Long Non-Coding PROX1-AS1 Expression Correlates with Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis and Aggressiveness
Abstract
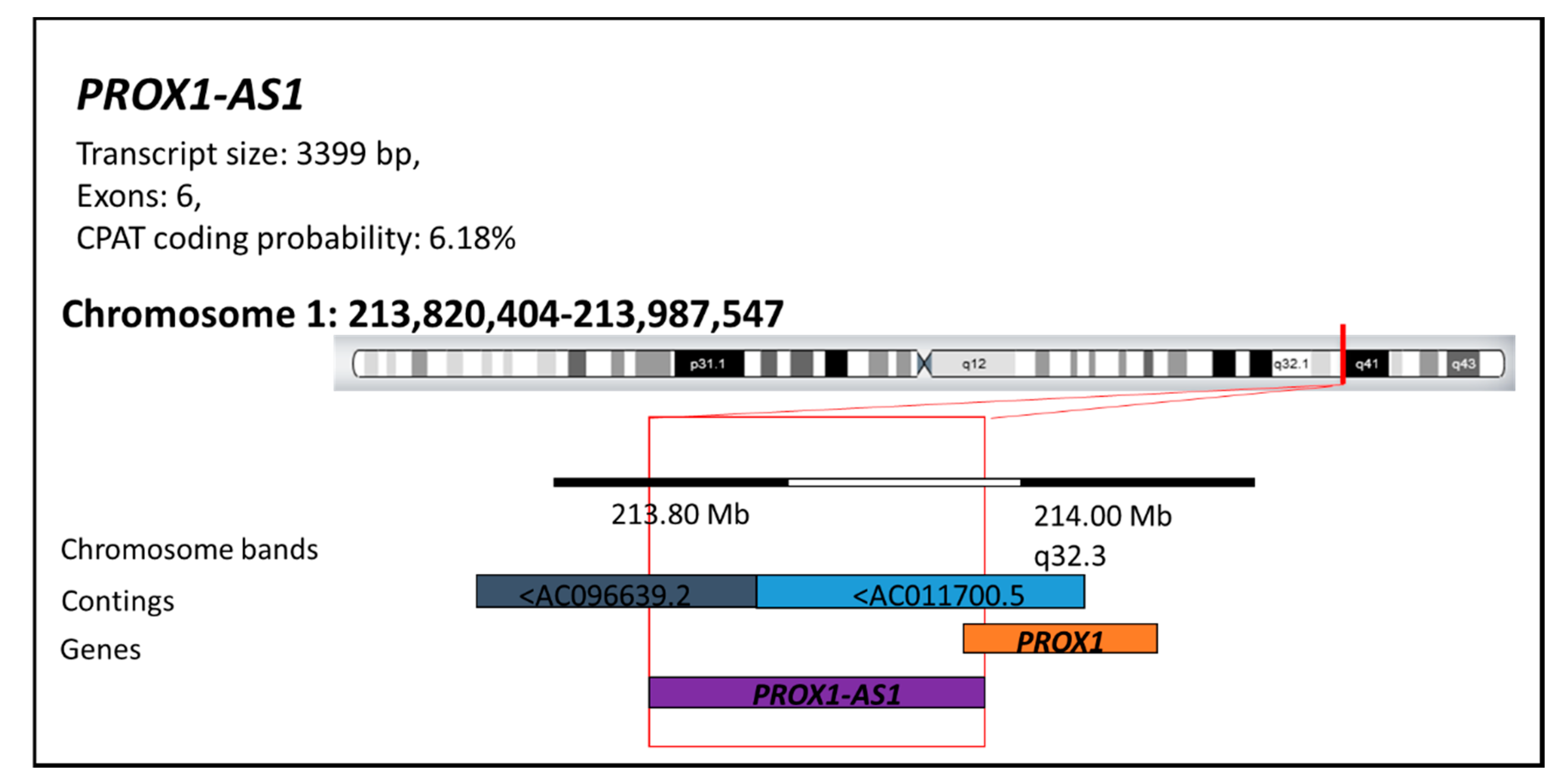
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissues Samples
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. RNA Isolation and Real-Time (RT)-qPCR
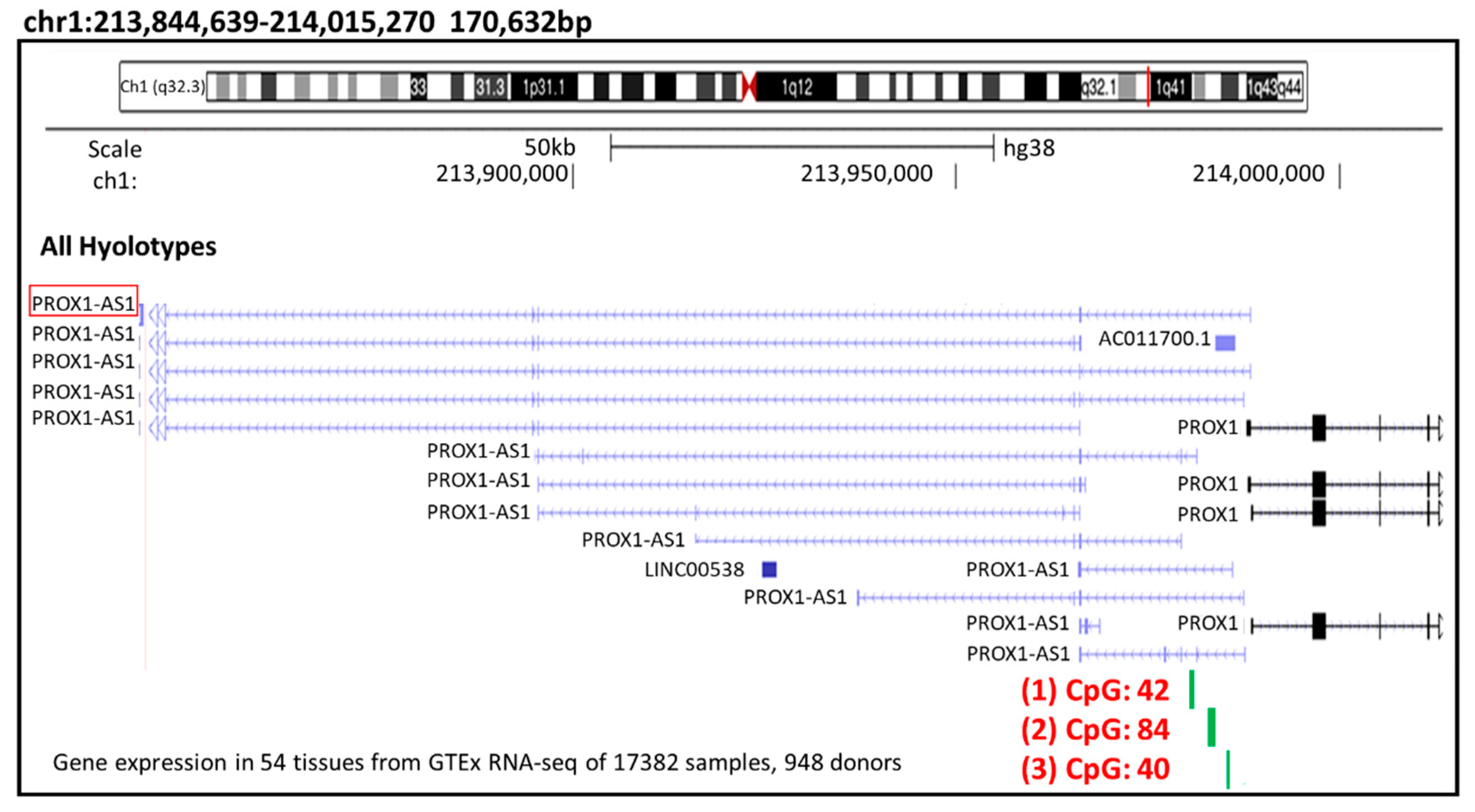
2.4. Methylation Analysis
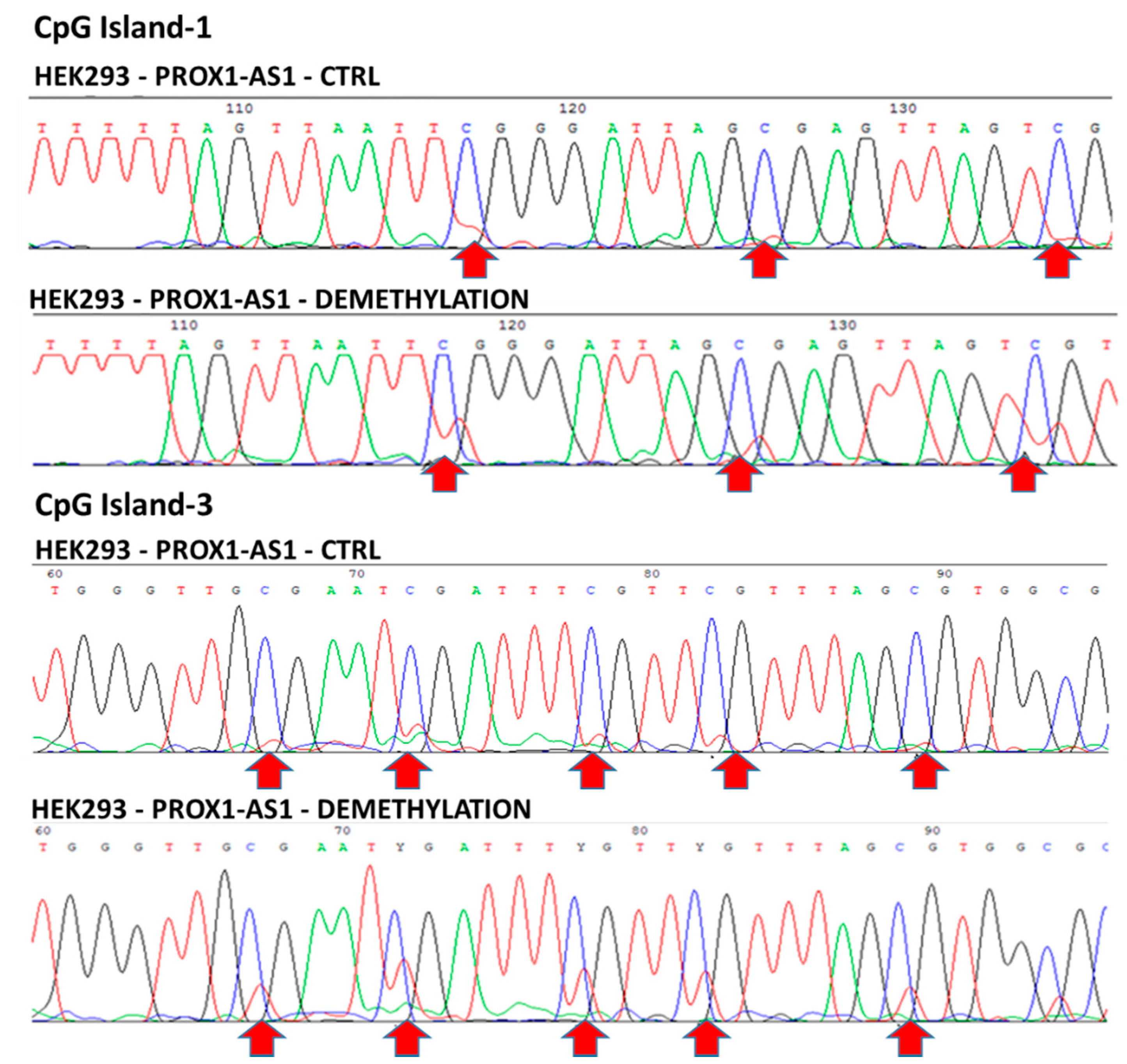
2.5. In Vitro Treatment of Cultured Cells with 5-Aza-2′-Deoxycytidine
2.6. DNA Isolation, Bisulfite Modification and Sequencing PCR
Bisulfite Sequencing PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
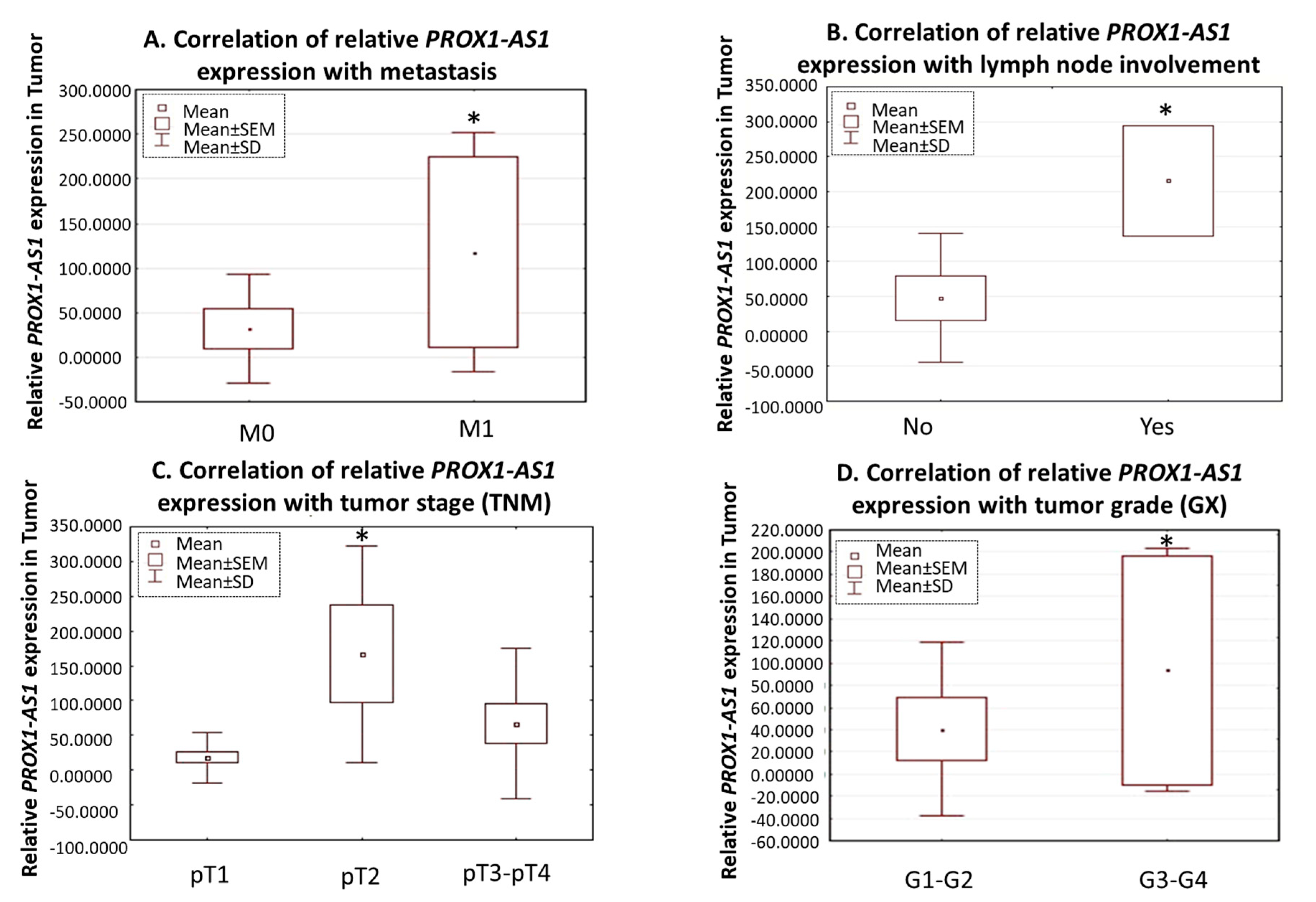
3.1. LncRNA PROX1-AS1 Expression Is Higher in RCC Specimens and Positively Correlates with Metastasis, Lymph Node Invasion, Tumor Stage, and Grade
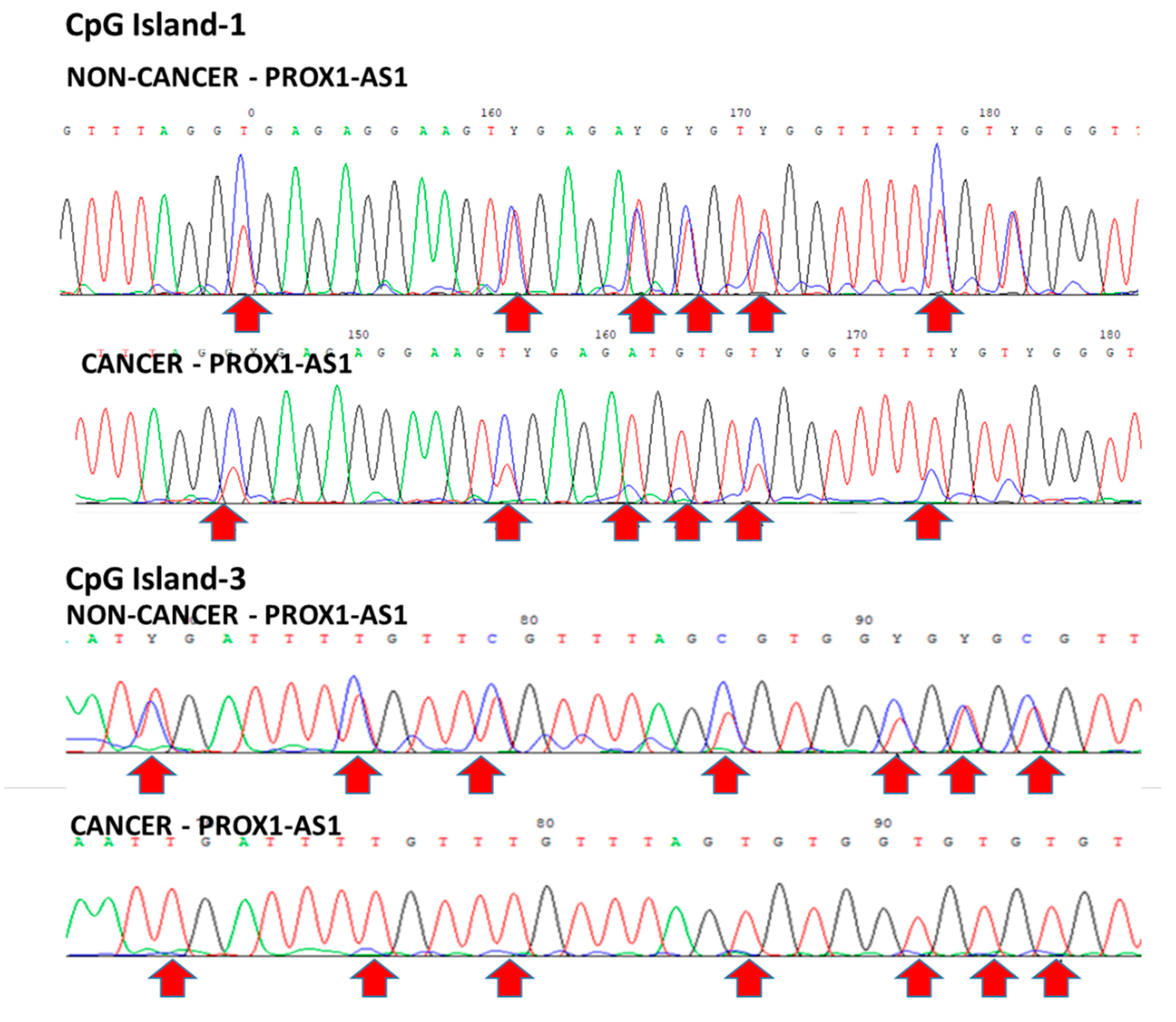
3.2. Methylation Could Regulate PROX1-AS1 Expression in Healthy Kidney and Renal Carcinoma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buti, S.; Bersanelli, M.; Sikokis, A.; Maines, F.; Facchinetti, F.; Bria, E.; Ardizzoni, A.; Tortora, G.; Massari, F. Chemotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma today? A systematic review. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 24, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, G.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Moloo, Z.; Girgis, S. Review of renal cell carcinoma and its common subtypes in radiology. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovastova, M.O.; Korolev, D.O.; Tsoy, L.V.; Varshavsky, V.A.; Xu, W.-H.; Vinarov, A.Z.; Zernii, E.Y.; Philippov, P.P.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Biomarkers of Renal Tumors: The Current State and Clinical Perspectives. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2017, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Stamatakis, L.; Singer, E.A.; Srinivasan, R. Renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, J.T.Y.; Colognori, D.; Lee, J.T. Long Noncoding RNAs: Past, Present, and Future. Genetics 2013, 193, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fullwood, M.J. Roles, Functions, and Mechanisms of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.-W.; Huang, K.; Yang, C.; Kang, C.-S. Non-coding RNAs as regulators in epigenetics. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 37, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B. Inference of Crosstalk Effects between DNA Methylation and lncRNA Regulation in NSCLC. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tan, H.; Yu, H.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. DNA methylation and gene expression profiles characterize epigenetic regulation of lncRNAs in colon adenocarcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 121, 2406–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chung, A.C.; Huang, X.R.; Dong, Y.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.Y. Identification of Novel Long Noncoding RNAs Associated with TGF-β/Smad3-Mediated Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis by RNA Sequencing. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudehen, K.; Farahani, S.; Kanchwala, M.; Chan, S.C.; Avdulov, S.; Mickelson, A.; Lee, D.; Gearhart, M.D.; Patel, V.; Xing, C.; et al. Long noncoding RNA Hoxb3os is dysregulated in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and regulates mTOR signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 9388–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Hu, F.; Xue, M.; Jia, Y.-J.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Li, Y.; Xue, Y.-M. Early growth response protein-1 upregulates long noncoding RNA Arid2-IR to promote extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2019, 316, C340–C352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.-D.; Han, L.; Lee, H.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Baddour, J.; Nagrath, D.; Wood, C.G.; Gu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Energy stress-induced lncRNA FILNC1 represses c-Myc-mediated energy metabolism and inhibits renal tumor development. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin-Hui, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.-Y.; Shi, J.-Z.; Liu, S.-P.; Liu, B.; Wu, D.-S.; Fang, Z.-Y.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, M.-M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MRCCAT1 promotes metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via inhibiting NPR3 and activating p38-MAPK signaling. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Cheng, K.; Ming, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, S. Long non-coding RNA TCL6 enhances preferential toxicity of paclitaxel to renal cell carcinoma cells. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, P.; Lv, W.