Abstract
The past two decades have seen considerable attention given to chemical sensing due to its quick, reproducible, and accurate results. These are extensively used for the detection of cations and anions in different environmental matrices. Organic-molecule-based sensors have proved to be a great promising tool in determining target species. This communication demonstrates the use of triphenylether derivatives (L1–L4) as receptors for the sensing of cations and anions, using voltammetry as a sensing tool. The effect of the oxidative/reductive nature of the ionophores and, hence, their selectivity behavior was studied in MeCN and MeOH solvents. Three receptors (L2–L4) responded selectively towards cyanide ions following the intramolecular charge-transfer mechanism, while sensing in the case of L1 was not studied because it lacked a proper cavity size.
1. Introduction
Analytical techniques that quickly screen organic contaminants with minimal sample processing are essential for assessing their environmental impact. Chemical sensors play an increasingly important role in environmental monitoring, and recent technological advancements make chemical sensing equipment easier to use. This communication focuses on the development of highly selective, sensitive, low-cost, stable, and resilient ion sensors. The development of a receptor for the selective detection of analytes such as cations, anions, gases, proteins, and charged species is challenging, as it requires several factors such as selectivity, sensitivity, time, and portability for the receptor. Apart from these parameters, the proper arrangement of heteroatoms/substituents in a given molecule plays an important role in defining the cavity of a receptor [1,2].
A transducer (e.g., optical or electrochemical), the other basic unit of a sensing system responsive to the presence of a target analyte, can then be enabled for recognition and sensing. In chemistry, photometric transducers have dominated the analytical procedures by the use of spectroscopic and colorimetric approaches. The basis of these transducers is built around electrochemical principles. The electrochemical transducers have received great attention in determining the oxidative/reductive behavior of the receptor and its complexation with the analyte. Thus, the widespread use of electrochemical techniques (potentiometry, amperometry, and voltammetry) stems from their real-life potential applicability, specificity, and affordable commercial availability [3,4,5].
In the receptor category, the N-H bond is widely studied due to its great ability in anion sensing. A variety of systems mainly containing urea and amide linkages have been extensively reviewed [6,7]. A large number of transducers having ferrocene integrated with amine [8,9], amide [10,11], amidine [12], and calix [4] arene-amine/imine [13] have also been extensively studied.
Apart from the N-H redox reactions, molecules containing N-H linkages are widely used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Azo dyes with aromatic amines are used in the dyeing industries. Compounds bearing N-H bonds are used for the removal of CO2 and H2S gas from industrially dispatched masses. In addition, amine-containing molecules are vastly used in pharmaceutical and agricultural chemical companies [14,15]. Antihistamines and chloropheniramine have the potential to help against insect bites, allergies, hay fever, etc. Keeping the N-H behavior in mind, here, we report four triphenylether receptors with varying electronic environments around the nitrogen atom.
It is well known that solvents play an important role in biology and chemistry, and the prediction of the solvent’s effects would be useful for diverse materials and drug development. This communication describes the effects of solvents (MeCN and MeOH) on four synthesized receptors as determined using differential pulse voltammetry. A detailed discussion on the selective behavior of L2–L4 (Figure S1) receptors towards cyanide ions is also presented.
2. Materials and Methods
Synthesis of L1 (2,2′-(1,3-phenylenebis(oxy))dianiline)
Step A: Synthesis of (1,3-bis(2-nitrophenoxy)benzene) (L0)
Compound L0 was synthesized using resorcinol (30.9 mmol), 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene (13.9 mmol), K2CO3 (79.3 mmol), and 18-crown-6 (0.2 mmol) in DMF. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 h. The completion of the reaction was checked using thin-layer chromatography. After the completion, the reaction mixture was diluted with CH2Cl2 (50 mL), water (50 mL), 2N NaOH (4 × 10 mL), and brine. The obtained organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and then evaporated using a rotary vacuum evaporator. A yellow-colored solid was obtained, which was further purified using silica-gel-column chromatography.
Step B: To obtain L1, L0 (5.2 mmol) was dissolved in dry methanol (50 mL). To this, a catalytic amount of Pd/C was added. The resultant solution was kept under H2 gas with constant stirring for 4 h. After the completion of the reaction, the solution was filtered and then evaporated, and the red-colored solid was obtained. The conversion of nitro (L0) to amine (L1) was confirmed by the NMR technique. A broad peak at position 3.7 ppm confirmed the presence of the amine group on the L1 molecule (Figures S2 (1H NMR) and S3 (13C NMR)).
