Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Methods for Identification of ncRNAs
3. Role of lncRNAs and Cancer
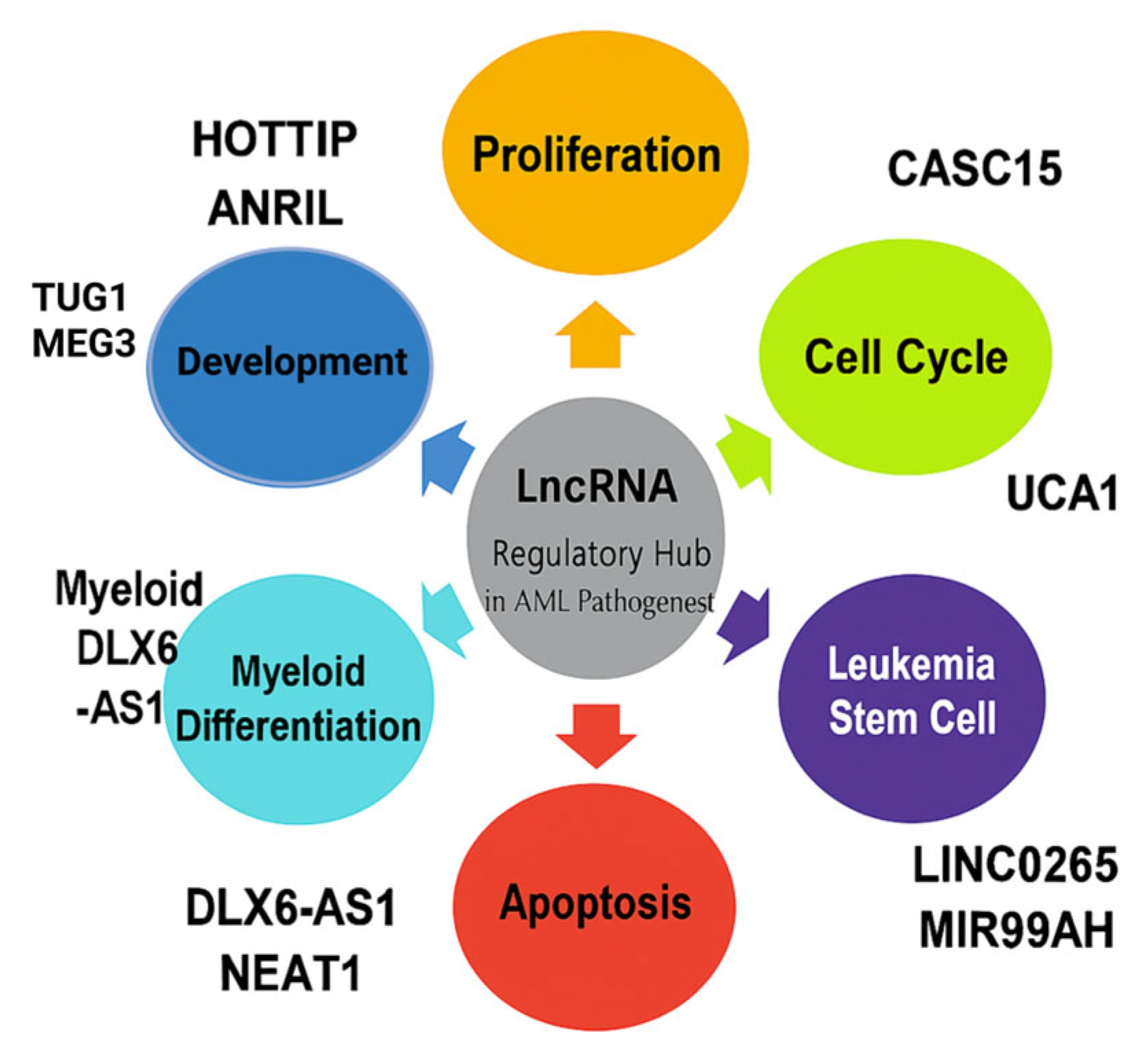
3.1. Overview of lncRNAs and Their Classification
3.2. Molecular Function of lncRNAs
4. Role of circRNAs in AML
5. Role of miRNAs in AML
6. Interplay and Crosstalk Among ncRNA Classes in AML Pathogenesis
6.1. lncRNA-miRNA Interaction
6.2. CircRNA-miRNa-mRNA Axis
7. LncRNAs: Emerging Clinical Utility
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kantarjian, H.; Kadia, T.; DiNardo, C.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Konopleva, M.; Ravandi, F. Acute myeloid leukemia: Current progress and future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.A.; Luznik, L.; Gojo, I. Treatment of AML Relapse After Allo-HCT. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 812207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelcovits, A.; Niroula, R. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Review. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2020, 103, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Badowski, C.; He, B.; Garmire, L.X. Blood-derived lncRNAs as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: The Good, the Bad and the Beauty. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, D.; Nicolet, D.; Ozer, H.G.; Mrózek, K.; Volinia, S.; Fadda, P.; Carroll, A.J.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Kolitz, J.E.; Wang, E.S.; et al. Prognostic and Biologic Relevance of Clinically Applicable Long Non-Coding RNA Profiling in Older Patients with Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; Pitcher, B.N.; Mardis, E.R.; Davies, S.R.; Friedman, P.N.; Snider, J.E.; Vickery, T.L.; Reed, J.P.; DeSchryver, K.; Singh, B.; et al. PAM50 gene signatures and breast cancer prognosis with adjuvant anthracycline- and taxane-based chemotherapy: Correlative analysis of C9741 (Alliance). NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourvest, M.; Brousset, P.; Bousquet, M. Long Noncoding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Functional Characterization and Clinical Relevance. Cancers 2019, 11, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.; Krainer, A.R.; Altman, S. RNA therapeutics: Beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze-de-Almeida, R.; David, C.; Titze-de-Almeida, S.S. The Race of 10 Synthetic RNAi-Based Drugs to the Pharmaceutical Market. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1339–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ke, P.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.; Tan, H.; Liang, Y.; Yao, S. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR inhibits proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2014, 24, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Baradaran, B. RNA Interference and its Role in Cancer Therapy. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The Transcriptional Landscape of the Mammalian Genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21890647/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connerty, P.; Lock, R.B. The tip of the iceberg—The roles of long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2023, 14, e1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.D.; Leedman, P.J.; Filipovska, A.; Rackham, O. Modulation of miRNA function by natural and synthetic RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3745–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Miao, L. Pivotal prognostic and diagnostic role of the long non-coding RNA colon cancer-associated transcript 1 expression in human cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Bu, P. Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Yun, B.; Choi, Y.J.; Son, S.W.; Cipolla, G.A.; Berti, F.C.B.; Malheiros, D.; Oh, T.-J.; Kuh, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.K. Oncogenic Role of Exosomal Circular and Long Noncoding RNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhu, G.; Xu, J.; Lai, Q.; Yan, B.; Guo, Y.; Fung, T.K.; Zeisig, B.B.; Cui, Y.; Zha, J.; et al. HOTTIP lncRNA Promotes Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal Leading to AML-like Disease in Mice. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 645–659.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourvest, M.; De Clara, E.; Wu, H.-C.; Touriol, C.; Meggetto, F.; De Thé, H.; Pyronnet, S.; Brousset, P.; Bousquet, M. A novel leukemic route of mutant NPM1 through nuclear import of the overexpressed long noncoding RNA LONA. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2784–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xing, C.; Yu, X.; Ji, Y. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes the self-renewal of leukemia stem cells through epigenetic silencing of p15. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 67, 32–40.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kershi, S.; Bhayadia, R.; Ng, M.; Verboon, L.; Emmrich, S.; Gack, L.; Schwarzer, A.; Strowig, T.; Heckl, D.; Klusmann, J.-H. The stem cell-specific long noncoding RNA HOXA10-AS in the pathogenesis of KMT2A-rearranged leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bill, M.; Papaioannou, D.; Karunasiri, M.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Pepe, F.; Walker, C.J.; Walker, A.E.; Brannan, Z.; Pathmanathan, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Expression and functional relevance of long non-coding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2169–2182. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30858548/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Knockdown of LncRNA-UCA1 suppresses chemoresistance of pediatric AML by inhibiting glycolysis through the microRNA-125a/hexokinase 2 pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6296–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Silencing long non-coding RNA XIST suppresses drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through down-regulation of MYC by elevating microRNA-29a expression. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H. HOTAIRM1 knockdown enhances cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity by suppression of glycolysis through the Wnt/β-catenin/PFKP pathway in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 680, 108244. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31904363/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; He, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Wang, H. Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00152 Regulates Self-Renewal of Leukemia Stem Cells and Induces Chemo-Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 694021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.K.; Mitchell, A.; Kennedy, J.A.; Chen, W.C.; McLeod, J.; Ibrahimova, N.; Arruda, A.; Popescu, A.; Gupta, V.; Schimmer, A.D.; et al. A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia. Nature 2016, 540, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Du, T.; Du, Y.; Peng, X.; et al. LncRNA NR-104098 Inhibits AML Proliferation and Induces Differentiation Through Repressing EZH2 Transcription by Interacting With E2F1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, B.Q.; Ummarino, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ebralidze, A.K.; Bassal, M.A.; Nguyen, T.M.; Heller, G.; Coffey, R.; Tenen, D.E.; van der Kouwe, E.; et al. Myeloid lncRNA LOUP mediates opposing regulatory effects of RUNX1 and RUNX1-ETO in t(8;21) AML. Blood 2021, 138, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fan, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H. LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 inhibits the self-renewal of leukaemic stem cells by promoting TET2-dependent DNA demethylation of the LRIG1 promoter in acute myeloid leukaemia. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hu, L.; Bu, P. Cytoplasmic NEAT1 Suppresses AML Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Leukemogenesis through Inactivation of Wnt Signaling. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, J.-D.; Zhang, T.-J.; Ma, J.-C.; Xiao, G.-F.; Chen, Q.; Deng, Z.-Q.; Lin, J.; Qian, J.; Yao, D.-M. Overexpression of lncRNA PANDAR predicts adverse prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4999–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, R. lncRNA FBXL19-AS1 is a diagnosis biomarker for paediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, H.Q.; Sun, G.W. Long non-coding RNA LINC00899 as a novel serum biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of acute myeloid leukemia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7364–7370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, K.; Han, B.-W.; Chen, Z.-H.; Lin, K.-Y.; Zeng, C.-W.; Li, X.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Luo, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q. A distinct set of long non-coding RNAs in childhood MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Biology and epigenetic target. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Xia, S.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Xia, L.; Guo, L.; Chen, F.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of lncRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich, S.; Streltsov, A.; Schmidt, F.; Thangapandi, V.R.; Reinhardt, D.; Klusmann, J.H. LincRNAs MONC and MIR100HG act as oncogenes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yu, X.; Lai, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA PVT1 is correlated with leukemic cell proliferation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.Y.; Moriarity, B.S.; Gong, W.; Akiyama, R.; Tiwari, A.; Kawakami, H.; Ronning, P.; Reuland, B.; Guenther, K.; Beadnell, T.C.; et al. PVT1 dependence in cancer with MYC copy-number increase. Nature 2014, 512, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Sharifi, M. Induction of apoptosis and necrosis in human acute erythroleukemia cells by inhibition of long non-coding RNA PVT1. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2018, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, M.; Sharifi, M.; Bagheri, M. Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 with Antisense Locked Nucleic Acid GapmeRs Exerts Tumor-Suppressive Functions in Human Acute Erythroleukemia Cells Through Downregulation of C-MYC Expression. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Weissman, S.M.; Newburger, P.E. Long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIRM1 regulates cell cycle progression during myeloid maturation in NB4 human promyelocytic leukemia cells. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Long, X.; He, Y.; Huang, J. lncRNA HOTAIRM1 Activated by HOXA4 Drives HUVEC Proliferation Through Direct Interaction with Protein Partner HSPA5. Inflammation 2024, 47, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Li, Q.Y.; Nie, L.; Ma, J.; Yao, C.J.; Chen, F.P. LncRNA ANRIL promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion during acute myeloid leukemia pathogenesis via negatively regulating miR-34a. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 119, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-Y.; Li, X.-J.; Sun, Y.-M.; Huang, W.; Fang, K.; Han, C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Luo, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Wang, W.-T. LncRNA ANRIL regulates AML development through modulating the glucose metabolism pathway of AdipoR1/AMPK/SIRT1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, T.R.; Contreras, J.R.; Zampini, M.; Rodriguez-Malave, N.I.; Alberti, M.O.; Anguiano, J.; Tran, T.M.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Gajeton, J.; Ung, N.M.; et al. The lncRNA CASC15 regulates SOX4 expression in RUNX1-rearranged acute leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT1 Acts as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate Cell Growth and Differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khazragy, N.; Elayat, W.; Matbouly, S.; Seliman, S.; Sami, A.; Safwat, G.; Diab, A. The prognostic significance of the long non-coding RNAs “CCAT1, PVT1” in t(8;21) associated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Gene 2019, 707, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Mo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Deng, T.; Zhou, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C. lncRNA-CCDC26, as a novel biomarker, predicts prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Yoshikawa, R.; Harada, H.; Harada, Y.; Ishida, A.; Yamazaki, T. Long noncoding RNA, CCDC26, controls myeloid leukemia cell growth through regulation of KIT expression. