Turbulence Intensity and the Friction Factor for Smooth- and Rough-Wall Pipe Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
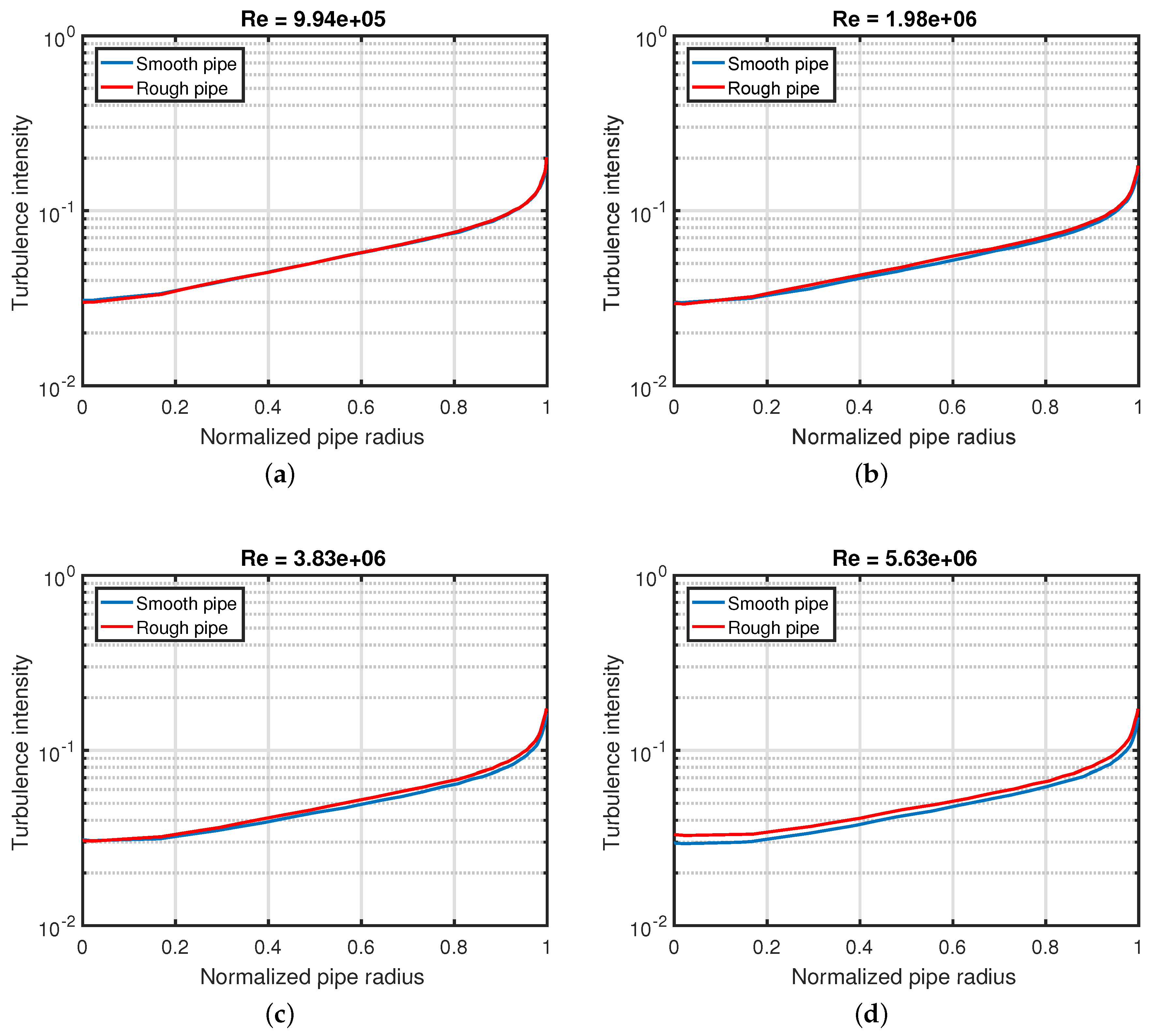
2. Turbulence Intensity Profiles
- The TIR on the axis is roughly one except for the highest , where it exceeds 1.1.
- In the intermediate region between the axis and the wall, an increase is already visible for the second-lowest , 1.98 × 106.
