Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Properties of Gangue–Fly Ash Composite Filling Materials: Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Slurry Preparation and Carbon Fixation Process
2.2.2. Carbon Sequestration Calculation
2.2.3. Rheological Test
2.2.4. XRD Test
2.2.5. FTIR Test
2.2.6. SEM Test
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties of CFS
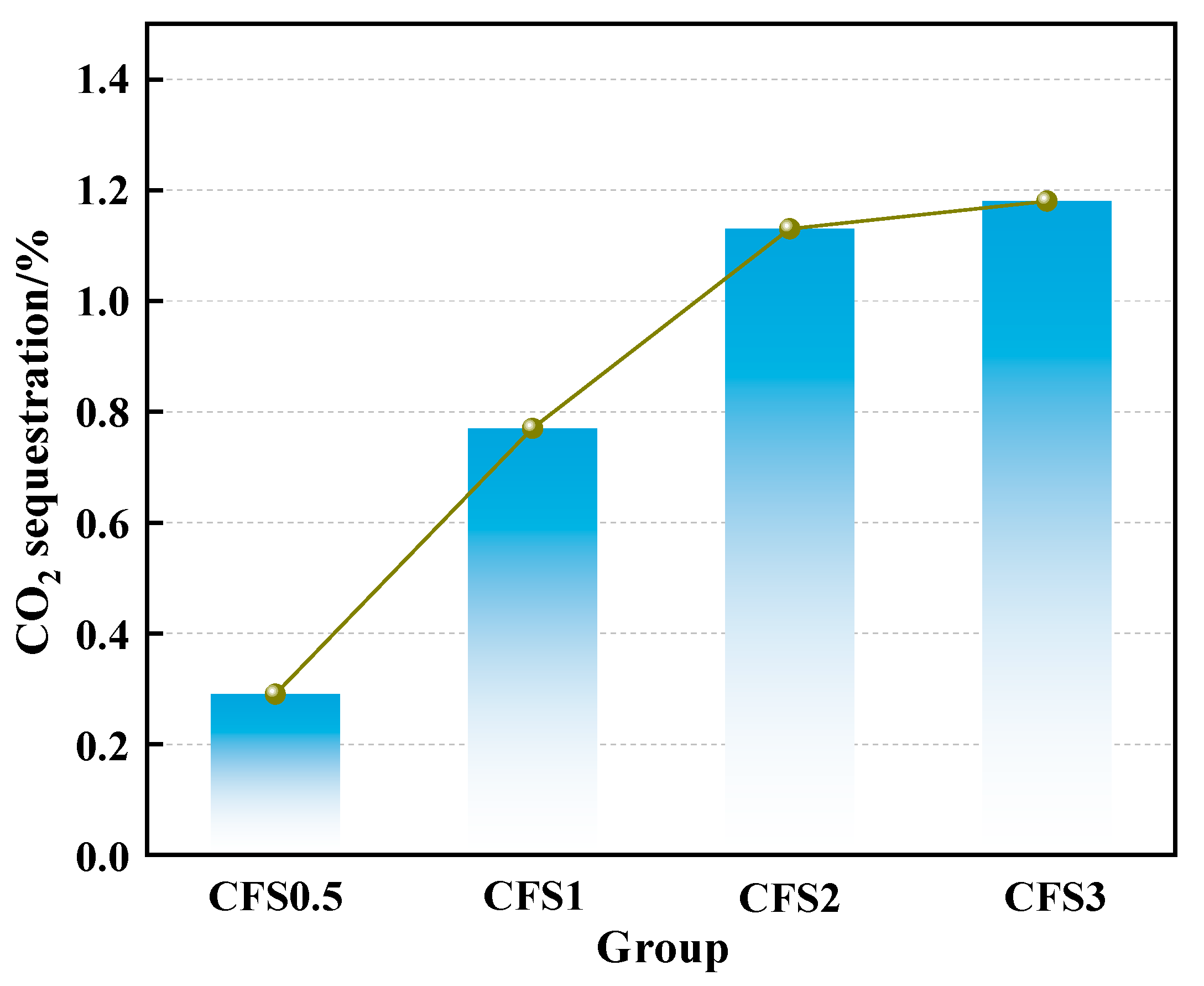
3.1.1. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on Carbon Fixation Amount of CFS
