Effective Elastic Modulus of Wavy Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approach
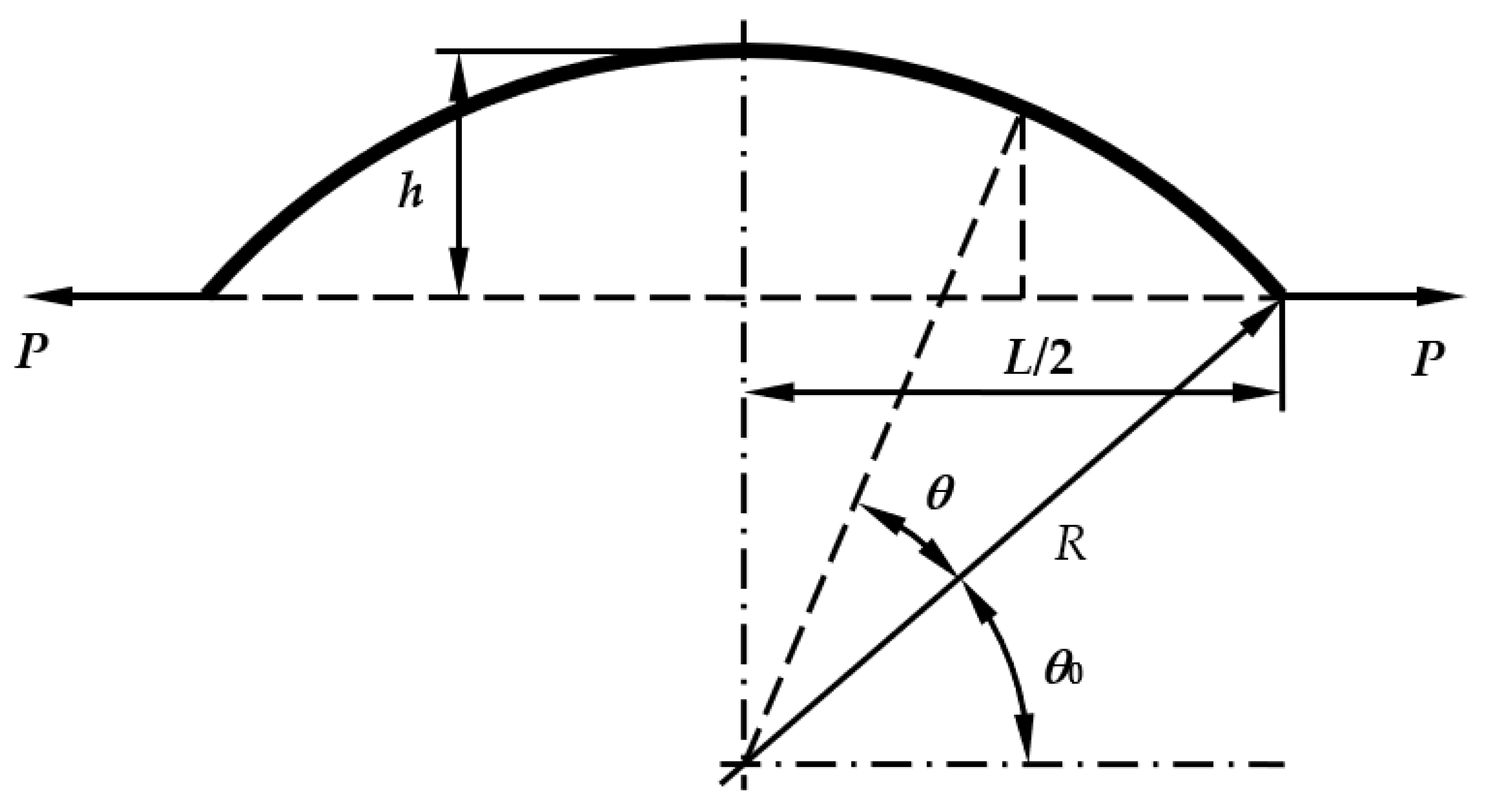
2.1. Analytical Model
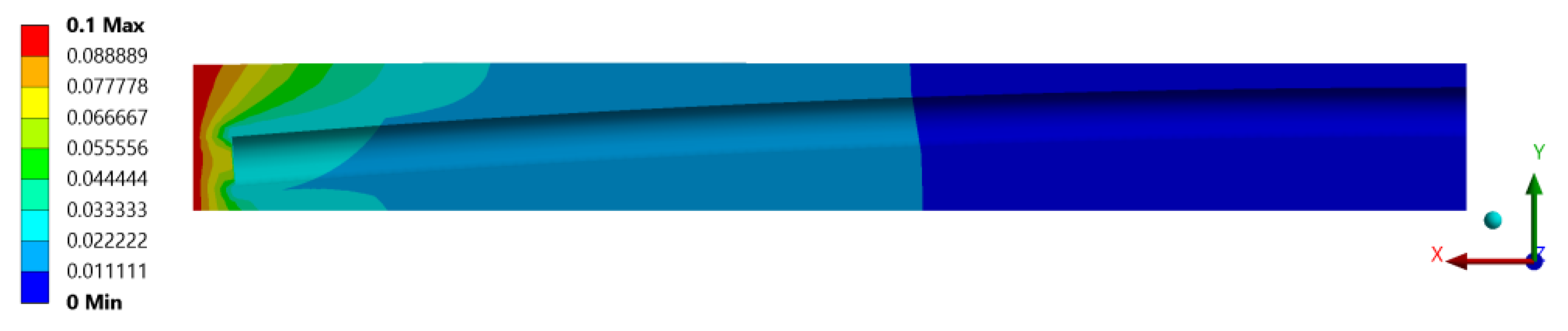
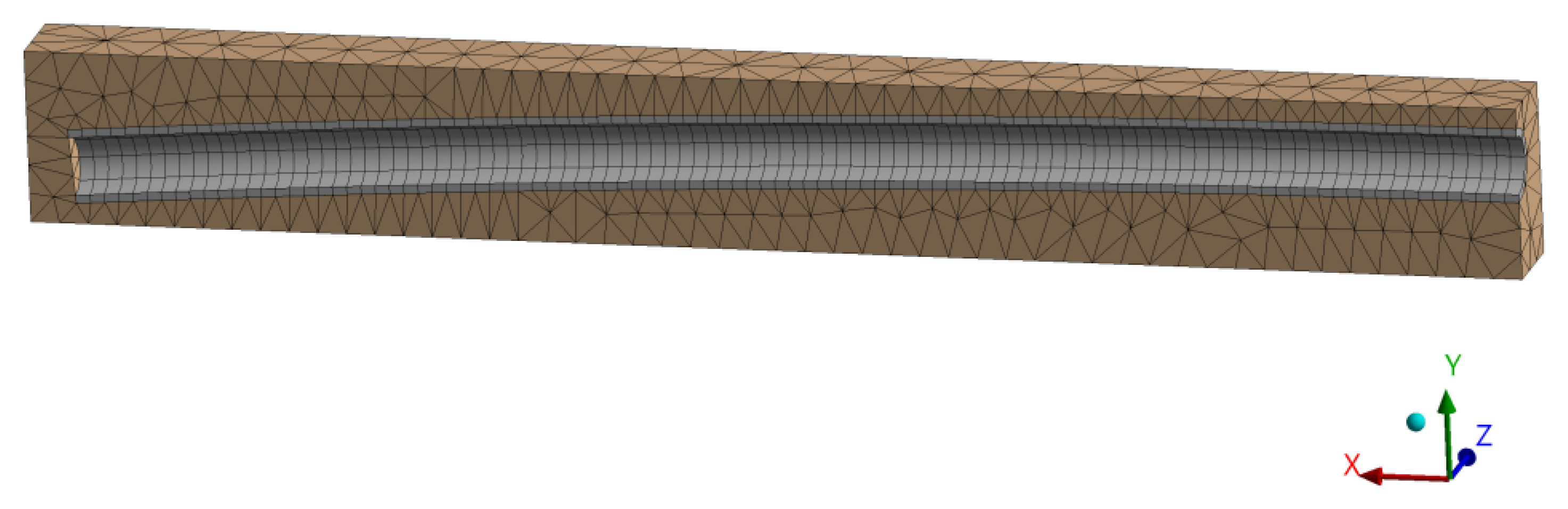
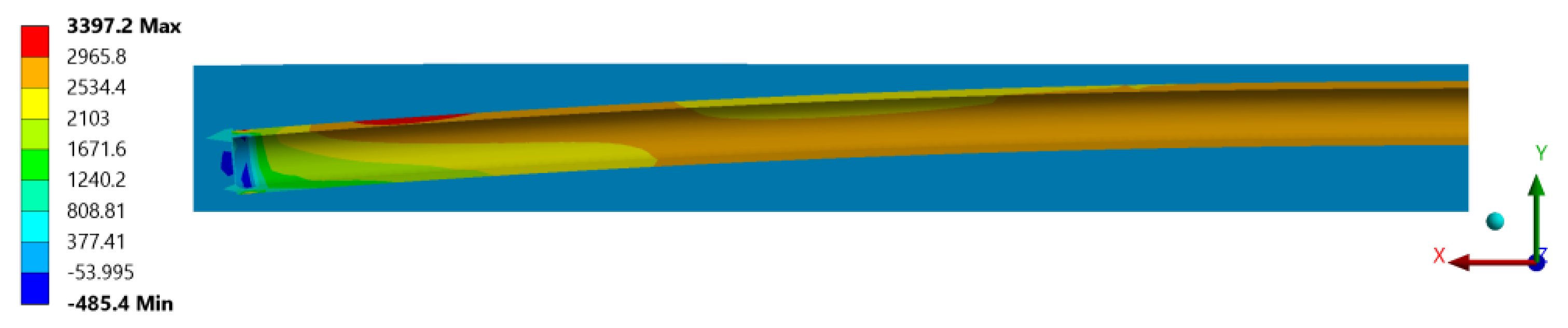
2.2. Finite Element Analysis
2.3. Monte Carlo Simulation
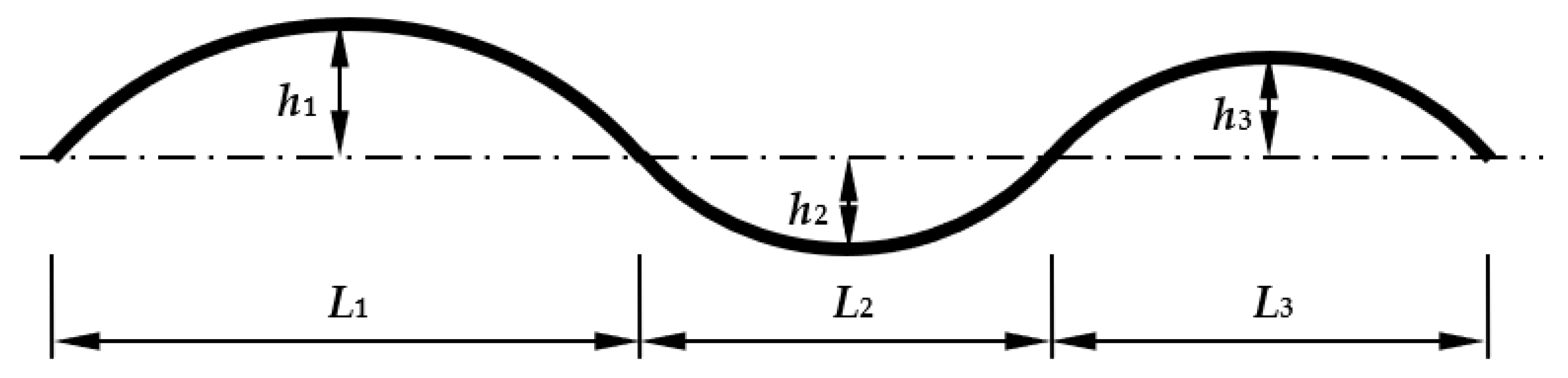
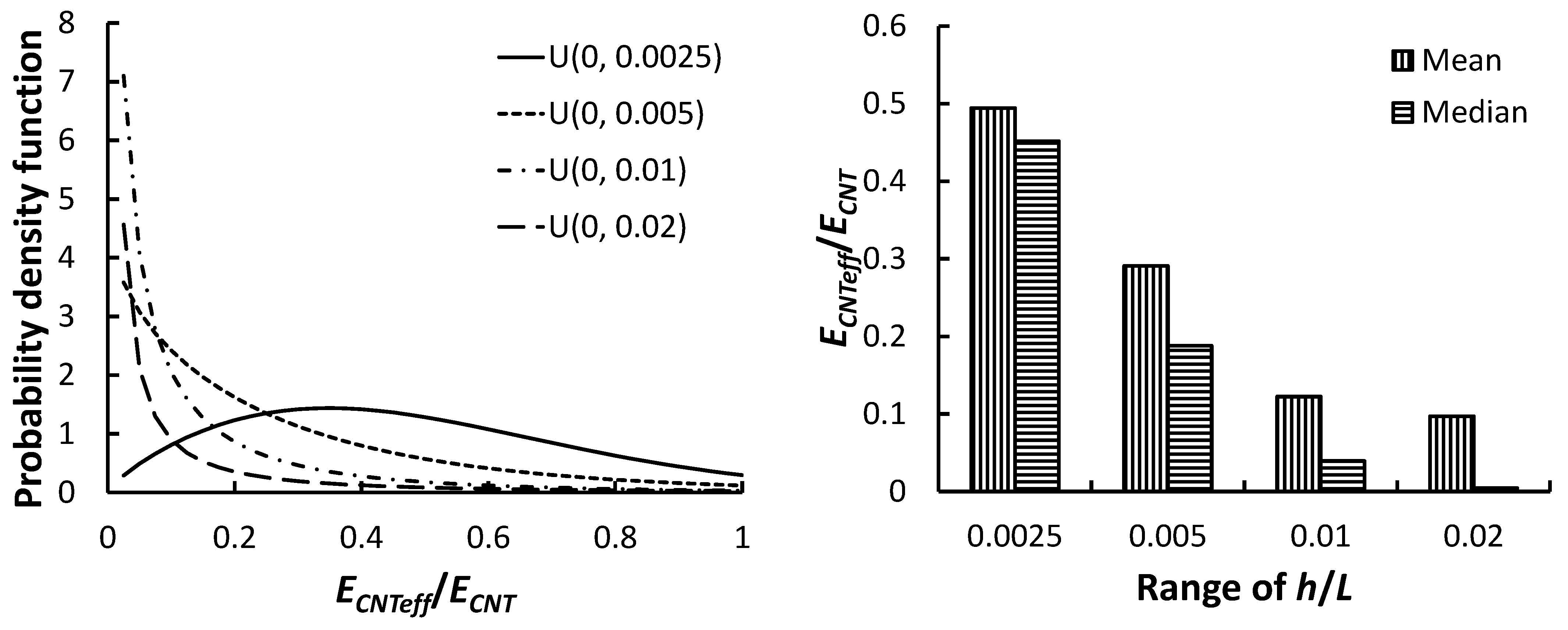
2.4. Waviness
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Curvature
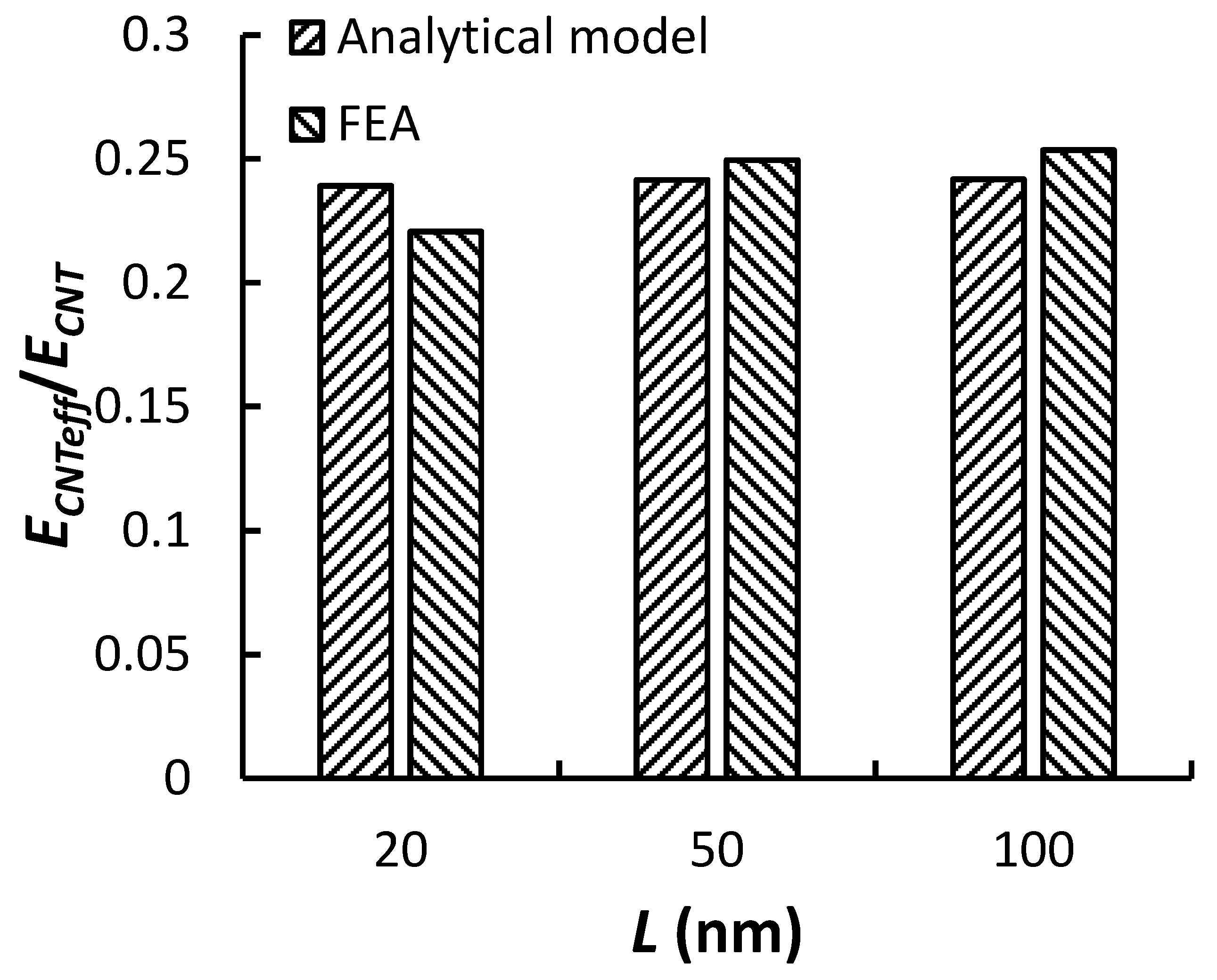
3.2. Results from FEA
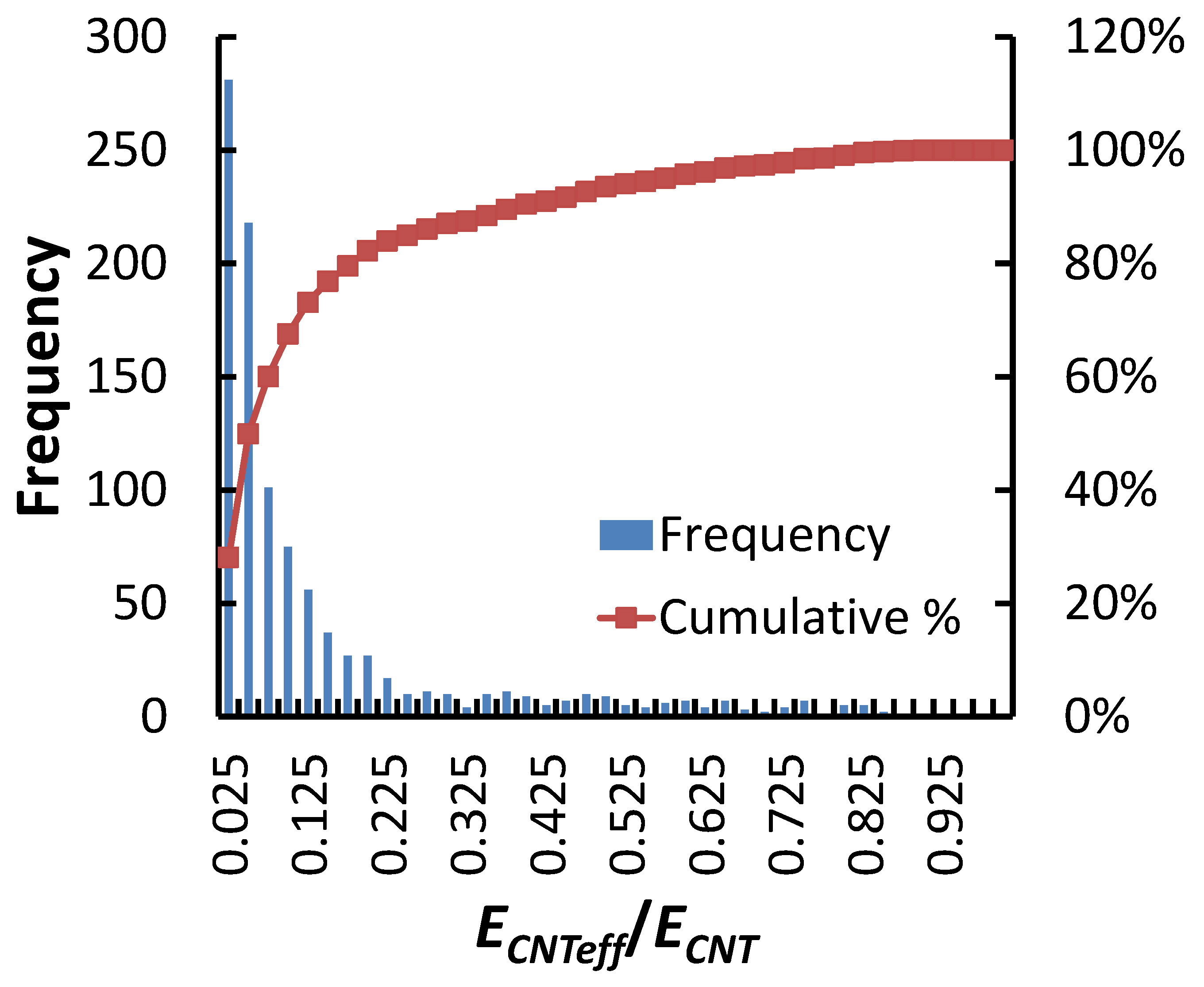
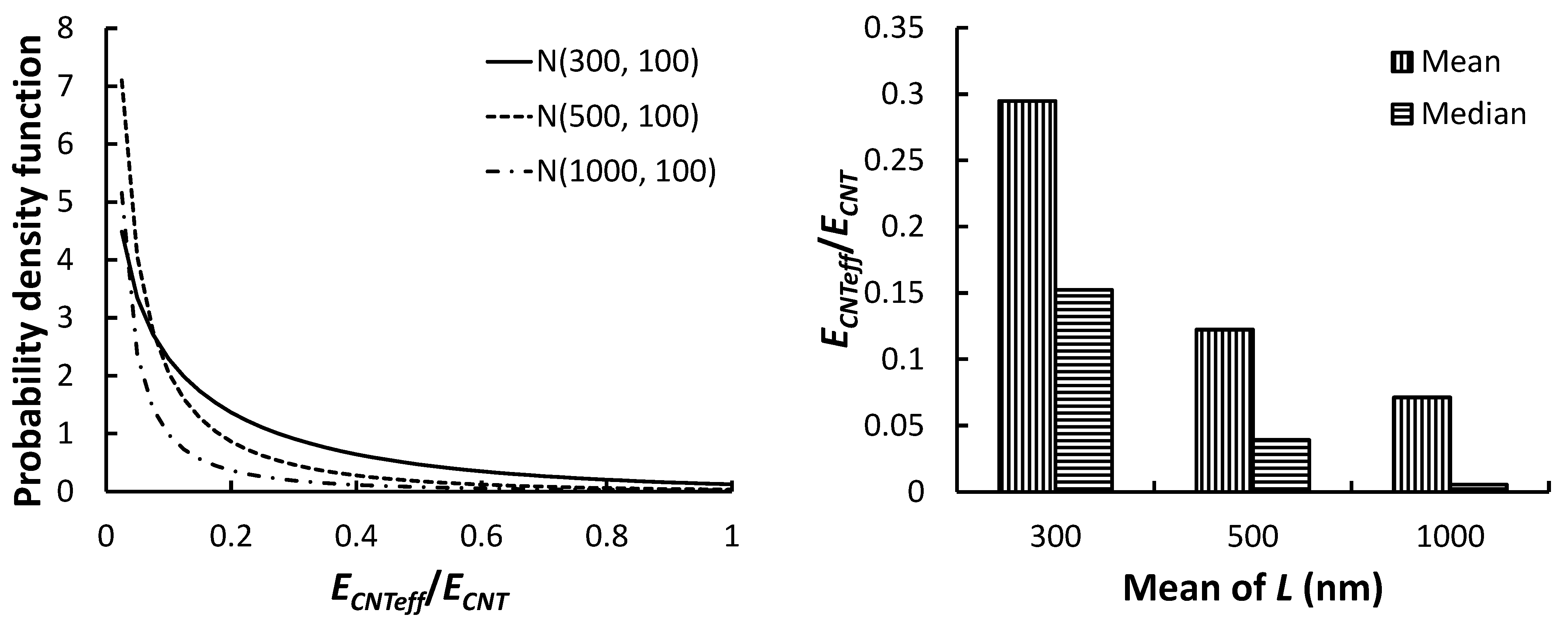
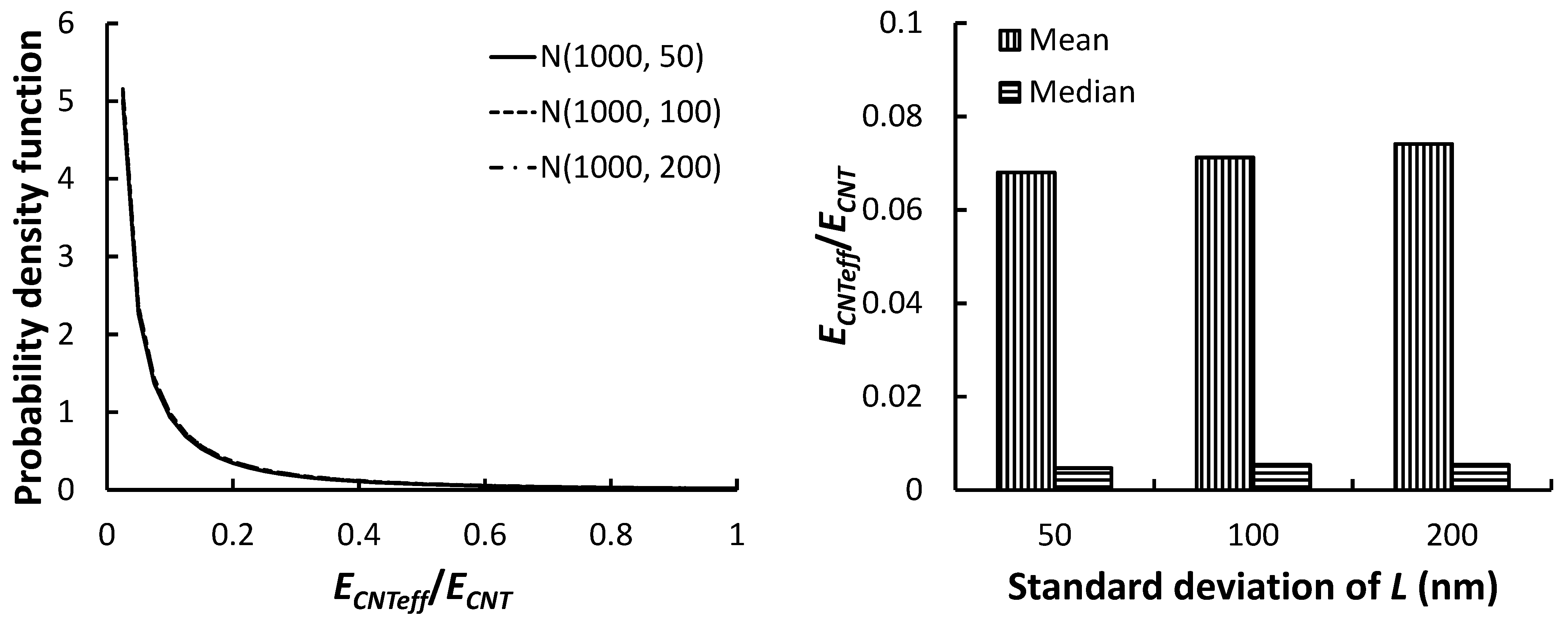
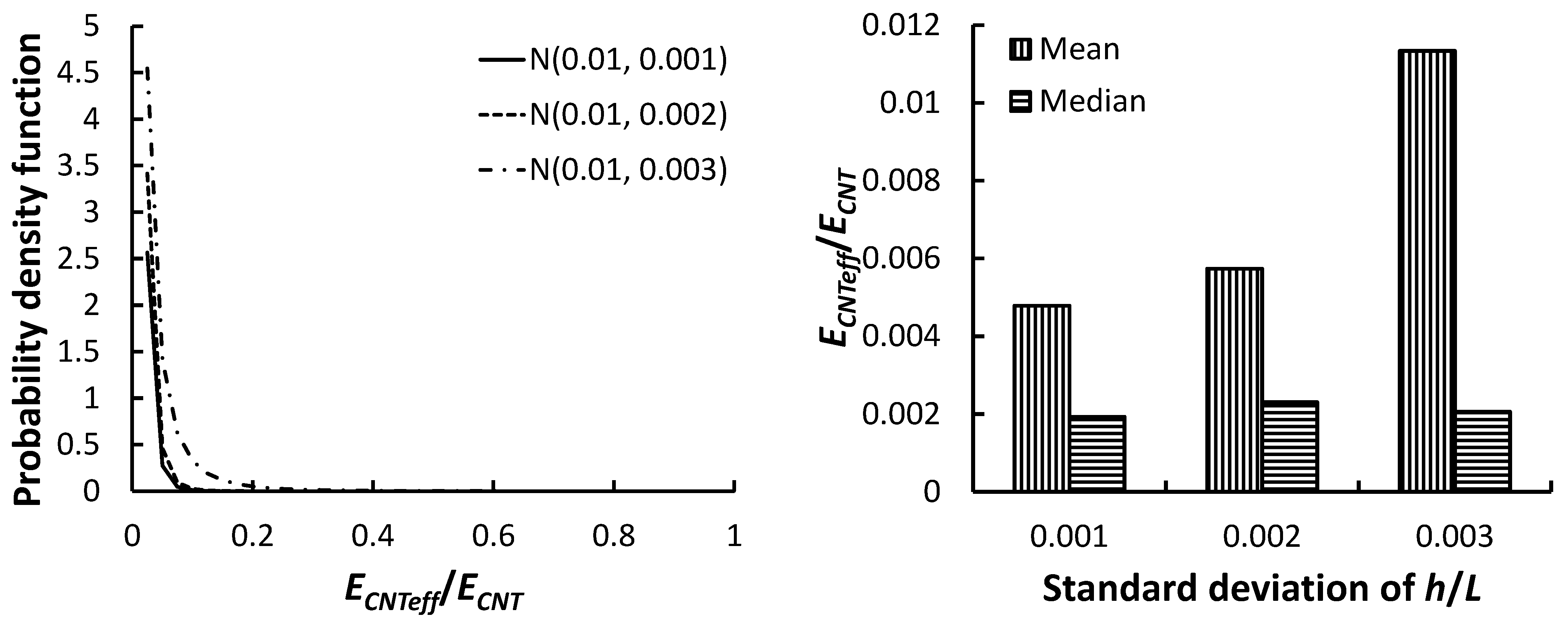
3.3. Effect of Statistical Distributions
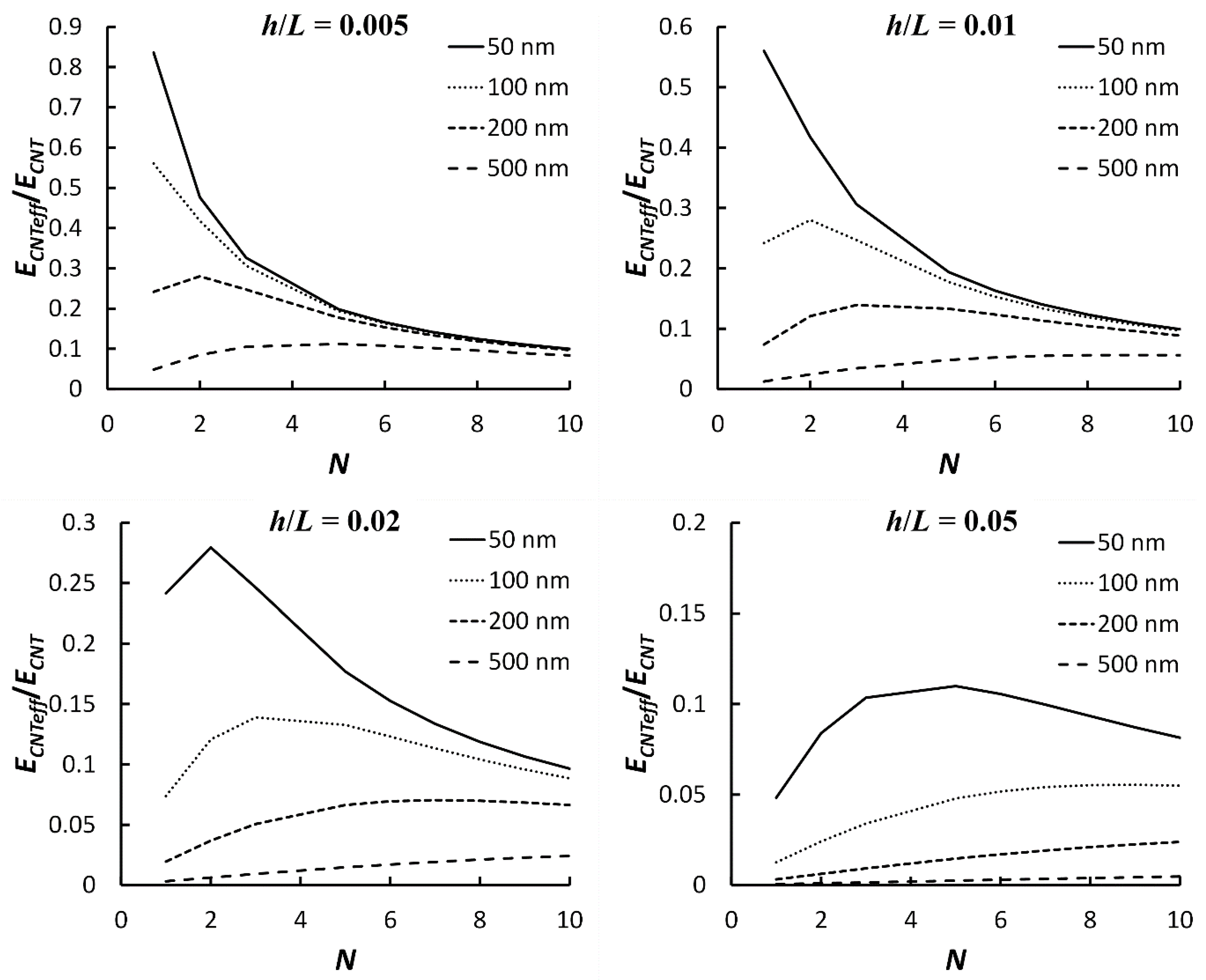
3.4. Effect of Waviness
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Set | Simulation | h/L | SWCNT Length (nm) | β | η | ECNTeff/ECNT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | ||||||
| 1 | 1 | U(0, 0.0025) | N(500, 100) | 1.77307 | 0.55544 | 0.49432 | 0.45171 |
| 2 | U(0, 0.005) | N(500, 100) | 0.92055 | 0.27978 | 0.29086 | 0.18789 | |
| 3 | U(0, 0.01) | N(500, 100) | 0.56502 | 0.07486 | 0.12238 | 0.03913 | |
| 4 | U(0, 0.02) | N(500, 100) | 0.31703 | 0.01327 | 0.09695 | 0.00418 | |
