MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines
Abstract
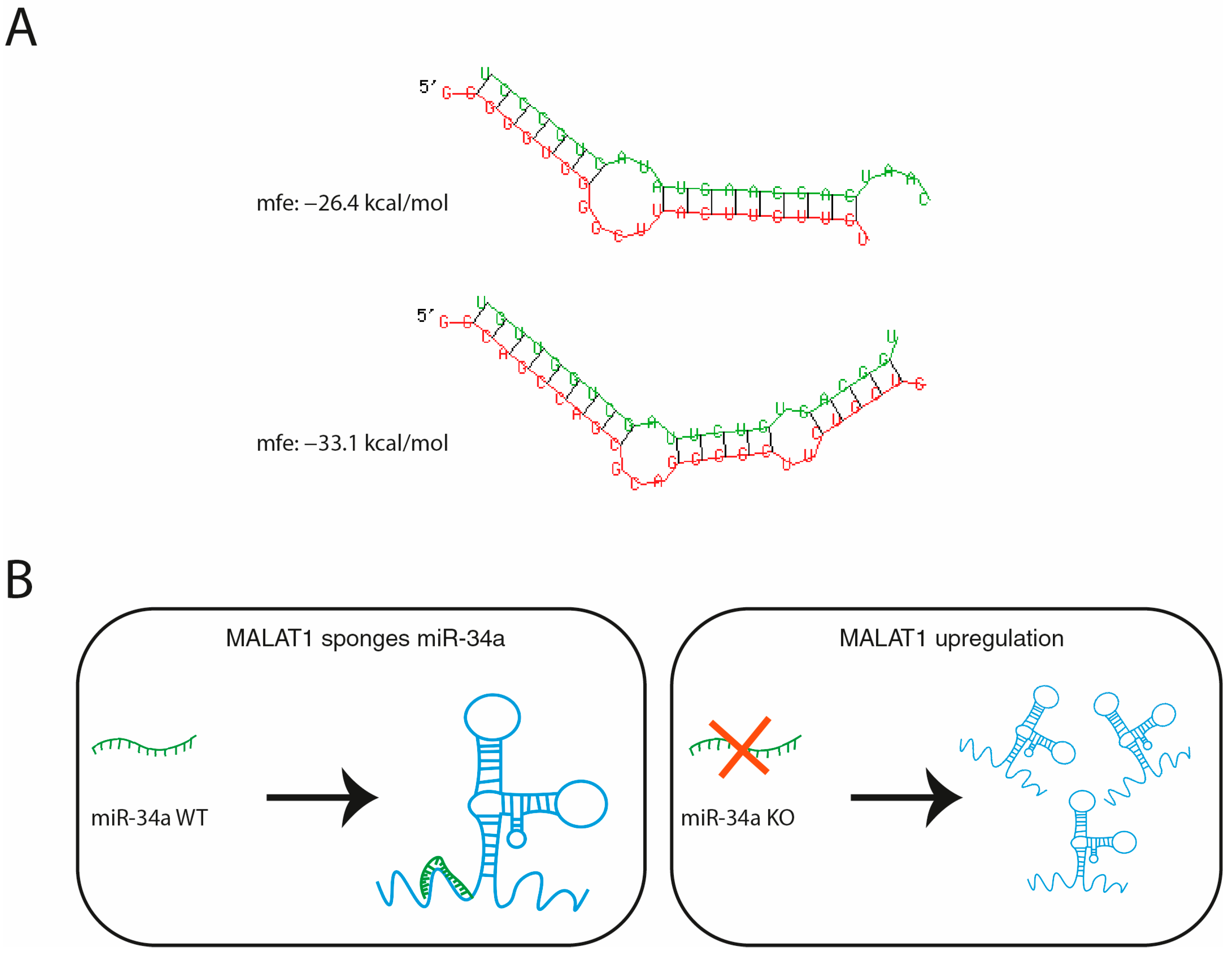
1. Introduction
2. Results
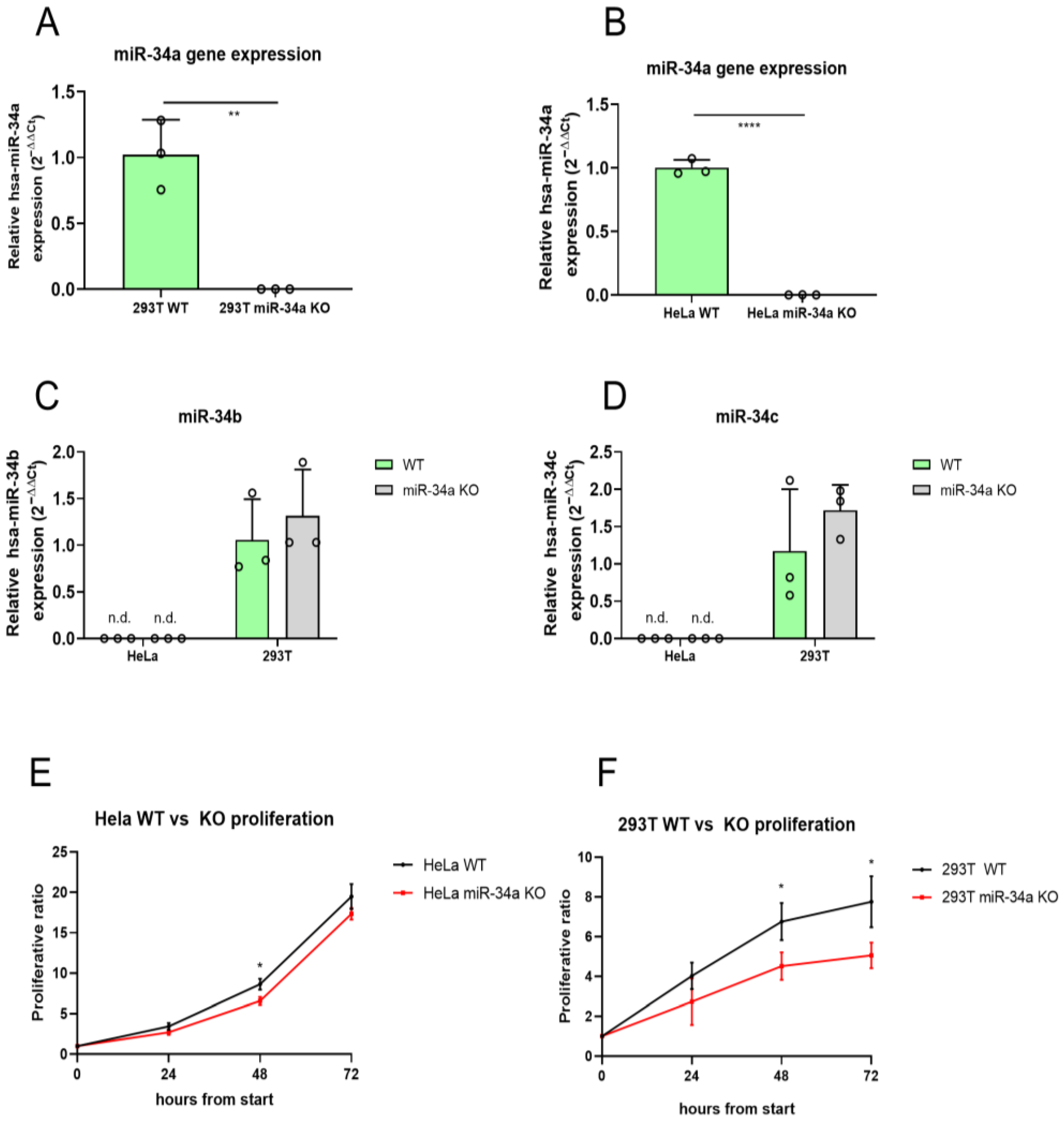
2.1. Generation and Characterization of miR-34a KO HeLa and 293T Cell Lines
2.2. Loss of miR-34a Alters Cellular Proliferation in 293T Cells
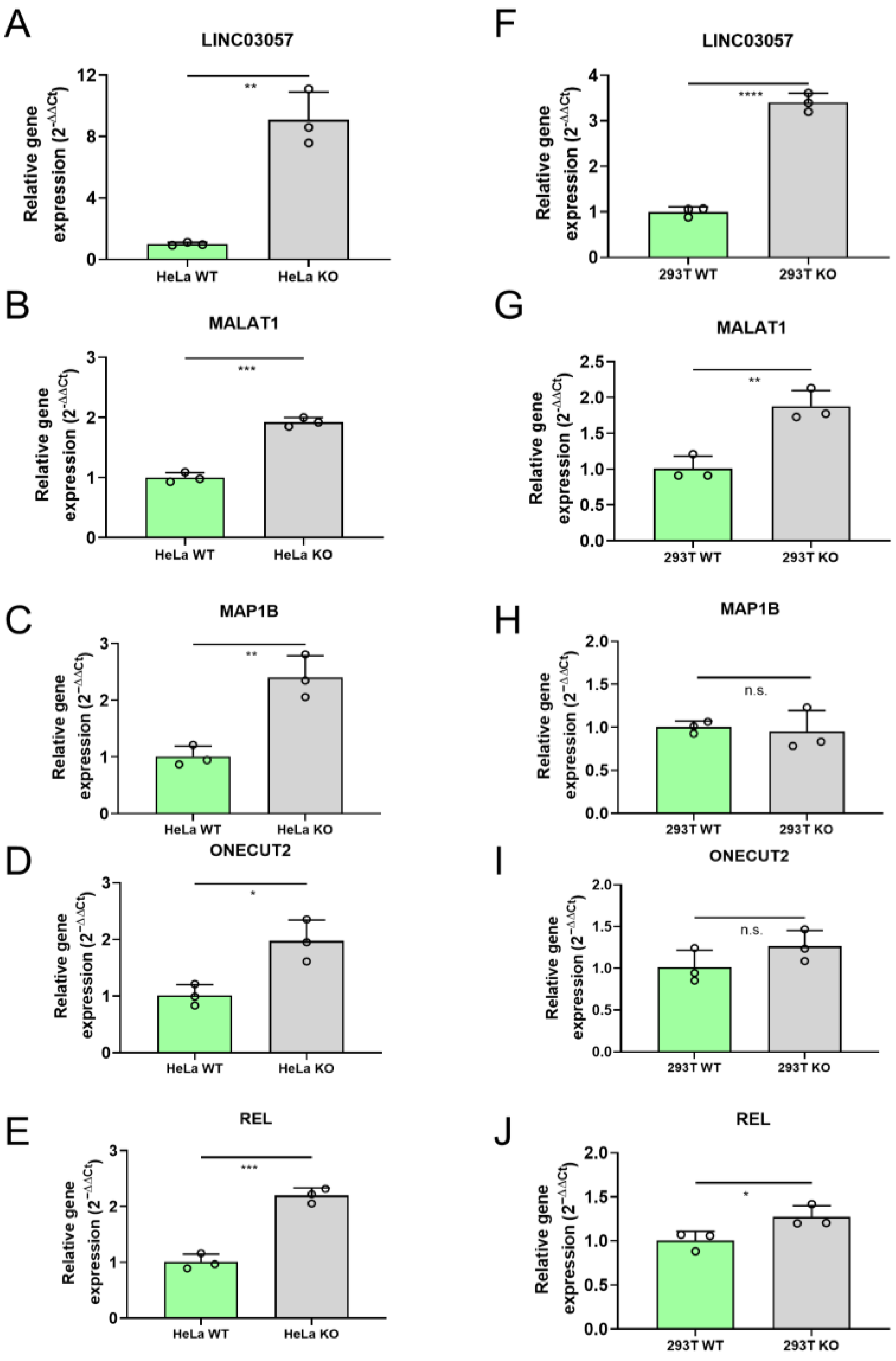
2.3. RNA-Seq Analysis Identifies Genes Deregulated in HeLa miR-34a KO Cells Compared to WT
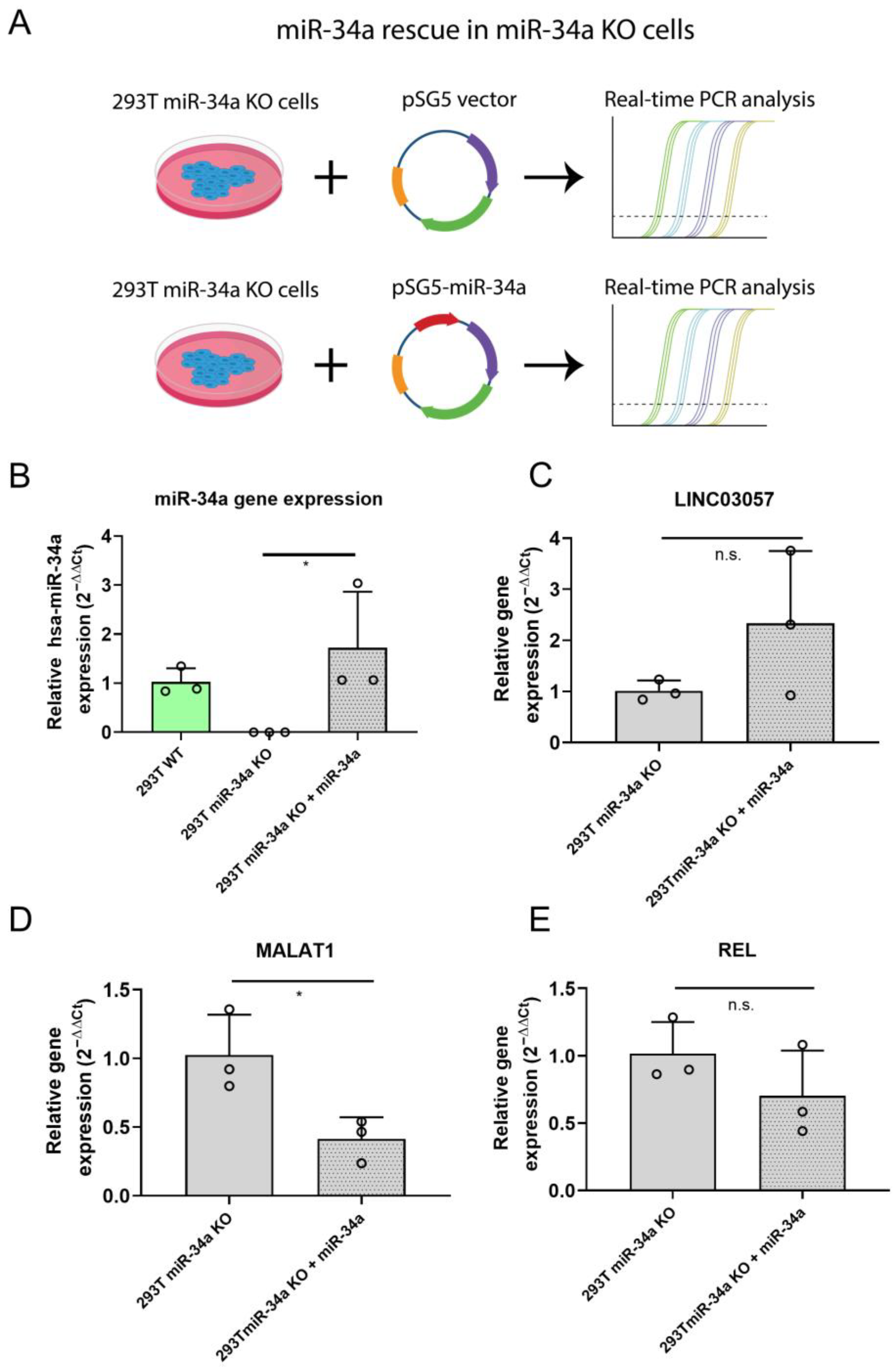
2.4. Rescue of miR-34a Expression in 293T miR34-a KO Inhibits MALAT1 Expression
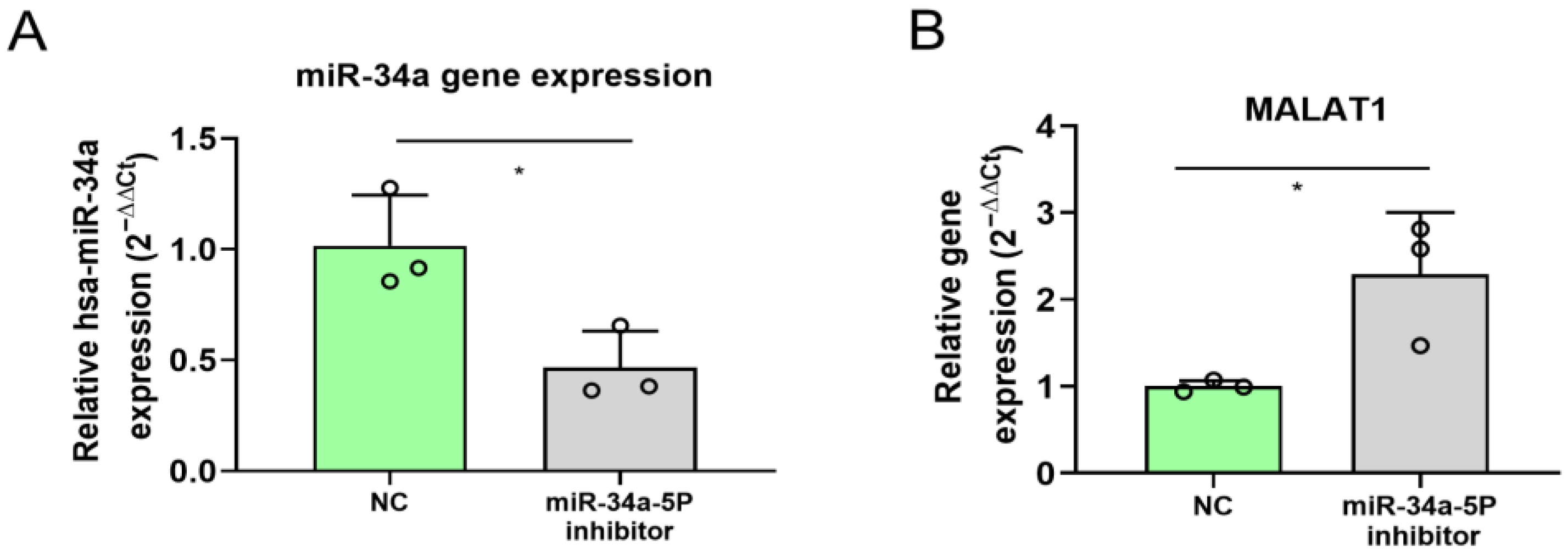
2.5. miR-34a Inhibition in A375 Melanoma Cells Affects MALAT1 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. miR-34a Knockout Cell Line Production
4.3. miR-34a Knock-Out Validation and miR-34b and miR-34c Expression Analysis
4.4. Cell Proliferation Analysis
4.5. RNA Extraction for Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) of HeLa WT and miR-34a KO Cells
4.6. Library Preparation and RNA-Sq of HeLa WT and miR-34a KO Cells
4.7. Data Processing for RNA-Seq of HeLa WT and miR-34a KO Cells
4.8. miR-34a Phenotypic Rescue in 293T KO Cell Line
4.9. miR-34a Inhibition in A375 Cell Line
4.10. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
4.11. Bioinformatic Prediction of miR-34a/MALAT1 Interaction
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3’-UTR | 3’-Untranslated Region |
| Akt | AKT Serine/Threonine kinase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ATF2 | Activating Transcription Factor 2 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| Bcl-xL | B-cell lymphoma extra large |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit 8 |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase 6 |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| Chk1 | Checkpoint Kinase 1 |
| c-Myc | MYC proto-oncogene |
| CRISPR-Cas9 | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats Cas9 associated |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal transition |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FC | Fold Change |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| gRNA | Guide RNA |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KO | Knock–out |
| LINC03057 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 3057 |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MAP1B | Microtubule-Associated Protein 1B |
| Met | MET proto-oncogene |
| miRNA | Micro-RNA |
| mfe | Minimum Free Energy |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target Of Rapamycin Kinase |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| ONECUT2 | One Cut Homeobox 2 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| REL | REL proto-oncogene, NF-κB subunit |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| RPLP0 | Ribosomal Protein Lateral Stalk Subunit P0 |
| RQN | RNA quality number |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription–quantitative PCR |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| TNM | Tumor, Node, Metastasis |
