Abstract
2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine (TMP), as a volatile heterocyclic nitrogen compound, has a wide range of applications. To explore an efficient and environmentally friendly way to produce TMP, Bacillus strains were isolated from Daqu using traditional separation and purification methods. The fermentation products were detected by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and the species relationship of strains was analyzed by morphological and phylogenetic tree construction. Single factors were selected to optimize the fermentation process of TMP production, and a Box–Behnken design was used for response surface testing. The LC-6 strain isolated from Daqu was Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and its fermentation products contained TMP, with a relatively high value of 0.071 ± 0.011 mg/g, indicating that the LC-6 strain was a potentially valuable TMP-producing bacterium. The results of single-factor testing showed that temperature, bottle capacity, and water addition significantly affected TMP production. Box–Behnken design and response surface analysis revealed that the order of influence on TMP yield was as follows: water addition > temperature > bottle capacity. Response surface optimization results showed that the optimal parameters for wheat medium fermentation were temperature 37 °C, bottle capacity 100 g/250 mL, and water addition 39 mL. Under these fermentation conditions, the average production of TMP was 0.446 ± 0.052 mg/g, which was 0.375 mg/g higher than that obtained before optimization. Compared with the previous period, the production of TMP indeed increased, providing a basis for further research on the solid-state fermentation process of TMP synthesis.
1. Introduction
Pyrazines are a class of volatile heterocyclic nitrogen compounds with a special flavor that can be used as spices; they are mainly produced when food is heated [1]. Alkylpyrazines are known as important contributors to the flavor of traditional fermented foods, with non-mutagenic and non-carcinogenic properties, which have great application potential in food industries [2]. Among them, 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine (TMP) is a high-grade spice that has gradually developed in recent years, with a strong aroma of roasted peanuts or potatoes [3]. The specific structural formula of TMP is shown in Figure 1. TMP is common in heated foods, like baked goods, roasted meat, coffee, peanuts, or popcorn, and is mainly formed by the Maillard reaction during food production [4]. In addition, TMP has also been found in traditional fermented foods, such as soybean- and cocoa-based fermented foods and Chinese Baijiu [2]. TMP has been detected in different flavors of Baijiu, but its yield varies greatly [5]. Studies have shown that the content of TMP varies in strong-flavored, sauce-flavored, light-flavored, sesame-flavored, and Laobaigan-flavored Baijiu, from 17.39 μg/kg to 1428.41 μg/kg [6]. TMP can be synthesized chemically, formed from the dehydrogenation reaction of 2,3,5-trimethyl-5,6-dihydropyrazine [7]. More recently, Jiang et al. [8] reported that a conversion reaction between methylglyoxal and glyoxal can form TMP.
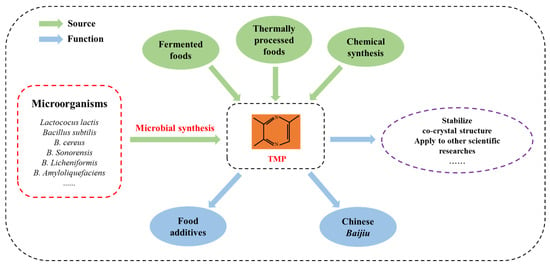
Figure 1.
Source and function of TMP.
In recent years, TMP has had a wide range of applications. Firstly, TMP is an important raw material for food, beverage, and tobacco flavor. In food industries, TMP can be directly used to improve various foods such as bread, pudding, chewing gum, soft drinks, milk, meat, etc. [9]. Secondly, TMP plays an important role in the formation of the flavor of Chinese Baijiu. Although the output of TMP in Baijiu is very low, it has a low flavor threshold and good aroma permeability [10]. TMP presents different aromas in different flavors of Baijiu. For instance, TMP presents the aroma of nuts in strong-flavor Baijiu [11], while in sauce-flavor Baijiu, it presents a barbecue and earthy taste [12]. TMP can be applied to other scientific research as well [13]. Zhang et al. [14] reported that TMP has the function of stabilizing the structure of 3, 5-dichlorosalicylic acid and pyrazine derivatives co-crystals by changing the bonding mode and intermolecular force of the co-crystals. Due to the important value of TMP in different industries, researchers are constantly exploring ways to produce it.
At present, the production of TMP mostly depends on chemical methods, but compared with biosynthesis, chemical methods have a greater destructive impact on the environment. TMP can be formed by the Maillard reaction, a non-enzymatic browning reaction of amino and reducing sugars during heating [15]. This reaction requires a very high temperature (more than 100 °C) to occur, and the reaction pathway is complex, resulting in many by-products [16]. Therefore, there is relatively little research on using the Maillard reaction to improve the yield of TMP. Nevertheless, studies on TMP biosynthesis are becoming more and more popular. In recent decades, simple pyrazines such as dimethylpyrazine, TMP, and tetramethylpyrazine have been reported to be derived from microbial fermentation. Although microorganisms have been discovered to produce TMP, their yields are relatively low [17,18]. Currently, the microorganisms that can synthesize TMP are Bacillus subtilis, B. sonorensis, B. licheniformis, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. cereus, Lactococcus lactis, etc. [4,19,20]. In Bacillus subtilis 168 cells, l-threonine-3-dehydrogenase (TDH) catalyzes the reaction of d-glucose and l-threonine to produce TMP [2]. The results of in vitro experiments showed that providing exogenous threonine and glucose as substrates can significantly enhance the production of TMP in Bacillus species [21]. Possible TMP biosynthetic pathways are shown in Figure 2 [1,17].
