Effect of Total Mixed Ration on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestion, and Rumen Microbiome in Angus Beef Cattle during the Growing and Fattening Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Feeding Management
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample and Data Collection
2.4. Serum Indices Measure
2.5. Apparent Digestibility of Nutrients
2.6. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.7. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Production Performance and Serum Biochemical Indicators in Angus Beef Cattle Undergo Significant Changes during the Growth and Fattening Periods
3.2. Rumen Fermentation Parameters
3.3. Nutrient Digestibility
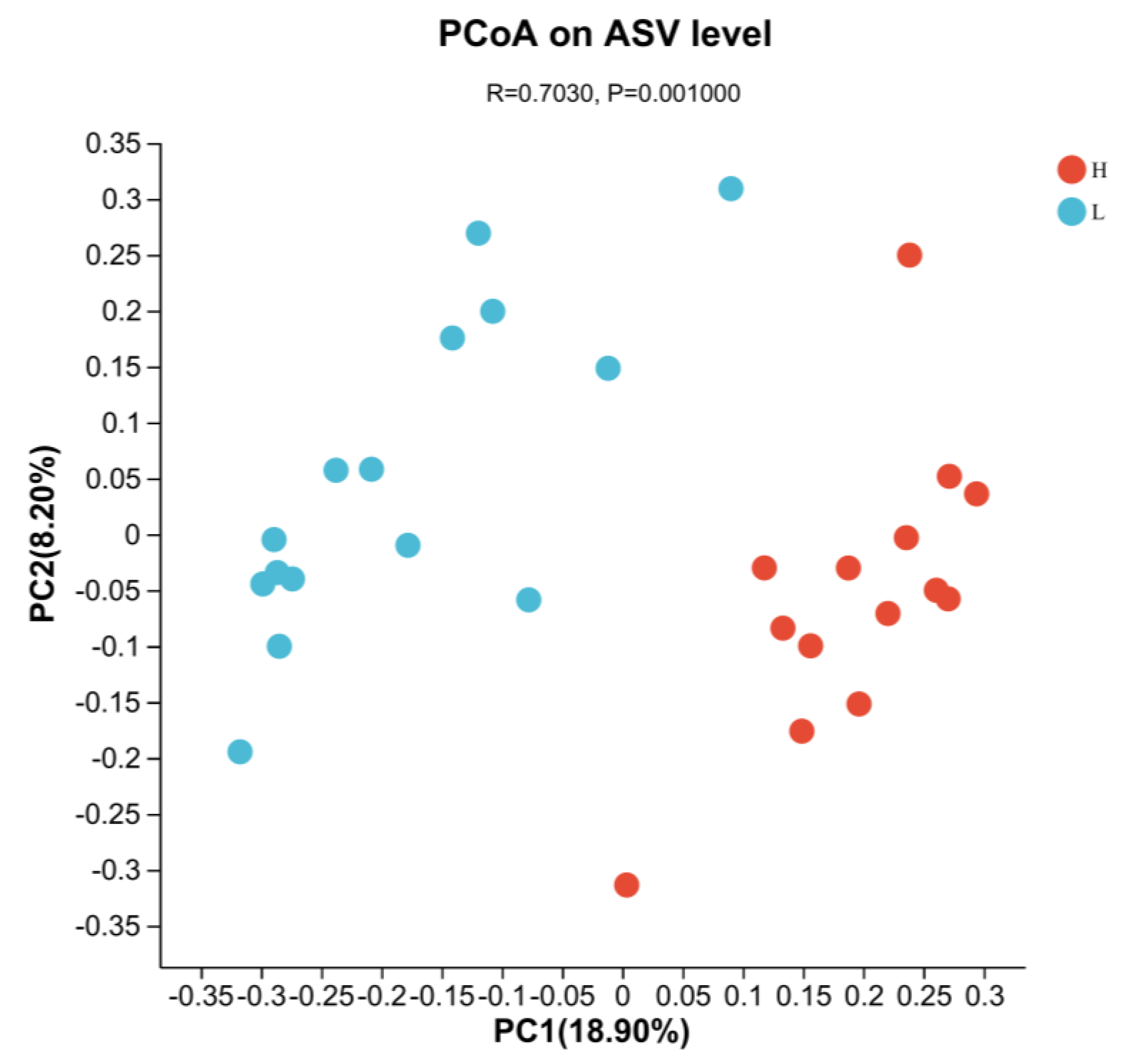
3.4. Indicators of Rumen Microbiota
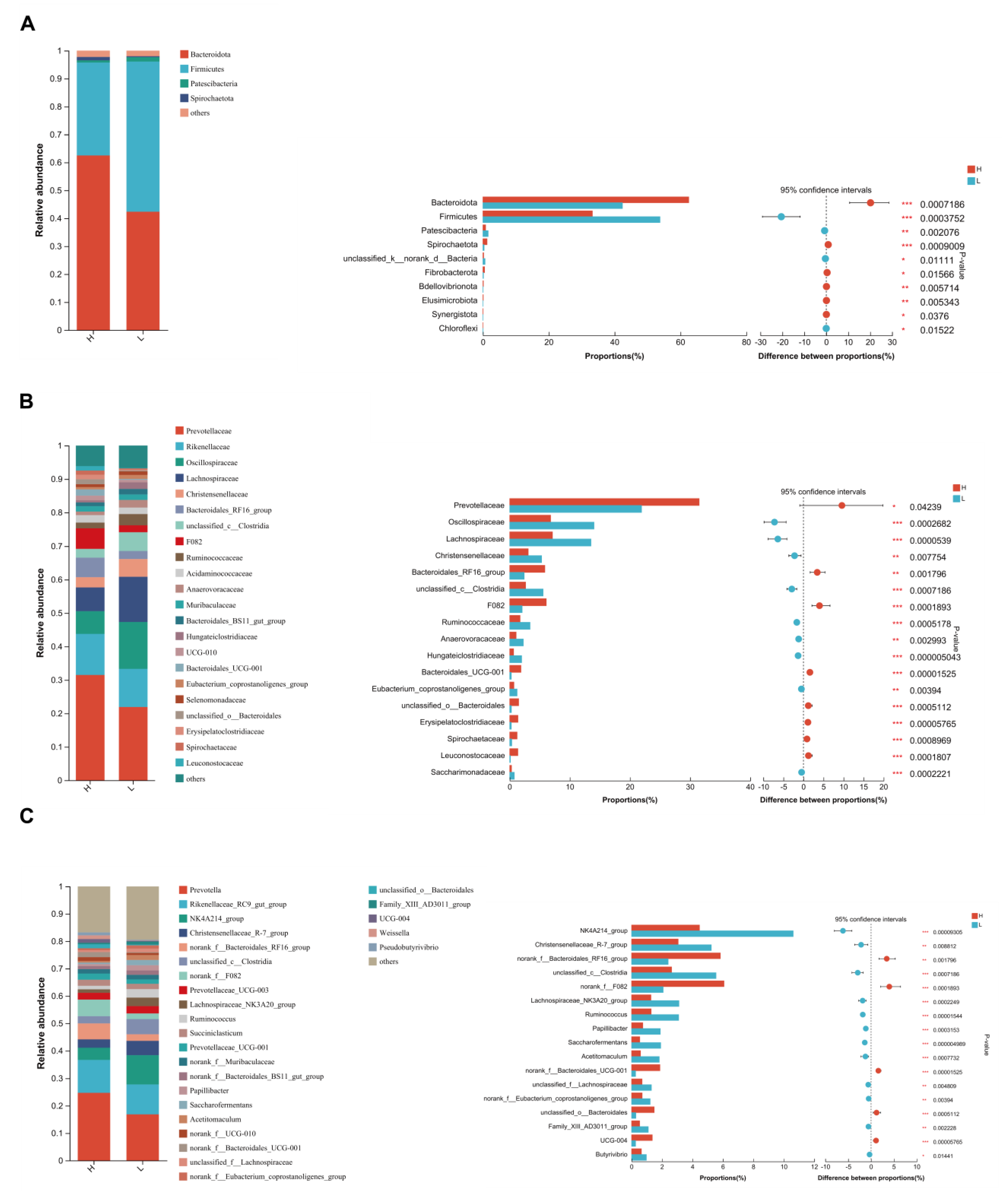
3.5. Significant Alterations of Bacterial Taxonomic Composition in Growing and Fattening Period
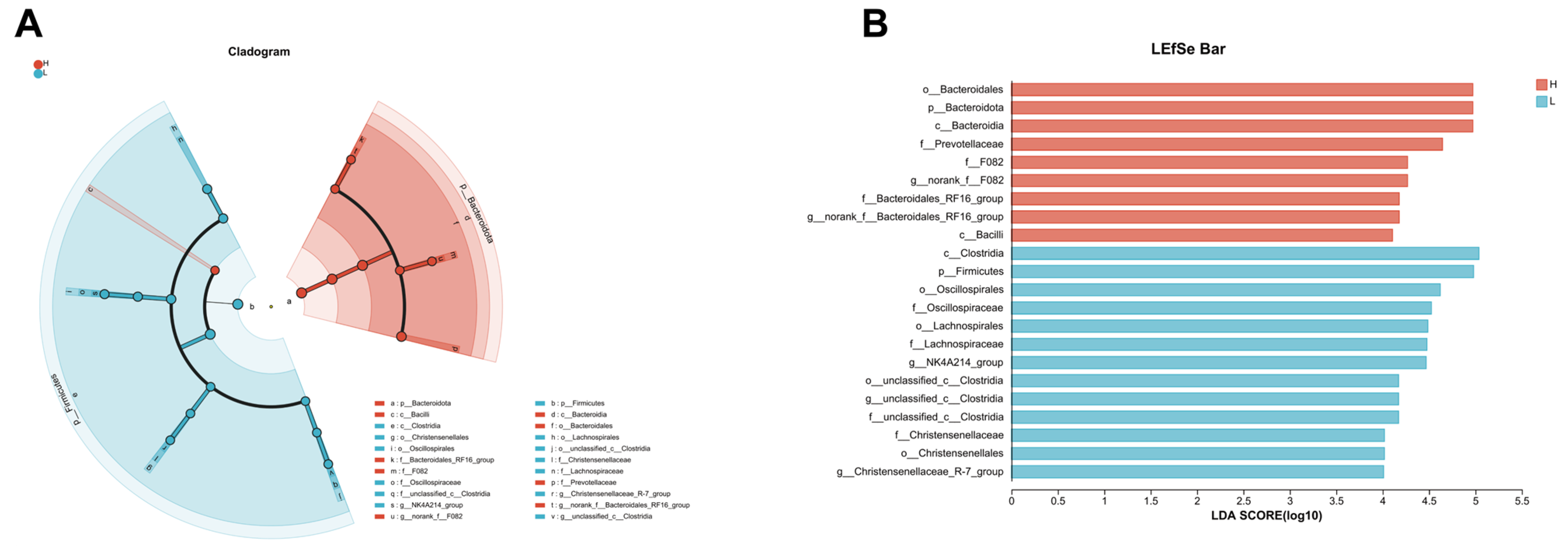
3.6. LEfSe Analysis Reveals Distinct Microbial Profiles between Growing and Fattening Period from Phylum to Genera Level
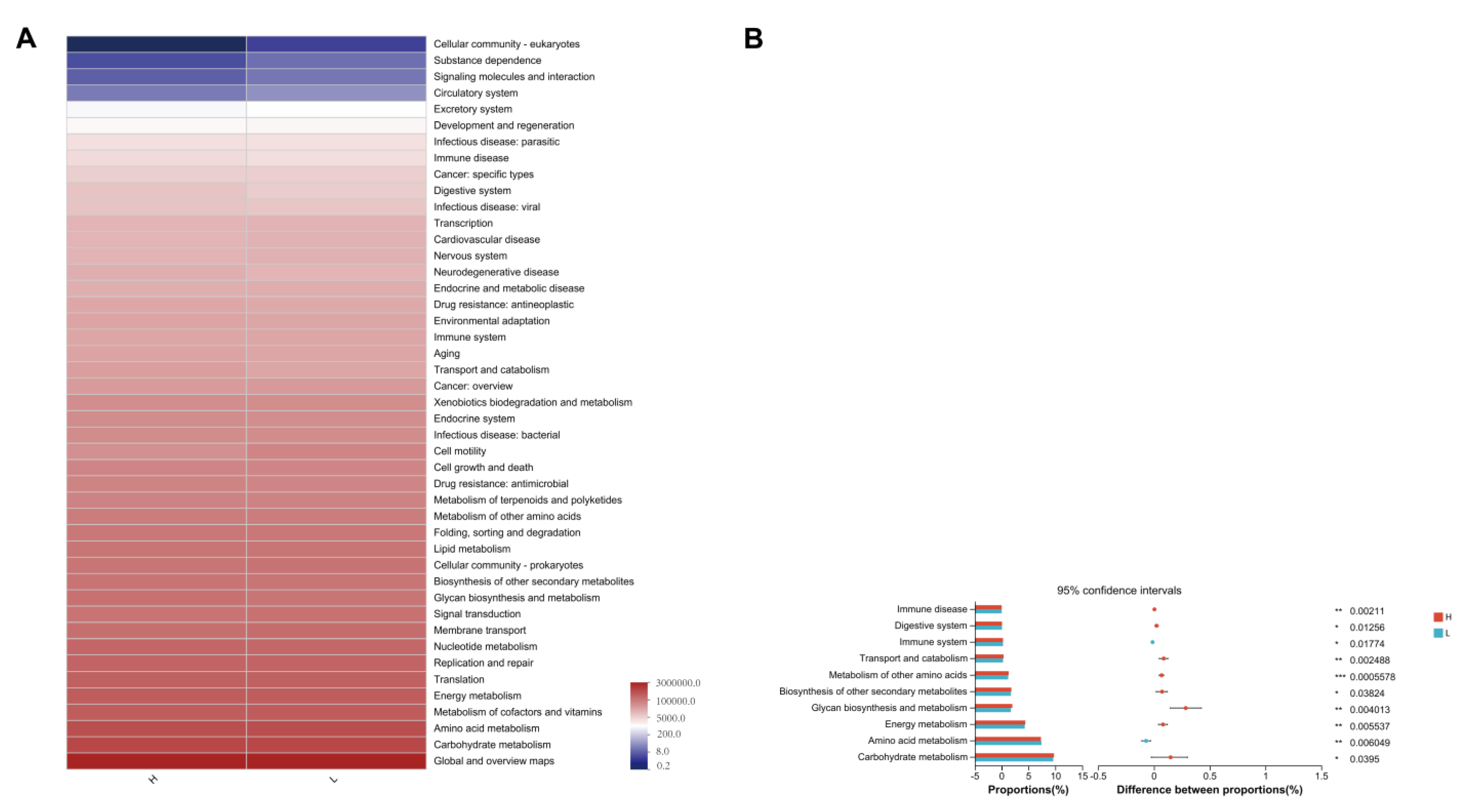
3.7. 16S rRNA Functional Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.E.; Li, J. Probe-Based Association Analysis Identifies Several Deletions Associated with Average Daily Gain in Beef Cattle. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krusinski, L.; Maciel, I.C.; Sergin, S.; Goeden, T.; Schweihofer, J.P.; Singh, S.; Rowntree, J.E.; Fenton, J.I. Fatty Acid and Micronutrient Profile of Longissimus Lumborum from Red Angus and Red Angus x Akaushi Cattle Finished on Grass or Grain. Foods 2022, 11, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morittu, V.M.; Spina, A.A.; Iommelli, P.; Poerio, A.; Oliverio, F.V.; Britti, D.; Tudisco, R. Effect of Integration of Linseed and Vitamin E in Charolaise\times Podolica Bulls’ Diet on Fatty Acids Profile, Beef Color and Lipid Stability. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossland, W.L.; Jobe, J.T.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Sawyer, J.E.; Callaway, T.R.; Tedeschi, L.O. Evaluation of Active Dried Yeast in the Diets of Feedlot Steers—I: Effects on Feeding Performance Traits, the Composition of Growth, and Carcass Characteristics. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Penner, G.B.; Li, M.; Oba, M.; Guan, L.L. Changes in Bacterial Diversity Associated with Epithelial Tissue in the Beef Cow Rumen during the Transition to a High-Grain Diet. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5770–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bian, G.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. High-Grain Feeding Causes Strong Shifts in Ruminal Epithelial Bacterial Community and Expression of Toll-like Receptor Genes in Goats. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, F.N.; Secrist, D.S.; Hill, W.J.; Gill, D.R. Acidosis in Cattle: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevans, D.W.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.; McKinnon, J.J.; McAllister, T.A. Effect of Rapid or Gradual Grain Adaptation on Subacute Acidosis and Feed Intake by Feedlot Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1116–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, T.G.; Lechtenberg, K.F. Acidosis in Feedlot Cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2007, 23, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, T.G.; Titgemeyer, E.C. Ruminal Acidosis in Beef Cattle: The Current Microbiological and Nutritional Outlook. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, E17–E38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsterhjelm, C.; Simola, O.; Keeling, L.; Valros, A.; Heinonen, M. Health Parameters in Tail Biters and Bitten Pigs in a Case–Control Study. Animal 2013, 7, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, J.M.; De Sousa, D.O.; De Mesquita, B.S.; Mesquita, L.G.; Silva, L.F.P. Effect of Sugarcane Fiber Digestibility, Conservation Method and Concentrate Level on the Ruminal Ecosystem of Beef Cattle. AMB Expr. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phesatcha, K.; Phesatcha, B.; Wanapat, M.; Cherdthong, A. The Effect of Yeast and Roughage Concentrate Ratio on Ruminal pH and Protozoal Population in Thai Native Beef Cattle. Animals 2021, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrell, C.L.; Jenkins, T.G. Body Composition and Energy Utilization by Steers of Diverse Genotypes Fed a High-Concentrate Diet during the Finishing Period: I. Angus, Belgian Blue, Hereford, and Piedmontese Sires. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, H.H.; Smuts, M.; Coertze, R.J. Characteristics and Efficiency of Fast-Growing Feedlot Steers Fed Different Dietary Energy Concentrations. