Abstract
Recently, our collaborative work in the fabrication of a magnetorheological fluid (MRF) containing high magnetization FeCo nanoparticles (NPs, fabricated in our laboratories using the chemical reduction technique; MS = 212 Am2/kg) as magnetic fillers have resulted in a new MRF with superior performance up to 616.7 kA/m. The MRF had a yield stress value of 2729 Pa and good reversibility after a demagnetization process. This value competes with the best ones reported in the most recent literature. Nevertheless, the fabrication process of this type of fluid is not an easy task since there is a strong trend to the aggregation of the FeCo NPs due to the strong magnetic dipolar interaction among them. Thus, now we present the analysis of some aspects concerning the fabrication process of our FeCo NPs containing MRF, mainly the type of surfactant used to cover those NPs (oleic acid or aluminium stearate) and its concentration, and the procedure followed (mechanical and/or ultrasound stirring) to achieve a good dispersion of those magnetic fillers within the fluid.
1. Introduction
Magnetorheological (MR) fluids are widely known as “intelligent” fluids due to their ability to exhibit reversible rheological behaviour that can be controlled by the application of an external magnetic field. That is, they are a new class of materials whose performance can be adapted to variable working conditions [1,2,3].
The magnetorheological fluid is composed of magnetic particles (or fillers) dispersed within a liquid carrier. Ideally, under no applied magnetic field, no magnetic interaction appears among the magnetic fillers and the observed MR behaviour is Newtonian-type, corresponding to a suspension of non-interacting particles. However, in real cases, there is always a weak magnetic interaction among those magnetic fillers owing to their remnant magnetization. The application of an external magnetic field makes the magnetic fillers exhibit a net magnetic moment, resulting in an attractive magnetostatic interaction among those magnetic particles. As a first consequence, chain-like structures directed along the direction of the applied field are formed. At the same time, the fluid suffers a very fast transition from a liquid to an almost solid-state, and now finite stress (the so-called yield stress) is needed to break the chain-like structures constructed by the magnetic fillers. On the one hand, it is already well known that this magnetic field-induced stress rises quadratically with the saturation magnetization of the magnetic particle [4,5]. On the other hand, the maximum field value of the yield stress will occur when the aligned particles become magnetically saturated. That is, while the magnetization process of the magnetic particles occurs when applying the external magnetic field, the flow of the fluid is hindered and the rheological behaviour changes to that of plastic material, with big changes in its viscosity and high values of the corresponding yield stress [6,7].
To date, the main goal in research about MRFs is to achieve high yield stress values and controllable rheology magnetic fluids. For this purpose, an exhaustive knowledge of the constituents of the MRF, as well as of the fabrication process is needed. This knowledge concerns not only the magnetic particle used (composition, size and morphology, magnetic properties) but also the liquid carrier (chemical properties and viscosity) and other additives often used to improve magnetic particle aggregation and preventing their sedimentation. The aim has also been to control the final fluid viscosity, stability and reversibility of the exhibited magneto-rheology [8,9,10].
In previous work, the authors gave detailed information on a new magnetorheological fluid fabricated with high magnetization FeCo nanoparticles as magnetic fillers. Our results showed superior performance with applied magnetic fields of about 616.7 kA/m, with a yield stress value of 2729 Pa and good reversibility after a demagnetization process [11]. This yield stress value competes with the best ones reported in the most recent literature [12,13].
