The Growth Behavior of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon a-C:H Layers on Industrial Polycarbonates—A Weak Interlayer and a Distinct Dehydrogenation Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
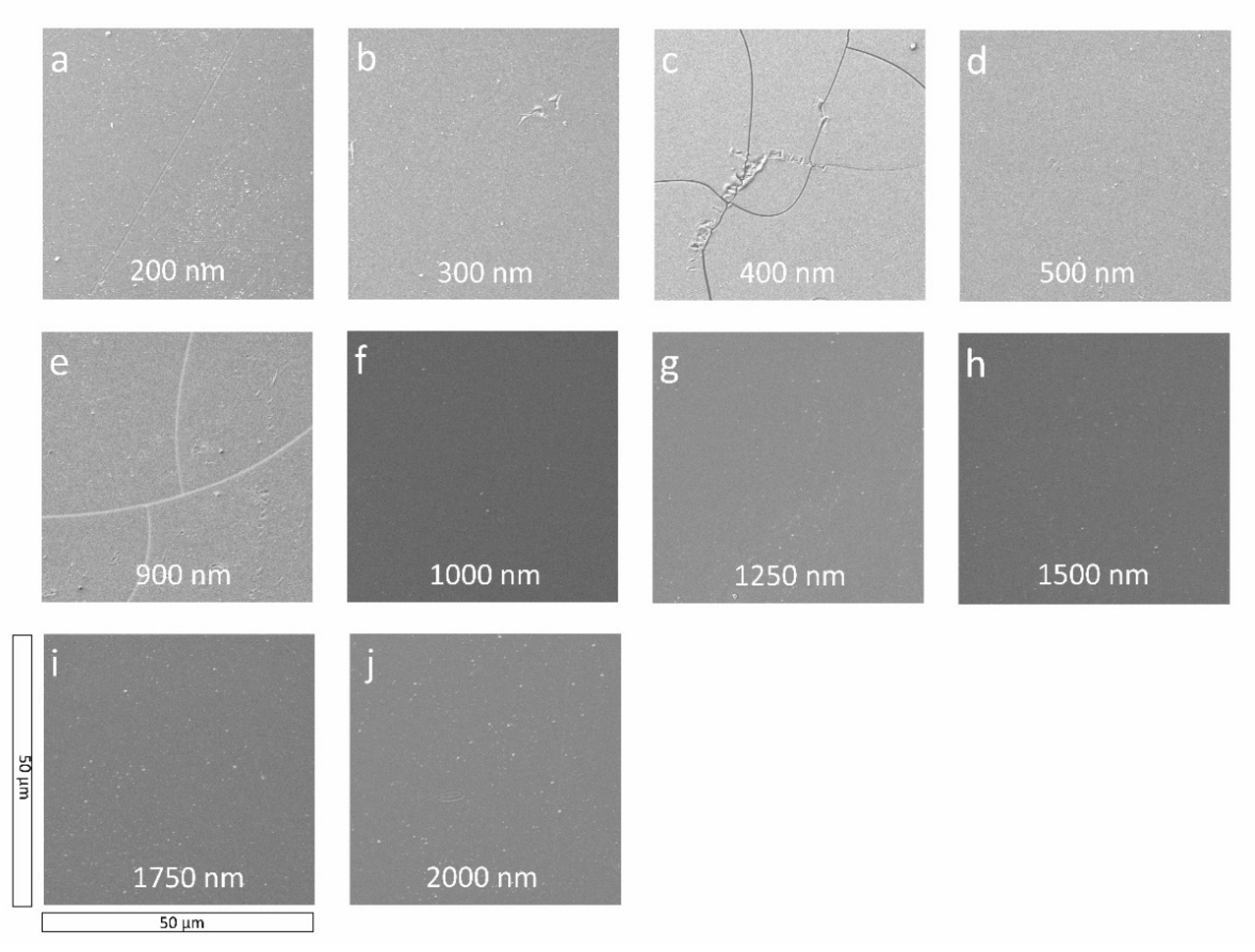
2.2. Sample Surface Morphology
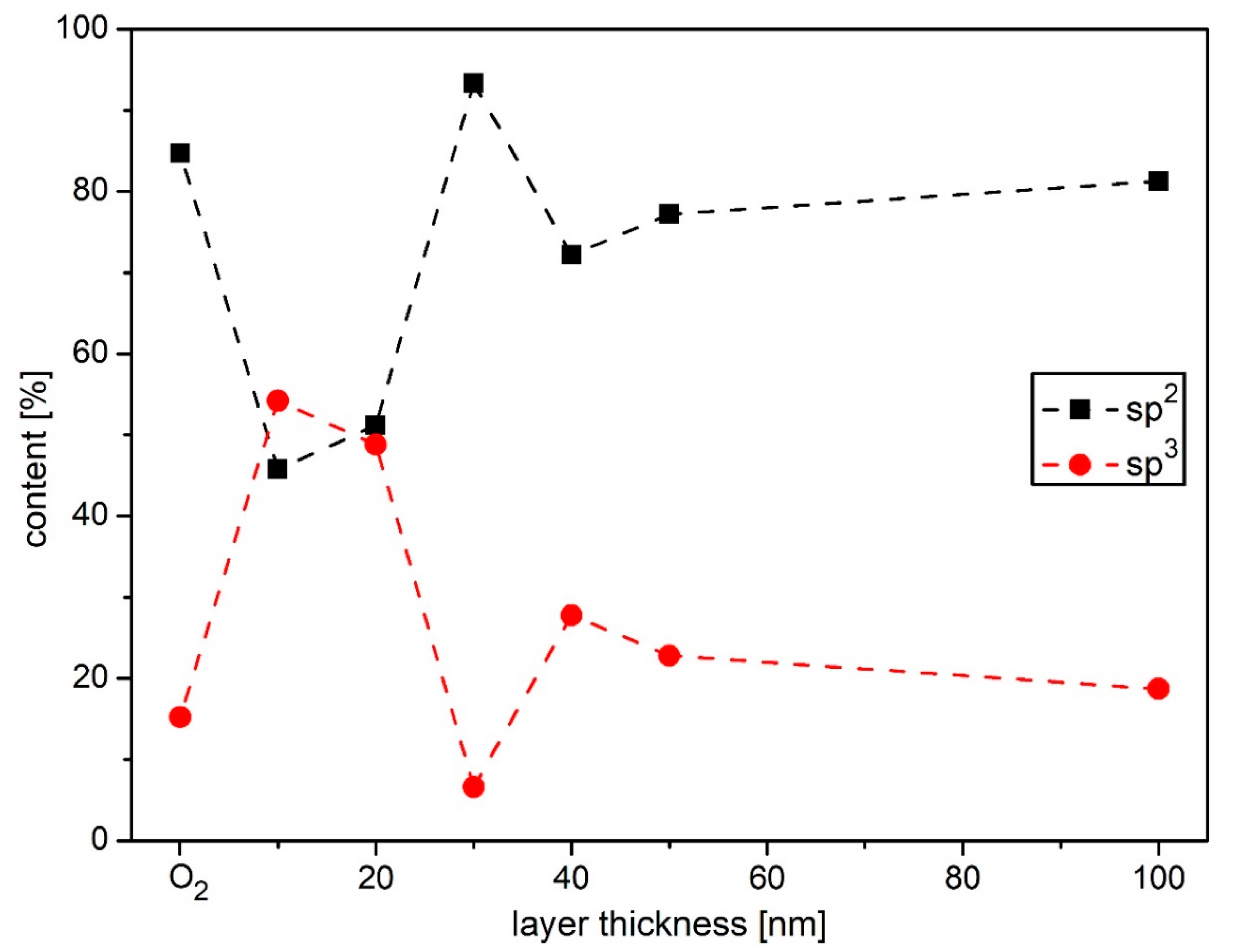
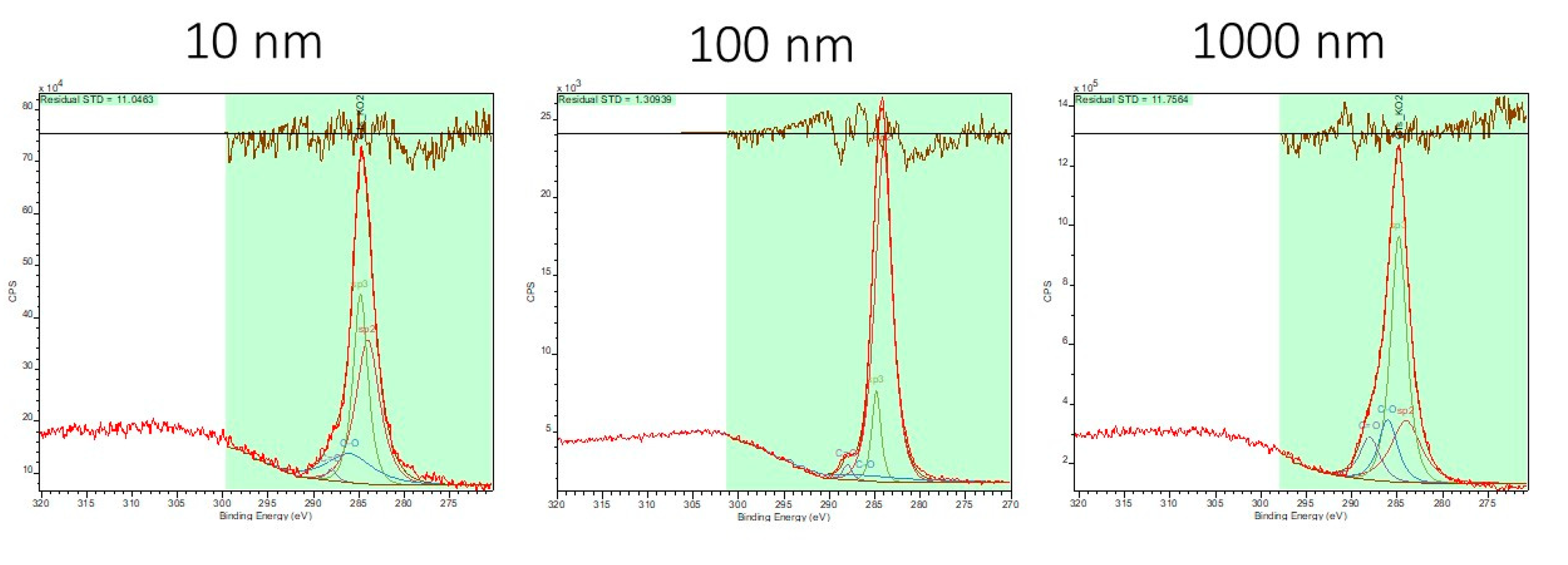
2.3. Sample Surface Chemical Composition
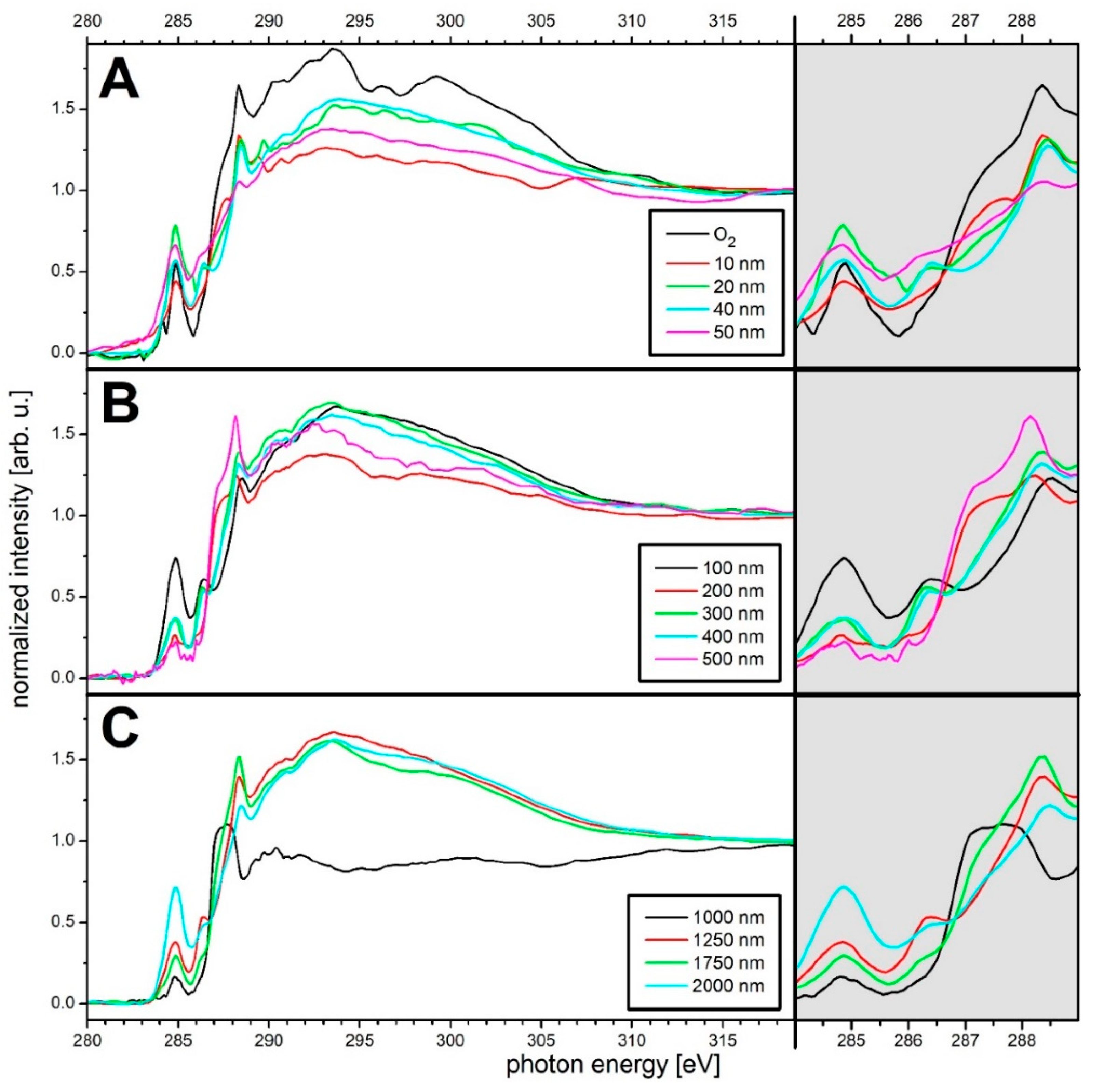
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Al Jaafari, A.A.; Ayesh, A.S. Physical characterizations of three phase polycarbonate nanocomposites. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 2011, 27, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. A review of filled and pristine polycarbonate blends and their applications. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 2018, 34, 60–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Stathis, P.; Permuth, S.F.; Tokes, L.; Feldman, D. Bisphenol-A: An estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, W.; Fischer, C.B.; Wehner, S.; Dang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Microstructures, mechanical properties and tribological behaviors of amorphous carbon coatings in-situ grown on polycarbonate surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 563, 150309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, A.; Guo, Q.; Kunze, M.R.; Agnello, S.; Gelardi, F.M.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Morphological and Chemical Evolution of Gradually Deposited Diamond-Like Carbon Films on Polyethylene Terephthalate: From Subplantation Processes to Structural Reorganization by Intrinsic Stress Release Phenomena. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10636–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, A. Plasma-deposited diamondlike carbon and related materials. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1999, 43, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, P.; Catherine, Y. Structure and physical properties of plasma-grown amorphous hydrogenated carbon films. Thin Solid Film. 1987, 146, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, A.; Agnello, S.; Rösken, L.M.; Bergen, H.; Recktenwald, E.; Bernsmann, F.; Busch, H.; Cannas, M.; Gelardi, F.M.; Hahn, B.; et al. Characteristics of industrially manufactured amorphous hydrogenated carbon (a-C:H) depositions on high-density polyethylene. Carbon 2016, 96, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohagheghpour, E.; Rajabi, M.; Gholamipour, R.; Larijani, M.M.; Sheibani, S. Ion beam energy dependence of surface and structural properties of amorphous carbon films deposited by IBSD method on Ni–Cu alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Das, S.N.; Dalui, S.; Gayen, R.N.; Roy, R.K.; Bhar, R.; Pal, A.K. Synthesis of DLC films with different sp2/sp3 ratios and their hydrophobic behaviour. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 41, 055309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Controlling the surface topology and hence the hydrophobicity of amorphous carbon thin films. Carbon 2010, 48, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovskaya, L.; Perevertailo, V.; Ralchenko, V.; Dementjev, A.; Loginova, O. Wettability and surface energy of oxidized and hydrogen plasma-treated diamond films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2002, 11, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, F.; Morell, G. Wettability of hydrogenated tetrahedral amorphous carbon. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2009, 18, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismarck, A.; Brostow, W.; Chiu, R.; Hagg Lobland, H.E.; Ho, K.K.C. Effects of surface plasma treatment on tribology of thermoplastic polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koidl, P.; Wild, C.; Dischler, B.; Wagner, J.; Ramsteiner, M. Plasma