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, I.; Mullighan, C.G.; Ishii, M.; Su, X.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Ganti, R.; Cai, Z.; Goorha, S.; Pounds, S.B.; et al. Genomic analysis reveals few genetic alterations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12944–12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcù, E.; Benetton, M.; Bisio, V.; Da Ros, A.; Tregnago, C.; Borella, G.; Zanon, C.; Bordi, M.; Germano, G.; Manni, S.; et al. The long non-coding RNA CDK6-AS1 overexpression impacts on acute myeloid leukemia differentiation and mitochondrial dynamics. iScience 2021, 24, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, S.; Jin, W.; Wang, K. Oncogenic role of lncRNA CRNDE in acute promyelocytic leukemia and NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; An, J.; Sheng, G. Oncogenic Long Noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Binding to microRNA-425. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820965580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morenos, L.; Chatterton, Z.; Ng, J.L.; Halemba, M.S.; Parkinson-Bates, M.; Mechinaud, F.; Elwood, N.; Saffery, R.; Wong, N.C. Hypermethylation and down-regulation of DLEU2 in paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia independent of embedded tumour suppressor miR-15a/16-1. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Shen, H.; Gu, C.M.; Zhang, M.Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; et al. MiRNA-142-3P and FUS can be Sponged by Long Noncoding RNA DUBR to Promote Cell Proliferation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 754936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, A.C.; Lee, J.D.; Chavez, A.; Lee, Y.-R.; Nachmani, D.; Vora, S.; Victor, J.; Sauvageau, M.; Monteleone, E.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. An Integrated Genome-wide CRISPRa Approach to Functionalize lncRNAs in Drug Resistance. Cell 2018, 173, 649–664.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.-F.; Jia, H.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Zhao, X.-S.; Zou, Y.-F.; Zhang, W.; Wan, J.; Chen, X.-F. LncRNA H19 regulates ID2 expression through competitive binding to hsa-miR-19a/b in acute myelocytic leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajj, J.; Nguyen, E.; Liu, Q.; Bouyer, C.; Adriaenssens, E.; Hilal, G.; Ségal-Bendirdjian, E. Telomerase regulation by the long non-coding RNA H19 in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-J.; Zhou, J.-D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Ma, J.-C.; Wen, X.-M.; Yuan, Q.; Li, X.-X.; Xu, Z.-J.; Qian, J. H19 overexpression promotes leukemogenesis and predicts unfavorable prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.Y.; Hu, X.Q.; Xie, F.Y.; Yu, Z.J.; Li, H.Y.; Bin-Zhou Wu, J.B.; Tang, L.Y.; Gao, S.M. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates c-KIT expression through sponging miR-193a in acute myeloid leukemia. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ding, C.; Wang, H.; Charwudzi, A.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Zhai, Z.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates myeloid differentiation through the upregulation of p21 via miR-17-5p in acute myeloid leukaemia. RNA Biol. 2020, 18, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Fang, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, R.; Li, X.; Pan, G.; Liu, J. Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 Suppresses Chemoresistance of Acute Myeloid Leukemia via the miR-520c-3p/S100A4 Axis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Frazão, J.B.; Condino-Neto, A.; Newburger, P.E. HOX antisense lincRNA HOXA-AS2 is an apoptosis repressor in all trans retinoic acid treated NB4 promyelocytic leukemia cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 2375–2383. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23649634/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, D.; Petri, A.; Dovey, O.M.; Terreri, S.; Wang, E.; Collins, F.A.; Woodward, L.A.; Walker, A.E.; Nicolet, D.; Pepe, F.; et al. The long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS3 regulates ribosomal RNA transcription in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Luo, H.; Feng, Y.; Guryanova, O.A.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Lai, Q.; Sharma, A.; Xu, B.; Zhao, Z.; et al. HOXBLINC long non-coding RNA activation promotes leukemogenesis in NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaiefar, H.; Izadifard, M.; Yaghmaie, M.; Montazeri, M.; Gheisari, E.; Ahmadvand, M.; Momeny, M.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Kasaeian, A.; Alimoghaddam, K.; et al. Low Expression of Long Noncoding RNA IRAIN Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Non-M3 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2018, 22, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Yu, D.; Wen, X.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, G.; Hoffman, A.R.; Hu, J.-F. A novel antisense long noncoding RNA within the IGF1R gene locus is imprinted in hematopoietic malignancies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 9588–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-T.; Chen, T.-Q.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Pan, Q.; Huang, W.; Han, C.; Fang, K.; Sun, L.-Y.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Wang, D.; et al. The lncRNA LAMP5-AS1 drives leukemia cell stemness by directly modulating DOT1L methyltransferase activity in MLL leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.H.; Yu, L.J. Long non-coding RNA LINC00641 promotes cell growth and migration through modulating miR-378a/ZBTB20 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7498–7509. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31539138/ (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Fang, X.; Pan, X.; Mai, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Wen, F. LINC00998 functions as a novel tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia via regulating the ZFP36 ring finger protein/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10363–10372. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34699314/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Connerty, P.; Moles, E.; de Bock, C.E.; Jayatilleke, N.; Smith, J.L.; Meshinchi, S.; Mayoh, C.; Kavallaris, M.; Lock, R.B. Development of siRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles Targeting Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01257 as a Novel and Safe Therapeutic Approach for t(8;21) Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1681. [Google Scholar]
