A Cost-Effective and Non-Invasive pfeRNA-Based Test Differentiates Benign and Suspicious Pulmonary Nodules from Malignant Ones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Features of the Participations
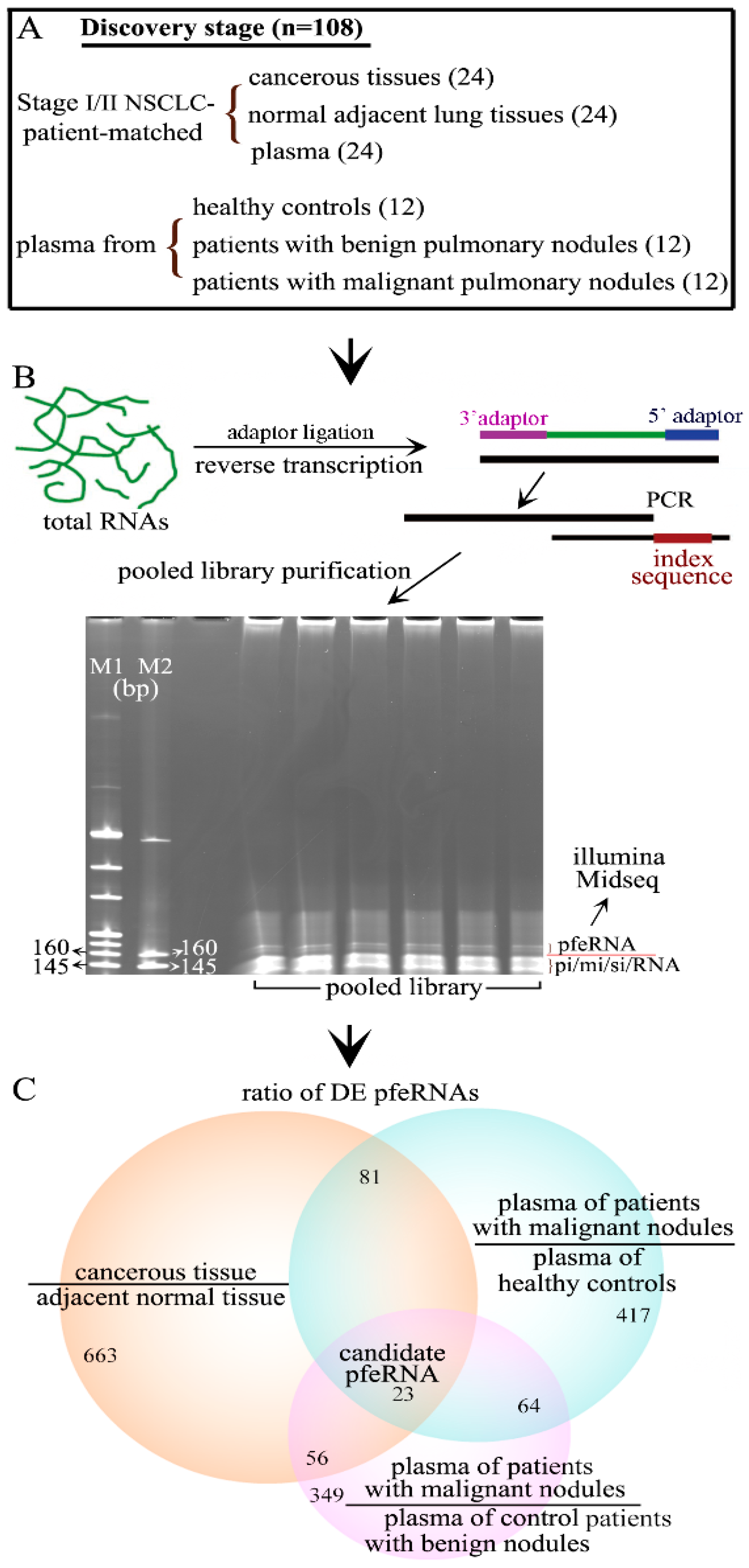
2.2. Differentially Expressed pfeRNAs in the Discovery Stage
2.3. Non-Invasive pfeRNA Panel
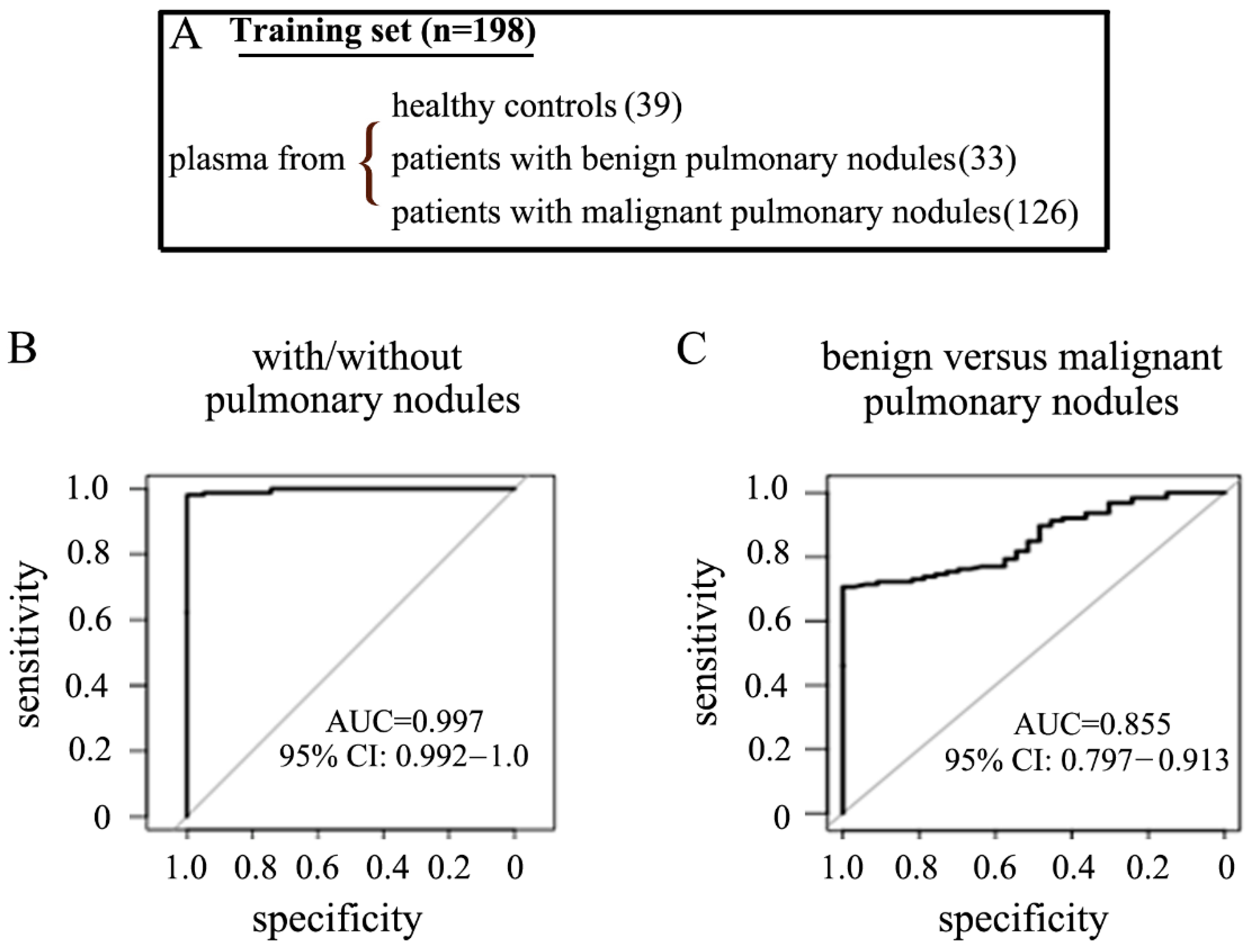
2.4. The Performance of the pfeRNA Panel in the Training Cohort
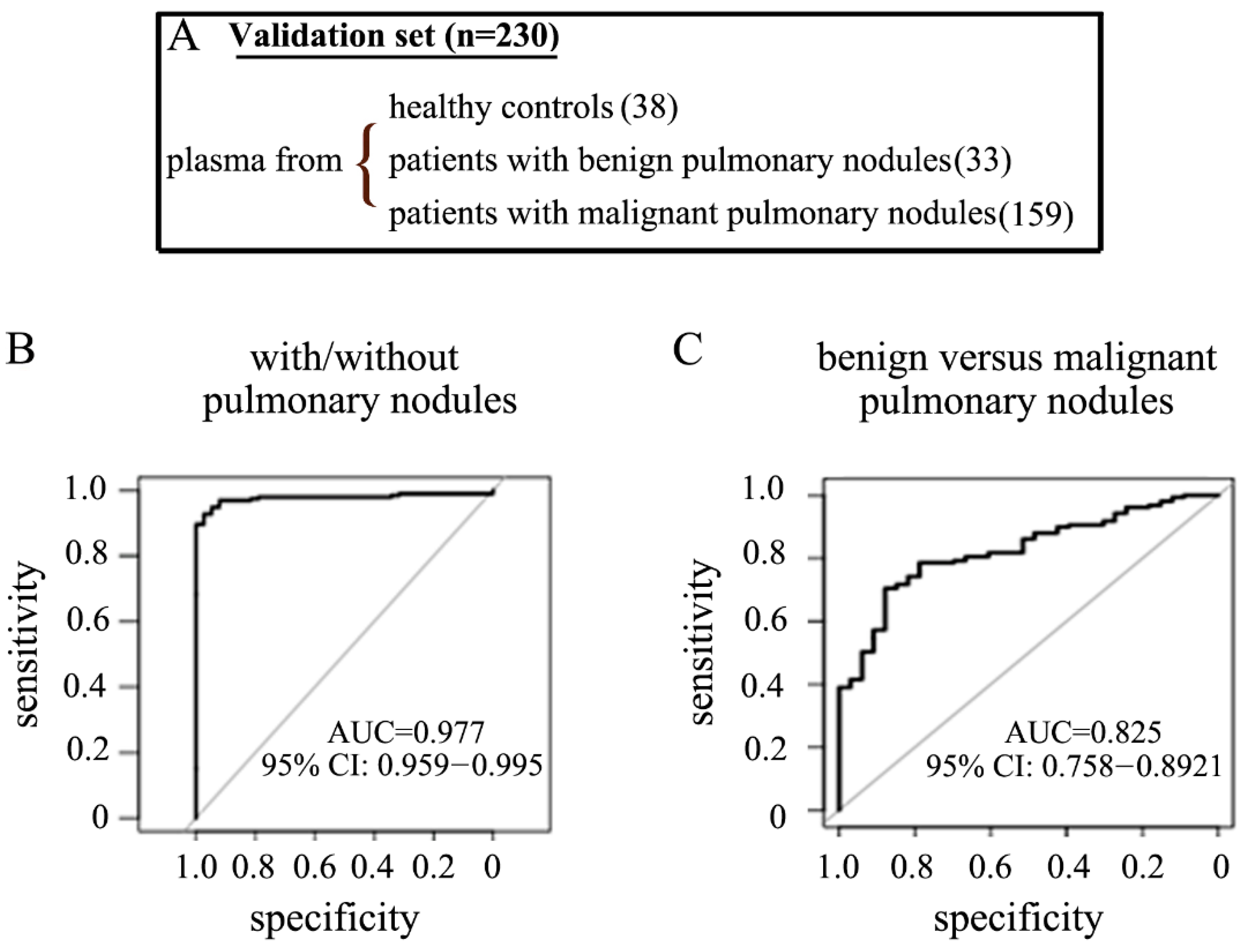
2.5. The Performance of the pfeRNA Panel in the Validation Cohort
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants, Plasma, and Tissues
4.2. CLIA Compliant LDT Assay
4.3. Total sncRNAs Extraction
4.3.1. Total RNAs Extracted from Tissues
4.3.2. Total sncRNAs Extracted from Plasma
4.4. Prepare pfeRNA Library for Deep Sequencing
4.5. RT and QuantStudio Dx PCR
4.6. Quantitation of pfeRNA Levels in Plasma
4.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.7.1. Sequences from sncRNA Deep Sequencing
4.7.2. Statistical Analysis for the Prediction Rules
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
7. Translational Relevance
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Silvestri, G.A.; Patel, S.; Kanne, J.P.; Kinsinger, L.S.; Wiener, R.S.; Wiener, R.S.; Detterbeck, F.C. Screening for Lung Cancer: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest 2018, 153, 954–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.S.; Sundaram, V.; Desai, M.; Gould, M.K. Accuracy of Models to Identify Lung Nodule Cancer Risk in the National Lung Screening Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.; Choi, H.K.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kou, L.; Ahmad, U.; Wang, X.; Mazzone, P.J. Development of a Risk Prediction Model to Estimate the Probability of Malignancy in Pulmonary Nodules Being Considered for Biopsy. Chest 2019, 156, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, G.A.; Tanner, N.T.; Kearney, P.; Vachani, A.; Massion, P.P.; Porter, A.; Springmeyer, S.C.; Fang, K.C.; Midthun, D.; Mazzone, P.J.; et al. Assessment of plasma proteomics biomarker’s ability to distinguish benign from malignant lung nodules: Results of the PANOPTIC (Pulmonary Nodule Plasma Proteomic Classifier) Trial. Chest 2018, 154, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosell, R.; Karachaliou, N. Lung cancer: Using ctDNA to track EGFR and KRAS mutations in advanced-stage disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA as Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolfo, C.; Mack, P.C.