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Qin, S. Long noncoding RNA lnc-DILC stabilizes PTEN and suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Zhu, R.; Ma, J.; Gong, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xue, W. A positive feed-forward loop between LncRNA-URRCC and EGFL7/P-AKT/FOXO3 signaling promotes proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Hinoda, Y.; Shahryari, V.; Deng, G.; Nakajima, K.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Ishii, N.; Dahiya, R. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Promotes Aggressive Renal Cell Carcinoma through Ezh2 and Interacts with miR-205. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Ding, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, B.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Sun, W.; Li, X.-F.; et al. Exosome-transmitted lncARSR promotes sunitinib resistance in renal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Ma, T.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Hou, F.F. lncRNA lnc-TSI Inhibits Metastasis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, L.B.; Kalebasty, A.R. Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in isolated retroperitoneal lymph node without evidence of primary tumor in kidneys: A case report. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayoni, A.; Paschall, A.K.; Malayeri, A.A. Assessing lymph node status in patients with kidney cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; An, H.; Lin, Z.; Xie, Y.; Chen, L. Impact of an Altered PROX1 Expression on Clinicopathology, Prognosis and Progression in Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzińska, M.; Grzanka, M.; Stachurska, A.; Mikula, M.; Paczkowska, K.; Stępień, T.; Paziewska, A.; Ostrowski, J.; Czarnocka, B. Molecular Signature of Prospero Homeobox 1 (PROX1) in Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzinska, M.; Ledwon, J.K.; Gawel, D.; Sikorska, J.; Czarnocka, B. The role of prospero homeobox 1 (PROX1) expression in follicular thyroid carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114136–114155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rudzińska, M.; Mikula, M.; Arczewska, K.D.; Gajda, E.; Sabalińska, S.; Stępień, T.; Ostrowski, J.; Czarnocka, B. Transcription Factor Prospero Homeobox 1 (PROX1) as a Potential Angiogenic Regulator of Follicular Thyroid Cancer Dissemination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Liao, C.H.; Tan, B.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Dang, B.W.