Effect of Biochar in Modulating Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Microbial Structure Community of Different Inoculum Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Swine Manure and Inoculum
2.2. Experimental Setup for the AD System
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Anaerobic Digestion Performance
3.1.1. Variations in NH4+-N, SCOD, and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
3.1.2. Biogas Production Performance
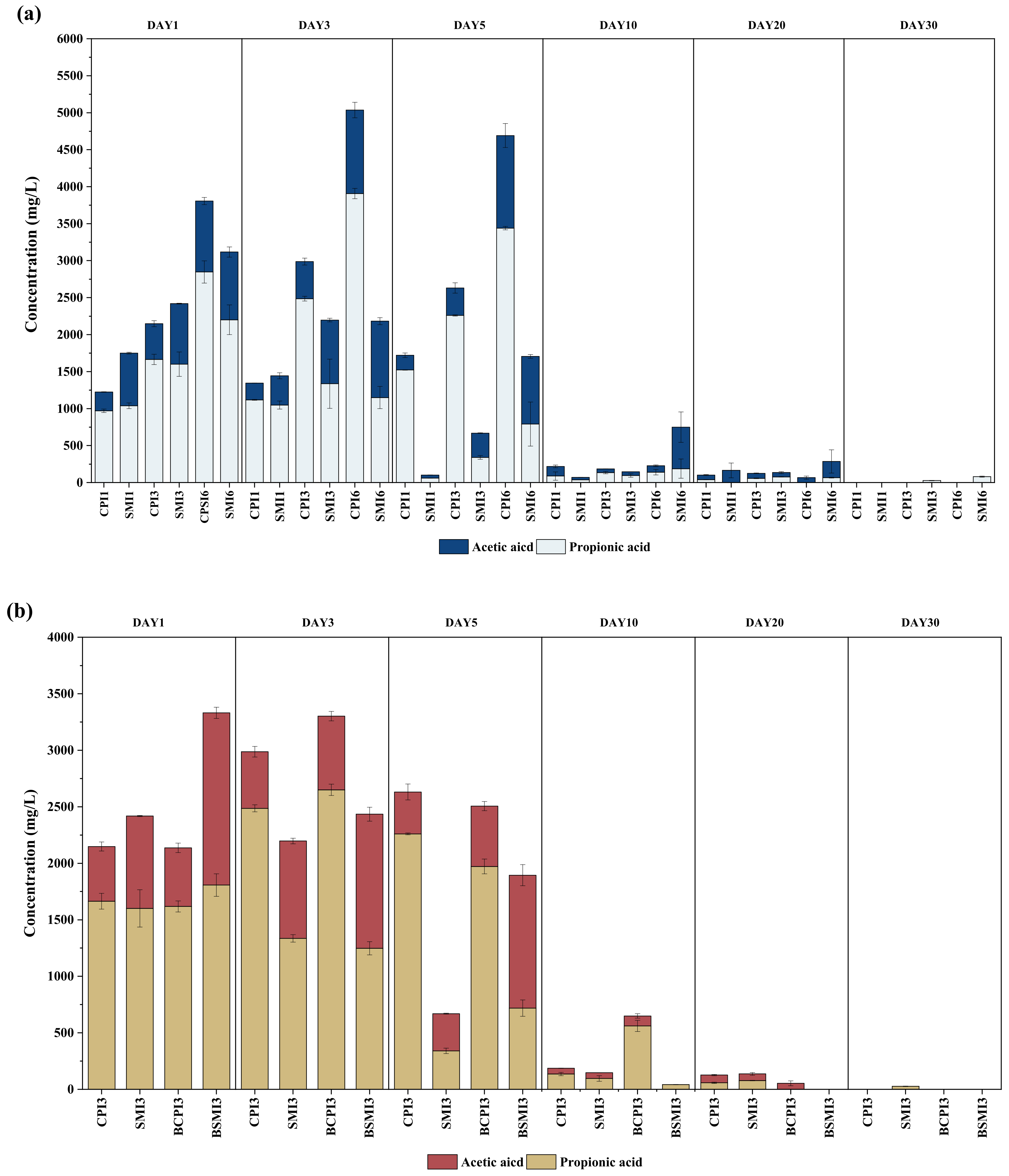
3.1.3. Variations in VFAs and pH in AD
3.2. Microbial Analysis
3.2.1. Diversity and Richness of Microbial Community
3.2.2. Changes in Bacterial Communities
3.2.3. Changes in Archaeal Communities
3.3. Challenges and Prospectives for Application of Biochar in Anaerobic Digestion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of physicochemical properties and bacterial community in aerobic composting of swine manure based on a patent compost tray. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 343, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Su, T.; Liang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, T. Dual character of methane production improvement and antibiotic resistance genes reduction by nano-Fe2O3 addition during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, F.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Zang, B.; Li, G.; Xie, X.; Luo, W. Emission of volatile sulphur compounds during swine manure composting: Source identification, odour mitigation and assessment. Waste Manag. 2022, 153, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman Khan, M.; Kiaer Ahring, B. Improving the biogas yield of manure: Effect of pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of the recalcitrant fraction of manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Jacobi, H.F.; Strach, K.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Liebetrau, J. Mono-fermentation of chicken manure: Ammonia inhibition and recirculation of the digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, I.W.; Lettinga, G. The influence of ammonium-nitrogen on the specific activity of pelletized methanogenic sludge. Agric. Wastes 1984, 9, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, S.; Desmond-Le Quéméner, E.; Madigou, C.; Bouchez, T.; Chapleur, O. Anaerobic digestion of biowaste under extreme ammonia concentration: Identification of key microbial phylotypes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Cayetano, R.D.A.; Kim, G.-B.; Park, J.; Kim, S.-H. The effects of ammonia acclimation on biogas recovery and the microbial population in continuous anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lei, Z.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shimizu, K. Enhanced solubilization of solid organics and methane production by anaerobic digestion of swine manure under nano-bubble water addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, F.; Huang, W.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhancing hydrogenotrophic activities by zero-valent iron addition as an effective method to improve sulfadiazine removal during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Duan, Y.; Zou, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, L.; Wong, J.W.C. Evaluations of biochar amendment on anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and sewage sludge: Waste-to-methane conversion, microbial community, and antibiotic resistance genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, B.; Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ye, H.; Qin, L.; Lai, C. Biochar-compost as a new option for soil improvement: Application in various problem soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 162024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Farghali, M.; El-Azazy, M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Fahim, R.A.; Maksoud, M.I.A.A.; Ajlan, A.A.; Yousry, M.; Saleem, Y.; et al. Biochar for agronomy, animal farming, anaerobic digestion, composting, water treatment, soil remediation, construction, energy storage, and carbon sequestration: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2385–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, T.; Song, X.; Nie, S.; Choi, S.