Nanostructure Quantification of Carbon Blacks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
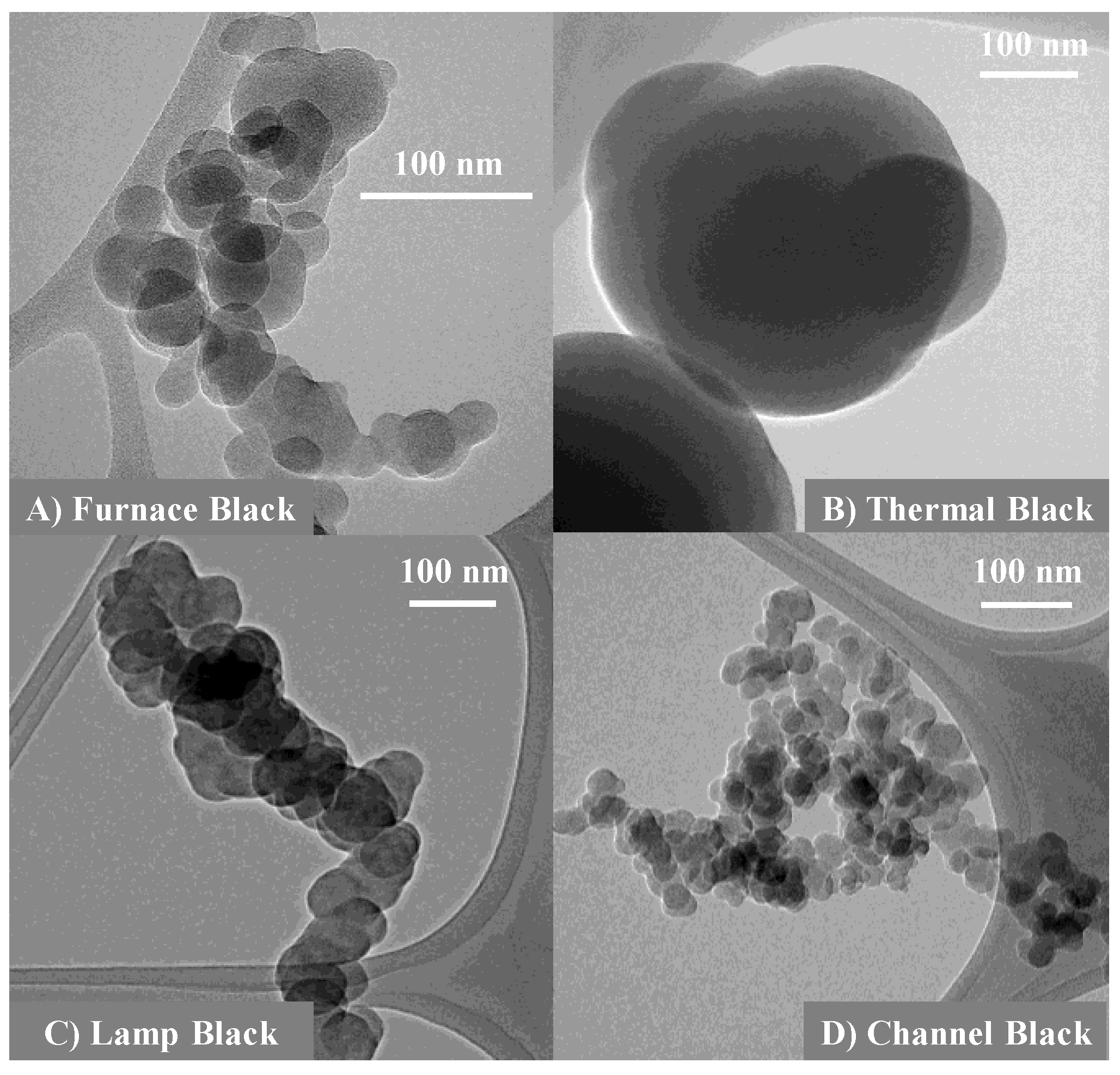
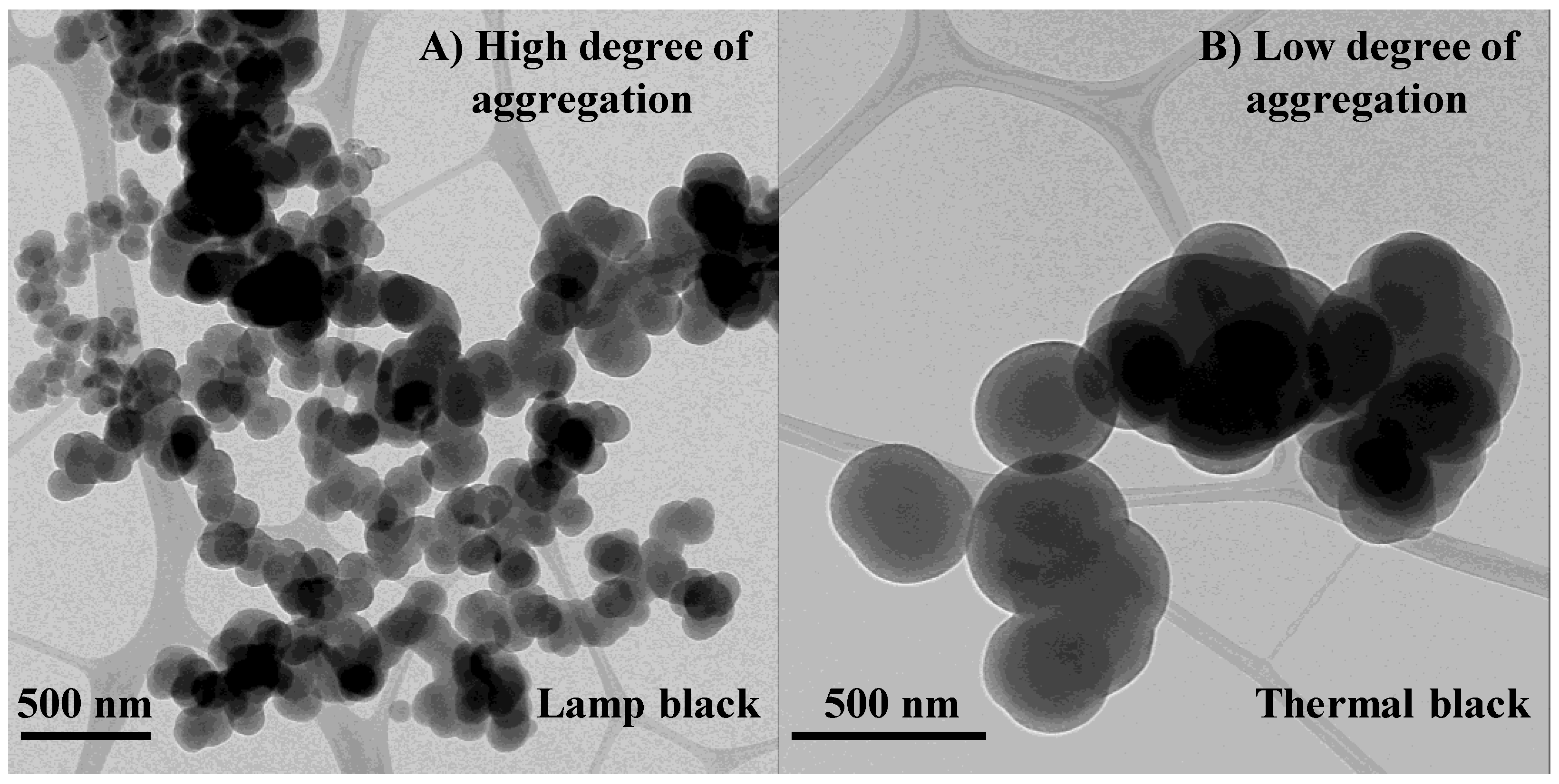
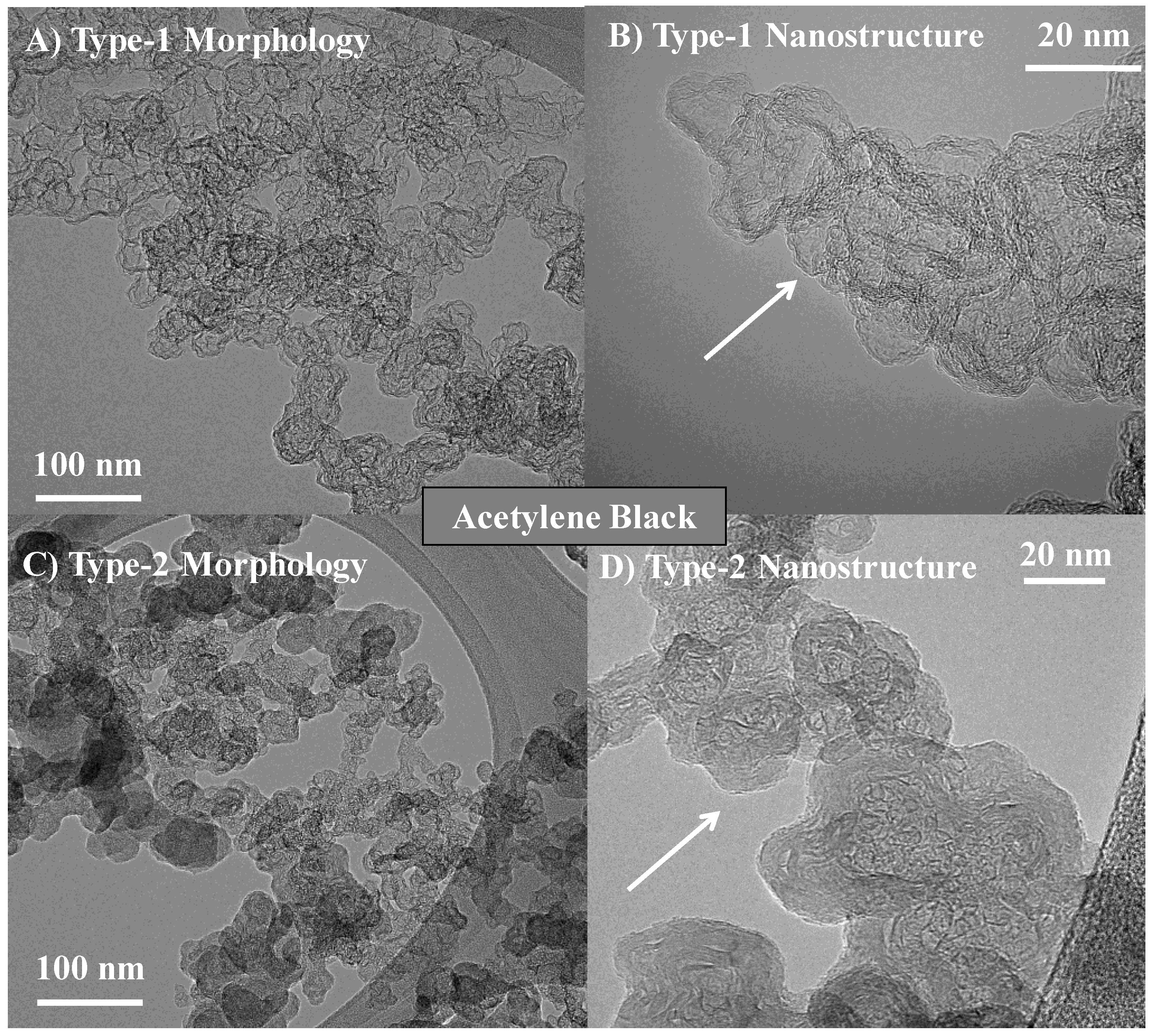
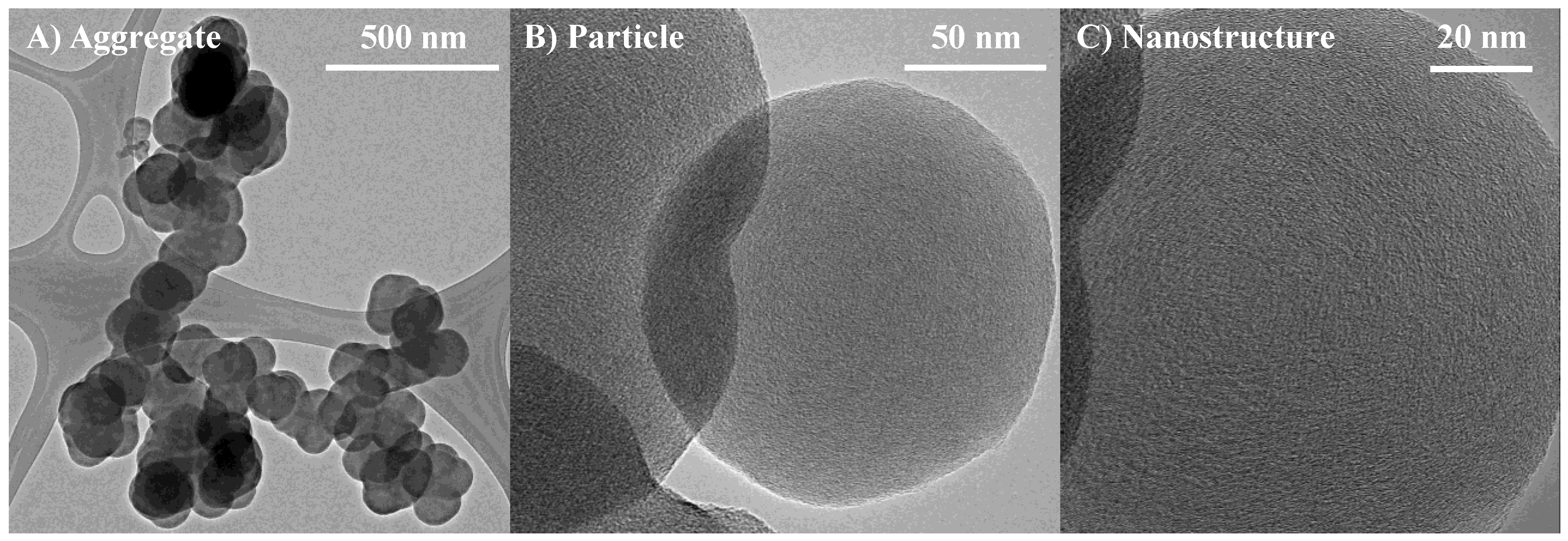
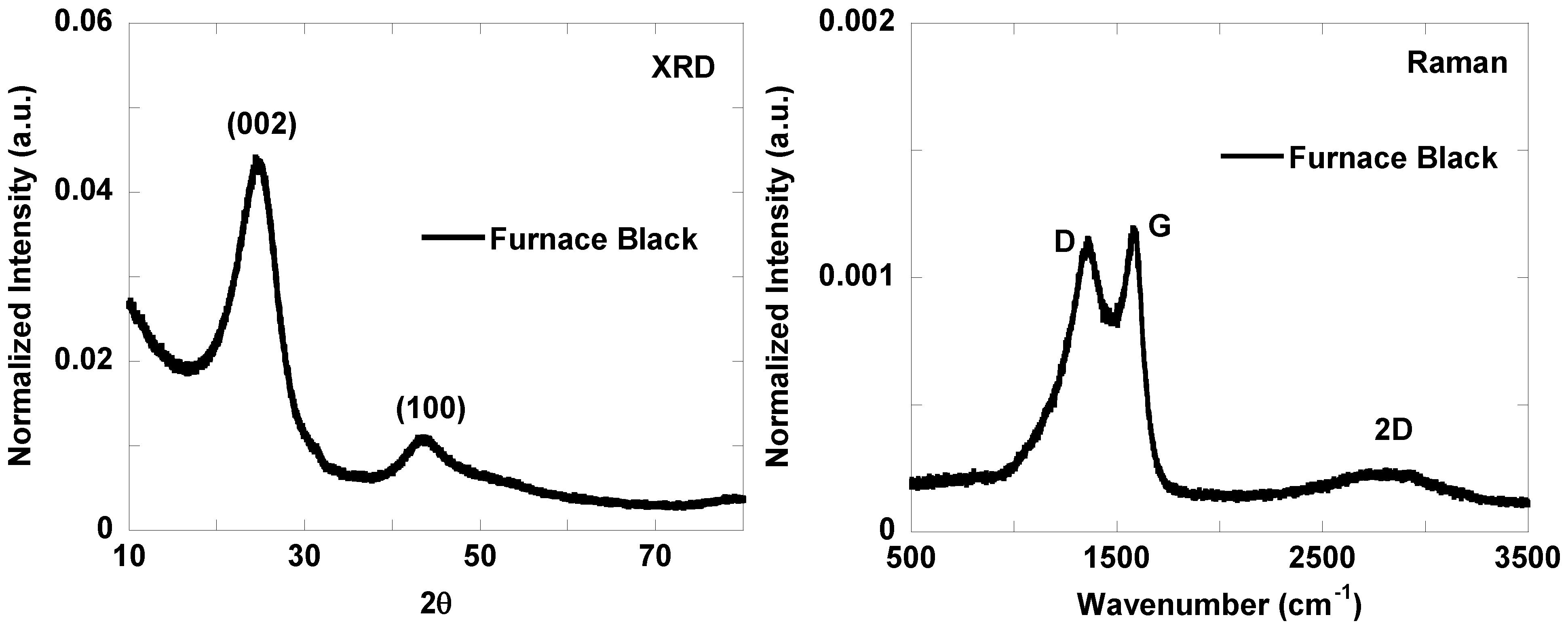
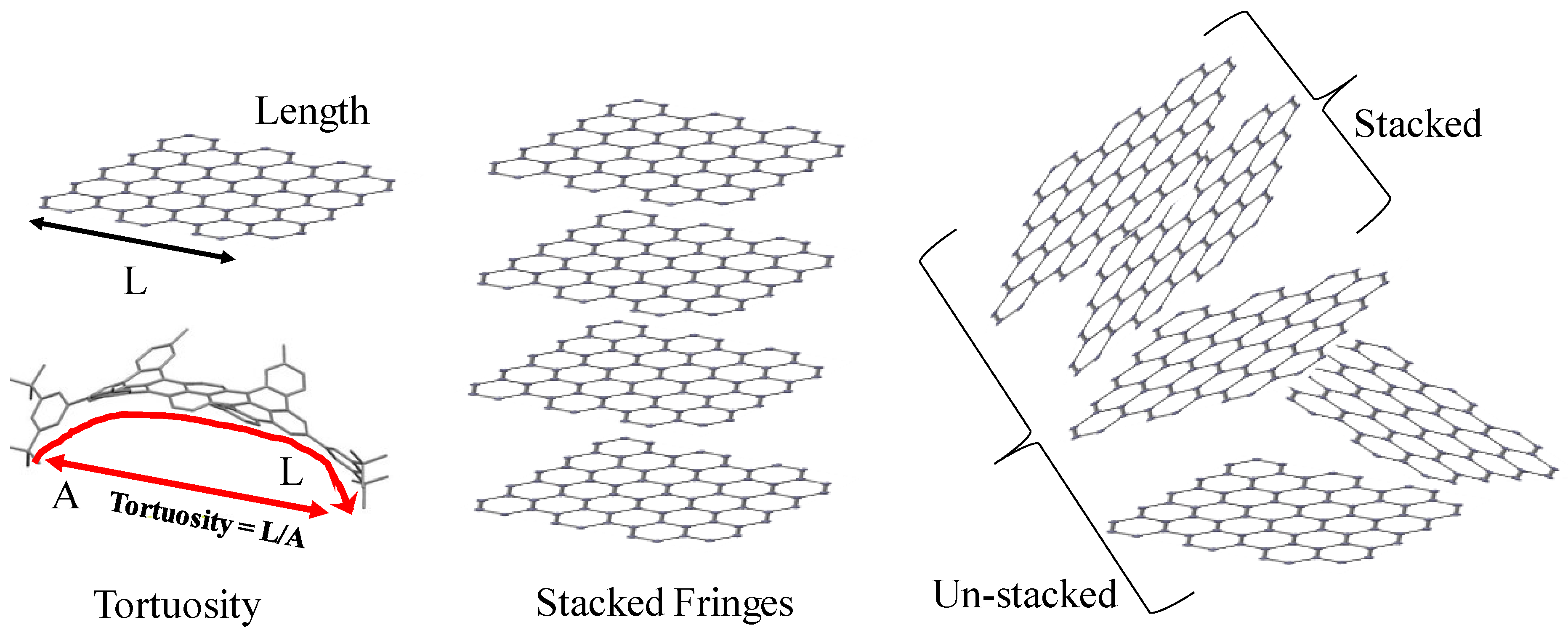
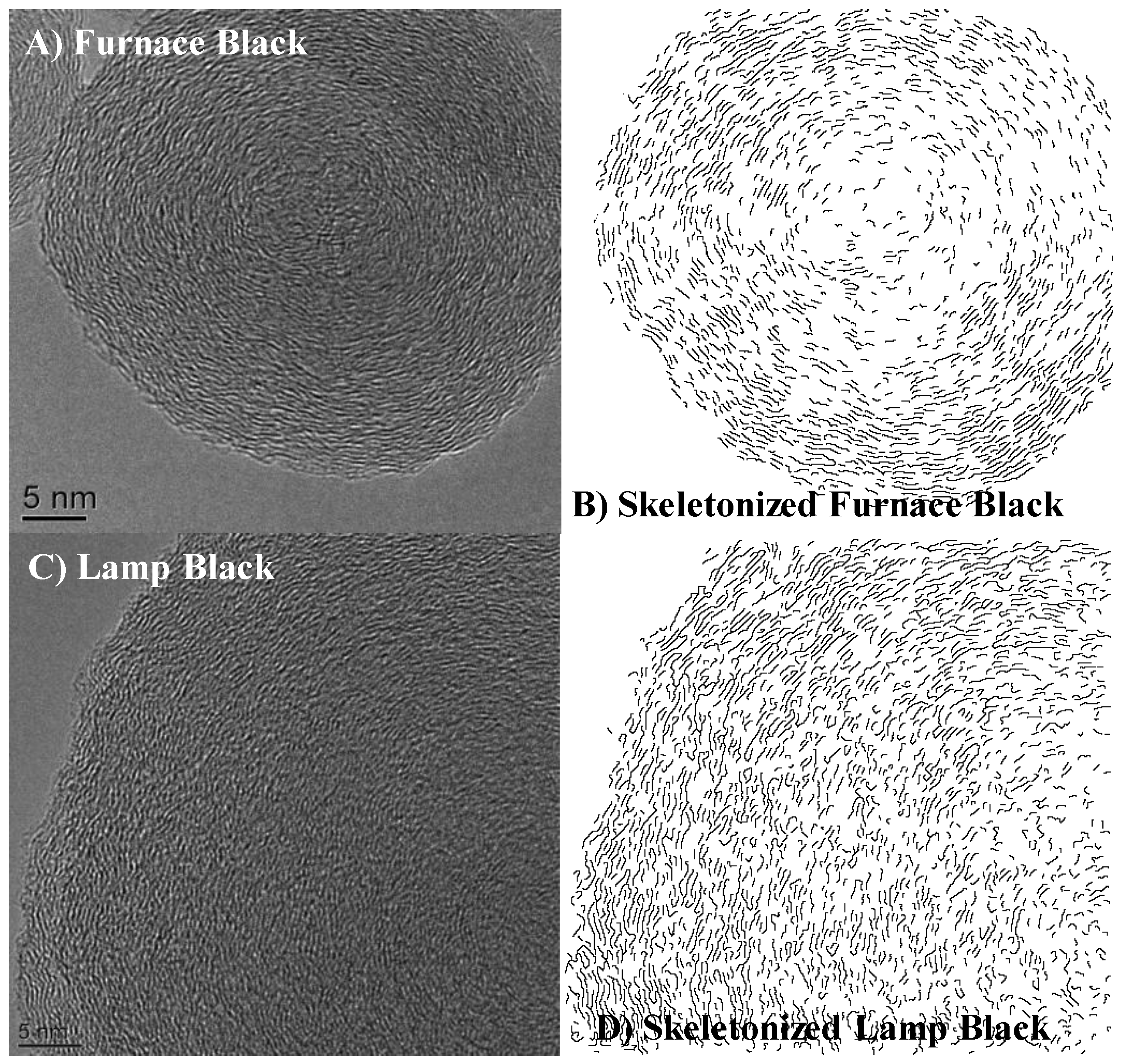
3.1. Length Scales
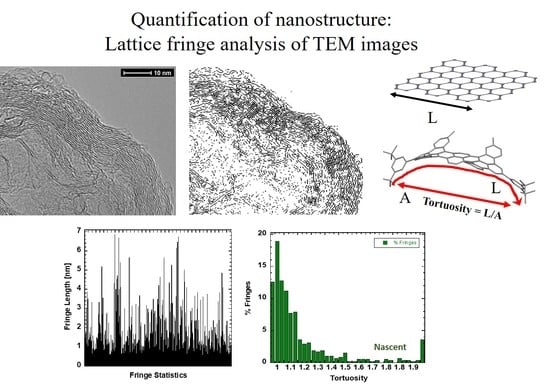
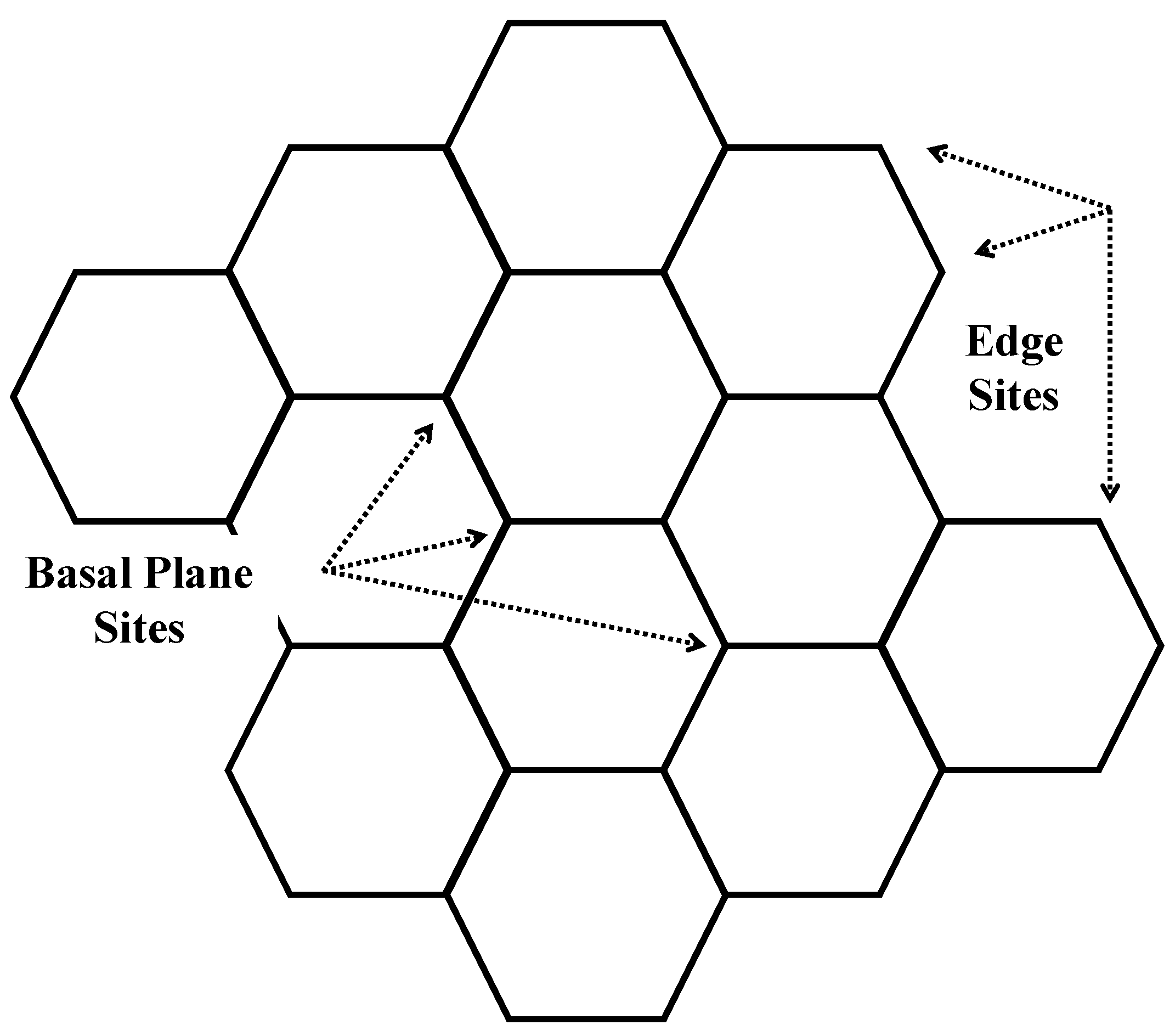
3.2. Nanostructure Quantification
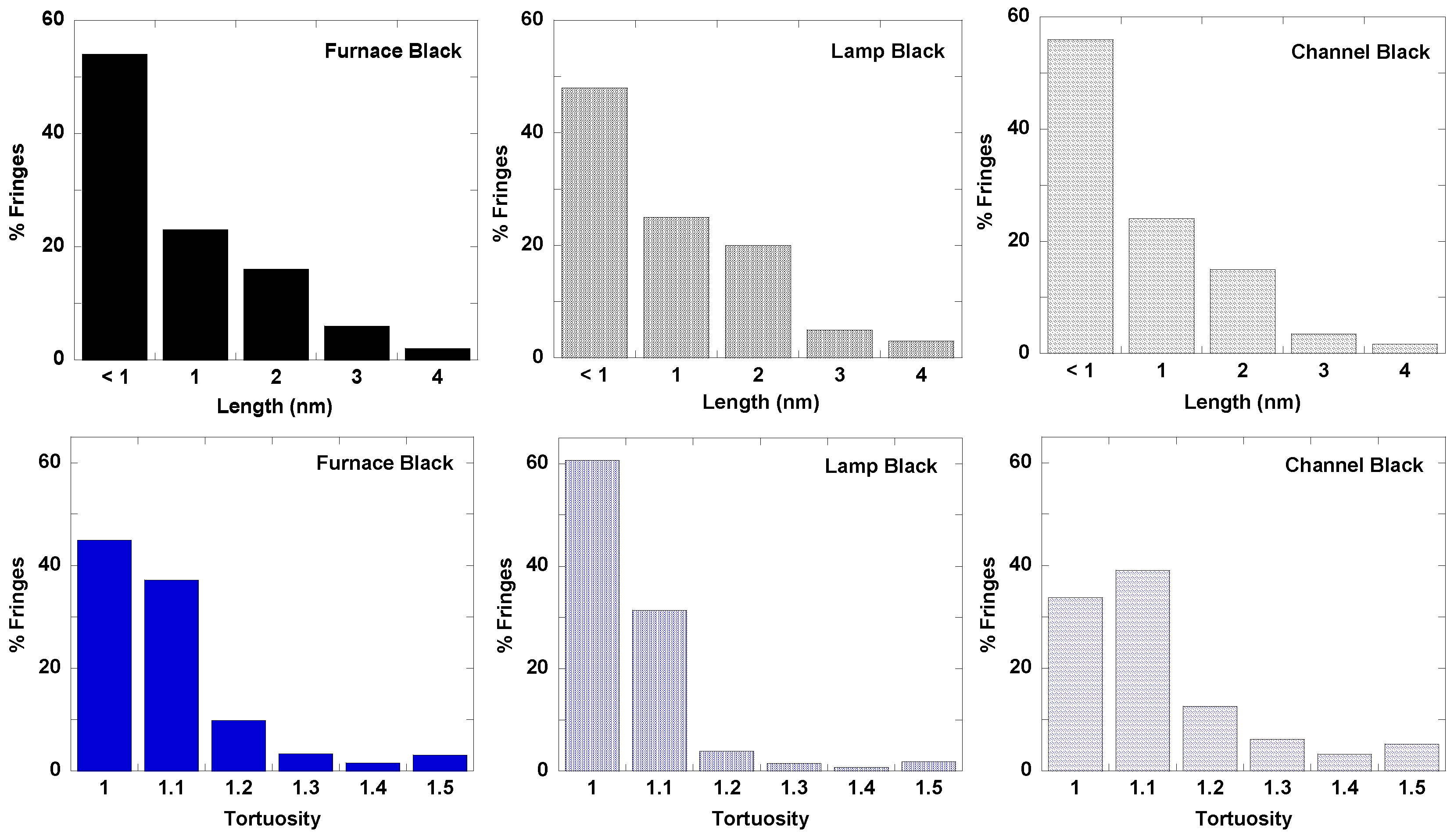
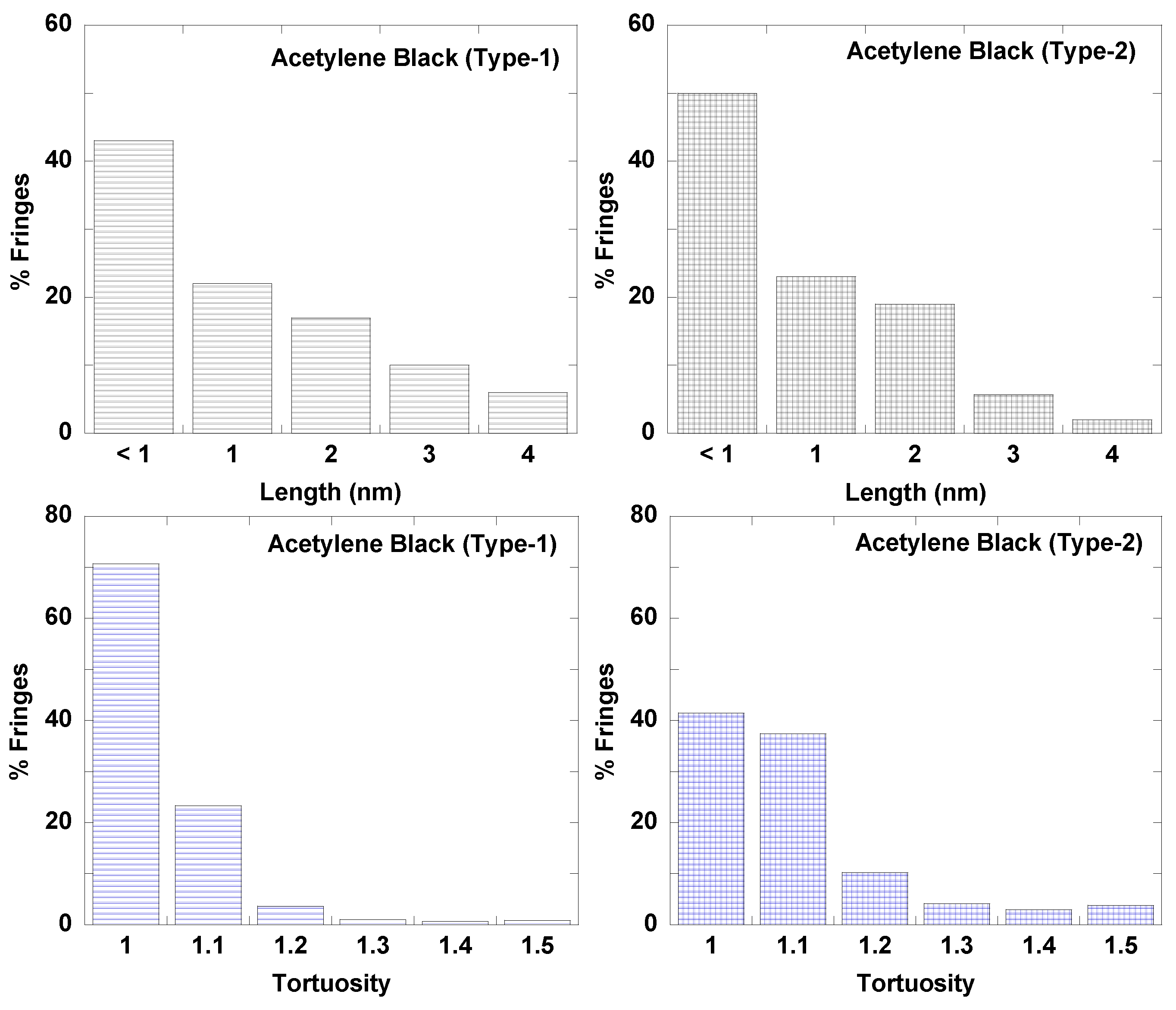
3.3. Fringe Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- What is Carbon Black? Orion Engineered Carbons. Available online: https://www.thecarycompany.com/media/pdf/specs/orion-what-is-carbon-black.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2018).