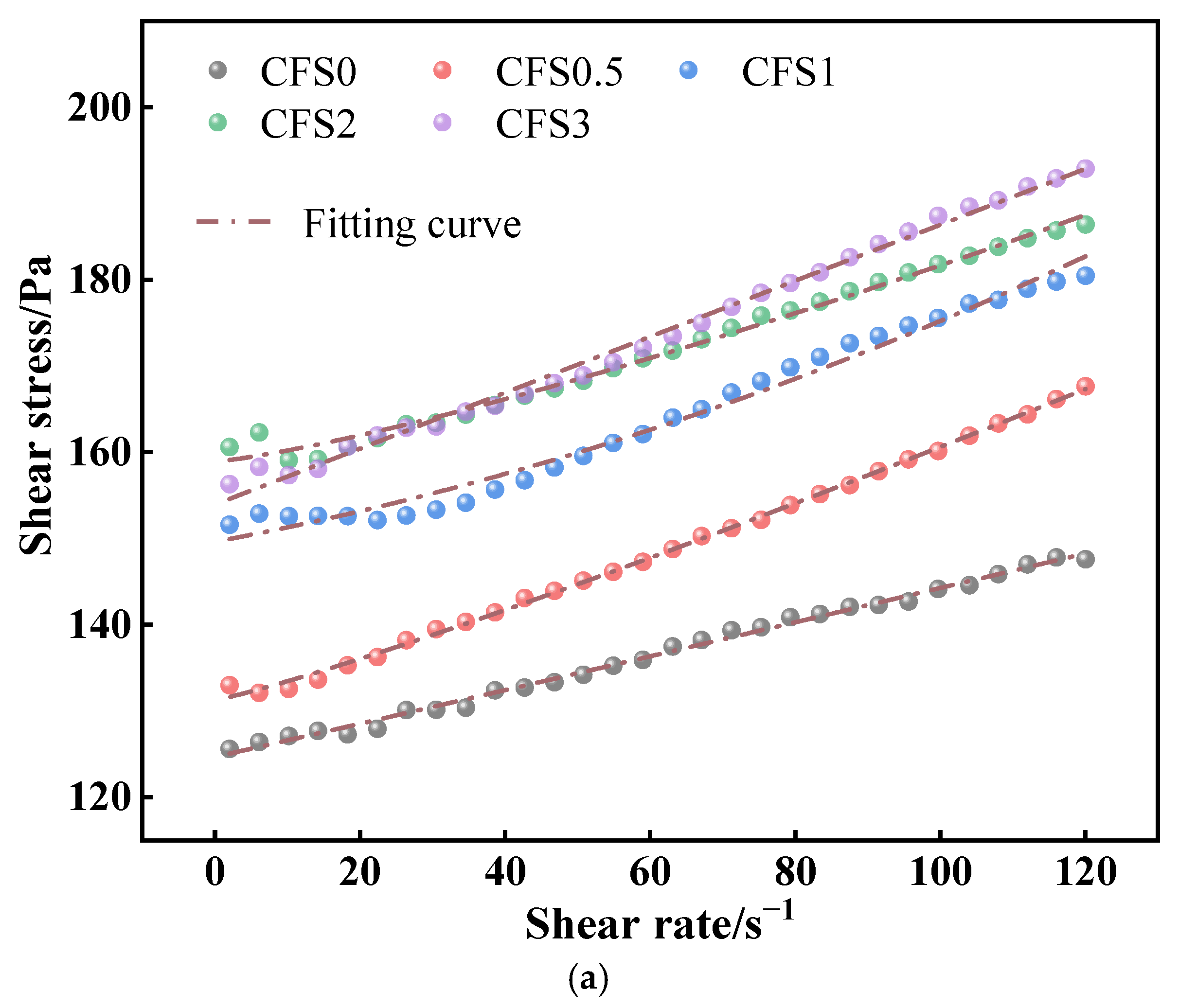
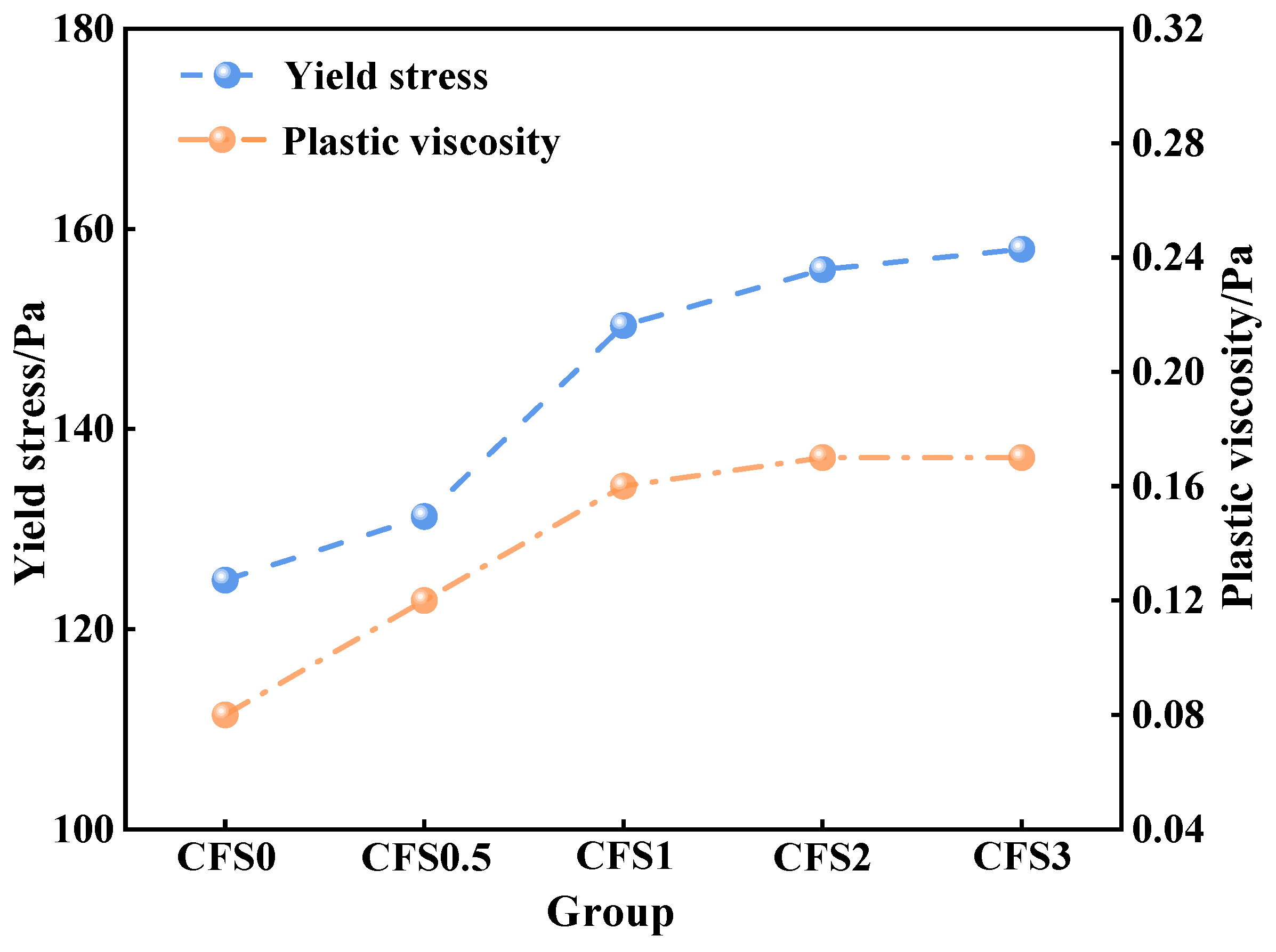
3.1.2. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on CFS Rheological Parameters
3.2. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Composition and Microstructure of CFS