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Baas, P.; Barlesi, F.; Bivona, T.G.; Herbst, R.S.; Mok, T.; Peled, N.; Pirker, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Statement Paper from the IASLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1248–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasaka, M.; Uddin, M.H.; Al-Hallak, M.N.; Rahman, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Sukari, A.; Azmi, A.S. Liquid biopsy for therapy monitoring in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early-and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.D.; Javed, A.A.; Thoburn, C.; Wong, F.; Tie, J.; Gibbs, P.; Schmidt, C.M.; Yip-Schneider, M.T.; Allen, P.J.; Schattner, M.; et al. Combined circulating tumor DNA and protein biomarker-based liquid biopsy for the earlier detection of pancreatic cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10202–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Yin, W.; Chen, H.; Cheng, C.; et al. Accurate diagnosis of pulmonary nodules using a non-invasive DNA methylation test. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, A.C.; Clark, D.; Gable, T.; MacKerell, A.D.; Ma, M.Z.; Weber, D.J.; Yang, A.J.; et al. A piRNA-like small RNA interacts with and modulates p-ERM proteins in human somatic cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gable, T.; Wang, Y.; Clark, D.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, A.C.; Li, M.; Mei, Y. A phosphorylation-wide sncRNA screen reveals Protein Functional Effector sncRNAs (pfeRNAs) in human lung somatic cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, M.; Mei, Y. Protein functional effector sncRNAs (pfeRNAs) in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gable, T.; Ma, M.Z.; Clark, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Mao, L.; Mei, Y. A piRNA-like small RNA induces chemoresistance to cisplatin-based therapy by inhibiting apoptosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 6, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seijo, L.M.; Peled, N.; Ajona, D.; Boeri, M.; Field, J.K.; Sozzi, G.; Pio, R.; Zulueta, J.J.; Spira, A.; Massion, P.P.; et al. Biomarkers in Lung Cancer Screening: Achievements, Promises, and Challenges. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Sears, C.; Arenberg, D.; Gaga, M.; Gould, M.K.; Massion, P.P.; Nair, V.S.; Powell, C.A.; Silvestri, G.A.; Vachani, A.; et al. Evaluating Molecular Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Lung Cancer: When Is a Biomarker Ready for Clinical Use? An Official American Thoracic Society Policy Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, e15–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, M.A. Developing a Standard Protocol for the Introduction of New Testing Into a Clinical Laboratory: Appendix 1. Lab. Med. 2009, 40, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, L.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Gulley, M.L. Recommended principles and practices for validating clinical molecular pathology tests. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2009, 133, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, I.; Aziz, N.; Jennings, L.J.; Richards, C.S.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Weck, K.E. Methods-Based Proficiency Testing in Molecular Genetic Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.-J.; Chong, Y.; Guo, Z.-W.; Xie, C.; Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.-P.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Min, J.; et al. A serum microRNA classifier for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicentre, retrospective, longitudinal biomarker identification study with a nested case-control study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Silva, A.M.; Calin, G.; Pantel, K. Which is the accurate data normalization strategy for microRNA quantification? Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, M.K.; Donington, J.; Lynch, W.R.; Mazzone, P.J.; Midthun, D.E.; Naidich, D.P.; Wiener, R.S. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: When is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e93S–e120S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacMahon, H.; Naidich, D.P.; Goo, J.M.; Lee, K.S.; Leung, A.N.C.; Mayo, J.R.; Mehta, A.C.; Ohno, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Prokop, M.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Incidental Pulmonary Nodules Detected on CT Images: From the Fleischner Society 2017. Radiology 2017, 284, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, C.; Choi, C.M.; Chu, C.M.; Anantham, D.; Hi, J.C.M.; Khan, A.Z.; Lee, J.-M.; Li, S.Y.; Saenghirunvattana, S.; Yim, A. Evaluation of Pulmonary Nodules: Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines for Asia. Chest 2016, 150, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ost, D.E.; Gould, M.K. Decision Making in Patients with Pulmonary Nodules. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ameri, A.; Malhotra, P.; Thygesen, H.; Plant, P.K.