- Mangiavacchi, A.; Sorci, M.; Masciarelli, S.; Larivera, S.; Legnini, I.; Iosue, I.; Bozzoni, I.; Fazi, F.; Fatica, A. The miR-223 host non-coding transcript linc-223 induces IRF4 expression in acute myeloid leukemia by acting as a competing endogenous RNA. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60155–60168. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Wen, X.; Xiao, J.; An, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y. Lnc-SOX6-1 upregulation correlates with poor risk stratification and worse treatment outcomes, and promotes cell proliferation while inhibits apoptosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Kou, D.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Qi, X.; Jia, L. LncRNA MEG3 contributes to drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by positively regulating ALG9 through sponging miR-155. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Aguilera, F.; Ramdas, B.; Daulatabad, S.V.; Srivastava, R.; Kotzin, J.J.; Carroll, M.; Wertheim, G.; Williams, A.; Janga, S.C.; et al. Targeting Bim via a lncRNA Morrbid Regulates the Survival of Preleukemic and Leukemic Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Gao, H.; Xia, H.; Li, S.; Li, N.; Gao, C.; Duan, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; et al. IncRNA MVIH correlates with disease features, predicts treatment response and survival in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebralidze, A.K.; Guibal, F.C.; Steidl, U.; Zhang, P.; Lee, S.; Bartholdy, B.; Jorda, M.A.; Petkova, V.; Rosenbauer, F.; Huang, G.; et al. PU.1 expression is modulated by the balance of functional sense and antisense RNAs regulated by a shared cis-regulatory element. Genes. Dev. 2008, 22, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, W.; Guo, R.; Sun, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, G.; Hoffman, A.R.; Hu, J.-F. An intragenic long noncoding RNA interacts epigenetically with the RUNX1 promoter and enhancer chromatin DNA in hematopoietic malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, C.K. Long noncoding RNA SNHG5 is up-regulated and serves as a potential prognostic biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3342–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L. Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 affects the proliferation and apoptosis of childhood acute myeloid leukaemia cells by modulating the miR-193b-3p/MCL1 axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Song, W.; Wang, J. TUG1 confers Adriamycin resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by epigenetically suppressing miR-34a expression via EZH2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Bao, H.; Li, H. Correlation of long non-coding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 with disease conditions and prognosis, as well as its effect on cell activities in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Yu, H.; Zou, X.; Ni, X.; Wei, J. Long non-coding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 correlates with unfavorable prognosis in patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia treated by purine analogue based chemotherapy regimens. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.D.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Wang, L.P.; Zhao, H.T.; Yang, S. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of human leukemia cells via sponging miR-126. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wanyan, Y. Silencing of lncRNA UCA1 curbs proliferation and accelerates apoptosis by repressing SIRT1 signals by targeting miR-204 in pediatric AML. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22435. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.M.; Legnini, I.; Salvatori, B.; Masciarelli, S.; Marchioni, M.; Fazi, F.; Morlando, M.; Bozzoni, I.; Fatica, A. C/EBPα-p30 protein induces expression of the oncogenic long non-coding RNA UCA1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18534–18544. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jiang, P. LncRNA LINC00909 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia via miR-625-mediated modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, G.; Loeb, D.M. Hypoxia-sensitive epigenetic regulation of an antisense-oriented lncRNA controls WT1 expression in myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119837. [Google Scholar]
- De Clara, E.; Gourvest, M.; Ma, H.; Vergez, F.; Tosolini, M.; Dejean, S.; Demur, C.; Delabesse, E.; Recher, C.; Touriol, C.; et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profile in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia identifies a distinct signature and a new biomarker in NPM1-mutated patients. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, S.A.; Ahmad, S.M.; Mumtaz, P.T.; Malik, A.A.; Dar, M.A.; Urwat, U.; Shah, R.A.; Ganai, N.A. Long non-coding RNAs: Mechanism of action and functional utility. Noncoding RNA Res. 2016, 1, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Chao, J.; Yao, H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 187, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Uddin, M.H.; Zonder, J.A.; Azmi, A.S.; Balasubramanian, S.K. Circular RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24039610/ (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Nicolet, B.P.; Engels, S.; Aglialoro, F.; van den Akker, E.; von Lindern, M.; Wolkers, M.C. Circular RNA expression in human hematopoietic cells is widespread and cell-type specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 8168–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-M.; Wen, X.; Han, X.-R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.