Response of Anaerobic Granular Sludge Reactor to Plant Polyphenol Stress: Floc Disintegration and Microbial Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum and Substrates
2.2. Experimental Design and Operation
2.3. Conventional Analysis Methods
2.4. EPS Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Microbial Community and mcrA Gene Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
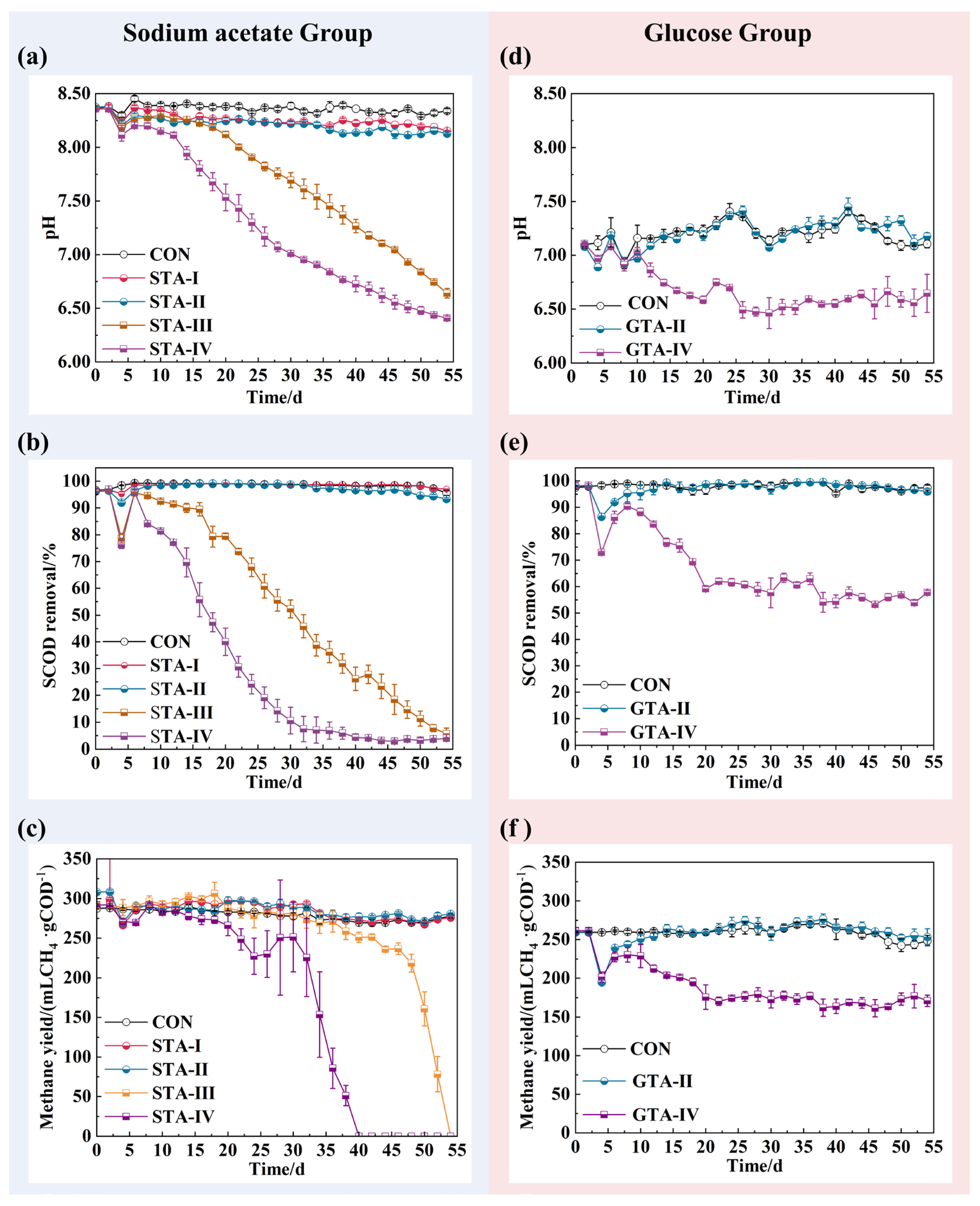
3.1. Performance of AnGS under Different TA Concentrations
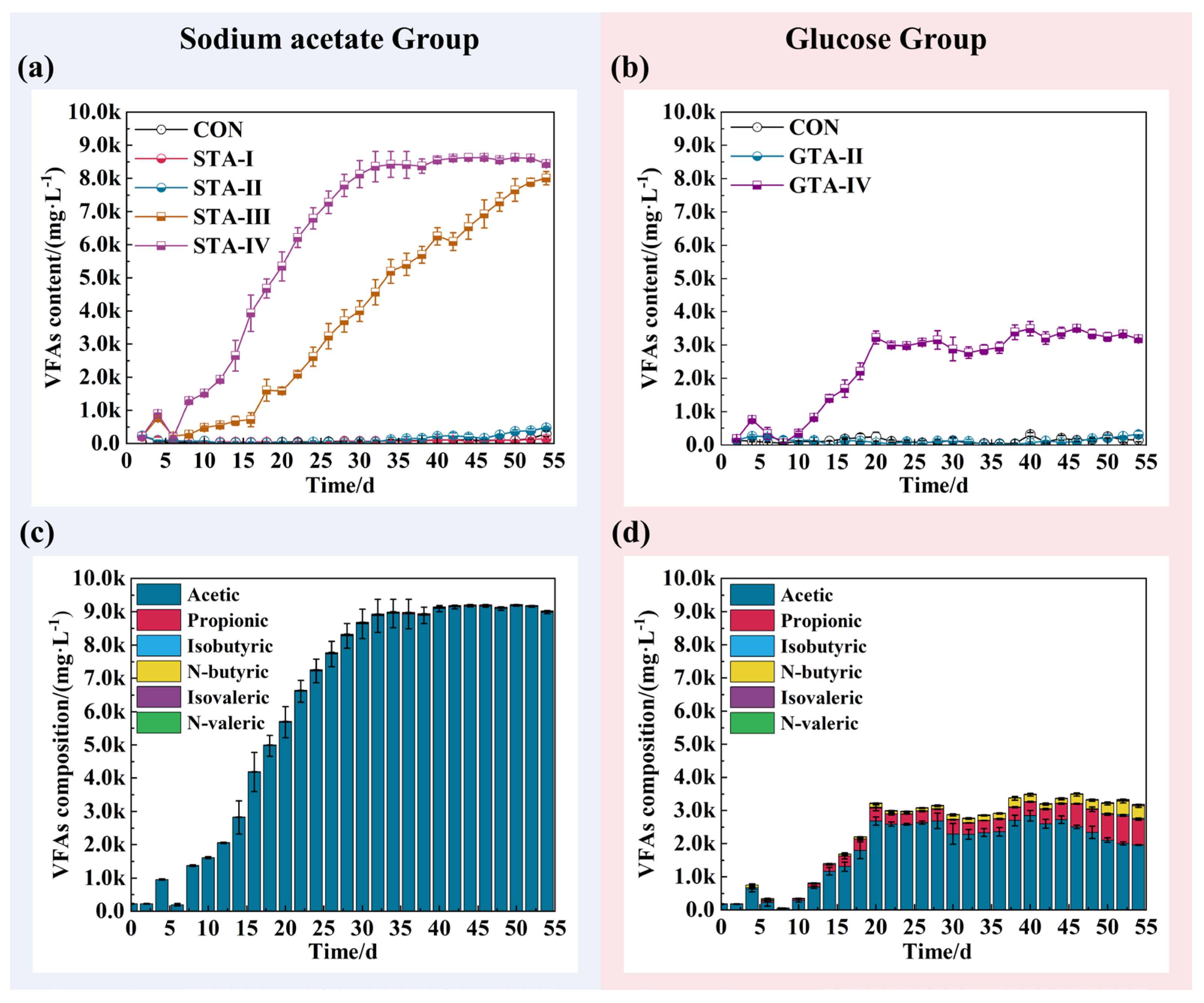
3.2. The Impact of TA on Effluent VFAs Concentration
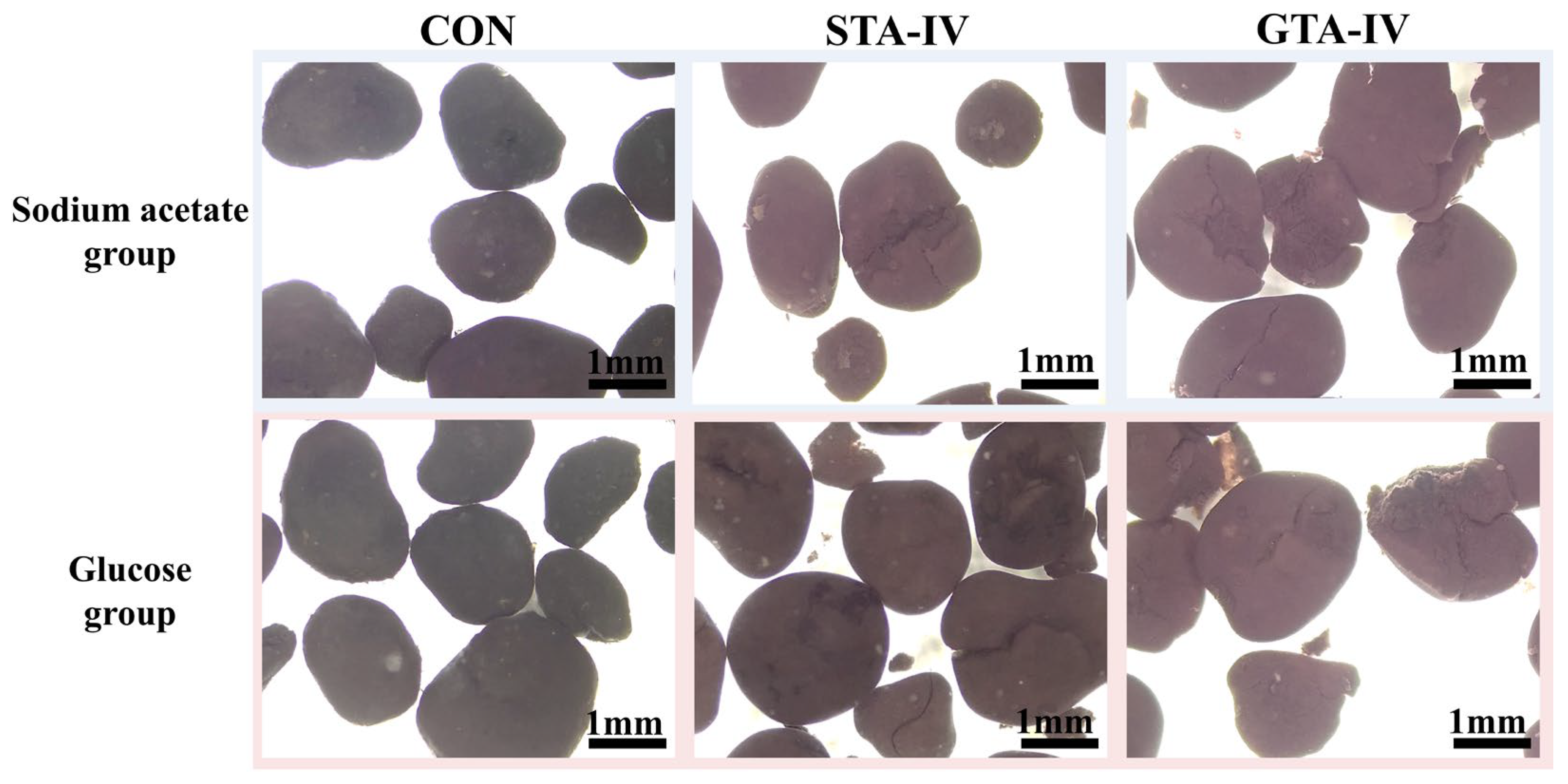
3.3. Deflocculation of AnGS by Toxicity of TA
3.4. Microbial Response to TA Stress
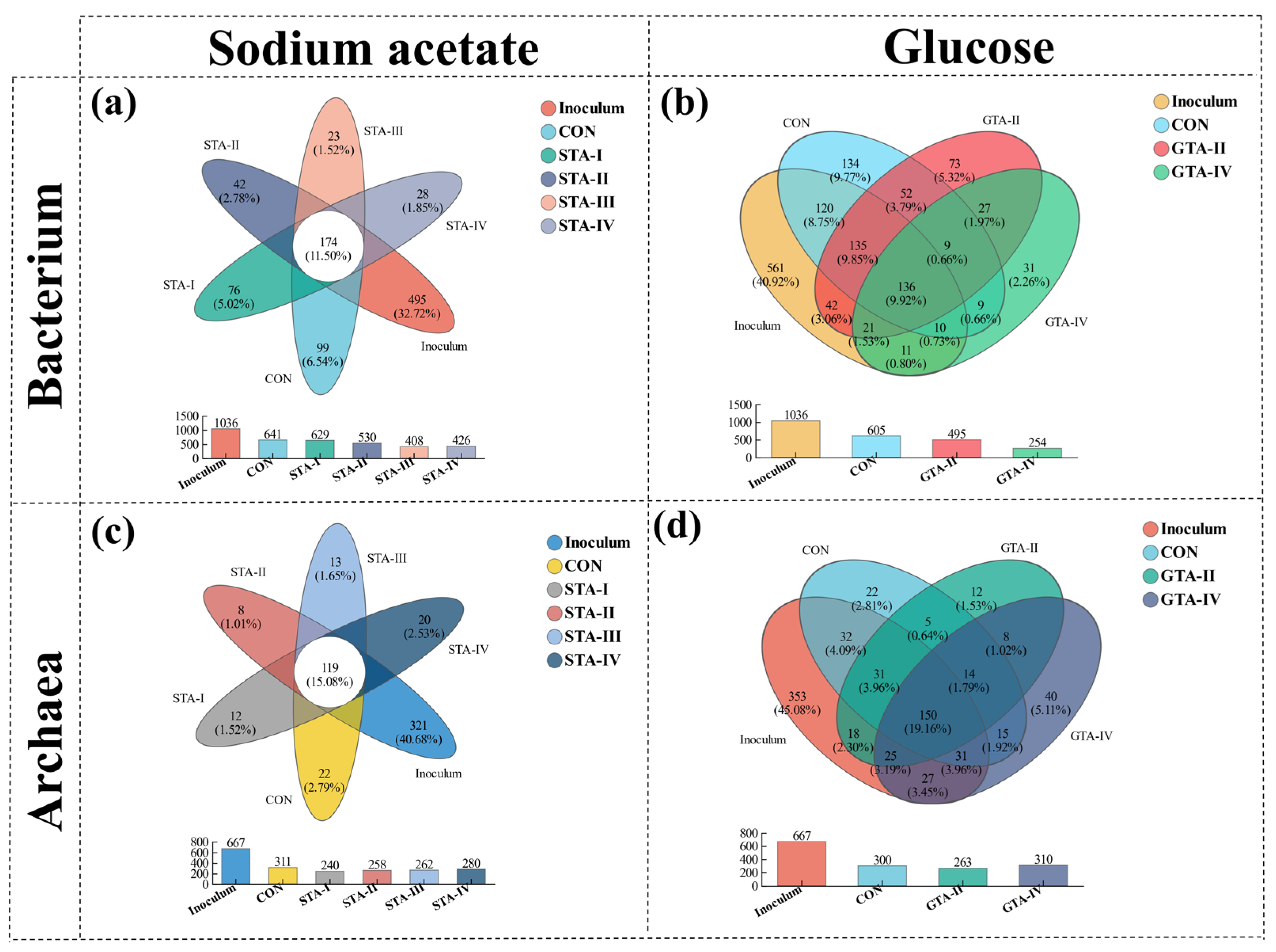
3.4.1. Microbial Diversity
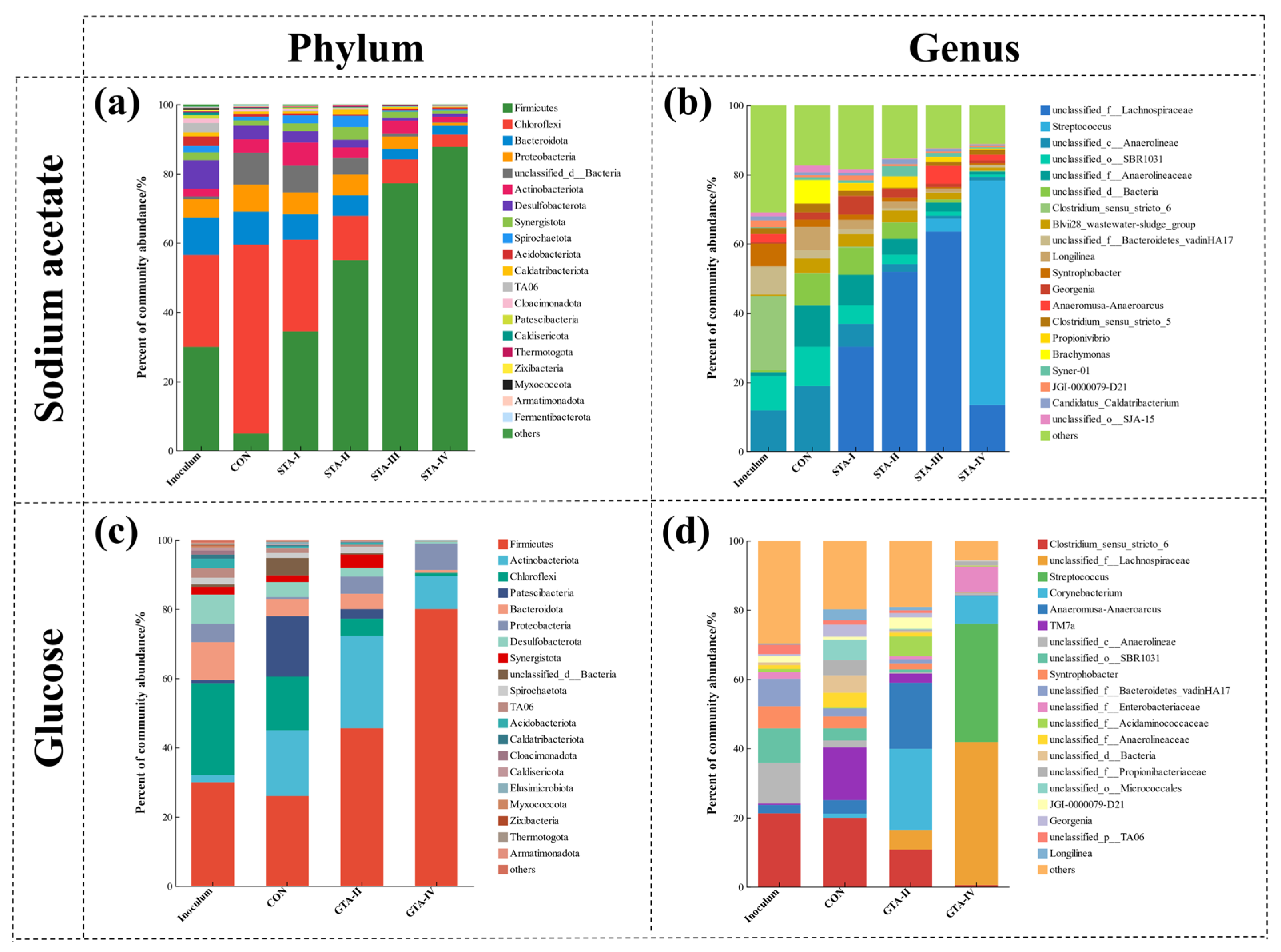
3.4.2. Bacterial Community
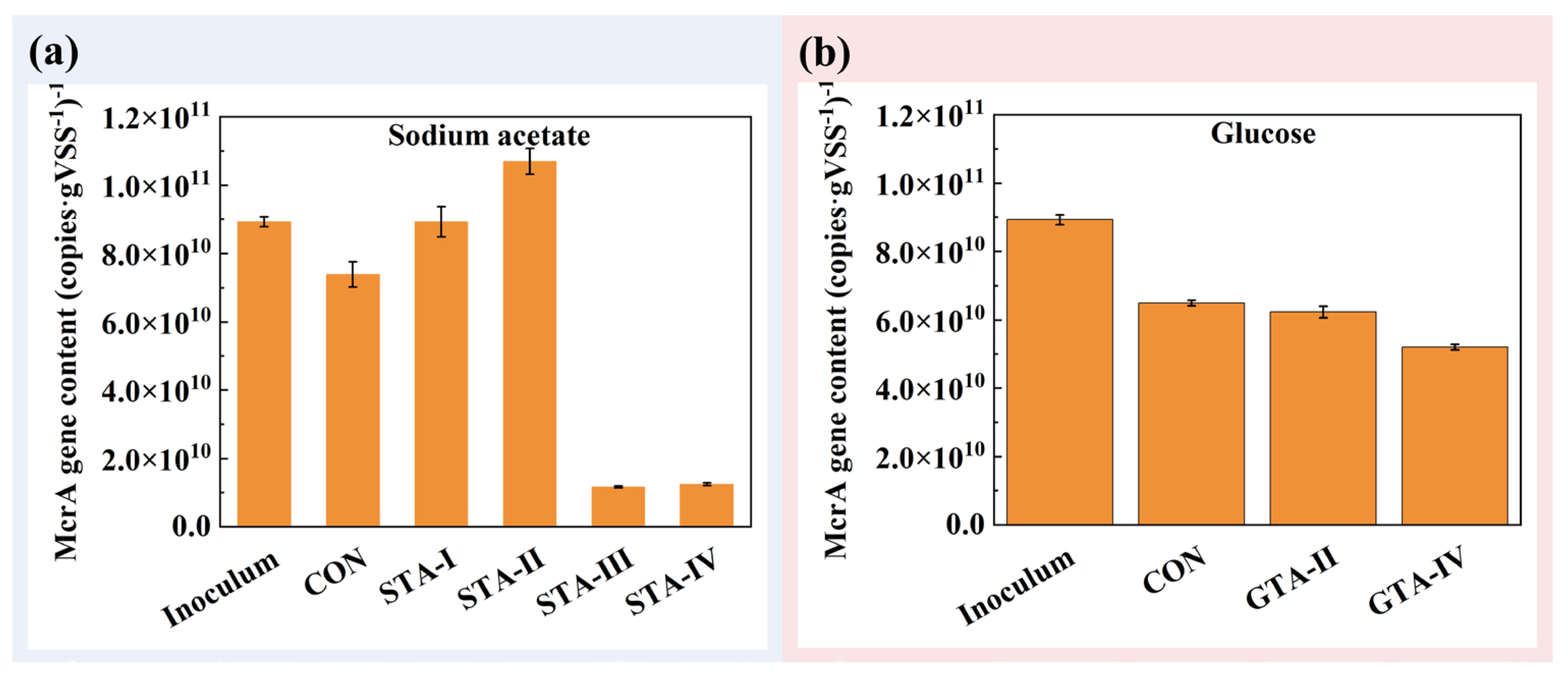
3.4.3. Archaeal Community
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, M.; Xue, J.; Qin, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y. Properties of polyphenols and polyphenol-containing wastewaters and their treatment by Fenton/Fenton-like reactions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Machado, M.; Madeira, L.M.; Nogales, B.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Treatment of cork boiling wastewater using chemical oxidation and biodegradation. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papuc, C.; Goran, G.V.; Predescu, C.N.; Nicorescu, V.; Stefan, G. Plant Polyphenols as Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agents for Shelf-Life Extension of Meat and Meat Products: Classification, Structures, Sources, and Action Mechanisms. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1243–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, N.R.; Brumaghim, J.L. A Review of the Antioxidant Mechanisms of Polyphenol Compounds Related to Iron Binding. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 53, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, V. Protein/Polyphenol Interactions: Past and Present Contributions. Mechanisms of Astringency Perception. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 724–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.F.P.; Silva, M.R.A.; Trovó, A.G. Influence of the iron source on the solar photo-Fenton degradation of different classes of organic compounds. Sol. Energy 2005, 79, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A.; Lettinga, G. The methanogenic toxicity and anaerobic degradability of a hydrolyzable tannin. Water Res. 1987, 21, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T. Tannins—Their occurrence and significance. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1957, 8, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Medina, E.; Vargas, J.; Brenes, M.; De Castro, A. In Vitro Activity of Olive Oil Polyphenols against Helicobacter pylori. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yao, K.; Sun, D.; Shi, B. Biodegradability of tannin-containing wastewater from leather industry. Biodegradation 2007, 18, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A.; Kortekaas, S.; Lettinga, G. The tannin theory of methanogenic toxicity. Biol. Wastes 1989, 29, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Yang, X.P.; Zhang, S.F. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Bayberry Tannin Extract on Anaerobic Fermentation. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 361–363, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Ngo, P.D.; Owens, V.L.; Yang, X.-P.; Mansoorabadi, S.O. The biosynthetic pathway of coenzyme F430 in methanogenic and methanotrophic archaea. Science 2016, 354, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaksmaa, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Ettwig, K.F.; Lüke, C. McrA primers for the detection and quantification of the anaerobic archaeal methanotroph ‘Candidatus Methanoperedens nitroreducens’. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynes, M.M.; Krukenberg, V.; Jay, Z.J.; Kohtz, A.J.; Gobrogge, C.A.; Spietz, R.L.; Hatzenpichler, R. Diversity and function of methyl-coenzyme M reductase-encoding archaea in Yellowstone hot springs revealed by metagenomics and mesocosm experiments. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.L.; Tale, V.P.; Mathai, P.P.; Zitomer, D.H.; Maki, J.S. mcrA Gene abundance correlates with hydrogenotrophic methane production rates in full-scale anaerobic waste treatment systems. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilen, B.M.; Jin, B.; Lant, P. The influence of key chemical constituents in activated sludge on surface and flocculating properties. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Tay, J.-H. The effects of extracellular polymeric substances on the formation and stability of biogranules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Han, F.; Su, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Gan, J.; Feng, B.; Wu, B. Using pig manure to promote fermentation of sugarcane molasses alcohol wastewater and its effects on microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Hua, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Enhanced methane production by semi-continuous mesophilic co-digestion of potato waste and cabbage waste: Performance and microbial characteristics analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 236, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.A.; Leyendeckers, M.J.H.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Lettinga, G.; Habets, L.H.A. The methanogenic toxicity of bark tannins and the anaerobic biodegradability of water soluble bark matter. Water Sci. Technol. 1988, 20, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wei, T.; Qing, S.; Han, F.; Tao, X. Application of Tea Polyphenols and Their Effects on Ultrafiltration Effluent Disinfection and Microbial Risk. Water 2021, 13, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowski, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th Edition. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 142, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modla, M. The Easy Guide to pH Measurement. Meas. Control. 2004, 37, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jirka, A.M.; Carter, M.J. Micro semi-automated analysis of surface and wastewaters for chemical oxygen demand. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesil, H.; Calli, B.; Tugtas, A.E. A hybrid dry-fermentation and membrane contactor system: Enhanced volatile fatty acid (VFA) production and recovery from organic solid wastes. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, M.; Peluso, J.V. Determination of Tannins by Photocolorimeter. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 1941, 24, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lv, N.; Li, C.; Ning, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, G. Impact of nano zero valent iron on tetracycline degradation and microbial community succession during anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.E.T.; Pai, T.Y.; Chiang, C.F.; Chao, K.P.; Liu, M.H.; Chuang, S.H.; Banks, C.J.; Wang, S.C.; et al. Modeling biogas production from organic fraction of MSW co-digested with MSWI ashes in anaerobic bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6329–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.H.P. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudy, A.F. Colorimetric Determination of Protein and Carbohydrate. Ind. Water Wastes 1962, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Blatner, N.R.; Wang, S.; Saadalla, A.; Trudeau, E.; Roers, A.; Weaver, C.T.; Lee, J.J.; Gilbert, J.A.; et al. Adenomatous polyps are driven by microbe-instigated focal inflammation and are controlled by IL-10-producing T cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5905–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-L.; Zhang, X.