Synthesis of L3 (1,1′-((((1,3-phenylenebis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene)) bis (methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-ol))
To a solution of L1 (1 mmol) in methanol (40 mL), 2-hydroxy naphthaldehyde (2.3 mmol) was added dropwise (dissolved in ethanol). The reaction mixture was allowed to reflux for 4–5 h. The yellow-colored solid was precipitated out, which was filtered and further washed with water and ethanol to obtain a pure compound (Figures S4 (1H NMR) and S5 (13C NMR)).
Synthesis of L2 ((1,1′-((((1,3-phenylenebis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanediyl))bis (methylene))bis(naphthalen-2-ol))
Compound L2 was synthesized using L3 as an initial precursor. To a solution of L2 (0.1 mmol) in THF:methanol (7:3), sodium borohydride (0.4 mmol) was added. The solution was allowed to stir at room temperature. Continuous monitoring of the reaction was carried out using TLC plates. Once the reaction was completed, it was portioned between water (20 mL) and CH2Cl2 (20 mL). The obtained organic layer was dried and then evaporated to obtain a solid product. Furthermore, the solid product was purified using silica-gel-column chromatography. During the progress of the reaction, the color of the solution changed from yellow (L2) to orange, which suggests the successful conversion of an imine to amine linkage. The obtained compound was characterized using the NMR technique. In 1H NMR, a clear peak was obtained at 4.8 ppm, which confirmed the presence of a reduced imine linkage (Figures S6 (1H NMR) and S7 (13C NMR)).
Synthesis of L4 (N,N’-((1,3-phenylenebis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(2-hydroxy -1-naphthamide))
