Computational Flow Diverter Implantation—A Comparative Study on Pre-Interventional Simulation and Post-Interventional Device Positioning for a Novel Blood Flow Modulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
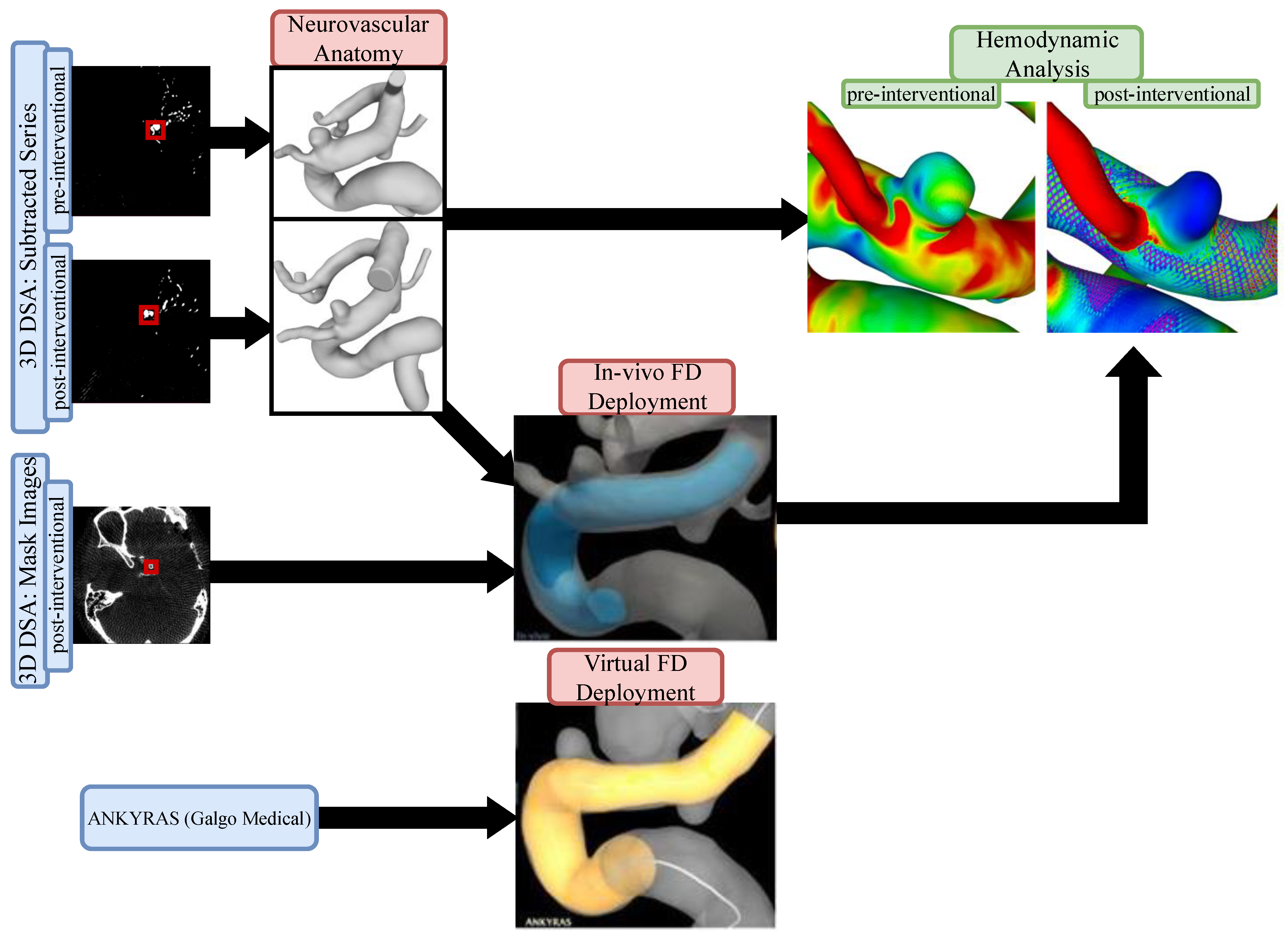
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Segmentation
2.3.1. Neurovascular Anatomy
2.3.2. In Vivo Flow Diverter Deployment
2.4. Virtual Stenting
2.5. Image-Based Blood Flow Simulation
2.6. Quantitative and Quantitative Analysis
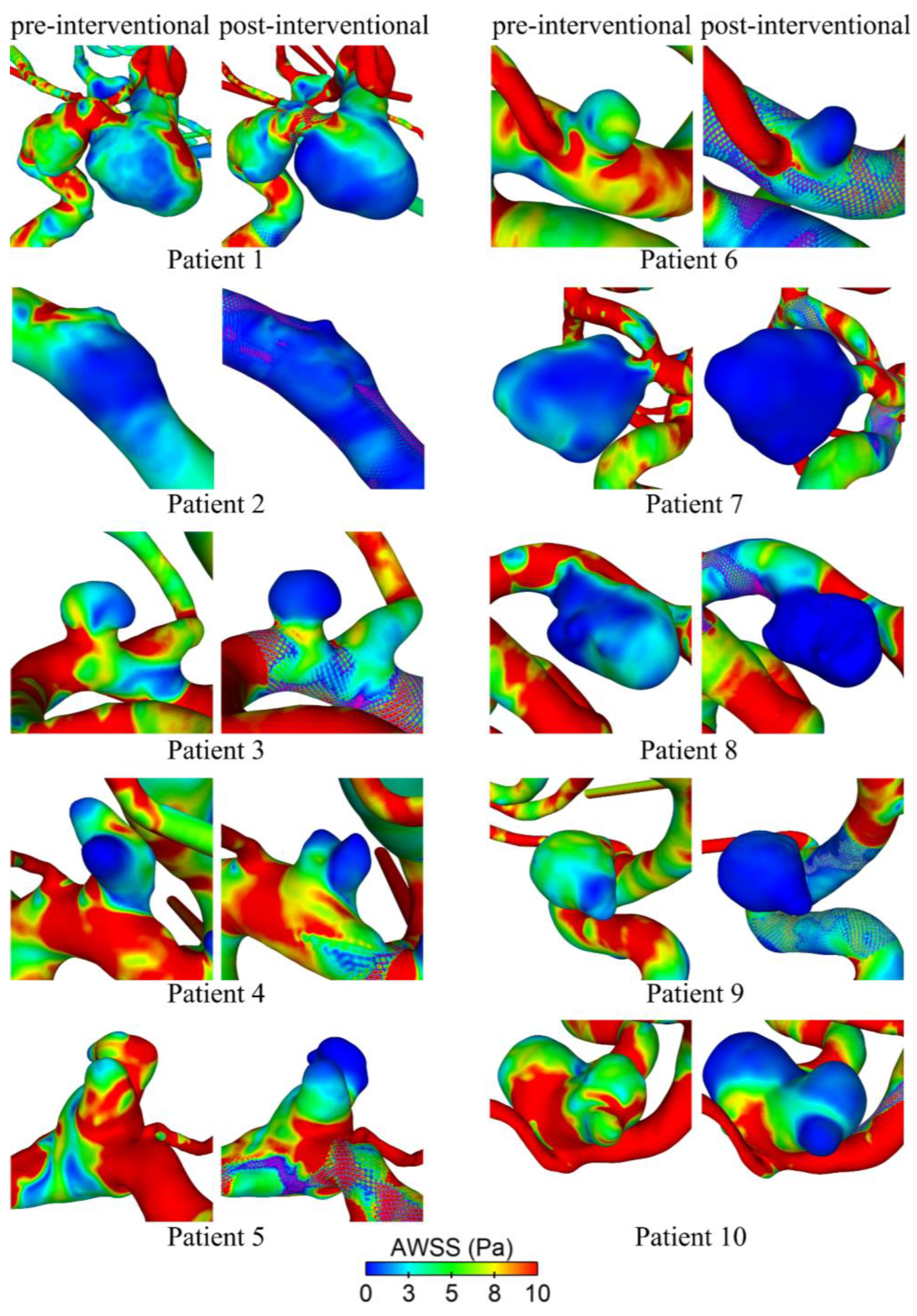
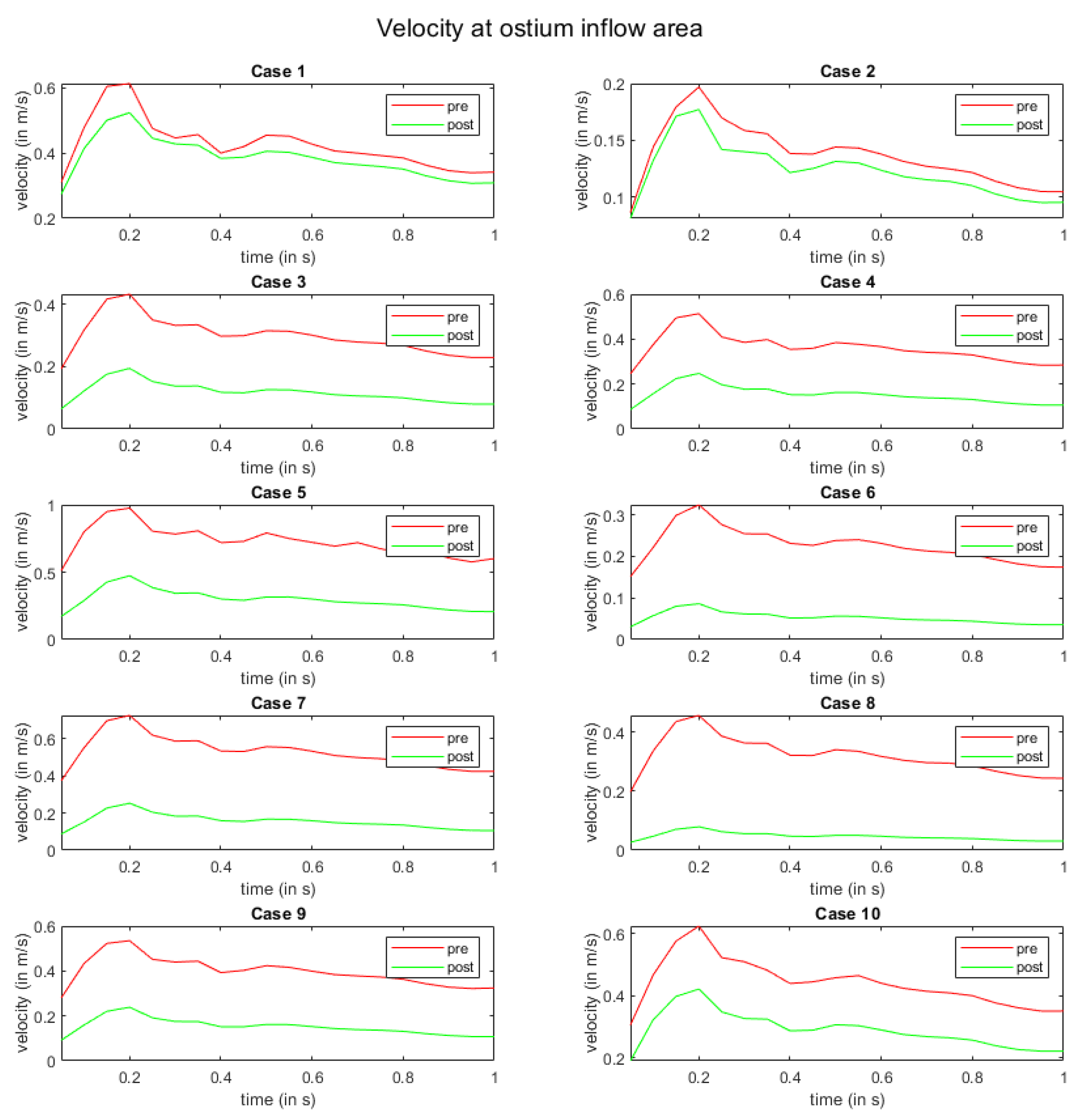
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACA | Anterior cerebral artery |
| AWSS | Time-averaged wall shear stress |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| FD | Flow diverter |
| FVS | Fast virtual stenting |
| DSA | Digital subtraction angiography |
| DED2 | Derivo® 2 flow diverter embolization device |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
References
- Brinjikji, W.; Murad, M.H.; Lanzino, G.; Cloft, H.J.; Kallmes, D.F. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms with Flow Diverters: A Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2013, 44, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschner, C.A.; Stracke, C.P.; Dorn, F.; Kadziolka, K.B.; Kreiser, K.; Solymosi, L.; Pham, M.; Buhk, J.H.; Turowski, B.; Reith, W.; et al. Derivo Embolization Device in the Treatment of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2021, 13, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Galdámez, M.; Biondi, A.; Kalousek, V.; Pereira, V.M.; Ianucci, G.; Gentric, J.C.; Mosimann, P.J.; Brisbois, D.; Schob, S.; Quäschling, U.; et al. Periprocedural Safety and Technical Outcomes of the New Silk Vista Baby Flow Diverter for the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: Results from a Multicenter Experience. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhlenbruch, M.A.; Kizilkilic, O.; Killer-Oberpfalzer, M.; Baltacioglu, F.; Islak, C.; Bendszus, M.; Cekirge, S.; Saatci, I.; Kocer, N. Multicenter Experience with FRED Jr Flow Re-Direction Endoluminal Device for Intracranial Aneurysms in Small Arteries. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, P.; Schob, S.; Jantschke, R.; Nestler, U.; Krause, M.; Weise, D.; Lobsien, D.; Hoffmann, K.T.; Quäschling, U. Stent-Assisted Coiling of Ruptured and Incidental Aneurysms of the Intracranial Circulation Using Moderately Flow-Redirecting, Braided Leo Stents-Initial Experience in 39 Patients. