High Performance of Alkaline Anion-Exchange Membranes Based on Chitosan/Poly (vinyl) Alcohol Doped with Graphene Oxide for the Electrooxidation of Primary Alcohols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
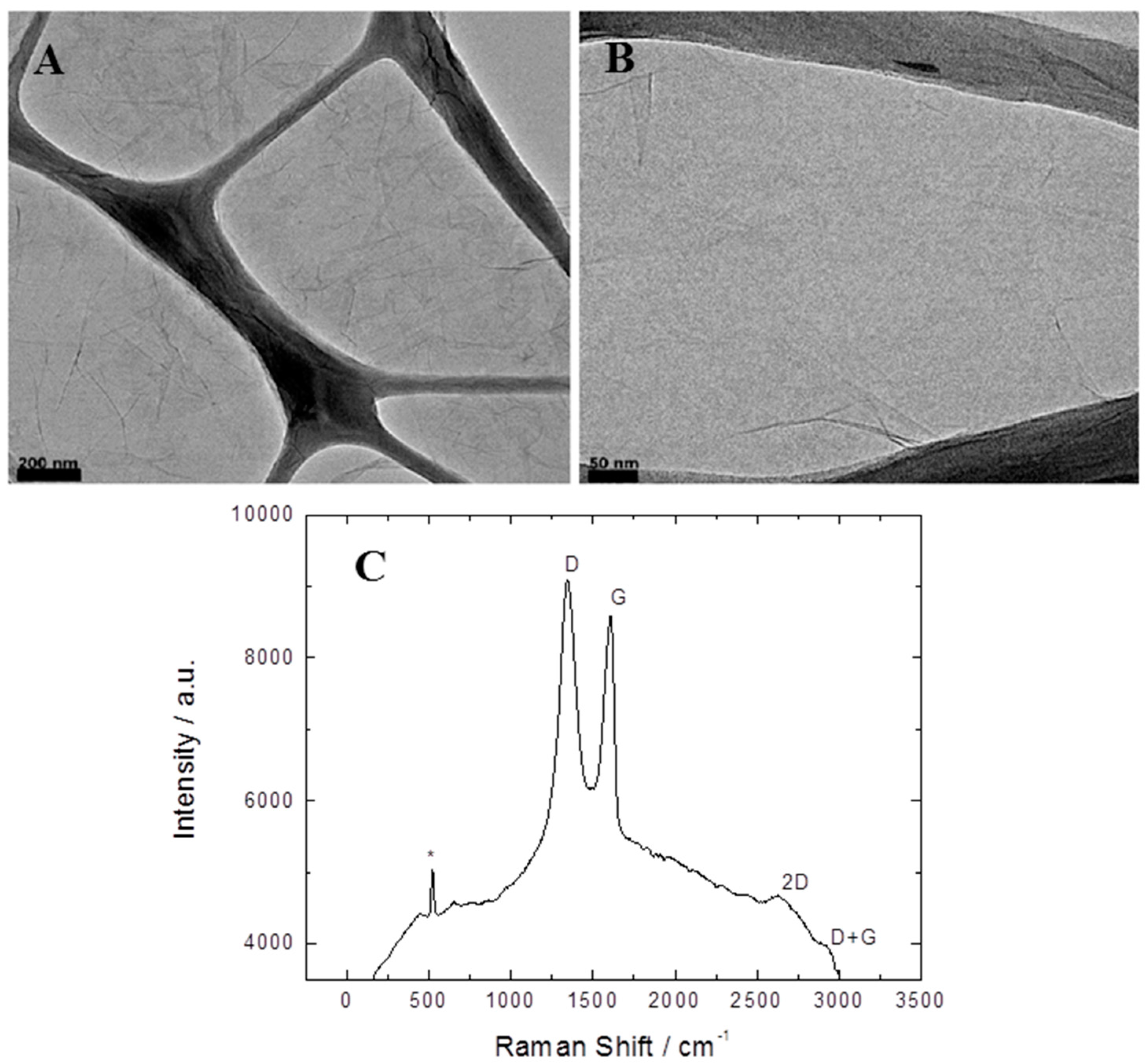
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Graphene Oxide
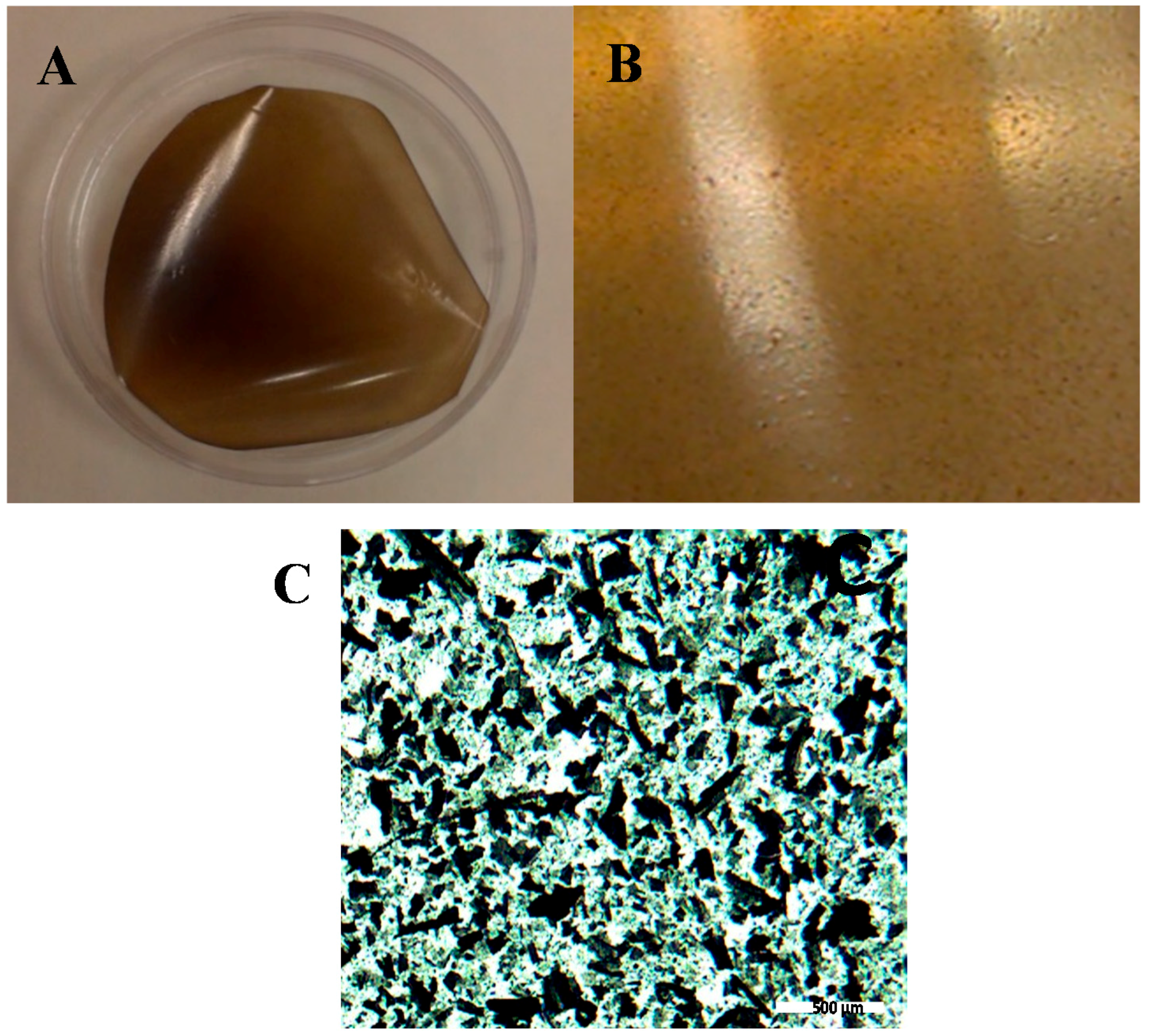
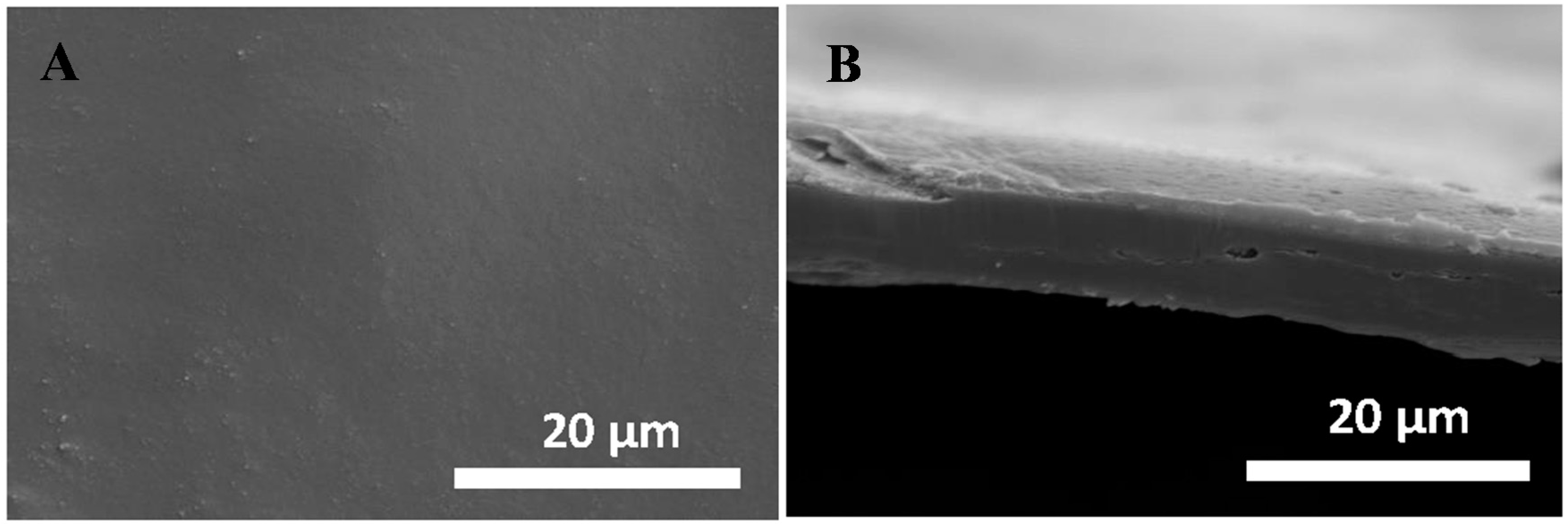
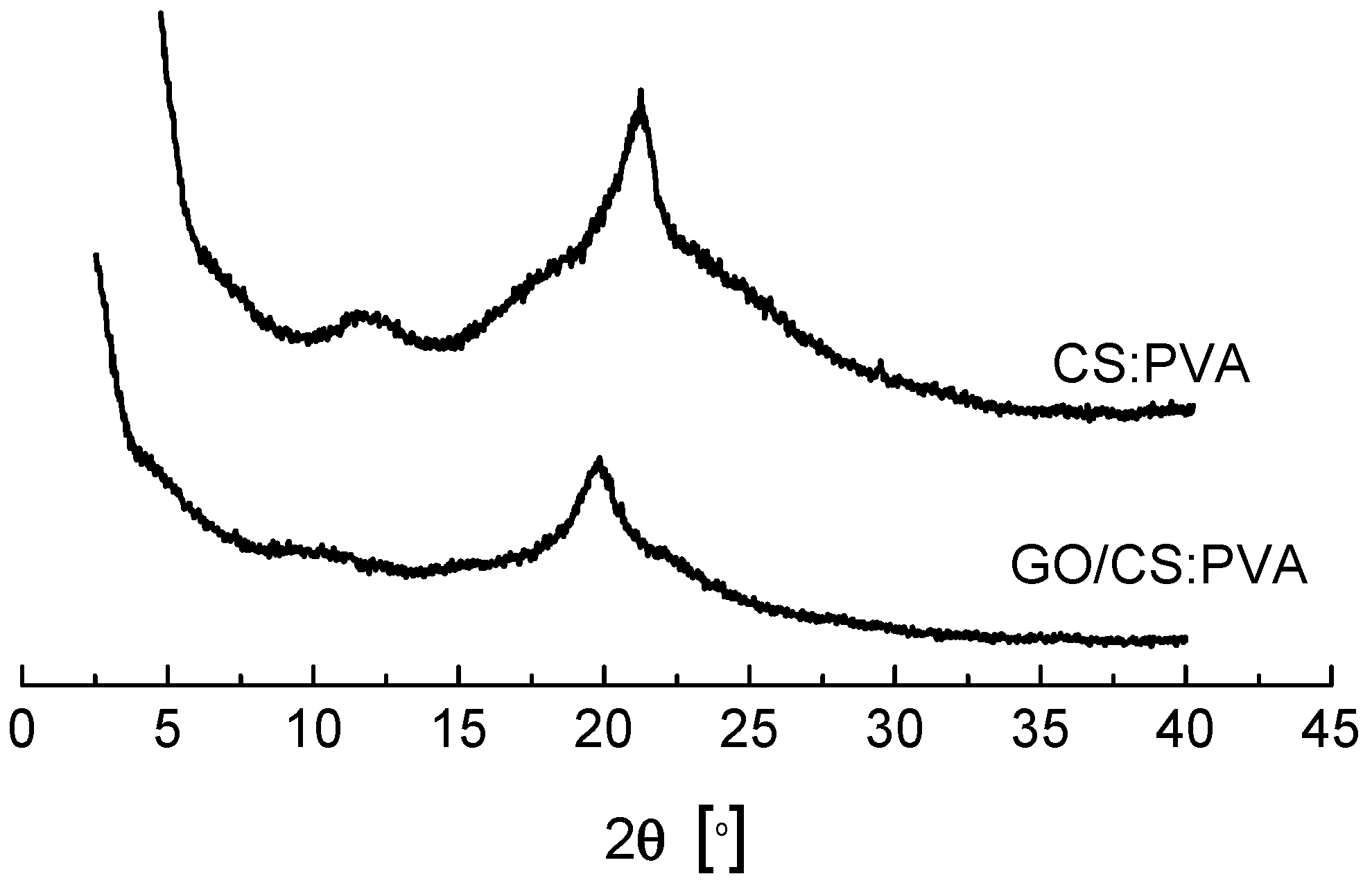
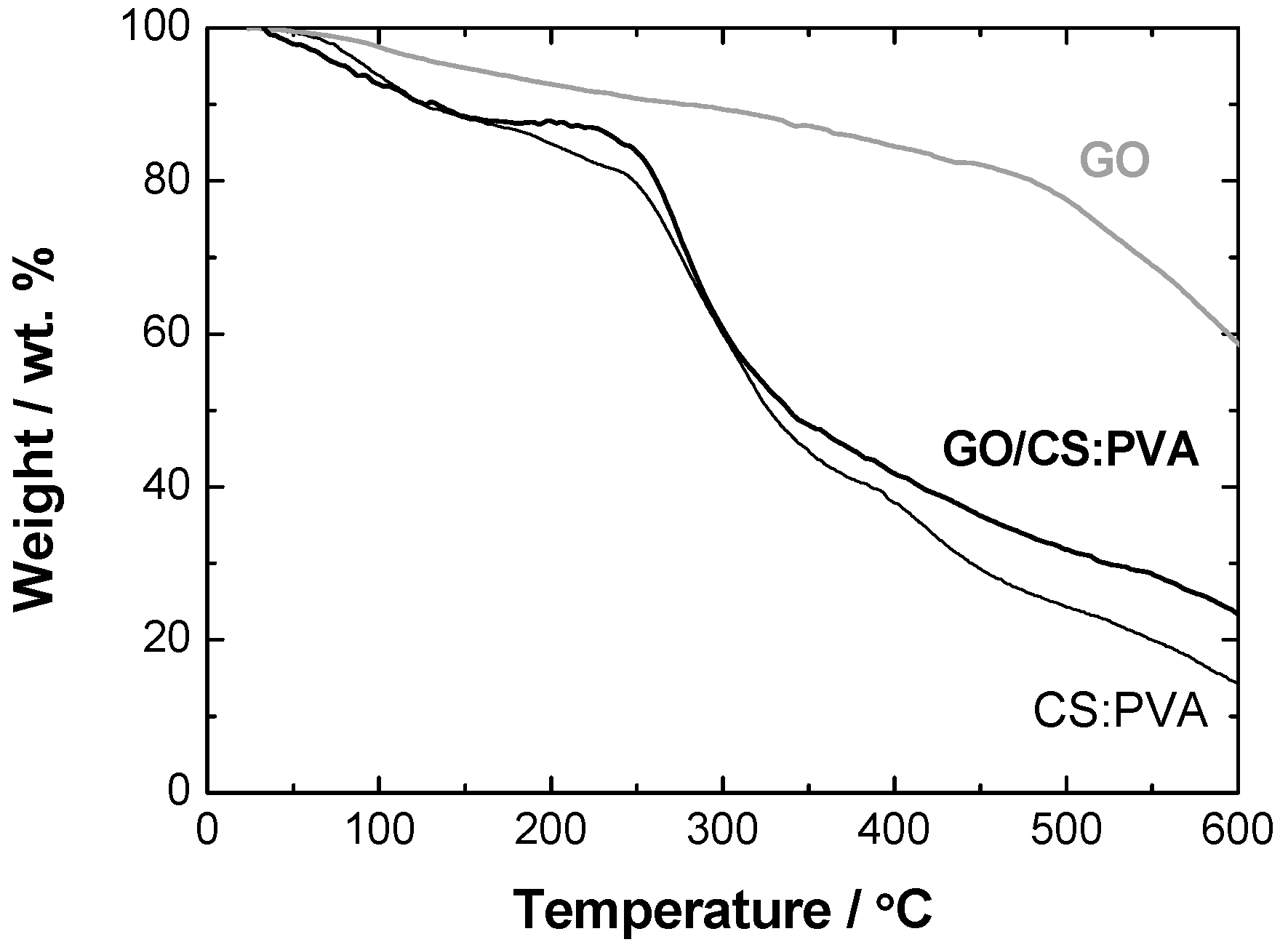
2.2. Structural and Chemical Characterization of GO/CS:PVA Membrane
2.3. Hydroxide Conductivity
2.4. Alcohol Permeability
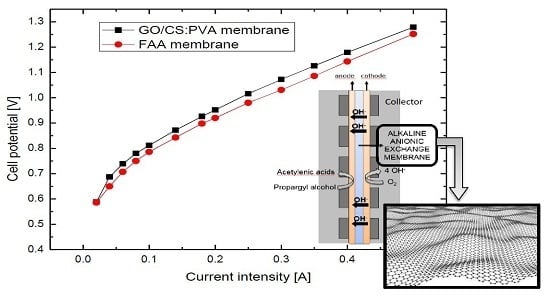
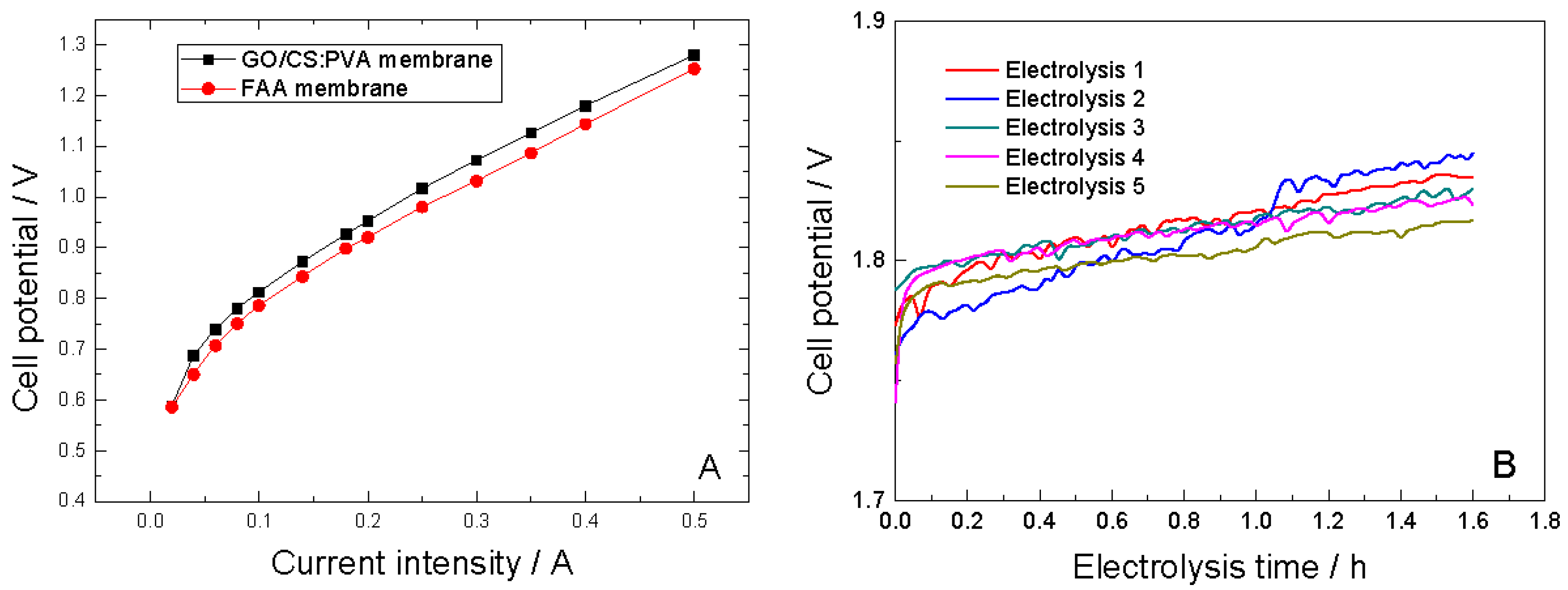
2.5. Electrochemical Performance of GO/CS:PVA Membranes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Membrane Preparation
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization of GO Solution and GO/CS:PVA Membrane
3.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.5. Alcohol Permeability Measurements
3.6. Polarization Curves and Electrolysis into a PEM Electrochemical Reactor
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleh, F.S.; Easton, E.B. Assessment of the ethanol oxidation activity and durability of Pt catalysts with or without a carbon support using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, A.; Garcia-Garcia, V.; Solla-Gullon, J.; Aldaz, A.; Montiel, V. Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of acetophenone using a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Electrochemical Reactor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Montiel, V.; Sáez, A.; Exposito, E.; García-García, V.; Aldaz, A. Use of MEA technology in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds: The electrosynthesis of N-acetyl-l-cysteine. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ogumi, Z.; Nishio, K.; Yoshizawa, S. Application of the SPE method to organic electrochemistry—II. Electrochemical hydrogenation of olefinic double bonds. Electrochim. Acta 1981, 26, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogumi, Z.; Inaba, M.; Ohashi, S.-I.; Uchida, M.; Takehara, Z.-I. Application of the SPE method to organic electrochemistry—VII. The reduction of nitrobenzene on a modified Pt-nafion. Electrochim. Acta 1988, 33, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cruz, L.