Nevertheless, within Reference [11], there is a lack of description about the full fabrication process to get the final product (or FeCo-MRF). Bearing this in mind, we offer an extensive overview of the work done concerning the magnetic nanoparticles’ trend to aggregation within the fluid and how to get their dispersion and the MRF stability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Aiming to further apply our fabricated FeCo-MRF to industry, we used as the liquid carrier, the widely known mineral oil [14]. It was purchased from Acros OrganicsTM (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) and had a density of 0.8697 g/cm3 (as determined by an Anton Paar DMA 500 densimeter) and a refractive index of 1.4766 (as determined by an RXA 156 refractometer). This mineral oil showed a viscosity of 123.79 mPa·s at 25 °C, as determined using an Anton Paar MCR 501 rotational rheometer working in a parallel disk configuration. For this last measurement, deformation velocity was continuously varied from 10 to 200 s−1.
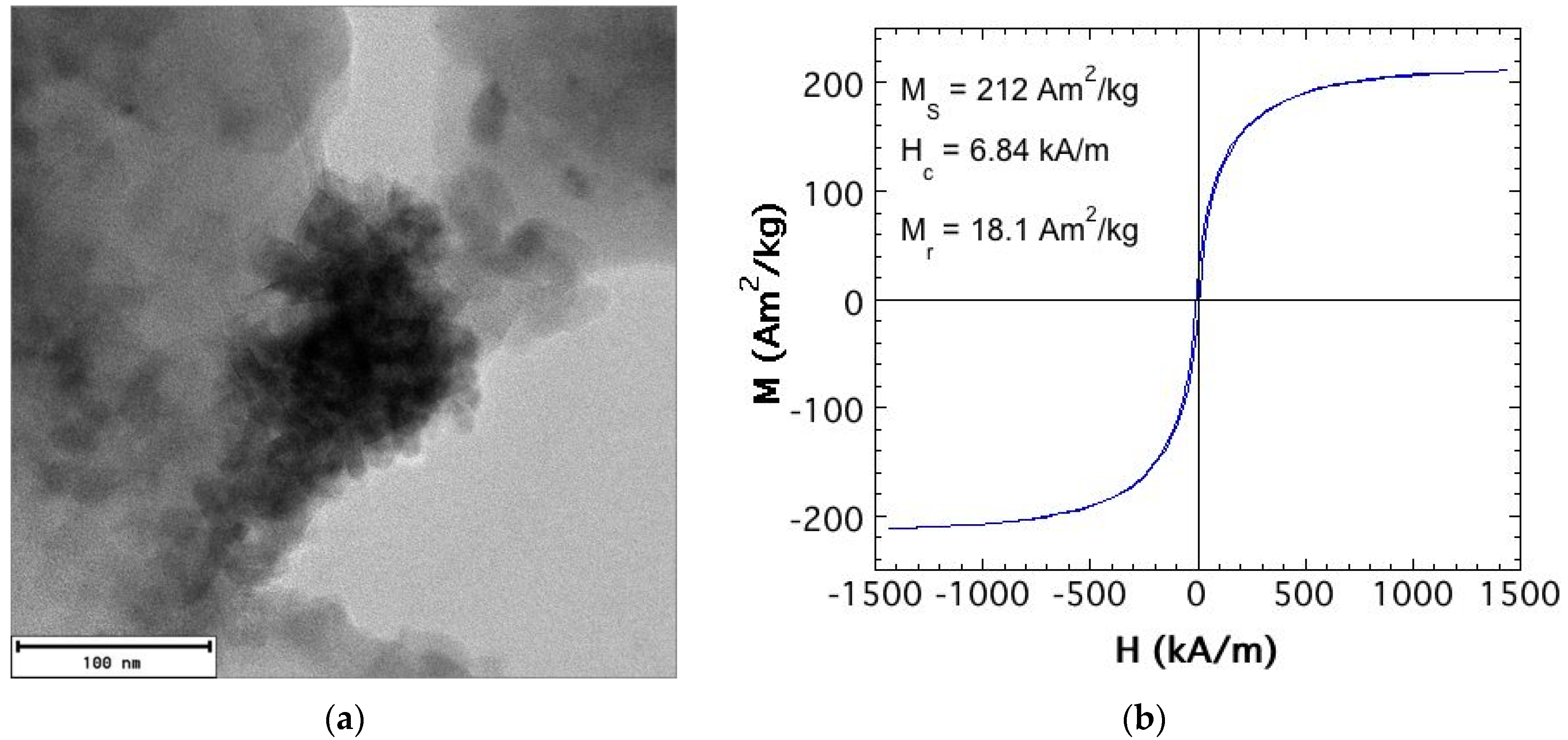
Concerning the magnetic filler (particle) to be added to the liquid carrier, the best performance was observed when they showed high saturation magnetization and magnetic permeability values, and low coercitivity strength [15,16]. That is soft magnetic particles. We used Fe47Co53 nanoparticles synthesized following the chemical reduction technique [17,18]. Exhaustive information about the fabrication procedure and the characterization of the final powder can be found in [11]. Briefly, they show a saturation magnetization value of MS = 212 Am2/kg, higher than that of pure Fe nanoparticles (see, for example, Reference [5]), coercitivity field of 6.84 kA/m, and magnetization remanence of Mr = 18.1 Am2/kg. In other words, they are high magnetization FeCo soft magnetic NPs. As probed by TEM imaging, the single nanoparticles were 30–500 nm in size, but they easily agglomerated to form clusters in the 200–500 nm range (see Figure 1).
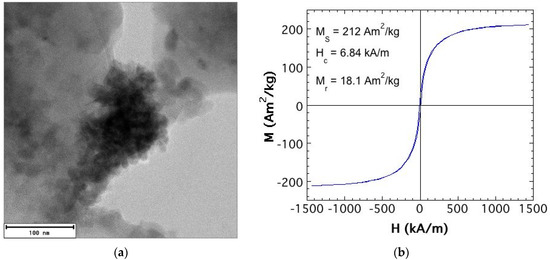
Figure 1.
(a) TEM microphotograph of an agglomerate (about 200 nm in size) of the synthesized FeCo single nanoparticles (about 30–50 nm in size); (b) Room temperature hysteresis loop of the FeCo nanoparticle powder obtained after fabrication by the chemical reduction technique.
To avoid such nanoparticle aggregation within the fluid that should reflect irreversible magnetorheological behaviour, we used and analyzed two different surfactant types to favor the desired dispersion of the nanoparticles: oleic acid (OA) and aluminium stearate (AlSt). Oleic acid is a fatty acid with the formula C18H34O2 and was purchased from VWR Chemicals. Its density was 0.8946 g/cm3 at 20 °C, following its technical specifications. This fatty acid is an amphiphilic compound with a polar positive head and a non-polar tail.
On the other hand, Al(III) stearate (Al(C18H35O2)3) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich. This is a salt formed by the stearate acid with also a hydrocarbon chain of 18 C but, unlike oleic acid, it does not contain one double bond.
Finally, and even if the stability of the synthesized fluid is already favored by the small size of the magnetic filler used (at the nanoscale), we added Aerosil 300 (Fumed silica) as a viscosifying agent. It was composed of nanoparticles in the range 5 to 50 nm that also aggregated and led to an increase in the viscosity of the final fabricated fluid.
2.2. Fabrication and Characterization of the Magnetorheological Fluids
The synthesis of the magnetorheological fluids studied in this work started with the corresponding amount of the liquid carrier, in our case mineral oil. Afterward, the Aerosil 300 viscosifying agent was added in the proportion of 1 g Aerosil/40 g of mineral oil. The mixture was then homogenized in two steps. First by using ultrasonic stirring for 5 min with the Transonic TI-HZ device. Second, by using mechanical stirring for 5 min with the Heidolph RZR 2051 device. This first step was common to all magnetorheological fluids fabricated.
The next step involves the addition of the employed surfactant in the desired concentration for the number of nanoparticles to be added. In the case of oleic acid, 28.49 mg AO/1 g FeCo NPs. For the aluminium stearate case, 6.51 mg AlSt/1 g FeCo NPs.
Finally, a 10%vol. content of FeCo NPs was added in a two-step procedure. First, 50% of these NPs amounts were added to the previously prepared mixture and dispersed first by 5 min of ultrasound stirring followed by 5 min of mechanical stirring. The remaining 50% of the FeCo NPs were added to the fluid and first dispersed by 5 min of ultrasound stirring, and subsequently, stirred mechanically for 24 h at a speed of 150 rpm.
