Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Strategy
3. Dysregulated Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis
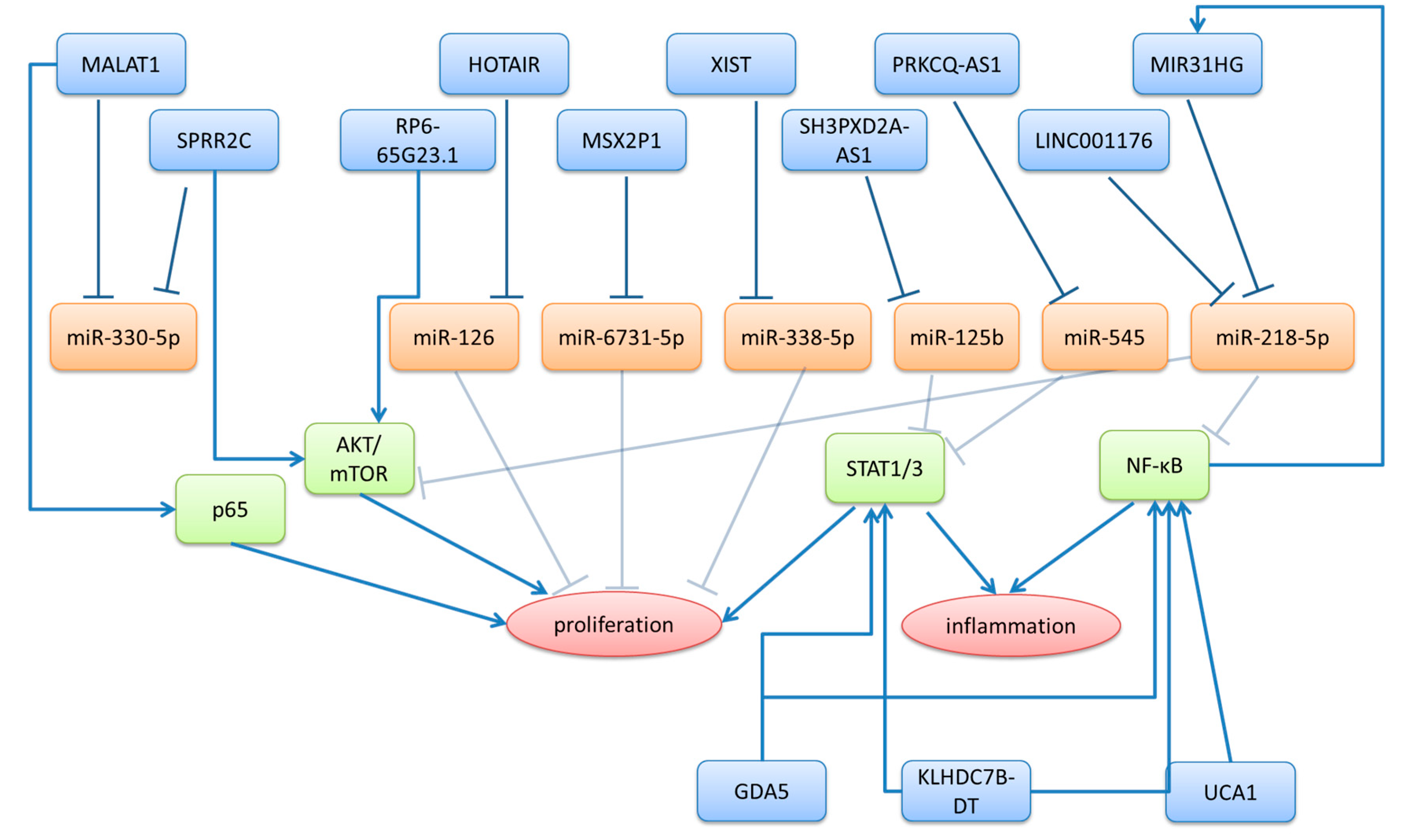
3.1. LncRNAs Upregulated in Psoriasis
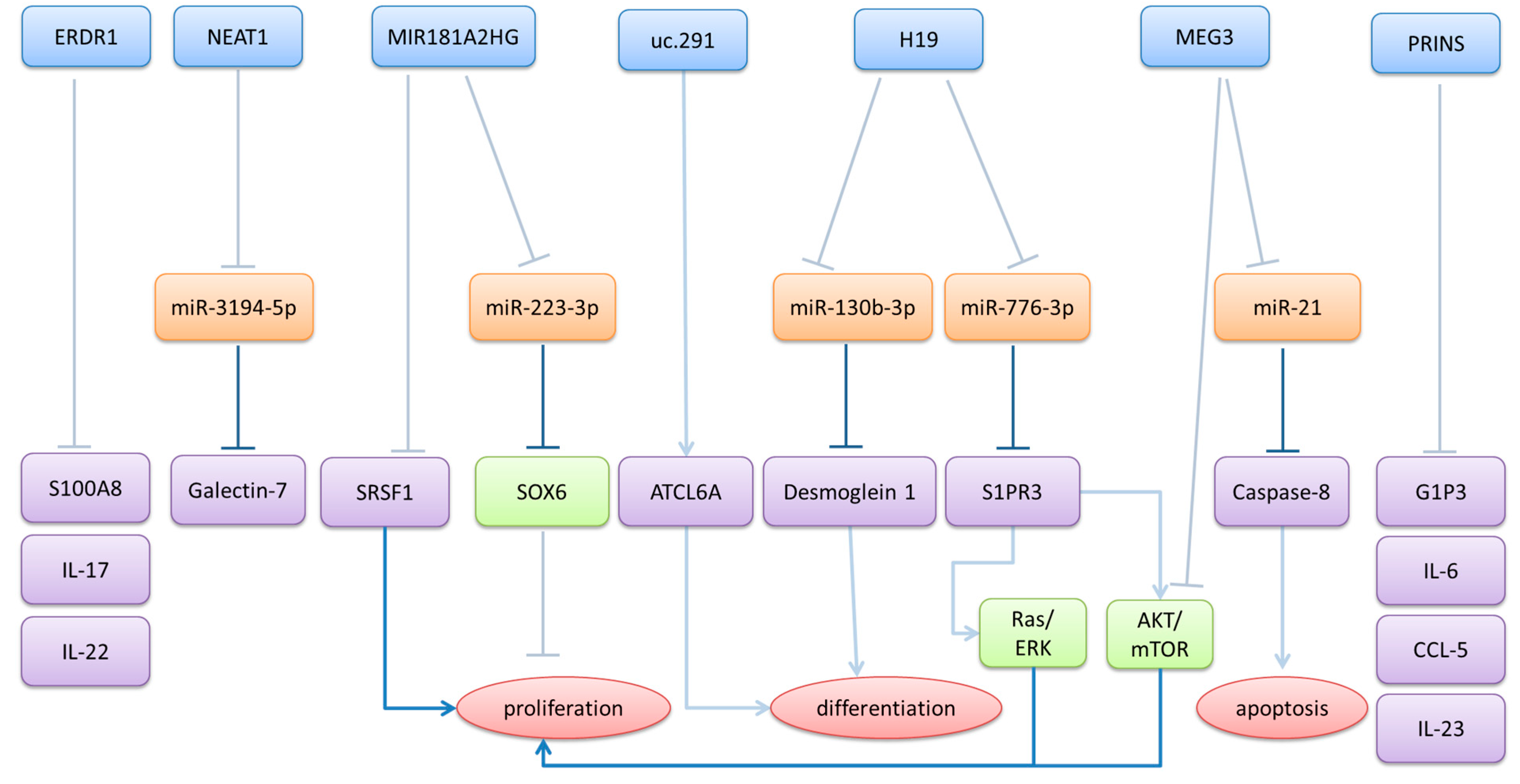
3.2. Downregulated lncRNAs in Psoriasis
| lncRNA | Expression in Psoriasis | Psoriasis-Related Functions of lncRNA | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC020916.1 | upregulated in lesional skin | expression correlates with expression of cell proliferation/epidermal differentiation genes | [29] |
| AGXT2L1-2:2 | upregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes and inhibits apoptosis | [68,69] |
| CYDAER | upregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes | upregulated by IL-17A and during early differentiation downregulated in late differentiation stages of keratinocytes knockdown of CYDAER promotes terminal differentiation | [35] |
| GAS5 | upregulated in psoriatic serum | [31] | |
| GDA-5 | upregulated in lesional skin | regulates FOXM1 expression promotes proliferation and inflammation in keratinocytes via STAT3 and NF-κB signaling | [70] |
| HOTAIR | upregulated in psoriatic serum | regulates apoptosis by acting as a ceRNA for miR-126 | [52,53] |
| KLHDC7B-DT | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation and inflammatory cytokine secretion (IL-6, IL-8) through STAT3 and NF-κB signaling | [71] |
| LINC00958 | upregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes | [27] |
| LINC01176 | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes acts as a ceRNA for miR-218-5p knockdown alleviated psoriasiform symptoms in IMQ-induced mouse model of psoriasis | [51] |
| LINC01215 | upregulated in lesional skin | expression correlates with response to biological therapy | [72,73] |
| LINC1206 | upregulated in lesional skin | [72] | |
| MALAT1 | upregulated in lesional and non-lesional skin and psoriatic serum | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes by binding to p65 regulates S100A7 expression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-330-5p | [41,42,43] |
| MIR31HG | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes | [48] |
| MSX2P1 | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation of keratinocytes by acting as a ceRNA for miR-6731-5p | [74] |
| PRKCQ-AS1 | upregulated in lesional skin | regulates JAK-STAT1 pathway by acting as a ceRNA for miR-545 exosomal PRKCQ-AS1 from keratinocytes promotes Th17 differentiation of CD4+ T-cells | [75,76] |
| RP6-65G23.1 | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via p-ERK1/2/p-AKT signaling pathway | [25,77] |
| SH3PXD2A-AS1 | upregulated in lesional skin | promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in keratinocytes regulates STAT3 expression by acting as ceRNA for miR-125b | [72,75,78] |
| SPRR2C | upregulated in lesional skin and psoriatic keratinocytes | promotes proliferation of keratinocyte, by increasing STAT1 and S100A7 expression through acting as a ceRNA for miR-330-5p and by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways | [79,80] |
| SPRR2G-2 | upregulated in lesional skin and psoriatic keratinocytes | promotes proliferation and inflammation by activating the STAT3 pathway | [81] |
| UCA1 | upregulated in lesional skin | positively regulates keratinocyte-driven inflammation via the NF-κB and HIF-1α pathways | [82] |
| XIST | upregulated in psoriatic serum | regulates proliferation and inflammation of keratinocytes, by acting as a ceRNA for miR-338-5p | [45,46] |
| lncRNA | Expression in Psoriasis | Psoriasis Related Functions of lncRNA | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERDR1 | downregulated in lesional skin | in IMQ-induced model, recombinant ERDR1 decreases psoriasis-like symptoms and expression of IL-17, IL-22, and S100A8 | [83,84] |
| H19 | downregulated in lesional skin | regulates proliferation and inflammation through the H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 axis regulates differentiation by acting as a ceRNA for miR-130b-3p | [85,86] |
| LINC00941 | downregulated in lesional skin | [87] | |
| LOC100130476 | downregulated in lesional skin | [25] | |
| LOC285194 | downregulated in lesional skin | [88,89] | |
| MEG3 | downregulated in lesional skin MEG3 and miR-21 are possible diagnostic markers for psoriasis | promotes apoptosis by acting as a ceRNA for miR-21 suppresses inflammation and promotes autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways | [58,59,60,61] |
| MIR181A2HG | downregulated in lesional skin | regulates proliferation of keratinocytes, by acting as a ceRNA for miR-223-3p and by binding to SRSF1 | [90,91] |
| NEAT1 | increased NEAT-1 expression in psoriatic blood samples downregulated in lesional skin downregulated in resolved epidermis compared to never lesional epidermis | regulates expression of galectin-7 by acting as a ceRNA for miR-3194-5p | [20,38,39,40] |
