Alleviation of Organic Load Inhibition and Enhancement of Caproate Biosynthesis via Fe3O4 Addition in Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Reagents
2.1.2. Substrate
2.1.3. Setup and Operation
2.1.4. Batch Test
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Analytical Methods
2.2.2. Calculations
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Organic Load on Anaerobic Fermentation
3.1.1. Effects of Organic Load on Substrate Hydrolysis
3.1.2. Effects of Organic Load on Acidification
3.2. Effects of Fe3O4 on Caproate Production
3.2.1. Effect of Fe3O4 Addition on Profile and Yields of Fatty Acids
3.2.2. Mechanisms of Fe3O4 Involved in Electron Shuttle
3.3. Microbial Community in Batch Fermentation and Continuous Operation of Fermenter
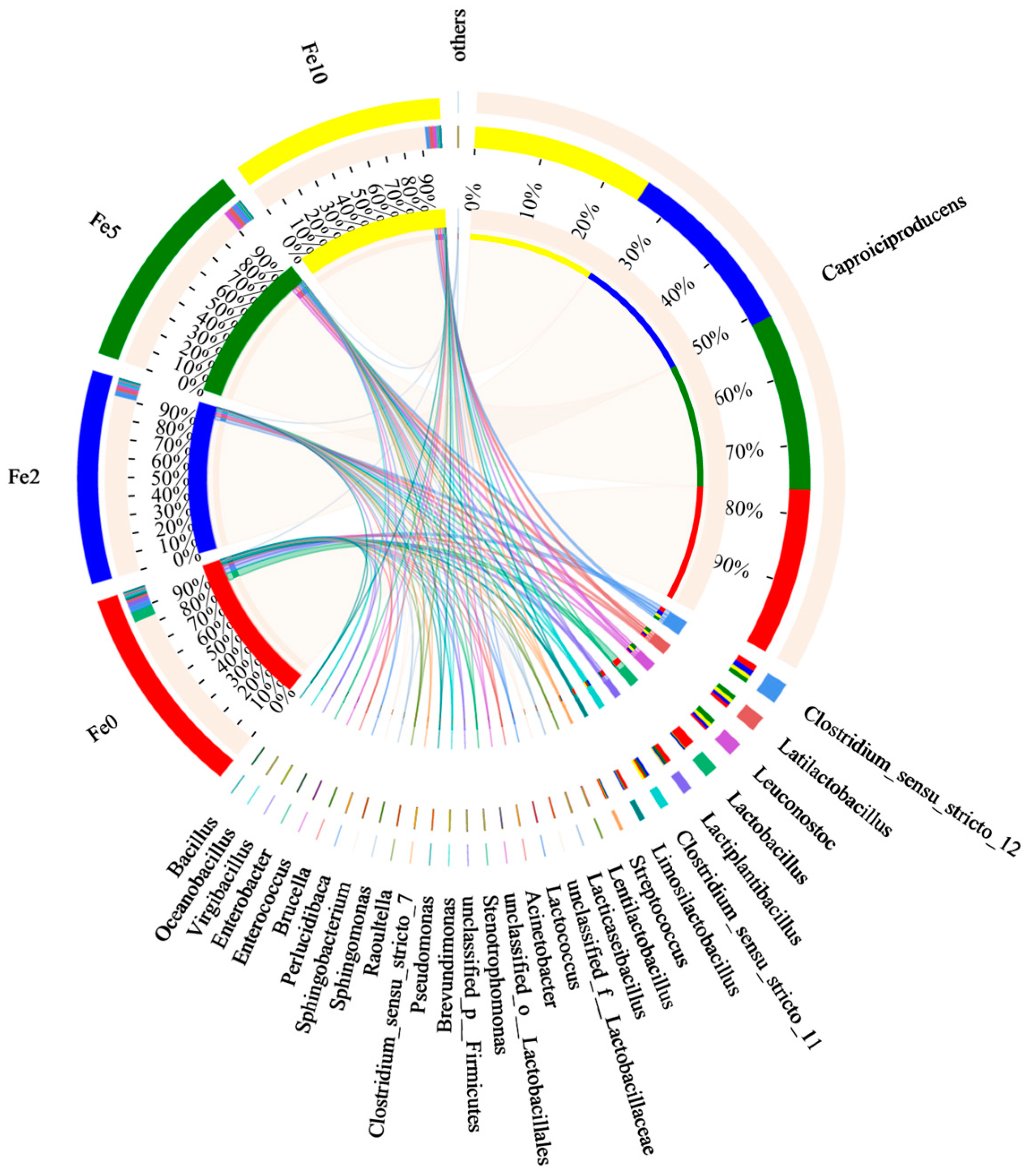
3.3.1. Microbial Diversity in Continuous Operation of Fermenter
3.3.2. Microbial Diversity in Batch Fermenters with Added Fe3O4
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, M.; Yan, B.; Wong, J.W.C.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced volatile fatty acids production from anaerobic fermentation of food waste: A mini-review focusing on acidogenic metabolic pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, M. Volatile fatty acids production from food waste: Effects of pH, temperature, and organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malav, L.C.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, G.K.; Krishnan, S.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Pham, Q.B.; Yadav, S.; et al. A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: Current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ou, Y.