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Karthik, S.; Scarsbrook, A.; Callister, M.E. Risk of malignancy in pulmonary nodules: A validation study of four prediction models. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larici, A.R.; Farchione, A.; Franchi, P.; Ciliberto, M.; Cicchetti, G.; Calandriello, L.; del Ciello, A.; Bonomo, L. Lung nodules: Size still matters. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, N.T.; Brasher, P.B.; Jett, J.; Silvestri, G.A. Effect of a Rule-in Biomarker Test on Pulmonary Nodule Management: A Survey of Pulmonologists and Thoracic Surgeons. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e89–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsky, P.F.; Gierada, D.S.; Black, W.; Munden, R.; Nath, H.; Aberle, D.; Kazerooni, E. Performance of Lung-RADS in the National Lung Screening Trial: A retrospective assessment. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, C.S.; Dharaiya, E.; Dalal, S.; Chen, R.; Haramati, L.B. Vancouver Risk Calculator Compared with ACR Lung-RADS in Predicting Malignancy: Analysis of the National Lung Screening Trial. Radiology 2019, 291, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmis, T.R.; Ding, K.; Seymour, L.; Shepherd, F.A.; Leighl, N.B.; Winton, T.L.; Whitehead, M.; Spaans, J.N.; Graham, B.C.; Goss, G.D. Age and Comorbidity As Independent Prognostic Factors in the Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Review of National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baser, S.; Shannon, V.R.; Eapen, G.A.; Jimenez, C.A.; Onn, A.; Lin, E.; Morice, R.C. Smoking Cessation After Diagnosis of Lung Cancer Is Associated With a Beneficial Effect on Performance Status. Chest 2006, 130, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindle, H.A.; Duncan, M.S.; Greevy, R.A.; Vasan, R.S.; Kundu, S.; Massion, P.P.; Freiberg, M.S. Lifetime Smoking History and Risk of Lung Cancer: Results From the Framingham Heart Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couraud, S.; Zalcman, G.; Milleron, B.; Morin, F.; Souquet, P.J. Lung cancer in never smokers—A review. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeckx, A.; Reyntiens, P.; Desbuquoit, D.; Spinhoven, M.J.; Van Schil, P.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Parizel, P.M. Evaluation of the solitary pulmonary nodule: Size matters, but do not ignore the power of morphology. Insights Imaging 2017, 9, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houghton, A.M. Mechanistic links between COPD and lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, N.M.; Kargl, J.; Busch, S.E.; Yang, G.H.Y.; Metz, H.E.; Zhang, H.; Hubbard, J.J.; Pipavath, S.N.J.; Madtes, D.K.; Houghton, A.M. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Alters Immune Cell Composition and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, E.M.; Sarvis, S.; Herndon, J.E., II; Patz, E.F., Jr. T1 Lung Cancers: Sensitivity of Diagnosis with Fluorodeoxyglucose PET. Radiology 2002, 223, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppen, S.A.; Blume, J.D.; Kensinger, C.D.; Morgan, A.M.; Aldrich, M.C.; Massion, P.P.; Walker, R.C.; McPheeters, M.L.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; Grogan, E.L. Accuracy of FDG-PET to diagnose lung cancer in areas with infectious lung disease: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 312, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cohort | Institution | Plasma from Healthy Persons | Plasma from Patients with Benign Pulmonary Nodules | Plasma from Patients with Malignant Pulmonary Nodules in Stage-I/II NSCLC | Normal Tissues from Patients with Malignant Pulmonary Nodules in Stage-I/II NSCLC | Cancerous Tissues from Patients with Malignant Pulmonary Nodules in Stage-I/II NSCLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery cohort | Cancer Center of JHU | 12 | 12 | |||
| Xuanwu Hospital | 12 | 24 | 24 | 24 | ||
| Training cohort | Cancer Center of JHU | 12 | 17 | 56 | ||
| Xuanwu Hospital | 17 | 11 | 40 | |||
| The Third Affiliated Hospital of SYU | 10 | 16 | ||||
| Peking Union Medical College Hospital | 5 | 14 | ||||
| Validation cohort | Cancer Center of JHU | 23 | 53 | |||
| Xuanwu Hospital | 30 | 4 | 90 | |||
| The Third Affiliated Hospital of SYU | 8 | |||||
| Peking Union Medical College Hospital | 6 | 16 |
| pfeRNA | Sequence (5′–3′) | Genomic Location |
|---|---|---|
| pfeRNAa | TAAAGTTGGTATACAACCCCCCACTGCTAAATTTGACTGGCTT | Genomic chr 1, 7, 8, 9, 12 and 17 |
| pfeRNAb | ATTGGTCGTGGTTGTAGTCCGTGCGAGAATACCA | Genomic chr 13 and X |
| pfeRNAc | TAGCTTATCAGACTGATGTTGACTGTTGAATCTCATGGCAACACCAGTT | Genomic chr 5 |
| pfeRNAd | GGCTGGTCCGATGGAAGTGGGTTATCAGAACTAATTAACTT | Genomic chr 2 (reverse strand), 6 and 7 |
| pfeRNAe | TCGGATCCGTCTGAGCTTGGCTGCCCGGCTAGCTCAGTCGGTAGAGCATGA | Genomic chr 1, 5, 6, 14, and 16 |
| pfeRNAf | AAGCACCCAACTTACACTTAGGAGATTTCAACTTAACTTGACCGCTCTGACCA | Genomic chr 7 and Mitochondria |
| pfeRNAg | GGCTGGTCCGATGGTAGTGGGTTATCAGAACTTATTAACT | Genomic chr 6 and 7 |
| pfeRNAh | TAGGATGGGTGTGATAGGTGGCACGGAGAATTACCAAA | Genomic chr 1 and Mitochondria |
| To Detect a Candidate with or without Pulmonary Nodule(s) |
|---|