Deposition, Properties and Structure of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon Films. MSF 1991, 52–53, 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 37, 129–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Song, X.; Li, E.; Li, G.; Zhao, S.; Yan, H. Control over the wettability of amorphous carbon films in a large range from hydrophilicity to super-hydrophobicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2690–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Beucher, L.; Bazzi, H.; Hahn, B.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Prediction of a-C:H layer failure on industrial relevant biopolymer polylactide acide (PLA) foils based on the sp2/sp3 ratio. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 368, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Beucher, L.; Bazzi, H.; Hahn, B.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Changing Contents of Carbon Hybridizations in Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon Layers (a-C:H) on Sustainable Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Exhibit a Significant Deterioration in Stability, Depending on Thickness. C 2019, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Plasma Deposition of Diamond-Like Carbon. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 01AF01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Tai, F.-C.; Wei, C.-H. Correlation between sp2/sp3 Ratio or Hydrogen Content and Water Contact Angle in Hydrogenated DLC Film. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2534–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Acharchi, H.; Hahn, B.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Refinement of Sustainable Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) with Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon Films (a-C:H) Revealing Film Instabilities Influenced by a Thickness-Dependent Change of sp2/sp3 Ratio. Materials 2020, 13, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.B.; Rohrbeck, M.; Wehner, S.; Richter, M.; Schmeißer, D. Interlayer formation of diamond-like carbon coatings on industrial polyethylene: Thickness dependent surface characterization by SEM, AFM and NEXAFS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 271, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbeck, M.; Körsten, S.; Fischer, C.B.; Wehner, S.; Kessler, B. Diamond-like carbon coating of a pure bioplastic foil. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 545, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyts, E.; Bogaerts, A.; Van de Sanden, M.C.M. Reaction mechanisms and thin a-C: H film growth from low energy hydrocarbon radicals. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 86, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, A.; Kunze, M.R.; Agnello, S.; Gelardi, F.M.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Amorphous hydrogenated carbon (a-C:H) depositions on polyoxymethylene: Substrate influence on the characteristics of the developing coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Rouabeh, W.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Specifying the interlayer turning point and dehydrogenation in a-C:H layers plasma deposited on high-density polyethylene with X-ray synchrotron techniques. Thin Solid Film. 2019, 691, 137617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Lüber, H.; Beucher, L.; Fritz, M.; Benjillali, Y.; Bentaouit, M.; Hahn, B.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Plasma Supported Deposition of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon (a-C:H) on Polyamide 6: Determining Interlayer Completion and Dehydrogenation Effects during Layer Growth. Polymers 2021, 13, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nefedov, A.; Wöll, C. Advanced Applications of NEXAFS Spectroscopy for Functionalized Surfaces. In Surface Science Techniques; Bracco, G., Holst, B., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 277–303. ISBN 978-3-642-34242-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; He, F.; Xie, J.; Xue, L. Calibration of Binding Energy Positions with C1s for XPS Results. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 35, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, B.; Thomsen, L.; Dastoor, P.C. Methods in carbon K-edge NEXAFS: Experiment and analysis. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2006, 151, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlebrowski, T.; Ouali, R.; Hahn, B.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Comparing the Influence of Residual Stress on Composite Materials Made of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon (a-C:H) Layers: Differences Caused by Single Side and Full Substrate Film Attachment during Plasma Coating. Polymers 2021, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, R.G.; Marques, F.C. Hard hydrogenated carbon films with low stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marques, F.C.; Lacerda, R.G.; Odo, G.Y.; Lepienski, C.M. On the hardness of a-C:H films prepared by methane plasma decomposition. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 332, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.C.; Lee, S.C.; Wei, C.H.; Tyan, S.L. Correlation between ID⁄IG Ratio from Visible Raman Spectra and sp2/sp3 Ratio from XPS Spectra of Annealed Hydrogenated DLC Film. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.L.; Madix, R.J.; Stöhr, J. Orientation and absolute coverage of benzene, aniline, and phenol on Ag(110) determined by NEXAFS and XPS. Surf. Sci. 1991, 255, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.M.; Horlacher, T.; Girard-Lauriault, P.-L.; Gross, T.; Lippitz, A.; Min, H.; Wirth, T.; Castelli, R.; Seeberger, P.H.; Unger, W.E.S. Adlayers of dimannoside thiols on gold: Surface chemical analysis. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4808–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöhr, J. NEXAFS Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; ISBN 978-3-662-02853-7. [Google Scholar]