| 5 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 100) | 0.35652 | 0.01508 | 0.07119 | 0.00539 | |
| 6 | U(0, 0.01) | N(300, 100) | 0.75143 | 0.24804 | 0.29487 | 0.15230 | |
| 7 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 50) | 0.34914 | 0.01340 | 0.06799 | 0.00469 | |
| 8 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 200) | 0.35343 | 0.01524 | 0.07411 | 0.00540 | |
| 2 | 1 | N(0.005, 0.001) | N(500, 100) | 1.40284 | 0.05015 | 0.04570 | 0.03862 |
| 2 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(500, 100) | 0.63766 | 0.00343 | 0.00478 | 0.00193 | |
| 3 | N(0.02, 0.001) | N(500, 100) | 1.00000 | 0.00180 | 0.00180 | 0.00125 | |
| 4 | N(0.01, 0.002) | N(500, 100) | 0.63626 | 0.00410 | 0.00574 | 0.00230 | |
| 5 | N(0.01, 0.003) | N(500, 100) | 0.45245 | 0.00463 | 0.01134 | 0.00206 | |
| 6 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(300, 100) | 0.93528 | 0.03499 | 0.03609 | 0.02365 | |
| 7 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 100) | 1.00000 | 0.00033 | 0.00033 | 0.00023 | |
| 8 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 50) | 1.00000 | 0.00033 | 0.00033 | 0.00023 | |
| 9 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 200) | 1.00000 | 0.00033 | 0.00033 | 0.00023 | |
| 3 | 1 | U(0, 0.0025) | U(300, 700) | 1.7050 | 0.5424 | 0.48384 | 0.43747 |