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadirvel, R.; Ding, Y.H.; Dai, D.; Rezek, I.; Lewis, D.A.; Kallmes, D.F. Cellular Mechanisms of Aneurysm Occlusion after Treatment with a Flow Diverter. Radiology 2014, 270, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, F.; Leone, G.; Marseglia, M.; Mariniello, G.; Caranci, F.; Brunetti, A.; Maiuri, F. Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms Using Flow-Diverter Devices: A Systematic Review. Neuroradiol. J. 2015, 28, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, K.; Salem, M.M.; Alturki, A.Y.; Thomas, A.J.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Moore, J.M. Endothelialization Following Flow Diversion for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puffer, R.C.; Piano, M.; Lanzino, G.; Valvassori, L.; Kallmes, D.F.; Quilici, L.; Cloft, H.J.; Boccardi, E. Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Aneurysms with Flow Diversion: Results in 44 Patients. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivelato, F.P.; Abud, D.G.; Ulhôa, A.C.; Waihrich, E.S.; Abud, T.G.; Castro Afonso, L.H.; Nakiri, G.S.; De Castro, G.D.; Parente, B.D.S.M.; Dos Santos Silva, R.; et al. Derivo Embolization Device for the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms. Stroke 2019, 50, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Burke, S.M.; Baig, A.A.; Khan, S.; Cappuzzo, J.M.; Waqas, M.; Dietrich, J.E.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Derivo Embolization Device: A Novel Surface-Modified Flow Diverter for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonafe, A.; Perez, M.A.; Henkes, H.; Lylyk, P.; Bleise, C.; Gascou, G.; Sirakov, S.; Sirakov, A.; Stockx, L.; Turjman, F.; et al. Diversion-P64: Results from an International, Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Arm Post-Market Study to Assess the Safety and Effectiveness of the P64 Flow Modulation Device. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becske, T.; Kallmes, D.F.; Saatci, I.; McDougall, C.G.; Szikora, I.; Lanzino, G.; Moran, C.J.; Woo, H.H.; Lopes, D.K.; Berez, A.L.; et al. Pipeline for Uncoilable or Failed Aneurysms: Results from a Multicenter Clinical Trial. Radiology 2013, 267, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killer-Oberpfalzer, M.; Kocer, N.; Griessenauer, C.J.; Janssen, H.; Engelhorn, T.; Holtmannspötter, M.; Buhk, J.H.; Finkenzeller, T.; Fesl, G.; Trenkler, J.; et al. European Multicenter Study for the Evaluation of a Dual-Layer Flow-Diverting Stent for Treatment of Wide-Neck Intracranial Aneurysms: The European Flow-Redirection Intraluminal Device Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mut, F.; Cebral, J.R. Effects of Flow-Diverting Device Oversizing on Hemodynamics Alteration in Cerebral Aneurysms. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosif, C.; Berg, P.; Ponsonnard, S.; Carles, P.; Saleme, S.; Ponomarjova, S.; Pedrolo-Silveira, E.; Mendes, G.A.C.; Waihrich, E.; Trolliard, G.; et al. Role of Terminal and Anastomotic Circulation in the Patency of Arteries Jailed by Flow-Diverting Stents: From Hemodynamic Changes to Ostia Surface Modifications. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narata, A.P.; Blasco, J.; Roman, L.S.; Macho, J.M.; Fernandez, H.; Moyano, R.K.; Winzenrieth, R.; Larrabide, I. Early Results in Flow Diverter Sizing by Computational Simulation: Quantification of Size Change and Simulation Error Assessment. Oper. Neurosurg. 2018, 15, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospel, J.M.; Gascou, G.; Costalat, V.; Piergallini, L.; Blackham, K.A.; Zumofen, D.W. Comparison of Pipeline Embolization Device Sizing Based on Conventional 2D Measurements and Virtual Simulation Using the Sim&Size Software: An Agreement Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, P.; Iosif, C.; Ponsonnard, S.; Yardin, C.; Janiga, G.; Mounayer, C. Endothelialization of Over- and Undersized Flow-Diverter Stents at Covered Vessel Side Branches: An in Vivo and in Silico Study. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, F.; Darsaut, T.E.; Salazkin, I.; Makoyeva, A.; Gevry, G.; Raymond, J. Stents and Flow Diverters in the Treatment of Aneurysms: Device Deformation In Vivo May Alter Porosity and Impact Efficacy. Neuroradiology 2013, 55, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, R.; Serowy, S.; Beuing, O.; Skalej, M. Deployment of Flow Diverter Devices: Prediction of Foreshortening and Validation of the Simulation in 18 Clinical Cases. Neuroradiology 2019, 61, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velvaluri, P.; Pravdivtseva, M.S.; Berg, P.; Wodarg, F.; Lima De Miranda, R.; Hövener, J.