Utilization of Cheese Whey for Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells: Performance Evaluation and Metagenomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
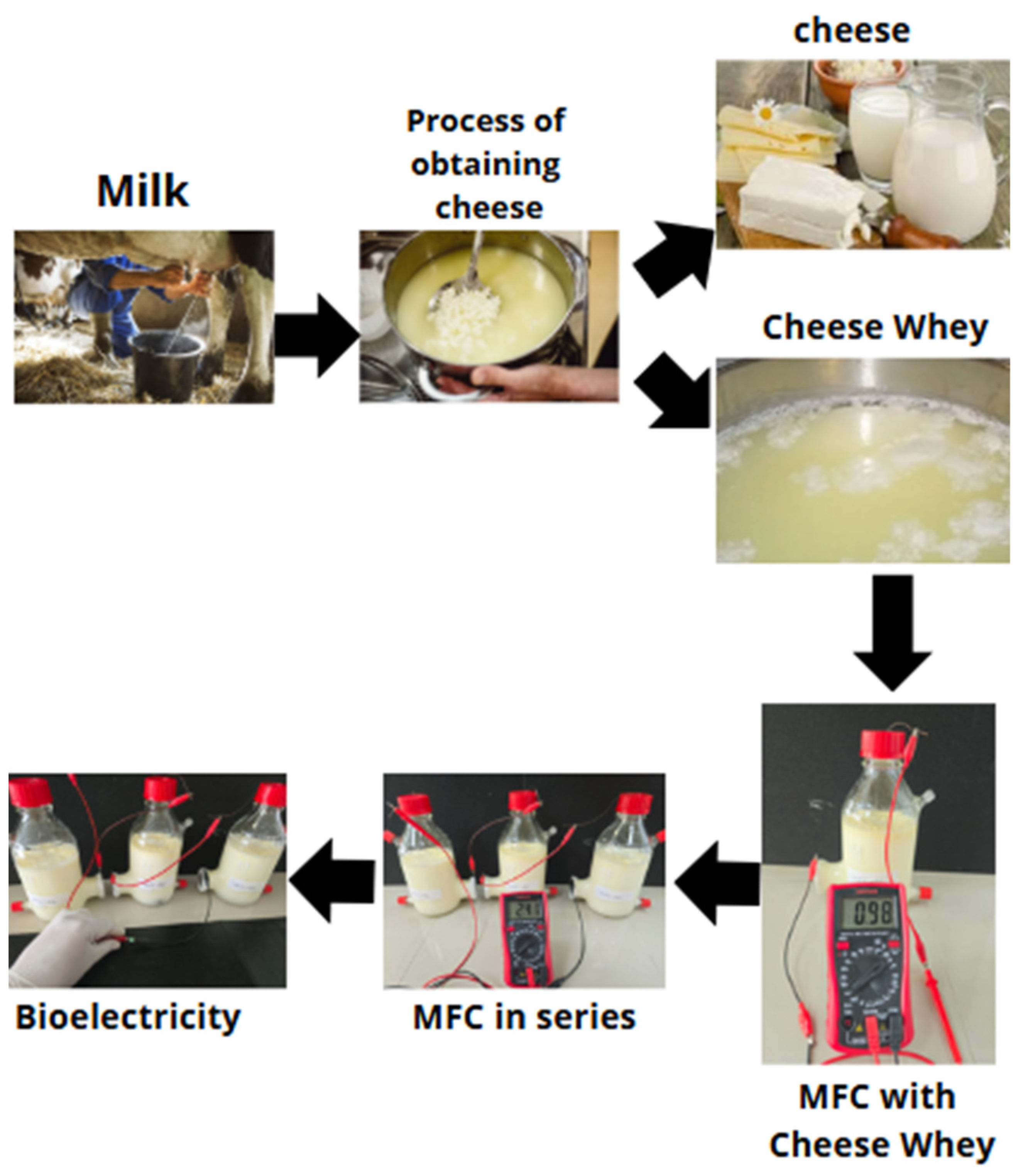
2.1. Obtaining Whey
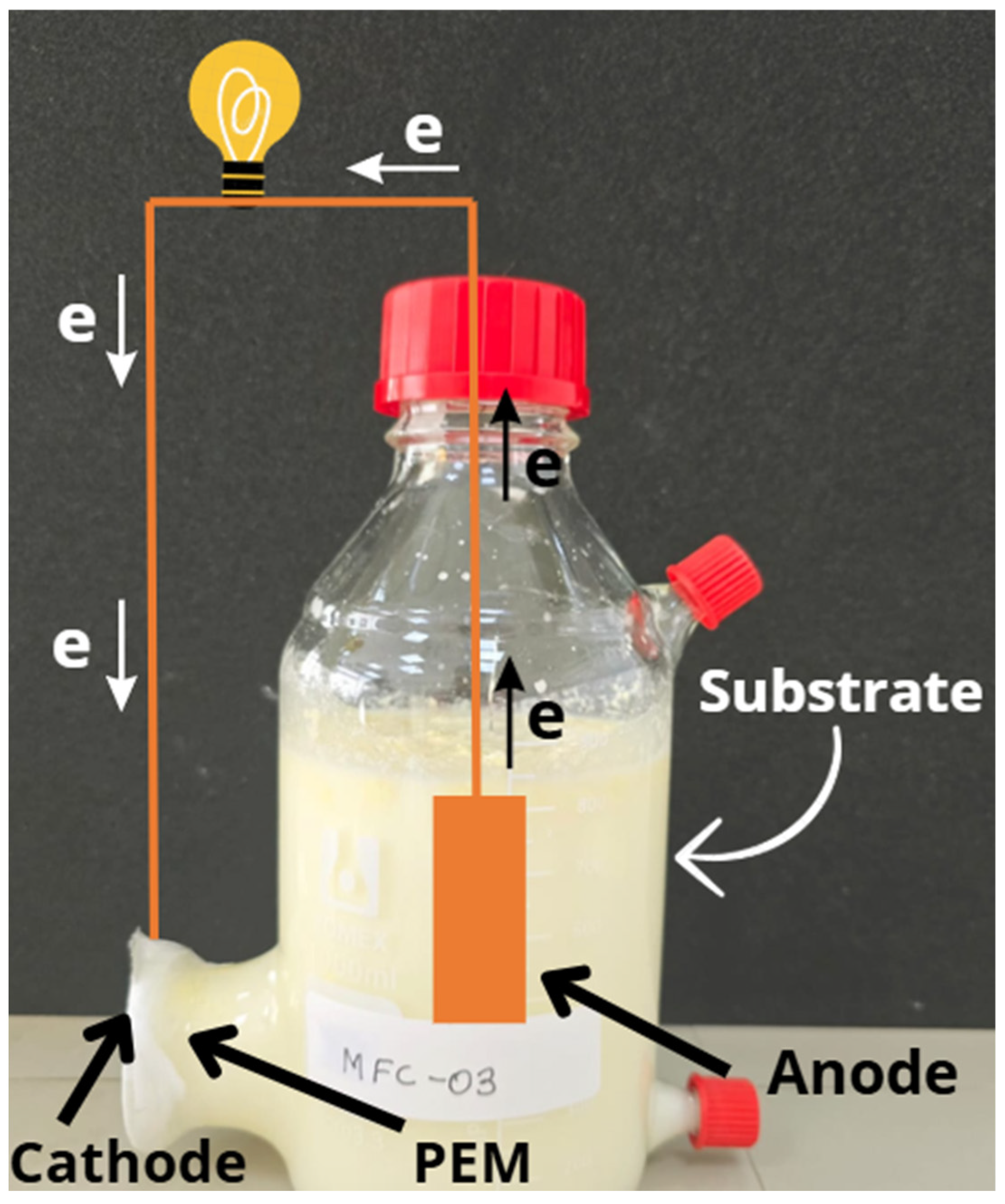
2.2. Design and Assembly of MFCs
2.3. Evaluation of the Performance of MFCs
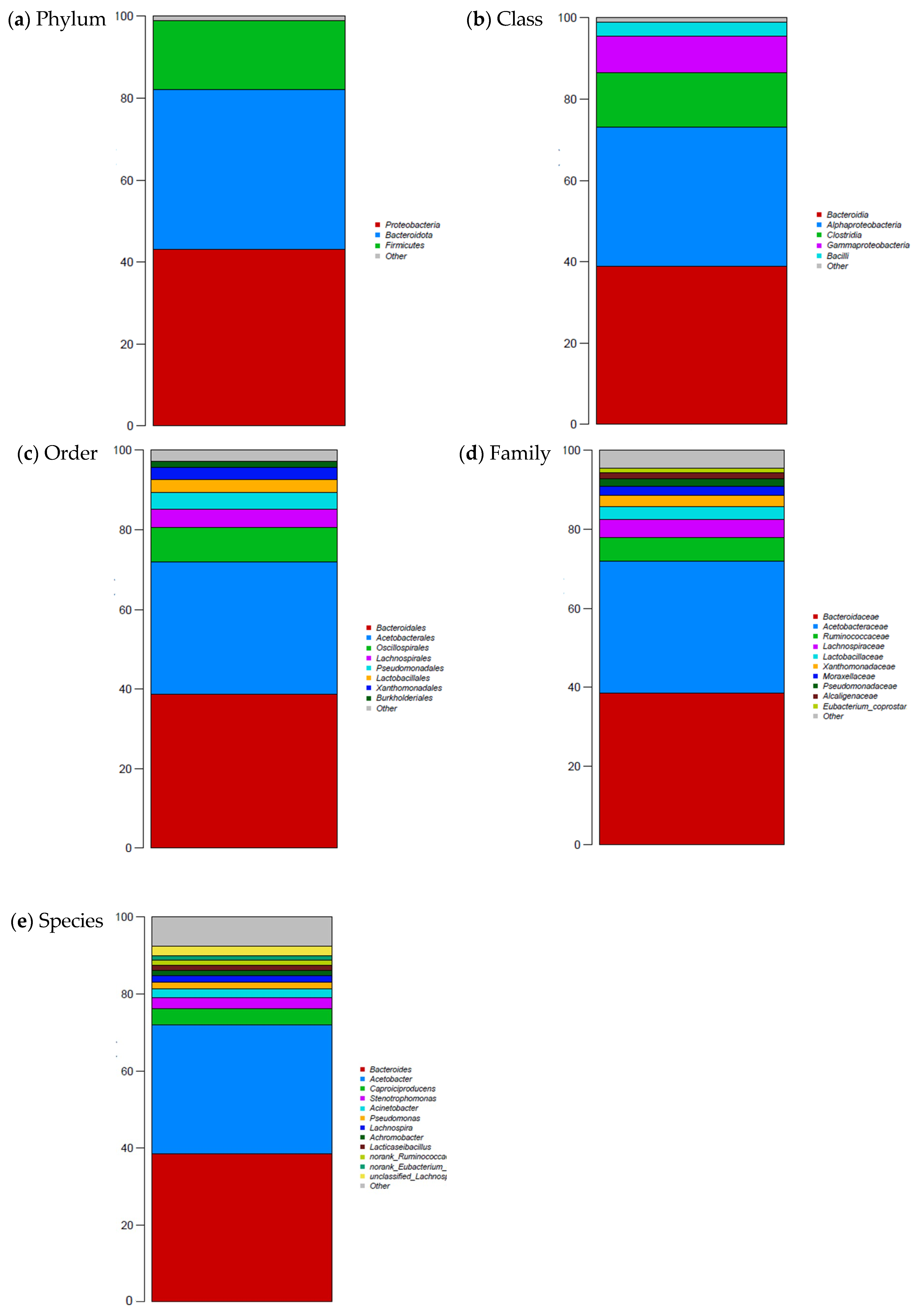
2.4. Metagenomic Analysis of Whey
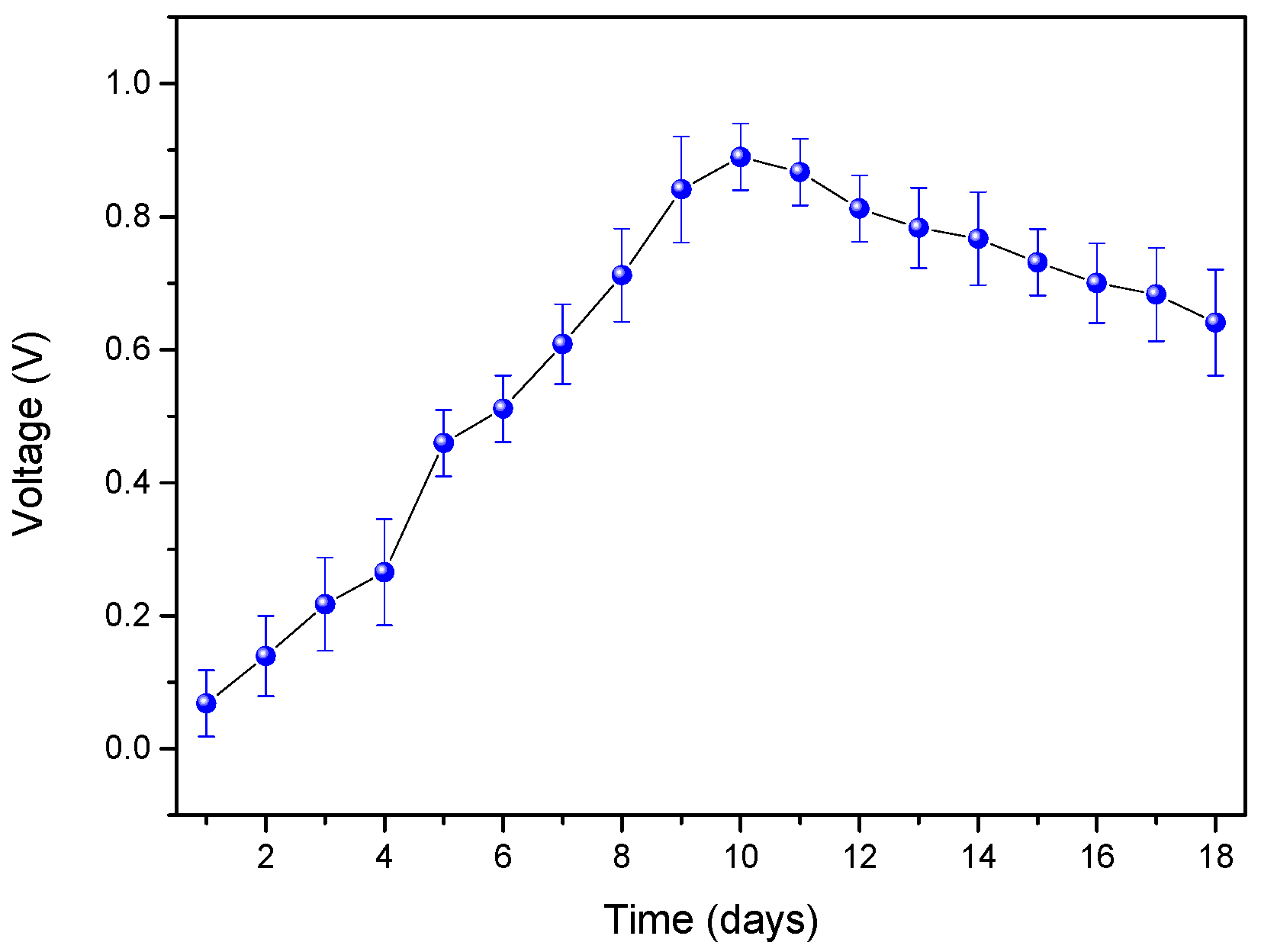
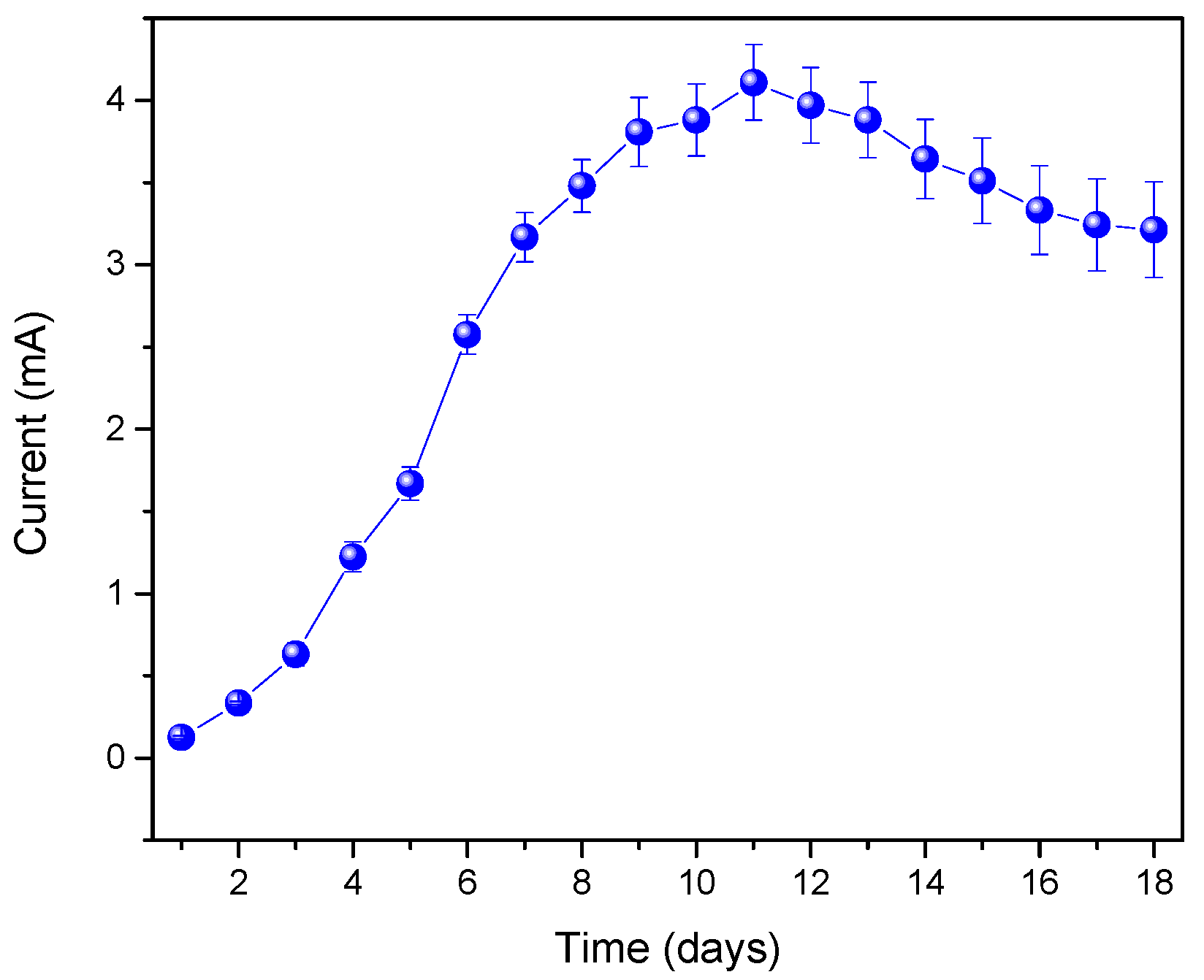
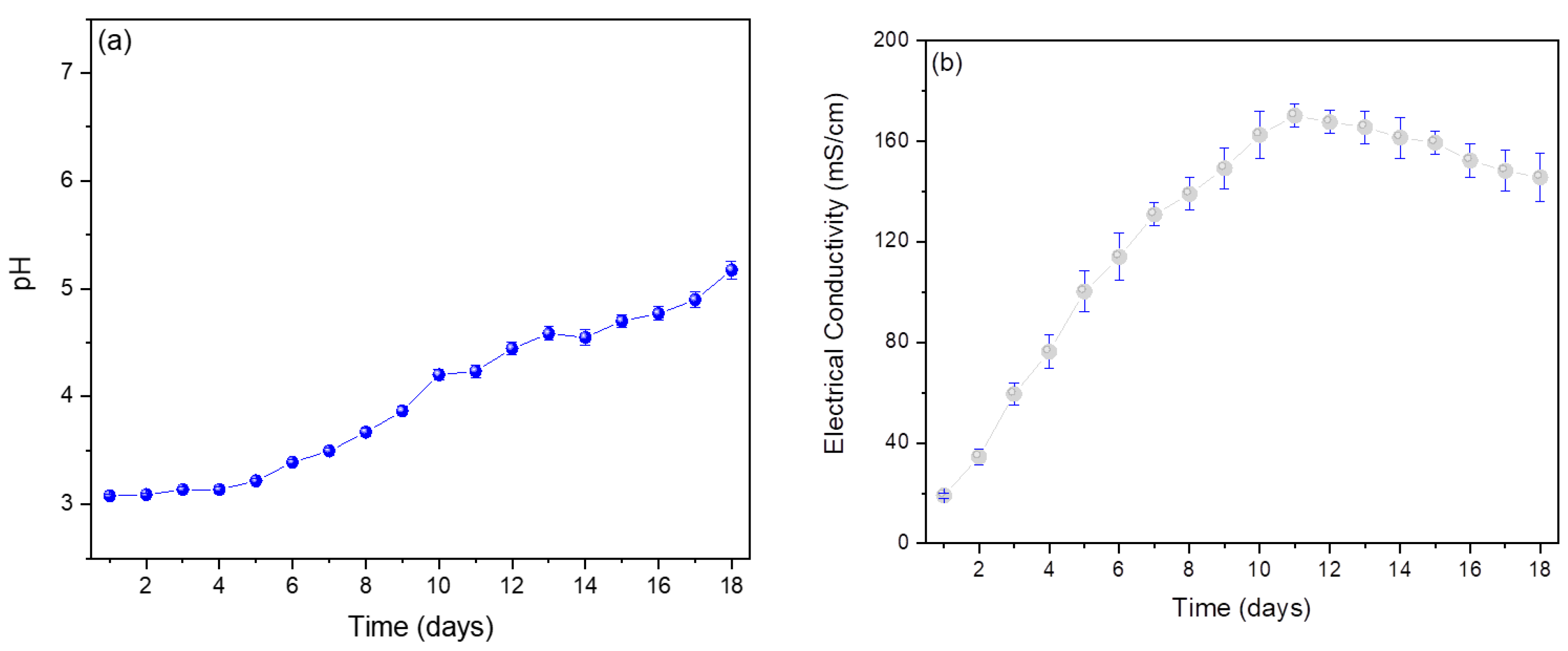
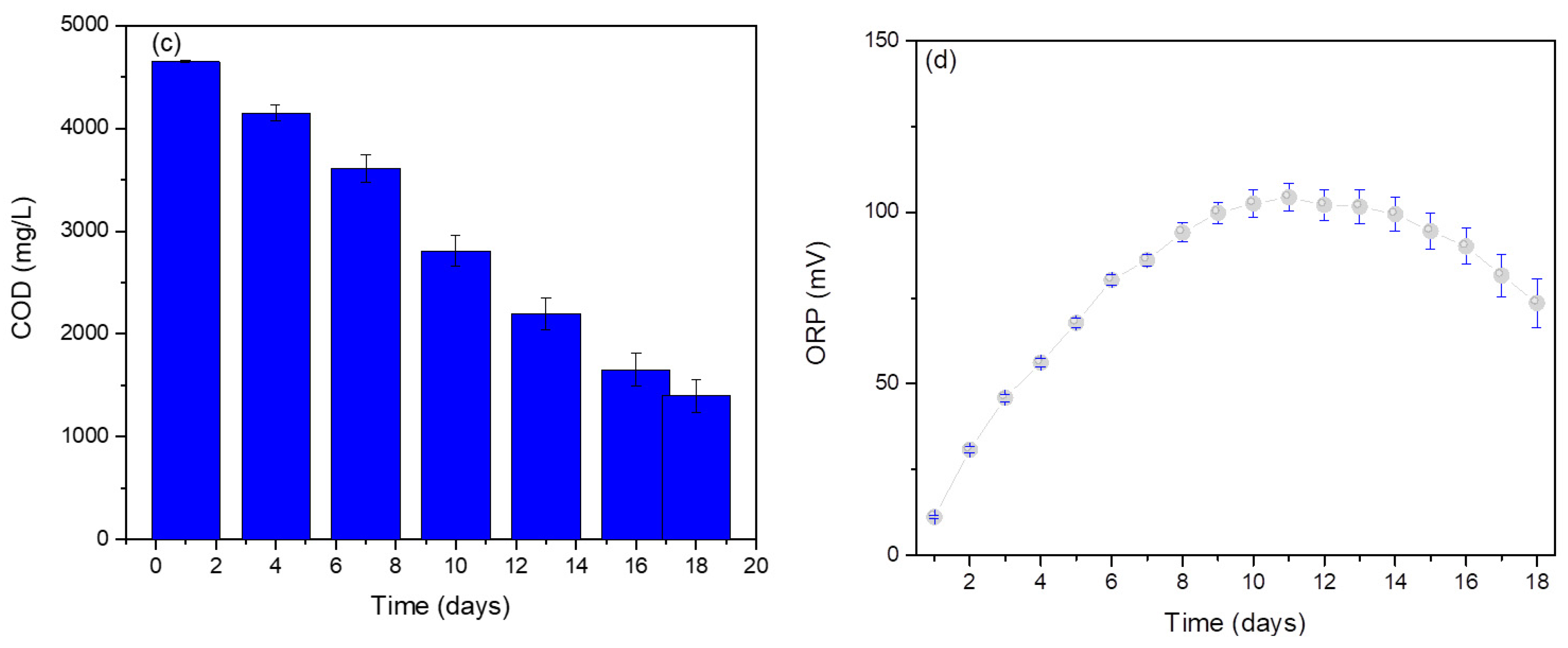
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Gaffey, J.; Sharma, M.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Moreau, B.; Newbold, J.; Clark, W.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, V.K. Valorization of dairy waste and by-products through microbial bioprocesses. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.D.; Paul, V.; Agarwal, A.; Sharma, R.; Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Rashidi, L.; Darani, K.K. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates using dairy processing waste—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Paul, A.; Kumar, V.; Sar, T.; Kumar, D.; Sarsaiya, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Binod, P.; Sindhu, R.; et al. Recent trends and developments on integrated biochemical conversion process for valorization of dairy waste to value added bioproducts: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, F.; Xin, F.; Wen, B. Methane production and characteristics of the microbial community in the co-digestion of potato pulp waste and dairy manure amended with biochar. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanany, I.; Wangsa, I.D.; Jeremi, N.A. A Multi-objective mixed-integer linear model for sustainable dairy supply chain with food waste and environmental pollutants. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2024, 8, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-C.; Mariuzza, D.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Ceylan, S.; Goldfarb, J.L. Integrated thermochemical conversion process for valorizing mixed agricultural and dairy waste to nutrient-enriched biochars and biofuels. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, B.; Venkatesh, Y.K.; Talesh, S.S.A.; Esmaeili, H.; Mohan, S.; Balakrishna, G.R. A Novel Biomass Derived Activated Carbon Mediated AC@ZnO/NiO Bifunctional Nanocatalyst to Produce High-Quality Biodiesel from Dairy Industry Waste Oil: CI Engine Performance and Emission. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufou, S.; Griffin, S.; Katsini, L.; Polańska, M.; Van Impe, J.F.; Valdramidis, V.P. The (potential) impact of seasonality and climate change on the physicochemical and microbial properties of dairy waste and its management. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqman, M.; Al-Ansari, T. A novel solution towards zero waste in dairy farms: A thermodynamic study of an integrated polygeneration approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 230, 113753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, K.; Rao, P.V. Anaerobic digestion of dairy wastewater: Effect of different parameters and co-digestion options—A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 2527–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermoula, P.; Khakimov, B.; Nielsen, J.H.; Engelsen, S.B. WHEY—The waste-stream that became more valuable than the food product. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenaria, Z.D.; Bahramimianroodb, B. Selection of factors affecting the supply chain and green suppliers by the TODIM method in the dairy industry. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 56, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sonawane, A.V.; Rikame, S.; Gaikwad, M.; Bhanvase, B.; Sonawane, S.S.; Mungray, A.K.; Gaikwad, R. A review of microbial fuel cell and its diversification in the development of green energy technology. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, P.; Ala, A.; Nazari, P.; Jalili, B.; Ganji, D.D. A comprehensive review of microbial fuel cells considering materials, methods, structures, and microorganisms. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, S.; Li, C. Metal-based cathode catalysts for electrocatalytic ORR in microbial fuel cells: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xu, X.; Dong, G.; Zhang, M.; Luo, S.; Leung, D.Y.; Wang, Y. Computational modeling studies on microfluidic fuel cell: A prospective review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 191, 114082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, N.; Akay, R.G. Components Used in Microbial Fuel Cells for Renewable Energy Generation: A Review of Their Historical and Ecological Development. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2024, 21, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, E.A.; Abasalt, A.; Talebi, S. Application of microbial fuel cells in wastewater treatment and green energy production: A comprehensive review of technology fundamentals and challenges. Fuel 2024, 370, 131855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.M.; Noor, Z.Z.; Mutamim, N.S.A.; Baharuddin, N.H.; Aris, A.; Faizal, A.N.M.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Suhaimin, N.S. A critical review of ceramic microbial fuel cell: Economics, long-term operation, scale-up, performances and challenges. Fuel 2024, 365, 131150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.; Musa, H.A.; Fardami, A.Y. Isolation And Identification of Bacteria Associated With Bioelectricity Generation From Fruit Wastes and Gutter Sludge Using Microbial Fuel Cells (MFC) In Kano Metropolis, Kano State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Sci. Eng. Infrastruct. 2024, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Korojdeh, M.S.; Hadavifar, M.; Birjandi, N.; Mehrkhah, R.; Li, Q. Enhanced bioenergy production through dual-chamber microbial fuel cells: Utilizing citric acid factory wastewater and grape waste as substrates. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Gamal, S.; Ghouri, Z.K.; Fadali, O.A.; Abdelraheem, O.H.; Hashem, M.; Moustafa, H.M. Graphitized mango seed as an effective 3D anode in batch and continuous mode microbial fuel cells for sustainable wastewater treatment and power generation. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 3163–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Perales, N.S.; Magro, G.P.D. Quantification of food losses and waste in Peru: A mass flow analysis along the food supply chain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Bedriñana, J.; Chirinos-Peinado, D.; Ríos-Ríos, E.; Machuca-Campuzano, M.; Gómez-Ventura, E. Dietary risk of milk contaminated with lead and cadmium in areas near mining-metallurgical industries in the Central Andes of Peru. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.; Reddy, S.N.; Hunter, H.N.; Butler, I.S.; Kozinski, J.A. Supercritical water gasification of Lactose as a model compound for valorization of dairy industry effluents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 9296–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, T.; Flores, V.G.A.; Zea, E.C.; Paredes, J.M. Cheese value chain in the highlands of Southern Peru: Critical success