| Wnt | Wnt Family Member 1 |
| WT | Wild-Type |
References
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Syeda, Z.; Langden, S.S.S.; Munkhzul, C.; Lee, M.; Song, S.J. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Kasinski, A.L.; Shen, H.; Slack, F.J.; Tang, D.G. MicroRNA-34a: Potent Tumor Suppressor, Cancer Stem Cell Inhibitor, and Potential Anticancer Therapeutic. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 640587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, A.G. miR-34—A microRNA Replacement Therapy Is Headed to the Clinic. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. The P53/miR-34 Axis in Development and Disease. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Desano, J.; Fan, D.; Xu, L. Restoration of Tumor Suppressor miR-34 Inhibits Human P53-Mutant Gastric Cancer Tumorspheres. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Fu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a Induces Cell Cycle Arrest. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Imani, S.; Wu, M.-Y.; Wu, R.-C. MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers 2023, 15, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H. MicroRNAs in the P53 Network: Micromanagement of Tumour Suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Cervellera, C.F.; Lanzillotti, C.; Touzé, A.; Gaboriaud, P.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Rotondo, J.C. MicroRNA Dysregulations in Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Hünten, S.; Kaller, M.; Menssen, A.; Götz, U.; Hermeking, H. miR-34 and SNAIL Form a Double-Negative Feedback Loop to Regulate Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4256–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raver-Shapira, N.; Marciano, E.; Meiri, E.; Spector, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Moskovits, N.; Bentwich, Z.; Oren, M. Transcriptional Activation of miR-34a Contributes to P53-Mediated Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-C.; Wentzel, E.A.; Kent, O.A.; Ramachandran, K.; Mullendore, M.; Lee, K.H.; Feldmann, G.; Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J.; et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by P53 Broadly Influences Gene Expression and Promotes Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasov, V.; Jung, P.; Verdoodt, B.; Lodygin, D.; Epanchintsev, A.; Menssen, A.; Meister, G.; Hermeking, H. Differential Regulation of microRNAs by P53 Revealed by Massively Parallel Sequencing: miR-34a Is a P53 Target That Induces Apoptosis and G1-Arrest. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommer, G.T.; Gerin, I.; Feng, Y.; Kaczorowski, A.J.; Kuick, R.; Love, R.E.; Zhai, Y.; Giordano, T.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Moore, B.B.; et al. P53-Mediated Activation of miRNA34 Candidate Tumor-Suppressor Genes. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labun, K.; Montague, T.G.; Krause, M.; Torres Cleuren, Y.N.; Tjeldnes, H.; Valen, E. CHOPCHOP v3: Expanding the CRISPR Web Toolbox beyond Genome Editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W171–W174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lan, Q.; Lai, W.