-B.; Jansen, O.; Quandt, E.; Velvaluri, P.; Quandt, E.; et al. Thin-Film Patient-Specific Flow Diverter Stents for the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillot, P.; Brina, O.; Yilmaz, H.; Farhat, M.; Erceg, G.; Lovblad, K.O.; Vargas, M.I.; Kulcsar, Z.; Pereira, V.M. Virtual-versus-Real Implantation of Flow Diverters: Clinical Potential and Influence of Vascular Geometry. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrabide, I.; Kim, M.; Augsburger, L.; Villa-Uriol, M.C.; Rüfenacht, D.; Frangi, A.F. Fast Virtual Deployment of Self-Expandable Stents: Method and In Vitro Evaluation for Intracranial Aneurysmal Stenting. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Závodszky, G.; Csippa, B.; Paál, G.; Szikora, I. A Novel Virtual Flow Diverter Implantation Method with Realistic Deployment Mechanics and Validated Force Response. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 2020, 36, e3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamooki, S.R.; Tutino, V.M.; Paliwal, N.; Damiano, R.J.; Waqas, M.; Nagesh, S.S.V.; Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; Vakharia, K.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Evaluation of Two Fast Virtual Stenting Algorithms for Intracranial Aneurysm Flow Diversion. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2020, 17, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Damiano, R.J.; Lin, N.; Snyder, K.V.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Levy, E.I.; Meng, H. High-Fidelity Virtual Stenting: Modeling of Flow Diverter Deployment for Hemodynamic Characterization of Complex Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiga, G.; Daróczy, L.; Berg, P.; Thévenin, D.; Skalej, M.; Beuing, O. An Automatic CFD-Based Flow Diverter Optimization Principle for Patient-Specific Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillot, P.; Brina, O.; Ouared, R.; Yilmaz, H.; Farhat, M.; Erceg, G.; Lovblad, K.O.; Vargas, M.I.; Kulcsar, Z.; Pereira, V.M. Geometrical Deployment for Braided Stent. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Yang, P.F.; Shen, J.; Huang, Q.H.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Y.; Liu, J.M. A Comparison of the Hemodynamic Effects of Flow Diverters on Wide-Necked and Narrow-Necked Cerebral Aneurysms. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 1520–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebral, J.R.; Mut, F.; Raschi, M.; Scrivano, E.; Ceratto, R.; Lylyk, P.; Putman, C.M. Aneurysm Rupture Following Treatment with Flow-Diverting Stents: Computational Hemodynamics Analysis of Treatment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Shan, Y.; Leng, X.; Chen, J.; Fiehler, J.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Hu, X.; Liu, A.; Xiang, J. Predicting Flow Diverter Sizing Using the AneuGuide TM Software: A Validation Study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, S.; Brehm, A.; Takao, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Karagiozov, K.; Fukudome, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Murayama, Y.; Psychogios, M.N. Hemodynamic Characteristics and Clinical Outcome for Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with the Derivo Embolization Device, a Novel Second-Generation Flow Diverter. World Neurosurg. 2021, 159, e252–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goertz, L.; Dorn, F.; Kraus, B.; Borggrefe, J.; Forbrig, R.; Schlamann, M.; Liebig, T.; Turowski, B.; Kabbasch, C. Improved Occlusion Rate of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with the Derivo Embolization Device: One-Year Clinical and Angiographic Follow-Up in a Multicenter Study. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e1503–e1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, E.; Onan, H.B.; Akpinar, S.; Balli, H.T.; Aksungur, E.H. The DERIVO Embolization Device in the Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms: Short- and Midterm Results. World Neurosurg. 2016, 95, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschner, M.G.; Petridis, A.; Turowski, B. Single-Center Experience with the New Generation Derivo Embolization Device in Ruptured Dissecting and Blister Aneurysms. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.; Marsh, L.M.M.; Thormann, M.; Ding, A.; Saalfeld, S.; Behme, D.; Berg, P. Assessment of the Flow-Diverter Efficacy for Intracranial Aneurysm Treatment Considering Pre- and Post-Interventional Hemodynamics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 156, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, H.; Macho, J.M.; Blasco, J.; Roman, L.S.; Mailaender, W.; Serra, L.; Larrabide, I. Computation of the Change in Length of a Braided Device When Deployed in Realistic Vessel Models. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2015, 10, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiga, G.; Rössl, C.; Skalej, M.; Thévenin, D. Realistic Virtual Intracranial Stenting and Computational Fluid Dynamics for Treatment Analysis. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durka, M.J.; Wong, I.H.; Kallmes, D.F.; Pasalic, D.; Mut, F.; Jagani, M.; Blanco, P.J.; Cebral, J.R.; Robertson, A.M. A Data-Driven Approach for Addressing the Lack of Flow Waveform Data in Studies of Cerebral Arterial Flow in Older Adults. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Preim, B.; Berg, P. Flow-Splitting-Based Computation of Outlet Boundary Conditions for Improved Cerebrovascular Simulation in Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tutino, V.M.; Snyder, K.V.; Meng, H. CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics or Confounding Factor Dissemination? The Role of Hemodynamics in Intracranial Aneurysm Rupture Risk Assessment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, N.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Hasan, D.; Pema, P.J.; Gould, G.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Jabbour, P.M. Spontaneous Delayed Migration/Shortening of the Pipeline Embolization Device: Report of 5 Cases. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Dargush, G.F.; Natarajan, S.K.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Computer Modeling of Deployment and Mechanical Expansion of Neurovascular Flow Diverter in Patient-Specific Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Daróczy, L.; Janiga, G. Virtual Stenting for Intracranial Aneurysms. In Computing and Visualization for Intravascular Imaging and Computer-Assisted Stenting; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 371–411. [Google Scholar]
- Dholakia, R.; Sadasivan, C.; Fiorella, D.J.; Woo, H.H.; Lieber, B.B. Hemodynamics of Flow Diverters. J. Biomech. Eng. 2017, 139, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcsár, Z.; Augsburger, L.; Reymond, P.; Pereira, V.M.; Hirsch, S.; Mallik, A.S.; Millar, J.; Wetzel, S.G.; Wanke, I.; Rüfenacht, D.A. Flow Diversion Treatment: Intra-Aneurismal Blood Flow Velocity and WSS Reduction Are Parameters to Predict Aneurysm Thrombosis. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, P.; Voß, S.; Saalfeld, S.; Janiga, G.; Bergersen, A.W.