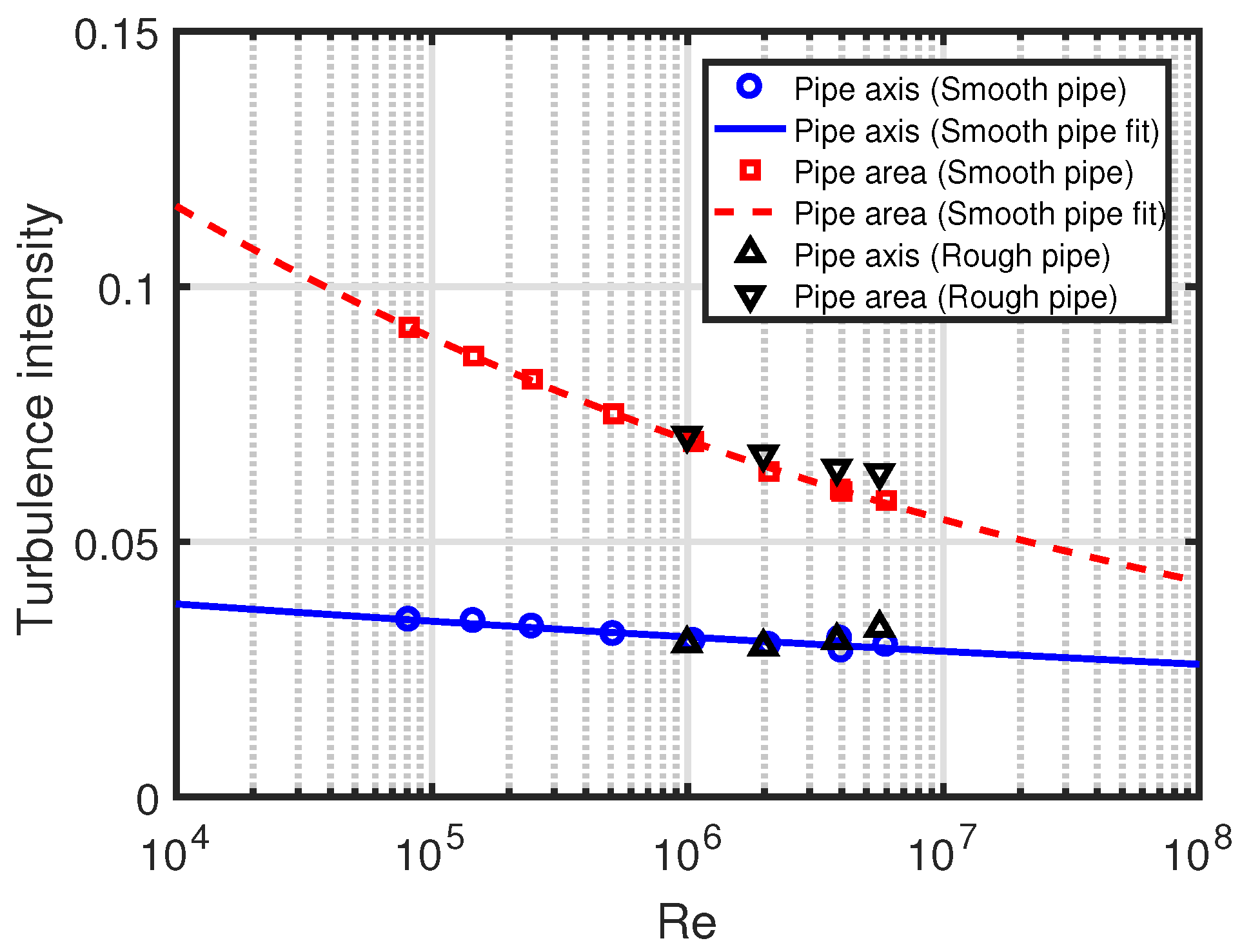
3. Turbulence Intensity Scaling
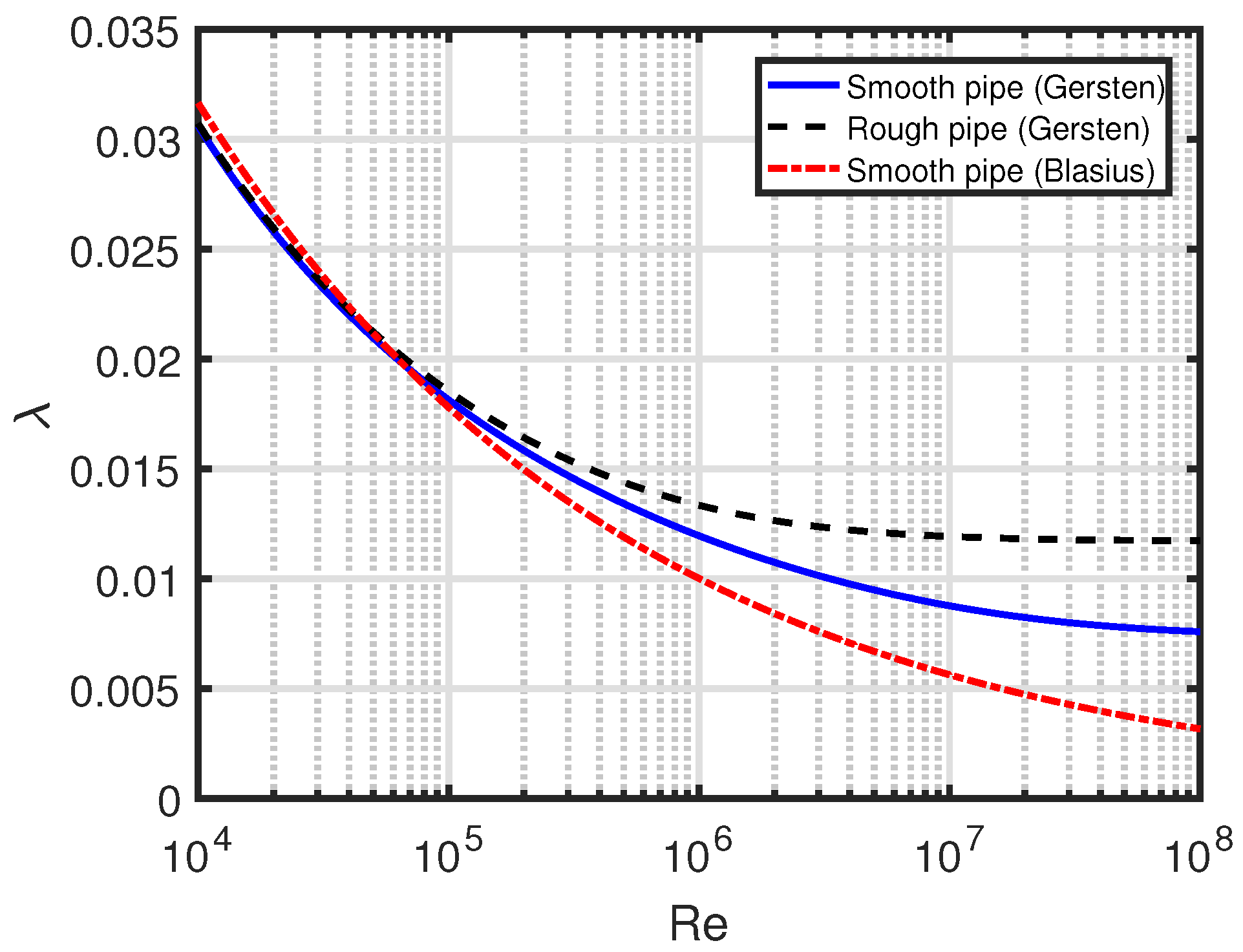
4. Friction Factor
5. Discussion
5.1. The Attached Eddy Hypothesis
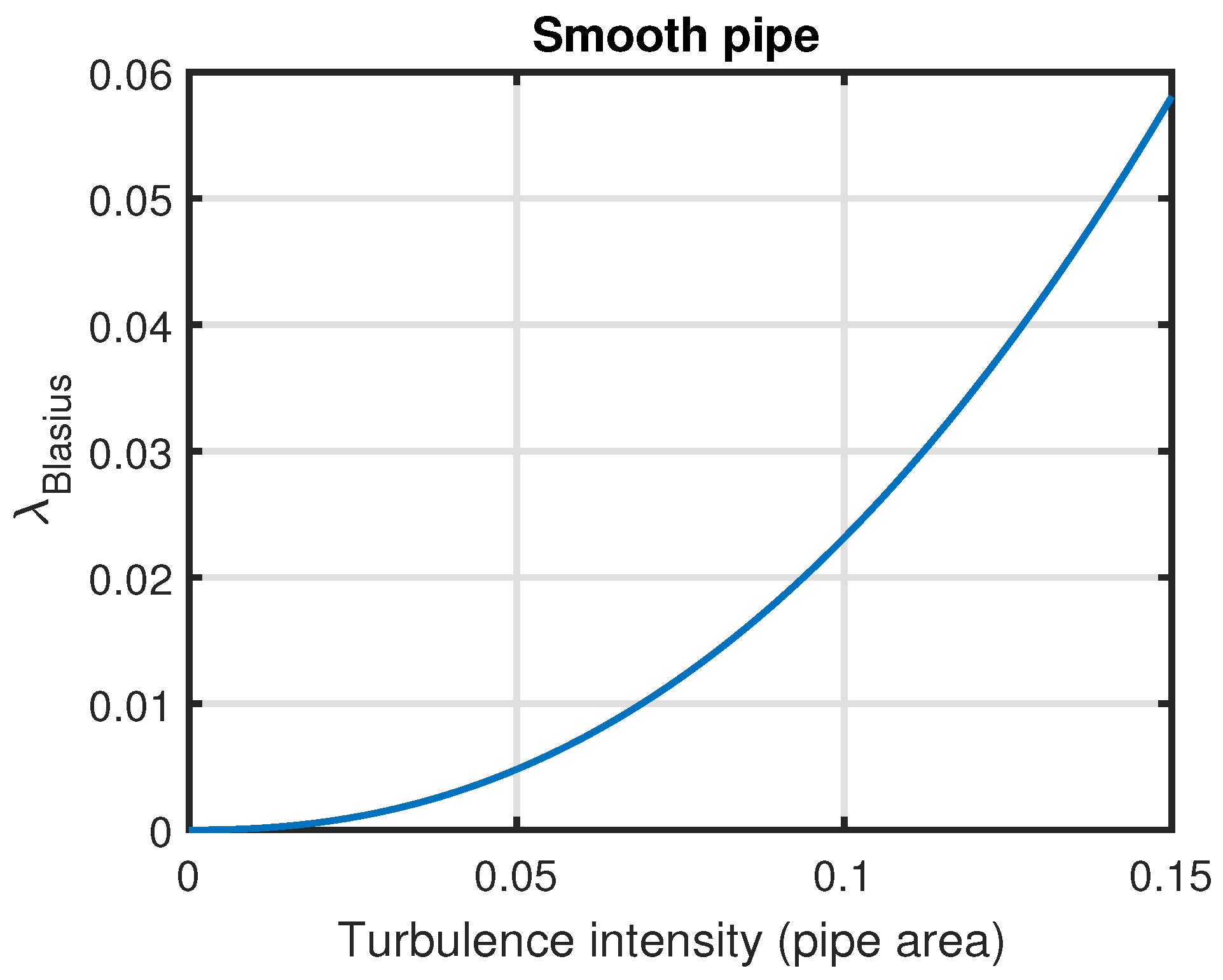
5.2. The Friction Factor and Turbulent Velocity Fluctuations