L4 was synthesized using a two-step procedure. The first step included the synthesis of acid chloride using 2-hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid (2 mmol) and PCl3 (2.4 mmol). The reaction mixture was kept at 80–90 °C with constant stirring. In the second step, the synthesized acid chloride was added into the corresponding amine L1 (0.7 mmol), having K2CO3 as a base. The reaction was kept under stirring for 5–6 h in DCM solvent at 0 °C. After the reaction was completed (checked by TLC), it was diluted with CH2Cl2 (30 mL) and water (30 mL). The combined organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and purified using silica-gel-column chromatography. 1H and 13C confirmed the formation of L3 due to the appearance of an amidic proton at 12.3 ppm and carbon at 171.5 ppm (Figures S8 (1H NMR) and S9 (13C NMR)).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Solvent on Electrochemical Behavior of L1–L4
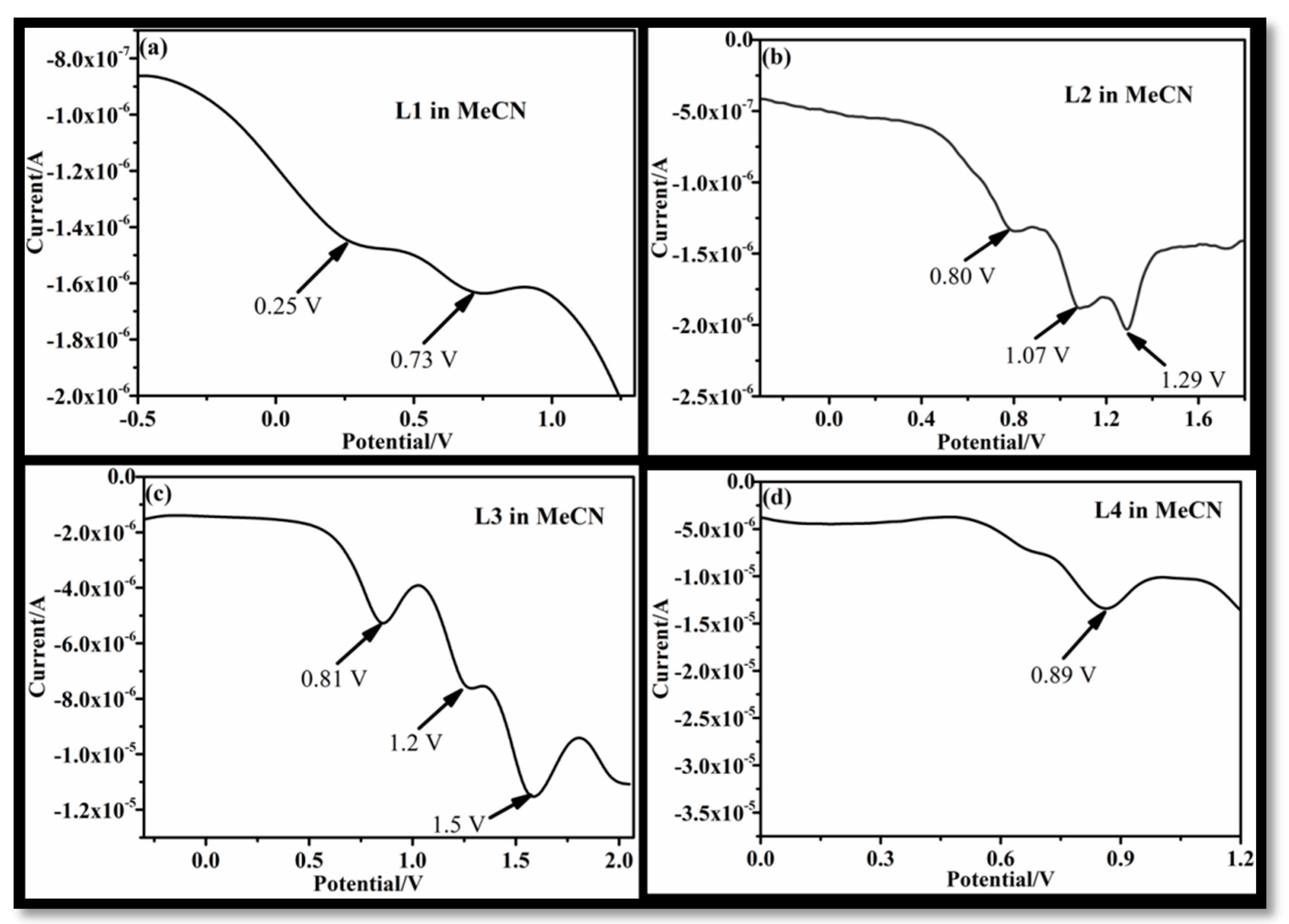
To study the solvent effect, the voltammetric responses of receptor L1–L4 were recorded in both protic and aprotic solvent systems. The electrochemical response was recorded using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) in two different solvents, and voltammograms were compared to understand the effect of the solvent. The anodic voltammogram of L1, recorded in MeCN, gave two peak maxima at 0.25 V and 0.73 V (Figure 1a). Upon changing the solvent system from MeCN to MeOH, only one sharp peak was observed at 0.25 V. The anodic peak maxima (0.25 V and 0.73 V) observed in MeCN could be assigned to the oxidation of lone pairs on the ethereal oxygen atoms and nitrogen atoms, but in the case of methanol, the observed single peak can be attributed to the ethereal linkage. This is because the lone pair on N is engaged by methanol through H-bonding.
Figure 1.
Anodic voltammogram of receptor L1 (a), L2 (b), L3 (c), and L4 (d) in MeCN medium.
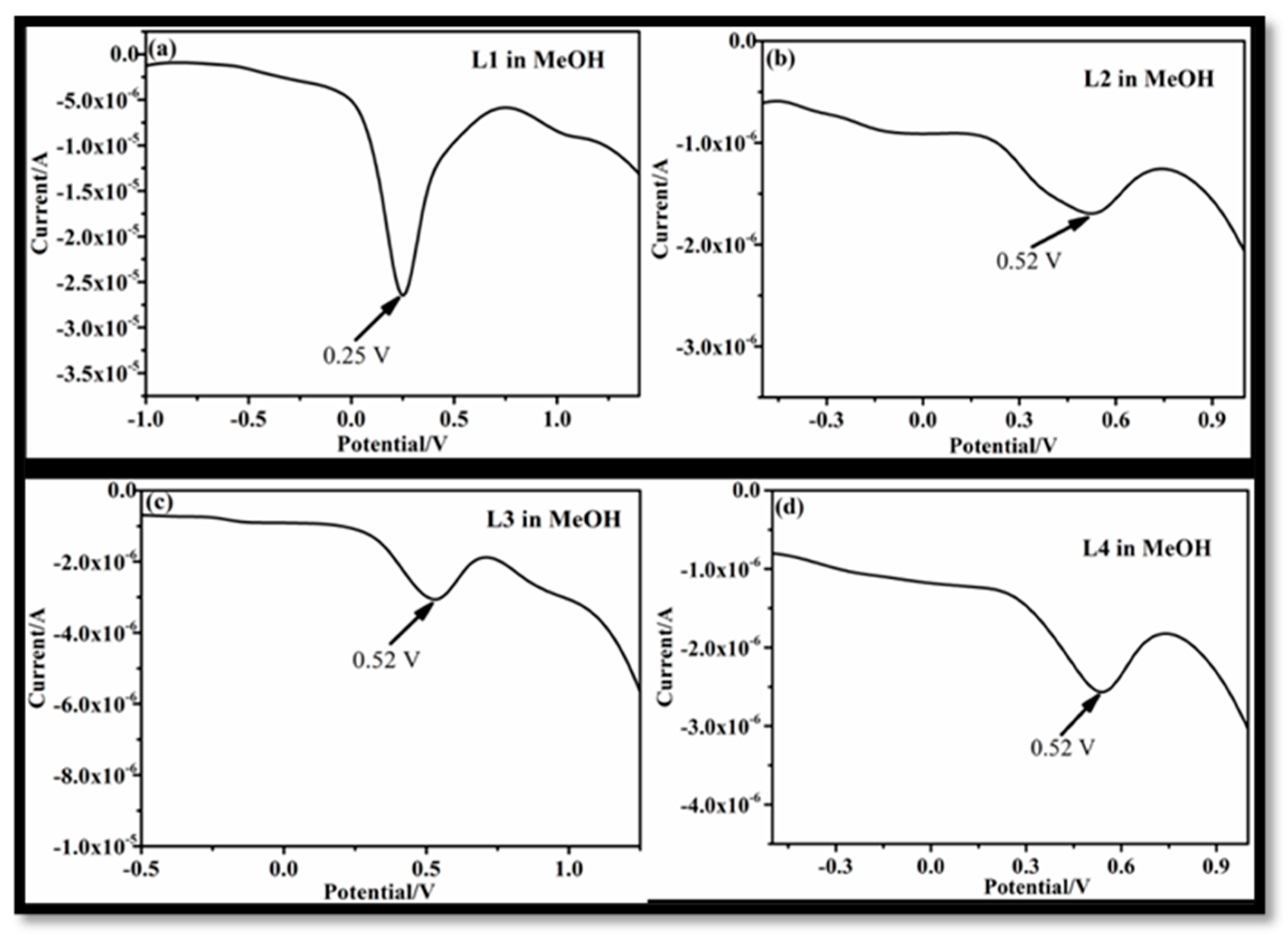