-Q.; et al. Role of Circular RNA DLEU2 in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00259-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Yi, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, P.; Deng, Z.Q. Circular RNA of vimentin expression as a valuable predictor for acute myeloid leukemia development and prognosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, L.-L.; Yi, Y.Y.; Yi, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, J.; Deng, Z.-Q. Circ-Foxo3 is positively associated with the Foxo3 gene and leads to better prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhong, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, P.; Cui, B.; Ji, C.; Ma, D. Characterization of hsa_circ_0004277 as a New Biomarker for Acute Myeloid Leukemia via Circular RNA Profile and Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, L.; Jian-Jun, C.; Chu-Shu, L.; Guang-Hua, L.; Ming, Z. Silencing of circ_0009910 inhibits acute myeloid leukemia cell growth through increasing miR-20a-5p. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2019, 75, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Z. Circ_0009910 sponges miR-491-5p to promote acute myeloid leukemia progression through modulating B4GALT5 expression and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zou, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Sheng, L.; Huang, H.; Ouyang, G.; et al. Hsa_circ_0012152 and Hsa_circ_0001857 Accurately Discriminate Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia From Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.M.; Ma, J.; Fang, W.B. Identification of non-coding RNA regulatory networks in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals circ-0004136 could promote cell proliferation by sponging miR-142. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 9251–9258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, W. Circular RNA-100290 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via sponging miR-203. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ming, X.; Wu, J. Hsa_circ_0002483 regulates miR-758-3p/MYC axis to promote acute myeloid leukemia progression. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, Y.; Yang, S. Hsa_circ_0079480 promotes tumor progression in acute myeloid leukemia via miR-654-3p/HDGF axis. Aging 2020, 13, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chen, W.-M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wei, T.-N.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Wu, W.-B. CircPAN3 contributes to drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through regulation of autophagy. Leuk. Res. 2019, 85, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Luo, X.; Fu, J.; Xiu, B.; Liang, A.; Zhang, W. Circular RNA profile of acute myeloid leukaemia indicates circular RNA annexin A2 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukaemia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Bu, Z.; Shen, J.; Shang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. A novel circular RNA (hsa_circ_0000370) increases cell viability and inhibits apoptosis of FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia cells by regulating miR-1299 and S100A7A. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Bezzi, M.; Jeong, J.C.; Paffenholz, S.V.; Berry, K.; Naldini, M.M.; Lo-Coco, F.; Tay, Y.; Beck, A.H.; Pandolfi, P.P. Oncogenic Role of Fusion-circRNAs Derived from Cancer-Associated Chromosomal Translocations. Cell 2016, 165, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K. Profiling and functional analysis of circular RNAs in acute promyelocytic leukemia and their dynamic regulation during all-trans retinoic acid treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 651. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29844435/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Zhao, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Circ-ANAPC7 is Upregulated in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Appears to Target the MiR-181 Family. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Pang, Y.; Cui, L.; Qian, T.; Quan, L.; Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Ke, X.; Fu, L. Role of microRNAs, circRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Marcucci, G.; Mrózek, K.; Radmacher, M.D.; Garzon, R.; Bloomfield, C.D. The prognostic and functional role of microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.A. Micro-RNAs and copy number changes: New levels of gene regulation in acute myeloid leukemia. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Sun, M.; Mi, S.; Zhang, H.; Luo, R.T.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; Qian, Z.; et al. Distinct microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15535–15540. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.A.; O’Connell, R.M. MicroRNAs and acute myeloid leukemia: Therapeutic implications and emerging concepts. Blood 2017, 130, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hui, L.; Xu, W. miR-181a sensitizes a multidrug-resistant leukemia cell line K562/A02 to daunorubicin by targeting BCL-2. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 269–277. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22285729/ (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Bai, H.; Cao, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C. miR-181a sensitizes resistant leukaemia HL-60/Ara-C cells to Ara-C by inducing apoptosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Price, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Wiley, A.; He, C.; Gurbuxani, S.; Kunjamma, R.B.; Huang, H.; et al. miR-9 is an essential oncogenic microRNA specifically overexpressed in mixed lineage leukemia–rearranged leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11511–11516. [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich, S.; Katsman-Kuipers, J.E.; Henke, K.; Khatib, M.E.; Jammal, R.; Engeland, F.; Dasci, F.; Zwaan, C.M.; Boer, M.L.D.; Verboon, L.; et al. miR-9 is a tumor suppressor in pediatric AML with t(8;21). Leukemia 2014, 28, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, A.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, M.; Fu, H.; Xu, K.; Li, D.; Deng, A.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A minicircuitry of microRNA-9-1 and RUNX1-RUNX1T1 contributes to leukemogenesis in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 653–661. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27770540/ (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Bi, L.; Sun, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Shen, Z. MicroRNA-10a/b are regulators of myeloid differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5611–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, P.; Arnovitz, S.; Radmacher, M.D.; Maharry, K.; Elkahloun, A.; Yang, X.; et al. Up-regulation of a HOXA-PBX3 homeobox-gene signature following down-regulation of miR-181 is associated with adverse prognosis in patients with cytogenetically abnormal AML. Blood 2012, 119, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Gerloff, D.; Grundler, R.; Wurm, A.A.; Bräuer-Hartmann, D.; Katzerke, C.; Hartmann, J.-U.; Madan, V.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Duyster, J.; Tenen, D.G.; et al. NF-κB/STAT5/miR-155 network targets PU.1 in FLT3-ITD-driven acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Hong, Z.; Yang, L. Decreased expression of microRNA-122 is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in childhood acute myeloid leukemia and function analysis indicates a therapeutic potential. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, Y.; Yan, W.; Cen, J.; Niu, Y.; Yan, Q.; He, H.; Chen, C.-S.; Hu, S. High level of miR-196b at newly diagnosed pediatric acute myeloid leukemia predicts a poor outcome. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Zhang, R.; Qi, H. Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of serum miR-195 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wen, Q. Downregulation of miR-135a predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and regulates leukemia progression via modulating HOXA10 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starczynowski, D.T.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Argiropoulos, B.; Sung, S.; Morin, R.; Muranyi, A.; Hirst, M.; Hogge, D.; Marra, M.; Wells, R.A.; et al. Identification of miR-145 and miR-146a as mediators of the 5q- syndrome phenotype. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornick, N.I.; Doron, B.; Abdelhamed, S.; Huan, J.; Harrington, C.A.; Shen, R.; Cambronne, X.A.; Verghese, S.C.; Kurre, P. AML suppresses hematopoiesis by releasing exosomes that contain microRNAs targeting c-MYB. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Dou, L.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-193a contributes to leukemogenesis in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia by activating the PTEN/PI3K signal pathway. Blood 2013, 121, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhayadia, R.; Krowiorz, K.; Haetscher, N.; Jammal, R.; Emmrich, S.; Obulkasim, A.; Fiedler, J.; Schwarzer, A.; Rouhi, A.; Heuser, M.; et al. Endogenous Tumor Suppressor microRNA-193b: Therapeutic and Prognostic Value in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1007–1016. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29432078/ (accessed on 11 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Qin, L. MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits cell proliferation of acute myeloid leukaemia by directly targeting SOX4. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5261–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ortí, L.; Cristóbal, I.; Cirauqui, C.; Guruceaga, E.; Marcotegui, N.; Calasanz, M.J.; Castello-Cros, R.; Odero, M.D. Integration of SNP and mRNA arrays with microRNA profiling reveals that MiR-370 is upregulated and targets NF1 in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, H.; He, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, M.; Gao, S. A novel miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry contributes to leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shu, X.; Chai, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Xi, Y. The non-coding competing endogenous RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia: Biological and clinical implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zhang, C.; Lu, T.; Liao, E.J.; Huang, H.; Wei, S. Roles of circRNAs in hematological malignancies. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, M.; Peng, G.; Zhao, Y. CRNDE: An important oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, X.A. Functional Interactions Between lncRNAs/circRNAs and miRNAs: Insights Into Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 810317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Shan, P.; Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Xing, L.; Yun, J.; Hao, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Mechanisms of circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA interactions and applications in disease and drug research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Khosroshahi, E.M.; Daneii, P.; Hassanpoor, A.; Eslami, M.; Koohpar, Z.K.; Asadi, S.; Zabihi, A.; Jamali, B.; Ghorbani, A.; et al. Emerging roles of CircRNA-miRNA networks in cancer development and therapeutic response. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2025, 10, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, R.; Lyu, H.; Xiao, S.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.-Z.; Tang, J.; Zhou, C. Long non-coding RNAs: Emerging regulators of invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. J. Adv. Res. 2025. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090123225000736 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Farajzadeh, M.; Fathi, M.; Jalali, P.; Kheshti, A.M.; Khodayari, S.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Jadidi, F. Long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia: Biomarkers, prognostic indicators, and treatment potential. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, M.; Lampis, A.; Ghidini, M.; Salati, M.; Mirchev, M.B.; Valeri, N.; Hahne, J.C. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as New Tools for Cancer Therapy: First Steps from Bench to Bedside. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldakhakhny, B.; Sutaih, A.M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Aqeeli, Y.M.; Awan, A.Z.; Alsayegh, M.Y.; Elsamanoudy, S.A.; Elsamanoudy, A. Exploring the role of noncoding RNAs in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, A.S.; Chava, H.; Balusu, R.