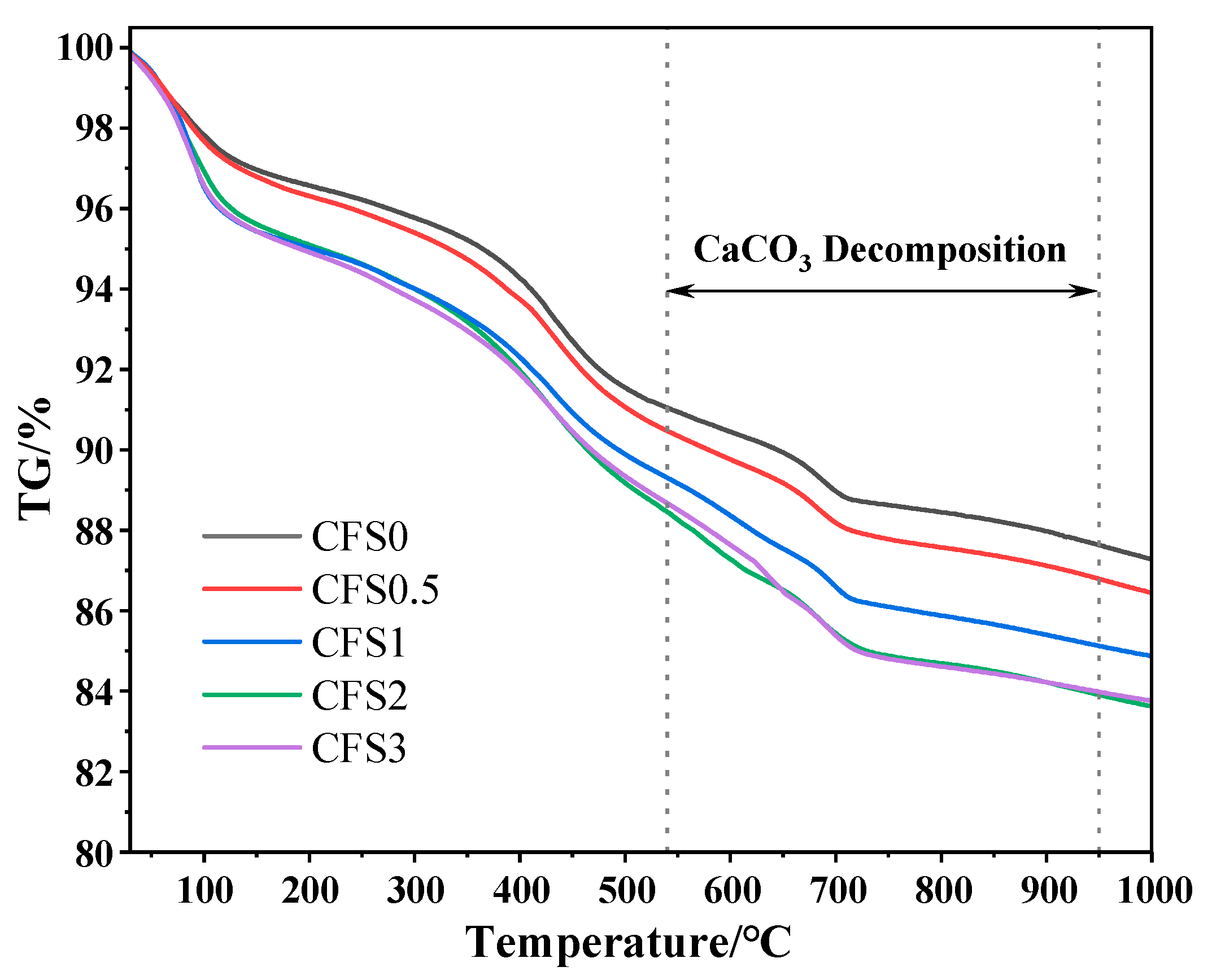
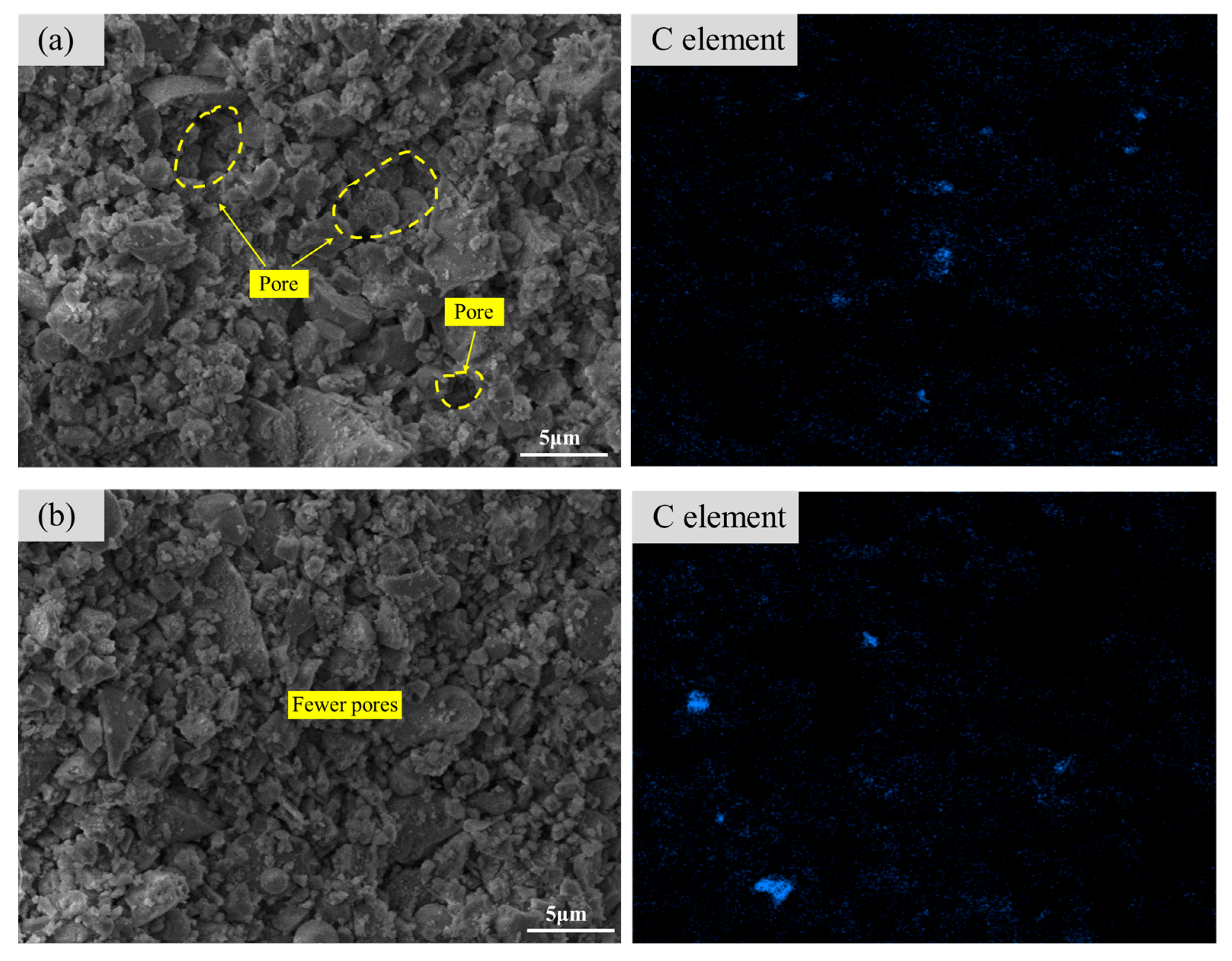
3.2.1. Morphology and Microstructure
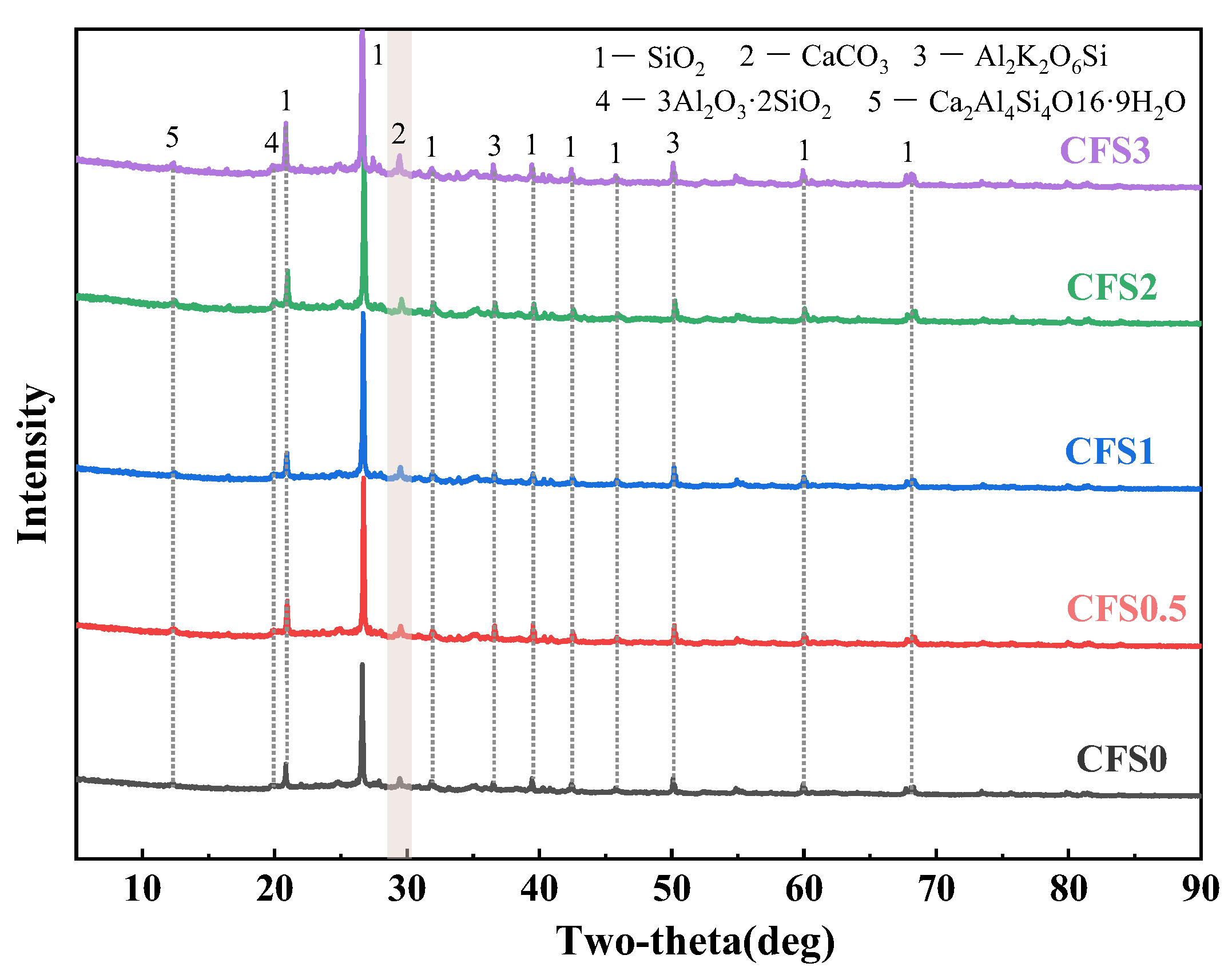
3.2.2. XRD
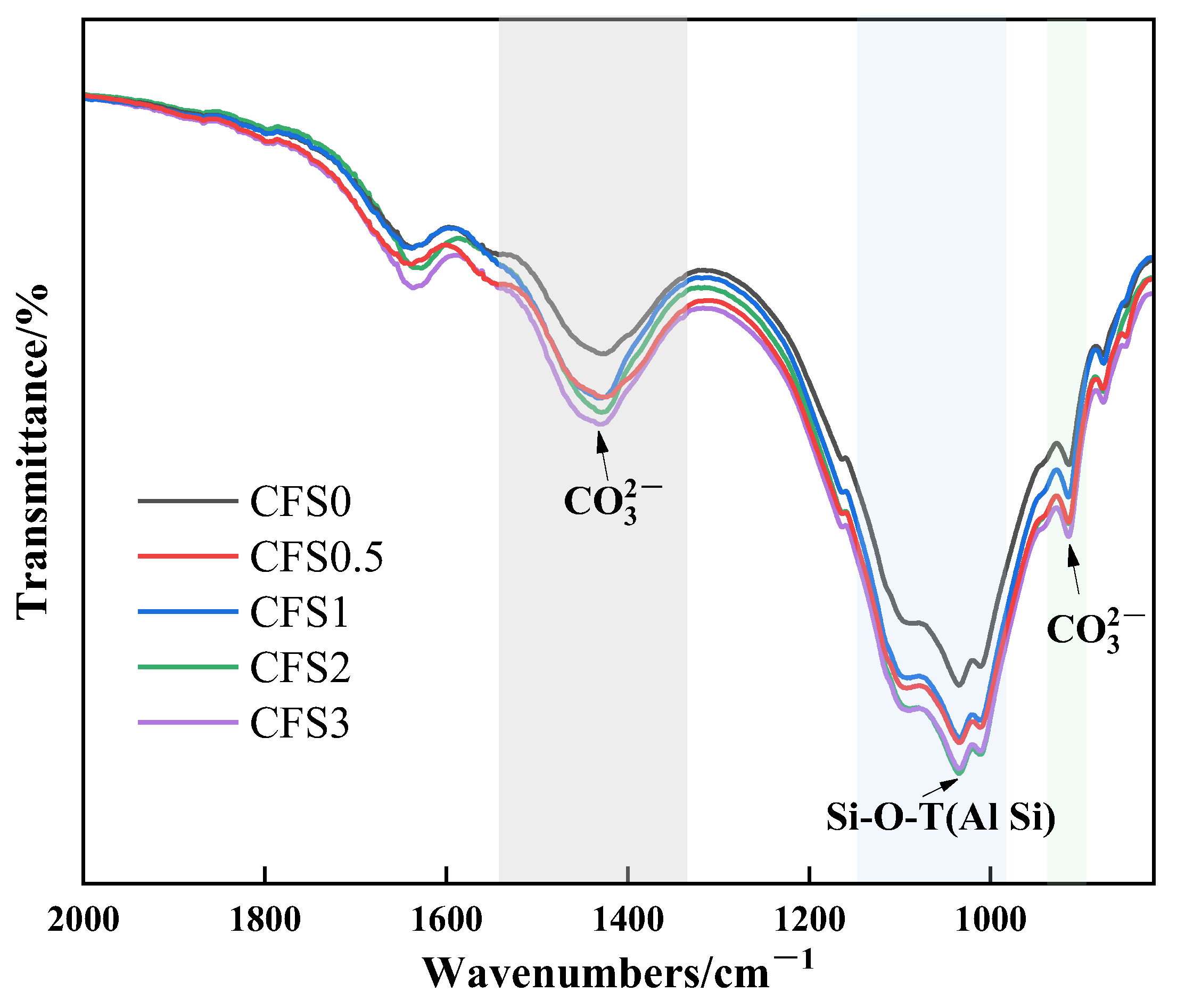
3.2.3. FTIR
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The carbon fixation amount of the CFS increases first and then tends to be stable with an increase in the carbonization time. When the carbon fixation time is 2 h, the carbon fixation amount is 1.13%.
