Sonic Eddy Model of the Turbulent Boundary Layer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- an eddy must complete a rotation to do anything, such as entrain or transport momentum, and
- (ii)
- entrainment is an intrinsically non-steady process.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison with Experiment and DNS
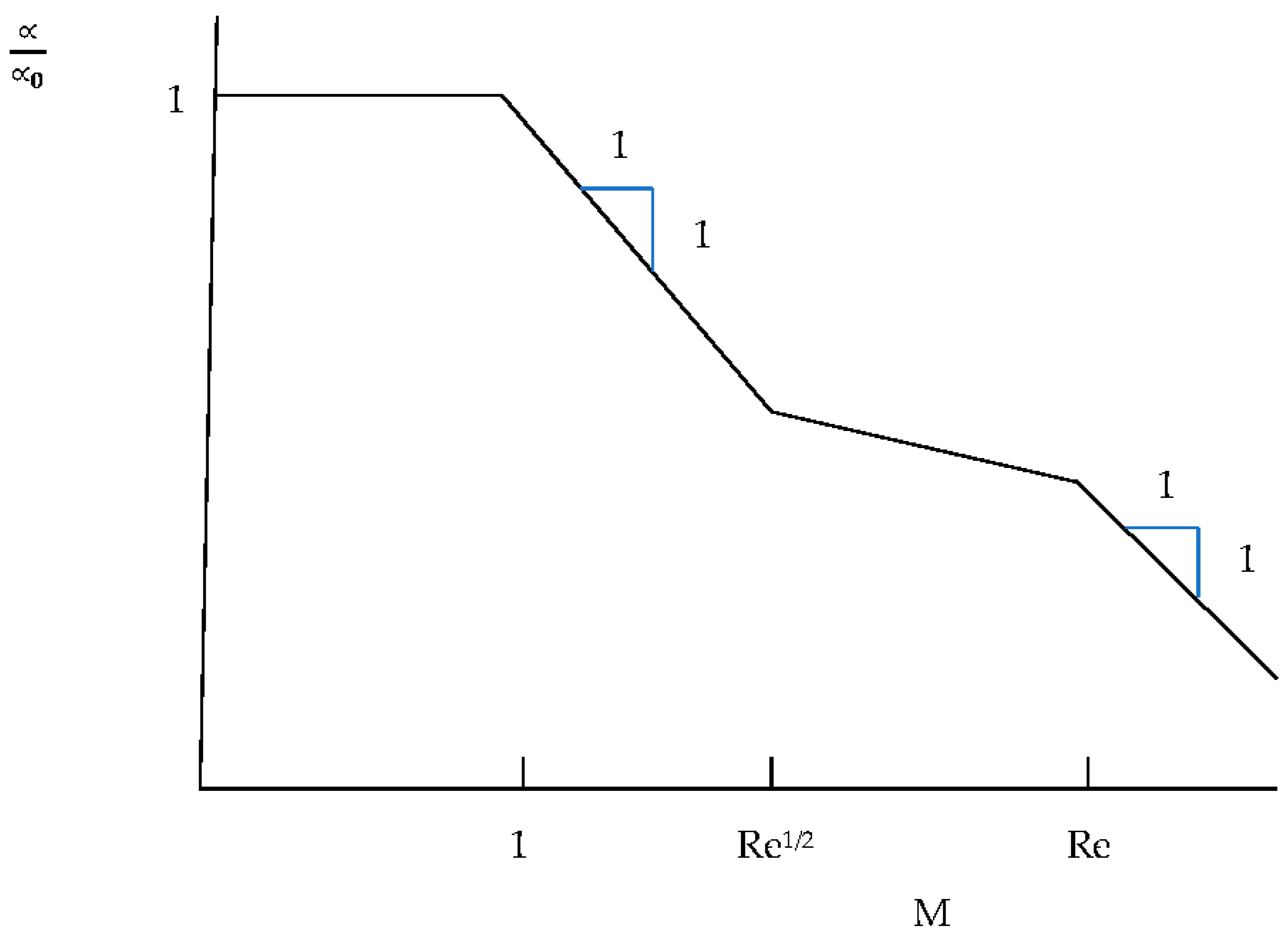
