XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
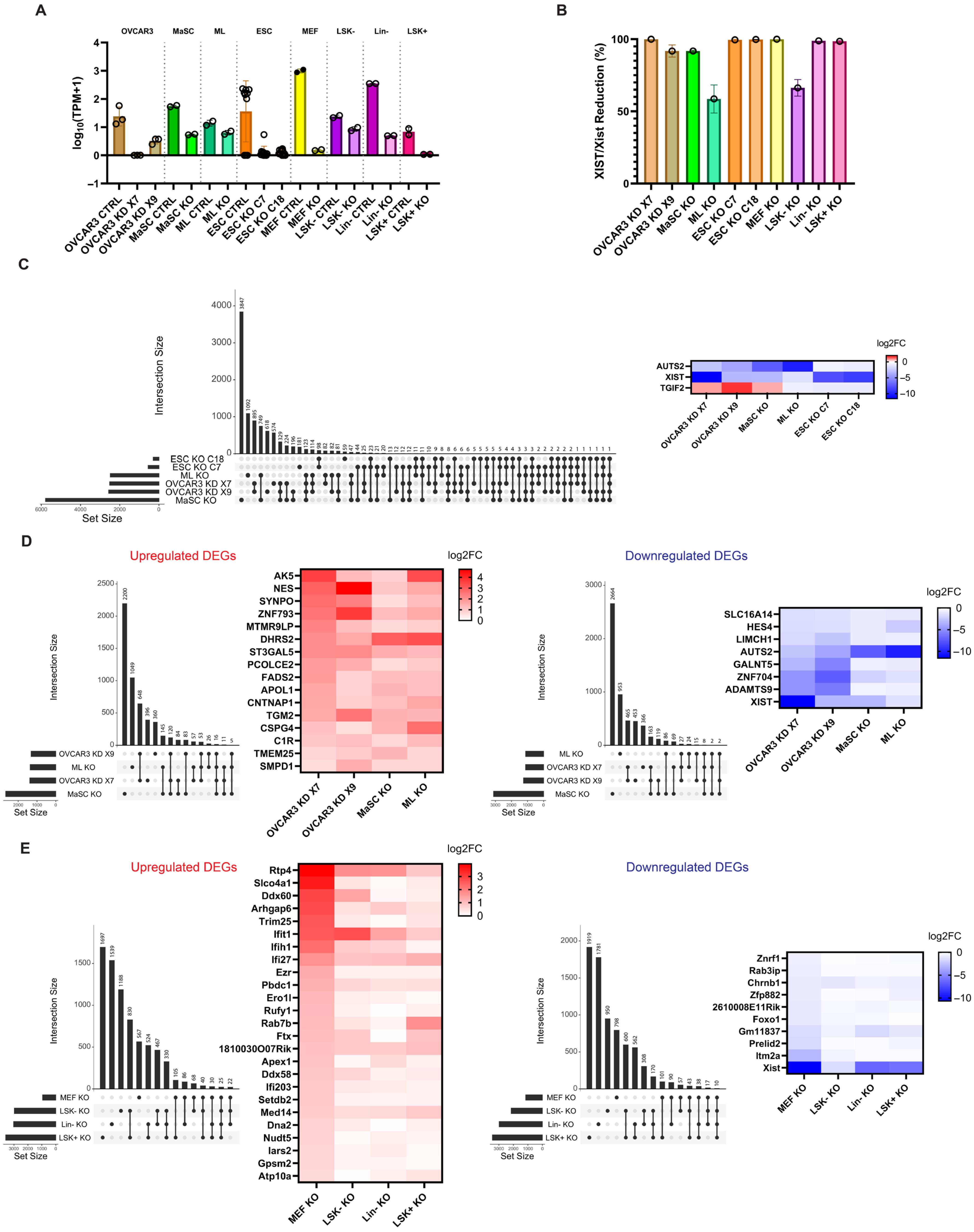
2.1. XIST/Xist Loss Induces Transcriptional Changes in the Human and Mouse Cells
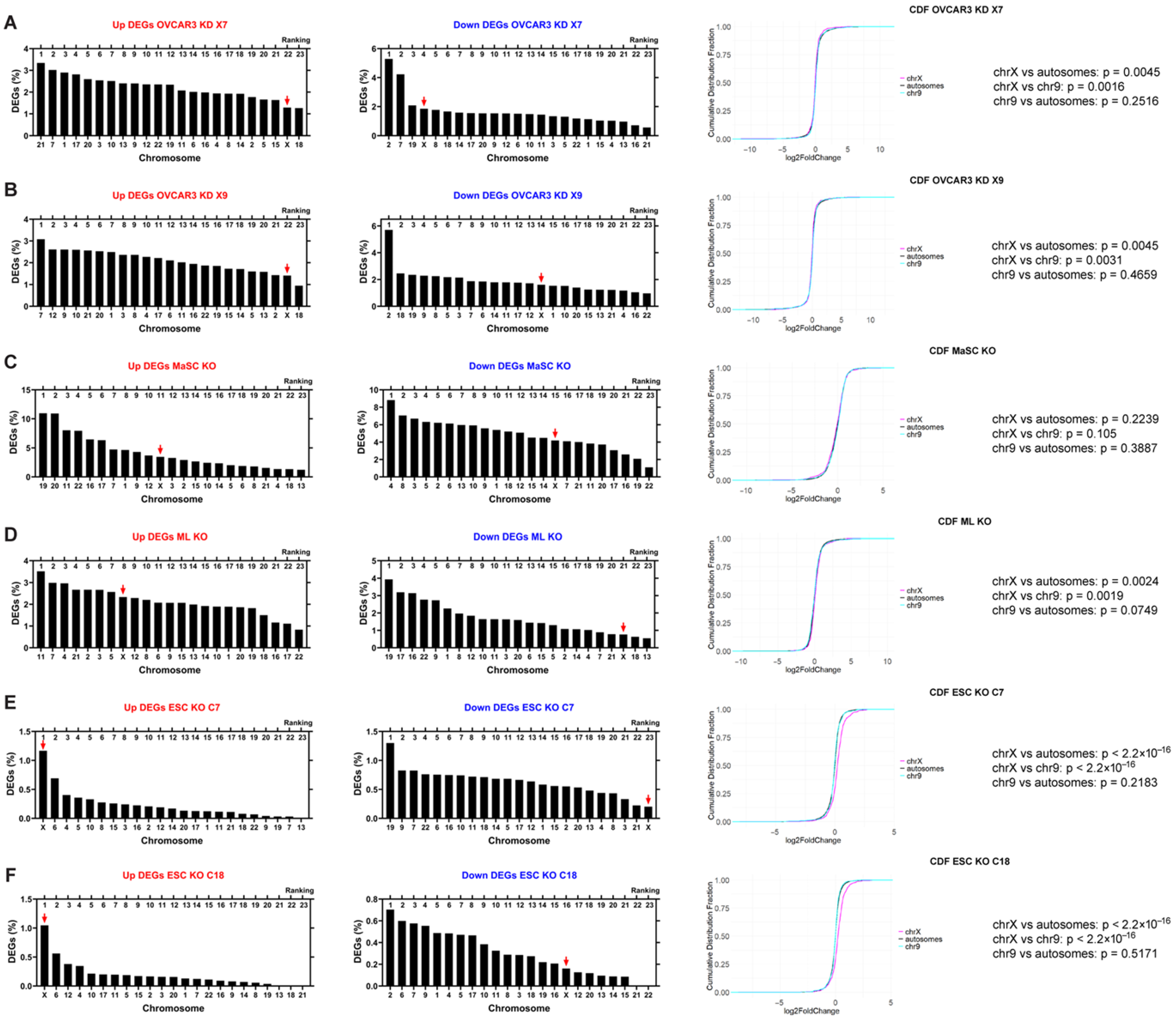
2.2. The Loss of XIST in Human Cells Causes Variable Transcriptional Changes to the X Chromosome
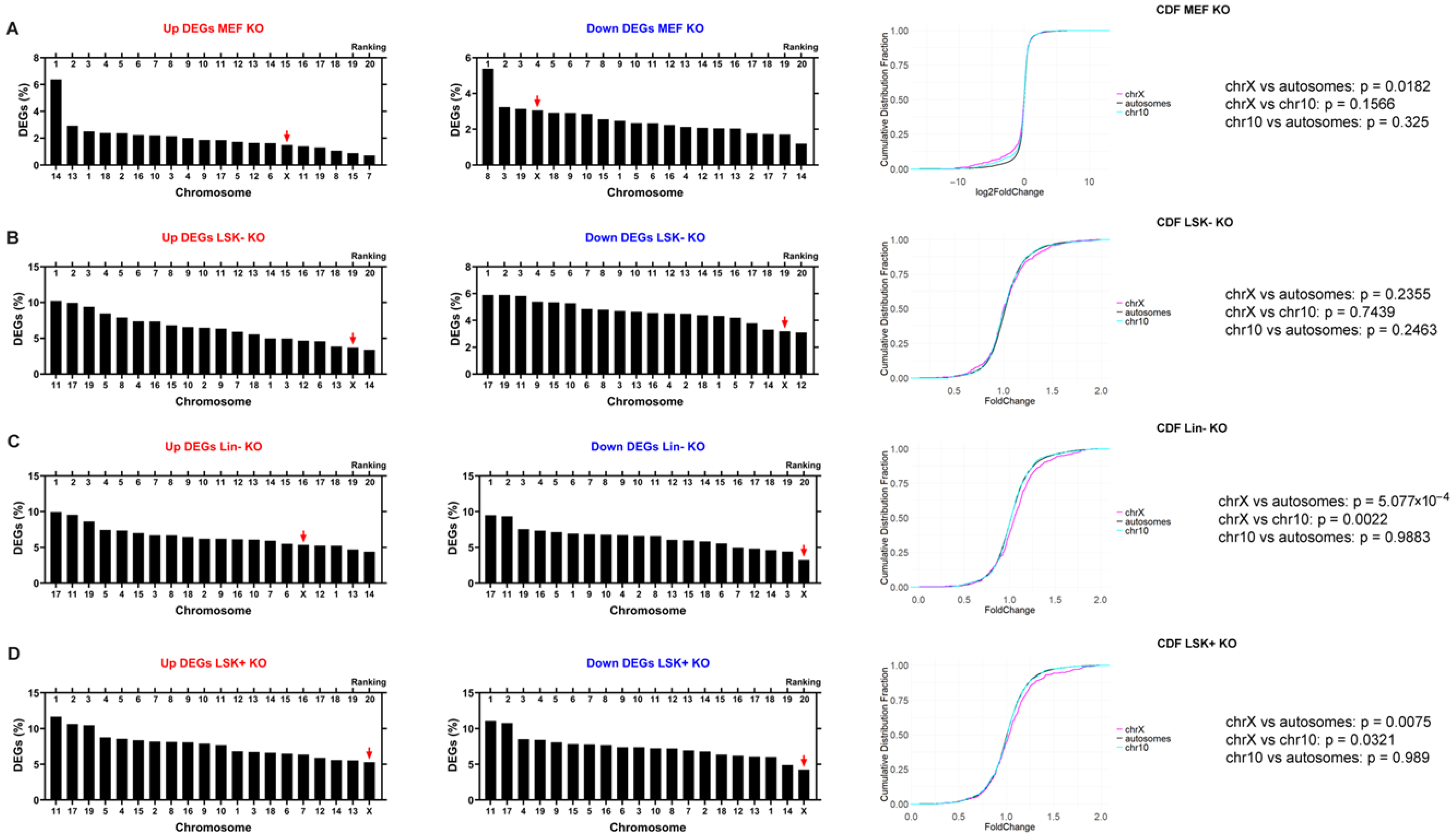
2.3. The Loss of Xist in Mouse Cells Causes Variable Transcriptional Changes to the X Chromosome
2.4. XIST Loss Causes Transcriptional Changes of XCI Inactive Genes and XCI Escape Genes in Ovarian Cancer Cells
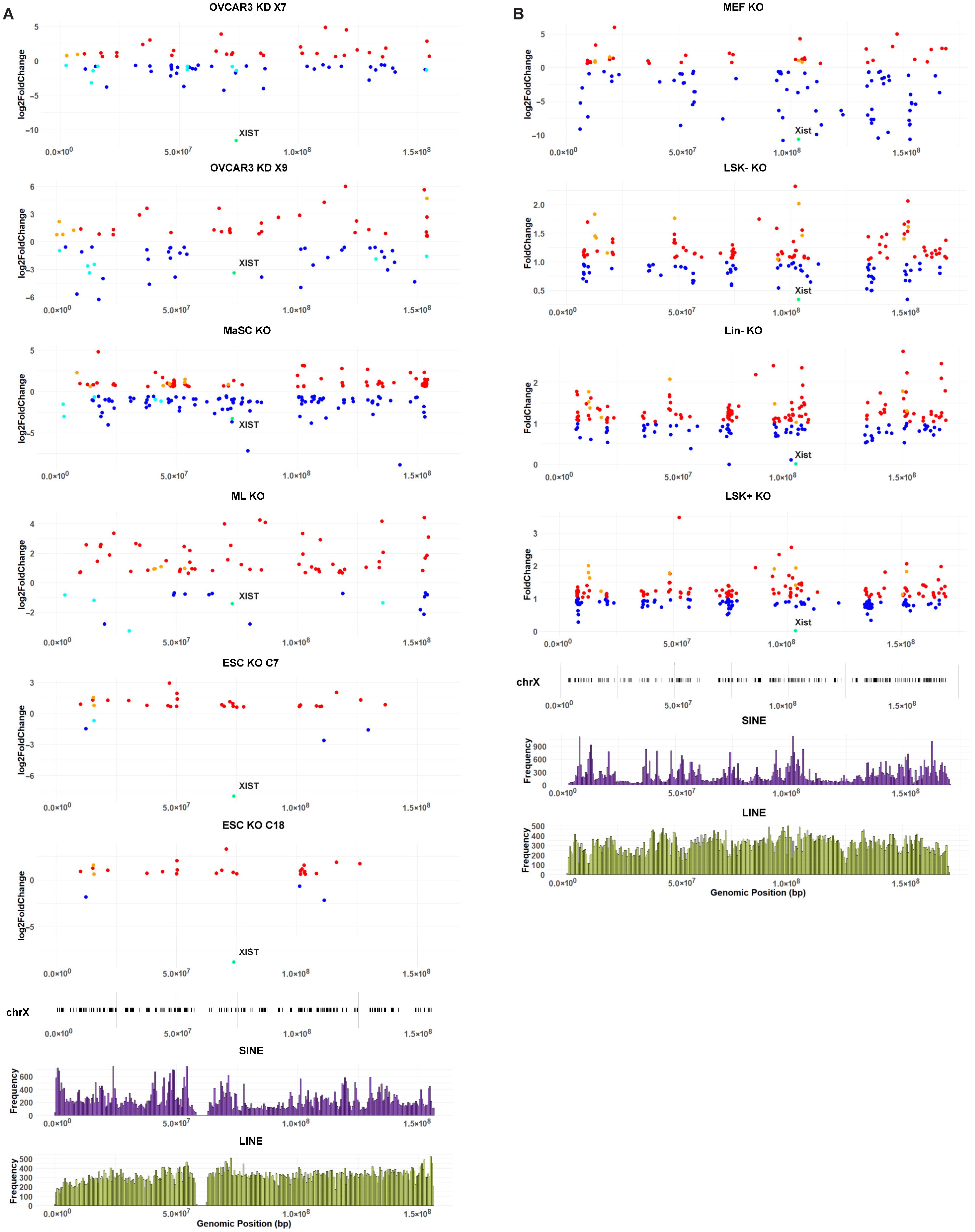
2.5. XIST/Xist Loss Leads to Transcriptional Changes in Genes Clustered Along the X Chromosome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA-Seq Datasets of Human and Mouse Cells with XIST/Xist Loss
4.2. Transcriptional Effect Analysis and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyon, M.F. Gene Action in the X-Chromosome of the Mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature 1961, 190, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payer, B.; Lee, J.T. X Chromosome Dosage Compensation: How Mammals Keep the Balance. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 733–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augui, S.; Nora, E.P.; Heard, E. Regulation of X-Chromosome Inactivation by the X-Inactivation Centre. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahakyan, A.; Yang, Y.; Plath, K. The Role of Xist in X-Chromosome Dosage Compensation. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migeon, B.R. X-Linked Diseases: Susceptible Females. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwrajka, N.; Anguera, M.C. The X in seX-Biased Immunity and Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ming, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; Ma, Q. Long Noncoding RNA XIST: Mechanisms for X Chromosome Inactivation, Roles in Sex-Biased Diseases, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, C.-H.; Faz-Lopez, B.; Guéry, J.