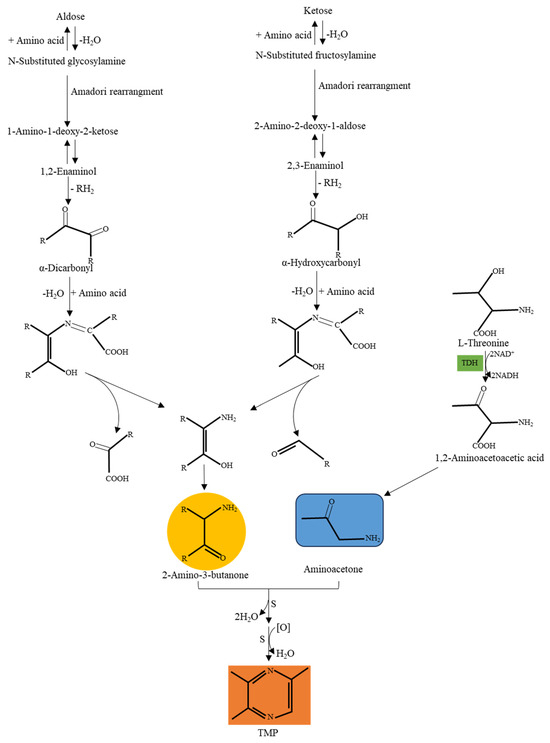
Figure 2.
Possible synthesis pathway of TMP.
The response surface method is often used to optimize fermentation media and culture conditions in microbial fermentation to produce metabolites [22,23]. Specifically, the optimum parameters of fermentation can be determined by establishing mathematical models, regression analysis, and variance analysis, while the Box–Behnken design is a commonly used statistical model in the response surface method [24,25]. Wheat is used as a kind of fermentation raw material in traditional Chinese liquor brewing and supplies enzymes and organic substances for fermentation [26]. Wheat is rich in starch and amino acids, which meet the nutrient conditions required for the synthesis of pyrazine. Despite the broad abundance of TMP in foods, literature on the production of TMP by solid-state fermentation and optimization of fermentation conditions is limited and mainly comprises data on the content determination in foods. Therefore, this study proposed a wheat solid-state fermentation method optimized by the response surface method to improve the production efficiency of TMP. The highest-yielding TMP strain screened from Daqu was used to produce TMP through solid-state fermentation, aiming to explore a solid-state fermentation method to improve the production of TMP so as to provide a reference for the improvement in TMP yield in traditional fermented foods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Culture Medium
Daqu samples were taken from a distillery located in Sichuan province for screening TMP-producing strains. LB medium (sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min) was used for strain activation and fermentation seed solution preparation. The wheat solid-state fermentation medium was used to produce TMP, which was prepared according to Du et al. [27] with the following adjustments: adding an appropriate amount of ground wheat, proportionately adding an appropriate amount of water, and sterilizing at 121 °C for 20 min. Wheat is a fermentation raw material in Chinese traditional liquor brewing, which provides enzymes and organic matter for fermentation. Wheat is rich in starch and amino acids, which meet the nutritional conditions required for the synthesis of pyrazines. In all fermentation experiments in this study, we used the same batch of wheat to ensure that the fermentation medium provided the same initial fermentation nutrients.
2.2. Screening and Identification of TMP-Producing Strains
After being ground under sterile conditions, 10 g Daqu samples were mixed with 90 mL of sterilized 0.85% v/v sodium chloride solution, incubated at 37 °C and 180 rpm for 30 min, followed by a water bath (80 °C) treatment for 15 min [5]. The enriched bacterial solution was diluted and spread on LB solid medium and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Single colonies were picked out and scribed on LB solid medium. After repeating the preceding steps three times, the better-growing single strains were isolated and selected. Strains with different morphological characteristics were numbered and stored at 4 °C.
The isolated single colonies were inoculated into LB liquid medium and cultured at 37 °C, 180 rpm for 16 h, separately. Thereafter, the seed solution was inoculated into the wheat solid-state fermentation medium at 6% inoculated amount. After 7 d of fermentation, the volatile components of fermentation products were analyzed by GC-MS. The TMP yield was analyzed, and strains with higher TMP yield were selected for subsequent experiments.
The bacterial DNA genome extraction kit was used to extract the genome of the selected strain [28]. PCR amplification of 16S rDNA was carried out with universal primers: 27F (5′-CAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCT-3′) and 1492R (5′-AGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3′). After detecting by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the PCR products were sent to Qingke Company for sequencing. Sequencing results were compared with microorganisms in NCBI by BLAST. The reliable strain sequences with high similarity were selected, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the neighbor-joining method (2000 bootstrap) of MEGA 7 software (v7.0.26).