- Brüster, B.; Amozoqueño, C.; Grysan, P.; Peral, I.; Watts, B.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P.; Addiego, F. Resolving Inclusion Structure and Deformation Mechanisms in Polylactide Plasticized by Reactive Extrusion. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.; Anders, S.; Zhou, X.; Moler, E.J.; Kellar, S.A.; Hussain, Z. Analysis of the π* and σ* bands of the x-ray absorption spectrum of amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhez, O.; Ade, H.; Urquhart, S.G. Calibrated NEXAFS spectra of some common polymers. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2003, 128, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.; Monteiro, O.R.; Hussain, Z. Structure of amorphous carbon from near-edge and extended x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 76, 094201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


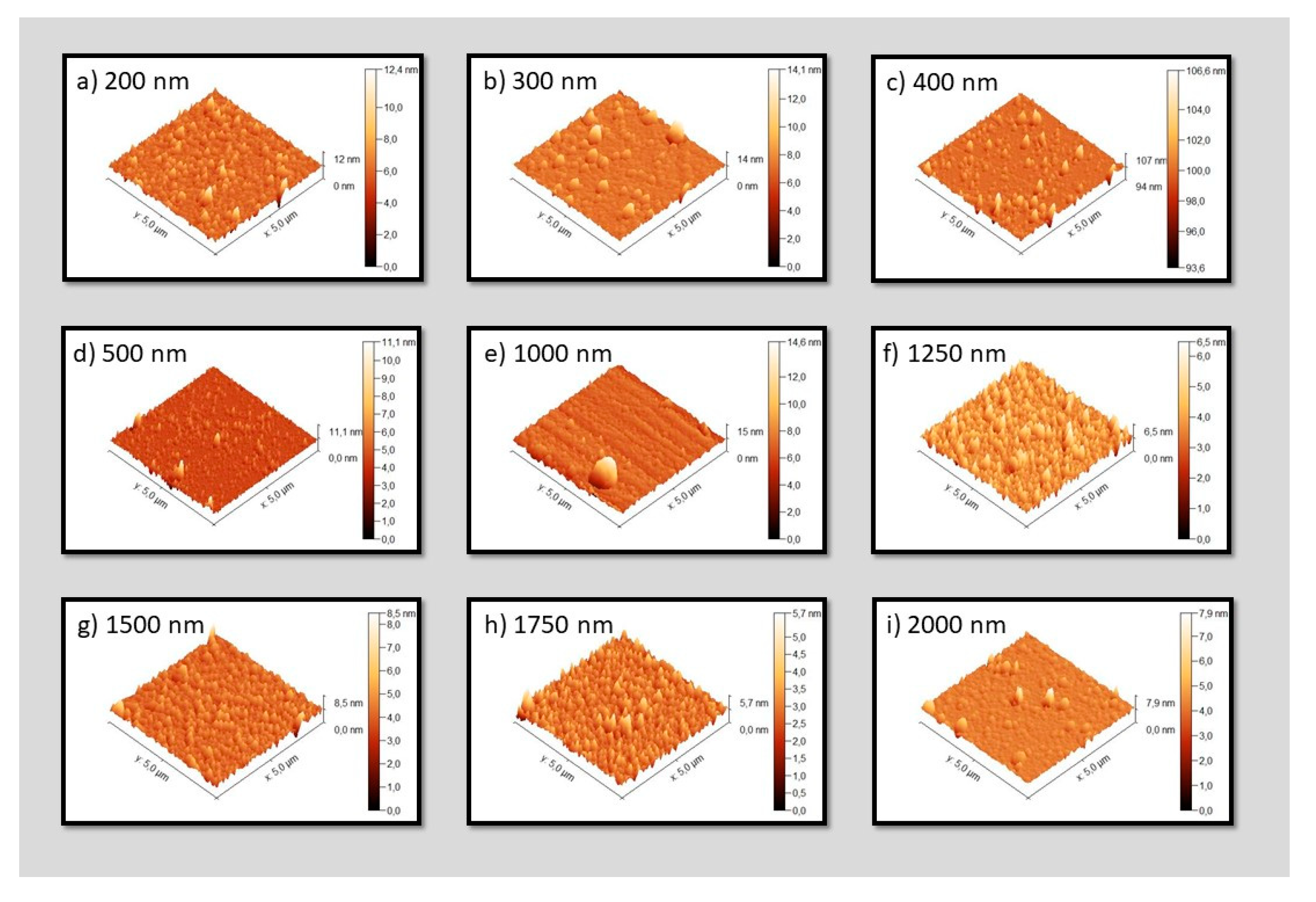

| Sample | Ra [nm] | Rq [nm] |
|---|---|---|
| O2 | 2.069 ± 1.578 | 5.256 ± 15.320 |
| 10 | 2.759 ± 2.095 | 4.775 ± 5.086 |
| 20 | 2.363 ± 0.401 | 2.999 ± 0.649 |
| 30 | 0.789 ± 0.240 | 1.350 ± 0.581 |
| 40 | 3.812 ± 0.719 | 4.932 ± 1.091 |
| 50 | 2.940 ± 1.744 | 5.155 ± 2.925 |
| 100 | 5.161 ± 1.383 | 7.140 ± 2.134 |
| 200 | 4.978 ± 1.381 | 6.946 ± 2.162 |
| 300 | 5.729 ± 3.585 | 9.890 ± 6.357 |
| 400 | 3.850 ± 1.968 | 6.783 ± 3.564 |
| 500 | 2.048 ± 1.395 | 3.886 ± 3.613 |
| 1000 | 7.443 ± 7.519 | 15.250 ± 16.670 |
| 1250 | 4.546 ± 1.454 | 6.432 ± 2.398 |
| 1500 | 3.790 ± 1.080 | 5.161 ± 2.387 |
| 1750 | 3.460 ± 1.274 | 4.813 ± 2.868 |
| 2000 | 2.139 ± 1.189 | 4.331 ± 2.745 |
| Sample | sp2 [%] | sp3 [%] | C-O [%] | C=O [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | 83.49 | 4.55 | 10.70 | 1.26 |
| 10 | 42.55 | 38.59 | 15.65 | 0.37 |