factors. J. Agribus. Dev. Emerg. Econ. 2025, 15, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos-Peinado, D.; Castro-Bedriñana, J.; Ríos-Ríos, E.; Mamani-Gamarra, G.; Quijada-Caro, E.; Huacho-Jurado, A.; Nuñez-Rojas, W. Lead and Cadmium Bioaccumulation in Fresh Cow’s Milk in an Intermediate Area of the Central Andes of Peru and Risk to Human Health. Toxics 2022, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhuas, J.N.; Capcha, K.B.; Garcia-Olarte, E.; Eulogio, C.Q. Production performance of rejected newborn lambs fed with different concentrations of whey in Perú. Rev. Ciên. Agrovet. 2024, 23, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segundo, R.-F.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Luis, C.-C.; Otiniano, N.M.; Soto-Deza, N.; Rojas-Villacorta, W.; De La Cruz-Cerquin, M. Reduction of Toxic Metal Ions and Production of Bioelectricity through Microbial Fuel Cells Using Bacillus marisflavi as a Biocatalyst. Molecules 2024, 29, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, E.; Sanin, S.L. Investigation of the electrical potential of whey using a river sediment microbial fuel cell. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2024, 38, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Oluwaferanmi, F.M.; Ogwu, C.E.; Johnson, A.I.; Desire, O.A. Bioelectricity Production from Abattoir Wastewater Using Microbial Fuel Cells Connected in Series. Science 2021, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Din, M.I.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, Z.; Khalid, R. Bioelectricity generation from waste potatoes using single chambered microbial fuel cell. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 12596–12606. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, L.P.; Gaikwad, V.B.; Patil, S. Study of different forms of microbial fuel cell technology (mfc) for generation of electricity from dairy effluent using a microbial consortium. Pollut. Res. 2021, 40, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Marassi, R.J.; Queiroz, L.G.; Silva, D.C.V.R.; dos Santos, F.S.; Silva, G.C.; de Paiva, T.C.B. Long-term performance and acute toxicity assessment of scaled-up air–cathode microbial fuel cell fed by dairy wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, J.; Antoniewska-Krzeska, A.; Żbikowska, A.; Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Volatile composition and sensory profile of lactose-free kefir, and its acceptability