In the case of L2 in MeCN, three anodic maxima were observed at 0.80 V, 1.07 V, and 1.29 V (Figure 1b) that can be assigned to the lone pair of electrons on primary amine, ethereal oxygen, and hydroxyl oxygen, respectively. The replacement of an amine group (L2) with an imine linkage (L3) also showed three peaks at 0.81 V, 1.2 V, and 1.5 V (Figure 2b) in MeCN. The three maxima in the case of L3 can be assigned to ethereal oxygen, imine nitrogen, and the reoxidation of a double bond of an imine linkage. It is interesting to note that, upon changing the amine linkage (L2) to imine (L3), the anodic peak (in L3) of the imine group then shifted to 0.80 V and 1.07 V, instead of 0.81 and 1.2 V (for L2), respectively. The change in sequence can be attributed to the larger basic character of the amine nitrogen in L2, as compared to the imine nitrogen of L3. Extended conjugation in L3 also exhibited a strong effect on the oxidation of a lone pair of hydroxyl oxygen at 0.5 V (Figure 1c) that appeared quite far compared to L2 (1.29 V) (Figure 1b). Thus, extended conjugation leads to a delayed oxidation process for the hydroxyl group of L3. However, on changing the solvent system from MeCN (Figure 1) to methanol (Figure 2), both L2 and L3 exhibited single anodic maxima at 0.52 V as shown in Figure 2b,c, respectively. The single peak indicated that only the lone pair on the ethereal oxygen atom was available for oxidation and all the other functional groups were engaged with the methanol solvent through H-bonding. The voltammogram for L4 in MeCN, due to the presence of an amide linkage in the molecule, exhibited one major peak at 0.89 V (Figure 1d). When the solvent was changed to MeOH, L4 gave anodic peak maxima at 0.52 V (Figure 2d). The anodic peak maxima in MeCN could be due to the oxidation of a lone pair of an amidic nitrogen atom, and the weak intensity of this peak could be assigned to the negative inductive effect of a –C = O group present adjacent to the amidic nitrogen [18].