3.1.1. Skin Friction
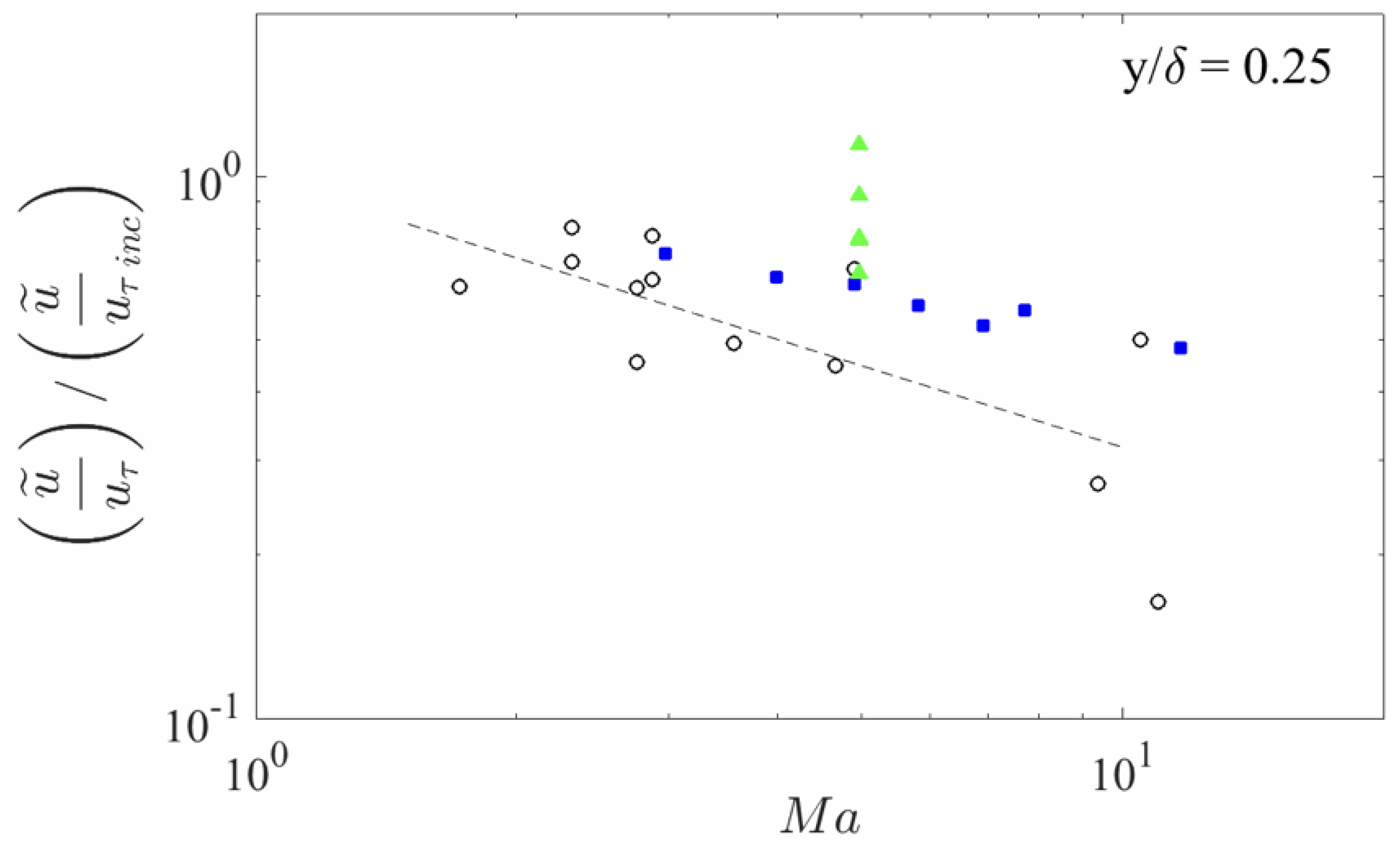
3.1.2. Velocity Fluctuations
3.1.3. Growth Rate
3.1.4. Eddy Celerity
3.1.5. Topology
3.2. Proposed New Experiment or Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roshko, A.; (California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA). Personal communication, 2016.