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Coulter, D.W.; Challagundla, K.B. The crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and cell-cycle events: A new frontier in cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2024, 32, 200785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, B.H.; Kamal, L.T.; Wardy, L.W.; Ragheb, M.; Hanna, M.M.; Elsharkawy, M.; Abdelnaser, A. Non-coding RNAs: Emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer and inflammatory diseases. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1534862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Specchia, G.; Musto, P.; Albano, F. Dysregulation of miRNA in Leukemia: Exploiting miRNA Expression Profiles as Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-D.; Park, S.-K.; Kang, D.; Hwang, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Hong, S.-W.; Moon, J.-H.; Shin, J.-S.; Jin, D.-H.; You, D.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-29a/miR-30c/DNMT3A axis controls SOD2 and mitochondrial oxidative stress in human mesenchymal stem cells. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Xu, Q.; Sha, R.; Bao, T.; Xi, X.; Guo, G. MicroRNA-29a inhibits cell proliferation and arrests cell cycle by modulating p16 methylation in cervical cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.-N.; Zhang, X.-L.; Luo, J.-S.; Peng, C.-J.; Tang, W.-Y.; Huang, L.-B.; Tang, Y.-L.; Luo, X.-Q. Up-regulated miR-155 is associated with poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and promotes cell proliferation targeting ZNF238. Hematology 2021, 26, 16–25. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/16078454.2020.1860187 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Narayan, N.; Bracken, C.P.; Ekert, P.G. MicroRNA-155 expression and function in AML: An evolving paradigm. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.; Wan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Sang, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Identification of circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Competitive Endogenous RNA Network as Novel Prognostic Markers for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Genes 2020, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Joseph, S.; Xia, M.; Teng, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Zhai, L.; Deng, W. Circular RNAs Acting as miRNAs’ Sponges and Their Roles in Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, B.; Garzon, R. Clinical Applications of MicroRNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Mini-Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.F. miRNA Targeting Drugs: The Next Blockbusters? Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1517, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in cancer: From developmental genes in worms to their clinical application in patients. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinlong, S.; Lin, F.; Yonghui, L.; Li, Y.; Weidong, W. Identification of let-7a-2-3p or/and miR-188-5p as Prognostic Biomarkers in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Thakral, D.; Gupta, R. Regulatory noncoding RNAs: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Blood Res. 2021, 11, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Chen, Y. Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancers: Progress and prospects. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mer, A.S.; Lindberg, J.; Nilsson, C.; Klevebring, D.; Wang, M.; Grönberg, H.; Lehmann, S.; Rantalainen, M. Expression levels of long non-coding RNAs are prognostic for AML outcome. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group Number | AML Type | Major Clinical Characteristics | Commonly Implicated Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities | Distinct genetic alterations. | FLT3, NPM1, CEBPA, RUNX1, etc. |
| Specific implications for treatment. | |||
| Varied prognosis. | |||
| 2 | AML with myelodysplasia-related changes | Overlapping features with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). | TP53, ASXL1, EZH2, etc. |
| Impacts on therapy choices. | |||
| 3 | Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms | Arises as a result of prior cancer treatments. | MLL rearrangements, TP53, etc. |
| Special considerations in diagnosis and therapy. | |||
| 4 | AML not otherwise specified | Broad category encompassing AML cases without specific features. | Various gene mutations |
| Diagnosis and treatment are more generalized. | |||
| Variable clinical presentations. | |||
| 5 | Myeloid sarcoma | Manifests as extramedullary tumors in various body tissues. | No single common gene implicated |
| Diverse symptoms depending on the location of the tumors. | |||
| Clinical complexity due to tumor heterogeneity. | |||
| 6 | Myeloid proliferations related to Down syndrome | Associated with individuals with Down syndrome. | GATA1 mutations |
| Diagnosis and treatment tailored to this patient group. |
| Name | Key Observation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| ANRIL | Oncogenic in nature, upregulated in AML, promotes proliferation, targets adipoR1 and miT-34/HFAC1, and maintains glucose metabolism | [50,51] |
| CASC15 | Oncogenic in nature, upregulated in RUNX1 rearranged AML, and activates SOX4 via regulating YY1 transcription factor | [52] |
| CCAT1 | Oncogenic in nature, upregulated in AML, and suppresses monocytic differentiation and promotes proliferation | [53,54] |
| CCDC26 | Upregulated, tumor suppressor, age-associated expression, reduces c-Kit expression, regulates AML cell proliferation, and induces drug resistance | [55,56,57] |
| CDK6-AS1 | Oncogenic in nature, it reduces RUNX1 transcription and is associated with a higher expression level, which is associated with poor treatment response | [58] |
| CRNDE | Upregulated in AML and regulates NOTCH2 in acute promyelocytic cells | [59] |
| DARS-AS1 | Oncogenic in nature and higher expression is associated with poor survival | [60] |
| DLEU2 | Tumor suppressor in AML | [61] |
| DUBR | Induces proliferation in AML cells | [62] |
| GAS6-AS2 | Oncogenic in nature and regulates GAS1 and AXL expression | [63] |
| H19 | Oncogenic in nature | [64,65,66] |
| HOTAIR | Upregulated, oncogenic in nature, and promotes proliferation and differentiation in AML cells | [26,67,68] |