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Fang, K.; Chu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Exosome-Derived Lnc-HOXB8-1:2 Induces Tumor-Associated Macrophage Infiltration to Promote Neuroendocrine Differentiated Colorectal Cancer Progression by Sponging Hsa-miR-6825-5p. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, R.A.; Khater, N.; El-Khouly, A.; Nafea, H.; Manie, T.; Habashy, D.; Gad, M.Z. Direct and Indirect Modulation of STAT3/CSE/H2S Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by Non-Coding RNAs: MALAT-1 lncRNA, miR-486-5p and miR-30a-5p. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2025, 265, 155729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Tan, A.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Q.; Guo, X.; Chen, J.; et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis in the HBV-Infected Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masrour, M.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Habibzadeh, A.; Fallahtafti, P. LncRNA MALAT1 as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Cui, L. LncRNA MALAT1 Silencing Represses CXCL12-Induced Proliferation, Invasion, and Homing Behavior in Multiple Myeloma by Inhibiting CXCR4. Hematology 2024, 29, 2422154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Hu, Q.; Gou, M.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cai, C.; Tian, T.; Tu, Z.; Du, Y.; et al. Expression of Microtubule-Associated Proteins in Relation to Prognosis and Efficacy of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 680402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, T.-M.; Chan, T.-C.; Huang, S.K.-H.; Yeh, B.-W.; Li, W.-M.; Huang, C.-N.; Li, C.-C.; Wu, W.-J.; Li, C.-F. Role of Microtubule-Associated Protein 1b in Urothelial Carcinoma: Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Kanda, T.; Hayashi, G.; Munenaga, R.; Yoshida, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyagawa, T.; Kurumada, Y.; Hasegawa, J.; Wada, T.; et al. A MAP1B–Cortactin–Tks5 Axis Regulates TNBC Invasion and Tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 223, e202303102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, D.; Jiang, H. Emerging Role of ONECUT2 in Tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.E.; Leslie, J.; Perkins, N.D. C-Rel and Its Many Roles in Cancer: An Old Story with New Twists. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Qiao, L.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, X. MALAT1 Regulates miR-34a Expression in Melanoma Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 Family: A Potential Tumor Suppressor and Therapeutic Candidate in Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Su, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lv, S.; Ji, X. The Role of microRNAs in Depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1129186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavamian, S.; Mellios, N.; Lalonde, J.; Fass, D.M.; Wang, J.; Sheridan, S.D.; Madison, J.M.; Zhou, F.; Rueckert, E.H.; Barker, D.; et al. Dysregulation of miR-34a Links Neuronal Development to Genetic Risk Factors for Bipolar Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andolina, D.; Di Segni, M.; Accoto, A.; Lo Iacono, L.; Borreca, A.; Ielpo, D.; Berretta, N.; Perlas, E.