Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
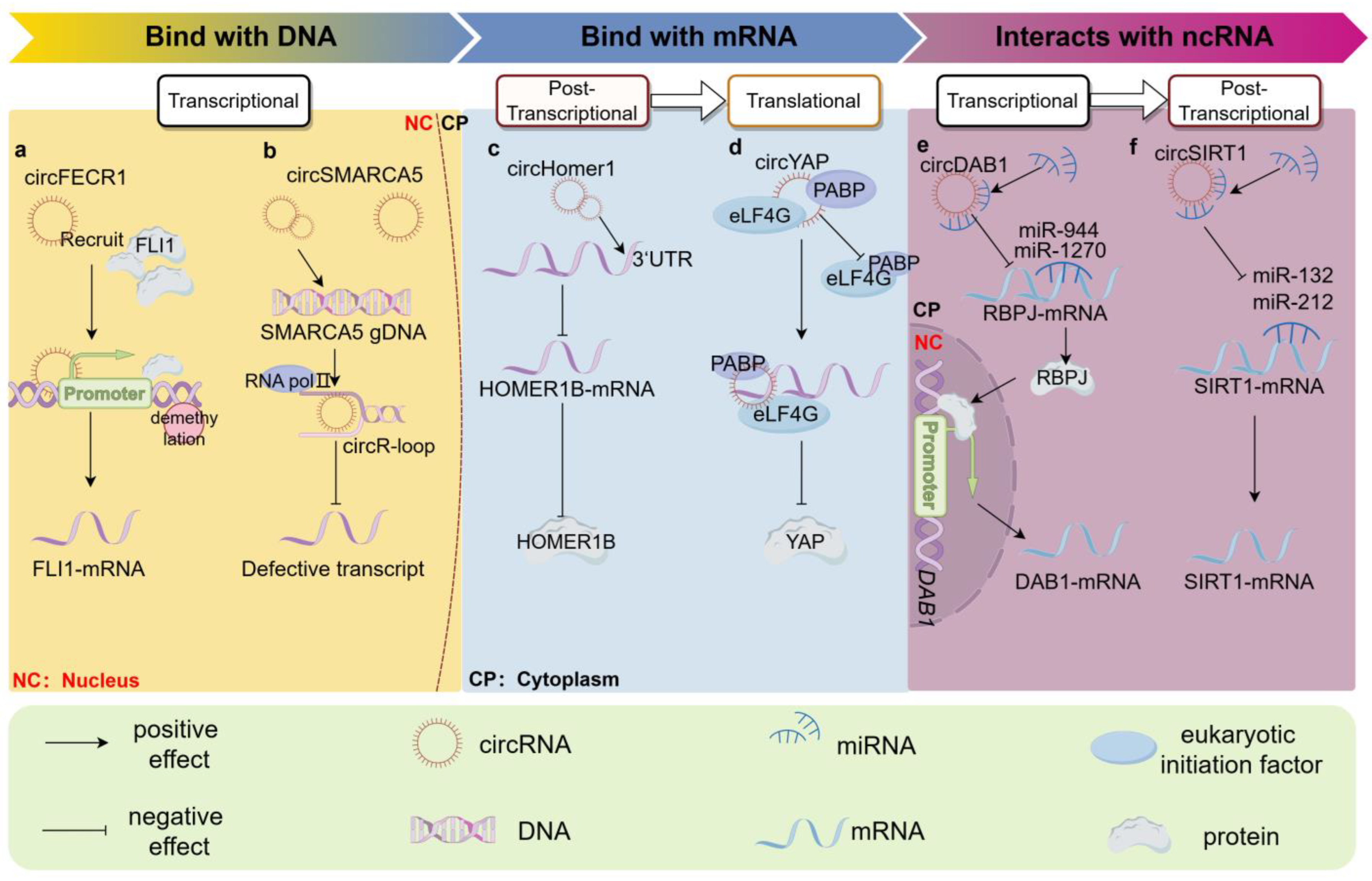
2. Interaction with Nucleic Acid Molecules
2.1. Binding to Host Gene DNA
2.1.1. Binding to Host Gene’s Promoter
2.1.2. The Formation of the circR-Loop
2.2. Binding to Host Gene mRNA
2.2.1. Interacting with Translated Region of Parental mRNA
2.2.2. Interacting with Untranslated Region of Parental mRNA
2.3. Acting as miRNA Decoys
2.3.1. ceRNA Hypothesis and miRNA “Sponge”
2.3.2. Direct Competition between circRNAs and mRNAs for miRNA Binding
2.3.3. Influencing Downstream Genes through the ceRNA Mechanism
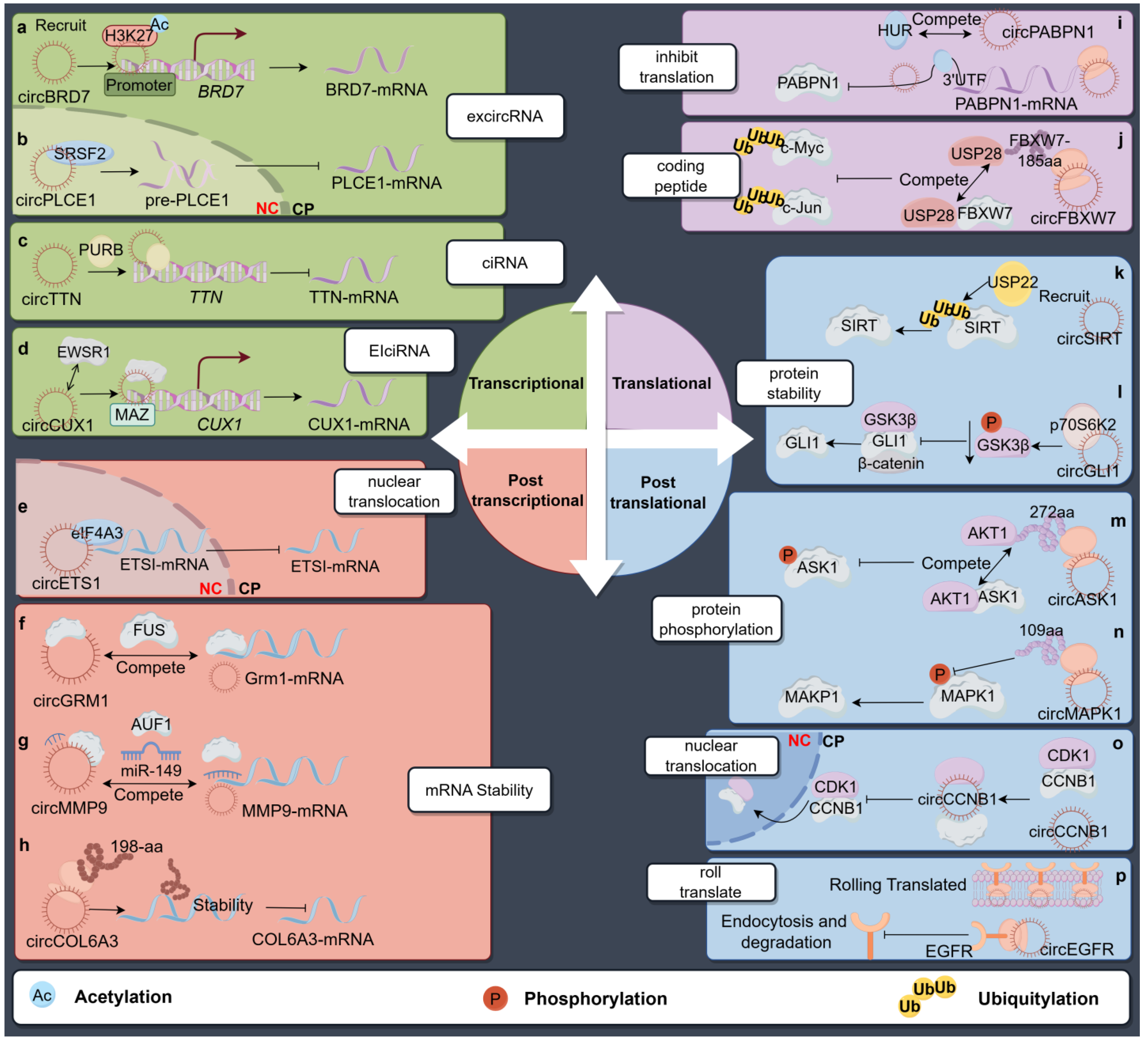
3. Binding to Proteins
3.1. CircRNAs Affect the Transcription of Host Genes
3.1.1. EcircRNAs in Parental Transcription Regulation
3.1.2. CiRNAs in Parental Transcription Inhibition
3.1.3. EIciRNAs in Parental Transcription Activation
3.2. CircRNA Affects Host Gene Expression in Post-Transcriptional Control
3.2.1. Regulation in Parental mRNA Nuclear Translocation
3.2.2. Regulation of Parental mRNA Stability
3.3. CircRNA Affects Host Gene Expression in Translational Control
3.4. CircRNA Affects Host Gene Expression in Post-Translation Control
3.4.1. Regulation in Parental Protein Stability
3.4.2. Regulating Phosphorylation of Parental Gene
3.4.3. Regulation of Nuclear Translocation of the Parental Protein
3.4.4. Rolling Translation of circRNAs
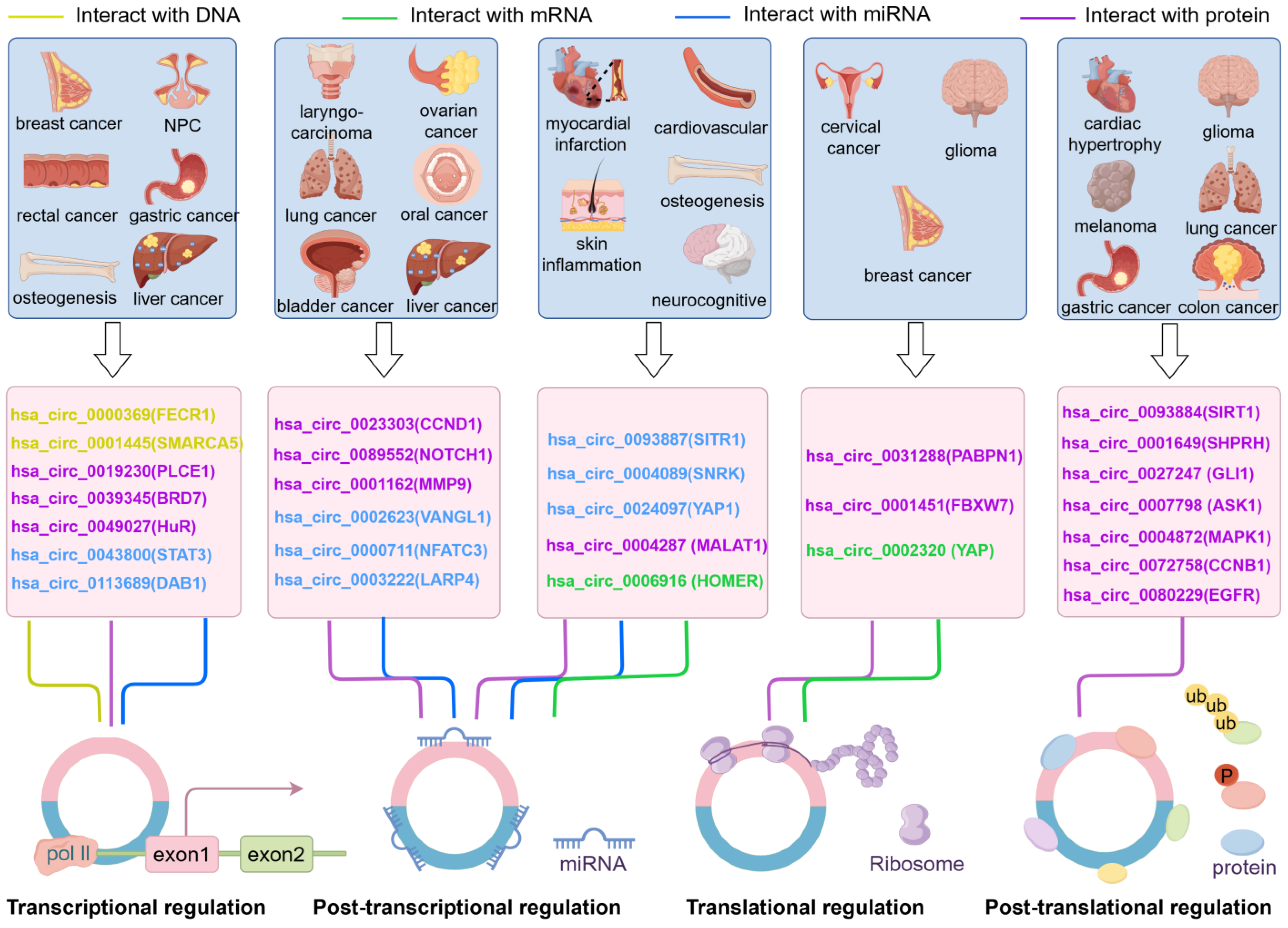
4. The Influence of Different Categories of circRNAs on Parental Gene Expression
5. Regulatory Network of circRNAs and Parental Genes as Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarkers in Human Diseases
6. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enuka, Y.; Lauriola, M.; Feldman, M.E.; Sas-Chen, A.; Ulitsky, I.; Yarden, Y. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryll, A.R.; Peterson, C.L. The circular logic of mRNA homeostasis. Transcription 2023, 14, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Huang, C. Physiological and pathological functions of circular RNAs in the nervous system. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, V.M.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Conn, S.J. Circular RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Yan, D.; Shen, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, L.; Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; et al. CircRNA DICAR as a novel endogenous regulator for diabetic cardiomyopathy and diabetic pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misir, S.; Wu, N.; Yang, B.B. Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, M.; Xue, C.; Chen, S.; Zheng, L.; Deng, H.; Tang, F.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Understanding the roles and regulation patterns of circRNA on its host gene in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Chen, L.L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.X.; Chen, X.; Xia, L.P.; Zhang, J.X.; Pan, Z.Z.; Ma, X.D.; Han, K.; Chen, J.W.; Judde, J.G.; Deas, O.; et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z.; Zang, X.; Shi, H.; Gao, J.; Cai, H.; et al. CircDIDO1 inhibits gastric cancer progression by encoding a novel DIDO1-529aa protein and regulating PRDX2 protein stability. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, W.; Yuan, X.; Yin, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, K.; et al. CircRNA inhibits DNA damage repair by interacting with host gene. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yuan, Z.; Du, K.Y.