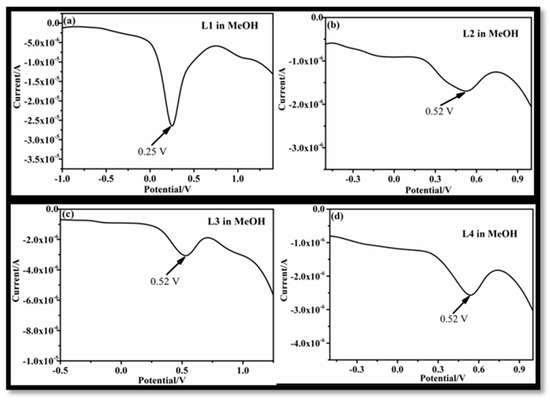
Figure 2.
Anodic voltammogram of receptor L1 (a), L2 (b), L3 (c), and L4 (d) in MeOH medium.
3.2. Behavior of L2–L4 towards Cyanide Ions
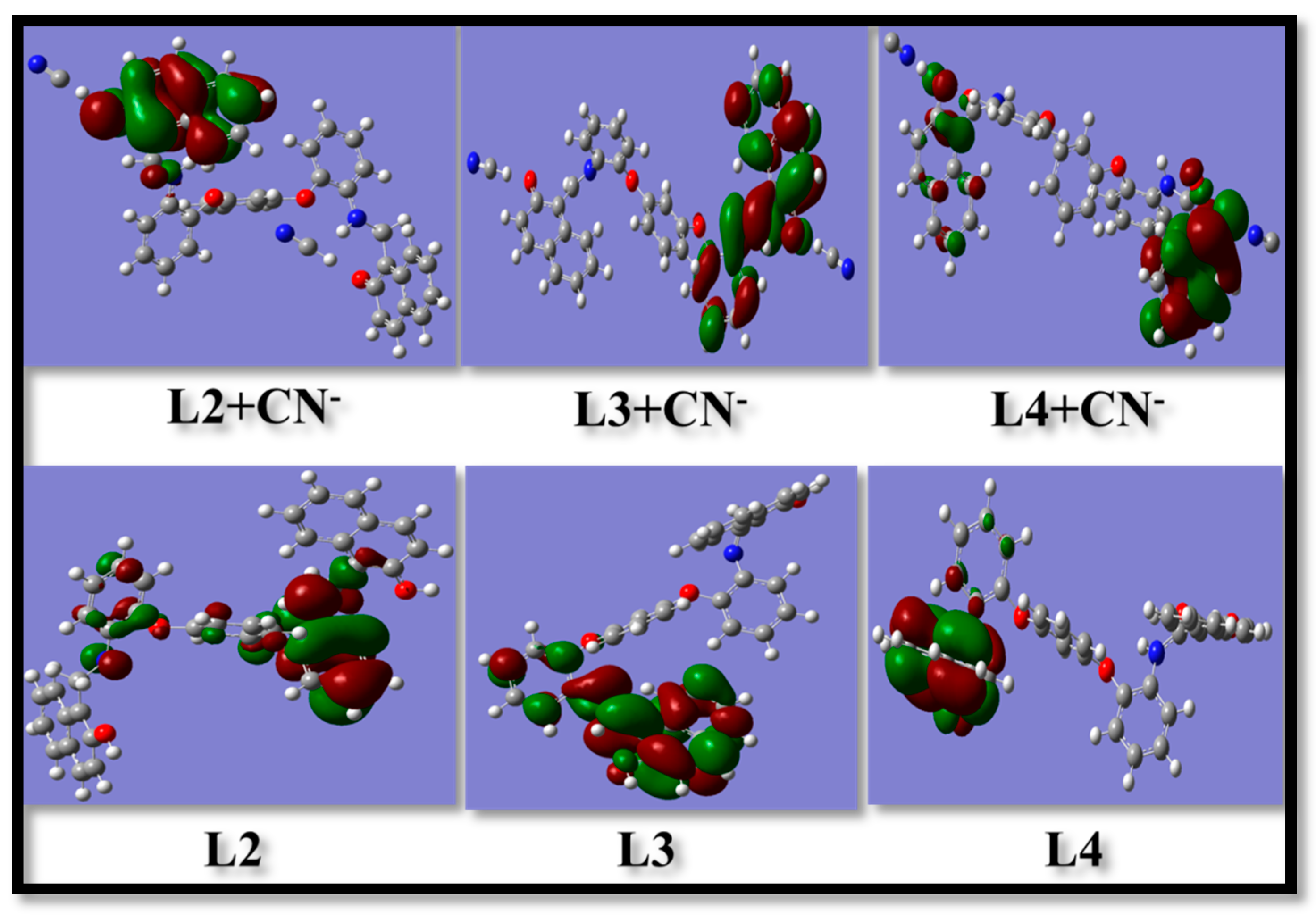
The behavior of all the triphenylether derivatives towards the cyanide ions has already been demonstrated in our previous communications [16,17,18]. The three receptors L2, L3, and L4 showed selective behavior towards cyanide ions according to differential pulse voltammetry. The receptors L2 and L4 did not give any peak in the cathodic voltammogram, but one peak was observed for L3 (Figure S10). This behavior of L3 is due to the electron-deficient nature of the imine linkage and, hence, the availability of a reduction site. When cyanide ions are introduced into the sample solution of L2–L4, the weak peak maximum of both L2 and L4 (Figure S10a,c) and cathodic maxima at 1.59 V in the case of L3 disappeared. Thus, no peak was observed in the L3–CN- complex (Figure S10b). This reorganization of the cathodic peak behavior in L2–L4 can be ascribed to the basic character of cyanide ions, which are readily available to take away the acidic proton of a hydroxyl group, following a deprotonation mechanism. After deprotonation, the negative charge generated on the phenolate ion becomes stabilized through conjugation over the entire naphthalene ring, and this