| Rule 1 = (−0.65)*A.H + 0.15*B.F − 0.1*C.H + 0.24*D.F + 0.37*E.F − 0.06*F.G − 0.42 |
| If Rule 1 > 0, classify it to be pulmonary nodules (benign + malignant nodules) |
| If Rule 1 ≥ 0, classify it to be healthy |
| To detect benign versus malignant pulmonary nodules |
| Condition 1 = −0.0900*A.F−0.0607*C.H + 0.0545*F.G − 0.0050*H.F + 1.3508*(F.G ≥ −1.8857) |
| Condition 2 = −0.0136*A.F−0.0223*C.H + 0.9837*( R1 ≥ 0.1794) + 0.6496*(condition 1) |
| Rule2 = −0.0569*A.F − 0.0141*B.E + (−0.0434)*B.H + (−0.0847)*C.D − 0.0420*C.H + (−0.0282)*D.E − 0.0621*H.F + 1.1040*( condition 1) ≥ 0.1794) + 0.4962*(condition 2) +1 |
| If Rule 2 > 0, classify it to be malignant pulmonary nodules |
| If Rule 2 ≤ 0, classify it to be benign pulmonary nodules |
| Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Training cohort | ||
| With versus without pulmonary nodules | 98.1 | 100 |
| Malignant versus benign pulmonary nodules | 76.2 | 69.7 |
| Validation cohort | ||
| With versus without pulmonary nodules | 94.3 | 94.7 |
| Malignant versus benign pulmonary nodules | 78 | 78.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Fackche, N.; Rodgers, K.; Lee, B.; Nizam, W.; Khan, H.; Lu, Z.; Kong, X.; et al. A Cost-Effective and Non-Invasive pfeRNA-Based Test Differentiates Benign and Suspicious Pulmonary Nodules from Malignant Ones. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040080
Liu W, Wang Y, Huang H, Fackche N, Rodgers K, Lee B, Nizam W, Khan H, Lu Z, Kong X, et al. A Cost-Effective and Non-Invasive pfeRNA-Based Test Differentiates Benign and Suspicious Pulmonary Nodules from Malignant Ones. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(4):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, Yuyan Wang, Hongchan Huang, Nadege Fackche, Kristen Rodgers, Beverly Lee, Wasay Nizam, Hamza Khan, Zhihao Lu, Xiangqian Kong, and et al. 2021. "A Cost-Effective and Non-Invasive pfeRNA-Based Test Differentiates Benign and Suspicious Pulmonary Nodules from Malignant Ones" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 4: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040080
APA StyleLiu, W., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Fackche, N., Rodgers, K., Lee, B., Nizam, W., Khan, H., Lu, Z., Kong, X., Li, Y., Liang, N., Zhao, X., Jin, X., Liu, H., Talbot, C. C., Jr., Huang, P., Eshleman, J. R., Lai, Q., ... Mei, Y. (2021). A Cost-Effective and Non-Invasive pfeRNA-Based Test Differentiates Benign and Suspicious Pulmonary Nodules from Malignant Ones. Non-Coding RNA, 7(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040080