| 2 | U(0, 0.005) | U(300, 700) | 0.8992 | 0.2718 | 0.28611 | 0.18081 | |
| 3 | U(0, 0.01) | U(300, 700) | 0.5054 | 0.0827 | 0.16220 | 0.04006 | |
| 4 | U(0, 0.02) | U(300, 700) | 0.3146 | 0.0124 | 0.09352 | 0.00387 | |
| 5 | U(0, 0.01) | U(100, 500) | 0.7780 | 0.2521 | 0.29160 | 0.15742 | |
| 6 | U(0, 0.01) | U(800, 1200) | 0.3289 | 0.0131 | 0.08298 | 0.00431 | |
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethune, D.S.; Kiang, C.H.; Devries, M.S.; Gorman, G.; Savoy, R.; Vazquez, J.; Beyers, R. Cobalt-catalyzed growth of carbon nanotubes with single-atomic-layerwalls. Nature 1993, 363, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thostenson, E.T.; Chou, T.-W. On the elastic properties of carbon nanotube-based composites: Modelling and characterization. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Kao, C.-C.; Young, R.J. The Effective Young’s Modulus of Carbon Nanotubes in Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.-L.; Feng, X.-Q.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hwang, K.-C.; Gao, H. The Effect of Nanotube Waviness and Agglomeration on the Elastic Property of Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thostenson, E.T.; Chou, T.-W. Effect of nanotube waviness on the electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, J.; Jürgens, J.