-E.; Si, C. Preparation and Application in Water Treatment of Magnetic Biochar. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 769667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyoto, N.M.S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of biochar addition on hydrogen and methane production in two-phase anaerobic digestion of aqueous carbohydrates food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, F.; Luo, C.; Shao, L.; He, P. Biochar alleviates combined stress of ammonium and acids by firstly enriching Methanosaeta and then Methanosarcina. Water Res. 2016, 90, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Linville, J.L.; Urgun-Demirtas, M.; Schoene, R.P.; Snyder, S.W. Producing pipeline-quality biomethane via anaerobic digestion of sludge amended with corn stover biochar with in-situ CO2 removal. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hou, D. Green immobilization of toxic metals using alkaline enhanced rice husk biochar: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and KOH concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Choi, Y.-K.; Kan, E. Effects of dairy manure-derived biochar on psychrophilic, mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestions of dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Świechowski, K.; Manczarski, P.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. The Effect of Biochar Addition on the Biogas Production Kinetics from the Anaerobic Digestion of Brewers’ Spent Grain. Energies 2019, 12, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucjan, P. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; Arnold, E., Greenberd Lenore, S., Clesceri Andrew, D., Eds.; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1992; 1025p, ISBN 0-87553-207-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lv, P.; Kang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Influence of the Feedstock Ratio and Organic Loading Rate on the Co-digestion Performance of Pennisetum hybrid and Cow Manure. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; Brekelmans, J.; Martín, M.A.; Chica, A.F.; Martín, A. Impact of ammonia and sulphate concentration on thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9040–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Xu, C.; Huang, W.; Jiang, M.; Yan, J.; Fan, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Xiao, B.; Song, G. Improving anaerobic digestion of piggery wastewater by alleviating stress of ammonia using biochar derived from rice straw. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhao, L.; Liao, L.; Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, M.; Huang, Z. Application of biochar in a CIC reactor to relieve ammonia nitrogen stress and promote microbial community during food waste treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohungbe, M.O.; Herbert, B.; Hurst, L.; Ibeto, C.N.; Semple, K.T. The challenges of anaerobic digestion and the role of biochar in optimizing anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2016, 61, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, M.; Sharaf, A.; Liu, Y. Granular activated carbon stimulated microbial physiological changes for enhanced anaerobic digestion of municipal sewage. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Dhar, B.R. Advances towards understanding and engineering direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, P.B.; Luckarift, H.R.; Johnson, G.R.; Roy, J.N.; Sizemore, S.R. Facile fabrication of scalable, hierarchically structured polymer-carbon architectures for bioelectrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Ran, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Instability diagnosis and syntrophic acetate oxidation during thermophilic digestion of vegetable waste. Water Res. 2018, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlar, F.E.; Tunca, B.; Yilmazel, Y.D. Carbon-based conductive materials enhance biomethane recovery from organic wastes: A review of the impacts on anaerobic treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of kitchen wastes with biochar: Link between different properties and critical mechanisms of promoting interspecies electron transfer. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Shen, D.; Li, N. Anaerobic digestion of food waste for volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production with different types of inoculum: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, S.; Fang, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Effect of Fe0 addition on volatile fatty acids evolution on anaerobic digestion at high organic loading rates. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Green, H.; Tao, W. Reversibility of propionic acid inhibition to anaerobic digestion: Inhibition kinetics and microbial mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Ma, J.; Zhai, L.; Luo, T.; Mei, Z.; Liu, H. Achievements of biochar application for enhanced anaerobic digestion: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Li, F.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of ammonia-rich swine manure by zero-valent iron: With special focus on the enhancement effect on hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, D.; Liu, G.J.; Deng, L.W.; Long, Y.; Fan, Z.H. Continuous dry fermentation of swine manure for biogas production. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Liu, M.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y. Mechanism of action of single and mixed antibiotics during anaerobic digestion of swine wastewater: Microbial functional diversity and gene expression analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonugli-Santos, R.C.; Marteres, T.J.; Luiz, F.N.; Somer, J.G.; Mari, N.G.; Passarini, M.R.Z. Prolonged acetogenic phase and biological succession during anaerobic digestion using swine manure. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, B.; Borja, R.; González, J.; Portillo, M.C.; Sáiz-Jiménez, C. Influence of organic loading rate and hydraulic retention time on the performance, stability and microbial communities of one-stage anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive mill solid residue. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.T.; Fan, X.L.; Zhao, X.X.; Fu, S.F.; He, S.; Manasa, M.R.K.; Guo, R.B. Effects of organic loading rate on biogas production from macroalgae: Performance and microbial community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, G.; Fernández, B.; Bonmatí, A. Addition of crude glycerine as strategy to balance the C/N ratio on sewage sludge thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yaohari, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sze, C.C.; Stuckey, D.C. Autoinducer-2-mediated quorum sensing partially regulates the toxic shock response of anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2019, 158, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhen, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Sun, Y. Methane production of rare earth element-rich Dicranopteris dichotoma and effects of La(III) on anaerobic digestion performance of lignocellulose. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, I.; Ma, J.; Mehboob, F.; Kafle, G.K.; Amin, B.A.Z.; Nazir, R.; Ndegwa, P.; Frear, C. Kinetic and microbial analysis of methane production from dairy wastewater anaerobic digester under ammonia and salinity stresses. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, L.; Kahala, M.; Tampio, E.; Vainio, M.; Ervasti, S.; Rasi, S. Effect of Inoculum Pretreatment on the Composition of Microbial Communities in Anaerobic Digesters Producing Volatile Fatty Acids. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Pandey, A.; Park, J.; Muhorakeye, A.; Morya, R.; Kim, S.-H. Predicting the impact of hydraulic retention time and biodegradability on the performance of sludge acidogenesis using an artificial neural network. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 372, 128629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Jin, Y.; Fan, J.; Zan, S.; Gu, C.; Wang, J. A new pathway for anaerobic biotransformation of marine toxin domoic acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 5150–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, D.; Wen, Q.; Ji, Y. Oriented acidification of wasted activated sludge (WAS) focused on odd-carbon volatile fatty acid (VFA): Regulation strategy and microbial community dynamics. Water Res. 2018, 142, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, L.; Hao, H.; Huang, H. Impact of Fe and Ni Addition on the VFAs’ Generation and Process Stability of Anaerobic Fermentation Containing Cd. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Yang, C.M. Impacts of different biochar types on the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 42375–42386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, H.; Chen, Q.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jha, A.K. Performance of anaerobic sludge and the microbial social behaviors induced by quorum sensing in a UASB after a shock loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, S.; Li, S.; Wei, C. Effects of biochar on anaerobic treatment systems: Some perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, G.N.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Gao, B. Catechol and Humic Acid Sorption onto a Range of Laboratory-Produced Black Carbons (Biochars). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Forrester, S.; Koval, J.; Urgun-Demirtas, M. Yearlong semi-continuous operation of thermophilic two-stage anaerobic digesters amended with biochar for enhanced biomethane production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Z. A comparison and evaluation of the effects of biochar on the anaerobic digestion of excess and anaerobic sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Hu, B.-B.; Wu, H.-Z.; Zhu, M.-J. Improved methane production with redox-active/conductive biochar amendment by establishing spatial ecological niche and mediating electron transfer. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Role of biochar in the granulation of anaerobic sludge and improvement of electron transfer characteristics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sheng, T.; Li, L. Feasibility of dry anaerobic digestion of beer lees for methane production and biochar enhanced performance at mesophilic and thermophilic temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Guo, M.; Xie, J.; Chang, Y.; Mabruk, A.; Zhang, T.C.; Chen, C. COD inhibition alleviation and anammox granular sludge stability improvement by biochar addition. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, N. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) promoted by pyrogenic biochar: Deciphering the interaction with extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Si, X.; Duan, X.; Quan, X. The adverse effect of biochar to aquatic algae—The role of free radicals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ran, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms of obligate anaerobes involved in biological waste treatment processes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-w.; Pei, S.-z.; Zhou, C.-s.; Liu, B.-f.; Cao, G.-l. Assessment of potential biotoxicity induced by biochar-derived dissolved organic matters to biological fermentative H2 production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | TS (%FM) | VS (%FM) | VS/TS (%) | C (%TS) | H (%TS) | N (%TS) | C/N (%TS) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 0.6 | 0.09 | 0.4 | 0.4 | ||
| Cellulose–peptone–swine inoculum | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | ||||||
| Swine manure inoculum | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.002 | ||||||
| Coconut shell biochar | 77.68 | 1.57 | 0.695 | 111.76 | 134.47 | 4.80 |
| Group | EC (ms/cm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 10 d | 20 d | 30 d | |