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Ventura, R. MicroRNA-34 Contributes to the Stress-Related Behavior and Affects 5-HT Prefrontal/GABA Amygdalar System through Regulation of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7401–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Lin, J.-J.; Lu, M.-K.; Tan, H.-P.; Jang, F.-L.; Lin, S.-H. Neurodevelopment Regulators miR-137 and miR-34 Family as Biomarkers for Early and Adult Onset Schizophrenia. npj Schizophr. 2021, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, C.E.L.; Tang, B.L. miR-34a in Neurophysiology and Neuropathology. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Pei, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, C.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, F.; Zhang, A.; Shen, Y.; et al. MiR34a Regulates Neuronal MHC Class I Molecules and Promotes Primary Hippocampal Neuron Dendritic Growth and Branching. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 573208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.C.; Gao, X.-M.; Tham, Y.K.; Kiriazis, H.; Winbanks, C.E.; Ooi, J.Y.Y.; Boey, E.J.H.; Obad, S.; Kauppinen, S.; Gregorevic, P.; et al. Silencing of miR-34a Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction in a Setting of Moderate, but Not Severe, Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Zhang, G.; Bai, Z.-H. miR-34a Attenuates Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mice via Targeting Pin-1. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, T.; Lin, N.; Lu, W.; Sun, Z.; Lin, H.; Chi, J.; Guo, H. Dihydromyricetin Prevents Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via miR-34a Suppression by Activating Autophagy. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2020, 34, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, R.A.; Iekushi, K.; Lechner, S.; Seeger, T.; Fischer, A.; Heydt, S.; Kaluza, D.; Tréguer, K.; Carmona, G.; Bonauer, A.; et al. MicroRNA-34a Regulates Cardiac Ageing and Function. Nature 2013, 495, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fochi, S.; Giuriato, G.; De Simone, T.; Gomez-Lira, M.; Tamburin, S.; Del Piccolo, L.; Schena, F.; Venturelli, M.; Romanelli, M.G. Regulation of microRNAs in Satellite Cell Renewal, Muscle Function, Sarcopenia and the Role of Exercise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.-C.; Liu, X.-M.; Liang, L.-R.; Wang, L.-F.; Zhong, J.-C. Targeting the microRNA-34a as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 784044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Luo, T.