Application of Highly Digestible Fermented Corn Protein Powder in Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of Corn Protein Powder
2.1.2. Preparation of Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Quality Evaluation of Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed and Commercially Available Dog Feed
2.2.2. Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed Experiment
2.2.3. Determination of Ammoniacal Nitrogen Content in Feces
2.2.4. Determination of Apparent Digestibility of Grain Nutrients
2.2.5. Analysis of Fecal Spoilage Odor
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Nutritional Index Analysis of Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed and Commercially Available Dog Feed
3.2. Quality Evaluation of Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed and Commercially Available Dog Feed
3.2.1. Analysis of Texture Characteristics
3.2.2. Gc-Ms Analysis of Volatile Components in Dog Feed
3.2.3. Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed Feeding Experiment
3.2.4. Changes in Body Weight of Test Dogs before and after the Experiment
3.2.5. Analysis of Ammoniacal Nitrogen Content in Feces
3.2.6. Analysis of the Effect of Dog Feed on the Apparent Digestibility of Nutrients in Experimental Dogs
3.2.7. Analysis of Fecal Spoilage Odor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le, P.D.; Aarnink, A.J.; Ogink, N.W.; Becker, P.M.; Verstegen, M.W. Odour from animal production facilities: Its relationship to diet. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2005, 18, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Fanzo, J.; Miller, D.D.; Pingali, P.; Post, M.; Steiner, J.L.; Thalacker-Mercer, A.E. Production and supply of high-quality food protein for human consumption: Sustainability, challenges, and innovations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1321, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Aoll, J.; Niclass, Y.; Velazco, M.I.; Wu, L.; Pika, J.; Starkenmann, C. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile constituents from latrines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7876–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotz, C.A. Management to reduce nitrogen losses in animal production. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, E119–E137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kokocińska-Kusiak, A.; Woszczyło, M.; Zybala, M.; Maciocha, J.; Barłowska, K.; Dzięcioł, M. Canine olfaction: Physiology, behavior, and possibilities for practical applications. Animals 2021, 11, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widyaratne, G.; Drew, M. Effects of protein level and digestibility on the growth and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens1. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novriadi, R.; Herawati, V.E.; Prayitno, S.B.; Windarto, S.; Mertz, K.; Duy, H.N. Effect of fermented corn protein concentrate on growth performance, haemocyte counts, histological structure of hepatopancreas and intestinal condition of pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 2, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, D. Effect of organic acids on fermentation quality and microbiota of horseshoe residue and corn protein powder. AMB Express 2024, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Chang, J.; Yin, Q.; Lu, M.; Di, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, E.; Lu, F. Fermented soybean meal improves the growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and microbial flora in piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.; Julien, B.B.; Islam, S.M.; Francis, D.S. Fermentation in aquafeed processing: Achieving sustainability in feeds for global aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T31216-2014; Complete Pet Food—Dog Food. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ1222-2021; Solid Waste—Determination of Water Content and Dry Matter—Gravimetric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T24318-2009; Determination of Total Nitrogen Content in Animal Feeding Stuffs by Combustion According to the Dumas Principle and Calculation of the Crude Protein Content. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T6433-2006; Determinaiion of Crude Fat in Feeds. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- NY/T1459-2022; Determination of Acid Detergent Fiber (ADF) in Feeds. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB5009.92-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Calcium in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.87-2016; Food Safety National Standard—Determination of Phosphorus in Food. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Pan, N.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Xiao, M.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z. The effects of five different drying methods on the quality of semi-dried Takifugu obscurus fillets. LWT 2022, 161, 113340–113351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Wadhwa, S.S. Industry-Relevant Approaches for Minimising the Bitterness of Bioactive Compounds in Functional Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostryk, V.I. Procedure of Continuation of Boundary Conditions in the Problems of Elasticity Theory. J. Math. Sci. 2024, 5, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamka, R.M.; Harmon, D.L.; Schoenherr, W.D.; Khoo, C.; Gross, K.L.; Davidson, S.J.; Joshi, D.K. In vivo measurement of flatulence and nutrient digestibility in dogs fed poultry by-product meal, conventional soybean meal, and low-oligosaccharide low-phytate soybean meal. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martis, L.; Patel, M.; Giertych, J.A.; Mongoven, J.W.; Owen, W.F. Methods and Compositions for Detection of Microbial Contaminants in Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions. US7618392B2, 17 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.B.; Song, D.H. Pet dog disease pre-diagnosis system for caregiver with possibilistic C-means clustering and disease database. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 20, 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Urrego, M.I.G.; Pedreira, R.S.; Santos, K.D.M.; Ernandes, M.C.; Santos, J.P.F.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Eberlin, M.N.; Balieiro, J.C.D.C.; Pontieri, C.F.F.; Brunetto, M.A. Dietary protein sources and their effects on faecal odour and the composition of volatile organic compounds in faeces of French Bulldogs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Oh, D.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Son, T.G.; Jung, Y.S. Silymarin Prevents Restraint Stress-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Reducing Inflammatory Response. Molecules 2015, 21, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, L.P. Disorders of Calcium and Phosphorus Metabolism. In Avery’s Diseases of the Newborn; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1333–1350.e4. [Google Scholar]
- Canfield, M.S.; Wrenn, W.J. Tyrophagus putrescentiae mites grown in dog food cultures and the effect mould growth has on mite survival and reproduction. Vet. Dermatol. 2010, 21, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-M.; Han, M.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.-S.; Yuan, C.-Q.