Table 1 shows all the fluids synthesized by following the previous procedure. All served to analyze the influence of different parameters during the fabrication process, as the surfactant type (oleic acid, -OA; aluminium stearate, -AlSt), the influence of the mixing process of the constituents (-MS: only mechanical stirring; -US: ultrasound stirring followed by mechanical stirring), and the surfactant concentration (-OA: 28.49 mg OA/1 g FeCo NPs; -2OA: twice the -OA value; -4OA: four times the -OA value).

Table 1.
Summary of the different magnetorheological fluids analyzed in this work.
That is, seven different fabricated MRFs. For all the fluids previously fabricated, the magneto-rheological behaviour was measured. For this purpose, an Anton Paar Physica MCR 501 rotational rheometer plus the cell MRD-70/1T (fed with an electrical current in the range 0 to 5 A) was used to apply the desired magnetic field. Measurements were made in a parallel disk configuration, and the magnetic field was applied perpendicular to the shear plane. That externally applied magnetic field ranged from 0 to 616.7 kA/m, and after each characterization measurement, a demagnetization cycling procedure was applied. In this way, the shear stress value was measured as a function of shear rate and applied magnetic field, simultaneously.
The magneto-rheological characterization was performed in three steps: (i) the cell containing the MR fluid spins at 140 rpm for 30 s to homogenize it; (ii) the corresponding magnetic field for the measurement was applied for 30 s, and then (iii) the characterization started. The applied magnetic field was kept constant while the shear rate increased in the range 0.01 to 600 s−1. The shear rate change was chosen to be logarithmic so that more data could be measured at low shear rate values. For a better accuracy on each shear stress value, measurement lasted for 3 s and 60 values of that measured shear stress were averaged.
Reversibility of all the studied MRFs was performed in three steps. (i) The desired magnetic field was applied. (ii) The fluid followed a demagnetizing process. (iii) The rheological behaviour at zero applied field was measured. In this way, we could determine the capability of each fluid to recover its rheology to the initial situation when no applied magnetic field was acting on it.
All these rheological characterization measurements were performed at 25 °C, being the temperature controlled by using a Refrigerated Heating Circulator Julabo F 25-MC.
3. Results
3.1. Magnetorheologic Behaviour
In all cases (all the fluids appearing in Table 1), we observed that under application of an external magnetic field, our fabricated MR fluids showed a non-Newtonian [16,19] behaviour. This fact made the conversion proposed by DIN 53018 [20] between the physical data of the rheometer (rotation speed and torque) and rheological parameters (shear rate and shear stress) not to be applicable in the present case. Thus, a correct analysis of the data was performed by applying the Rabinowitsch conversion method [21,22].
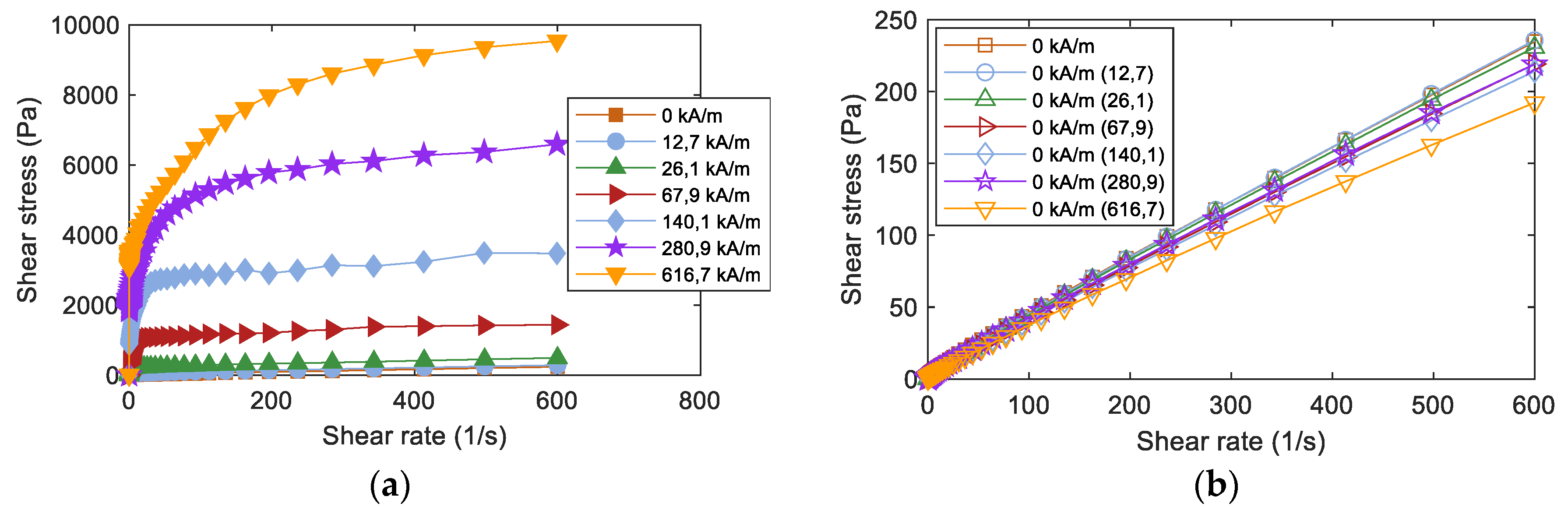
All the studied fluids showed a similar strong magnetorheological response, with increasing shear stress values as the magnetic field intensity increased. An example of such behaviour can be seen in Figure 2a. The yield stress value is one of the main parameters that can be extracted from the measured rheological curves under the application of an external magnetic field. To account for this value, the obtained data from rheological measurements were fitted using the Herschel-Bulkley (HB) model [23] that accounts for the parametric description of the rheological post-yield behavior of both magnetic fluids as a function of the magnetic field intensity:
where is the shear stress, is the yield stress, is the shear rate, K is the consistency index (that gives an idea about the viscosity of the fluid), and n is the pseudo-plasticity or flow behaviour index.
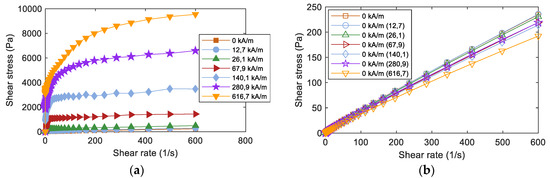
Figure 2.