2.3. Extraction and Detection Conditions for Volatile Substances
The fermented wheat media were accurately weighed 4.0 g and put in a 15 mL bottle for extraction. After heating in a water bath at 60 °C for 15 min, samples were adsorbed in the headspace for 30 min. GC-MS was used to detect the volatile substances. 2-ethylbutyric acid was used as the internal standard substance. The conditions for GC-MS were set as follows. GC conditions: the specifications of capillary columns (DB-WAX) were 60 m × 250 μm, 0.25 μm. Using manual injection, the inlet temperature was 230 °C. The programmed heating process was as follows: the initial temperature was 40 °C, stabilized for 3 min, then increased to 120 °C with a rate of 5 °C/min, raised to 230 °C at a rate of 7 °C/min, and held for 10 min. MS conditions: scanning range 20–500 u, electron energy 70 eV, ion source temperature 230 °C, and interface temperature 230 °C.
2.4. Single-Factor Analysis
According to the previous reports on solid-state fermentation [18,29,30], temperature, bottling capacity, and water addition were selected as single factors to investigate their effects on the TMP production in wheat medium. With the method of control variables, the temperatures were 19 °C, 28 °C, 37 °C, 46 °C, and 55 °C (with fixed bottling capacity of 100 g/250 mL and water addition of 50 mL); the bottling capacities were 80 g/250 mL, 90 g/250 mL, 100 g/250 mL, 110 g/250 mL, and 120 g/250 mL (with fixed temperature of 37 °C and water addition of 50 mL); and the water additions were 30 mL, 40 mL, 50 mL, 60 mL, and 70 mL (with fixed temperature of 37 °C and bottling capacity of 100 g/250 mL). The optimal parameter range was determined according to the TMP yield and selected for Box–Behnken design.
2.5. Box–Behnken Design
Box–Behnken design was used to optimize fermentation conditions, and a three-factor and three-level experiment was performed [23]. Based on the results of previous single-factor experiments, three factors (temperature, bottle capacity, and water addition) that impacted the production of TMP were applied to the experiment. The levels and codes of each factor are shown in Table 1. The response surface method was used to evaluate the fermentation conditions, and optimization was performed to determine the optimal fermentation conditions for TMP production in wheat medium. In total, the response surface analysis with 17 groups and 5 central points was conducted. Multiple regression analysis was performed to obtain the regression equation. Three-dimensional surface diagrams were drawn by Design-Expert 12.0 software (v12.0.3.0).

Table 1.
Coded and actual values of factors in Box–Behnken design.
3. Results
3.1. Screening and Identification of TMP-Producing Strains
A total of eight Bacillus strains were isolated from Daqu and numbered LC-1 to LC-8. The fermentation products of these strains were detected by GC-MS, and three strains (LC-3, LC-6, and LC-8) were found to produce TMP (Table 2). The TMP production of the LC-6 strain reached 0.071 ± 0.011 mg/g (g means the total amount of volatile and non-volatile substances in the wheat medium after fermentation), the highest TMP yield among the isolated strains. Therefore, the LC-6 strain was chosen as the initial strain for the subsequent experiments.

Table 2.
The initial TMP production of 3 Bacillus strains.
The morphology of the LC-6 colony was milky white, with a dry and flat surface and irregular edges. The LC-6 strain was Gram-stained, and the purple rod shape was observed. The LC-6 strain was identified as a Gram-positive bacterium. The neighbor-joining method in MEGA 7 was chosen to construct the phylogenetic tree. As shown in Figure 3, the genetic distance between the LC-6 strain and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NBRC 15535 was the closest, so it was named Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LC-6 (LC-6).
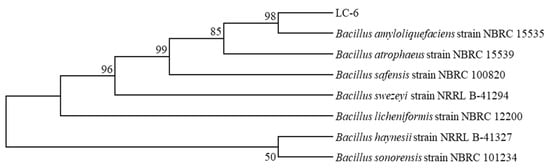
Figure 3.
The constructed phylogenetic tree of LC-6 strain.
3.2. Single-Factor Analysis
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on TMP Production
As we know, fermentation temperature is a crucial parameter during the fermentation process. Inappropriate fermentation temperature will affect the growth state of cells and the production of metabolites. To ensure balanced cell growth and strong metabolism, it is important to select an appropriate fermentation temperature for TMP production. As shown in Figure 4A, with the increase in temperature, the TMP yield presented a trend of slowly increasing at first and then decreasing. The highest TMP yield was 0.119 ± 0.002 mg/g at a temperature of 37 °C. Therefore, 37 °C was considered as the optimal fermentation temperature.