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalapiedra-Hijar, G.; Abo-Ismail, M.; Carstens, G.E.; Guan, L.L.; Hegarty, R.; Kenny, D.A.; McGee, M.; Plastow, G.; Relling, A.; Ortigues-Marty, I. Biological Determinants of Between-Animal Variation in Feed Efficiency of Growing Beef Cattle. Animal 2018, 12, s321–s335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.P.; Crowley, J.J. Cell Biology Symposium: Genetics of Feed Efficiency in Dairy and Beef Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1594–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Qin, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Hao, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y. Serum Biochemical Parameters, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Bacterial Communities Are Partly Driven by the Breed and Sex of Cattle When Fed High-Grain Diet. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunun, N.; Sanjun, I.; Kaewpila, C.; Foiklang, S.; Cherdthong, A.; Wanapat, M.; Polyorach, S.; Khota, W.; Kimprasit, T.; Kesorn, P. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Hydrolyzed Yeast on Growth Performance, Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Hematology in Growing Beef Cattle. Animals 2022, 12, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Z. Small Intestine Microbiome and Metabolome of High and Low Residual Feed Intake Angus Heifers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 862151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences. Medicine Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle; National Academies of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottyn, B.G.; Boucque, C.V. Rapid Method for the Gas-Chromatographic Determination of Volatile Fatty Acids in Rumen Fluid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1968, 16, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtmann, H.; Pfirter, H.P.; Prabucki, A.L. A New Method of Determining Metabolisability of Energy and Digestibility of Fatty Acids in Broiler Diets. Br. Poult. Sci. 1975, 16, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Wu, B.; Ma, J.; Cui, X.; Deng, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; A, R.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Effects of Dietary Capsaicin and Yucca Schidigera Extracts as Feed Additives on Rumen Fermentation and Microflora of Beef Cattle Fed with a Moderate-Energy Diet. Fermentation 2022, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firkins, J.L. Effects of Feeding Nonforage Fiber Sources on Site of Fiber Digestion. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, H.F.; Moe, P.W. Effect of Intake on Digestive Efficiency. J. Dairy Sci. 1975, 58, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, D.E.; John, K.; Trabbic, C.J.; Luniwal, A.; Hankins, M.W.; Baum, J.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin Binding to PPARα Inhibits Lipid Accumulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.M.; Blomquist, T.M.; Miruzzi, S.A.; McCullumsmith, R.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. RNA Sequencing in Human HepG2 Hepatocytes Reveals PPAR-α Mediates Transcriptome Responsiveness of Bilirubin. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, U.; Koeleman, C.A.; Sokolova, M.V.; Bang, H.; Kleyer, A.; Rech, J.; Unterweger, H.; Schicht, M.; Garreis, F.; Hahn, J.; et al. IgA Subclasses Have Different Effector Functions Associated with Distinct Glycosylation Profiles. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.K.; Aschenbach, J.R. Ureases in the Gastrointestinal Tracts of Ruminant and Monogastric Animals and Their Implication in Urea-N/Ammonia Metabolism: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungate, R.E. The Rumen Microbial Ecosystem. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1975, 6, 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Cerrilla, M.E.; Mendoza Martínez, G. Starch Digestion and Glucose Metabolism in the Ruminant: A Review. Interciencia 2003, 28, 380–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, X. Comparative Analysis of Rumen Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Profiles during Adaption to Different Fattening Stages in Beef Cattle Fed TMR with Various Forage Silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 278, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firkins, J.L.; Yu, Z.; Morrison, M. Ruminal Nitrogen Metabolism: Perspectives for Integration of Microbiology and Nutrition for Dairy. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, E1–E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.E.; Ranilla, M.J.; Tejido, M.L.; Ramos, S.; Carro, M.D. Comparison of Fermentation of Diets of Variable Composition and Microbial Populations in the Rumen of Sheep and Rusitec Fermenters. I. Digestibility, Fermentation Parameters, and Microbial Growth. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3684–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.N.; Chattaway, M.A.; Rajakurana, L.; Gharbia, S.E. Prevotella. In Bergey’s Man Syst Archaea Bact; Whitman, W.B., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shabat, S.K.B.; Sasson, G.