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Xue, X.; Fang, G. The Novel Long Noncoding RNA RP11-357H14.17 Acts as an Oncogene by Promoting Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Diffuse-Type Gastric Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, T.; Wenting, W.; Meixiang, Z.; Chunlei, Z.; Chengxia, H. Long Noncoding RNA RP11-357H14.17 Plays an Oncogene Role in Gastric Cancer by Activating ATF2 Signaling and Enhancing Treg Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6635936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ma, Y.; Han, S.; Sun, P. Genome-Wide Investigation of lncRNAs Revealed Their Tight Association with Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, D.; Ding, L. Investigating Diagnostic Potential of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using TCGA Database and Clinical Specimens. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Essen, D.; Zhu, Y.; Saccani, S. A Feed-Forward Circuit Controlling Inducible NF-κB Target Gene Activation by Promoter Histone Demethylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, T.D.; Gerondakis, S. The C-Rel Transcription Factor in Development and Disease. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenneth, N.S.; Mudie, S.; Rocha, S. IKK and NF-kappaB-Mediated Regulation of Claspin Impacts on ATR Checkpoint Function. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, J.; Hunter, J.E.; Collins, A.; Rushton, A.; Russell, L.G.; Ramon-Gil, E.; Laszczewska, M.; McCain, M.; Zaki, M.Y.W.; Knox, A.; et al. C-Rel-Dependent Chk2 Signaling Regulates the DNA Damage Response Limiting Hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Afzal, O.; Gupta, G.; Bhat, A.A.; Almalki, W.H.; Alzarea, S.I.; Kazmi, I.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Subramaniyan, V.; Thangavelu, L.; et al. Unveiling the Connection: Long-Chain Non-Coding RNAs and Critical Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 249, 154736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Aggarwal, D.; Spector, D.L. MALAT1 Long Non-Coding RNA: Functional Implications. Noncoding RNA 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarei, M.; Shahabi Rabori, V.; Ghasemi, N.; Salehi, M.; Rayatpisheh, N.; Jahangiri, N.; Saberiyan, M. LncRNA MALAT1 Signaling Pathway and Clinical Applications in Overcome on Cancers Metastasis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 4457–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Valinezhad, K.; Adel, E.; Munirathinam, G. MALAT-1 Is a Key Regulator of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Metastasis. Cancers 2024, 16, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Afzal, M.; Almalki, W.H.; Kazmi, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Saleem, S.; Prasher, P.; Oliver, B.; Singh, S.K.; et al. From Carcinogenesis to Therapeutic Avenues: lncRNAs and mTOR Crosstalk in Lung Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 253, 155015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri-Mohammadi, S.; Karamivandishi, A.; Mahdavi, S.A.; Siahposht-Khachaki, A. New Sights on Long Non-Coding RNAs in Glioblastoma: A Review of Molecular Mechanism. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya; Garg, M.; Talwar, R.; Bharadwaj, M.; Ruwali, M.; Pandey, A.K. Clinical Relevance of Long Non-Coding RNA in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Leuk. Res. 2024, 147, 107595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, G. Interplay between lncRNAs and microrNAs in Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 1250–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Fadul, M.M.; Taha, R.; Siddig, O.; Elhafiz, M.; Yousef, B.A.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L. Dynamic Role of Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNA in Liver Diseases: Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Aspects. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 1715–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, B.; Majumder, S.; Gaikwad, A.B. LncRNA MALAT1 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target in Kidney Diseases. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2025, 266, 155783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, B. Long Non-Coding RNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1) Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting c-Met and SOX4 via miR-34a/c-5p and miR-449a/b. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Knockdown of MALAT1 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Progression via Regulating the miR-34a/Cyclin D1 Axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Mendhe, B.; Parker, E.; Kent, A.; Isales, C.M.; Hill, W.D.; McGee-Lawrence, M.; Fulzele, S.; Hamrick, M.W. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Is Depleted With Age in Skeletal Muscle in Vivo and MALAT1 Silencing Increases Expression of TGF-Β1 in Vitro. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 742004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Is Upregulated and Involved in Cell Proliferation, Migration and Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3055–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, A.; Liu, R.; Wu, X. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Is up-Regulated in Ovarian Cancer Tissue and Promotes SK-OV-3 Cell Proliferation and Invasion. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, F. Upregulated MALAT-1 Contributes to Bladder Cancer Cell Migration by Inducing Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattie, M.D.; Benz, C.C.; Bowers, J.; Sensinger, K.; Wong, L.; Scott, G.K.; Fedele, V.; Ginzinger, D.; Getts, R.; Haqq, C. Optimized High-Throughput microRNA Expression Profiling Provides Novel Biomarker Assessment of Clinical Prostate and Breast Cancer Biopsies. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilming Elgaaen, B.; Olstad, O.K.; Haug, K.B.F.; Brusletto, B.; Sandvik, L.; Staff, A.C.; Gautvik, K.M.; Davidson, B. Global miRNA Expression Analysis of Serous and Clear Cell Ovarian Carcinomas Identifies Differentially Expressed miRNAs Including miR-200c-3p as a Prognostic Marker. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekky, R.Y.; Ragab, M.F.; Manie, T.; Attia, A.A.; Youness, R.A. MALAT-1: Immunomodulatory lncRNA Hampering the Innate and the Adaptive Immune Arms in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 31, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, E.; Patella, F.; Waage, J.; Holmstrøm, K.; Lindow, M.; Porse, B.; Kauppinen, S.; Lund, A.H. microRNA-9 Targets the Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 for Degradation in the Nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Park, S.; Kang, K.; Yoon, J.-S.; Ko, Y.H.; Kurie, J.M.; et al. MiR-34a and miR-34b/c Have Distinct Effects on the Suppression of Lung Adenocarcinomas. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajossy, B.; Slominski, A.T.; Wolnicka-Glubisz, A. Inhibition of the RIPK4 Enhances Suppression of Human Melanoma Growth through Vitamin D Signaling. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2025, 607, 112603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X.; You, Y.; Liu, X. Establishment of a TRPV2 Knockout Human Embryonic Stem Cell Line (WAe009-A-1Y) Using Episomal Vector-Based CRISPR/Cas9. Stem Cell Res. 2025, 87, 103744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.I.; Arkelius, K.; Swanson, R.A.; Ma, D.K.; Singhal, N.S. PATJ Regulates Cell Stress Responses and Vascular Remodeling Post-Stroke. Redox Biol. 2025, 85, 103709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, L.; Shalygin, A.; Erbacher, A.; Zaisserer, J.; Gudermann, T.; Chubanov, V. TRPM7 Underlies Cadmium Cytotoxicity in Pulmonary Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Rollo, B.; Sumer, H.; Cromer, B. Targeting the AAVS1 Site by CRISPR/Cas9 with an Inducible Transgene Cassette for the Neuronal Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2495, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.J.; Saee-Marand, M.; Nyström, N.N.; Evans, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Martinez, F.M.; Hamilton, A.M.; Ronald, J.A. Safe Harbor-Targeted CRISPR-Cas9 Homology-Independent Targeted Integration for Multimodality Reporter Gene-Based Cell Tracking. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, R.C.; Ostrominski, J.W.; Tunc, I.; Hong, S.G.; Zou, J.; Dunbar, C.E. CRISPR/Cas9-Based Safe-Harbor Gene Editing in Rhesus iPSCs. Curr. Protoc. Stem Cell Biol. 2017, 43, 5A.11.1–5A.11.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome Engineering Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fochi, S.; Bergamo, E.; Serena, M.; Mutascio, S.; Journo, C.; Mahieux, R.; Ciminale, V.; Bertazzoni, U.; Zipeto, D.; Romanelli, M.G. TRAF3 Is Required for NF-κB Pathway Activation Mediated by HTLV Tax Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Lee, J.; Eusebi, A.; Niewielska, A.