(a) Obtained rheological curves as a function of the applied magnetic field; (b) Reversibility of the rheological curves after applying a magnetic field and subsequent demagnetizing process. Measurements shown correspond to the nominal fluid FeCo-MRF-OA-MS.
The first observation was that all the obtained τ0 yield stress values were in a close range between 2100 and 2600 Pa. K values indicated that the MRFs were much more viscous as the magnetic field was applied. Moreover, we considered that for pseudo-plastic fluids, it is usually n < 1 [24,25]. From the obtained values of the n index, we could affirm that the post-yield behaviour, for all the studied fluids, was pseudoplastic.
Looking to the reversibility of the response of the MRFs, measurements were made in a two-step process. First, by measuring at a zero applied magnetic field. Second, by measuring again at a zero applied magnetic field but now this zero intensity was obtained after applying different intensities of the magnetic field and the subsequent application of a demagnetization process to the fluid. Figure 2b shows such reversibility measured curves for the nominal fluid FeCo-MRF-OA-MS. All these measurements were made up to a shear rate of 600 s−1. To give a number to the degree of reversibility in the performance of the studied MRFs, we calculated the difference:
where is the yield stress value (at the maximum shear rate of 600 s−1) measured when no magnetic field was acting upon the fluid, and is the yield stress value (at the maximum shear rate of 600 s−1) measured when the maximum magnetic field (616.7 kA/m) plus the subsequent demagnetization process to reach again zero magnetic fields were applied.
3.2. Influence of the Surfactant Type
Our laboratory fabricated FeCo nanoparticles showed a strong tendency to aggregation, as previously mentioned, also translating when immersed in a fluid. The reason for this fact arose from the strong magnetic dipolar interaction among them due to their high magnetization value. Thus, dispersing as best as possible those NPs within the fluid was the first task of our study. For this purpose, it is well known that the use of an adequate surfactant favors the performance of the fabricated MRF. The surfactant will surround the magnetic nanoparticles hiding to a certain degree the magnetic interaction among them. Following this line of reasoning, we tested two different surfactants: Aluminium (III) stearate (AlSt), which is widely used in the fabrication of magnetorheological fluids, and oleic acid (OA).
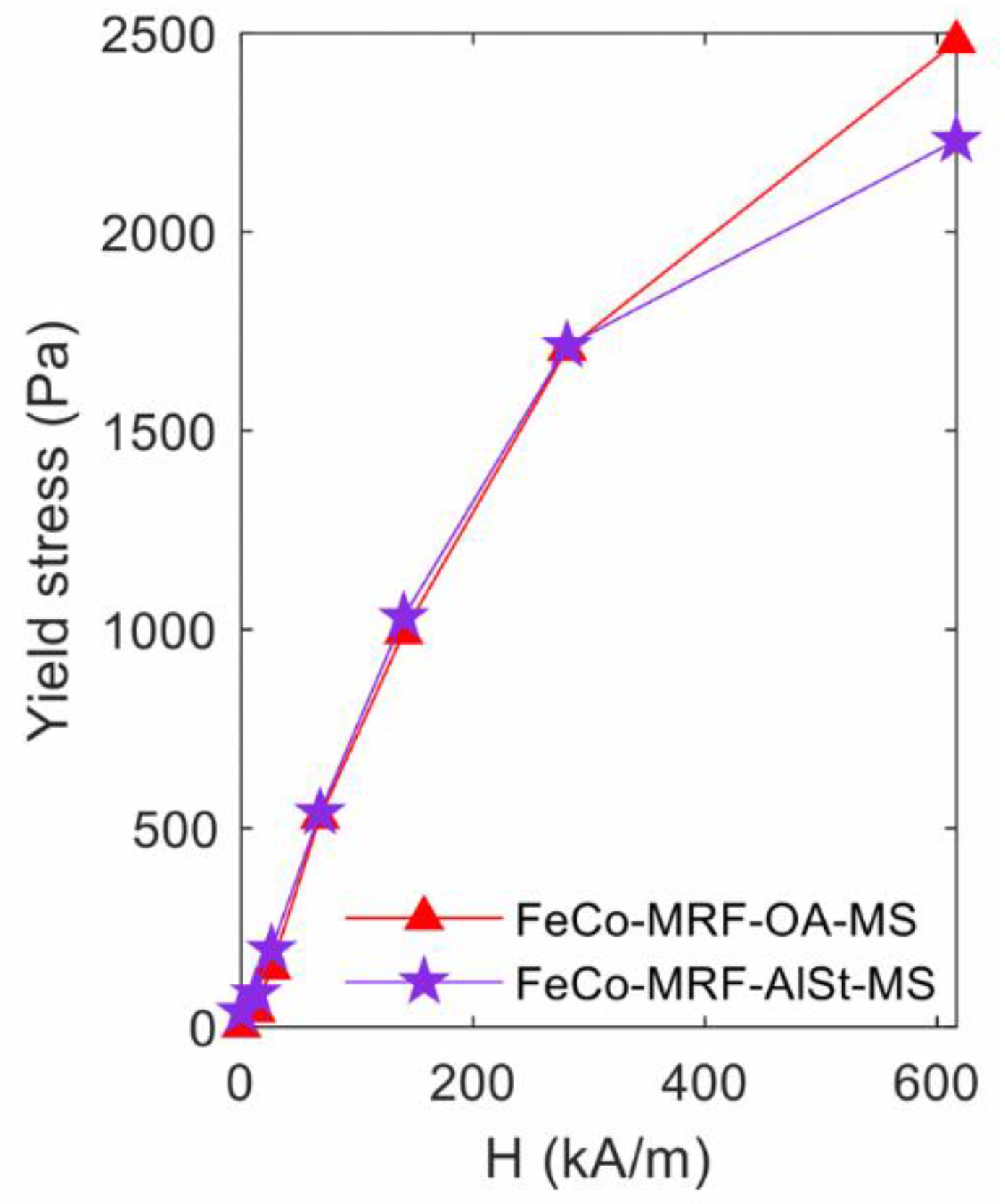
Figure 3 shows the yield stress values measured as a function of the applied magnetic field, for both fabricated fluids. As the intensity of the applied magnetic field increased, the measured yield stress value increased, and with the same results for both types of surfactants. Nevertheless, at the maximum applied magnetic field of 616.7 kA/m, the HB method fit value was 10% lower for the fluid containing aluminium stearate (FeCo-MRF-AlSt-MS) as it appears in Table 2.