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Durman, T.; Yaacoby, S.; Berg Miller, M.E.; White, B.A.; Shterzer, N.; Mizrahi, I. Specific Microbiome-Dependent Mechanisms Underlie the Energy Harvest Efficiency of Ruminants. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2958–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Wong, M.H.; Thelin, A.; Hansson, L.; Falk, P.G.; Gordon, J.I. Molecular Analysis of Commensal Host-Microbial Relationships in the Intestine. Science 2001, 291, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zened, A.; Combes, S.; Cauquil, L.; Mariette, J.; Klopp, C.; Bouchez, O.; Troegeler-Meynadier, A.; Enjalbert, F. Microbial Ecology of the Rumen Evaluated by 454 GS FLX Pyrosequencing Is Affected by Starch and Oil Supplementation of Diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Abbeele, P.; Belzer, C.; Goossens, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Thas, O.; De Weirdt, R.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Van De Wiele, T. Butyrate-Producing Clostridium Cluster XIVa Species Specifically Colonize Mucins in an in Vitro Gut Model. ISME J. 2013, 7, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyonyo, T.; Shinkai, T.; Mitsumori, M. Improved Culturability of Cellulolytic Rumen Bacteria and Phylogenetic Diversity of Culturable Cellulolytic and Xylanolytic Bacteria Newly Isolated from the Bovine Rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Carrasco, J.M.; Cabral, C.; Redondo, L.M.; Pin Viso, N.D.; Colombatto, D.; Farber, M.D.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Impact of Chestnut and Quebracho Tannins on Rumen Microbiota of Bovines. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9610810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitman, W.B. (Ed.) Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-118-96060-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Segre, J.A. Signaling in Host-Associated Microbial Communities. Cell 2016, 164, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, M.; Goodrich, J.K.; Jackson, M.A.; Yet, I.; Davenport, E.R.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Debelius, J.; Pallister, T.; Mangino, M.; Raes, J.; et al. Heritable Components of the Human Fecal Microbiome Are Associated with Visceral Fat. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics for Different Ratios of Soluble to Insoluble Dietary Fiber by Fresh Fecal Microbiota from Growing Pigs. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15158–15167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar, M.; Escribano, J.; Ferré, N.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Selma-Royo, M.; Feliu, A.; Castillejo, G.; Luque, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Metabolic Health in Children with Obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Watanabe, Y. Description of Christensenella minuta gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces, which forms a distinct branch in the order Clostridiales, and proposal of Christensenellaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Items | Content | |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (% of DM) | Growing Period | Fattening Period |
| Ground corn | 31.900 | 59.771 |
| Soybean meal | 9.350 | 13.229 |
| Jujube powder | 8.250 | |
| Whole plant corn silage | 24.750 | 15.736 |
| Corn stalker | 20.250 | 7.868 |
| NaCl | 1.100 | 0.481 |
| Limestone | 0.712 | |
| MgO | 0.236 | |
| Premix 1 | 2.200 | 0.786 |
| CaHPO4 | 1.100 | |
| NaHCO3 | 1.100 | 1.180 |
| nutrient level | 100.000 | 100.000 |
| DM | 53.210 | 63.940 |
| NDF | 41.75 | 27.27 |
| CP | 11.330 | 15.440 |
| starch | 20.64 | 26.776 |
| EE | 1.63 | 2.406 |
| ME 2 MJ/kg DM | 10.550 | 13.850 |
| Items | L | H | Mean | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of animals | 15 | 15 | |||
| Performance traits | |||||
| Initial weight, kg | 537.571 | 630.286 | 583.929 | 12.634 | <0.001 |
| Final weight, kg | 608.714 | 709.714 | 659.214 | 14.340 | <0.001 |
| ADG, kg/d | 1.147 | 1.261 | 1.204 | 0.051 | 0.238 |
| DMI, kg/d | 10.970 | 11.881 | 11.425 | 0.242 | 0.002 |
| G:F | 0.105 | 0.106 | 0.105 | 0.003 | 0.905 |
| Serum biochemistry | |||||
| TP (g/L) | 72.158 | 78.183 | 75.171 | 0.882 | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 38.000 | 37.417 | 37.708 | 0.347 | 0.191 |
| GLB (g/L) | 34.158 | 40.767 | 37.463 | 0.950 | <0.001 |
| TBiLL (U/L) | 2.217 | 1.706 | 1.961 | 0.149 | 0.023 |
| GLU (mmol/L) | 4.994 | 2.489 | 3.742 | 0.271 | <0.001 |
| UREA (mmol/L) | 3.141 | 10.329 | 6.735 | 0.769 | <0.001 |
| T-AOC (mmol/L) | 0.237 | 0.429 | 0.333 | 0.020 | <0.001 |
| Items | L | H | Mean | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of animals | 15 | 14 | |||
| pH | 6.898 | 6.372 | 6.61 | 0.043 | <0.001 |
| NH3-N, mg/100 mL | 4.471 | 10.238 | 7.355 | 0.661 | <0.001 |
| TVFA, mmol/L | 63.384 | 72.445 | 67.9145 | 3.708 | 0.175 |
| Acetate | 44.495 | 51.097 | 47.796 | 2.51 | 0.194 |
| Propionate | 10.025 | 10.667 | 10.346 | 0.591 | 0.597 |