5.3. The Turbulence Intensity and the Diagnostic Plot
5.4. Applicability of Turbulence Intensity Scaling with Friction Factor
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Fits to the Turbulence Intensity Profile
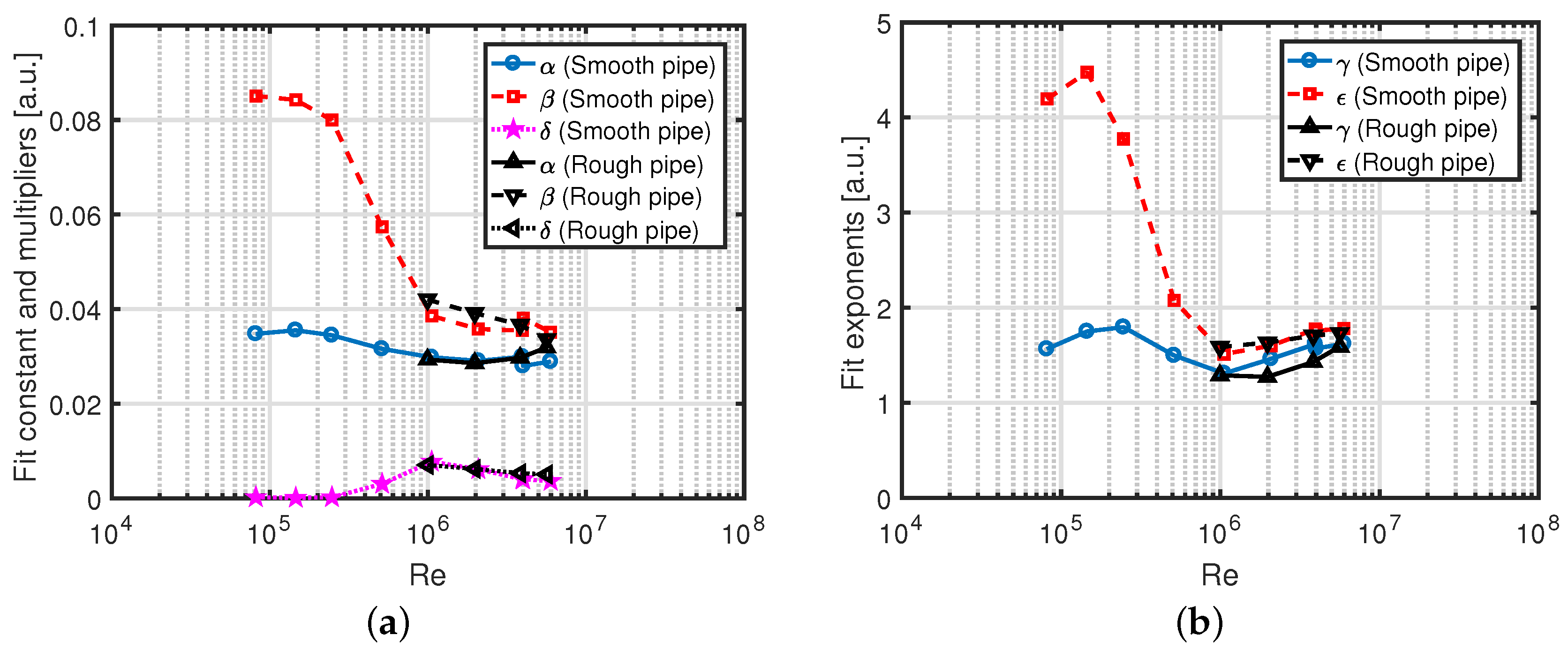