-L.; Lin, J.-G. Co-composting of green waste and food waste at low C/N ratio. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, W.d.A.; Leitao, R.C.; Gehring, T.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Santaella, S.T. Anaerobic fermentation for n-caproic acid production: A review. Process Biochem. 2017, 54, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groof, V.; Coma, M.; Arnot, T.; Leak, D.J.; Lanham, A.B. Selecting fermentation products for food waste valorisation with HRT and OLR as the key operational parameters. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, M.; Boni, M.R.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; De Gioannis, G.; Muntoni, A.; Spiga, D. Fermentative H2 production from food waste: Parametric analysis of factor effects. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, R.; Ashika, L.; Xunchang, F.; Jangho, L.; Saurabh, M.; Abid, H. The Effect of pH on the Production and Composition of Short- and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids from Food Waste in a Leachate Bed Reactor at Room Temperature. Fermentation 2023, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Davila, C.A.; Carrion, V.J.; Vonk, V.R.; Buisman, C.N.J.; Strik, D.P. Consecutive lactate formation and chain elongation to reduce exogenous chemicals input in repeated-batch food waste fermentation. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Zuo, J. Performance and mechanisms of medium-chain fatty acid production by anaerobic fermentation of food waste without external electron donors. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Dávila, C.A.; Zuidema, N.