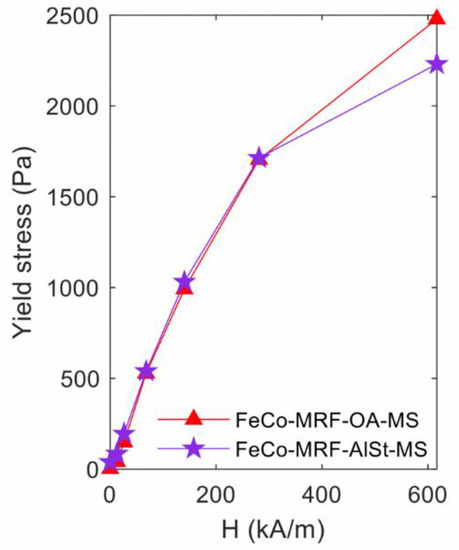
Figure 3.
Influence of the surfactant type: yield stress values obtained from the fit to the Herschel-Bulkley expression, for the different applied magnetic field intensities.

Table 2.
Summary of the values of the different parameters obtained when using the Herschel-Bulkley model, for all the magnetorheological fluids analyzed in this work.
On the contrary, at zero magnetic fields, the fluid containing aluminium stearate showed higher stress values at the maximum shear stress than the one containing the oleic acid (see values in Table 3). Despite this fact, the degree of reversibility estimated for both fluids was higher (77.8%) for the FeCo-MRF-OA-MS than for the FeCo-MRF-AlSt-MS. This lasted with only a 53.5% degree of reversibility.

Table 3.
Values of the stress measured at the maximum shear rate (600 s−1) under different applied magnetic field conditions, for the two different surfactants studied.
From our measurements, it was easy to infer that searching for good reversibility of our fabricated MRF, oleic acid worked better as a surfactant than aluminium(III) stearate. There were two main differences between these surfactants. Despite both of them having a hydrocarbon chain of 18 C, stearate is in the form of an organometallic compound with an Al3+ cation and the organic chain does not contain an unsaturated double bond like oleic acid. The dispersion of FeCo NPs in the oils would be favored with only amphiphilic chains with a polar head attached to iron and cobalt atoms on the external surface of the NPs and tails immersed in the oil [26]. In the case of the stearate, Al3+ ions must also be accommodated around the NPs, which could make an adequate dispersion difficult. Moreover, the interaction between double bonds in oleic acid could also assist to stabilize densely packed layers on the surface of the nanoparticles.
As a first consequence, in the following sections, all appearing magnetorheological fluids were synthesized using OA as a surfactant constituent.
3.3. Influence of the Dispersion of the Magnetic Nanoparticles
We also studied the influence of the degree of dispersion of the FeCo nanoparticles on the magnetorheological behaviour exhibited by the fabricated fluids. To do this, we have used an MRF of identical composition (constituents and quantities), but in one of them, the process of mixing the magnetic FeCo NPs was mechanical stirring at 150 rpm for 24 h (FeCo-MRF-OA-MS fluid). Meanwhile, for the other first, we applied ultrasound stirring for 12 h followed by mechanical stirring at 150 rpm for 12 h (FeCo-MRF-OA-US fluid).
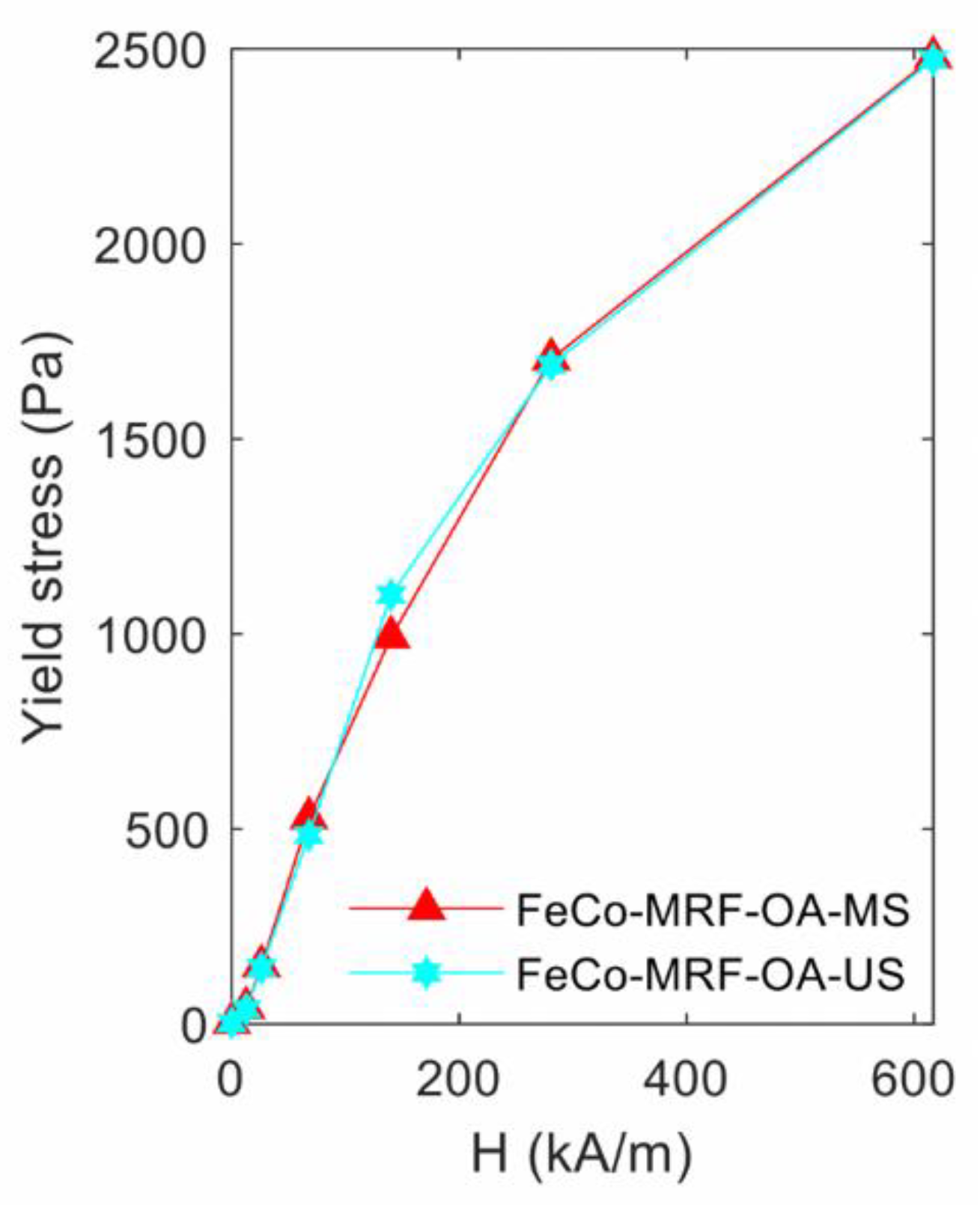
Figure 4 shows the obtained yield stress values when using the Herschel-Bulkley method fit. The first observation told us that at the maximum applied magnetic field of 616.7 kA/m, the HB method fit value was practically the same (above 2470 Pa) for both fabricated fluids. No clear conclusion can be extracted from these measurements. Nevertheless, and at the same time, the K value was 12% higher for the FeCo-MRF-OA-US fluid, as shown in Table 2. That is, this fluid was a bit more viscous than the FeCo-MRF-OA-MS fluid. However, and despite its lower viscosity, for the FeCo-MRF-OA-MS fluid, the degree of reversibility was lower (77.8%) than for the FeCo-MRF-OA-US one (89.4%), as shown in Table 4.