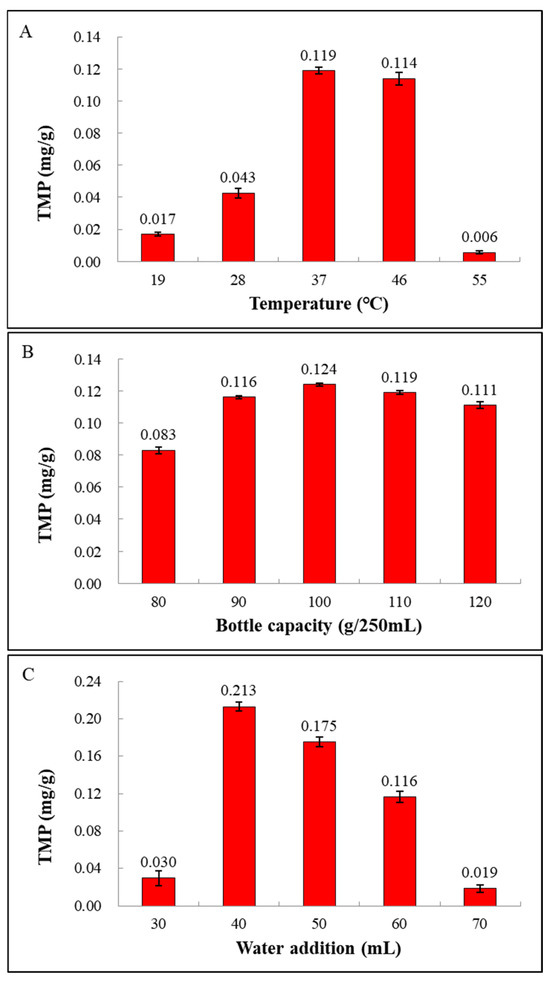
Figure 4.
Effects of single factors on TMP production: (A) temperature, (B) bottle capacity, and (C) water addition.
3.2.2. Effect of Bottling Capacity on TMP Production
In the solid-state fermentation process, the bottling capacity will affect the content of oxygen in the fermentation system, thus affecting the growth and metabolism of microorganisms. Different microorganisms have different oxygen requirements for different metabolic activities. So, the effects of different bottling capacities on the production of TMP by fermentation of the LC-6 strain were investigated, and the results are shown in Figure 4B. With the increase in the bottling capacity, the TMP yield showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the bottling capacity was 100 g/250 mL, the TMP production reached a peak of 0.124 ± 0.001 mg/g. Therefore, 100 g/250 mL was selected as the optimal bottling capacity.
3.2.3. Effect of Water Addition on TMP Production
The appropriate water content in the solid-state substrate will be conducive to the growth of microorganisms and the production of metabolites. Too low water content can affect the absorption and utilization of nutrients in the solid-state substrate by microorganisms, while too high water content can cause particle caking, which leads to a decrease in dissolved oxygen. Hence, the effects of different initial water additions on the fermentation of the LC-6 strain were studied. As shown in Figure 4C, with the increase in water addition, the yield of TMP presents a trend of climbing up and then declining. When the water addition was 40 mL, the maximum yield of TMP was 0.213 ± 0.005 mg/g. Therefore, 40 mL was considered as the optimal water addition amount.
3.3. Response Surface Testing
Based on the results from single-factor experiments, a Box–Behnken design was carried out to optimize the fermentation conditions for TMP production, with the fermentation temperature, bottling capacity, and water addition as independent variables. The response value was the production of TMP, and the results are shown in Table 3. Specifically, the response surface test design included 17 tests in total: 12 factorial tests and 5 central tests.

Table 3.
Box–Behnken design and determination of TMP production in wheat medium.
The Design-Expert 12.0 software was used to perform multiple regression fitting analysis on data in Table 3, and the response surface regression equation was obtained as follows:
y = 0.455 + 0.0221A − 0.0195B − 0.0231C − 0.0097AB + 0.0035AC + 0.0243BC − 0.2303A2 − 0.183B2 − 0.1267C2.
Based on p-values, the order of single factors effect on TMP production was C (0.0137) > A (0.0167) > B (0.0283), namely, water addition > temperature > bottling capacity (Table 4). The p-value of the established regression model was <0.0001, which means that the regression model was highly significant. The lack of fit p = 0.5748 > 0.05 indicates that the pure error is not significant. Among them, the primary items A, B, C, and secondary items BC were significant (p < 0.05), and the items affected by the secondary factors, A2, B2, and C2, were extremely significant (p < 0.01), indicating that related factors have a high impact on TMP yield in wheat medium. The coefficient of determination R2 = 0.9943 indicates that the regression model has a good fit with the actual situation. The corrected quadratic model R2Adj = 0.9871 indicates that each factor in the regression model has a significant effect on TMP yield. R2Adj − R2Pred < 0.2 indicates that the regression model can fully explain the process, which means the regression model is effective and can be used to predict and analyze the influence of various factors on the TMP yield.

Table 4.
Response surface regression model analysis of variance.