| PRINS | upregulated in non-lesional skin and in psoriatic keratinocytes downregulated in psoriatic serum, along with its interactors G1P3 and NPM-1 high PRINS expression in the buccal epithelium with low expression in psoriatic keratinocytes lead to severe psoriasis with prolonged exacerbation and unfavorable prognosis | regulates G1P3 expression in keratinocytes binds to NPM-1 and regulates the UVB-induced nucleolar shuttling of NPM-l downregulates IL-6 and CCL-5 expression, by binding to the respective mRNAs and downregulates IL-23a in keratinocytes | [11,30,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| uc.291 | downregulated in lesional skin | regulates differentiation by interacting with ATCL6A promotes proliferation of keratinocytes | [92,93] |
| 7SL-RNA | downregulated in lesional skin | [94] |
4. Genetic Associations and Clinical Implications of lncRNAs in Psoriasis
| lncRNA | Associated Variant | Type of Association | Publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANRIL | rs1063192 | associated with response to apermilast therapy | [109] |
| rs1333048 | more prevalent in psoriatic patients | [108] | |
| rs10120688 | associated with response to apermilast therapy | [109] | |
| rs10757178 | more prevalent and increased risk in psoriatic patients | [108] | |
| rs2518723 | more prevalent in psoriatic patients | [107] | |
| rs3217992 | more prevalent in psoriatic patients | [107] | |
| rs4977574 | protective against psoriasis | [108] | |
| HOTAIR | rs12826786 | increased risk of psoriasis | [99] |
| rs4759314 | increased risk of psoriasis | [99,100] | |
| LINC00941 | rs12297445 | associated with response to apermilast therapy | [109] |
| MALAT1 | rs619586 | increased risk of psoriasis | [101] |
| TARF3IP2-AS1 | rs13210247 | increased risk of psoriasis | [102,103,104,105,106] |
5. Therapeutic Targeting of lncRNAs in Psoriasis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ANRIL | CDKN2B-AS1, antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus |
| CCL-5 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 |
| CCL20 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 20 |
| C/EBP | CCAAT enhancer binding protein |
| ceRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| ERDR1 | Erythroid differentiation regulator 1 |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box protein M1 |
| G1P3 | Interferon, alpha-inducible protein 6 (IFI6) |
| GAS5 | Growth arrest-specific 5 |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| HOTAIR | HOX transcript antisense RNA |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| IL-22 | Interleukin-22 |
| IL-23 | Interleukin-23 |
| IL-36G | Interleukin-36 gamma |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IMQ | Imiquimod |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| LINC00958 | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 958 |
| LINC01176 | Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1176 |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEG3 | Maternally expressed gene 3 |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| ncRNA | Non-coding RNA |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NPM-1 | Nucleophosmin 1 |
| p65 (RELA) | NF-κB subunit p65 |
| p-ERK1/2 | Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PRINS | Psoriasis susceptibility-related RNA gene induced by stress |
| PRKCQ-AS1 | Protein kinase C theta antisense RNA 1 |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| S100A7 | S100 calcium-binding protein A7 (psoriasin) |
| S1PR3 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 |
| shRNA | Short hairpin RNA |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| SOX6 | SRY-box transcription factor 6 |
| SPRR2C | Small proline-rich protein 2C |
| SRSF1 | Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1 |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| Th17 | T-helper 17 cell |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TRAF3IP2 | TNF receptor-associated factor 3 |
| TRAF3IP2-AS1 | TRAF3IP2 antisense RNA 1 |
| UCA1 | Urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 |
| UVB | Ultraviolet B radiation |
| XIST | X-inactive-specific transcript |
References
- Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Parisi, R.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Systematic review examining changes over time and variation in the incidence and prevalence of psoriasis by age and gender. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strober, B.; Karki, C.; Mason, M.; Guo, N.; Holmgren, S.H.; Greenberg, J.D.; Lebwohl, M. Characterization of disease burden, comorbidities, and treatment use in a large, US-based cohort: Results from the Corrona Psoriasis Registry. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhadou, F.; Mintoff, D.; Del Marmol, V. Psoriasis: Keratinocytes or Immune Cells—Which Is the Trigger? Dermatology 2019, 235, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Dai, C.; Zeng, F. Cellular Mechanisms of Psoriasis Pathogenesis: A Systemic Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Chakith, M.R.; Pradeep, S.; Gangadhar, M.; Chaithra Maheshwari, N.; Pasha, S.; Kollur, S.P.; Nagashree, S.; Shivamallu, C.; Mallanna, S.A. Advancements in understanding and treating psoriasis: A comprehensive review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic approaches. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Hammerberg, C.; Voorhees, J.J.; Cooper, K.D. Kinetics and regulation of human keratinocyte stem cell growth in short-term primary ex vivo culture. Cooperative growth factors from psoriatic lesional T lymphocytes stimulate proliferation among psoriatic uninvolved, but not normal, stem keratinocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Howie, S.; Weller, R.; Sabin, E.; Hunter, J.; McKenzie, R. Psoriatic Keratinocytes Show Reduced IRF-1 and STAT-1alpha Activation in Response to gamma-IFN. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.; Sabin, E. Aberrant Signalling and Transcription Factor Activation as an Explanation for the Defective Growth Control and Differentiation of Keratinocytes in Psoriasis: A Hypothesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körver, J.E.M.; Van Duijnhoven, M.W.F.M.; Pasch, M.C.; Van Erp, P.E.J.; Van De Kerkhof, P.C.M. Assessment of epidermal subpopulations and proliferation in healthy skin, symptomless and lesional skin of spreading psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Széll, M.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Koreck, A.; Pivarcsi, A.; Polyánka, H.; Szeg, C.; Gaál, M.; Dobozy, A.; Kemény, L. Proliferating keratinocytes are putative sources of the psoriasis susceptibility-related EDA + (extra domain A of fibronectin) oncofetal fibronectin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Pivarcsi, A.; Polyánka, H.; Kenderessy-Szabó, A.; Molnár, G.; Szentpáli, K.; Bari, L.; Megyeri, K.; Mándi, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel, psoriasis susceptibility-related noncoding RNA gene, PRINS. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24159–24167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, K.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Dallos, A.; Bebes, A.; Francziszti, L.; Dobozy, A.; Kemény, L.; Széll, M. Regulatory Networks Contributing to Psoriasis Susceptibility. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2014, 94, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozó, R.; Danis, J.; Flink, L.B.; Vidács, D.L.; Kemény, L.; Bata-Csörgő, Z. Stress-related regulation is abnormal in the psoriatic uninvolved skin. Life 2021, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, E.; Bozó, R.; Groma, G.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L.; Danis, J.; Széll, M. The Psoriatic Nonlesional Skin: A Battlefield between Susceptibility and Protective Factors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2785–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, L.; Bacsa, S.; Sonkoly, E.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L.; Dobozy, A.; Széll, M. Comparison of stress-induced PRINS gene expression in normal human keratinocytes and HaCaT cells. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozó, R.; Flink, L.B.; Ambrus, B.; Ghaffarinia, A.; Koncz, B.; Kui, R.; Gyulai, R.; Kemény, L.; Bata-Csörgő, Z. The Expression of Cytokines and Chemokines Potentially Distinguishes Mild and Severe Psoriatic Non-Lesional and Resolved Skin from Healthy Skin and Indicates Different Stages of Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, B.S.; Swain, A.F.; Fry, L.; Valdimarsson, H. Epidermal T lymphocytes and HLA-DR expression in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1984, 110, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prens, E.P.; Benne, K.; van Joost, T.; Benner, R. The autologous mixed epidermal cell-T lymphocyte reaction is elevated in psoriasis: A crucial role for epidermal HLA-DR+/CD1a- antigen-presenting cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placek, W.; Haftek, M.; Thivolet, J. Sequence of changes in psoriatic epidermis. Immunocompetent cell redistribution precedes altered expression of keratinocyte differentiation markers. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1988, 68, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghaffarinia, A.; Ayaydin, F.; Póliska, S.; Manczinger, M.; Bolla, B.S.; Flink, L.B.; Balogh, F.; Veréb, Z.; Bozó, R.; Szabó, K.; et al. Psoriatic Resolved Skin Epidermal Keratinocytes Retain Disease-Residual Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Profiles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmacharya, P.; Chakradhar, R.; Hulshizer, C.A.; Gunderson, T.M.; Ogdie, A.; Davis, J.M., III; Wright, K.; Tollefson, M.M.; Duarte-García, A.; Bekele, D.; et al. Multimorbidity in psoriasis as a risk factor for psoriatic arthritis: A population-based study. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Johnston, A.; Xing, X.; Voorhees, J.J.; Elder, J.T.