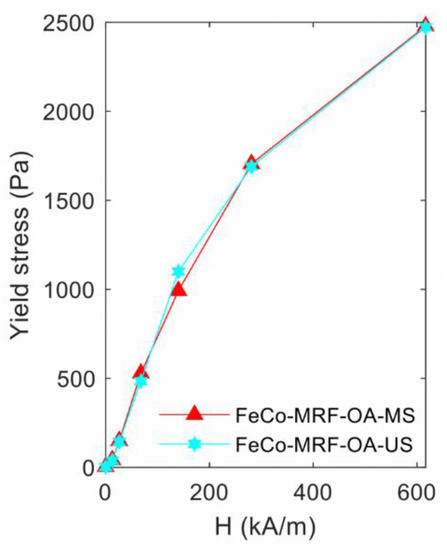
Figure 4.
Influence of the magnetic nanoparticles dispersion method: yield stress values obtained from the fit to the Herschel-Bulkley expression, for the different applied magnetic field intensities.

Table 4.
Values of the stress measured at the maximum shear rate (600 s−1) under different applied magnetic field conditions, for the two different magnetic filler dispersion methods.
The FeCo-MRF-OA-US fluid was fabricated by applying both ultrasound and mechanical stirring procedures. This procedure favors: (i) the FeCo NPs to be covered by the oleic acid surfactant, and (ii) that the size of the NPs or their aggregates was smaller than when the fluid was fabricated using only the mechanical stirring mixing process. In opposition, when using only mechanical stirring, big aggregates should remain within the fabricated fluid, giving rise to the observed high viscosity as deduced from the yield stress and consistency index values, K.
3.4. Influence of the Concentration of Oleic Acid (Surfactant) Used
Finally, we studied the influence of the concentration of the surfactant used (oleic acid) in the magnetorheological properties of the fabricated fluids. Tested surfactant concentrations were: -OA: 28.49 mg AO/1 g FeCo NPs; -2OA: twice the -OA value; -4OA: four times the -OA value. Moreover, to validate our previous observations, MRF fluids were fabricated not only by the mechanical stirring (-MS samples) mixing process but also using both the ultrasound and mechanical stirring (-US samples) procedures. From values obtained by the HB fit method (see Table 2), we observed an increase from 2479 to 2571 Pa of the values as the amount of oleic acid increased for the -MS fabricated fluids. For the case of -US fabricated fluids, there was no clear trend and the values ranged between 2189 to 2472 Pa.
Nevertheless, measurements under zero applied for the magnetic field showed that, in all cases, the same trend was observed both for -MS and -US fabricated fluids. There was a continuous increase in the measured value as the concentration of surfactant used increased. Besides this fact, measured values of were higher for the -US fabricated fluids than for the -MS fabricated ones (see data in Table 5 and Table 6).

Table 5.
Values of the yield stress measured at the maximum shear rate (600 s−1) under different applied magnetic field conditions, for the -MS fabricated fluids with different oleic acid surfactant concentrations studied.

Table 6.
Values of the yield stress measured at the maximum shear rate (600 s−1) under different applied magnetic field conditions, for the -US fabricated fluids with different oleic acid surfactant concentrations studied.