| Isobutyrate | 0.749 | 0.708 | 0.729 | 0.032 | 0.529 |
| Butyrate | 6.647 | 8.296 | 7.471 | 0.433 | 0.055 |
| Isovalerate | 1.075 | 1.274 | 1.175 | 0.057 | 0.081 |
| Valerate | 0.393 | 0.403 | 0.398 | 0.031 | 0.876 |
| VFAs, molar% of TVFA | |||||
| Acetate | 70.333 | 70.597 | 70.465 | 0.302 | 0.529 |
| Propionate | 15.766 | 14.595 | 15.18 | 0.218 | 0.01 |
| Isobutyrate | 1.259 | 1.003 | 1.131 | 0.059 | 0.041 |
| Butyrate | 10.245 | 11.533 | 10.889 | 0.267 | 0.001 |
| Isovalerate | 1.773 | 1.745 | 1.759 | 0.046 | 0.756 |
| Valerate | 0.624 | 0.528 | 0.576 | 0.023 | 0.051 |
| A/P | 4.469 | 4.873 | 4.671 | 0.084 | 0.015 |
| Items | L | H | Mean | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMD, % | 72.32 | 56.30 | 67.74 | 1.227 | <0.001 |
| CPD, % | 66.12 | 55.45 | 62.90 | 1.118 | <0.001 |
| NDFD, % | 83.58 | 54.94 | 80.11 | 1.167 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Ye, B.; Wu, B.; Yi, X.; Li, X.; A, R.; Cui, X.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. Effect of Total Mixed Ration on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestion, and Rumen Microbiome in Angus Beef Cattle during the Growing and Fattening Phases. Fermentation 2024, 10, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040205
Li W, Ye B, Wu B, Yi X, Li X, A R, Cui X, Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Zhu X, et al. Effect of Total Mixed Ration on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestion, and Rumen Microbiome in Angus Beef Cattle during the Growing and Fattening Phases. Fermentation. 2024; 10(4):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040205
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Boping Ye, Baoyun Wu, Xin Yi, Xiang Li, Runa A, Xiaojing Cui, Zhiyu Zhou, Yang Cheng, Xiaowen Zhu, and et al. 2024. "Effect of Total Mixed Ration on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestion, and Rumen Microbiome in Angus Beef Cattle during the Growing and Fattening Phases" Fermentation 10, no. 4: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040205
APA StyleLi, W., Ye, B., Wu, B., Yi, X., Li, X., A, R., Cui, X., Zhou, Z., Cheng, Y., Zhu, X., Tang, X., Fu, X., Li, N., Wu, H., & Zhou, Z. (2024). Effect of Total Mixed Ration on Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestion, and Rumen Microbiome in Angus Beef Cattle during the Growing and Fattening Phases. Fermentation, 10(4), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040205