-M.; Deng, F.-D.; Han, X.-G.; Xiao, C.-W.; Han, S.-J.; Wang, Z.-P. Microbial methane production is affected by secondary metabolites in the heartwood of living trees in upland forests. Trees 2020, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dareioti, M.A.; Vavouraki, A.I.; Kornaros, M. Effect of pH on the anaerobic acidogenesis of agroindustrial wastewaters for maximization of bio-hydrogen production: A lab-scale evaluation using batch tests. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; Shi, G.; Arhin, S.G.; Papadakis, V.G.; Goula, M.A.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, W. Methane production from acetate, formate and H2/CO2 under high ammonia level: Modified ADM1 simulation and microbial characterization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, E.; Silva, M.S.; García-Estévez, I.; Williams, P.; Mateus, N.; Doco, T.; de Freitas, V.; Soares, S. The role of wine polysaccharides on salivary protein-tannin interaction: A molecular approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, V.; Block, J.C.; Manem, J. Bioflocculation in activated sludge: An analytic approach. Water Res. 1993, 27, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.I.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Fernandes, I.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Mechanistic approach by which polysaccharides inhibit α-amylase/procyanidin aggregation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4352–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Ni, B.-J.; Makinia, J.; Harmand, J.; Alliet, M.; Brepols, C.; Ruano, M.V.; Robles, A.; Heran, M.; Gulhan, H.; et al. Biological processes modelling for MBR systems: A review of the state-of-the-art focusing on SMP and EPS. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, S.; Aleem, M.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, F.; Xue, Z.; Luo, J. Phosphorus recovery as vivianite from waste activated sludge via optimizing iron source and pH value during anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.