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Strik, D.P.B.T.B. Reactor microbiome enriches vegetable oil with n-caproate and n-caprylate for potential functionalized feed additive production via extractive lactate-based chain elongation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakarika, M.; Regueira, A.; Rabaey, K.; Ganigue, R. Thermophilic caproic acid production from grass juice by sugar-based chain elongation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemeinhardt, K.; Jeon, B.S.; Ntihuga, J.N.; Wang, H.; Schlaiß, C.; Lucas, T.N.; Bessarab, I.; Nalpas, N.; Zhou, N.; Usack, J.G.; et al. Toward industrial C8 production: Oxygen intrusion drives renewable n-caprylate production from ethanol and acetate via intermediate metabolite production. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 2931–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; He, P.; Shao, L.; Lu, F. Road to full bioconversion of biowaste to biochemicals centering on chain elongation: A mini review. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 86, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.I.; Vogel, H.J. Current understanding of fatty acid biosynthesis and the acyl carrier protein. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-L.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, W.; Song, L.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.-J. Unveiling the mechanisms of medium-chain fatty acid production from waste activated sludge alkaline fermentation liquor through physiological, thermodynamic and metagenomic investigations. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Fu, X.; Bao, M.; Ye, R.; Shao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Shi, X.; Lu, W. Strategy of electron acceptors for ethanol-driven chain elongation from kitchen waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, F.; Shao, L.; He, P. Alcohol-to-acid ratio and substrate concentration affect product structure in chain elongation reactions initiated by unacclimatized inoculum. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ren, W.T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.-Z.; Wu, Q.-L.; Guo, W.-Q. Upgrading soybean dreg to caproate via intermediate of lactate and mediator of biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 406, 130958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Wu, S.-L.; Ni, B.-J. Zerovalent Iron Effectively Enhances Medium-Chain Fatty Acids Production from Waste Activated Sludge through Improving Sludge Biodegradability and Electron Transfer Efficiency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10904–10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Hu, A.; Ren, G.; Chen, M.; Tang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, S.; He, Z. Enhancing sludge methanogenesis with improved redox activity of extracellular polymeric substances by hematite in red mud. Water Res. 2018, 134, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Xu, Q.; Wei, W.; Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.-J. Performance and Mechanism of Fe3O4 Improving Biotransformation of Waste Activated Sludge into Liquid High-Value Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Guo, H.