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, C.; He, A.; Eshaghi, E.; Zeng, K.; Ma, J.; et al. Translation of yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation machinery. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Gao, G.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Ou, X.; Xie, X.; Tang, H. circFBXW7 Inhibits Malignant Progression by Sponging miR-197-3p and Encoding a 185-aa Protein in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.; Ain, R. Regulation of Transcription by Circular RNAs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X. Circular RNA circITGA7 inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the Ras pathway and upregulating transcription of its host gene ITGA7. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Gabryelska, M.; Toubia, J.; Kirk, K.; Gantley, L.; Powell, J.A.; Cildir, G.; Marri, S.; Liu, R.; Stringer, B.W.; et al. Circular RNAs drive oncogenic chromosomal translocations within the MLL recombinome in leukemia. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1309–1326.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.L.; Lim, B.T.; Anene-Nzelu, C.G.; Ackers-Johnson, M.; Dashi, A.; See, K.; Tiang, Z.; Lee, D.P.; Chua, W.W.; Luu, T.D.; et al. A landscape of circular RNA expression in the human heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siede, D.; Rapti, K.; Gorska, A.A.; Katus, H.A.; Altmuller, J.; Boeckel, J.N.; Meder, B.; Maack, C.; Volkers, M.; Muller, O.J.; et al. Identification of circular RNAs with host gene-independent expression in human model systems for cardiac differentiation and disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Patop, I.L.; Krishnamoorthy, A.; Bartok, O.; Maya, R.; Lerner, N.; Ashwall-Fluss, R.; Konakondla, J.V.V.; Beatus, T.; Kadener, S. circMbl functions in cis and in trans to regulate gene expression and physiology in a tissue-specific fashion. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Wiklund, E.D.; Bramsen, J.B.; Villadsen, S.B.; Statham, A.L.; Clark, S.J.; Kjems, J. miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shyamal, S.; Panda, A.C. Detecting RNA-RNA interactome. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2022, 13, e1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Shyamal, S.; Das, A.; Panda, A.C. Global identification of mRNA-interacting circular RNAs by CLiPPR-Seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, G.; Yan, X.; Lv, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Du, Z.; et al. A novel FLI1 exonic circular RNA promotes metastasis in breast cancer by coordinately regulating TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, R.; Hao, Y.; Li, M.; Bai, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, X.; Song, X.; Ma, C.; et al. Super enhancer-associated circRNA-circLrch3 regulates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells pyroptosis by formation of R-loop with host gene. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 130853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehrs, C.; Luke, B. Regulatory R-loops as facilitators of gene expression and genome stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Hugouvieux, V.; Nayak, A.; Conos, S.A.; Capovilla, G.; Cildir, G.; Jourdain, A.; Tergaonkar, V.; Schmid, M.; Zubieta, C.; et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.L.; Lei, Y.N.; Liu, X.Q.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Nan, F.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; et al. Linking circular intronic RNA degradation and function in transcription by RNase H1. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, M.; Rossi, F.; Bozzoni, I. CircZNF609 as a prototype to elucidate the biological function of circRNA-mRNA interactions. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2022, 9, 2055939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.K.; Zimmerman, A.J.; Papageorgiou, G.; Chandrasekaran, J.; Amoah, S.K.; Lin, R.; Lozano, E.; Pierotti, C.; Dell′Orco, M.; Hartley, B.J.; et al. A bidirectional competitive interaction between circHomer1 and Homer1b within the orbitofrontal cortex regulates reversal learning. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, D.-H.; Wu, N.; Xiao, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Ma, W. ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical implications. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlstad Olesen, M.T.; Kristensen, L.S. Circular RNAs as microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversies. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzler, R.; Agarwal, V.; Stefano, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Assessing the ceRNA hypothesis with quantitative measurements of miRNA and target abundance. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Okholm, T.L.H.; Veno, M.T.; Kjems, J. Circular RNAs are abundantly expressed and upregulated during human epidermal stem cell differentiation. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.F.; Bindereif, A.; Bozzoni, I.; Hanan, M.; Hansen, T.B.; Irimia, M.; Kadener, S.; Kristensen, L.S.; Legnini, I.; Morlando, M.; et al. Best practice standards for circular RNA research. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Duan, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Jin, L.; Yu, Y. Circular RNA circ-VANGL1 as a competing endogenous RNA contributes to bladder cancer progression by regulating miR-605-3p/VANGL1 pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 3887–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. CircRNA-ENO1 promoted glycolysis and tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma through upregulating its host gene ENO1. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Chang, N.; Yen, L.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.J. Noncoding Effects of Circular RNA CCDC66 Promote Colon Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, L. Circ-XPO1 upregulates XPO1 expression by sponging multiple miRNAs to facilitate osteosarcoma cell progression. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 117, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Miao, Y.; Xu, T.; Sun, W.; Sang, Y.; Jia, F.; Zhang, X. Circ-EPB41L5 regulates the host gene EPB41L5 via sponging miR-19a to repress glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Aging 2020, 12, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Hong, T.; He, X.; Hu, X.; Gao, Y. A circular RNA derived from MMP9 facilitates oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through regulation of MMP9 mRNA stability. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Hsueh, C.Y.; Yuan, X.; Heng, Y.; Zhou, L. Diagnostic Role of Dysregulated Circular RNA hsa_circ_0036722 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5709–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, B.; Tai, Y. circRNA circ-CCND1 promotes the proliferation of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through elevating CCND1 expression via interacting with HuR and miR-646. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, Q. CircRNA circYY1 (hsa_circ_0101187) Modulates Cell Glycolysis and Malignancy Through Regulating YY1 Expression by Sponging miR-769-3p in Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, P.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zeng, Z.; Tang, H. circGFRA1 and GFRA1 act as ceRNAs in triple negative breast cancer by regulating miR-34a. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.C.; Xu, Z.; Zhong, S.L.; Zhang, H.D.; Jiang, L.H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.P.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.Y.; Yang, S.J.; et al. Circular RNA circASS1 is downregulated in breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and suppressed invasion and migration. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, F.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Pang, S.; Shi, B.; Zhou, F.; Yao, L.; et al. CircKEAP1 Suppresses the Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via the miR-141-3p/KEAP1/NRF2 Axis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 672586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, Q. circRNA hsa_circ_0018414 inhibits the progression of LUAD by sponging miR-6807-3p and upregulating DKK1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L. Identification of the tumor-suppressive function of circular RNA FOXO3 in non-small cell lung cancer through sponging miR-155. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7692–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. Circular RNA circ-PTEN elevates PTEN inhibiting the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cao, W.; Lu, C.; Zuo, L.; Liu, X.; Qi, M. circ3323 Motivates Host Gene to Promote the Aggressiveness of Bladder Cancer. Biochem. Genet. 2022, 60, 2327–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Ou, Z.; Yeh, S.; Huang, C.P.; You, B.; Tsai, Y.C.; Sheu, T.J.; Zu, X.; Chang, C. Androgen receptor-regulated circFNTA activates KRAS signaling to promote bladder cancer invasion. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Yao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, S.; Deng, M.; Zhang, Q. circNFATC3 sponges miR-548I acts as a ceRNA to protect NFATC3 itself and suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 1252–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kang, H.; Gao, M.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Xiao, L. Exosome-transmitted circ_MMP2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by upregulating MMP2. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Peng, E.; Qiu, X.; Lyu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. circFBLIM1 act as a ceRNA to promote hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging miR-346. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Li, S.; Tong, Q.; Mao, Y. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0003141 promotes tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via a miR-1827/UBAP2 axis. Aging 2020, 12, 9793–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via multiple miRNAs sponge. Aging 2019, 11, 3362–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, D.; Ma, S. A circular RNA derived from COL6A3 functions as a ceRNA in gastric cancer development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, S. Analysis of co-expression networks for circular RNAs and mRNAs reveals that circular RNAs hsa_circ_0047905, hsa_circ_0138960 and has-circRNA7690-15 are candidate oncogenes in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, W.; Chen, W. Hsa_circ_0000069 