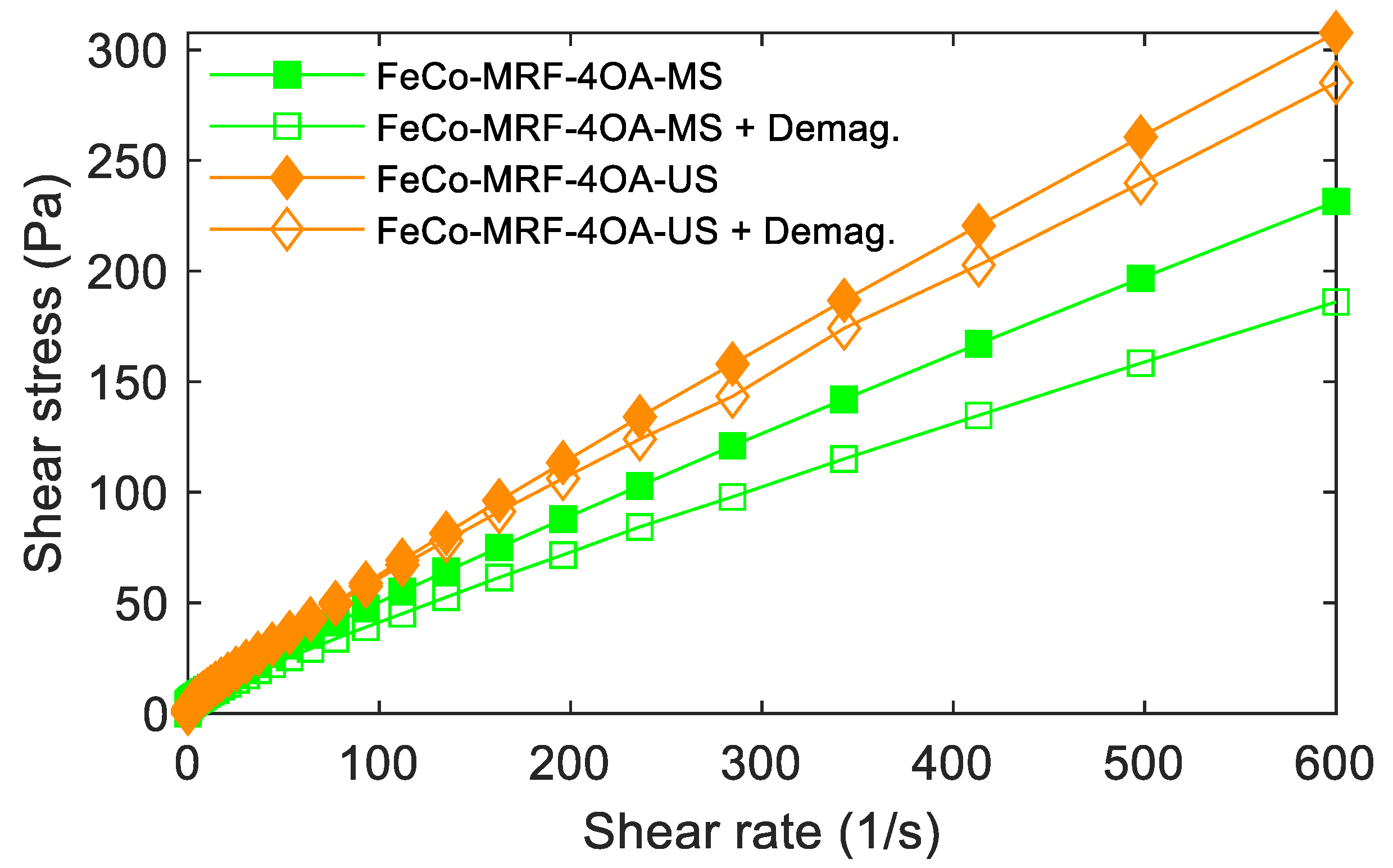
As previously described in Section 3.1. Magnetorheological behaviour, the reversibility of the response of the MRFs was studied in a two-step process. First, by measuring at a zero applied magnetic field. The second step, by measuring again at a zero applied magnetic field but with zero intensity obtained after applying different intensities of the magnetic field and subsequent application of a demagnetization process to the fluid. Figure 5 shows an example of such type of measurements for the FeCo-MRF-4OA-MS and FeCo-MRF-4OA-US fluids.
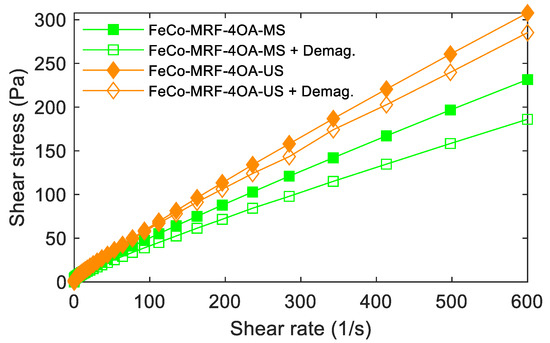
Figure 5.
Reversibility behaviour was observed for the MRFs fabricated with the maximum amount of oleic acid (-4OA). Curves measured at 0 kA/m applied magnetic field (full symbols) and after applying 616.7 kA/m, plus the subsequent demagnetization process to reach a zero magnetic field (open symbols).
At a single glance, we observed that the -US fabricated fluids showed better reversibility behaviour. This was an 80,4% maximum value for the FeCo-MRF-4OA-MS fluid, while for the FeCo-MRF-4OA-US fluid, this reversibility reached an excellent 92.7%. This was explained by the hypothesis that higher quantities of oleic acid would not strictly increase the number of molecules of oleic acid recovering each nanoparticle. Raw calculations of the number of molecules of oleic acid on the nanoparticles (around 17.060 molecules per NP for the -OA concentration, on a particle surface of 5026 nm2) together with our results suggested that the increasing amounts of -2OA and -4OA would participate in the mixing process with the oil, instead of the attachment to the NP surface.
In the following section, we give a summary and overview and further discuss our observations.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
In the previous sections, we extensively discussed the influence of several factors on the fabrication of MRFs containing high magnetization FeCo nanoparticles. Our findings can be summarized as:
- Oleic acid (OA) works better than aluminium stearate (AlSt) as a surfactant for FeCo nanoparticles.
- Ultrasound stirring (12 h) followed by mechanical stirring (+12 h; -US fluids) shows a better reversibility behaviour of the fabricated MRFs, most probably due to a better dispersion of FeCo nanoparticles within the fluid than when only the mechanical stirring (24 h; -MS fluids) procedure is used.
- Increasing the concentration of the surfactant oleic acid up to 113.96 mg AO/1 g FeCo NPs (-4OA) gives as a result of an MRF with excellent reversible behaviour, up to 92,7% after applying a 616.7 kA/m magnetic field and subsequent demagnetizing process.