leads to the intramolecular charge-transfer process (ICT). The proposed mechanism of deprotonation and ICT was also supported by computational studies, as shown in Figure 3. The computational study helped in optimizing the structure of the molecules and theircyanide complexes as well as in calculating the energy of these molecules. Table 1 shows that the energy of the complexes decreased compared to the energy of the receptor, suggesting that stable complexation had taken place. From the DFT pictures, it was observed that there was a shift in electron density from phenyl groups to naphthyl rings in the presence of cyanide ions, which supports the proposed mechanism of ICT. Apart from this, the electrochemical behavior was supported by 1HNMR titrations as well [16,17,18]. The receptor L1 did not show any property of a receptor, indicating the importance of a steric character for the receptor. Additionally, the electron-rich electronic environment could not be created, as there was no possibility of the abstraction of a proton due to no group being present in L1 (Figure S1).
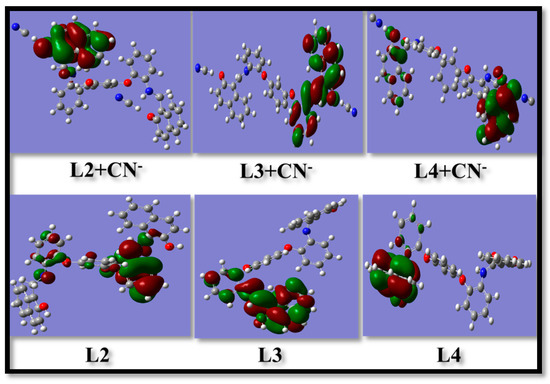
Figure 3.
Optimized structure of receptors (L2–L4) and their cyanide complexes determined using DFT calculations (basis set-631-G).

Table 1.
Energy values (in a.u.) of receptors (L2–L4) and their complexes with CN− determined using DFT calculations.