| CPI1 | 0.07 abc | 0.02 b | 0.12 ab | 0.11 bc | 0.07 abc | 0.03 a |
| SMI1 | 0.24 d | 0.17 d | 0.12 b | 0.03 f | 0.22 d | 0.12 c |
| CPI3 | 0.06 ab | 0.03 ab | 0.16 ab | 0.24 ab | 0.04 ab | 0.02 a |
| SMI3 | 0.25 d | 0.14 cd | 0.06 ab | 0.13 f | 0.15 d | 0.01 bc |
| CPI6 | 0.03 a | 0.30 a | 0.24 a | 0.03 a | 0.07 a | 0.03 a |
| SMI6 | 0.06 cd | 0.65 bc | 0.88 ab | 0.11 e | 0.19 cd | 0.08 b |
| BCPI3 | 0.03 bc | 0.09 b | 0.12 ab | 0.09 d | 0.03 bc | 0.13 b |
| BSMI3 | 0.53 ab | 0.14 bc | 0.26 ab | 0.1 cd | 0.01 d | 0.01 d |
| Sample with Days | Number | OTUs | Shannon | Chao | Ace | Shannoneven | Coverage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculum | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | Bacteria | Archaea | |
| SMI | 40,446 | 36,548 | 682 | 40 | 4.16 | 1.16 | 777.41 | 40.33 | 782.32 | 41.03 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| CPI | 46,971 | 52,231 | 603 | 41 | 3.75 | 1.26 | 703.90 | 44.33 | 719.70 | 44.06 | 0.58 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| SMI3 | 1 | 42,284 | 51,691 | 750 | 42 | 4.29 | 1.55 | 865.56 | 42.75 | 862.01 | 43.51 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 49,505 | 68,489 | 754 | 38 | 4.44 | 1.17 | 873.54 | 41.00 | 867.66 | 45.70 | 0.67 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 | 53,921 | 38,351 | 746 | 39 | 4.50 | 1.15 | 842.00 | 41.00 | 837.32 | 42.77 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| BSMI3 | 1 | 50,825 | 49,236 | 776 | 41 | 4.28 | 1.60 | 862.47 | 44.75 | 859.37 | 52.30 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 56,134 | 62,736 | 794 | 43 | 4.47 | 1.41 | 864.49 | 46.00 | 870.09 | 48.55 | 0.67 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 | 66,887 | 75,712 | 814 | 41 | 4.50 | 1.51 | 922.33 | 44.75 | 907.90 | 47.90 | 0.67 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| CPI3 | 1 | 47,148 | 65,583 | 656 | 35 | 3.75 | 1.51 | 793.47 | 45.00 | 771.41 | 40.06 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 44,174 | 58,738 | 677 | 39 | 4.10 | 1.10 | 785.01 | 39.75 | 799.18 | 41.55 | 0.63 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 | 55,700 | 69,863 | 703 | 37 | 4.08 | 0.87 | 814.06 | 38.50 | 816.51 | 38.30 | 0.62 | 0.24 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| BCPI3 | 1 | 54,292 | 62,894 | 615 | 38 | 3.95 | 1.39 | 706.47 | 38.20 | 684.98 | 39.29 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 5 | 47,809 | 44,592 | 745 | 35 | 4.04 | 1.34 | 889.90 | 35.50 | 869.21 | 35.74 | 0.61 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 | 47,022 | 59,001 | 714 | 37 | 4.23 | 1.03 | 825.78 | 38.50 | 828.18 | 40.36 | 0.64 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, J.; Zhen, F.; Kong, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, L. Effect of Biochar in Modulating Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Microbial Structure Community of Different Inoculum Sources. Fermentation 2024, 10, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030151
Ding J, Zhen F, Kong X, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Gong L. Effect of Biochar in Modulating Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Microbial Structure Community of Different Inoculum Sources. Fermentation. 2024; 10(3):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030151
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Jingran, Feng Zhen, Xiaoying Kong, Yunzi Hu, Yi Zhang, and Lang Gong. 2024. "Effect of Biochar in Modulating Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Microbial Structure Community of Different Inoculum Sources" Fermentation 10, no. 3: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030151
APA StyleDing, J., Zhen, F., Kong, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Gong, L. (2024). Effect of Biochar in Modulating Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Microbial Structure Community of Different Inoculum Sources. Fermentation, 10(3), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030151






