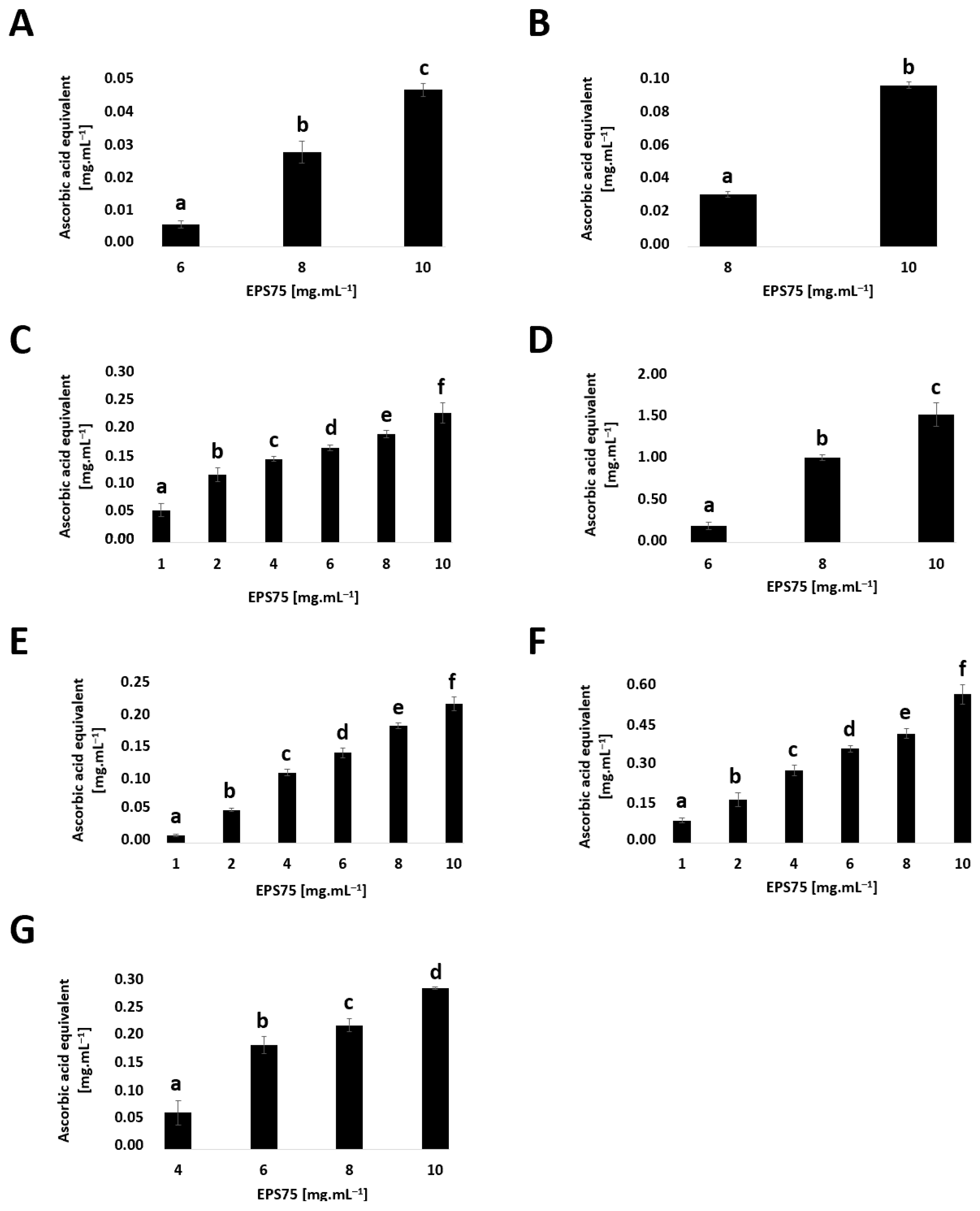
2.5.1. Antioxidant Capacity
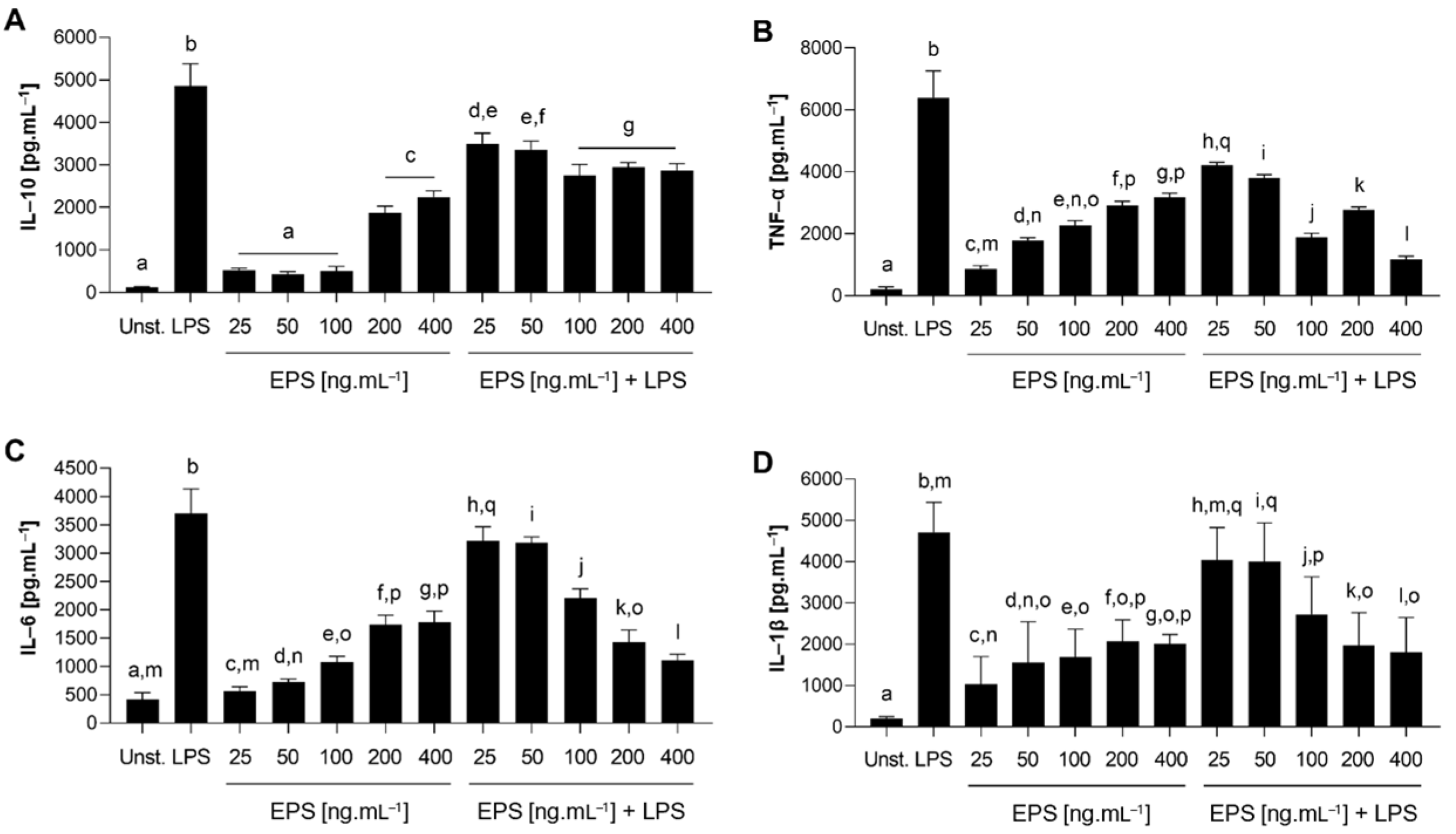
2.5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.5.3. Laxative Activity in Mice
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
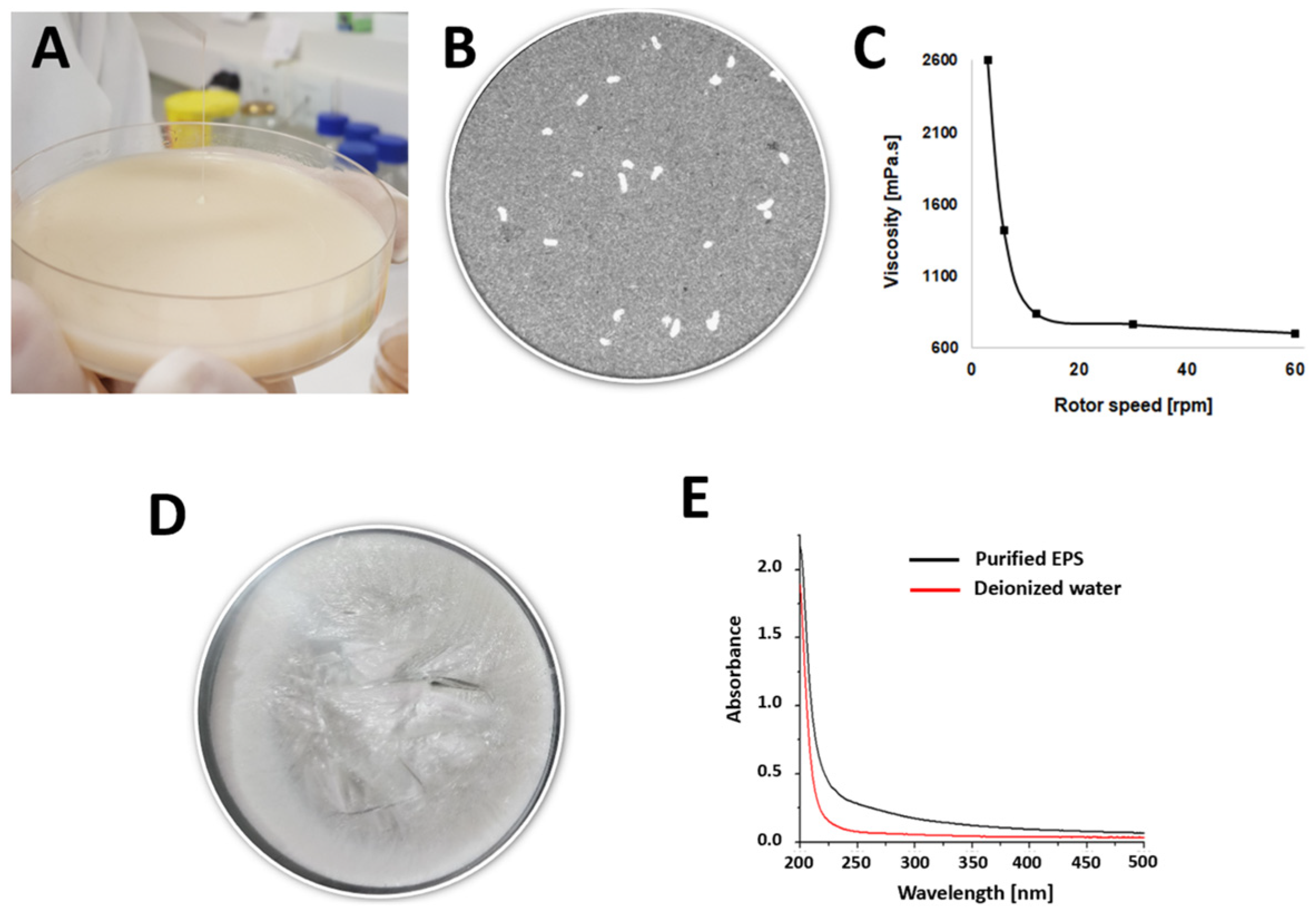
3.1. Milk Fermentation and EPS Isolation
3.2. EPS Partial Characterization Approaches
3.2.1. Composition Analysis and MW
3.2.2. Hydrodynamic Analysis
3.2.3. Vibrational Spectroscopies Analysis
3.3. Physical Properties
3.3.1. Chromatic Characterization
3.3.2. Thermal Properties
3.4. Biological Properties
3.4.1. Antioxidant
3.4.2. Cytotoxicity and Immunostimulatory Capacity
3.4.3. Anti-Inflammatory Capacity
3.4.4. Laxative Property
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| a* | Redness values |
| A2 | Virial coefficient |
| ABTS•+ | 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| b* | Yellowness values |
| C* | Chroma |
| CFUs | Microbial colony-forming units |
| cm–1 | Wavenumber |
| CPS | Capsular polysaccharide |
| Da | Daltons |
| dC | Concentration increment |
| Dh | Hydrodynamic diameter |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Dn | Refractive index increment |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DTA | Differential thermal analysis |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| EPS | Exopolysaccharide |
| eq. | Equivalent |
| FM | Fermented milk |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| FT-R | Fourier transform Raman |
| G | Gram |
| G | Group |
| g(1) | Autocorrelation function |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal transit |
| H | Hour |
| HePS | Heteropolysaccharide |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IR | Infrared |
| kDa | Kilodaltons |
| L | Liter |
| L* | Lightness values |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| m | Mass |
| M | Molar |
| mm | Millimeter |
| mg | Milligram |
| min | Minute |
| mL | Milliliter |
| mPa | Mili Pascal |
| MRS | De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe |
| MTT | 1-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-3,5-diphenyl formazan |
| Mw | Molecular weight |
| ng | Nanogram |
| nm | Nanometer |
| p | Statistical probability |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| pg | Picogram |
| RSM | Reconstituted skimmed milk |
| s | Second |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| SLS | Static light scattering |
| TD | Degradation temperature |
| TM | Melting temperature |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| U | Unit |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| V | Volume |
| VC | Ascorbic acid |
| WI | Whiteness index |
| xg | Relative centrifugal force |
| YI | Yellow index |
| λmax | Maximum absorption wavelength |
| ΔH | Enthalpy change |
| μL | Microliter |
| μM | Micromolar |
| µs | Microsecond |
| °C | Celsius degrees |
| °H | Hue angle |
| Δ | Rate |
| % | Percentage |
References