by elderly consumers. Molecules 2022, 27, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, S.; Marescotti, F.; Sanmartin, C.; Macaluso, M.; Taglieri, I.; Venturi, F.; Zinnai, A.; Facioni, M.S. Lactose: Characteristics, Food and Drug-Related Applications, and Its Possible Substitutions in Meeting the Needs of People with Lactose Intolerance. Foods 2022, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Zulfakar, N.A.M. Bioelectricity production from food waste leachate using double chamber microbial fuel cell: Effect of electrolyte ph level, electrodes sizing, and positioning. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2024, 33, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammam, A.M.; Mohamed, M.S.; Moubasher, H. Optimization of Agro-Industrial Waste Bioconversion into Bioelectricity. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 68, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Benites, S.M.; Segundo, R.-F.; Renny, N.-N.; Otiniano, N.M.; Delfín-Narciso, D.; Romero, C.V. New Fuel Source: Lemon Waste in MFCs-SC for the Generation of Bioelectricity. In Renewable Energy Resources and Conservation; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Apollon, W.; Rusyn, I.; Kuleshova, T.; Luna-Maldonado, A.I.; Pierre, J.F.; Gwenzi, W.; Kumar, V. An overview of agro-industrial wastewater treatment using microbial fuel cells: Recent advancements. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 58, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.N.M.; Al-Zaqri, N.; Yaakop, A.S.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Guerrero-Barajas, C. Stimulating bioelectric generation and recovery of toxic metals through benthic microbial fuel cell driven by local sago (Cycas revoluta) waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 18750–18764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plakar, G.P.Z.; Kovo, A.S.; Oguzie, K.L.; Oguzie, E.E. Valorization of mixed blackwater/agricultural wastes for bioelectricity and biohydrogen production: A microbial treatment pathway. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-saned, A.J.O.; Kitafa, B.A.; Badday, A.S. Microbial fuel cells (MFC) in the treatment of dairy wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1067, 012073. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Calay, R.K.; Das, S. Effect of pH, COD, and HRT on the performance of microbial fuel cell using synthetic dairy wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.; Gonçalves, L.; Peixoto, J.M.; Peixoto, L.; Brito, A.G.; Martins, G. Resources recovery in the dairy industry: Bioelectricity production using a continuous microbial fuel cell. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Calay, R.K.; Thakur, S.; Mustafa, M.Y. A study on the impact of electrode and membrane modification in stacked microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2025, 9, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabangu, K.P.; Chetty, M.; Bakare, B.F. Metagenomic Insights into Pollutants in Biorefinery and Dairy Wastewater: rDNA Dominance and Electricity Generation in Double Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, K.; Kumar, N.; Murugesan, S.; Yadav, R.; Chandel, H.; Saxena, G. Microbial fuel cell (MFC) in bioremediation, wastewater treatment, resource recovery, and bioelectricity generation: Advances, challenges, and, opportunities. In Development in Waste Water Treatment Research and Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 221–254. [Google Scholar]
- Ravinuthala, S.; Settu, S. Multi-response parametric optimization and biofilm studies of low-cost ceramic microbial fuel cell for dairy wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.; Bhunia, B.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Ray, R.N. The overall performance improvement of microbial fuel cells connected in series with dairy wastewater treatment. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.; Ray, R.N.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Basak, B.; Muthuraj, M.; Bhunia, B. Process engineering for stable power recovery from dairy wastewater using microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakop, A.S.; Ahmad, A.; Hussain, F.; Oh, S.-E.; Alshammari, M.B.; Chauhan, R. Domestic Organic Waste: A Potential Source to Produce the Energy via a Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 2023, 2425735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Omine, K.; Sivasankar, V.; Sano, H.; Chicas, S. Development of low-cost solid phase microbial fuel cell using organic waste and recycling of materials after power generation: Characterization of carbon anode. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 154, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanvitaya, P.; Boocha, S. Performance of Dairy Wastewater Intrinsic Bacteria in Microbial Fuel Cell. Thai Environ. Eng. J. 2021, 35, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Pham, N.; Pham, H.T. Wastewater treatment performance and microbial community of anode electrodes of membrane and membrane-less MFCs under effect of sunlight. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 42, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, H.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, Y. Metagenomic analysis of microbial community and gene function of anodic biofilm for nonylphenol removal in microbial fuel cells. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Lin, X.-Q.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Liang, B.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Sun, K.; Zhou, A.-N.; et al. Microbial fuel cell-upflow biofilter coupling system for deep denitrification and power recovery: Efficiencies, bacterial succession and interactions. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, M.; Li, Q.; Zheng, S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M. Bioelectrocatalytic reduction by integrating pyrite assisted manganese cobalt-doped carbon nanofiber anode and bacteria for sustainable antimony catalytic removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, R.; Cai, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Harnessing electroactive microbial community for energy recovery from refining wastewater in microbial fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 102, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Gao, J.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Jin, H. Thermal pretreatment enhances the degradation and humification of lignocellulose by stimulating thermophilic bacteria during dairy manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Su, X.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z. First report of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia causing root soft rot of Sanqi (Panax notoginseng) in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiabani, A.; Sarabi-Jamab, M.; Shakeri, M.-S.; Pahlevanlo, A.; Emadzadeh, B. Exploring the Acetobacteraceae family isolated from kombucha SCOBYs worldwide and comparing yield and characteristics of biocellulose under various fermentation conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isipato, M. Application of Microbial Electrochemical Systems for Valorisation of Cheese Whey in Biorefinery Framework. 