-C. Influence of X Chromosome in Sex-Biased Autoimmune Diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 137, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huret, C.; Ferrayé, L.; David, A.; Mohamed, M.; Valentin, N.; Charlotte, F.; Savignac, M.; Goodhardt, M.; Guéry, J.-C.; Rougeulle, C.; et al. Altered X-Chromosome Inactivation Predisposes to Autoimmunity. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, E.; Kirby, J.E.; Brown, D.E.; Mercier, F.E.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Scadden, D.T.; Lee, J.T. Xist RNA Is a Potent Suppressor of Hematologic Cancer in Mice. Cell 2013, 152, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-K.; Yen, Y. The Ambivalent Role of lncRNA Xist in Carcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qi, M.; Fei, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. Long Non-Coding RNA XIST: A Novel Oncogene in Multiple Cancers. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richart, L.; Picod-Chedotel, M.-L.; Wassef, M.; Macario, M.; Aflaki, S.; Salvador, M.A.; Héry, T.; Dauphin, A.; Wicinski, J.; Chevrier, V.; et al. XIST Loss Impairs Mammary Stem Cell Differentiation and Increases Tumorigenicity through Mediator Hyperactivation. Cell 2022, 185, 2164–2183.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naciri, I.; Liang, M.; Yang, Y.; Karner, H.; Lin, B.; De Lourdes Andrade Ludena, M.; Hanse, E.A.; Lebron, A.; Razorenova, O.V.; Nicholas, D.; et al. Loss of XIST lncRNA Unlocks Stemness and Cellular Plasticity in Ovarian Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2418096121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plath, K.; Talbot, D.; Hamer, K.M.; Otte, A.P.; Yang, T.P.; Jaenisch, R.; Panning, B. Developmentally Regulated Alterations in Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 Proteins on the Inactive X Chromosome. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, J.; Le Baccon, P.; Wutz, A.; Heard, E. A Novel Role for Xist RNA in the Formation of a Repressive Nuclear Compartment into Which Genes Are Recruited When Silenced. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colognori, D.; Sunwoo, H.; Kriz, A.J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lee, J.T. Xist Deletional Analysis Reveals an Interdependency Between Xist RNA and Polycomb Complexes for Spreading along the Inactive X. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 101–117.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Pandya-Jones, A.; McDonel, P.; Shishkin, A.; Sirokman, K.; Surka, C.; Kadri, S.; Xing, J.; Goren, A.; Lander, E.S.; et al. The Xist lncRNA Exploits Three-Dimensional Genome Architecture to Spread Across the X Chromosome. Science 2013, 341, 1237973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.D.; Pinter, S.F.; Fang, R.; Sarma, K.; Rutenberg-Schoenberg, M.; Bowman, S.K.; Kesner, B.A.; Maier, V.K.; Kingston, R.E.; Lee, J.T. High-Resolution Xist Binding Maps Reveal Two-Step Spreading During X-Chromosome Inactivation. Nature 2013, 504, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, Y.; Chong, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Jacobson, E.C.; Luong, C.; Tan, S.Y.X.; Jachowicz, J.W.; Strehle, M.; Maestrini, D.; Banerjee, A.K.; et al. Xist Nucleates Local Protein Gradients to Propagate Silencing Across the X Chromosome. Cell 2021, 184, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgetti, L.; Lajoie, B.R.; Carter, A.C.; Attia, M.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, C.J.; Kaplan, N.; Chang, H.Y.; Heard, E.; et al. Structural Organization of the Inactive X Chromosome in the Mouse. Nature 2016, 535, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Jégu, T.; Chu, H.-P.; Oh, H.J.; Lee, J.T. SMCHD1 Merges Chromosome Compartments and Assists Formation of Super-Structures on the Inactive X. Cell 2018, 174, 406–421.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappala, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Kriz, A.; Michalk, H.; Tan, K.; Lee, J.T.; Sanbonmatsu, K.Y. Four-Dimensional Chromosome Reconstruction Elucidates the Spatiotemporal Reorganization of the Mammalian X Chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107092118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plath, K.; Fang, J.; Mlynarczyk-Evans, S.K.; Cao, R.; Worringer, K.A.; Wang, H.; De La Cruz, C.C.; Otte, A.P.; Panning, B.; Zhang, Y. Role of Histone H3 Lysine 27 Methylation in X Inactivation. Science 2003, 300, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.; Mak, W.; Zvetkova, I.; Appanah, R.; Nesterova, T.B.; Webster, Z.; Peters, A.H.F.M.; Jenuwein, T.; Otte, A.P.; Brockdorff, N. Establishment of Histone H3 Methylation on the Inactive X Chromosome Requires Transient Recruitment of Eed-Enx1 Polycomb Group Complexes. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, B.P.; Willard, H.F. Multiple Spatially Distinct Types of Facultative Heterochromatin on the Human Inactive X Chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17450–17455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wutz, A. Gene Silencing in X-Chromosome Inactivation: Advances in Understanding Facultative Heterochromatin Formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrelo, R.; Wutz, A. ConteXt of Change—X Inactivation and Disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borensztein, M.; Syx, L.; Ancelin, K.; Diabangouaya, P.; Picard, C.; Liu, T.; Liang, J.-B.; Vassilev, I.; Galupa, R.; Servant, N.; et al. Xist-Dependent Imprinted X Inactivation and the Early Developmental Consequences of Its Failure. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianse, R.L.; Smith, K.; Gatbonton-Schwager, T.; Sripathy, S.P.; Lao, U.; Foss, E.J.; Boers, R.G.; Boers, J.B.; Gribnau, J.; Bedalov, A. Perturbed Maintenance of Transcriptional Repression on the Inactive X-Chromosome in the Mouse Brain after Xist Deletion. Epigenetics Chromatin 2018, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yildirim, E.; Kirby, J.E.; Press, W.; Lee, J.T. Widespread Organ Tolerance to Xist Loss and X Reactivation except under Chronic Stress in the Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, E.C.; Pandya-Jones, A.; Plath, K. A Lifelong Duty: How Xist Maintains the Inactive X Chromosome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2022, 75, 101927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Ou, J.; Yildirim, E. Xist Exerts Gene-Specific Silencing during XCI Maintenance and Impacts Lineage-Specific Cell Differentiation and Proliferation During Hematopoiesis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Ahern, D.T.; Kondaveeti, Y.; Qiu, C.W.; Pinter, S.F. Contiguous Erosion of the Inactive X in Human Pluripotency Concludes with Global DNA Hypomethylation. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenes, A.J.; Yoshikawa, H.; Bensaddek, D.; Mirauta, B.; Seaton, D.; Hukelmann, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Stegle, O.; Lamond, A.I. Erosion of Human X Chromosome Inactivation Causes Major Remodeling of the iPSC Proteome. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, I.; Chitiashvili, T.; Tan, S.Y.X.; Cano, C.T.; Sahakyan, A.; Markaki, Y.; Chronis, C.; Collier, A.J.; Deng, W.; Liang, G.; et al. XIST Directly Regulates X-Linked and Autosomal Genes in Naive Human Pluripotent Cells. Cell 2024, 187, 110–129.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Roman, A.K.; Godfrey, A.K.; Skaletsky, H.; Bellott, D.W.; Groff, A.F.; Harris, H.L.; Blanton, L.V.; Hughes, J.F.; Brown, L.; Phou, S.; et al. The Human Inactive X Chromosome Modulates Expression of the Active X Chromosome. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukiainen, T.; Villani, A.-C.; Yen, A.; Rivas, M.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Satija, R.; Aguirre, M.; Gauthier, L.; Fleharty, M.; Kirby, A.; et al. Landscape of X Chromosome Inactivation across Human Tissues. Nature 2017, 550, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Bonora, G.; Berletch, J.B.; Deng, X.; Noble, W.S.; Disteche, C.M. X-Chromosome Inactivation and Escape from X Inactivation in Mouse. In X-Chromosome Inactivation; Sado, T., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1861, pp. 205–219. ISBN 978-1-4939-8765-8. [Google Scholar]
- Topa, H.; Benoit-Pilven, C.; Tukiainen, T.; Pietiläinen, O. X-Chromosome Inactivation in Human iPSCs Provides Insight into X-Regulated Gene Expression in Autosomes. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.C.; Caldas, P.; Jeremias, J.; Arez, M.; Cazaux Mateus, F.; Barbosa, P.; Sousa-Luís, R.; Água, F.; Oxley, D.; Mupo, A.; et al. Gene Reactivation upon Erosion of X Chromosome Inactivation in Female hiPSCs Is Predictable yet Variable and Persists through Differentiation. Stem Cell Rep. 2025, 20, 