3.4. Response Surface Interaction
Combined with the response surface regression analysis and regression equation, a three-dimensional surface diagram was drawn by Design-Expert 12.0 software to explore the influence of interactions between each of the two factors on the production of TMP (Figure 5). When the contour lines on the surface show a circle, it indicates that the pairwise interaction is weak and the influence is not significant. When the contour lines show an oval shape, it indicates that the interaction is strong and the influence is significant. As shown in Figure 5, the interaction between temperature and bottling capacity had an impact on the TMP yield, but the impact was not significant (Figure 5A). Similarly, the interaction between temperature and water addition had an impact on the TMP yield, whereas the impact was not significant (Figure 5B). Interestingly, the interaction between bottling capacity and water addition had a significant impact on the TMP yield (Figure 5C). The significance of the pairwise interaction in Figure 5 is consistent with the analysis results of the interaction item p-value in Table 4. When the graph shows a bulge trend, it indicates that the regression model has a maximum corresponding value. The optimal conditions for TMP production simulated in this study were as follows: temperature was 37.437 °C, bottling capacity was 99.389 g/250 mL, and water addition was 39.043 mL. Under these fermentation conditions, the maximum computed TMP production was 0.457 mg/g.

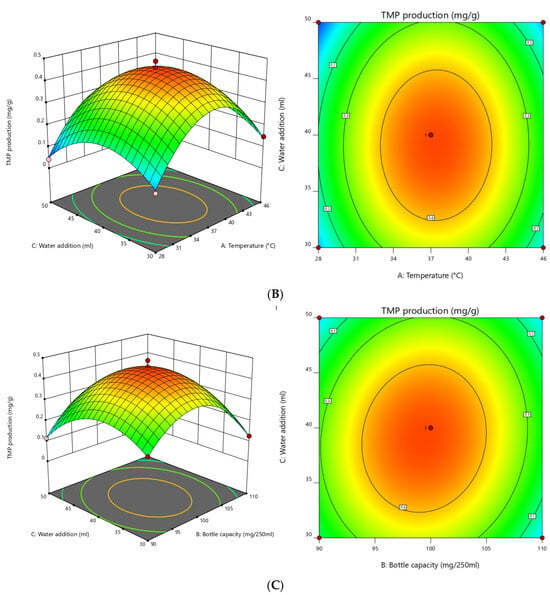
Figure 5.
Response surface and contour plots for TMP production: (A) effect of temperature and bottle capacity, (B) effect of temperature and water addition, and (C) effect of bottle capacity and water addition.
3.5. Verification Experiments
The role of verification experiments is to verify the reliability of the regression model in the actual situation. Considering the actual operation feasibility, the fermentation conditions were determined as follows: temperature 37 °C, bottling capacity 100 g/250 mL, and water addition 39 mL. Three repeated experiments were performed under these conditions, and the results are shown in Figure 6. After optimization, the average production of TMP was 0.446 ± 0.052 mg/g, which differed from the theoretical value by 0.011 mg/g, indicating that the established regression model is reliable and the regression equation can be used for fermentative TMP production.
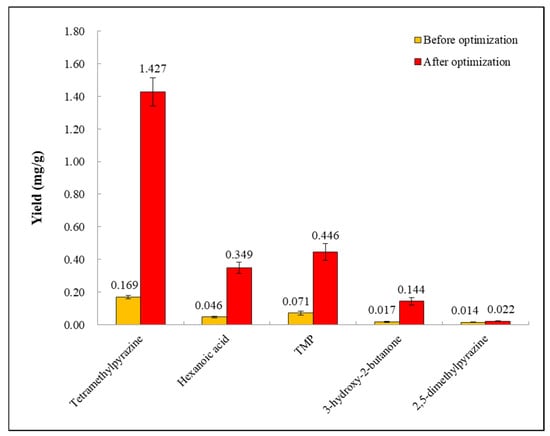
Figure 6.
The comparison of some volatile substances produced by LC-6 strain before and after fermentation optimization in wheat medium.
The TMP production before and after fermentation optimization were compared. TMP production before optimization was 0.071 ± 0.011 mg/g, whereas this value reached 0.446 ± 0.052 mg/g after optimization (Figure 6). Optimization increased the TMP production by 0.375 mg/g. Furthermore, the production of other volatile substances produced with TMP during fermentation had also been found to increase after fermentation optimization (Figure 6). Specifically, after optimization, the production of tetramethylpyrazine, hexanoic acid, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, and 2,5-dimethylpyrazine increased from 0.169 ± 0.011 mg/g, 0.046 ± 0.006 mg/g, 0.017 ± 0.005 mg/g, and 0.014 ± 0.002 mg/g to 1.621 ± 0.094 mg/g, 0.349 ± 0.033 mg/g, 0.144 ± 0.022 mg/g, and 0.022 ± 0.003 mg/g, respectively (Figure 6). The results indicated that optimization may promote the growth and metabolism of the LC-6 strain in the solid-state fermentation system.