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Bruening, J.; Goubergrits, L.; Spuler, A.; Cancelliere, N.M.; et al. Multiple Aneurysms AnaTomy CHallenge 2018 (MATCH): Phase I: Segmentation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, A.; Boccadifuoco, A.; Celi, S.; Salvetti, M.V. Hemodynamics and Stresses in Numerical Simulations of the Thoracic Aorta: Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis to Inlet Flow-Rate Waveform. Comput. Fluids 2021, 230, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, S.; Morbiducci, U.; Gallo, D.; Ponzini, R.; Rizzo, G.; Bignardi, C.; Passoni, G. Uncertainty Propagation of Phase Contrast-MRI Derived Inlet Boundary Conditions in Computational Hemodynamics Models of Thoracic Aorta. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 20, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
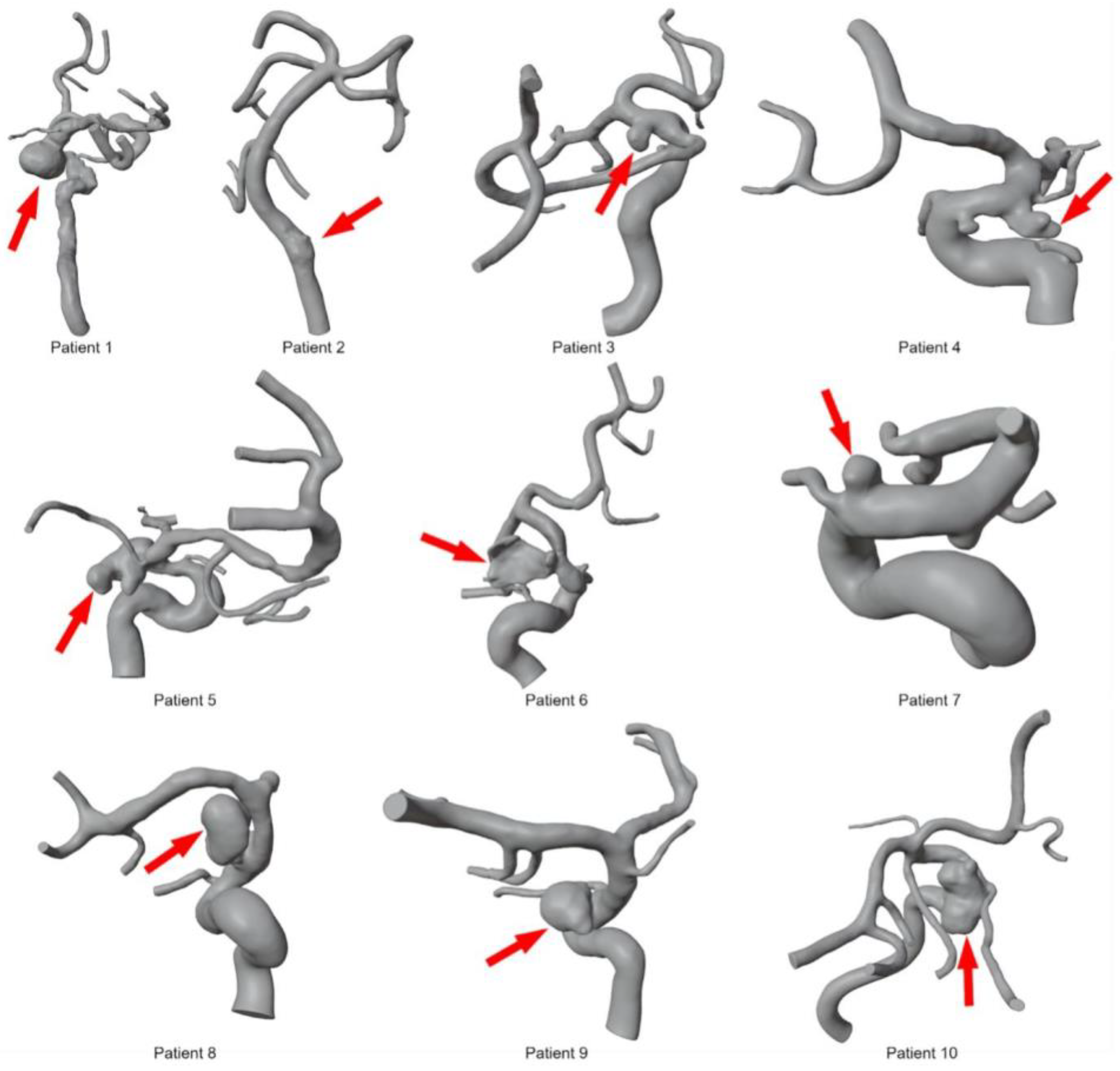

| Pat. Nr. | Sex | Age | Location | Morphology | Ruptured y/n | Aneurysm Size (mm) (Max-Neck-Dome) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | female | 67 | ICA C6 | saccular | n | 10-7-14 |
| 2 | male | 54 | Vertebral artery V4 | saccular | n | 2.5-5-5 |
| 3 | female | 63 | ICA C7 | blister | n | 3-2-4 |
| 4 | female | 78 | Posterior communicating artery | saccular | y | 5.3-3.3-4.3 |
| 5 | female | 88 | Posterior communicating artery | saccular | y | 13.5-7-7.5 |
| 6 | male | 66 | ICA C6 | saccular | n | 5-4-4 |
| 7 | female | 43 | MCA M1/M2 | saccular | n | 2-2-2 |
| 8 | female | 49 | ICA C7 | dissecting | y | 3-3.5-2.5 |
| 9 | female | 51 | ICA C6 | saccular | n | 6-1.8-6.5 |
| 10 | female | 64 | ICA C6 | saccular | n | 7-11-3.45 |
| Patient | FD Size | In Vivo- Length | Virtual Length | % ∆ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 5.5 × 30 | 58.6 | 47.08 | −20% |
| 02 | 5 × 25 | 38.9 | 39.71 | 2% |
| 03 | 5 × 25 | 34.66 | 37.84 | 9% |
| 04 | 5 × 20 | 31.818 | 33.71 | 6% |
| 05 | 5 × 20 | 37.42 | 43.04 | 15% |
| 06 | 5 × 15 | 30.56 | 32.21 | 5% |
| 07 | 4 × 20 | 29.33 | 32.6 | 11% |
| 08 | 4 × 15 | 22.5 | 23.686 | 5% |
| 09 | 4 × 15 | 22.48 | 24.51 | 9% |
| 10 | 3.5 × 15 | 19.85 | 19.66 | −1% |
| Patient | Location | Stent Diameter (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Simulation | In Vivo | ||
| 01 | Proximal | 3.77 | 3.46 |
| Min–Max | 2.09–4.55 | 2.82–5.67 | |
| Distal | 2.6 | 2.36 | |
| Aneurysm | 4.55 | 5.67 | |
| 02 | Proximal | 3.66 | 4.39 |
| Min–Max | 3.51–4.27 | 3.51–5.15 | |
| Distal | 3.57 | 3.61 | |
| Aneurysm | 4.14 | 5.15 | |
| 03 | Proximal | 4.13 | 4.32 |
| Min–Max | 3.17–5.23 | 2.30–4.71 | |
| Distal | 3.17 | 2.67 | |