-H.; Li, B.; Li, X.-Y. An integrated membrane bioreactor system with iron-dosing and side-stream co-fermentation for enhanced nutrient removal and recovery: System performance and microbial community analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, R.-Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.-L.; Fu, Y.-Y.; Yu, H.-Q. Carbon source shaped microbial ecology, metabolism and performance in denitrification systems. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xia, K.; Yang, X.; Tang, C. Growth strategy of microbes on mixed carbon sources. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.; Pan, F.; Ge, H.; Yang, Q.; Duan, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Fermented egg-milk beverage alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through the modulation of intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acids. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.M.; Shaw, N.A.; Nagashima, S.; Venkiteswaran, J.J.; Schiff, S.L.; Watanabe, T.; Fukui, M.; Hanada, S.; Tank, M.; Neufeld, J.D. Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre. Nature 2024, 627, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, G. Simultaneous denitrification and antibiotic degradation of low-C/N-ratio wastewater by a three-dimensional biofilm-electrode reactor: Performance and microbial response. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gong, B.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. Bacterial community structure in simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and organic matter removal process treating saline mustard tuber wastewater as revealed by 16S rRNA sequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Huang, X.; Dai, X. Differential variations of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes between treatment units in centralized sewage sludge treatment plants. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, A.S.; Stewart, L.C.; Blanchard, J.L.; Leschine, S.B. Untangling the Genetic Basis of Fibrolytic Specialization by Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae in Diverse Gut Communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Miyanaga, K.; Toyama, K.; Uy, D.; Tanji, Y. Changes in composition and microbial communities in excess sludge after heat-alkaline treatment and acclimation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Tursun, H.; Hou, X.; Odey, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, T. Microbial community dynamics in a pilot-scale MFC-AA/O system treating domestic sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, K.C.; Leigh, J.A. Metabolic versatility in methanogens. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 29, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R. Microbial Ecology of Methanogens and Methanotrophs. In Advances in Agronomy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 96, pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]



| Index | Sodium Acetate Group | Glucose Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | S-CON | STA-I | STA-II | STA-III | STA-IV | G-CON | GTA-II | GTA-IV | |
| HRT a | h | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| TA b | mg·L−1 | 0 | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 0 | 1000 | 2000 |
| Substrate COD c | mgCOD·L−1 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 |
| NaHCO3 | mg·L−1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 6400 | 6400 | 6400 |
| Number | Reaction | Process |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | → | Acidification |
| (2) | Methanogenesis | |
| (3) | → + | |
| (4) |
| Index Type | Inoculum | Sodium Acetate | Glucose | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | STA-I | STA-II | STA-III | STA-IV | CON | GTA-II | GTA-IV | ||