4. Discussion
Alkylpyrazines are important flavor substances in food. Although most alkylpyrazines have a relatively low threshold, they have a great impact on food flavor and quality. TMP is a kind of alkylpyrazine with wide application prospects. This study aims to increase the yield of TMP by biosynthesis. Firstly, eight Bacillus strains were isolated from Daqu using traditional separation and purification methods. The fermentation products of these strains were detected by GC-MS, and three strains were found to produce TMP (Figure 3A). Among them, strain LC-6 (B. amyloliquefaciens) had a relatively higher TMP yield of 0.071 ± 0.011 mg/g (Figure 3). This yield was higher than that obtained by Liang et al. [4] using B. sonorensis for solid-state fermentation. Previous research showed that the main microorganisms producing TMP belong to Bacillus species [4,19]. Overall, it is reasonable to select a high-yield TMP-producing Bacillus strain as the initial strain in this study.
In the traditional solid-state fermentation process, temperature plays a crucial role in the performance of microorganisms [31], so it is necessary to select an appropriate temperature for fermentation experiments. Previous research showed that under low-temperature conditions, the growth and metabolism of microorganisms are not active, which leads to low metabolite production [30]. However, under high-temperature conditions, although microorganisms grow fast, harmful metabolites are formed along with the target metabolites, which in turn inhibit the growth of microorganisms, resulting in a reduction in target metabolites [30]. In addition, temperature can affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane, the activity of enzymes, and the production of secondary metabolites during fermentation [29,32]. Consistent with the results in this study, the yield of TMP was not high under low-temperature conditions, which might be caused by the enzyme activity and the fluidity of the cell membrane being reduced (Figure 4A). Wu et al. [33] reported that more pyrazines were produced when the fermentation temperature reached 50 °C and 60 °C, which contradicts the results in this study. This may be due to there being multiple microorganisms in the fermentation medium used by Wu et al. [33], which have different exchanges of microbial interaction at different temperatures [34]. Under a high-temperature condition, the exchange of microbial interaction can promote the production of pyrazines [34]. In this study, there was only one Bacillus strain and no exchange of microbial interaction, so it reached the highest yield at 37 °C in wheat medium (Figure 4A). Therefore, 28 °C, 37 °C, and 46 °C were selected for response surface analysis to determine the optimal temperature.
Previous research found that a decrease in dissolved oxygen in the substrate can lead to the abnormality of metabolites [35]. However, although excessive oxygen can satisfy the growth conditions of microorganisms, it may not achieve the purpose of increasing metabolite production [35,36,37]. In solid-state fermentation, the oxygen content in the fermentation system is affected by bottling capacity. Therefore, the effect of bottling capacity on TMP production was investigated in this study. As a result, bottling capacities of 90 g/250 mL, 100 g/250 mL, and 110 g/250 mL were selected for response surface analysis to determine the optimal bottling capacity (Figure 4B).
In a solid-state fermentation system, too low water content may affect the growth of microorganisms, while too high water content causes particles to cake. Particle clumping interferes with microbial respiration, resulting in poor growth of microorganisms [38]. This may be the reason for the high water content generating low TMP yield in this study (Figure 4C). Meanwhile, studies have shown that too low water content will lead to too low nutrient dissolution and high water content will hinder the efficiency of enzymes [32]. In addition, Liu et al. [39] reported that water content and acidity are the driving factors of microbial evolution. Therefore, to ensure the normal growth and metabolism of microorganisms, appropriate water addition should be applied to meet the requirements of TMP production. Finally, water additions of 30 mL, 40 mL, and 50 mL were selected for response surface analysis.
As we know, response surface analysis is a clear, accurate, and widely used method. The response surface method is usually used to optimize medium composition and fermentation conditions so as to increase the yield of various enzymes, exopolysaccharides, amino acids, and other metabolites produced by Bacillus [40,41]. In this study, the central point of the response surface and the level of each factor were determined by single-factor experiments, and a three-dimensional surface diagram was drawn by Design-Expert 12.0 software (Figure 5). The diagram can directly reflect the influence of various factors on the response value so as to find the optimal parameters and their interactions [42]. The greater the curvature of the convex diagram, the more significant the interaction between the two factors [43]. In this study, the interaction between bottling capacity and water addition had a significant impact on the TMP yield (Figure 5C), which coincided with the analysis results in Table 4. By analyzing the three single factors in this study, it can be found that the bottling capacity was composed of wheat and water addition (the two constituted the wheat solid-state fermentation medium), and there was indeed a possibility of interaction between the two. Therefore, the above results might indicate that the regression model and analysis constructed in this study are reliable.
The Box–Behnken design was used to optimize the solid-state fermentation conditions to increase TMP production (Table 1 and Table 2). The three factors influenced TMP production in the following order of significance: water addition > temperature > bottle capacity (Table 4). After optimizing each factor, the predicted TMP production was 0.457 mg/g under the optimal fermentation conditions: temperature of 37.437 °C, bottle capacity amount of 99.389 g/250 mL, and water addition amount of 39.043 mL (Figure 5). Considering the feasibility of practical operation, the temperature of 37 °C, the bottling capacity of 100 g/250 mL, and the water addition of 39 mL were selected as the actual fermentation conditions. Under these conditions, three repeated experiments were performed, and the final TMP yield obtained was 0.446 ± 0.052 mg/g, which was 0.375 mg/g higher than that under initial fermentation conditions before optimization (Figure 6). Optimizing the solid-state fermentation conditions significantly affected TMP production. Using B. amyloliquefaciens as the fermentation strain, the yield of TMP was higher than the yield (0.122 mg/g) achieved by Ming et al. [21] using B. licheniformis under optimizing fermentation conditions. The value was increased by 0.324 ± 0.052 mg/g. Different fermentation strains combined with different fermentation conditions had significant effects on TMP yield.