2021. Available online: https://tesidottorato.depositolegale.it/handle/20.500.14242/69531 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Tesfaw, A. The current trends of bioethanol production from cheese whey using yeasts: Biological and economical perspectives. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1183035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, A.; Bashir, Y.; Das, S. Dairy Wastewater as a Potential Feedstock for Valuable Production with Concurrent Wastewater Treatment through Microbial Electrochemical Technologies. Energies 2022, 15, 9084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-González, C.S.; Gómez-Falcon, N.; Brar, S.K.; Ramírez, A.A. Cheese whey as a potential feedstock for pro-ducing renewable biofuels: A review. Energies 2022, 15, 6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 3.07 ± 0.01 |
| Oxidation-Reduction Potential (mV) | 11.163 ± 0.513 |
| Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm) | 19.101 ± 1.025 |
| Fat (%) | 0.4 |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand (mg/L) | 4650.52 ± 10.54 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.026 |
| Temperature (°C) | 23 |
| Lactose (%) | 4.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segundo, R.-F.; Luis, C.-C.; Otiniano, N.M.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Gallozzo-Cardenas, M. Utilization of Cheese Whey for Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells: Performance Evaluation and Metagenomic Analysis. Fermentation 2025, 11, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040176
Segundo R-F, Luis C-C, Otiniano NM, De La Cruz-Noriega M, Gallozzo-Cardenas M. Utilization of Cheese Whey for Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells: Performance Evaluation and Metagenomic Analysis. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegundo, Rojas-Flores, Cabanillas-Chirinos Luis, Nélida Milly Otiniano, Magaly De La Cruz-Noriega, and Moises Gallozzo-Cardenas. 2025. "Utilization of Cheese Whey for Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells: Performance Evaluation and Metagenomic Analysis" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040176
APA StyleSegundo, R.-F., Luis, C.-C., Otiniano, N. M., De La Cruz-Noriega, M., & Gallozzo-Cardenas, M. (2025). Utilization of Cheese Whey for Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells: Performance Evaluation and Metagenomic Analysis. Fermentation, 11(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040176