| HOTAIRM1 | Upregulated in AML cells, regulates myeloid differentiation, and is a tumor suppressor | [31,49,67] |
| HOXA10-AS | Upregulated, HSC-specific lncRNA that induces proliferation | [27] |
| HOX-AS2 | Oncogenic in nature and apoptosis repressor | [69,70] |
| HOXB-AS3 | Upregulated and regulates proliferation in leukemic cells | [71] |
| HOXBLINC | Upregulated as a chromatin modulator | [72] |
| IRAIN | Downregulated in Mal cells and restricts tumor cell migration | [73,74] |
| LAMP5-AS1 | Upregulated and maintains methyl transferase activity | [75] |
| LINC00152 | Regulate PARP1 | [32] |
| LINC00641 | Oncogenic in nature | [76] |
| LINC00998 | Tumor suppressor and reduced expression associated with poor survival | [77] |
| LINC01257 | Oncogenic in nature and higher expression associated with poor survival | [78] |
| LINC-223 | Oncogenic in nature and induces differentiation | [79] |
| Lnc-SOX6-1 | Oncogenic in nature, and increased expression is associated with poor survival | [80] |
| LONA | Upregulated, promotes leukemogenesis, and is involved in differentiation | [25] |
| LOUP | Downregulated and tumor Suppressor | [35] |
| MAGI2-AS3 | Tumor suppressor | [36] |
| MEG3 | Tumor suppressor | [81] |
| MIR100HG | Oncogenic in nature | [43] |
| MONC | Oncogenic | [43] |
| MORRID | Upregulated in AML cells and induces proliferation | [82] |
| MVIH | Oncogenic, and increased expression affects treatment response | [83] |
| NEAT1 | Tumor suppressor regulates myeloid differentiation | [37] |
| NR-104098 | Tumor suppressor | [34] |
| PANDAR | Upregulated in AML | [38] |
| PU.1-AS | Oncogenic | [84] |
| PVT-1 | Oncogenic | [44,46,54] |
| RUNXOR | Upregulated in AML and oncogenic | [85] |
| SNHG5 | Upregulated in AML | [86] |
| SNHG14 | Oncogenic in nature | [87] |
| TUG1 | Upregulated in AML cells, oncogenic, and induces proliferation | [88,89,90] |
| UCA1 | Upregulated in CN-AML and maintains leukemic cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | [29,91,92,93] |
| LINC00909 | Oncogenic and higher expression associated with poor survival | [94] |
| WT1-AS | Tumor suppressor | [95] |
| XIST | DOX resistance | [30] |
| XLOC_109948 | Higher expression is associated with poor prognosis | [96] |
| circRNAs | Role in AML | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| f-circPR | Promotion of proliferation and colony formation in leukemia cells | [117] |
| circ_100290 | Upregulation of proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis utilizing the miR-203/Rab10 axis | [118] |
| circ_0009910 | Upregulation of proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and prediction of poor prognosis | [107] |
| circ_DLEU2 | Promotion of AML cell proliferation and inhibition of cell apoptosis and AML tumor formation in vivo via suppression of miR-496 and promotion of PRKACB expression | [61,103] |
| circ_HIPK2 | Influence on ATRA-induced differentiation of APL cells and impairment of AML1- and p53-mediated transcription | [118] |
| has_circ_0004277 | Elevation of hsa_circ_0004277 is associated with chemotherapy | [106] |
| f-circM9 | Promotion of proliferation and colony formation in leukemia cells | [117] |
| circ_0000370 | Upregulated in AML, i.e., correlated with poor prognosis | [116] |
| circ_vim | Tumor promoter | [104] |
| circ_Foxo3 | Downregulated in AML cells | [105] |
| circ_009910 | Upregulated in AML cells and a critical regulator of cell cycle progression, proliferation, and apoptosis in leukemic cells. | [107,108] |
| circ_ANAPC7 | Upregulated in AML cells | [119] |
| has_circ_0012152 | Upregulated in AML cells | [109] |
| Circ_004136 | Upregulated in pediatric AML | [110] |
| has_circ_100290 | Upregulated in AML patients | [111] |
| has_circ_002483 | Upregulated in AML patients | [112] |
| has_circ_007980 | Reduces the expression associated with the lower viability of leukemic cells | [113] |
| circPAN3 | Upregulated in AML cases | [118] |
| miRNA | AML Subtype | Role in AML | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-9 | MLL-rearranged AML | Overexpressed, it promotes cell growth and inhibits apoptosis | [127] |
| miR-9 | Pediatric AML with t(8;21) | Downregulated; acts as a tumor suppressor and induces differentiation | [128] |
| miR-9-1 | t(8;21) AML | Downregulation and overexpression induce differentiation and inhibit proliferation | [129] |
| miR-10b | NPM1 and DNMT3A mutation AML | Correlated with higher BM blast percentage | [130] |
| miR-181 | CN-AML with CEBPA mutations, FLT3-ITD, t(15;17) | Overexpressed | [131] |
| miR-155 | FLT3-ITD-associated AML | Upregulated; targets PU.1; knockdown represses proliferation and induces apoptosis | [132] |
| miR-122 | FAB subtype M7 | Downregulation and overexpression inhibit cell proliferation | [133] |
| miR-196b | Pediatric AML with M4/5 subtypes | Higher expression predicts a poor outcome | [134] |
| miR-195 | FAB-M7, unfavorable karyotypes | A decrease in BM and serum is associated with these factors | [135] |
| miR-135a | Downregulated in AML | [136] | |
| miR-144-3p | Antiapopotic | [137] | |
| miR-150 | Suppressed hematopoiesis via releasing exosomes loaded with miRNA | [138] | |
| miR-193a | Induces the oncogenic activity of AML-ETO | [139] | |
| miR-193b | Induces apoptosis and block G1/S phase | [140] | |
| miR-339-5p | Inhibits the cell proliferation of AML cells | [141] | |
| miR-370 | Activates the RAS signaling pathway | [142] | |
| miR-375 | Playing a role in DNA hypomethylation | [143] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maurya, S.S.; Maurya, S.; Chaturvedi, S.K. Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050070
Maurya SS, Maurya S, Chaturvedi SK. Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Non-Coding RNA. 2025; 11(5):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050070
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaurya, Shailendra S., Sarita Maurya, and Sumit K. Chaturvedi. 2025. "Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Non-Coding RNA 11, no. 5: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050070
APA StyleMaurya, S. S., Maurya, S., & Chaturvedi, S. K. (2025). Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Non-Coding RNA, 11(5), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050070