As a source of food aroma, researchers have been focusing on uncovering the generation mechanism of TMP and developing new strategies for promoting TMP formation. This study provides information about what microorganisms may participate in the formation of TMP in traditional fermented foods and proposes a possibility for higher-efficiency production of TMP by using microorganisms. Biosynthetic methods with high yield, safety, and low environmental pollution to produce TMP are needed for a wider range of applications in the future. However, there is still a need to strengthen and deepen awareness of the formation of TMP and other alkylpyrazines in fermented foods to obtain high-quality functional foods and beverages. Furthermore, attention should also be paid to the analysis of the functions of various genes in the TMP biosynthesis pathways, which will contribute to the construction of high-yield TMP engineering strains and lay a certain theoretical foundation for effectively controlling the production and application of TMP in the future.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a strain with a relatively high TMP yield was found by GC-MS from eight previously isolated Bacillus strains, which was identified as B. amyloliquefaciens LC-6. In order to increase the yield of TMP produced by solid-state fermentation of the LC-6 strain in wheat medium, the effects of temperature, bottling capacity, and water addition on TMP production were analyzed through single-factor experiments. Combined with Box–Behnken design and response surface analysis, a reliable regression model was established, and the optimal fermentation conditions (combined with reality) were a temperature of 37 °C, a bottle capacity of 100 g/250 mL, and the addition of 39 mL of water. The results obtained by verification experiments are consistent with the predicted value, which proves the reliability of the regression model. The highest TMP yield obtained by experiments was 0.446 ± 0.052 mg/g, which was about six times as high as the yield obtained before optimization. Furthermore, the yields of tetramethylpyrazine, hexanoic acid, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, and 2,5-dimethylpyrazine were also increased after optimization. This study provides a reference for TMP solid-state fermentation and its subsequent industrial application by optimizing the solid-state fermentation conditions with wheat medium.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and W.Y.; methodology, X.L.; software, H.G. and A.A.B.; validation, W.Y. and H.G.; formal analysis, X.L. and W.Y.; investigation, W.Y., H.G. and A.A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L. and W.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and X.L.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, X.L.; funding acquisition, J.L., X.L. and W.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (No. 2022NSFSC1782), the Sichuan Province Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars (2022), the Industry–University–Research Collaboration project of Wuliangye Co., Ltd. (No. CXY2020ZR02), and the Innovation Fund of Postgraduate, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Y20220 91).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jun Liu has received research grants from Company Wuliangye Co., Ltd. The funding imformation: the Industry–University–Research Collaboration project of Wuliangye Co., Ltd. (No. CXY2020ZR02). However, there are no conflict of interest in this work.
References
- Yu, H.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhou, W. Control strategies of pyrazines generation from Maillard reaction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Tong, J.; Xu, Y. An alkylpyrazine synthesis mechanism involving L-threonine-3-dehydrogenase describes the production of 2,5-dimethylpyrazine and 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine by Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01807-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.L.; Bories, G.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Flachowsky, G.; Gropp, J.; Kolar, B.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pyrazine derivatives including saturated ones belonging to chemical group 24 when used as flavourings for all animal species. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Dirndorfer, S.; Somoza, V.; Krautwurst, D.; Lang, R.; Hofmann, T. Metabolites of Key Flavor Compound 2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine in Human Urine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15134–15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Nie, Y.; Xu, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Pyrazines and Their Perceptual Interactions in Soy Sauce Aroma Type Baijiu. Foods 2021, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-F.; Xu, Y. Comparison of pyrazine compounds in seven Chinese liquors using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction and GC-nitrogen phosphourus detection. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibamoto, T.; Akiyama, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Enomoto, Y.; Masuda, H. A study of pyrazine formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Du, M.; Wu, C.; Xu, X. Mechanism of Carbon Skeleton Formation of 2,3,5-Trimethylpyrazine via a Conversion Reaction between Methylglyoxal and Glyoxal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Guo, G.; Chen, X.; Lu, P.; Zhang, K. Advances in synthesis of 2, 3, 5-trimethylpyrazine. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2014, 43, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Qin, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; et al. Mechanism of Enhancing Pyrazines in Daqu via Inoculating Bacillus licheniformis with Strains Specificity. Foods 2023, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Shi, D.; Sun, J.; Li, A.; Sun, B.; Zhao, M.; Chen, F.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; et al. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Gujinggong Chinese Baijiu by gas chromatography-olfactometry, quantitative measurements, and sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Optimization and validation of a head space solid-phase microextraction-arrow gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method using central composite design for determination of aroma compounds in Chinese liquor (Baijiu). J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Song, S.; Dong, F.; He, Z. Efficient degradation of 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine by catalytic ozonation over MnOx supported on biochar derived from waste tea leaves. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-A.; Yan, C.-M.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.-Q.; Li, T.; Sun, B.