102472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial Sequencing and Analysis of the Human Genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyanagi, K. Epigenetic Regulation of Transcription and Possible Functions of Mammalian Short Interspersed Elements, SINEs. Genes Genet. Syst. 2013, 88, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallot, C.; Ouimette, J.; Rougeulle, C. Establishment of X Chromosome Inactivation and Epigenomic Features of the Inactive X Depend on Cellular Contexts. BioEssays 2016, 38, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintacuda, G.; Cerase, A. X Inactivation Lessons from Differentiating Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brockdorff, N.; Bowness, J.S.; Wei, G. Progress Toward Understanding Chromosome Silencing by Xist RNA. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaligné, R.; Popova, T.; Mendoza-Parra, M.-A.; Saleem, M.-A.M.; Gentien, D.; Ban, K.; Piolot, T.; Leroy, O.; Mariani, O.; Gronemeyer, H.; et al. The Inactive X Chromosome Is Epigenetically Unstable and Transcriptionally Labile in Breast Cancer. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kirby, J.E.; Sunwoo, H.; Lee, J.T. Female Mice Lacking Xist RNA Show Partial Dosage Compensation and Survive to Term. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jeon, Y.; Kesner, B.; Lee, J.T. Xist RNA Binds Select Autosomal Genes and Depends on Repeat B to Regulate Their Expression. eLife 2024, 13, RP101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, C.; Rougeulle, C.; Ouimette, J.-F. Unleashing XIST from X-Chromosome Inactivation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2025, 92, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garieri, M.; Stamoulis, G.; Blanc, X.; Falconnet, E.; Ribaux, P.; Borel, C.; Santoni, F.; Antonarakis, S.E. Extensive Cellular Heterogeneity of X Inactivation Revealed by Single-Cell Allele-Specific Expression in Human Fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13015–13020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.A.; Carrel, L.; Chakravarti, A.; Eichler, E.E. Molecular Evidence for a Relationship Between LINE-1 Elements and X