- About Carbon Black. Mitsubishi Chemical. Available online: http://www.carbonblack.jp/en/cb/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Carbon Black—A Global Market Overview. PR Newswire. 2016. Available online: http://ezaccess.libraries.psu.edu/login?url=https://search.proquest.com/docview/1757675949?accountid=13158 (accessed on 18 November 2018).
- Spahr, M.; Rothon, R. Carbon Black as a Polymer Filler. In Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Palsule, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, R.D.; Hess, W.M.; Ban, L.L. A test object and criteria for high resolution electron microscopy. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1968, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, R.L.V.; Tomasek, A.J.; Street, K.; Hull, D.R.; Thompson, W.K. Carbon Nanostructure Examined by Lattice Fringe Analysis of High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy Images. Appl. Spectrosc. 2004, 58, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Yehliu, K.; Wal, R.L.V.; Boehman, A.L. Development of an HRTEM image analysis method to quantify carbon nanostructure. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 1837–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, F.A. Microstructure of Carbon Black. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1964, 37, 1245–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, R.S.; de, S.K. Crosslinking of rubbers by fillers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2002, 75, 475–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, R.L.V. Soot Nanostructure: Definition, Quantification and Implications. SAE Tech. Pap. 2005, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E. X-Ray Diffraction in Random Layer Lattices. Phys. Rev. 1941, 59, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.E. The interpretation of diffuse X-ray diagrams of carbon. Acta Crystallogr. 1950, 3, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.A.; Walker, P.L. Measurement of interlayer spacings and crystal sizes in turbostratic carbons. Carbon N. Y. 1963, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlyta, M.; Rouzaud, J.