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Muren. Determination and Analysis of Main Physiological and Biochemical Indexes of White Cashmere Goats in Erdos Region. Anim. Husb. Feed. Sci. 2009, 30, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Katklarn, F.; Otu, A.; Kalitesi, S.; Yklabilirlii, R.; Kodu, Y. Effects of Different Additives on the Quality of Grass Silage and Rumen Degradability and Rumen Parameters of the Grass Silage in Rams. Kafkas Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Dergisi. 2009, 15, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, B.; Laflamme, D. Effect of diet on markers of intestinal health in dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2002, 72, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

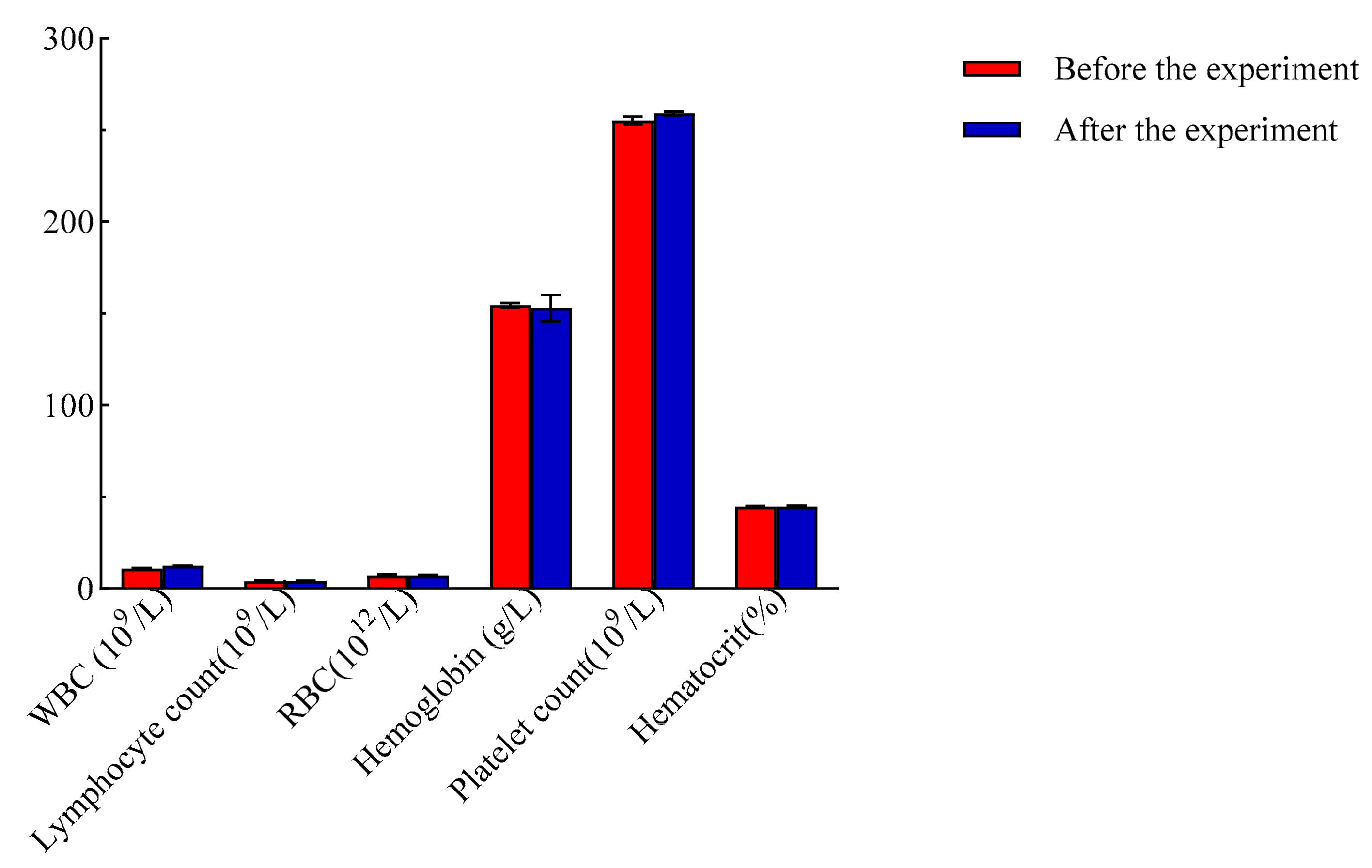

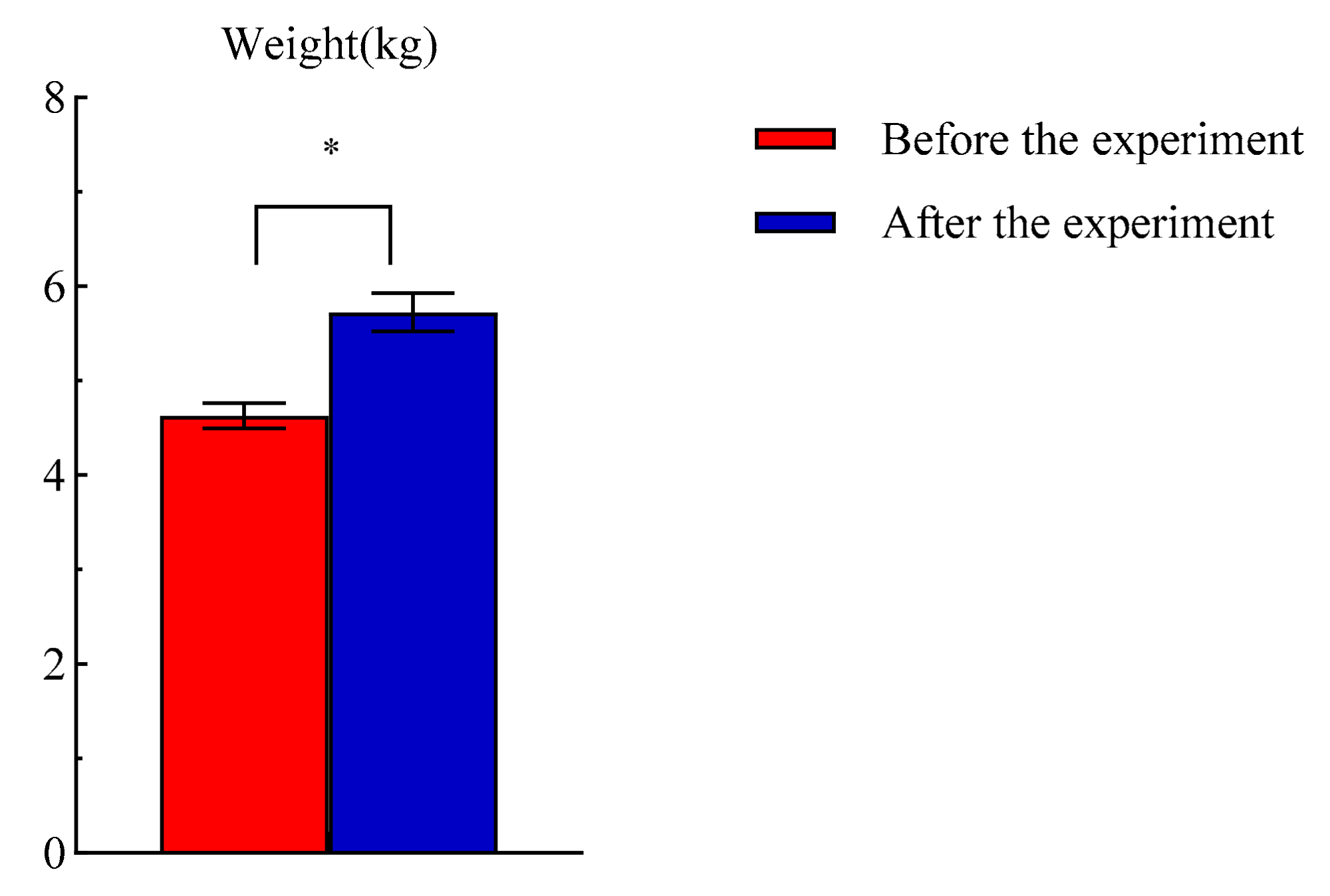
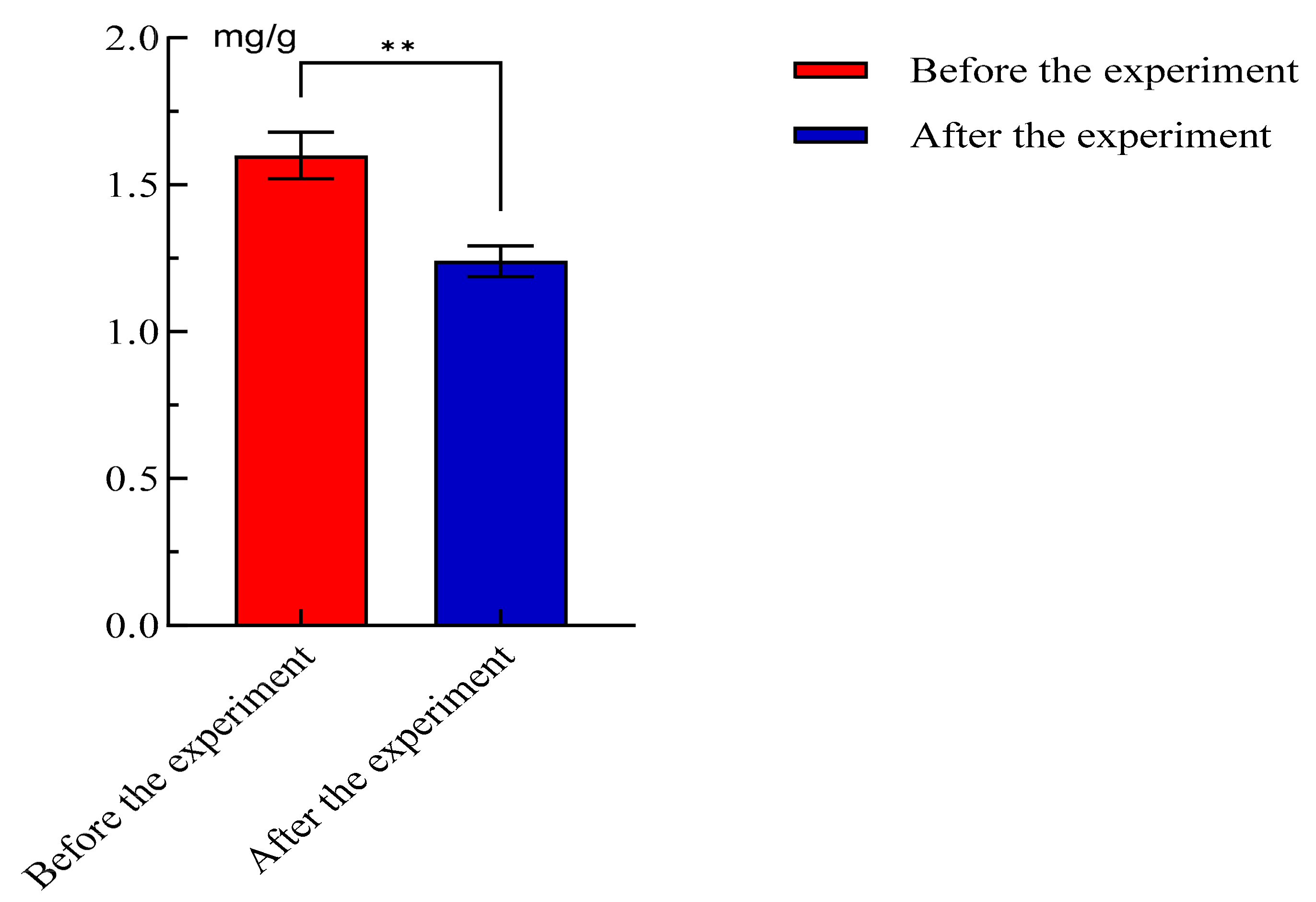
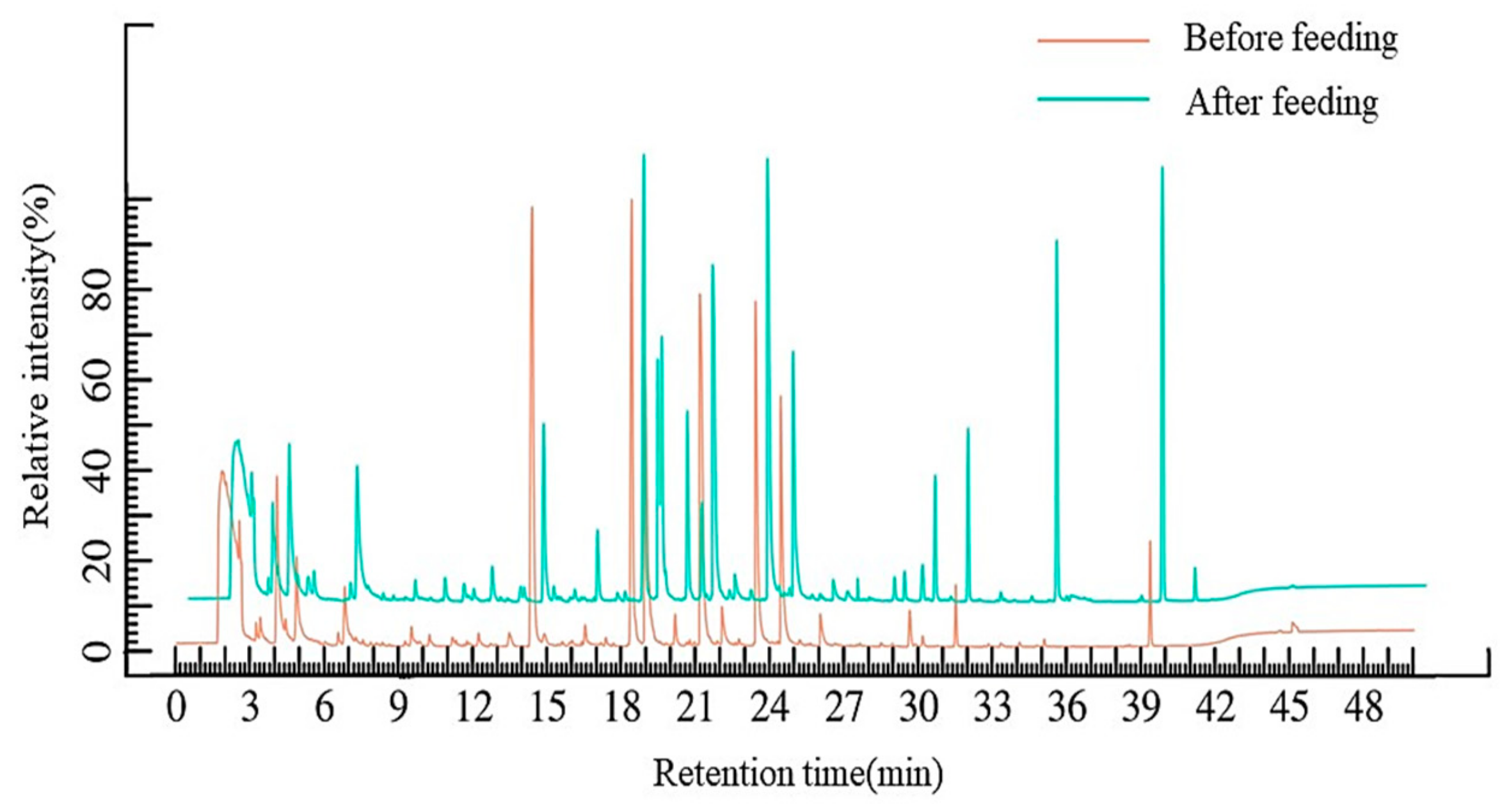
| Sample | Moisture (%) | Crude Protein (%) | Ash (%) | Crude Fat (%) | Starch (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal low-odor adult dog feed | 6.51 ± 0.14 | 46.27 ± 0.80 | 5.78 ± 0.07 | 10.56 ± 0.22 | 30.12 ± 0.32 |
| Commercially available dog feed | 6.77 ± 0.09 | 45.67 ± 0.29 | 5.66 ± 0.25 | 11.06 ± 0.49 | 30.66 ± 0.01 |
| Sample | Hardness (N) | Cohesion (Ratio) | Chewiness (mj) | Elasticity (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal low-odor adult dog feed | 45.40 ± 3.05 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 13.57 ± 0.60 | 2.73 ± 0.02 * |
| Commercially available dog feed | 43.66 ± 3.21 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 16.79 ± 0.08 * | 0.77 ± 0.03 |
| Category | Name of Volatile Components | Aroma | Absolute Peak Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially Available Dog Feed | Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed | |||
| Aldehyde | 3-Methylbutanal | Barbecue flavor, malt flavor | 107.24 | 431.55 |