Knockdown Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Exosomes with Downregulated hsa_circ_0000069 Suppress Malignant Transformation via Inhibition of STIL in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9859–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chou, F.J.; Chen, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; You, B.; Niu, Y.; Huang, C.P.; Yeh, S.; Xing, N.; et al. Targeting the radiation-induced TR4 nuclear receptor-mediated QKI/circZEB1/miR-141-3p/ZEB1 signaling increases prostate cancer radiosensitivity. Cancer Lett. 2020, 495, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Ye, H.; You, K.; Chen, L. Up-regulation of circ_LARP4 suppresses cell proliferation and migration in ovarian cancer by regulating miR-513b-5p/LARP4 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Guan, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. CircCRIM1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by working as ceRNAs of CRIM1 and targeting miR-383-5p/ZEB2 axis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Mo, L.; Tang, H.; Leng, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Xu, Y. circRNA-AKT1 Sequesters miR-942-5p to Upregulate AKT1 and Promote Cervical Cancer Progression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, F.; Zhu, L.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; et al. circAMOTL1 Motivates AMOTL1 Expression to Facilitate Cervical Cancer Growth. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Huang, S.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Y.; Yin, D. Circular RNA YAP1 attenuates osteoporosis through up-regulation of YAP1 and activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, C.; Lan, R.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Circ-SIRT1 inhibits cardiac hypertrophy via activating SIRT1 to promote autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Dou, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.-H.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Yong, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-B.; Hu, H.-J.; et al. circ-Sirt1 controls NF-κB activation via sequence-specific interaction and enhancement of SIRT1 expression by binding to miR-132/212 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3580–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Meng, G.; Hua, L. Circular RNA CCDC66 facilitates abdominal aortic aneurysm through the overexpression of CCDC66. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, X.-X.; Deng, Y.-F. Negative feedback of SNRK to circ-SNRK regulates cardiac function post-myocardial infarction. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 29, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Transcription activation of circ-STAT3 induced by Gli2 promotes the progression of hepatoblastoma via acting as a sponge for miR-29a/b/c-3p to upregulate STAT3/Gli2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.-G.; Zhang, C. A circular RNA derived from DAB1 promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via RBPJ/DAB1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, Q.; Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Leng, X.; Shao, L. miR-449c-5p availability is antagonized by circ-NOTCH1 for MYC-induced NOTCH1 upregulation as well as tumor metastasis and stemness in gastric cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 4052–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, B.; Yan, G.; Wang, N.; Yang, Z.; Sun, M. YAP derived circ-LECRC functions as a “brake signal” to suppress hyperactivation of oncogenic YAP signalling in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 532, 215589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, N.; Schoppe, L.; Schuster, S.; Laufs, U.; Boeckel, J.N. Circular RNA Splicing. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, G.; Yang, Y.; Yan, D.; Xing, T.; Fan, J.; Tang, H.; Peng, Z. Phospholipase C epsilon plays a suppressive role in incidence of colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. CircPLCE1 facilitates the malignant progression of colorectal cancer by repressing the SRSF2-dependent PLCE1 pre-RNA splicing. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7244–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Dong, D.; Shen, X.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Z.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; et al. Circular RNA TTN Acts As a miR-432 Sponge to Facilitate Proliferation and Differentiation of Myoblasts via the IGF2/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, N.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Liufu, S.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Ma, H.; et al. Circular Intronic RNA circTTN Inhibits Host Gene Transcription and Myogenesis by Recruiting PURB Proteins to form Heterotypic Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, F.; Hu, A.; Wang, X.; Fang, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of circ-CUX1/EWSR1/MAZ axis inhibits glycolysis and neuroblastoma progression. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Maskey, N.; Zheng, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Hsa_circ_0004296 inhibits metastasis of prostate cancer by interacting with EIF4A3 to prevent nuclear export of ETS1 mRNA. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, L.; Zhu, R.; Huang, S.; Xiao, W.; Yu, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Hsa_circ_0004287 inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation in an N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent manner in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Kong, Q.; Cai, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, C. circ-Grm1 promotes pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via suppression of GRM1 expression by FUS. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 48, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, J.A. G protein-coupled oestrogen receptor promotes cell growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells via YAP1/QKI/circNOTCH1/m6A methylated NOTCH1 signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, J.; Zhou, X.; Pan, W. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0006401 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hu, A.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, K.; et al. Circ-HuR suppresses HuR expression and gastric cancer progression by inhibiting CNBP transactivation. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Yan, S.; Xiao, F.; Chen, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H. Circ-GLI1 promotes metastasis in melanoma through interacting with p70S6K2 to activate Hedgehog/GLI1 and Wnt/β-catenin pathways and upregulate Cyr61. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichijo, H.; Nishida, E.; Irie, K.; ten Dijke, P.; Saitoh, M.; Moriguchi, T.; Takagi, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Miyazono, K.; Gotoh, Y. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 1997, 275, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; She, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, S.; Xie, D.; Sun, X.; Hu, X.; et al. A novel protein encoded by circASK1 ameliorates gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by competitively activating ASK1-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xia, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Xuan, Z.; Xie, L.; Qiu, S.; He, Z.; et al. A novel protein encoded by circMAPK1 inhibits progression of gastric cancer by suppressing activation of MAPK signaling. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Du, W.W.; Lyu, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; He, A.; Kwok, Y.S.S.; Ma, J.; Wu, N.; et al. Enhanced breast cancer progression by mutant p53 is inhibited by the circular RNA circ-Ccnb1. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Du, W.W.; Awan, F.M.; Dong, J.; Yang, B.B. The circular RNA circ-Ccnb1 dissociates Ccnb1/Cdk1 complex suppressing cell invasion and tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishihara, M.; Nakano, Y.; Shibata, A.; Maruyama, H.; Shuto, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yoshida, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. Rolling Circle Translation of Circular RNA in Living Human Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zeng, R.; et al. Rolling-translated EGFR variants sustain EGFR signaling and promote glioblastoma tumorigenicity. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.; Chen, C.Y.; Chuang, T.J. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2015, 6, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Xue, C.; Zheng, L.; Duan, Y.; Deng, H.; Fan, S.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, M. CircBRD7 attenuates tumor growth and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via epigenetic activation of its host gene. Cancer Sci. 2023, 115, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Rong, J.; Yu, Y. Circular RNA circ0005276 promotes the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by interacting with FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. Rna 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, B.; Wang, X.; Shan, G.; Chen, L. Systematic identification and characterization of exon-intron circRNAs. Genome Res. 2024, 34, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, H.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; et al. Expanded Expression Landscape and Prioritization of Circular RNAs in Mammals. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3444–3460.e3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, J.; Qian, H.; Yan, Y.; Xu, W. Exosomal circRNA: Emerging insights into cancer progression and clinical application potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Han, L.; Wei, M.; He, M. Potential therapeutic strategy for cancer: Multi-dimensional cross-talk between circRNAs and parental genes. Cancer Lett. 2024, 588, 216794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Wu, Y.; Lian, J. Circular RNA vaccine in disease prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | CircRNA ID 1 | Exp.circR 2 | Host Gene | Exp.mR 3 | Rel. miRNA | Val. Meth 4 | MREs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGM | hsa_circ_0008278 | down | EPB41L5 | down | miR-19a | i, v, vi | 1 | [46] |
| OSCC | hsa_circ_0001162 | up | MMP9 | up | miR-149 | v, vi | 1 | [47] |
| LSCC | hsa_circ_0036722 | down | RHCG | down | miR-1248 | i, vi | 2 | [48] |
| hsa_circ_0023303 | up | CCND1 | up | miR-646 | i, v, vi | 3 | [49] | |