| Coverage | 0.995 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| Chao 1 | 1178.665 | 708.890 | 693.746 | 596.611 | 588.622 | 555.362 | 678.079 | 573.907 | 320.279 |
| Pielou | 0.577 | 0.588 | 0.545 | 0.437 | 0.440 | 0.314 | 0.586 | 0.518 | 0.355 |
| Shannon | 4.005 | 3.797 | 3.515 | 2.743 | 2.644 | 1.901 | 3.755 | 3.214 | 1.967 |
| Index Type | Inoculum | Sodium Acetate | Glucose | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | STA-I | STA-II | STA-III | STA-IV | CON | GTA-II | GTA-IV | ||
| Coverage | 0.993 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| Chao 1 | 937.234 | 433.526 | 312.857 | 328.222 | 357.067 | 346.978 | 372.226 | 320.130 | 376.500 |
| Pielou | 0.299 | 0.284 | 0.192 | 0.223 | 0.276 | 0.301 | 0.325 | 0.330 | 0.347 |
| Shannon | 1.946 | 1.630 | 1.052 | 1.237 | 1.535 | 1.694 | 1.856 | 1.839 | 1.993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, S.; Lian, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Response of Anaerobic Granular Sludge Reactor to Plant Polyphenol Stress: Floc Disintegration and Microbial Inhibition. Fermentation 2024, 10, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10050262
Bi S, Lian H, Zhang H, Liu Z, Chen Y, Zhang J. Response of Anaerobic Granular Sludge Reactor to Plant Polyphenol Stress: Floc Disintegration and Microbial Inhibition. Fermentation. 2024; 10(5):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10050262
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Shilin, Hua Lian, Huiya Zhang, Zexiang Liu, Yong Chen, and Jian Zhang. 2024. "Response of Anaerobic Granular Sludge Reactor to Plant Polyphenol Stress: Floc Disintegration and Microbial Inhibition" Fermentation 10, no. 5: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10050262
APA StyleBi, S., Lian, H., Zhang, H., Liu, Z., Chen, Y., & Zhang, J. (2024). Response of Anaerobic Granular Sludge Reactor to Plant Polyphenol Stress: Floc Disintegration and Microbial Inhibition. Fermentation, 10(5), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10050262