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Modulation of Epidermal Transcription Circuits in Psoriasis: New Links between Inflammation and Hyperproliferation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tsoi, L.C.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Johnston, A.; Ding, J.; Stuart, P.E.; Xing, X.; Kochkodan, J.J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of psoriasis in a large case-control sample: RNA-seq provides insights into disease mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervaniemi, M.; Katayama, S.; Skoog, T.; Siitonen, H.; Vuola, J.; Nuutila, K.; Sormunen, R.; Johnsson, A.; Linnarsson, S.; Suomela, S.; et al. NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Iyer, M.K.; Stuart, P.E.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Sarkar, M.K.; Li, B.; Ding, J.; Voorhees, J.J.; et al. Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Meisgen, F.; Pasquali, L.; Munkhammar, S.; Xia, P.; Ståhle, M.; Landén, N.X.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies the Keratinocyte-Specific miRNA Signature of Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2547–2550.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Pasquali, L.; Srivastava, A.; Freisenhausen, J.C.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. The Long Noncoding RNA LINC00958 Is Induced in Psoriasis Epidermis and Modulates Epidermal Proliferation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogle, R.; Patrick, M.T.; Sreeskandarajan, S.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, R.; Ma, F.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Plazyo, O.; et al. Profiling Long Noncoding RNA in Psoriatic Skin Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 1060–1069.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.Y.; Tawfik, N.Z.; Soliman, N.H.; Eldeen, L.A.T. The lncRNA PRINS-miRNA-mRNA Axis Gene Expression Profile as a Circulating Biomarker Panel in Psoriasis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 26, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Shehata, W.; Maraee, A.; Abd El Monem Ellaithy, M.; Tayel, N.; Abo-Ghazala, A.; Mohammed El-Hefnawy, S. Circulating long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 as a diagnostic marker and indicator of degree of severity in plaque psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. The non-coding skin: Exploring the roles of long non-coding RNAs in epidermal homeostasis and disease. Bioessays 2013, 35, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, K.R.; Cheng, A.; Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.L. The Emerging Functions of Long Noncoding RNA in Immune Cells: Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 848790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, R.; Gupta, R.; Lai, K.; Chopra, N.; Arron, S.T.; Liao, W. Network analysis of psoriasis reveals biological pathways and roles for coding and long non-coding RNAs. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freisenhausen, J.C.; Luo, L.; Kelemen, E.; Elton, J.; Skoog, V.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. RNA Sequencing Reveals the Long Non-Coding RNA Signature in Psoriasis Keratinocytes and Identifies CYDAER as a Long Non-Coding RNA Regulating Epidermal Differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2025, 34, e70054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA Hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a Hidden RNA Language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.; Kim, W. Roles of Oncogenic Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer Development. Genomics Inform. 2018, 16, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Sabry, D.; Aboraia, N.; Fawzy, A.; Abou-Elalla, A.A. Dyslipidemia initiates keratinocytes proliferation through upregulation of lncRNA NEAT in psoriasis patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7597–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Aziz, H.; Mohammed, E. Role of LncRNA NEAT-1 In Pathogenesis of Psoriasis in Egyptian Patients. Fayoum Univ. Med. J. 2024, 13, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cheng, S.; Zou, G.; Ding, X. Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation and migration of psoriatic keratinocytes via the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-3194-5p/Galectin-7 axis. Anticancer. Drugs 2022, 33, e423–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamir, A.M.; Shaker, O.G.; El-Komy, M.H.; Mahmoud Sharabi, M.; Aboraia, N.M. The role of LncRNA MALAT-1 and MiRNA-9 in Psoriasis. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, X.; Pan, M. Interleukin-17 Regulates Keratinocyte Proliferation in Psoriasis Through the MALAT1/miR-125b/BRD4 Axis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2024, 20, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, J. LncRNA MALAT-1 regulates the growth of interleukin-22-stimulated keratinocytes via the miR-330-5p/S100A7 axis. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Skarmoutsou, E.; Granata, M.; Trovato, C.; Rossi, G.A.; Mazzarino, M.C. S100A7: A rAMPing up AMP molecule in psoriasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 32, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Chen, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. LncRNA XIST Engages in Psoriasis via Sponging miR-338-5p to Regulate Keratinocyte Proliferation and Inflammation. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 35, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Wu, X.; Xiang, Y. Sinomenine suppressed keratinocyte proliferation and imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis by regulating lncRNA XIST. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 35, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhu, T.; Tian, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.-L. Exploration of ferroptosis and necroptosis-related genes and potential molecular mechanisms in psoriasis and atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1372303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Hua, M.; Guo, J.; Nong, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhong, F.; Qin, L. Knockdown of lncRNA MIR31HG inhibits cell proliferation in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Waye, M.M.Y.; Fu, W.; Zhang, J. MiR-218 Mediates tumorigenesis and metastasis: Perspectives and implications. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 334, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Osaka, E.; Fujiwara, K.; Fujii, R.; Takayama, T.; Tokuhashi, Y.; Nakanishi, K. miRNA-218 targets multiple oncogenes and is a therapeutic target for osteosarcoma. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Lu, S.; Feng, Y.; Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X. The LINC01176-miR-218-5p-IL-36G Network is Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis by Promoting Inflammation. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, A.; Elamir, A.; Mohammed, B.; Elsayed, H. LncRNA HOTAIR as a novel biomarker in Psoriasis. Fayoum Univ. Med. J. 2023, 12, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Guo, B.; Chen, S.; Lu, J.; Shan, Y. Role of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/miR-126 axis in an in vitro psoriasis model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Zou, J.; Mao, J.; Guo, D.; Wu, M.; Xu, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Jin, W. Plasma miR-126 expression correlates with risk and severity of psoriasis and its high level at baseline predicts worse response to Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in combination with acitretin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, S. MiR-126 correlates with increased disease severity and promotes keratinocytes proliferation and inflammation while suppresses cells’ apoptosis in psoriasis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzina, E.; Dosenko, V.; Drevytska, T.; Litus, O.; Bardova, K.; Vozianova, S. Relationship between mir-126 expression in children with psoriasis, disease progression and therapeutic response. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ling, A.; Pareek, S.; Huang, R.S. Oncogene or tumor suppressor? Long noncoding RNAs role in patient’s prognosis varies depending on disease type. Transl. Res. 2021, 230, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, W.-J.; Xu, G.-W.; Zhang, J.-F.; Tang, Z.-L. LncRNA MEG3 influences the proliferation and apoptosis of psoriasis epidermal cells by targeting miR-21/caspase-8. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nour, Z.; Elwan, Y.; Nassar, Y.; Fathy Elmasry, M.; Rashed, L.; Salama Ashour, S. Possible role of LncRNA MEG3-microRNA-21 and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress proteins in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Vulgaris. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 11, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedittis, G.; D’Antonio, A.; Latini, A.; Morgante, C.; Conigliaro, P.; Triggianese, P.; Bergamini, A.; Novelli, G.; Ciccacci, C.; Chimenti, M.S.; et al. Study of lncRNAs expression profile in the response to biological drugs in Psoriatic Arthritis: MEG3 could be a potential genomic biomarker of therapy efficacy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 134, 112239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-L.; Zhang, K.; Lv, S.-C.; Xu, G.-W.; Zhang, J.-F.; Jia, H.-Y. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit inflammation in TNF-α-treated keratinocytes and psoriatic mice. Cytokine 2021, 148, 155657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedi, K.; Göblös, A.; Bacsa, S.; Antal, M.; Németh, I.B.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L.; Dobozy, A.; Széll, M. Expression and Functional Studies on the Noncoding RNA, PRINS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murzina, E.; Dosenko, V.; Drevytska, T. Expression of Long Non-Coding RNA PRINS and G1P3 in Children with Psoriasis. Педиатрия. Вoстoчная Еврoпа 2021, 9, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedi, K.; Sonkoly, E.; Nagy, N.; Németh, I.B.