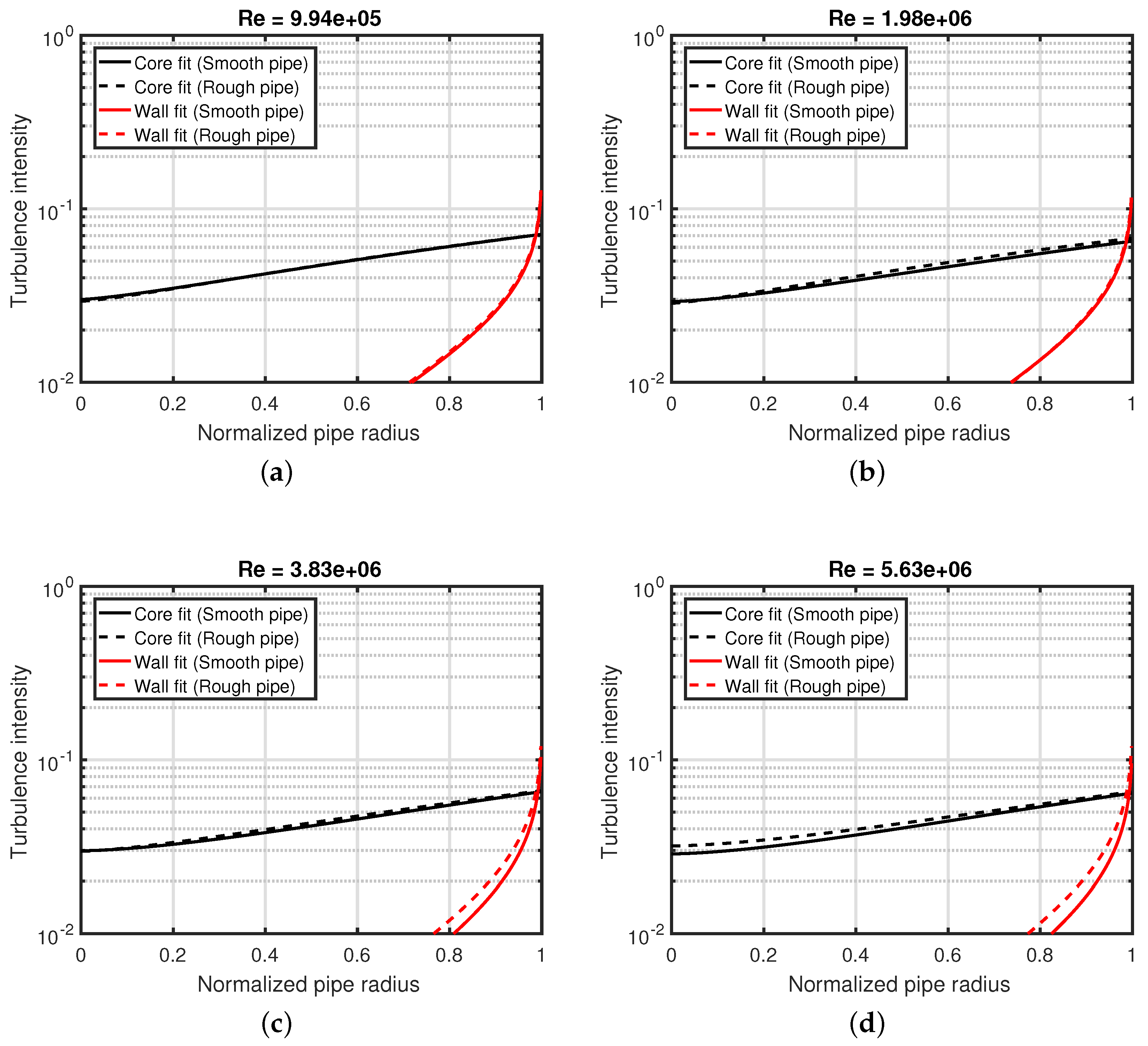
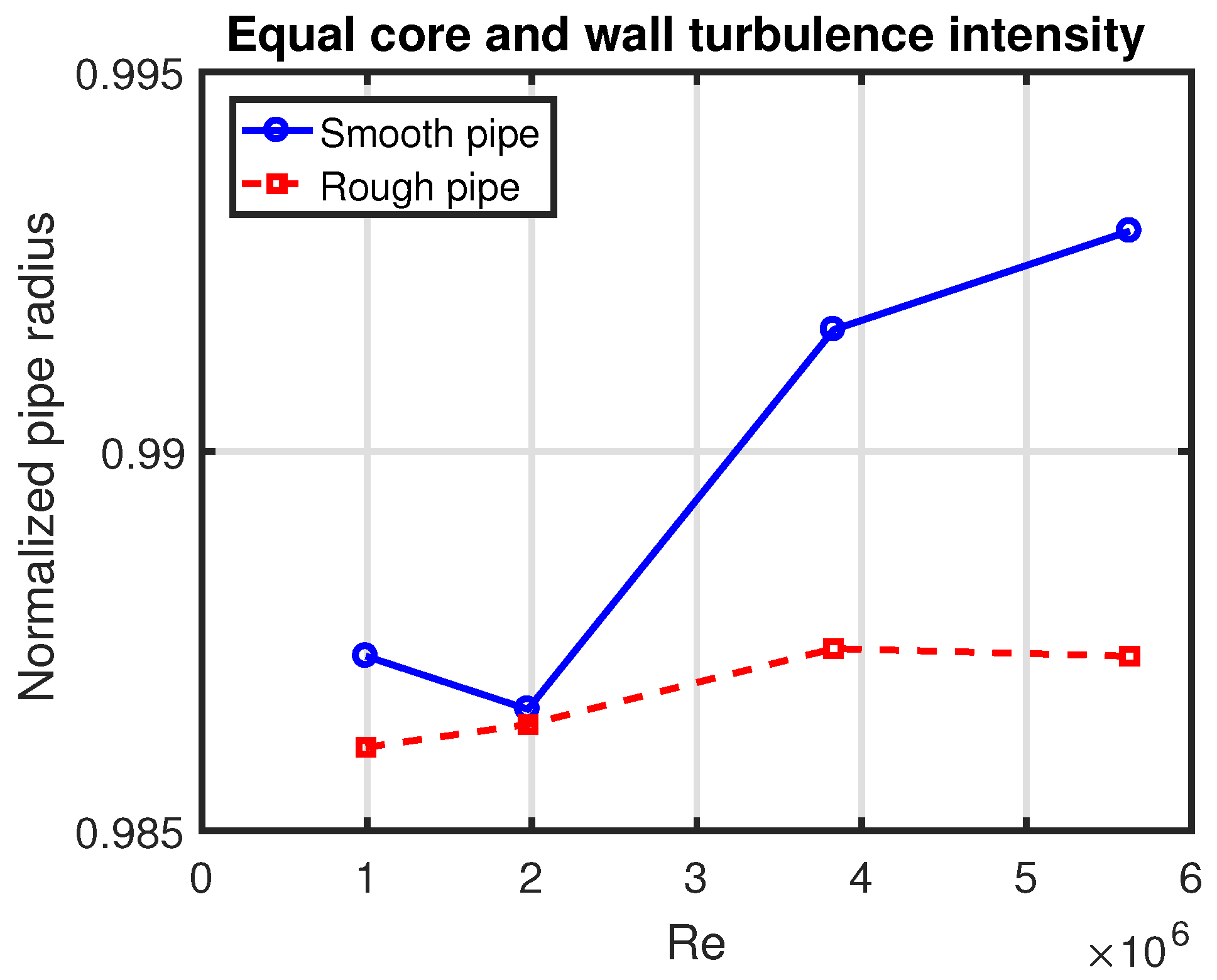
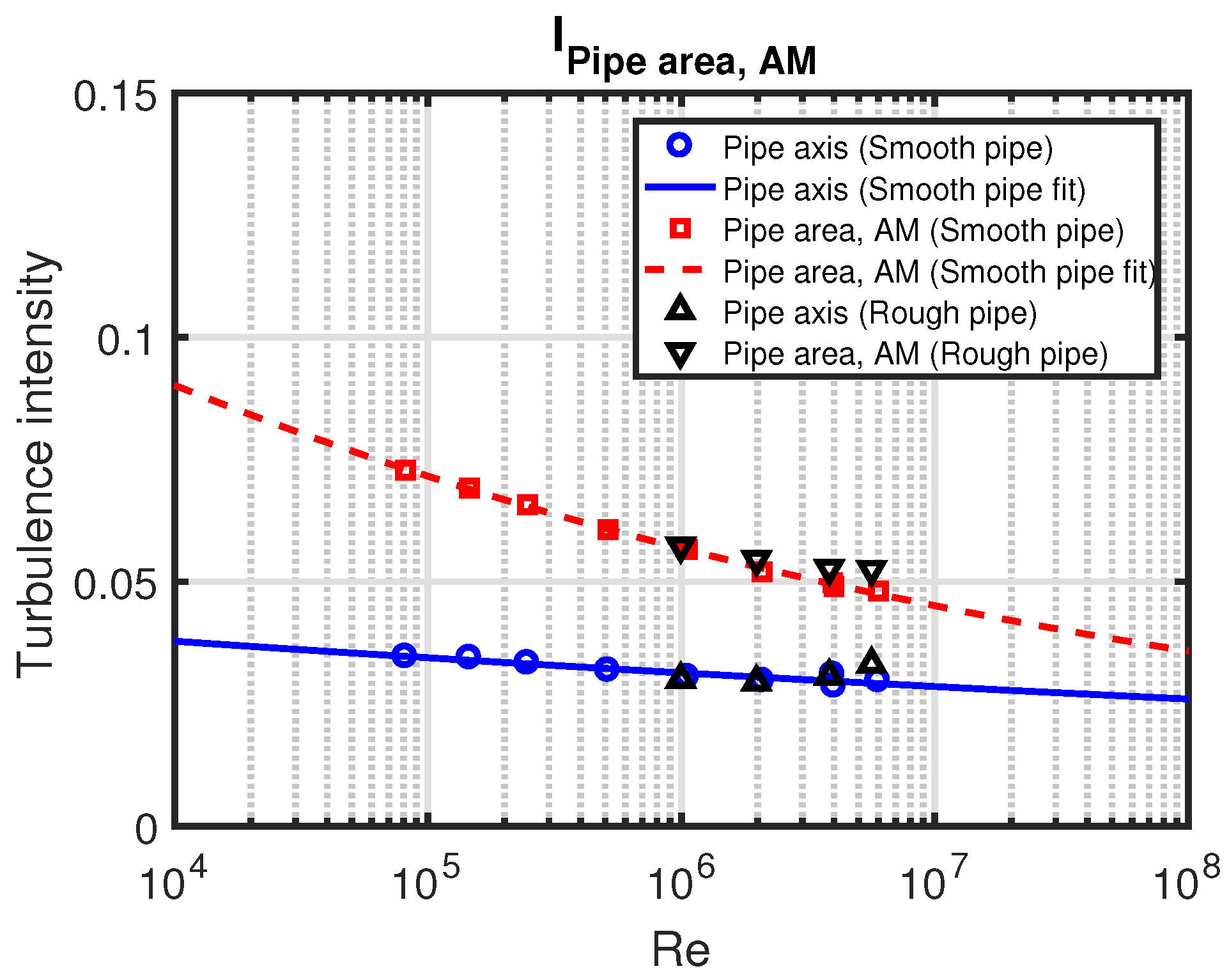
Appendix B. Arithmetic Mean Definition of Turbulence Intensity Averaged Over the Pipe Area

References
- Marusic, I.; McKeon, B.J.; Monkewitz, P.A.; Nagib, H.M.; Smits, A.J.; Sreenivasan, K.R. Wall-bounded turbulent flows at high Reynolds numbers: Recent advances and key issues. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 065103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultmark, M.; Vallikivi, M.; Bailey, S.C.C.; Smits, A.J. Turbulent pipe flow at extreme Reynolds numbers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 094501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultmark, M.; Vallikivi, M.; Bailey, S.C.C.; Smits, A.J. Logarithmic scaling of turbulence in smooth- and rough-wall pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 728, 376–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Princeton Superpipe. 2017. Available online: https://smits.princeton.edu/superpipe-turbulence-data/ (accessed on 7 June 2017).