That is, the final fluid fabricated with nominal denomination FeCo-MRF-4OA-US shows good magnetorheological behaviour with excellent reversibility after the demagnetisation process. Table 7 shows a brief comparison with other recent results within this research field, showing that our final product competes well with results obtained from other authors.

Table 7.
Comparison of different MR fluids prepared with nanoparticles of Fe and FeCo as magnetic fillers. Adapted from Table 2 in [11].
The future collaborative work between the UPV/EHU (University of the Basque Country) and MGEP (University of Mondragon) in the fabrication of magnetorheological fluids (MRFs) containing high magnetization nanoparticles should point to different (but essential) questions concerning the performance of the fabricated fluid. To test new mineral oils as liquid carriers and to study and improve other aspects of their performance, as the important task of particle sedimentation.
Author Contributions
Magnetic nanoparticles fabrication and characterization: V.V., M.I. and I.G.d.M.; magnetorheological fluids fabrication and characterization: A.G., V.V., J.B. and M.M.B.-A.; data analysis: A.G. and V.V.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G.; writing—review and editing, J.G., M.I., M.M.B.-A., J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
All the authors want to thank the financial support provided by the Basque Government under the MMMfavIN (KK-2020/00099, Elkartek program) and also the Research Groups (IT1009-16, IT1226-19 and IT1245-19) projects.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to current research project privacy.
Acknowledgments
Technical and human support provided by the General Research Services of the UPV/EHU (SGIker) is gratefully acknowledged. In particular, the technical help received and the fruitful discussions with Iñaki Orue.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Carlson, J.; Jolly, M.R. MR fluid, foam and elastomer devices. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F. A Review of the State of the Art in Magnetorheological Fluid Technologies—Part I: MR fluid and MR fluid models. Shock Vib. Dig. 2006, 38, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vicente, J.; Klingenberg, D.J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Magnetoreological fluids: A review. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Carlson, J.D.; Muñoz, B.C. A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasategi, J.; Gomez, A.; Bou-Ali, M.M.; Gutiérrez, J.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Beketov, I.V.; Safronov, A.P.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Fe nanoparticles produced by electric explosion of wire for new generation of magneto-rheological fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M. Behaviour of magnetorheological fluids. MRS Bull 1998, 23, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossis, G.; Volkova, O.; Lacis, S.; Meunier, A. Magnetorheology: Fluids, Structures and Rheology in Ferrofluids; Odenbach, S., Ed.; Springer: Bremen, Germany, 2002; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- de Vicente, J.; López-López, M.T.; González-Caballero, F.; Durán, J.D.G. Rheological study of the stabilization of magnetizable colloidal suspensions by addition of silica nanoparticles. J. Rheol. 2003, 47, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.C.; Karli, J.O.; Vavreck, A.N.; Zimmerman, D.T.; Ngatu, G.T.; Wereley, N.M. Magnetorheology of submicron diameter iron microwires dispersed in silicone oil. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 015028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzhir, P.; López-López, M.T.; Bossis, G. Magnetorheology of fiber suspensions. II. Theory. J. Rheol. 2009, 53, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadillo, V.; Gómez, A.; Berasategui, J.; Gutiérrez, J.; Insausti, M.; Gil De Muro, I.; Garitaonandia, J.S.; Arbe, A.; Iturrospe, A.; Bou-Ali, M.M.; et al. High magnetization FeCo nanoparticles for magnetorheological fluids with enhanced response. Soft Matter 2020, 17, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noma, J.; Abe, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Furusho, J.; Naito, M. Magnetorheology of colloidal dispersion containing Fe nanoparticles synthesized bythearc-plasma method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1868–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Qi, M. Iron nanoparticles-based magnetorheological fluids: A balance between MR effect and sedimentation stability. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 491, 165556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.D.; Nixon, D.A.; Carlson, J.D.; Margida, J.R. Thixotopic Magnetorheological Materials. U.S. Patent 5,645,752, 7 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Liu, S. Preparation and chemical stability of iron-nitride-coated iron microparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, S.; Phulé, P.P. Rheological properties of magnetorheological fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandapallil, B.; Colborn, R.E.; Bonitatibus, P.J.; Johnson, F. Synthesis of high magnetization Fe and FeCo nanoparticles by high temperature chemical reduction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 378, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klencsár, Z.; Németh, P.; Sándor, Z.; Horváth, T.; Sajo, I.E.; Mészáros, S.; Mantilla, J.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Garg, V.K.; Kuzmann, E.; et al. Structure and magnetism of Fe-Co alloy nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydar, G.; Evrensel, C.A.; Gordaninejad, F.; Fuchs, A. A low force magneto-rheological (MR) fluid damper: Design, fabrication and characterization. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 18, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung. Measurement of the Dynamic Viscosity of Newtonian Fluids with Rotational Viscometers; DIN 53018; Deutsches Institut fur Normung E.V. (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitsch, B. The viscosity and elasticity of sols. Z. Phys. Chem. 1929, 1, 26–145. [Google Scholar]
- Soskey, P.R.; Winter, H.H. Large Step Shear Strain Experiments with Parallel-Disk Rotational Rheometers. J. Rheol. 1984, 28, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, T.G. The Rheology Handbook; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Scott Blair, G.W.; Hening, J.C.; Wagstaff, A. The Flow of Cream through Narrow Glass Tubes. J. Phys. Chem. 1939, 43, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Karki, A.B.; Rutman, D.; Young, D.P.; Wang, A.; Cocke, D.; Ho, T.H.; Guo, Z. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite fibers reinforced with Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Fabrication and property analysis. Polymer. 2009, 50, 4189–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Renner, P.; Liang, H. Dispersion of Nanoparticles in Lubricating Oil: A Critical Review. Lubricants 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, F.; Lu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, Y.; Dong, X. Controlled synthesis of CoFe2O4/MoS2 nanocomposites with excel-lent sedimentation stability for magnetorheological fluid. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).