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Lopez, R.; Butcher, S. The EMBL-EBI Job Dispatcher Sequence Analysis Tools Framework in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W521–W525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.K. Differential Expression Analysis of Multifactor RNA-Seq Experiments with Respect to Biological Variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping Identifiers for the Integration of Genomic Datasets with the R/Bioconductor Package biomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A Free Online Platform for Data Visualization and Graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.; Rheinheimer, S.; Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Menegatti, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Grässer, F.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Identification of miR-34a-Target Interactions by a Combined Network Based and Experimental Approach. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34288–34299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmsmeier, M.; Steffen, P.; Höchsmann, M.; Giegerich, R. Fast and Effective Prediction of microRNA/Target Duplexes. RNA 2004, 10, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| gRNA | Target Sequence | gRNA Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| gRNA 1 | TTCTTTGGCAGTGTCTTAGCTGG | Fw: CACCGTTCTTTGGCAGTGTCTTAGC Rv: AAACGCTAAGACACTGCCAAAGAAC |
| gRNA 2 | GCCAGCTGTGAGTGTTTCTTTGG | Fw: CACCGCCAGCTGTGAGTGTTTCTT Rv: AAACAAGAAACACTCACAGCTGGC |
| gRNA 3 | TAGAAGTGCTGCACGTTGTGGGG | Fw: CACCGCACAACGTGCAGCACTTCTA Rv: AAACTAGAAGTGCTGCACGTTGTGC |
| Target | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| REL | Fw: ATTTGACGACTGCTCTTCCTC Rv: TCCTCTGACACTTCCACAATTC |
| MAP1B | Fw: CTCCTTCCAGAACTTCATAGAGATT Rv: TTCAGGACAGAACAGGGTTAAG |
| ONECUT2 | Fw: GGAATCCAAAACCGTGGAGTAA Rv: CTCTTTGCGTTTGCACGCTG |
| MALAT1 | Fw: ATGCGAGTTGTTCTCCGTCT Rv: TATCTGCGGTTTCCTCAAGC |
| LINC03057 | Fw: TGTTCTGCGTCTGTGTCTAC Rv: CCACTCCCTTTCTTCCTTGAA |
| RPLP0 | Fw: ACATGTTGCTGGCCAATAAGGT Rv: CCTAAAGCCTGGAAAAAGGAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corsi, A.; De Simone, T.; Valentino, A.; Orlandi, E.; Stefani, C.; Patuzzo, C.; Fochi, S.; Bruno, M.G.; Trabetti, E.; Rotondo, J.C.; et al. MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines. Non-Coding RNA 2025, 11, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040060
Corsi A, De Simone T, Valentino A, Orlandi E, Stefani C, Patuzzo C, Fochi S, Bruno MG, Trabetti E, Rotondo JC, et al. MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines. Non-Coding RNA. 2025; 11(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorsi, Andrea, Tonia De Simone, Angela Valentino, Elisa Orlandi, Chiara Stefani, Cristina Patuzzo, Stefania Fochi, Maria Giusy Bruno, Elisabetta Trabetti, John Charles Rotondo, and et al. 2025. "MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines" Non-Coding RNA 11, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040060
APA StyleCorsi, A., De Simone, T., Valentino, A., Orlandi, E., Stefani, C., Patuzzo, C., Fochi, S., Bruno, M. G., Trabetti, E., Rotondo, J. C., Mazziotta, C., Valenti, M. T., Ruggiero, A., Zipeto, D., Bombieri, C., & Romanelli, M. G. (2025). MALAT1 Expression Is Deregulated in miR-34a Knockout Cell Lines. Non-Coding RNA, 11(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna11040060