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L.; Dobozy, A.; Széll, M. The anti-apoptotic protein G1P3 is overexpressed in psoriasis and regulated by the non-coding RNA, PRINS. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danis, J.; Göblös, A.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L.; Széll, M. PRINS Non-Coding RNA Regulates Nucleic Acid-Induced Innate Immune Responses of Human Keratinocytes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.-M.; Palanisamy, K.; Sun, K.-T.; Day, Y.-J.; Shu, K.-H.; Wang, I.-K.; Shyu, W.-C.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.-L.; Li, C.-Y. RANTES mediates kidney ischemia reperfusion injury through a possible role of HIF-1α and LncRNA PRINS. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, E.; Ádám, É.; Sági, S.; Göblös, A.; Kemény, L.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Széll, M.; Danis, J. Psoriasis-Associated Inflammatory Conditions Induce IL-23 mRNA Expression in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Du, J.; Lu, X. The long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression profiles in keratinocytes from patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 9206–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lin, L.; Lu, X.; Du, J.; Xu, J. LncRNA AGXT2L1-2:2 facilitates keratinocytes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by interacting with estrogen-related receptor alpha in psoriasis. Mol. Cell. Probes 2022, 62, 101803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Ju, J.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, Q. Long Non-Coding RNA-GDA-1 Promotes Keratinocyte Proliferation and Psoriasis Inflammation by Regulating the STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway via Forkhead Box M1. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Chen, C.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Wen, H.; Sun, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. ILF2 Contributes to Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in a KLHDC7B-DT-Dependent Manner in Psoriasis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 890624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, V.M.; Kõks, S. Genome-Wide Differential Transcription of Long Noncoding RNAs in Psoriatic Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y. Integrated analysis of immune-related long noncoding RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers in psoriasis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J.; Sun, Q. Up-regulated lncRNA-MSX2P1 promotes the growth of IL-22-stimulated keratinocytes by inhibiting miR-6731-5p and activating S100A7. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 363, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y. Transcriptome wide analysis of long non-coding RNA-associated ceRNA regulatory circuits in psoriasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6925–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Gao, X.; Lin, L.; Zhang, M.; Luo, D.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, C.; et al. Identification of PRKCQ-AS1 as a Keratinocyte-Derived Exosomal lncRNA That Promotes Th17 Differentiation and IL-17 secretion in Psoriasis Through Bioinformatics, Machine Learning Algorithms, and Cell Experiments. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 6557–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Shao, Y.; Zheng, Y. LncRNA RP6-65G23.1 accelerates proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via p-ERK1/2/p-AKT signaling pathway on keratinocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 4580–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Luo, M.; Zhou, R. STAT3/SH3PXD2A-AS1/miR-125b/STAT3 positive feedback loop affects psoriasis pathogenesis via regulating human keratinocyte proliferation. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Huang, P.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C. Weighted gene coexpression network and experimental analyses identify lncRNA SPRR2C as a regulator of the IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cell phenotype through the miR-330/STAT1/S100A7 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Chen, C.; Sun, Q. Role of the long non-coding RNA, SPRR2C, based on an in vitro psoriatic keratinocyte cell model. Eur. J. Dermatology 2022, 32, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, R.