- (2)
- After further increasing the carbon fixation time, the carbon fixation amount gradually tends to be stable. On the one hand, this is because the calcium ions in the solution are gradually consumed, and, on the other hand, it is because the generated calcium carbonate is deposited on the surface of the particles, thereby forming a calcification layer, which hinders the diffusion of CO2 into the particles.
- (3)
- Prolonged carbonation promotes calcium carbonate formation, which increases the packing density within the slurry microstructure. This microstructural evolution adversely impacts the rheological performance of the CFS. Combined with the CO2 storage capacity, 2 h can be used as the optimal carbonization time. At this time, the yield stress and plastic viscosity of the CFS are 155.93 Pa and 0.17 Pa·s, respectively.
- (4)
- After the CFS fixes carbon, the generated calcium carbonate and hydration products fill the pores of the sample, making the microstructure of the CFS denser and the pore structure reduced.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Zheng, S.L.; Di, Y.H.; Sun, Z. A review of the synthesis and application of zeolites from coal-based solid wastes. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmansouri, A.A.; Zhang, Z.G.; AzariJafari, H.; Shi, X.M. Biochar-amended high-strength engineered cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 164, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Gu, Z.D.; Qin, Y.; Xing, A.X.; Cheng, R.D. Synergistic preparation of cemented backfill from multiple coal-based solid wastes and investigation of its properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.H.; Jiao, X.M.; Zheng, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.N.; Xie, H.P.; Guo, Z.Q. Demand and fluctuation range of China’s coal production under the dual carbon target. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 3267–3282. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.S. Opportunities, challenges and modification methods of coal gangue as a sustainable soil conditioner—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 58231–58251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.M.; Li, M.J.; Zheng, Z.X.; Xi, S.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Yang, W.L. Assessing the progress of the mining industry towards green growth in China: A three-stage dynamic network slacks-based measure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Herrera, D.; Pal, M. Effect of Ge content on diode parameters of superstrate type Cu2ZnSn1−xGexS4/CdS heterostructures prepared by all-solution process. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 2416–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Kong, D.Z.; Song, G.F. Research hotspots and development trends of green coal mining: Exploring the path to sustainable development of coal mines. Resour. Policy 2024, 92, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Wu, W.; Shi, B.; Liu, L.B.; Cao, Y.J.; Deng, J.S.; Cui, J.S.; Cui, J.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Kang, Y.T.; et al. Research on carbon emission accounting and carbon emission reduction path of coal preparation plant. Miner. Eng. 2024, 217, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yue, S.J.; Chen, H.T. Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: From the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.Y.; Xu, F.Y.; Guo, Y.Z.; Ramsey, T. Analysis of the characteristics and robustness of China’s inter-industry carbon transfer complex network based on hypergraph. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 523, 146424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Shang, L.; Tang, D.C.; Li, Z.J. Research Themes, Evolution Trends, and Future Challenges in China’s Carbon Emission Studies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Li, H.Z.; Tang, C.; Guo, G.L.; Yuan, Y.F. Carbon sequestration in coal mine goafs: Innovations in high-water material solidification with supercritical carbon dioxide for global carbon neutrality initiatives. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Xu, J.Z.; Wei, Z.H.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, P.Q.; Zhai, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.X. Study on the influence of carbide slag incorporation on the carbon sequestration efficiency and material properties of fly ash-based carbon-negative filling materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.W.J.; Celia, M.A.; Bandilla, K.W.; Doster, F.; Kann, C.M. A Model To Estimate Carbon Dioxide Injectivity and Storage Capacity for Geological Sequestration in Shale Gas Wells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9222–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, K.A.; Mehra, A. Dunite carbonation in batch-tubular reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31439–31445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Min, Q.S.; Zeng, X.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.H.; Liu, L.B. Effects of calcium carbide slag on properties and carbon sequestration efficiency of cement pastes mixed under direct CO2 injection conditions. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 84, 102835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, J.X.; Jing, P.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K. Experimental study on the macroscopic and microscopic properties of cement paste backfill after treatment with carbon dioxide carbonize filling slurries during the mixing process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, Y.L.; Liu, S.S. The effect of carbonation pressure on microbial assisted steel slag-based carbon sequestration material. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, M.; Huo, B.B.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.J.; Xing, S.H.; Fu, X.H. Rheological and CO2 sequestration properties of alkali-activated gangue-based backfill slurry: Effect of temperature. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cheng, H.G.; Liu, X.; Di, Z.C.; Song, H.P.; Zhang, D.K.; Cheng, F.Q. CO2 Mineralized Full Solid Waste Cementitious Material for Coal Mine Goaf Filling and Carbon Sequestration Potential Assessment. Engineering 2025, 48, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.C.; Guo, Q.; Huo, B.B.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, Y.J.; Li, M.; Gu, W.Z. Effect of Carbonization Pressure on CO2 Sequestration and Rheological Properties of Coal Gangue-Based Backfilling Slurry. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xia, L.; Fang, Z.Y.; Jia, Q.F.; Gao, Y.H.; He, W.; Liu, Z.Z. Performance study of modified magnesium-coal based solid waste negative carbon backfill material: Strength characteristics and carbon fixation efficiency. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.X.; Pei, J.W.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhang, X. Steel slag powder-CO2 contact state in static or rotary process of carbon fixation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xie, L.; Ruan, S.S.; Zhu, M.B.; Yang, P.Y.; Liu, D.S. Influence of internal and external factors on the fluidity of modified magnesium slag-based backfill materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; He, P.P.; Liu, J.H.; Peng, Z.Y.; Song, B.X.; Hu, X. Microstructure of Portland cement paste subjected to different CO2 concentrations and further water curing. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 53, 101714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.P.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Y.X. Flue gas carbonation curing of cement paste and concrete at ambient pressure. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, V.; Shao, Y.X.; Boyd, A.J.; He, Z. Microstructure of cement paste subject to early carbonation curing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.y.; Bao, W.J.; Guo, Z.C.; Li, H.Q. Carbon Dioxide Sequestration via Steelmaking Slag Carbonation in Alkali Solutions: Experimental Investigation and Process Evaluation. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2018, 31, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pan, F.; Shen, X.Y.; Lu, J.Y.; Ye, S.X.; Wang, H.C.; Ling, T.C.; Ran, Q.P. Utilization of solid wastes to sequestrate carbon dioxide in cement-based materials and methods to improve carbonation degree: A review. J. CO2 Util. 2023, 72, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Yang, P.; Qu, H.S. A preliminary study of aeolian sand-cement-modified gasification slag-paste backfill: Fluidity, microstructure, and leaching risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Nogueira, R.; de Brito, J.; Liu, J.P. Quantitative analysis of the influence of fine aggregate’s grading on mortar’s rheology. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.C.; Wu, J.S.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.R.; Han, P.; Song, G.J. Modification of carbon fibers surfaces with polyetheramines: The role of interphase microstructure on adhesion properties of CF/epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39 (Suppl. S4), E2346–E2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.C.; Liao, S.H.; Yen, M.Y.; Liu, P.L.; Pu, N.W.; Wang, C.A.; Ma, C.M. Preparation of Covalently Functionalized Graphene Using Residual Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3092–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
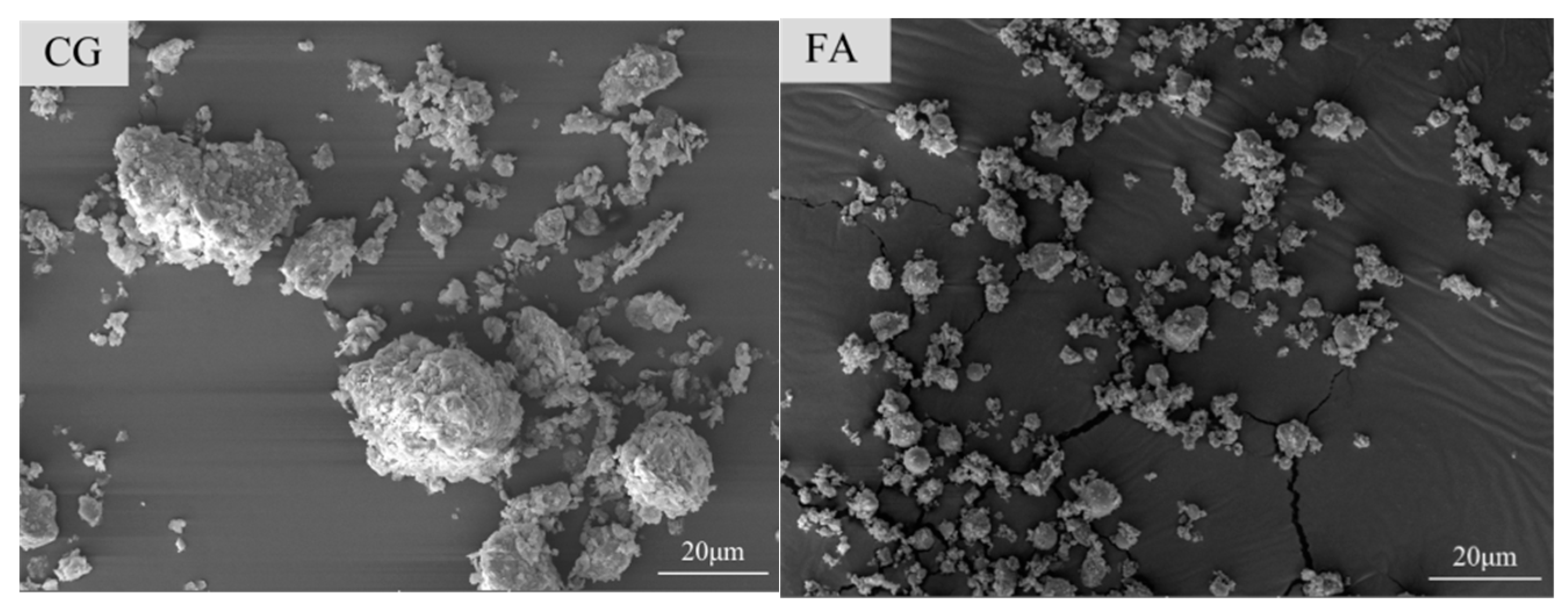
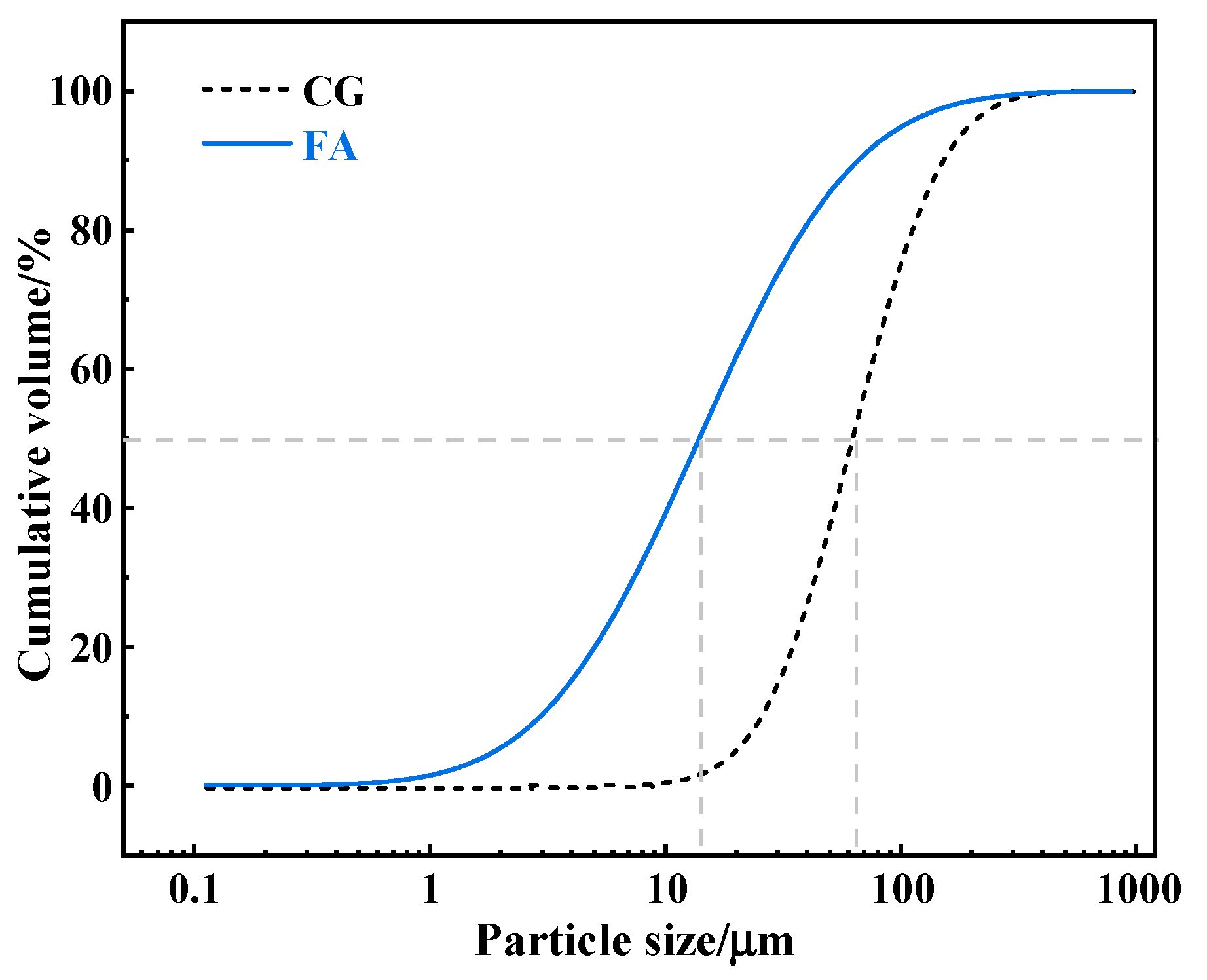


| No. | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | Na2O | TiO2 | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 54.45 | 22.88 | 9.64 | 0.98 | 3.64 | 2.71 | 1.92 | 1.08 | 1.46 |
| FA | 56.79 | 27.25 | 4.61 | 3.28 | 2.45 | 1.21 | 0.63 | 1.38 | 1.79 |
| Croup | Cementitious Materials | Water–Binder Ratio | Carbon Sequestration Time/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | FA | |||
| CFS0 | 80% | 20% | 0.5 | 0 |
| CFS0.5 | 0.5 | |||
| CFS1 | 1 | |||
| CFS2 | 1.5 | |||
| CFS3 | 2 | |||
| No. | Rheological Model | Fitting Results | τ0/Pa | η/Pa·s | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFS0 | H-B | τ = 124.89 + 0.08γ0.86 | 124.89 | 0.08 | 0.9987 |
| CFS0.5 | τ = 131.27 + 0.12γ0.84 | 131.27 | 0.12 | 0.9989 | |
| CFS1 | τ = 150.34 + 0.16γ0.92 | 150.34 | 0.16 | 0.9995 | |
| CFS2 | τ = 155.93 + 0.17γ0.97 | 155.93 | 0.17 | 0.9992 | |
| CFS3 | τ = 157.97 + 0.17γ0.98 | 157.97 | 0.17 | 0.9994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, B.; Li, M. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Properties of Gangue–Fly Ash Composite Filling Materials: Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties. C 2025, 11, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030071
Liu H, Guo Q, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Huo B, Li M. Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Properties of Gangue–Fly Ash Composite Filling Materials: Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties. C. 2025; 11(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haiquan, Qiang Guo, Yong Chen, Yifan Zhang, Binbin Huo, and Meng Li. 2025. "Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Properties of Gangue–Fly Ash Composite Filling Materials: Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties" C 11, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030071
APA StyleLiu, H., Guo, Q., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Huo, B., & Li, M. (2025). Effect of Carbon Fixation Time on the Properties of Gangue–Fly Ash Composite Filling Materials: Carbon Fixation Amount and Rheological Properties. C, 11(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030071