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Iniesta, J.; Montiel, V.; Irabien, Á. Chitosan:poly (vinyl) alcohol composite alkaline membrane incorporating organic ionomers and layered silicate materials into a PEM electrochemical reactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Qiao, J.; Baker, R.; Zhang, J. Alkaline polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5768–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K. Electrochemical Oxygen Technology; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, K.; Abe, T.; Nishio, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Ogumi, Z. Use of layered double hydroxides to improve the triple phase boundary in anion-exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6500–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Doubek, G.; Sekol, R.C.; Linardi, M.; Taylor, A.D. Development and electrochemical studies of membrane electrode assemblies for polymer electrolyte alkaline fuel cells using FAA membrane and ionomer. J. Power Sources 2013, 230, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Presser, V. Carbon Nanomaterials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tascón, J.M.D. Novel Carbon Adsorbents, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.L.; Tian, Z.; Simon, G.P.; Li, D. Scalable production of graphene via wet chemistry: Progress and challenges. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Yao, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y. A selective voltammetric method for detecting dopamine at quercetin modified electrode incorporating graphene. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Graphene electrochemistry: An overview of potential applications. Analyst 2010, 135, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Lingling, X.; Hongli, L. Electrochemical biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoparticles entrapped in chitosan/silica sol-gel hybrid membranes for determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 682, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, Q.; Wang, X. Graphene Oxide-MnO2 nanocomposites for supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Chang, D.W.; Baek, J.B.; Lu, W. Carbon nanomaterials for advanced energy conversion and storage. Small 2012, 8, 1130–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandele, A.M.; Ionita, M.; Crica, L.; Dinescu, S.; Costache, M.; Iovu, H. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro studies of graphene oxide/chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, W.