-N.; Duber, S. Raman microspectroscopy characterization of carbon blacks: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon N. Y. 2015, 84, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adar, F. Raman Spectroscopy of Carbon—More Information Than You Would Think. Spectroscopy 2009, 24, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipara, D.M.; Chipara, A.C.; Chipara, M. Raman Spectroscopy of Carbonaceous Materials: A Concise Review. Spectroscopy 2011, 26, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wal, R.L.V. A TEM Methodology for the Study of Soot Particle Structure. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1997, 126, 333–351. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.J.F.; Tsang, S.C. High-resolution electron microscopy studies of non-graphitizing carbons. Philos. Mag. A 1997, 76, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.F. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Carbon: A Brief History. C 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luow, E. Structure and Combustion Reactivity of Inertinite-Rich and Vitrinite Rich South African Coal Chars: Quantification of the Structural Factors Contributing to Reactivity Differences. Ph.D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yehliu, K.; Wal, R.L.V.; Boehman, A.L. A comparison of soot nanostructure obtained using two high resolution transmission electron microscopy image analysis algorithms. Carbon N. Y. 2011, 49, 4256–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, R.L.V.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot oxidation: Dependence upon initial nanostructure. Combust. Flame 2003, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gaddam, C.K.; Wal, R.L.V.; Chen, X.; Yezerets, A.; Kamasamudram, K. Reconciliation of carbon oxidation rates and activation energies based on changing nanostructure. Carbon N. Y. 2016, 98, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Srilomsak, M.; Wang, Y.; Hanamura, K.; Wal, R.V. Nanostructure changes in diesel soot during NO2–O2 oxidation under diesel particulate filter-like conditions toward filter regeneration. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezerets, A.; Currier, N.W.; Eadler, H.A.; Suresh, A.; Madden, P.F.; Branigin, M.A. Investigation of the oxidation behavior of diesel particulate matter. Catal. Today 2003, 88, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, I.C.; Gaddam, C.K.; Wal, R.L.V.; Lighty, J.S. Effect of nanostructure, oxidative pressure and extent of oxidation on model carbon reactivity. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, R.L.V.; Tomasek, A.J. Soot nanostructure: Dependence upon synthesis conditions. Combust. Flame 2004, 136, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Matarrese, R.; Castoldi, L.; Lietti, L. Oxidation of model soot by NO2 and O2 in the presence of water vapor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 173, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalagedara, L.; Sharma, H.; Kuo, C.H.; Dharmarathna, S.; Joshi, A.; Suib, S.L.; Mhadeshwar, A.B. Structure and Oxidation Activity Correlations for Carbon Blcks and Diesel Soot. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6757–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wal, R.L.V.; Strzelec, A.; Toops, T.J.; Daw, C.S.; Genzale, C.L. Forensics of soot: C5-related nanostructure as a diagnostic of in-cylinder chemistry. Fuel 2013, 113, 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Long, C.M.; Nascarella, M.A.; Valberg, P.A. Carbon black vs. black carbon and other airborne materials containing elemental carbon: Physical and chemical distinctions. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India Carbon Black Market to Grow at 14% CAGR Until 2020 Claims TechSci Research Study. PR Newswire Europe Including UK Disclose. 2015. Available online: http://ezaccess.libraries.psu.edu/login?url=https://search.proquest.com/docview/1667661272?accountid=13158 (accessed on 11 January 2018).