| 20 | 48.58 | 43.42 | 5.38 | 2.63 |
| 30 | 90.14 | 4.24 | 2.39 | 3.24 |
| 40 | 72.19 | 7.02 | 20.79 | 0.00 |
| 50 | 74.58 | 12.97 | 9.84 | 2.62 |
| 100 | 79.39 | 11.43 | 7.29 | 1.90 |
| 200 | 34.02 | 48.81 | 14.04 | 3.12 |
| 300 | 51.77 | 35.44 | 12.26 | 0.53 |
| 400 | 80.51 | 4.05 | 13.76 | 1.69 |
| 500 | 68.10 | 22.99 | 0.00 | 8.91 |
| 1000 | 23.63 | 50.68 | 14.96 | 10.73 |
| 1250 | 84.95 | 14.40 | 0.00 | 0.65 |
| 1500 | 83.12 | 16.88 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1750 | 82.94 | 10.70 | 5.20 | 1.17 |
| 2000 | 82.58 | 0.31 | 16.06 | 1.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schlebrowski, T.; Fritz, M.; Beucher, L.; Wang, Y.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. The Growth Behavior of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon a-C:H Layers on Industrial Polycarbonates—A Weak Interlayer and a Distinct Dehydrogenation Zone. C 2021, 7, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7030059
Schlebrowski T, Fritz M, Beucher L, Wang Y, Wehner S, Fischer CB. The Growth Behavior of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon a-C:H Layers on Industrial Polycarbonates—A Weak Interlayer and a Distinct Dehydrogenation Zone. C. 2021; 7(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchlebrowski, Torben, Melanie Fritz, Lucas Beucher, Yongxin Wang, Stefan Wehner, and Christian B. Fischer. 2021. "The Growth Behavior of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon a-C:H Layers on Industrial Polycarbonates—A Weak Interlayer and a Distinct Dehydrogenation Zone" C 7, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7030059
APA StyleSchlebrowski, T., Fritz, M., Beucher, L., Wang, Y., Wehner, S., & Fischer, C. B. (2021). The Growth Behavior of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon a-C:H Layers on Industrial Polycarbonates—A Weak Interlayer and a Distinct Dehydrogenation Zone. C, 7(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7030059