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. New insight into mechanisms of ferroferric oxide enhancing medium-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge through anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Zheng, K.; Wei, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ni, B.-J.; Zhu, T.; Horn, H.; Liu, Y. Ferric oxide stimulates medium-chain carboxylic acids synthesis from waste activated sludge via ethanol-driven chain elongation: Mechanisms and implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 389, 136044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, N.; Tajima, N.; Kawai, M.; Niwa, C.; Kurosawa, N.; Matsuyama, T.; Yusoff, F.M.; Toda, T. Maximum organic loading rate for the single-stage wet anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.-S.; Wang, X.C. High-rate mesophilic co-digestion with food waste and waste activated sludge through a low-magnitude increasing loading regime: Performance and microorganism characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groof, V.; Coma, M.; Arnot, T.C.; Leak, D.J.; Lanham, A.B. Adjusting Organic Load as a Strategy to Direct Single-Stage Food Waste Fermentation from Anaerobic Digestion to Chain Elongation. Processes 2020, 8, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.-K.; Geng, Z.-Q.; Sun, T.; Dai, K.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, R.J.; Zhang, F. Caproate production from xylose by mesophilic mixed culture fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 308, 123318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, H.; Molenaar, D.; dos Santos, F.B.; Teusink, B. Experimental evolution and the adjustment of metabolic strategies in lactic acid bacteria. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S201–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yang, H.; Pu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Jin, N.; He, X.; Wang, X.C. Caproic acid production from food waste using indigenous microbiota: Performance and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Fang, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) by blast furnace dust (BFD): Feasibility and mechanism. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17709–17719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Dai, K.; Wang, Q.-T.; Zheng, S.-J.; Hong, S.-D.; Zeng, R.J.; Zhang, F. Caproate production from xylose via the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway by genus Caproiciproducens dominated mixed culture fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Yin, F.; Cao, Q.; Lian, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, H. Medium-chain carboxylates production from co-fermentation of swine manure and corn stalk silage via lactic acid: Without external electron donors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wu, H.; Gu, Q.; Li, P. Probiotic potential of a folate-producing strain Latilactobacillus sakei LZ217 and its modulation effects on human gut microbiota. Foods 2022, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
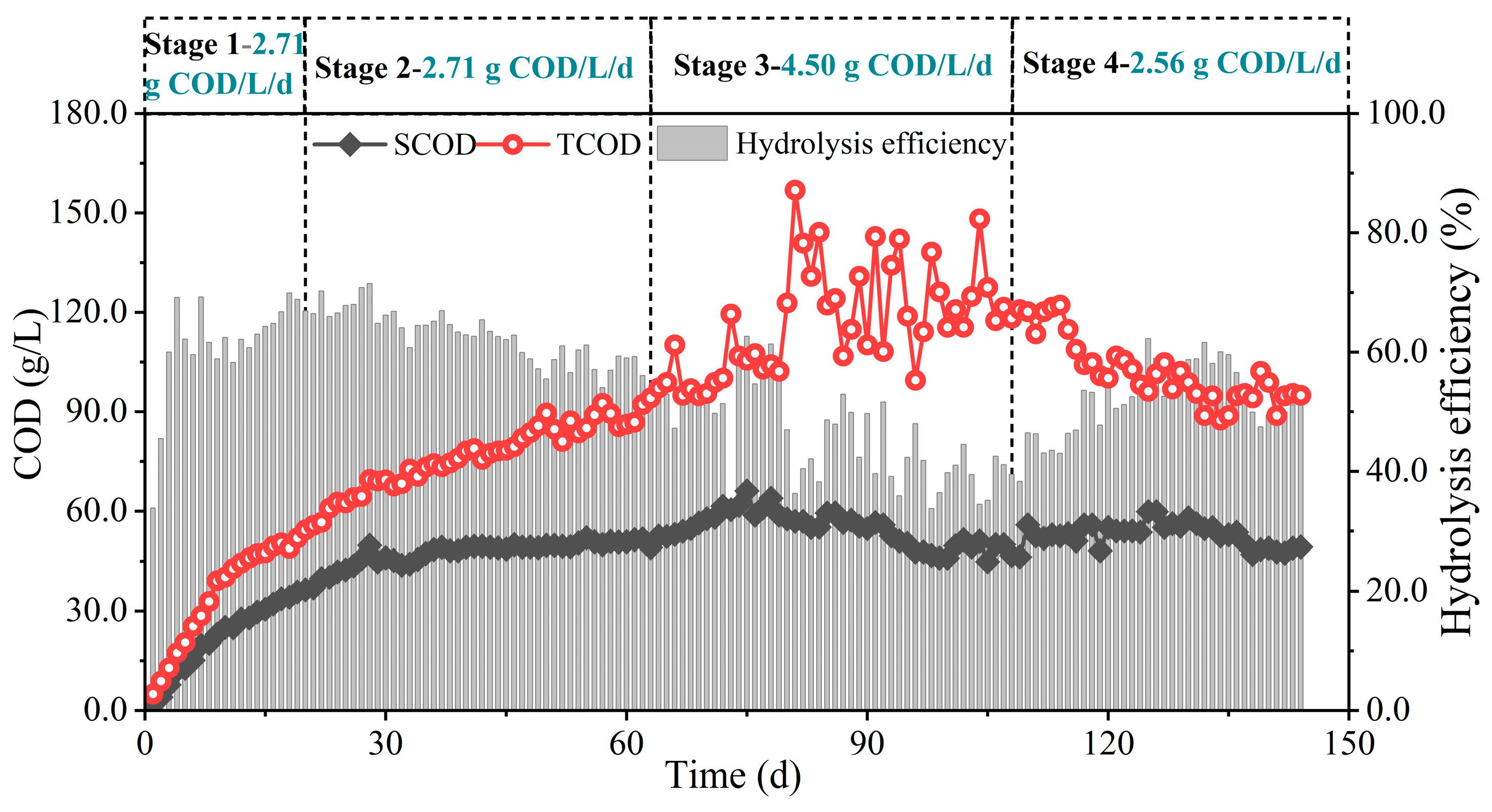

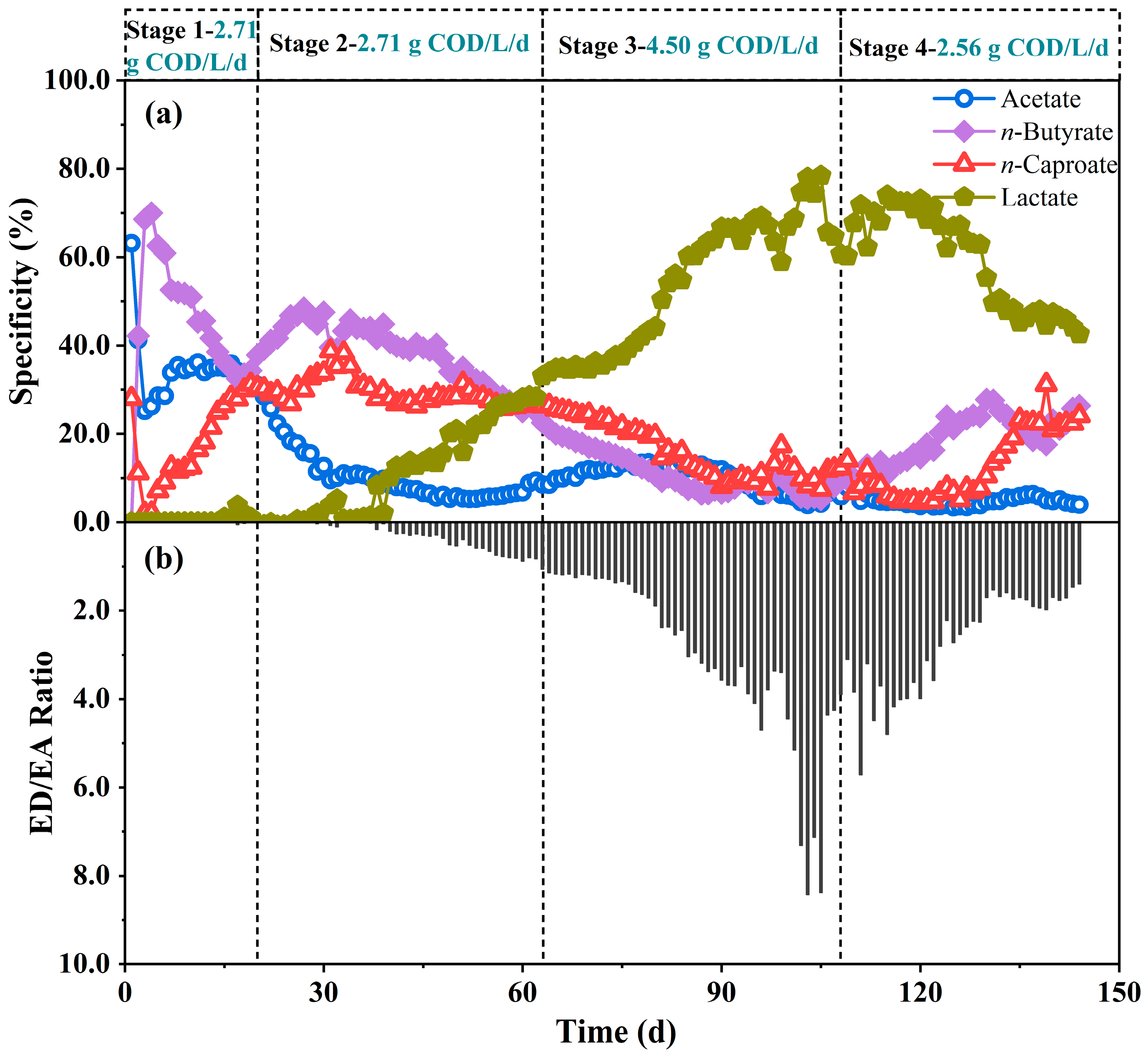
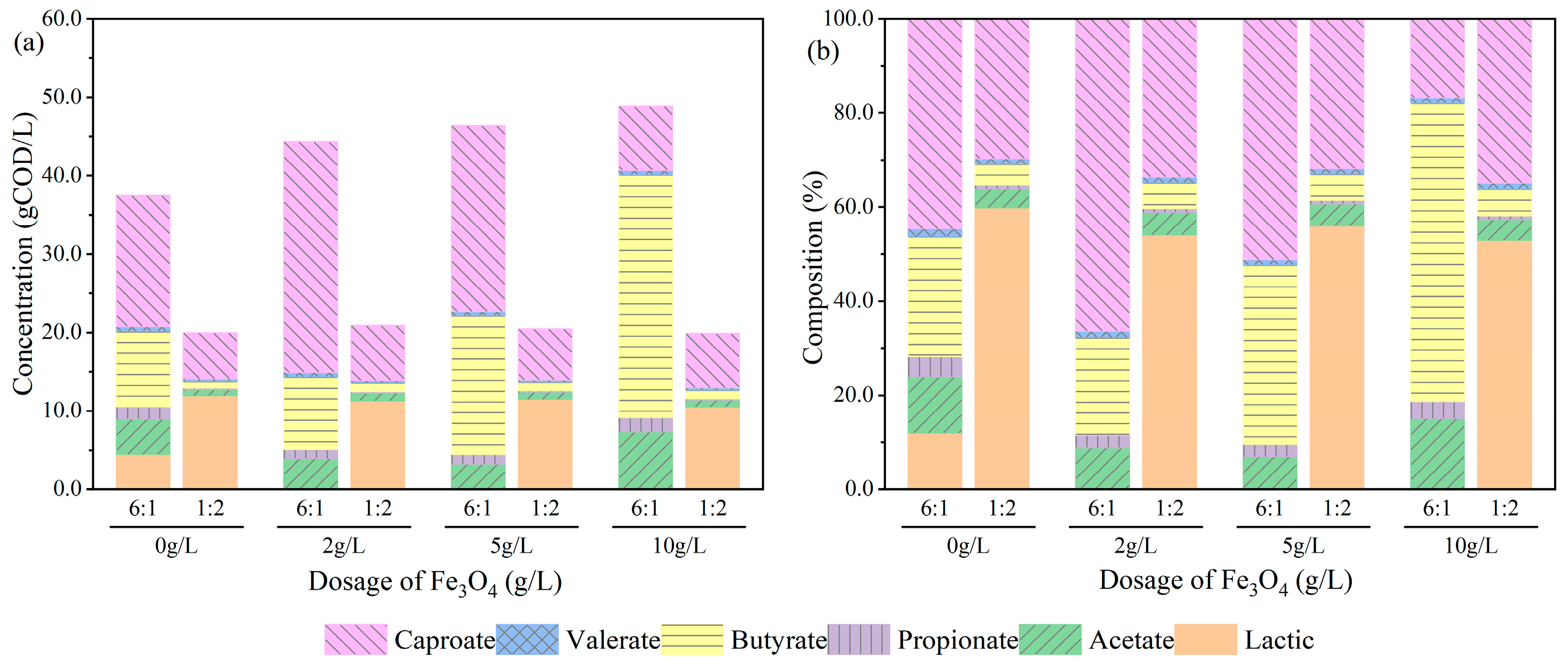
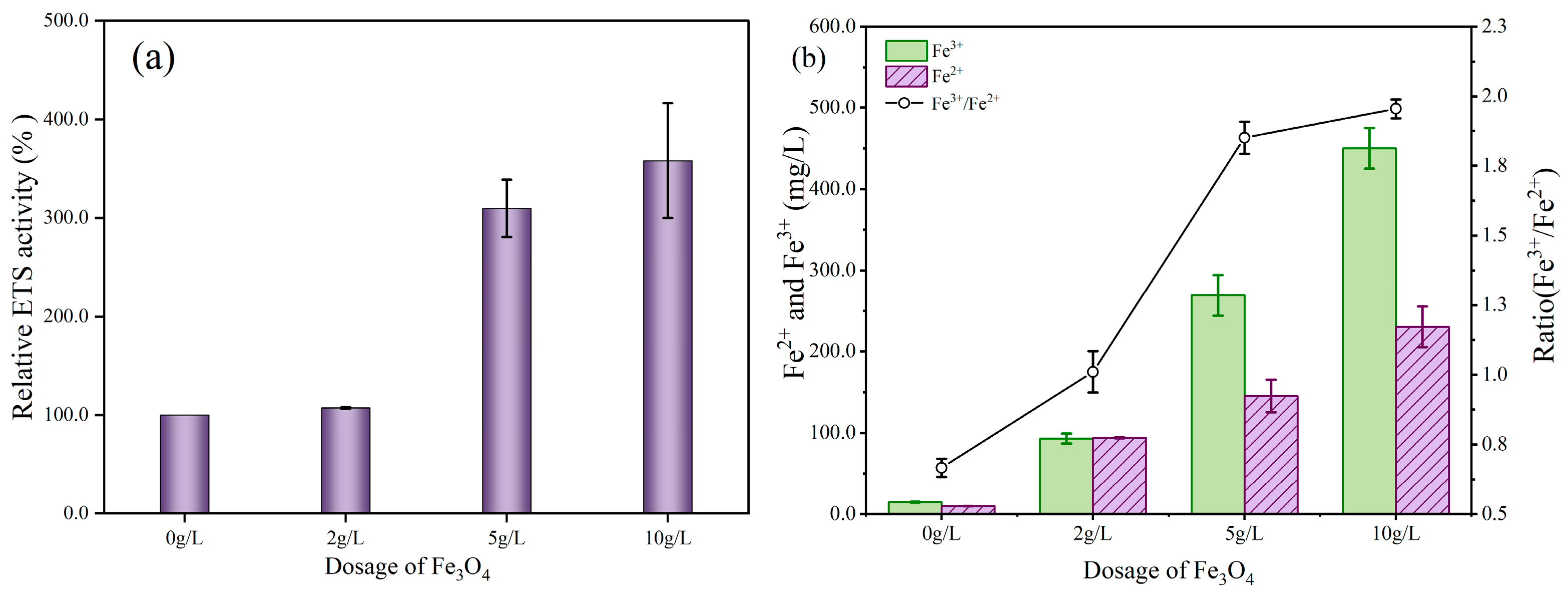


| Period (d) | OLR (g COD/L/d) |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 (0~20) | 2.71 |