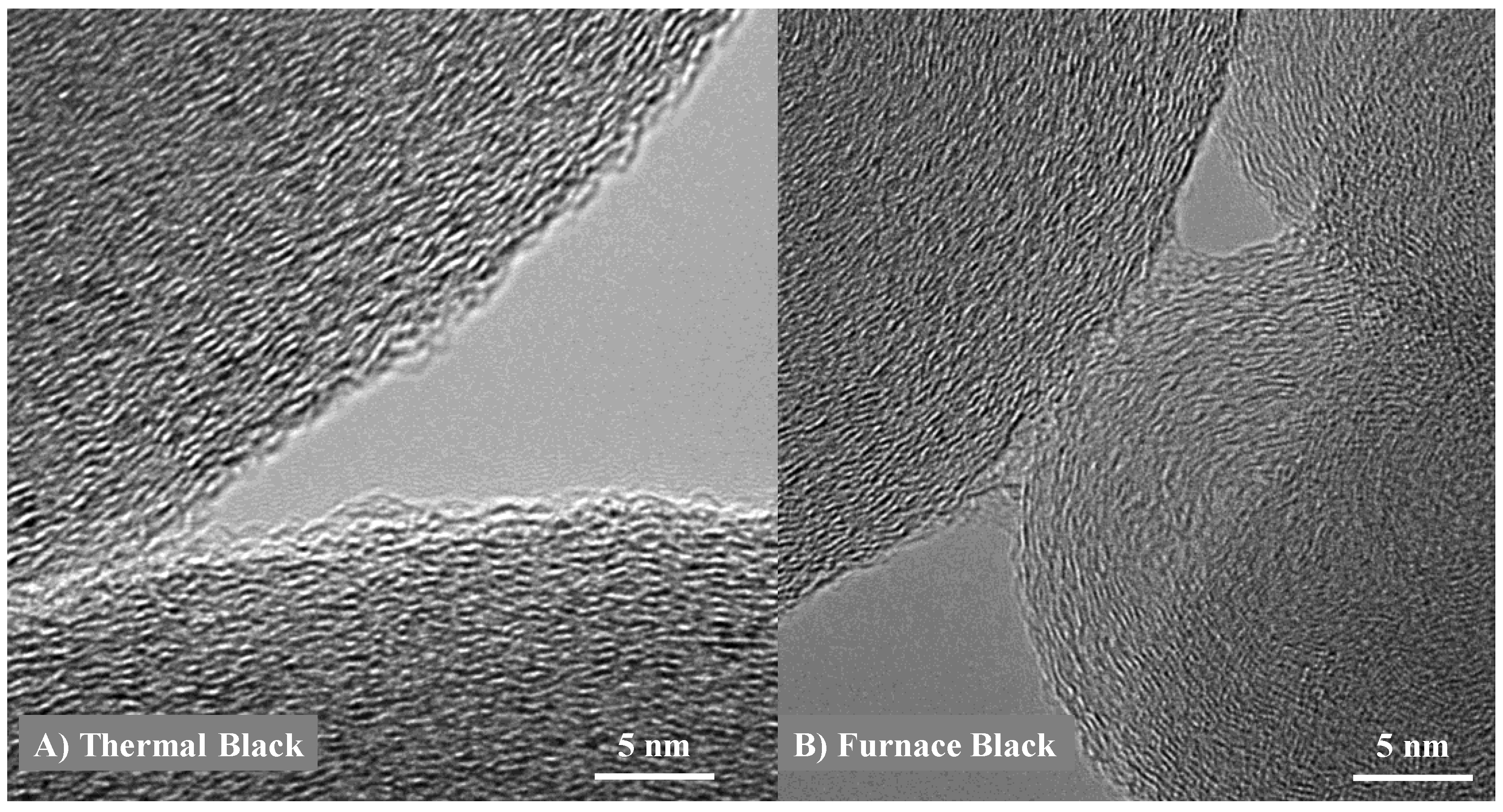
| Lattice Parameter | Furnace Black | Thermal Black | Lamp Black | Channel Black | Acetylene Black-1 | Acetylene Black-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d002 (Å) | 3.60 | 3.58 | 3.56 | 3.70 | 3.54 | 3.45 |
| Lc (using 002) (nm) | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.6 |
| La (using 100) (nm) | 5.6 | 4.5 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, M.; Vander Wal, R.L. Nanostructure Quantification of Carbon Blacks. C 2019, 5, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010002
Singh M, Vander Wal RL. Nanostructure Quantification of Carbon Blacks. C. 2019; 5(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Madhu, and Randy L. Vander Wal. 2019. "Nanostructure Quantification of Carbon Blacks" C 5, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010002
APA StyleSingh, M., & Vander Wal, R. L. (2019). Nanostructure Quantification of Carbon Blacks. C, 5(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010002