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, C.B. LncRNA PROX1-AS1 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 24, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volders, P.-J.; Anckaert, J.; Verheggen, K.; Nuytens, J.; Martens, L.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. LNCipedia 5: Towards a reference set of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D135–D139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RNAcentral Consortium; Sweeney, A.B.; Petrov, I.A.; Ribas, E.C.; Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Szymanski, M.; Karlowski, W.M.; Seemann, E.S.; Gorodkin, J.; et al. RNAcentral 2021: Secondary structure integration, improved sequence search and new member databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D212–D220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.D.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D682–D688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, J.-F.; Tong, X.-J. Long noncoding RNA PROX1-AS1 promoted ovarian cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing KLF6. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6561–6568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Liao, C.-H.; Tan, B.-F.; Chen, Y.-F.; Dang, B.-W.; Chen, J.-L.; Liu, C.-B. LncRNA PROX1-AS1 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration in prostate cancer via targeting miR-647. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2938–2944. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzińska, M.; Parodi, A.; Maslova, V.D.; Efremov, Y.M.; Gorokhovets, N.V.; Makarov, V.A.; Popkov, V.A.; Golovin, A.V.; Zernii, E.Y.; Zamyatnin, J.A.A. Cysteine Cathepsins Inhibition Affects Their Expression and Human Renal Cancer Cell Phenotype. Cancers 2020, 12, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichelberg, C.; Junker, K.; Ljungberg, B.; Moch, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Molecular Markers for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Critical Appraisal of the Current State of Research and Clinical Applicability. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Han, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Qin, L.-X. Long noncoding RNAs, emerging and versatile regulators of tumor-induced angiogenesis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Balas, M.M.; Johnson, A.M. Exploring the mechanisms behind long noncoding RNAs and cancer. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Böttcher, R.; Croce, C.M.; Jenster, G.; Visakorpi, T.; Calin, G.A. Long Noncoding RNA in Prostate, Bladder, and Kidney Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, A.J. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, V.; Ferrero, G.; Reineri, S.; Caizzi, L.; Annaratone, L.; Ricci, L.; Cutrupi, S.; Castellano, I.; Cordero, F.; De Bortoli, M. Luminal long non-coding RNAs regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in a ligand-independent manner show functional roles in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3201–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-S.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-S.; Lin, K.-H. Functional roles of non-coding RNAs regulated by thyroid hormones in liver cancer. Biomed. J. 2020, 27, 2319–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredholt, G.; Mannelqvist, M.; Stefansson, I.M.; Birkeland, E.; Bø, T.H.; Oyan, A.M.; Trovik, J.; Kalland, K.-H.; Jonassen, I.; Salvesen, H.B.; et al. Tumor necrosis is an important hallmark of aggressive endometrial cancer and associates with hypoxia, angiogenesis and inflammation responses. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 39676–39691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, E.; Kanai, Y. Genetic and epigenetic alterations during renal carcinogenesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 4, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arai, E.; Ushijima, S.; Tsuda, H.; Fujimoto, H.; Hosoda, F.; Shibata, T.; Kondo, T.; Imoto, I.; Inazawa, J.; Hirohashi, S.; et al. Genetic Clustering of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on Array-Comparative Genomic Hybridization: Its Association with DNA Methylation Alteration and Patient Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5531–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, E.; Chiku, S.; Mori, T.; Gotoh, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Kanai, Y. Single-CpG-resolution methylome analysis identifies clinicopathologically aggressive CpG island methylator phenotype clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.M.-; Gu, J.; Herrera, L.A.; Tannir, N.M.; Matin, S.F.; Karam, J.A.; Huang, M.; Chang, D.W.; Wood, C.G.; Wu, X. Genomic DNA Hypomethylation and Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Case–Control Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, N.; Vallumsetla, N.; Zou, Y.; Galeas, J.N.; Shrivastava, M.; Hu, C.; Susztak, K.; Verma, A. Role of DNA methylation in renal cell carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, M. DNA methylation in cancer: Too much, but also too little. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5400–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlando, M.; Fatica, A. Alteration of Epigenetic Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; An, Y.; Li, L.; Li, D. Genome-wide DNA methylation regulation analysis of long non-coding RNAs in glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malouf, G.; Zhang, J.; Tannir, N.M.; Thompson, E.; Spano, J.-P.; Khayat, D.; Su, X. Charting DNA methylation of long non-coding RNA in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, I.; Carvalho, S.; Tavares, J.; Grosso, A.R. A pan-cancer analysis of MYC-PVT1 reveals CNV-unmediated deregulation and poor prognosis in renal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47033–47041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Cen, B.; Ji, A. Regulation of lncRNA expression. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Urrutia, E.; Montes, L.P.B.; Cervantes, D.L.D.G.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. Crosstalk Between Long Non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs: Deciphering Molecular Mechanisms of Master Regulators in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| lncRNA | Expression in Renal Tumor | Role in Renal Tumor | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FILNC1 | Downregulated | -Inhibition of energy metabolism, -Suppression of tumor development | Downregulation of tyrosine-protein kinase Met (c-Myc) protein | [14] |
| TCL6 | Downregulated | -Sensitization of clear cell renal carcinoma to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis | Downregulation of miR-221 | [16] |
| lnc-DILC | Downregulated | -Inhibition of proliferation, migration and invasion of clear cell renal carcinoma cells | Binding with phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and suppression of its degradation | [17] |
| MRCCAT1 | Upregulated | -Promotion of proliferation, invasion and metastasis | Inhibition of natriuretic peptide receptor 3 (NPR3) and activation of p38-MAPK signaling | [15] |
| URRCC | Upregulated | -Enhancement of proliferation and metastasis ofclear cell renal carcinoma cells | Positive feed-forward loop with EGF like domain multiple 7 (EGFL7)/phosphor-serine/threonine-specific protein kinase (P-AKT)/forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) signaling | [18] |