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. A chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite film reinforced with natural halloysite nanotubes. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, G.; Sun, J.; Song, R. Chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite films with enhanced interfacial interaction and their electrochemical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshmani, S.; Amini, R. Preparation and characterization of some graphene based nanocomposite materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, N.; Rajasekar, R.; Mahalakshmi, S.; Sathishkumar, T.P.; Sasikumar, K.S.K.; Sahoo, S. Graphene and modified graphene-based polymer nanocomposites—A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1158–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghi, H.; Javanbakht, M.; Bagheri, A.; Salarizadeh, P.; Ghafarian-Zahmatkesh, H.; Kashefi, S.; Kowsari, E. Novel nanocomposite membranes based on blended sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/poly(vinyl alcohol) containing sulfonated graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanosheets for DMFC applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74054–74064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, S.; Sharma, P.P.; Kulshrestha, V.; Jha, P.K. SGO/SPES-based highly conducting polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5595–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Choi, B.G.; Choi, D.; Park, H.S. Nanoindentation of annealed Nafion/sulfonated graphene oxide nanocomposite membranes for the measurement of mechanical properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. Sulfonated polyether ether ketone—Sulfonated graphene oxide composite membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.C.; Tsai, L.D.; Huang, C.P.; Kang, C.Y.; Lin, J.N.; Chang, F.C. Sulfonated graphene oxide/Nafion composite membranes for high-performance direct methanol fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2013, 38, 13792–13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Cao, Y.C.; Kumar, R.