| Stage 2 (21~63) | 2.71 |
| Stage 3 (64~108) | 4.50 |
| Stage 4 (109~144) | 2.56 |
| Fe3O4 Dosage (g/L) | Coverage (%) | Ace | Chao | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 99.97 | 85.52 | 83.27 | 1.57 | 0.33 |
| 2.0 | 99.97 | 92.34 | 92.6 | 1.74 | 0.32 |
| 5.0 | 99.96 | 101.47 | 101.00 | 1.63 | 0.32 |
| 10.0 | 99.96 | 113.05 | 97 | 1.54 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Ghasimi, D.S.M.; Zhang, X. Alleviation of Organic Load Inhibition and Enhancement of Caproate Biosynthesis via Fe3O4 Addition in Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste. Fermentation 2025, 11, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040160
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Wang P, Wu B, Li X, Liu H, Ghasimi DSM, Zhang X. Alleviation of Organic Load Inhibition and Enhancement of Caproate Biosynthesis via Fe3O4 Addition in Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040160
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yue, Yan Zhou, Pengyao Wang, Bo Wu, Xin Li, Hongbo Liu, Dara S. M. Ghasimi, and Xuedong Zhang. 2025. "Alleviation of Organic Load Inhibition and Enhancement of Caproate Biosynthesis via Fe3O4 Addition in Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040160
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, P., Wu, B., Li, X., Liu, H., Ghasimi, D. S. M., & Zhang, X. (2025). Alleviation of Organic Load Inhibition and Enhancement of Caproate Biosynthesis via Fe3O4 Addition in Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste. Fermentation, 11(4), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040160