- Lynch, K.M.; Zannini, E.; Coffey, A.; Arendt, E.K. Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides in Foods and Beverages: Isolation, Properties, Characterization, and Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, M.; Silva, C.R.-D.; Garcia, C.; Remize, F. Lactic acid bacterial production of exopolysaccharides from fruit and vegetables and associated benefits. Fermentation 2020, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, R.; Alam, M.K.; Perpetuini, G.; Perla, C.; Pittia, P.; Corsetti, A. Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides Producers: A Sustainable Tool for Functional Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthold-Pluta, A.M.; Pluta, A.S.; Garbowska, M.; Stasiak-Różańska, L. Exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacteria–health-promoting properties and application in the dairy industry. Postep. Mikrobiol. 2019, 58, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraskova, D.; Ribeiro, S.C.; Silva, C.C.G. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria: From Biosynthesis to Health-Promoting Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Llamas, M.G.; Iraporda, C.; Duenas, M.T.; Abraham, A.G.; Garrote, G.L. Impact of growth temperature on exopolysaccharide production and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus paracasei strains isolated from kefir grains. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, M.; Miljković, M.S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Markelić, M.B.; Veljović, K.; Tolinački, M.; Soković, S.; Korać, A.; Golić, N. EPS-SJ exopolisaccharide produced by the strain Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei BGSJ2-8 is involved in adhesion to epithelial intestinal cells and decrease on E. coli association to Caco-2 cells. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Sadiqb, F.A.; Li, X.; Mi, S.; Sang, Y. Immunoregulatory effect of Lactobacillus paracasei VL8 exopolysaccharide on RAW264. 7 cells by NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 95, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Xia, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide synthesized by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus B6 and its immunomodulatory activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzi, F.; Torino, M.I.; de Valdez, G.F. Identification of exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacteria: A method for the isolation of polysaccharides in milk cultures. In Food Microbiology Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, R.E.; Gómez, M.I.; de Valdez, G.F.; Torino, M.I. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of a gastroprotective exopolysaccharide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus CRL1190. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaningelgem, F.; Zamfir, M.; Mozzi, F.; Adriany, T.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; De Vuyst, L. Biodiversity of exopolysaccharides produced by Streptococcus thermophilus strains is reflected in their production and their molecular and functional characteristics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, R.E.; Figueroa, T.; Navarro, D.; Gomez, M.I.; Font de Valdez, G.; Torino, M.I. Techno-functional properties of HoPS from lactic acid bacteria of different origins as potential food additives. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, R.E.; Orrillo, P.A.; Ribotta, S.B.; de Valdez, G.F.; Garcia, M.S.; Cabello, J.C.R.; Torino, M.I. Structural characterization of a homopolysaccharide produced by Weissella cibaria FMy 2-21-1 and its potential application as a green corrosion inhibiting film. Int. J. Biol Macromol. 2022, 212, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasheminya, S.-M.; Dehghannya, J. Novel ultrasound-assisted extraction of kefiran biomaterial, a prebiotic exopolysaccharide, and investigation of its physicochemical, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 243, 122645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Techi, M.; Abid, U.; Kandasamy, S.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Effect of γ-irradiation on physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of galactan exopolysaccharide from Weissella confusa KR780676. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Structural characteristics and antioxidant properties of exopolysaccharides isolated from soybean protein gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Ashraf, M.; Fang, H.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; Khurshid, M.; Zhao, L.; He, Z. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide mediated silver nanoparticle synthesized by Lactobacillus brevis isolated from Chinese koumiss. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; Lü, X. Optimization, partial characterization and antioxidant activity of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum KX041. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchi, H.; Sebei, K.; Mottawea, W.; Al Kasaa, I.; Hammami, R. An agar-based bioassay for accurate screening of the total antioxidant capacity of lactic acid bacteria cell-free supernatants. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 195, 106437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H.; Yu, Z.B.; Lu, Y.; Zhai, H.; Bai, F.; Shi, Y.; Lan, M. Effects of essential oil from Croton tiglium L. on intestinal transit in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-W.; Lv, S.; Shi, T.-T.; Liu, K.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Zha, X.-Q.; Luo, J.-P. Exopolysaccharides from yoghurt fermented by Lactobacillus paracasei: Production, purification and its binding to sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exarhopoulos, S.; Raphaelides, S.N.; Kontominas, M.G. Conformational studies and molecular characterization of the polysaccharide kefiran. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, S.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.W.; Xie, M. Conformational properties of a bioactive polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum by light scattering and molecular modeling. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Cheung, Y.-C.; Leung, P.-H.; Wu, J.-Y. Ultrasonic treatment for improved solution properties of a high-molecular weight exopolysaccharide produced by a medicinal fungus. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5517–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, K.; Wiater, A.; Choma, A.; Wiącek, D.; Bieganowski, A.; Siwulski, M.; Waśko, A. Fungal (1 → 3)-α-d-glucans as a new kind of biosorbent for heavy metals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wagner, M.; Horn, H.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. Towards a nondestructive chemical characterization of biofilm matrix by Raman microscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Y.; Han, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, Z. Isolation and characterization of dextran produced by Leuconostoc citreum NM105 from manchurian sauerkraut. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, R.; Bin, X. Purification and characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Weissella cibaria YB-1 from pickle Chinese cabbage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kong, F.; Ni, H.; Mo, Z.; Wan, J.-B.; Hua, D.; Yan, C. Structural characterization, α-glucosidase inhibitory and DPPH scavenging activities of polysaccharides from guava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ibrahim, S.; Gao, S.-S.; Yang, H.; Huang, W. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes residue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 145, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S.-N.; Choi, S.-M.; Phillips, D.L.; Ma, C.-Y. Raman and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxymethylated non-starch polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Qiao, X.; Zhao, F.; Song, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of dextran produced by Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides from homemade wine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chylińska, M.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Zdunek, A. FT-IR and FT-Raman characterization of non-cellulosic polysaccharides fractions isolated from plant cell wall. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhiro, B.; Osorio-Román, I.O.; Torres, R. Vibrational spectroscopy characterization and anticoagulant activity of a sulfated polysaccharide from sea cucumber Athyonidium chilensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Delattre, C.; Devi, P.B.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Shetty, P.H.; Andhare, P. Physical and functional characterization of succinoglycan exopolysaccharide produced by Rhizobium radiobacter CAS from curd sample. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Ma, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, B.; Cui, S.W.; Zhang, T. Physicochemical properties of a water soluble extracellular homopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus reuteri SK24. 003. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H.; Cheng, Q.; Abbas, Z.; Tong, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X. Optimization of exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum R301 and its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Foods 2023, 12, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, D.; Tang, N.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Dong, M.; Li, W. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide and structural characterization by Lacticaseibacillus paracasei ZY-1 isolated from Tibetan kefir. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Burgos, M.; Moreno-Fernández, J.; Alférez, M.J.; Díaz-Castro, J.; López-Aliaga, I. New perspectives in fermented dairy products and their health relevance. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, M.F.; Piermaria, J.A.; Abraham, A.G. Selection of EPS-producing Lactobacillus strains isolated from kefir grains and rheological characterization of the fermented milks. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Exopolysaccharides of lactic acid bacteria: Structure, bioactivity and associations: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Feng, M.; Rui, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Microbiological, physicochemical and rheological properties of fermented soymilk produced with exopolysaccharide (EPS) producing lactic acid bacteria strains. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-p.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.-l.; You, R.-x.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Structural differences and conformational characterization of five bioactive polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Niu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, J.; Lu, B.; Niu, G. Physicochemical characterization and antioxidant activity of cell-bound exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus fermentum S1 obtained by two extraction methods. Process Biochem. 2019, 85, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Q.; Feng, L.; Rui, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X. Influences of drying methods on the structural, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, L.G.; Løkke, M.M.; Micklander, E.; Engelsen, S.B. Vibrational microspectroscopy of food. Raman vs. FT-IR. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, B.; Bajaj, B.K. Hypocholesterolemic potential and bioactivity spectrum of an exopolysaccharide from a probiotic isolate Lactobacillus paracasei M7. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2019, 19, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, C. Methods used to evaluate the free radical scavenging activity in foods and biological systems. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2002, 8, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Tseng, K.C.; Chiang, S.S.; Lee, B.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Pan, T.M. Immunomodulatory and antioxidant potential of Lactobacillus exopolysaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, T.; Palpperumal, S.; Kathiresan, D.; Sankaralingam, S.; Balachandran, C.; Baskar, K.; Hashem, A.; Alqarawi, A.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Biomedical and therapeutic potential of exopolysaccharides by Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from sauerkraut: Screening and characterization. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kıray, E.; Raheel, N.M. New Approach to Exopolysaccharides of Post Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei L1 Strain: Anti-quarum Sensing Activity. Balkan Med. J. 2023, 40, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarique, M.; Ali, A.H.