- Russo, F.; Basse, N.T. Scaling of turbulence intensity for low-speed flow in smooth pipes. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2016, 52, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelandsvik, L.I.; Kunkel, G.J.; Smits, A.J. Flow in a commercial steel pipe. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 595, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikuradse, J. Strömungsgesetze in Rauhen Rohren; Springer-VDI-Verlag GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, J. Turbulent flows over rough walls. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flack, K.A.; Schultz, M.P. Review of hydraulic roughness scales in the fully rough regime. J. Fluids Eng. 2010, 132, 041203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; MacDonald, M.; Chung, D.; Hutchins, N.; Ooi, A. A systematic investigation of roughness height and wavelength in turbulent pipe flow in the transitionally rough regime. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 771, 743–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Fluent User’s Guide, Release 18.0. 2017. Available online: http://www.ansys.com/products/fluids/ (accessed on 7 June 2017).
- Blasius, H. Das Ähnlichkeitsgesetz bei Reibungsvorgängen in Flüssigkeiten; Springer-VDI-Verlag GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1913; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gersten, K. Fully developed turbulent pipe flow. In Fluid Mechanics of Flow Metering; Merzkirch, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H.; Gersten, K. Boundary-Layer Theory, 8th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McKeon, B.J.; Zagarola, M.V.; Smits, A.J. A new friction factor relationship for fully developed pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 538, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.A. The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Marusic, I.; Nickels, T.N.A.A. Townsend. In A Voyage through Turbulence; Davidson, P.A., Kaneda, Y., Moffatt, K., Sreenivasan, K.R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McKeon, B.J.; Morrison, J.F. Asymptotic scaling in turbulent pipe flow. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. A 2007, 365, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millikan, C.B. A critical discussion of turbulent flows in channels and circular tubes. In Proceedings of the 5th International Congress for Applied Mechanics, New York, NY, USA, 12–16 September 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, A.E.; Abell, C.J. Scaling laws for pipe-flow turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 67, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.E.; Abell, C.J. Asymptotic similarity of turbulence structures in smooth- and rough-walled pipes. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 79, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusic, I.; Kunkel, G.J. Streamwise turbulence intensity formulation for flat-plate boundary layers. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultmark, M. A theory for the streamwise turbulent fluctuations in high Reynolds number pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 707, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, D.; Philip, K.; Marusic, I. Revisiting the law of the wake in wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 811, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusic, I.; Monty, J.P.; Hultmark, M.; Smits, A.J. On the logarithmic region in wall turbulence. JFM Rapids 2013, 716, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullin, D.I.; Inoue, M.; Saito, N. On the asymptotic state of high Reynolds number, smooth-wall turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 015116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhot, V.; Bailey, S.C.C.; Smits, A.J. Scaling of global properties of turbulence and skin friction in pipe and channel flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 652, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, P. The importance of wall-normal Reynolds stress in turbulent rough channel flows. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsson, P.H.; Örlü, R. The diagnostic plot—A litmus test for wall bounded turbulence data. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2010, 29, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsson, P.H.; Segalini, A.; Örlü, R. A new scaling for the streamwise turbulence intensity in wall-bounded turbulent flows and what it tells us about the “outer” peak. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 041702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsson, P.H.; Örlü, R.; Segalini, A. A new formulation for the streamwise turbulence intensity distribution in wall-bounded turbulent flows. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2012, 36, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.P.; Segalini, A.; Alfredsson, P.H. Outer-layer turbulence intensities in smooth- and rough-wall boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 727, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basse, N.T. Turbulence Intensity and the Friction Factor for Smooth- and Rough-Wall Pipe Flow. Fluids 2017, 2, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2020030
Basse NT. Turbulence Intensity and the Friction Factor for Smooth- and Rough-Wall Pipe Flow. Fluids. 2017; 2(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasse, Nils T. 2017. "Turbulence Intensity and the Friction Factor for Smooth- and Rough-Wall Pipe Flow" Fluids 2, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2020030
APA StyleBasse, N. T. (2017). Turbulence Intensity and the Friction Factor for Smooth- and Rough-Wall Pipe Flow. Fluids, 2(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2020030