| MALAT1 | Upregulated | -Promotion of proliferation and invasion, -Inhibition of apoptosis, -Adverse correlation with patient survival | Interaction with enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (Ezh2) and miR-205 | [19] |
| lnc-ARSR | Upregulated | -Promotion of sunitinib-resistance | Competitive binding miR-34/miR-449, facilitation of AXL receptor tyrosine kinase and c-MET expression | [20] |
| lnc-TSI | Upregulated | -Inhibitor of clear cell renal carcinoma cells metastasis | Suppression of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β) induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition | [21] |
| No. | CpG-Islands (UCSC hg38) | Primers | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Fragment Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | chr1:213985384–213985737 | F: GTATTTTTAGTAGGTTGAGAGGG R: CTAAATCTAACAAAAACTCCAACCC | 66 | 233 |
| 2 | chr1:213982658–213983508 | F: TGGTATATTGGAGGAGGTATATAGG R: TACACTTCCAAACTATAACAAAAT | 58 | 140 |
| 3 | chr1:213979872–213980325 | F: GAGGTTGTTAGGAGTTTGGTTTGTA R: AAAAAACTCTCCCACCCCCAAC | 65 | 239 |
| Clinical and Pathological Features | Number | PROX1-AS1 Expression in Tumor | p-Value | PROX1-AS1 Expression in Non-Tumor Tissue | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RQ | SD | Mean RQ | SD | ||||||
| Entire Group | 42 | 51.9 | 95.6 | p = 0.6 | 47.4 | 86.3 | p = 0.6 | ||
| Gender | Women | 20 | 77.3 | 120.4 | p = 0.88 | 37.4 | 79.5 | p = 0.57 | |
| Men | 22 | 28.9 | 59.6 | 56.4 | 93.0 | ||||
| Age Group | <45 yrs | 5 | 37.8 | 77.3 | p = 0.43 | 27.6 | 45.8 | p = 0.9779 | |
| ≤45–65 yrs | 22 | 73.3 | 115.3 | 45.1 | 81.9 | ||||
| ≥65 yrs | 15 | 25.6 | 59.8 | 57.1 | 104.5 | ||||
| Histopathological Type | KIRC | 33 | 54.3 | 93.4 | p = 0.64 | 42.0 | 74.9 | p = 0.1910 | |
| KIRP | 3 | 7.1 | 11.9 | 12.3 | 15.2 | ||||
| KICH | 3 | 111.6 | 190.8 | 1.4 | 0.3 | ||||
| AML | 3 | 11.0 | 10.6 | 187.1 | 166.7 | ||||
| * pTNM | Tumor Stage | pT1 | 23 | 18.0 | 37.0 | p = 0.07; (pT1 vs. pT2 p = 0.03) | 44.8 | 84.8 | p = 0.820 |
| pT2 | 5 | 167.1 | 156.1 | 28.1 | 45.7 | ||||
| pT3–pT4 | 14 | 66.6 | 107.9 | 58.4 | 101.9 | ||||
| Lymph Node Invasion | pN0 | 37 | 38.3 | 79.5 | p = 0.04 | 50.6 | 90.2 | p = 0.734 | |
| pN1 | 2 | 215.6 | 55.9 | 57.0 | 73.1 | ||||
| Metastasis | pM0 | 32 | 32.1 | 64.5 | p = 0.04 | 44.3 | 80.1 | p = 0.578 | |
| pM1 | 7 | 117.2 | 141.2 | 81.1 | 123.7 | ||||