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Scott, K. A polybenzimidazole/sulfonated graphite oxide composite membrane for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11359–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.G.; Huh, Y.S.; Park, Y.C.; Jung, D.H.; Hong, W.H.; Park, H. Enhanced transport properties in polymer electrolyte composite membranes with graphene oxide sheets. Carbon 2012, 50, 5395–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A. Composite membranes based on sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) and SDBS-adsorbed graphene oxide for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24862–24869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, J.T.; Zhang, H.Q.; Ma, C.M.; Liu, J.D.; Cao, S.K.; Zhang, X. Enhancement of proton conductivity of chitosan membrane enabled by sulfonated graphene oxide under both hydrated and anhydrous conditions. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Shang, X. Preparation of graphene/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties and water resistance. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.N.; Huang, N.M.; Loo, C.H. Facile preparation of graphene-based chitosan films: Enhanced thermal, mechanical and antibacterial properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Chen, D.J.; Lu, P. Enhanced mechanical properties of graphene-based poly(vinyl alcohol) composites. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Gomez, M.A.; Martinez, G. Polymeric modification of graphene through esterification of graphite oxide and poly(vinyl alcohol). Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6331–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shen, X.P.; Wu, J.L.; Shen, K.C. Preparation and characterization of graphene/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Guo, Z. Graphene oxide cross-linked chitosan nanocomposite membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, T.; Bao, H.; Li, L. Green fabrication of chitosan films reinforced with parallel aligned graphene oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.M.; Wimalasiri, Y.; Ginic-Markovic, M.; Zou, L. Improving the fouling resistance of brackish water membranes via surface modification with graphene oxide functionalized chitosan. Desalination 2015, 365, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, G.P.; Lou, Y.Y.; Dong, Z.Y.; Shen, J.; Jin, W.Q. A graphene oxide membrane with highly selective molecular separation of aqueous organic solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6929–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.P.; Gahlot, S.; Bhil, B.M.; Gupta, H.; Kulshrestha, V. An environmentally friendly process for the