-P.; Kuhn, E.; Ploshikhin, V. Effects of curvature and alignment of carbon nanotubes on the electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube-reinforced polymers investigated by mesoscopic simulations. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 53, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.T.; Bradshaw, R.D.; Brinson, L.C. Fiber waviness in nanotube-reinforced polymer composites—I: Modulus predictions using effective nanotube properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, R.D.; Fisher, F.T.; Brinson, L.C. Fiber waviness in nanotube-reinforced polymer composites—II: Modeling via numerical approximation of the dilute strain concentration tensor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, G.P.; Weng, G.J. Average stress in the matrix and effective moduli of randomly oriented composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1986, 27, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudlou, M.A.; Barbaz Isfahani, R.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Sadighi, M. Effect of interphase, curvature and agglomeration of SWCNTs on mechanical properties of polymer-based nanocomposites: Experimental and numerical investigations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginga, N.J.; Chen, W.; Sitaraman, S.K. Waviness reduces effective modulus of carbon nanotube forests by several orders of magnitude. Carbon 2014, 66, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.H.; Luo, R.Y.; Bai, S.L.; Wang, J. Prediction of effective moduli of carbon nanotube–reinforced composites with waviness and debonding. Compos. Struct. 2009, 87, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Narh, K.A. Numerical simulation of the effect of nanotube orientation on tensile modulus of carbon-nanotube-reinforced polymer composites. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, H. Buckling of Carbon Nanotubes: A State of the Art Review. Materials 2011, 5, 47–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Lim, C.W.; Li, S. Nonlinear in-plane thermal buckling of rotationally restrained functionally graded carbon nanotube reinforced composite shallow arches under uniform radial loading. Appl. Math. Mech. 2022, 43, 1821–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Seki, Y.; Kimura, H.; Sakurai, S.; Yumura, M.; Hata, K.; Futaba, D.N. Diameter control of single-walled carbon nanotube forests from 1.3–3.0 nm by arc plasma deposition. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, J.A.; Hároz, E.H.; Ihly, R.; Gui, H.; Blackburn, J.L.; Simpson, J.R.; Lam, S.; Hight Walker, A.R.; Doorn, S.K.; Zheng, M. Isolation of >1 nm Diameter Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube Species Using Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5377–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.C.; Lambin, P. Electronic structure of carbon nanotubes with chiral symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, R15037–R15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Chhowalla, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Sesti, F. Single-walled carbon nanotubes are a new class of ion channel blockers. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50212–50216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Lian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Iijima, S.; Zhou, L.; Yue, K.T.; Zhang, S. Mass-production of single-wall carbon nanotubes by arc discharge method11This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 29671030. Carbon 1999, 37, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinno, M.; Ando, Y.; Bandow, S.; Fan, J.; Yudasaka, M.; Iijima, S. Raman scattering study for heat-treated carbon nanotubes: The origin of ≈1855cm−1 Raman band. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 418, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Raman spectroscopy for carbon nanotube applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S. Controlling the Diameter of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Improving the Dispersion of the Uniform Catalyst Nanoparticles on Substrate. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, H.; Picher, M.; Andrieux-Ledier, A.; Fossard, F.; Michel, T.; Kozawa, A.; Maruyama, T.; Anglaret, E.; Loiseau, A.; Jourdain, V. Unveiling the Evolutions of Nanotube Diameter Distribution during the Growth of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3081–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Set | Simulation | h/L | SWCNT Length (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | U(0, 0.0025) | N(500, 100) |
| 2 | U(0, 0.005) | N(500, 100) | |
| 3 | U(0, 0.01) | N(500, 100) | |
| 4 | U(0, 0.02) | N(500, 100) | |
| 5 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 100) | |
| 6 | U(0, 0.01) | N(300, 100) | |
| 7 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 50) | |
| 8 | U(0, 0.01) | N(1000, 200) | |
| 2 | 1 | N(0.005, 0.001) | N(500, 100) |
| 2 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(500, 100) | |
| 3 | N(0.02, 0.001) | N(500, 100) | |
| 4 | N(0.01, 0.002) | N(500, 100) | |
| 5 | N(0.01, 0.003) | N(500, 100) | |
| 6 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(300, 100) | |
| 7 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 100) | |
| 8 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 50) | |
| 9 | N(0.01, 0.001) | N(1000, 200) | |
| 3 | 1 | U(0, 0.0025) | U(300, 700) |
| 2 | U(0, 0.005) | U(300, 700) | |
| 3 | U(0, 0.01) | U(300, 700) | |
| 4 | U(0, 0.02) | U(300, 700) | |
| 5 | U(0, 0.01) | U(100, 500) | |
| 6 | U(0, 0.01) | U(800, 1200) |
| Effective Modulus, ECNTeff/ECNT | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| L (nm) | Analytical Model | FEA | Relative Difference |
| 20 | 0.2390 | 0.2205 | 8.37% |
| 50 | 0.2414 | 0.2495 | −3.24% |
| 100 | 0.2417 | 0.2534 | −4.63% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, C. Effective Elastic Modulus of Wavy Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C 2023, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9020054
Dong C. Effective Elastic Modulus of Wavy Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C. 2023; 9(2):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Chensong. 2023. "Effective Elastic Modulus of Wavy Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes" C 9, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9020054
APA StyleDong, C. (2023). Effective Elastic Modulus of Wavy Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. C, 9(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/c9020054