| Hexanal | Avocado flavor | 636.7 | 440.87 | |
| Benzaldehyde | Almond flavor | 34.15 | 141.54 | |
| 2-Heptanenal | Oil flavor, green fragrance | 397.51 | 198.12 | |
| 1-Hexanol | Resin flavor, floral fragrance | 18.28 | 130.97 | |
| Alcohols | 1-Pentanol | Fruit aroma, tomato aroma | 51.02 | 134.69 |
| 2,3-Butanediol | Special fragrance | 0.00 | 51.20 | |
| 2,3-Hexanediol | Special fragrance | 0.00 | 62.51 | |
| Polypropylene glycol | Special fragrance | 91.81 | 12.89 | |
| Acids | Caproic acid | Sour | 636.75 | 440.87 |
| 4-Methylvaleric acid | Sour | 7.75 | 79.89 | |
| Propionic acid | Sour | 460.38 | 37.87 | |
| Ketones | 2 (5H)-furanone | – | 5.82 | 69.55 |
| 1-Hydroxy-2-acetone | – | 3.75 | 592.57 | |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone | – | 0.00 | 198.65 | |
| 2-Methyl-3-hydroxy-γ-pyranone | Malt flavor | 0.00 | 75.16 | |
| Alkanes | 3-Methylhexane | Alkane odor | 39.13 | 0.00 |
| 2-Methylpentane | Alkane odor | 630.69 | 0.00 | |
| 2,4-Dimethylheptane | Alkane odor | 371.58 | 0.00 | |
| 2,6-Dimethyldecane | Alkane odor | 0.00 | 39.11 | |
| Furfural | Sweet and roasted taste | 77.89 | 326.77 | |
| Other heterocycles | 2-Pentylfuran | Green bean flavor, butter flavor | 0.00 | 106.61 |
| 2,3-Dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-one | – | 0.90 | 43.10 | |
| Nutrient Apparent Digestibility (%) | Commercial Dog Feed | Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Matter | 80.01 ± 3.14 | 85.65 ± 1.55 |
| Crude Protein | 80.88 ± 4.38 | 89.01 ± 5.25 |
| Crude Fat | 70.47 ± 1.23 | 65.79 ± 2.31 |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber | 62.33 ± 2.51 | 62.41 ± 2.01 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber | 55.99 ± 0.18 | 50.26 ± 3.33 |
| Calcium | 40.93 ± 1.11 | 41.03 ± 2.30 |
| Phosphorus | 41.60 ± 0.58 | 41.26 ± 1.03 |