| Aneurysm | 3.58 | 2.88 | |
| 04 | Proximal | 3.02 | 3.88 |
| Min–Max | 2.19–4.61 | 2.67–4.33 | |
| Distal | 2.59 | 3.45 | |
| Aneurysm | 2.44/2.36 | 3.48 | |
| 05 | Proximal | 3.94 | 4.12 |
| Min–Max | 1.42–4.11 | 0.92–4.12 | |
| Distal | 1.52 | 1.03 | |
| Aneurysm | 3.11 | 3.71 | |
| 06 | Proximal | 3.47 | 4.15 |
| Min–Max | 1.05–3.66 | 1.71–4.15 | |
| Distal | -- | 2.03 | |
| Aneurysm | 1.41 | 2.93 | |
| 07 | Proximal | 2.54 | 3.83 |
| Min–Max | 2.54–3.58 | 2.37–3.83 | |
| Distal | 2.6 | 2.95 | |
| Aneurysm | 3.19/2.68 | 3.11/2.85 | |
| 08 | Proximal | 3.52 | 3.91 |
| Min–Max | 2.66–4.11 | 2.18–4.14 | |
| Distal | 2.75 | 2.89 | |
| Aneurysm | 3.32 | 4.14 | |
| 09 | Proximal | 3.43 | 3.23 |
| Min–Max | 3.03–3.69 | 2.73–3.7 | |
| Distal | 3.27 | 3.34 | |
| Aneurysm | 3.69 | 3.7 | |
| 10 | Proximal | -- | 3.48 |
| Min–Max | 2.10–3.40 | 2.34–3.62 | |
| Distal | 3.36 | 2.58 | |
| Aneurysm | 2.65 | 3.62 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thormann, M.; Stahl, J.; Marsh, L.; Saalfeld, S.; Sillis, N.; Ding, A.; Mpotsaris, A.; Berg, P.; Behme, D. Computational Flow Diverter Implantation—A Comparative Study on Pre-Interventional Simulation and Post-Interventional Device Positioning for a Novel Blood Flow Modulator. Fluids 2024, 9, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9030055
Thormann M, Stahl J, Marsh L, Saalfeld S, Sillis N, Ding A, Mpotsaris A, Berg P, Behme D. Computational Flow Diverter Implantation—A Comparative Study on Pre-Interventional Simulation and Post-Interventional Device Positioning for a Novel Blood Flow Modulator. Fluids. 2024; 9(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleThormann, Maximilian, Janneck Stahl, Laurel Marsh, Sylvia Saalfeld, Nele Sillis, Andreas Ding, Anastasios Mpotsaris, Philipp Berg, and Daniel Behme. 2024. "Computational Flow Diverter Implantation—A Comparative Study on Pre-Interventional Simulation and Post-Interventional Device Positioning for a Novel Blood Flow Modulator" Fluids 9, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9030055
APA StyleThormann, M., Stahl, J., Marsh, L., Saalfeld, S., Sillis, N., Ding, A., Mpotsaris, A., Berg, P., & Behme, D. (2024). Computational Flow Diverter Implantation—A Comparative Study on Pre-Interventional Simulation and Post-Interventional Device Positioning for a Novel Blood Flow Modulator. Fluids, 9(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9030055