Chromosome Inactivation: The Lyon Repeat Hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6634–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ciaudo, C.; Fazzari, M.J.; Mise, N.; Servant, N.; Glass, J.L.; Attreed, M.; Avner, P.; Wutz, A.; Barillot, E.; et al. LINE-1 Activity in Facultative Heterochromatin Formation during X Chromosome Inactivation. Cell 2010, 141, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loda, A.; Brandsma, J.H.; Vassilev, I.; Servant, N.; Loos, F.; Amirnasr, A.; Splinter, E.; Barillot, E.; Poot, R.A.; Heard, E.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Features Direct Differential Efficiency of Xist-Mediated Silencing at X-Chromosomal and Autosomal Locations. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, S.B.; Posynick, B.J.; Brown, C.J. Out of the Silence: Insights into How Genes Escape X-Chromosome Inactivation. Epigenomes 2023, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrel, L.; Willard, H.F. X-Inactivation Profile Reveals Extensive Variability in X-Linked Gene Expression in Females. Nature 2005, 434, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, A.M.; Ge, B.; Light, N.; Adoue, V.; Pastinen, T.; Brown, C.J. Analysis of Expressed SNPs Identifies Variable Extents of Expression from the Human Inactive X Chromosome. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Naciri, I.; Wu, J.; Sun, S. XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States. Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050067
Chen D, Naciri I, Wu J, Sun S. XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States. Non-Coding RNA. 2025; 11(5):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050067
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dongning, Ikrame Naciri, Jie Wu, and Sha Sun. 2025. "XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States" Non-Coding RNA 11, no. 5: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050067
APA StyleChen, D., Naciri, I., Wu, J., & Sun, S. (2025). XIST Loss Induces Variable Transcriptional Responses Dependent on Cell States. Non-Coding RNA, 11(5), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11050067