- van Driest, E.R. Turbulent Boundary Layer in Compressible Fluids. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1951, 18, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkovin, M.V. Effects of compressibility on turbulent flows. In Mecanique de la Turbulence; Favre, A.J., Ed.; Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS): Marseille, France, 1961; pp. 367–380. [Google Scholar]
- Breidenthal, R.E. Sonic eddy-A model for compressible turbulence. AIAA J. 1992, 30, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanoff, D.W. Compressible effects in turbulent shear layers. AIAA J. 1983, 21, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.K.; Winkler, E.M.; Persh, J. U.S. Naval Ordnance Laboratory Report 3880; U.S. Naval Ordnance Laboratory: White Oak, MD, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, D.E. The turbulent boundary layer in a compressible fluid. Appendix A: A manual of experimental boundary-layer practice for low-speed flow. In Rand Rep. R-403-PR, ARC 24473: Appendix A: A Manual of Experimental Practice for Low-Speed Flow; The Rand Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Liepmann, H.W.; Roshko, A. Elements of Gasdynamics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1957; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff, P.S. Characteristics of Turbulence in a Boundary Layer with Zero Pressure Gradient. In NACA TN 3178, 1954, and NACA TR 1247; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, IL, USA, 1955; pp. 1135–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Kistler, A.L. Fluctuation Measurements in a Supersonic Turbulent Boundary Layer. Phys. Fluids 1959, 2, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, C.C.; Owen, F.K. Turbulent Properties of a Compressible Boundary Layer. AIAA J. 1972, 10, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussoy, M.I.; Horstman, C.C. An Experimental Documentation of a Hypersonic Shock-Wave Turbulent Boundary Layer Interaction Flow with and without Separation. In NASA TM X 62,412; NASA Marshall Space Flight Center: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1975; p. 21554. [Google Scholar]
- Kussoy, M.I.; Horstman, C.C.; Acharya, M. An Experimental Documentation of Pressure Gradient and Reynolds Number Effects on Compressible Turbulent Boundary Layers. In NASA TM 78-488; US Gov. Public: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Laderman, A.J.; Demetriades, A. Turbulent Shear Stresses in Compressible Boundary Layers. AIAA J. 1979, 17, 79–4095. [Google Scholar]
- Elena, M.; Lacharme, J.; Galviglio, J. Comparison of hot-wire and laser Doppler anemometry methods in supersonic turbulent boundary layers. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Laser Anemometry, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 17–22 November 1985; pp. 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Spina, E.F.; Smits, A.J. Organized structures in a compressible, turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 182, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, E.F.; Donovan, J.F.; Smits, A.J. Convection velocity in supersonic turbulent boundary layers. Phys. Fluids A 1991, 3, 3124–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, C.B.; Spina, E.F.; Sheplak, M. Turbulence measurements in a Mach 11 helium turbulent boundary layer. In Proceedings of the AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–23 June 1994. Paper 94-2364. [Google Scholar]
- Konrad, W.; Smits, A.J. Turbulence measurements in a three-dimensional boundary layer in supersonic flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 372, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latin, R.M.; Bowersox, R.E.W. Flow properties of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer with wall roughness. AIAA J. 2000, 38, 1804–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekoto, I.W.; Bowersox, R.D.W.; Beutner, T.; Goss, L. Response of supersonic turbulent boundary layers to local and global mechanical distortions. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 630, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichenor, N.R.; Humble, R.A.; Bowersox, R.D.W. Response of a hypersonic turbulent boundary layer to favourable pressure gradients. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 722, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGraaff, D.B.; Eaton, J.K. Reynolds-number scaling of the flat-plate turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 422, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.L.; Ng, W.F.; Rettew, A.L.; Walker, D.A.; Schetz, J.A. Turbulence measurements in a high-speed shear flow using a dual-wire probe. In Proceedings of the AIAA 24th Joint Propulsion Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 11-13 July 1988. Paper 88-3055A. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, R.; (Rocketdyne, Los Angeles, CA, USA). Personal communication, 2016.
- Owen, F.K.; Horstman, C.C. Turbulence measurements in an equilibrium hypersonic boundary layer. In Proceedings of the AIAA 12th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 30 January–1 February 1974. Paper 74-93. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, O.; Sahoo, D.; Baumgartner, M.; Smits, A.J. Experiments on the structure and scaling of hypersonic boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 834, 237–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, L.; Beekman, I.; Martin, M.P. Direct numerical simulation of hypersonic turbulent boundary layers. Part 3. Effect of Mach number. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 672, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, L.; Beekman, I.; Martin, M.P. Direct numerical simulation of hypersonic turbulent boundary layers. Part 2. Effect of wall temperature. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 655, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breidenthal, R.E.; Dintilhac, P.; Williams, O. Sonic eddy model of the turbulent boundary layer. In Proceedings of the APS Fluid Dynamics Annual Meeting, Portland, Oregon, 20–22 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Roshko, A.; (California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA); Thomke, G.J.; (Douglas Aircraft Company, Santa Monica, CA, USA). Douglas Aircraft Aero Physics Tri-Sonic Wind Tunnel. Personal communication, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.L.; Roshko, A. On density effects and large structure in turbulent mixing layers. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 64, 775–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clements, N.T.; Mungal, M.G. Two- and three-dimensional effects in the supersonic mixing layer. AIAA J. 1992, 30, 90–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Papamoschou, D. Zones of influence in the compressible shear layer. Fluid Dyn. Res. 1993, 11, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimotakis, P.E. Two-dimensional shear-layer entrainment. AIAA J. 1986, 24, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dintilhac, P.; Breidenthal, R. Sonic Eddy Model of the Turbulent Boundary Layer. Fluids 2022, 7, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010037
Dintilhac P, Breidenthal R. Sonic Eddy Model of the Turbulent Boundary Layer. Fluids. 2022; 7(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDintilhac, Paul, and Robert Breidenthal. 2022. "Sonic Eddy Model of the Turbulent Boundary Layer" Fluids 7, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010037
APA StyleDintilhac, P., & Breidenthal, R. (2022). Sonic Eddy Model of the Turbulent Boundary Layer. Fluids, 7(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids7010037