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Ju, J.; Wen, H.; Sun, Q. LncRNA lnc-SPRR2G-2 contributes to keratinocyte hyperproliferation and inflammation in psoriasis by activating the STAT3 pathway and downregulating KHSRP. Mol. Cell. Probes 2024, 76, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Lei, L.; Jiang, L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, C.; Guo, H.; Dong, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. LncRNA UCA1 promotes keratinocyte-driven inflammation via suppressing METTL14 and activating the HIF-1α/NF-κB axis in psoriasis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.E.; Houh, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, D.; Park, H.J. Downregulation of erythroid differentiation regulator 1 (Erdr1) plays a critical role in psoriasis pathogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Houh, Y.; Park, H.; Cho, D. Therapeutic Effects of Erythroid Differentiation Regulator 1 on Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Q. The lncRNA H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 Axis Contributes to the Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis via the AKT/mTOR Pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9991175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Kong, Y.; Chen, F.; Liang, J.; Yu, H.; Yao, Z. H19 lncRNA regulates keratinocyte differentiation by targeting miR-130b-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, C.; Graf, J.; Faderl, S.; Schedlbauer, J.; Strieder, N.; Förstl, B.; Spang, R.; Bruckmann, A.; Merkl, R.; Hombach, S.; et al. The long non-coding RNA LINC00941 and SPRR5 are novel regulators of human epidermal homeostasis. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e46612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fang, Y.; Tao, M.; Ma, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, C.; Yang, J.; Yang, X. LOC285194 inhibits proliferation of human keratinocytes through regulating miR-616/GATA3 pathway. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 53, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cao, Y.; Ma, L.; Tao, M.; Yang, X. Keratinocyte exosomal LOC285194 ameliorates psoriasis by inhibiting the differentiation of CD4+T cells to Th17 cells through regulating miR-211-5p/SIRT1 axis. IUBMB Life 2025, 77, e2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Niu, M.; Fan, X.; Chen, F.; Cao, H.; Liu, Q.; Gan, S.; Yue, P.; Gao, J. LncRNA MIR181A2HG inhibits keratinocytes proliferation through miR-223-3p/SOX6 axis. Aging 2024, 16, 9846–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Li, M.; Niu, M.; Chen, F.; Mo, Z.; Yue, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Liang, B.; Gan, S.; et al. LncRNA MIR181A2HG negatively regulates human keratinocytes proliferation by binding SRSF1. Cytotechnology 2024, 76, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Sergio, S.; Cappello, A.; Farkas, T.; Bernassola, F.; Scarponi, C.; Albanesi, C.; Melino, G.; Candi, E. Involvement of transcribed lncRNA uc.291 in hyperproliferative skin disorders. Biol. Direct 2023, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panatta, E.; Lena, A.M.; Mancini, M.; Smirnov, A.; Marini, A.; Delli Ponti, R.; Botta-Orfila, T.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Mauriello, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Long non-coding RNA uc.291 controls epithelial differentiation by interfering with the ACTL6A/BAF complex. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e46734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazıcı, S.; Guner, R.Y.; Akyol, M.; Tuzemen Bayyurt, E.B.; Arslan, S. Research on Hotair and 7SL-RNA Gene Expression Levels in Psoriasis Vulgaris. Indian J. Dermatol. 2021, 66, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lønnberg, A.S.; Skov, L.; Skytthe, A.; Kyvik, K.O.; Pedersen, O.B.; Thomsen, S.F. Heritability of psoriasis in a large twin sample. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dand, N.; Duckworth, M.; Baudry, D.; Russell, A.; Curtis, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Evans, I.; Mason, K.J.; Alsharqi, A.; Becher, G.; et al. HLA-C*06:02 genotype is a predictive biomarker of biologic treatment response in psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Okada, Y. The current landscape of psoriasis genetics in 2020. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 99, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minotti, L.; Agnoletto, C.; Baldassari, F.; Corrà, F.; Volinia, S. SNPs and Somatic Mutation on Long Non-Coding RNA: New Frontier in the Cancer Studies? High-Throughput 2018, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshan, A.; Zarrinpour, N.; Moradi, A.; Ahadi, M.; Omrani, M.D.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Taheri, M. A single nucleotide polymorphism within HOX Transcript Antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is associated with risk of psoriasis. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2020, 47, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Hao, S.; Xue, T.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Association of HOTAIR Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Psoriasis in a Chinese Han Population. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5522075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Gholipour, M.; Abak, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Kholghi Oskooei, V.; Taheri, M.; Rakhshan, A. Association analysis of MALAT1 polymorphisms and risk of psoriasis among Iranian patients. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2022, 49, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wu, S.; Gao, R.; Chen, J.; Peng, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhu, L.; Du, Y.; Sun, W.; Ma, X.; et al. Identification of a Long Noncoding RNA TRAF3IP2-AS1 as Key Regulator of IL-17 Signaling through the SRSF10–IRF1–Act1 Axis in Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębniak, T.; Soczawa, E.; Boer, M.; Różewicka-Czabańska, M.; Wiśniewska, J.; Serrano-Fernandez, P.; Mirecka, A.; Paszkowska-Szczur, K.; Lubinski, J.; Krysztoforska, L.; et al. Common variants of ZNF750, RPTOR and TRAF3IP2 genes and psoriasis risk. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kane, S.; Chen, H.; Leon, A.; Levin, E.; Nguyen, T.; Debbaneh, M.; Millsop, J.W.; Gupta, R.; Huynh, M.; et al. The Role of 39 Psoriasis Risk Variants on Age of Psoriasis Onset. ISRN Dermatol. 2013, 2013, 203941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Xing, X.; Stuart, P.E.; Chen, C.S.; Aphale, A.; Nair, R.P.; Voorhees, J.J.; Elder, J.T.; Johnston, A.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Heterogeneity of Inflammatory and Cytokine Networks in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinghaus, E.; Ellinghaus, D.; Stuart, P.E.; Nair, R.P.; Debrus, S.; Raelson, J.V.; Belouchi, M.; Fournier, H.; Reinhard, C.; Ding, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a psoriasis susceptibility locus at TRAF3IP2. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Zhou, K.; Yu, P.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, L.; Tong, N.; Li, Y. ANRIL polymorphisms in psoriasis vulgaris patients in northern China. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2022, 32, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshan, A.; Zarrinpour, N.; Moradi, A.; Ahadi, M.; Omrani, M.D.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Taheri, M. Genetic variants within ANRIL (antisense non coding RNA in the INK4 locus) are associated with risk of psoriasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liadaki, K.; Zafiriou, E.; Giannoulis, T.; Alexouda, S.; Chaidaki, K.; Gidarokosta, P.; Roussaki-Schulze, A.-V.; Tsiogkas, S.G.; Daponte, A.; Mamuris, Z.; et al. PDE4 Gene Family Variants Are Associated with Response to Apremilast Treatment in Psoriasis. Genes 2024, 15, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Low, H.Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Ellinghaus, E.; Han, J.; Estivill, X.; Sun, L.; Zuo, X.; Shen, C.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel associations and ethnic heterogeneity of psoriasis susceptibility. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Liang, X.-H.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, R.M. Antisense technology: A review. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Mir, F.; Yokota, T. Enhancing the Effectiveness of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Using Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugation, Chemical Modification, and Carrier-Based Delivery Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautrin, A.; Manchon, L.; Garcel, A.; Campos, N.; Lapasset, L.; Laaref, A.M.; Bruno, R.; Gislard, M.; Dubois, E.; Scherrer, D.; et al. Both anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties of novel drug candidate ABX464 are mediated by modulation of RNA splicing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Sands, B.E.; Tilg, H.; Tulassay, Z.; Kempinski, R.; Danese, S.; Bunganič, I.; Nitcheu, J.; Santo, J.; Scherrer, D.; et al. ABX464 (obefazimod) for moderate-to-severe, active ulcerative colitis: A phase 2b, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled induction trial and 48 week, open-label extension. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolit, C.; Campos, N.; Vautrin, A.; Begon-Pescia, C.; Lapasset, L.; Scherrer, D.; Gineste, P.; Ehrlich, H.; Garcel, A.; Santo, J.; et al. ABX464 (Obefazimod) Upregulates miR-124 to Reduce Proinflammatory Markers in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danis, J.; Széll, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications. Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050069
Danis J, Széll M. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications. Non-Coding RNA. 2025; 11(5):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050069
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanis, Judit, and Márta Széll. 2025. "Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications" Non-Coding RNA 11, no. 5: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050069
APA StyleDanis, J., & Széll, M. (2025). Long Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review of Expression Profiles, Mechanistic Insights, Genetic Associations, and Their Clinical Implications. Non-Coding RNA, 11(5), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050069