synthesis of an fGO modified anion exchange membrane for electro-membrane applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38712–38721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.S.; Cheng, M.Y.; Xie, X.L.; Rick, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Chang, F.C.; Hwang, B.J. Alkali doped polyvinyl alcohol/graphene electrolyte for direct methanol alkaline fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movil, O.; Frank, L.; Staser, J.A. Graphene oxide-polymer nanocomposite anion-exchange membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F419–F426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Im, H.; Heo, Y.; Kim, J. Crosslinked sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol)/sulfonated multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 380, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Su, Y.H.; Chang, C.M.; Suryani; Wang, D.M.; Lai, J.Y. Preparation and applications of Nafion-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4409–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Kakade, B.A.; Pillai, V.K. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells using nafion-based composite membranes with functionalized carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2653–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan composite anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, J.; Kakati, N.; Lee, S.H.; Jee, S.H.; Viswanathan, B.; Yoon, Y.S. Where do poly(vinyl alcohol) based membranes stand in relation to Nafion® for direct methanol fuel cell applications? J. Power Sources 2012, 216, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Xing, W.; Yu, B.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Simultaneous reduction and surface functionalization of graphene oxide by chitosan and their synergistic reinforcing effects in PVA films. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 12906–12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Wang, S.A. Preparation of graphene-based poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan nanocomposites membrane for alkaline solid electrolytes membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 477, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.M.; Shin, H.J.; Yoon, H.W.; Park, H.B. Graphene and graphene oxide and their uses in barrier polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39628–39650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Chiu, H.C. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan blended membrane for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 419–420, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.J.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Yadav, S.K.; Cho, J.W. Synthesis of click-coupled graphene sheet with chitosan: Effective exfoliation and enhanced properties of their nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Coterillo, C.; Andres, F.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J.; Irabien, A. Synthesis and characterization of ETS-10/Chitosan nanocomposite membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, L.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Iniesta, J.; Montiel, V.; Irabien, Á. Preparation and characterization of novel chitosan-based mixed matrix membranes resistant in alkaline media. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42240–42249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Creber, K.A.M.; Peppley, B.; Bui, V.T. Chitosan-based solid electrolyte composite membranes I. Preparation and characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.L.; Guo, Y.Q.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites based on graphene and graphite oxide: A comparative investigation of property and mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13942–13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malah, K.; Abu-Jdayil, B. Clay-based heat insulator composites: Thermal and water retention properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 37, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Kang, M.S.; Seo, B.K. Preparation and electrochemical characterizations of anion-permselective membranes with structurally stable ion-exchange sites. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudin, K.N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H.C.; Prud’homme, R.K.; Aksay, I.A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franck-Lacaze, L.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P. Determination of the pKa of poly (4-vinylpyridine)-based weak anion exchange membranes for the investigation of the side proton leakage. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.C.; Dong, H.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Si, Z.H.; Gu, F.L.; Yan, F. Alkaline stable C2-substituted imidazolium-based anion-exchange membranes. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, S.J.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Moon, S.H. Effect of pressure on through-plane proton conductivity of polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Niya, S.M.; Hoorfar, M. Study of proton exchange membrane fuel cells using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy technique—A review. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Liu, X. Electrocatalytic oxidation of cyclohexanol on a nickel oxyhydroxide modified nickel electrode in alkaline solutions. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cruz, L.; Saez, A.; Ania, C.O.; Solla-Gullon, J.; Thiemann, T.; Iniesta, J.; Montiel, V. Electrocatalytic activity of Ni-doped nanoporous carbons in the electrooxidation of propargyl alcohol. Carbon 2014, 73, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, C.M.; Exposito, E.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Garcia-Garcia, V.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Calculation of the characteristic performance indicators in an electrochemical process. J. Chem. Educ. 2003, 80, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F. A First Course in Electrochemical Engineering; Electrochemical Consultancy: Hants, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]

| Element | CS:PVA Membrane | GO Membrane | GO |
|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s | 284.29 | 284.57 | 284.56 |
| (40.71) | (27.03) | (32.19) | |
| C–C–C–H | Graphite, C–C, C–H | Graphite, C–C, C–H | |
| C 1s | 285.85 | 286.20 | 286.56 |
| (25.41) | (28.87) | (27.18) | |
| C–N, C–O | C–N, C–O | –C–O | |
| C 1s | 287.62 | 287.9 | 287.81 |
| (7.12) | (9.47) | (9.29) | |
| –C=O | –C=O | –C=O | |
| C | 73.24 | 65.37 | 68.66 |
| N 1s | 399.15 | 399.54 | |
| (4.01) | (4.69) | ||
| NH–C, NH2 | N–C | ||
| N 1s | 400.8 | 401.09 | |
| (0.68) | (0.68) | ||
| C–N | C–N | ||
| N | 4.69 | 5.37 | |
| O 1s | 531.03 | 531.15 | 531.12 |
| (5.44) | (4.14) | (5.79) | |
| O=C | O=C | O=C | |
| O 1s | 532.22 | 532.49 | 532.52 |
| (16.61) | (25.12) | (25.55) | |
| O–C | O–C | O–C | |
| O | 22.06 | 29.26 | 31.34 |
| Membranes | Thickness (µm) | WC (wt.%) | WU (%) | IEC (meq·g−1) | Specific Conductivity, σ (mS·cm−1) | Propanol Permeability, P (10−7·cm2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS:PVA | 156 ± 0.001 | 23.11 ± 4 | 139.5 [6] | 0.253 ± 0.050 [6] | 0.15–0.29 [6] | 1.76 [6] |