| ** Grade | G1-G2 | 34 | 40.6 | 82.6 | p = 0.05 | 46.4 | 88.3 | p = 0.081 | |
| G3-G4 | 5 | 93.3 | 115.3 | 81.6 | 94.5 | ||||
| CpG Island-1 | CpG Island-2 | CpG Island-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position (hg38): | chr1:213985384 | chr1:213982658 | chr1:213979872 |
| –213985737 | –213983508 | –213980325 | |
| Band: | 1q32.3 | 1q32.3 | 1q32.3 |
| Size (bp): | 354 | 851 | 454 |
| CpG count: | 40 | 84 | 42 |
| Percentage CpG: | 22.6% | 19.7% | 18.5% |
| Percentage C or G | 66.7% | 71.7% | 70.0% |
| CpG PROX1-AS1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| methC | demethC | methC | demethC | methC | demethC | |
| contr | 5-AZA | contr | 5-AZA | contr | 5-AZA | |
| HEK293 | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| 786-P | + | − | + | − | + | − |
| A498 | + | − | + | − | + | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudzinska, M.; Czarnecka-Chrebelska, K.H.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Maryanchik, S.V.; Parodi, A.; Korolev, D.O.; Potoldykova, N.; Svetikova, Y.; Vinarov, A.Z.; Nemtsova, M.V.; et al. Long Non-Coding PROX1-AS1 Expression Correlates with Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis and Aggressiveness. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020025
Rudzinska M, Czarnecka-Chrebelska KH, Kuznetsova EB, Maryanchik SV, Parodi A, Korolev DO, Potoldykova N, Svetikova Y, Vinarov AZ, Nemtsova MV, et al. Long Non-Coding PROX1-AS1 Expression Correlates with Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis and Aggressiveness. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudzinska, Magdalena, Karolina H. Czarnecka-Chrebelska, Ekaterina B. Kuznetsova, Sofya V. Maryanchik, Alessandro Parodi, Dmitry O. Korolev, Nataliya Potoldykova, Yulia Svetikova, Andrey Z. Vinarov, Marina V. Nemtsova, and et al. 2021. "Long Non-Coding PROX1-AS1 Expression Correlates with Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis and Aggressiveness" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020025
APA StyleRudzinska, M., Czarnecka-Chrebelska, K. H., Kuznetsova, E. B., Maryanchik, S. V., Parodi, A., Korolev, D. O., Potoldykova, N., Svetikova, Y., Vinarov, A. Z., Nemtsova, M. V., & Zamyatnin, A. A., Jr. (2021). Long Non-Coding PROX1-AS1 Expression Correlates with Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis and Aggressiveness. Non-Coding RNA, 7(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020025