| BC | hsa_circ_0101187 | up | YY1 | up | miR-769-3p | ii, v, vi | 1 | [50] |
| hsa_circ_0005239 | up | GFRA1 | up | miR-34a | i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi | 2 | [51] | |
| hsa_circ_0089105 | down | ASS1 | down | miR-4443 | i, iii, v | 1 | [52] | |
| hsa_circ_0001451 | down | FBXW7 | down | miR-197-3p | i, ii, v, vi | 2 | [16] | |
| LCa | hsa_circ_0000013 | up | ENO1 | up | miR-22-3p | i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi | 2 | [43] |
| hsa_circ_0049271 | down | KEAP1 | down | miR-141-3p | i, ii, v, vi | 1 | [53] | |
| hsa_circ_0018414 | down | DKK1 | down | miR-6807-3p | i, ii, v, vi | 1 | [54] | |
| has_circ_0006404 | down | FOXO3 | down | miR-155 | i, ii, v | 1 | [55] | |
| hsa_circ_0094342 | down | PTEN | down | miR-155/miR-330-3p | i, ii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [56] | |
| BCa | hsa_circ_0002623 | up | VANGL1 | up | miR-605-3p | i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [42] |
| hsa_circ_0003323 | up | APP | up | miR-186-5p | i, ii, v, vi | 1 | [57] | |
| hsa_circ_0084171 | up | FNTA | up | miR-370-3p | i, ii, iv, v, vi | 2 | [58] | |
| HCC | hsa_circ_0000711 | down | NFATC3 | down | miR-548i | i, iv, v, vi | 1 | [59] |
| hsa_circ_0039411 | up | MMP2 | up | miR-136-5p | i, iv, v, vi | 1 | [60] | |
| hsa_circ_0010090 | up | FBLIM1 | up | miR-346 | i, iv, v, vi | 1 | [61] | |
| hsa_circ_0003141 | up | UBAP2 | up | miR-1827 | i, iii, iv, vi | 1 | [62] | |
| hsa_circ_0001649 | down | SHPRH | down | miR-127-5p/miR-612/ miR-4688 | ii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [63] | |
| GC | hsa_circ_0006401 | up | COL6A3 | up | miR-3064-5p | i, v, vi | 1 | [64] |
| hsa_circ_0069765 | up | KIT | up | miR-142-5p/miR-144-3p/miR-485-3p | i, ii | N/A | [65] | |
| hsa_circ_0084097 | up | PLAT | up | miR-142-5p/miR-144-3p/miR-485-3p | i, ii | N/A | [65] | |
| hsa_circ_0079741 | up | ETV1 | up | miR-142-5p/miR-144-3p/miR-485-3p | i, ii, iii | N/A | [65] | |
| PC | hsa_circ_0000069 | up | STIL | up | miR-144 | i, ii, iii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [66] |
| PCa | hsa_circ_0004907 | up | ZEB | up | miR-141-3p | ii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [67] |
| OC | hsa_circ_0003222 | down | LARP4 | down | miR-513b-5p | i, v, vi | 1 | [68] |
| hsa_circ_0002346 | up | CRIM1 | up | miR-145-5p | ii, iv, vi | 1 | [69] | |
| CC | hsa_circ_0033550 | up | AKT1 | up | miR-942-5p | i, ii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [70] |
| hsa_circ_0004214 | up | AMOTL1 | up | miR-485-5p | i, ii, iv, v, vi | 1 | [71] | |
| OS | hsa_circ_0001016 | up | XPO1 | up | miR-23a-3p/miR-23b-3p/ miR-23c/miR-130a-5p | i, ii, v, vi | 1 * | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Liao, X.; Hu, D.; Guan, D.; Tian, M. Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10050049
Yuan H, Liao X, Hu D, Guan D, Tian M. Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease. Non-Coding RNA. 2024; 10(5):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10050049
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Haomiao, Xizhou Liao, Ding Hu, Dawei Guan, and Meihui Tian. 2024. "Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease" Non-Coding RNA 10, no. 5: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10050049
APA StyleYuan, H., Liao, X., Hu, D., Guan, D., & Tian, M. (2024). Back to the Origin: Mechanisms of circRNA-Directed Regulation of Host Genes in Human Disease. Non-Coding RNA, 10(5), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna10050049