| GO/CS:PVA | 105 ± 0.001 | 19.00 ± 7.1 | 138.4 | 0.379 ± 0.037 | 0.19 | 2.43 |
| PCG 0.1 [40] | 106.9 | 42 | 17.83 | |||
| PCsG 0.1 [40] | 132.3 | 47.6 | 17.29 | |||
| FAA [6] | 130 ± 0.001 | 33.83 | 16.19 | 0.318 ± 0.018 | 2.92 | 2.34 |
| Electrooxidation Conditions | Initial PGA Amount (mole) | Anolyte Flow Rate (mL·min−1) | Catholyte Flow Rate (mL·min−1) | Current Density (mA·cm−2) | Temperature (°C) | Anolyte pH | ||||||
| 0.0075 mole (0.25 M) | 12 | 50 | 20 | 25 ± 1 °C | 14 | |||||||
| Electrooxidation | Membrane | Conversion, χPGA | Current efficiency, | Products | Space time yield (Kg·m−3·day−1) | Specific electrolytic energy consumption (kWh·kg−1) | Average cell potential (V) | |||||
| FAA | 0.74 | 0.31 | Z-PPA | 14574 | 3.32 | 1.21 ± 0.01 | ||||||
| GO/CS:PVA | ||||||||||||
| (1) | 0.64 | 0.28 | Z-PPA | 13163 | 5.5 | 1.81 ± 0.01 | ||||||
| (2) | 0.52 | 0.22 | Z-PPA | 13163 | 7.0 | 1.81 ± 0.02 | ||||||
| (3) | 0.47 | 0.20 | Z-PPA | 9402 | 7.7 | 1.81 ± 0.01 | ||||||
| (4) | 0.51 | 0.23 | Z-PPA | 10813 | 6.70 | 1.80 ± 0.2 | ||||||
| (5) | 0.45 | 0.20 | Z-PPA | 9402 | 7.66 | 1.80 ± 0.01 | ||||||
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Cruz, L.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Irabien, Á.; Montiel, V.; Iniesta, J. High Performance of Alkaline Anion-Exchange Membranes Based on Chitosan/Poly (vinyl) Alcohol Doped with Graphene Oxide for the Electrooxidation of Primary Alcohols. C 2016, 2, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020010
García-Cruz L, Casado-Coterillo C, Irabien Á, Montiel V, Iniesta J. High Performance of Alkaline Anion-Exchange Membranes Based on Chitosan/Poly (vinyl) Alcohol Doped with Graphene Oxide for the Electrooxidation of Primary Alcohols. C. 2016; 2(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Cruz, Leticia, Clara Casado-Coterillo, Ángel Irabien, Vicente Montiel, and Jesus Iniesta. 2016. "High Performance of Alkaline Anion-Exchange Membranes Based on Chitosan/Poly (vinyl) Alcohol Doped with Graphene Oxide for the Electrooxidation of Primary Alcohols" C 2, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020010
APA StyleGarcía-Cruz, L., Casado-Coterillo, C., Irabien, Á., Montiel, V., & Iniesta, J. (2016). High Performance of Alkaline Anion-Exchange Membranes Based on Chitosan/Poly (vinyl) Alcohol Doped with Graphene Oxide for the Electrooxidation of Primary Alcohols. C, 2(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020010