| Volatile Component | Odor Characteristics | Absolute Peak Area | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Feeding | After Feeding | ||
| Acetic acid | Spicy vinegar flavor | 48.62 | 24.51 |
| Caproic acid | Spicy vinegar flavor | 12.95 | 0.00 |
| Butyrate | Stimulating yogurt, buttery flavor | 0.78 | 0.31 |
| Valeric acid | Vinegar flavor | 54.62 | 58.55 |
| Heptanoic acid | Fatty and rancid taste | 92.03 | 152.19 |
| Cyclohexadiene | – | 118.36 | 103.95 |
| Octadecanoic acid | Vinegar flavor | 0.96 | 0.35 |
| Indole | Fecal odor | 245.03 | 100.75 |
| Isovaleraldehyde | Meat spoilage odor | 68.45 | 6.95 |
| 3-Methylbutanoic acid | Sour and foul-smelling foot sweat odor | 12.43 | 34.91 |
| 2-Ethyl hexanol | 2-Ethyl hexanol | 73.59 | 20.03 |
| Phenol | – | 20.48 | 18.30 |
| 4-Methylindole | Fecal odor | 126.34 | 123.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.; Ma, M.; Wang, W.; Ren, J. Application of Highly Digestible Fermented Corn Protein Powder in Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed. Fermentation 2024, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080390
Liu J, Liu L, Sun H, Ma M, Wang W, Ren J. Application of Highly Digestible Fermented Corn Protein Powder in Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed. Fermentation. 2024; 10(8):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ji, Ling Liu, Huaxin Sun, Minghui Ma, Wei Wang, and Jian Ren. 2024. "Application of Highly Digestible Fermented Corn Protein Powder in Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed" Fermentation 10, no. 8: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080390
APA StyleLiu, J., Liu, L., Sun, H., Ma, M., Wang, W., & Ren, J. (2024). Application of Highly Digestible Fermented Corn Protein Powder in Fecal Low-Odor Adult Dog Feed. Fermentation, 10(8), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080390