4. Conclusions
Triphenylether-based receptors were synthesized and characterized using 1H and 13C NMR. The four receptors (L1–L4) differ from each in terms of their substitution from an imine to amine to amide linkage. A detailed discussion on their electrochemical behavior in the protic and aprotic solvent systems was carried out. All four molecules exhibited strong anodic behavior in the aprotic solvent according to differential pulse voltammetry. However, when the solvent system was changed from aprotic to protic, the hydrogen bonding played a great role in defining the electrochemical behavior of the molecules. Due to hydrogen bonding between the receptor and hydroxyl group of methanol, strong anodic behavior was exhibited by ethereal oxygen only. In terms of the sensing behavior of the synthesized molecules, L2–L4 showed a strong response to cyanide ions following a deprotonation and intramolecular charge-transfer mechanism. The voltammetric response and sensing mechanism of both receptors and their cyanide complexes were supported by computational studies. Both the electronic environment and steric factor are responsible for defining the sensing behavior of the molecule; therefore, L1 does not show the property of a receptor due to its lack of the above-mentioned factors.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary information provides the NMR and Voltammogram data to support the present studies. The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/c7040085/s1. Figure S1: Molecular structure of L1–L4; Figure S2: 1H NMR of L1; Figure S3: 13C NMR of L1; Figure S4: 1H NMR of L2; Figure S5: 13C NMR of L2; Figure S6: 1H NMR of L3; Figure S7: 13C NMR of L3; Figure S8: 1H NMR of L4; Figure S9: 13C NMR of L4; Figure S10: Cathodic voltammogram behavior of L2–L4 towards CN− ions in MeCN medium
Author Contributions
S.K.M.: Conceptualization, visualization, and supervision; S.G.: Writing—original draft, editing, and software; M.C.: Synthesis, discussion and analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their gratitude to the Director, Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, for providing an essential assessment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lehn, J.-M. Supramolecular chemistry—Scope and perspectives molecules, supermolecules, and molecular devices (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 1988, 27, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, J. A new trend in rhodamine-based chemosensors: Application of spirolactam ring-opening to sensing ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, U.; Vonau, W.; Zosel, J. Recent developments in electrochemical sensor application and technology—A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Chen, T.-W.; Chen, S.-M.; Baskar, T.; Kannan, R.; Elumalai, P.; Raja, P.; Jeyapragasam, T.; Dinakaran, K.; Ghana Kumar, G.P. A review of the advanced developments of electrochemical sensors for the detection of toxic and bioactive molecules. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 3418–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.K.; Chhibber, M.; Gupta, S. Imine derivative as an analytical probe for Al+3, F− and CN− sensing with antibacterial activity against E. coli—An application of electrochemical and spectrofluorimetric techniques. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A. Anion recognition and sensing: The state of the art and future perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 486–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, R.; Beer, P.D.; Davis, J.J. Electrochemical anion sensing: Supramolecular approaches. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1888–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, P.D.; Bernhardt, P.V. A ferrocene functionalised macrocyclic receptor for cations and anions. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2001, 9, 1428–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.V.; Creevey, N.L. Electrochemical anion recognition with ferrocene functionalised macrocycles. Dalton Trans. 2004, 6, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, L.-J.; Liao, J.-H.; Chen, C.-T.; Huang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Fang, J.-M. Two-arm ferrocene amide compounds: Synclinal conformations for selective sensing of dihydrogen phosphate ion. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Yu, H.; Huo, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. Electrochemical assessment of the interaction of dihydrogen phosphate with a novel ferrocenyl receptor. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15141–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, D.; González-Vadillo, A.M.; Bruña, S.; Pastor, C.J.; Kaifer, A.E.; Cuadrado, I. Pt (II)-activated coupling of aminoethylferrocene with benzonitrile. A facile access route to a new redox-active bis (ferrocenyl-amidine) anion sensor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10398–10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaabani, B.; Shaghaghi, Z. Anion-binding properties of two calix[4]arene derivatives containing two ferrocene imine or ferrocene amine units at the upper rim. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 25, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwob, T.; Kempe, R. A reusable Co catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of functionalized nitroarenes and the direct synthesis of imines and benzimidazoles from nitroarenes and aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15175–15179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, K.; Senthamarai, T.; Sohail, M.; Alshammari, A.S.; Pohl, M.-M.; Beller, M.; Jagadeesh, R.V. Cobalt-based nanoparticles prepared from MOF–carbon templates as efficient hydrogenation catalysts. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8553–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Chhibber, M.; Mittal, S.K. Amine derivative of triphenyl ether as an optical sensor for the detection of cyanide ions and traces of water in acetonitrile supported with voltammetric studies. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2020, 50, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Chhibber, M.; Mittal, S.K. A new ionophore for chemical sensing of F−, CN− and Co2+ using voltammetric, colorimetric and spectrofluorimetric techniques. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 51153–51160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Mittal, S.K.; Chhibber, M. Triphenyl Ether Amide as a Probe for Electrochemical and Optical Sensing of Copper, Cyanide and Arginine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 167506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).