-W. Three new cocrystals derived from liquid pyrazine spices: X-ray structures and Hirshfeld surface analyses. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 5745–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Ren, C.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, X.-S. Pyrazines in food samples: Recent update on occurrence, formation, sampling, pretreatment and analysis methods. Food Chem. 2023, 430, 137086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancker, F.V.; Adams, A.; Kimpe, N.D. Formation of pyrazines in Maillard model systems of lysine-containing dipeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 8, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.L. The Study of 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine Biosynthetic Pathway by Bacillus subtilis and Construction of a High-Yield Strain; Jiangnan University: Wuxi, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, D.; Yao, X. Optimization of flavor components fermentation conditions of Bacillus licheniformis from Daqu by central composite design. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2015, 36, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Liu, P.; Che, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Characterization of odor components of Pixian Douban (broad bean paste) by aroma extract dilute analysis and odor activity values. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, G.; Mikulski, D.; Pielech-Przybylska, K. Pyrazines Biosynthesis by Bacillus Strains Isolated from Natto Fermented Soybean. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Ma, Y.; Xie, M.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, D. Rectal bacteria produce sex pheromones in the male oriental fruit fly. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Xu, F.; Tan, L.; Wu, H.; Chu, Z.; Wang, Q. Optimization of enzymatic process for vanillin extraction using response sur-face methodology. Molecules 2012, 17, 8753–8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, B.; Li, P.; Su, J. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Biocatalytic Conversion of Decanoic Acid to Trans-2-Decenoic Acid. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X. The development of a Panax notoginseng medicinal liquor processing technology using the response surface method and a study of its antioxidant activity and its effects on mouse melanoma B16 cells. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4251–4264. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, A.; Feng, X.; Sheng, Y.; Song, Z. Optimization of the Artemisia Polysaccharide Fermentation Process by Aspergillus niger. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 842766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Zou, W. Wheat Qu and Its Production Technology, Microbiota, Flavor, and Metabolites. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Lin, S.K.C.; Koutinas, A.; Wang, R.; Dorado, P.; Webb, C. A wheat biorefining strategy based on solid-state fermentation for fermentative production of succinic acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8310–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L. Characterization of feruloyl esterase from Klebsiella oxytoca Z28 and its ap-plication in the release of ferulic acid from de-starching wheat bran. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboué, Q.; Rébufa, C.; Hamrouni, R.; Roussos, S.; Bombarda, I. Statistical approach to evaluate effect of temperature and moisture content on the production of antioxidant naphtho-gamma-pyrones and hydroxycinnamic acids by Aspergillus tubingensis in solid-state fermentation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Ahluwalia, V.; Saran, S.; Kumar, J.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.R. Recent developments on solid-state fermentation for production of microbial secondary metabolites: Challenges and solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Ashraf, S.A.; Khan, S.; Alshammari, E.; Awadelkareem, A.M. Effect of pH, temperature and incubation time on cordycepin production from Cordyceps militaris using solid-state fermentation on various substrates. CYTA J. Food 2017, 15, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Kumar, J.; Ahluwalia, V. A critical review on current strategies and trends employed for removal of inhibitors and toxic materials generated during biomass pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Daqu microbiota adaptability to altered temperature determines the formation of characteristic com-pounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 385, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Volatile organic compound-mediated antifungal activity of Pichia spp. and its effect on the metabolic profiles of fermentation communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02992-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Xiang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, C. High-level production of microbial prodigiosin: A review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çalík, P.; Çalík, G.; Özdamar, T.H. Oxygen transfer effects in serine alkaline protease fermentation by Bacillus licheniformis: Use of citric acid as the carbon source. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1997, 23, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hugenholtz, J.; Chen, J.; Lun, S.Y. Enhancement of pyruvate production by Torulopsis glabrata using a two-stage oxygen supply control strategy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 60, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singhania, R.R.; Patel, A.K.; Soccol, C.R.; Pandey, A. Recent advances in solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R.; Han, S.; Hou, J.; Pan, C. Dynamic changes and correlations of microbial communities, physicochemical properties, and volatile metabolite during Daqu fermentation of Taorong-type Baijiu. LWT 2023, 173, 114290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, G.; Krishnan, S. Enhanced biomass production study on probiotic Bacillus subtilis SK09 by medium optimization using response surface methodology. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8078–8084. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, R.; Singh, R. Contemporaneous Production of Amylase and Protease through CCD Response Surface Methodology by Newly Isolated Bacillus megaterium Strain B69. Enzym. Res. 2014, 2014, 601046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, X. Optimization of the extraction of total flavonoids from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi using the response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, S.W.; Tang, J.; Gu, X. Optimization of extraction process of rude polysaccharides from boat-fruited sterculia seeds by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).