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Gan, R.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Ayyash, M. Investigating the biological activities and prebiotic potential of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus: Implications for gut microbiota modulation and rheological properties in fermented milk. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2023, 4, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, N.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, M.; Li, W. Characterization and immunological activity of exopolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei GL1 isolated from Tibetan kefir grains. Foods 2022, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Hou, B.; Hung, W.; He, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Man, C. The probiotic fermented milk of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei JY062 and Lactobacillus gasseri JM1 alleviates constipation via improving gastrointestinal motility and gut microbiota. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1857–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, M.-R.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Seong, Y.-J.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.-J.; Jin, H.; Johnston, T.V. In vivo functional effects of Weissella confusa VP30 exopolysaccharides on loperamide-induced constipation in rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| a | B | L | °H | C* | WI | YI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.21 ± 0.12 | 1.92 ± 0.89 | 78.29 ± 0.91 | 85.99 ± 2.32 | 1.92 ± 0.99 | 78.19 ± 0.91 | 3.46 ± 1.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobo, R.E.; Ávila, A.M.; Laiño, J.; Molina, V.; Navarro, D.; Gómez, M.I.; Torino, M.I.; Taranto, M.P. Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Constipation Stress Modulation by a Heteropolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL75. Fermentation 2025, 11, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040224
Lobo RE, Ávila AM, Laiño J, Molina V, Navarro D, Gómez MI, Torino MI, Taranto MP. Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Constipation Stress Modulation by a Heteropolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL75. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040224
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobo, René Emanuel, Ana Magdalena Ávila, Jonathan Laiño, Verónica Molina, Diego Navarro, María Inés Gómez, María Inés Torino, and María Pía Taranto. 2025. "Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Constipation Stress Modulation by a Heteropolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL75" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040224
APA StyleLobo, R. E., Ávila, A. M., Laiño, J., Molina, V., Navarro, D., Gómez, M. I., Torino, M. I., & Taranto, M. P. (2025). Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Constipation Stress Modulation by a Heteropolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL75. Fermentation, 11(4), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040224






