Emulsion Flow Analysis of a Sensor Probe for Sustainable Machine Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multiphase Flow Analysis
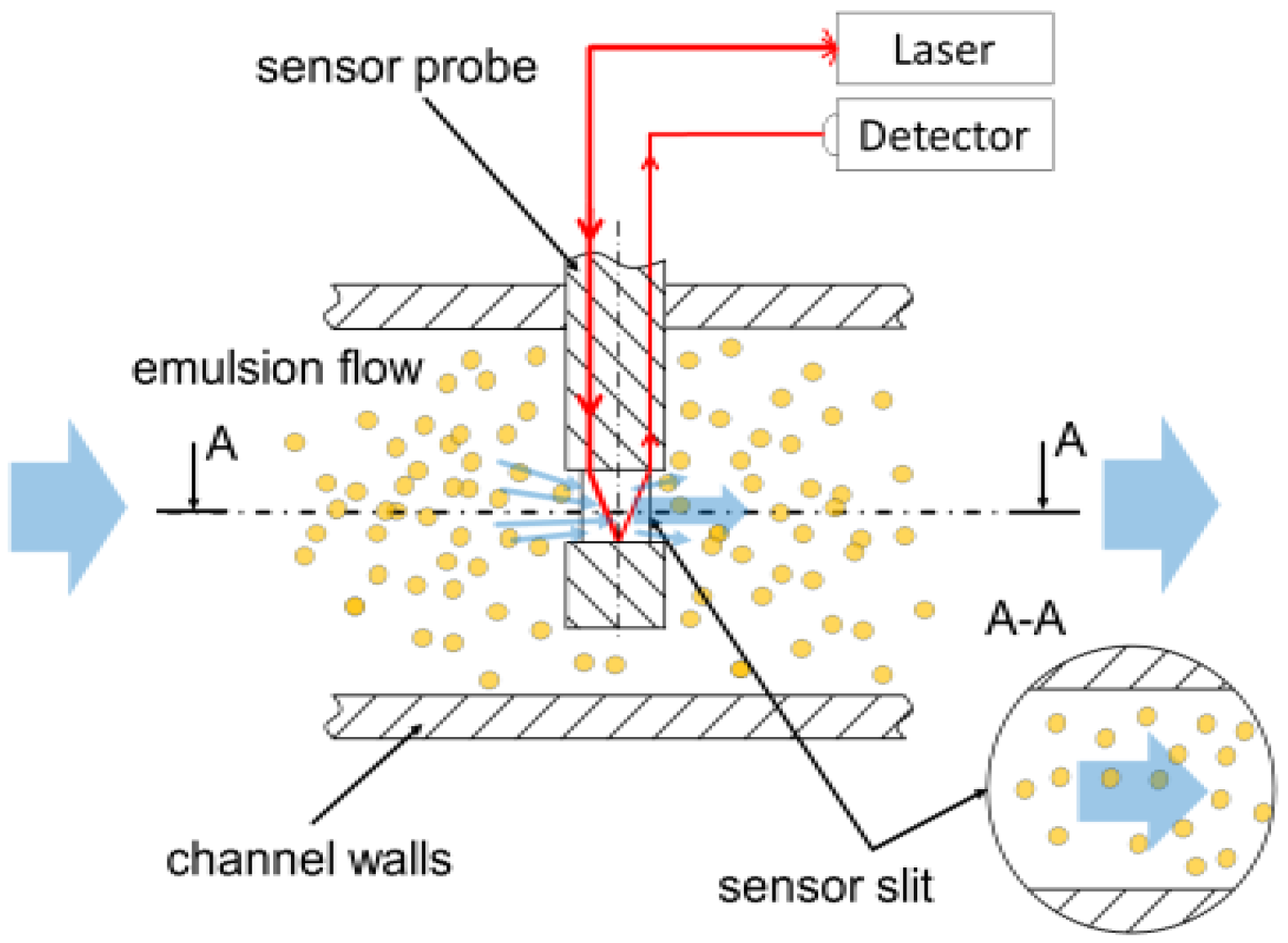
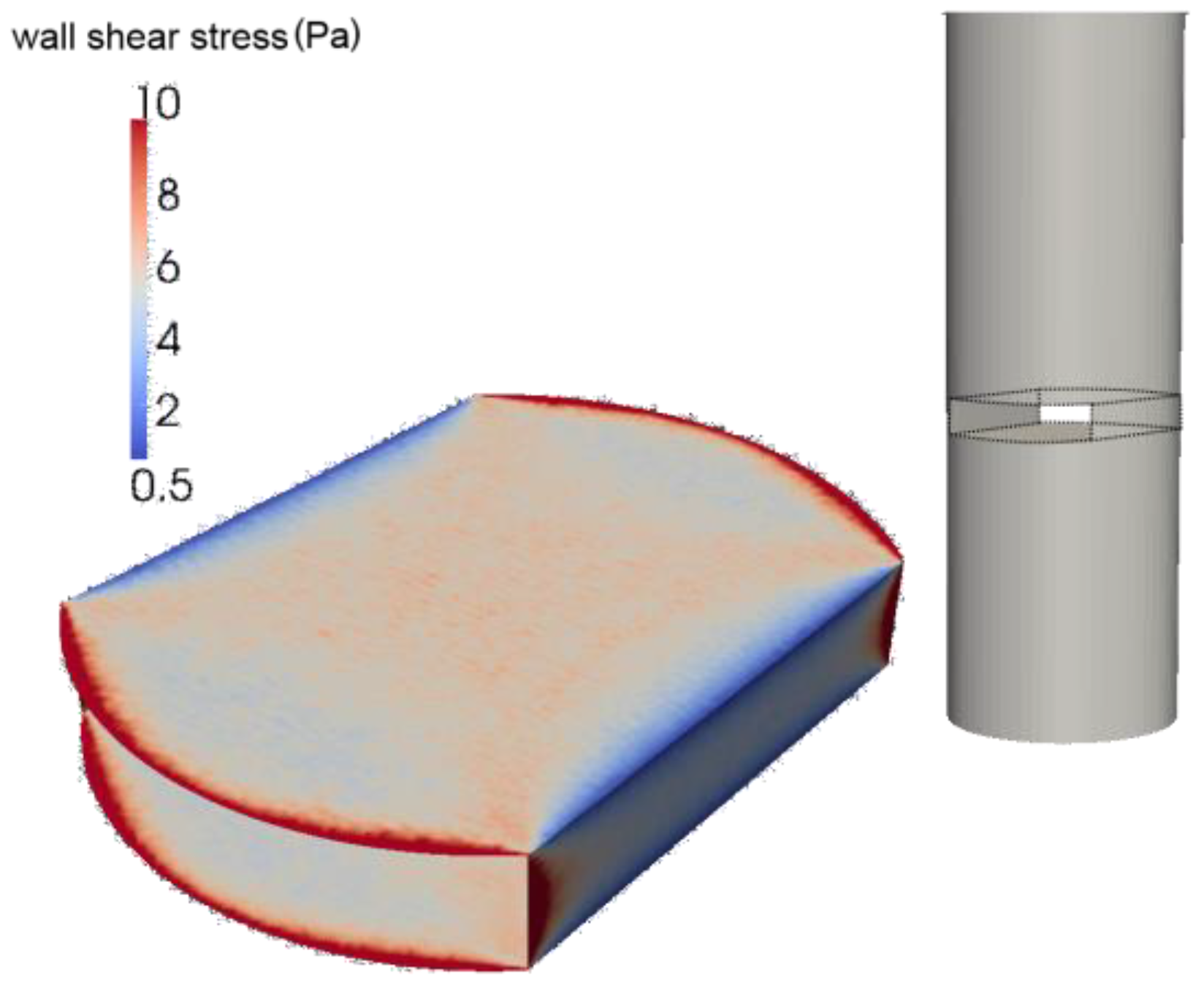
2.1. Measurement Facilities
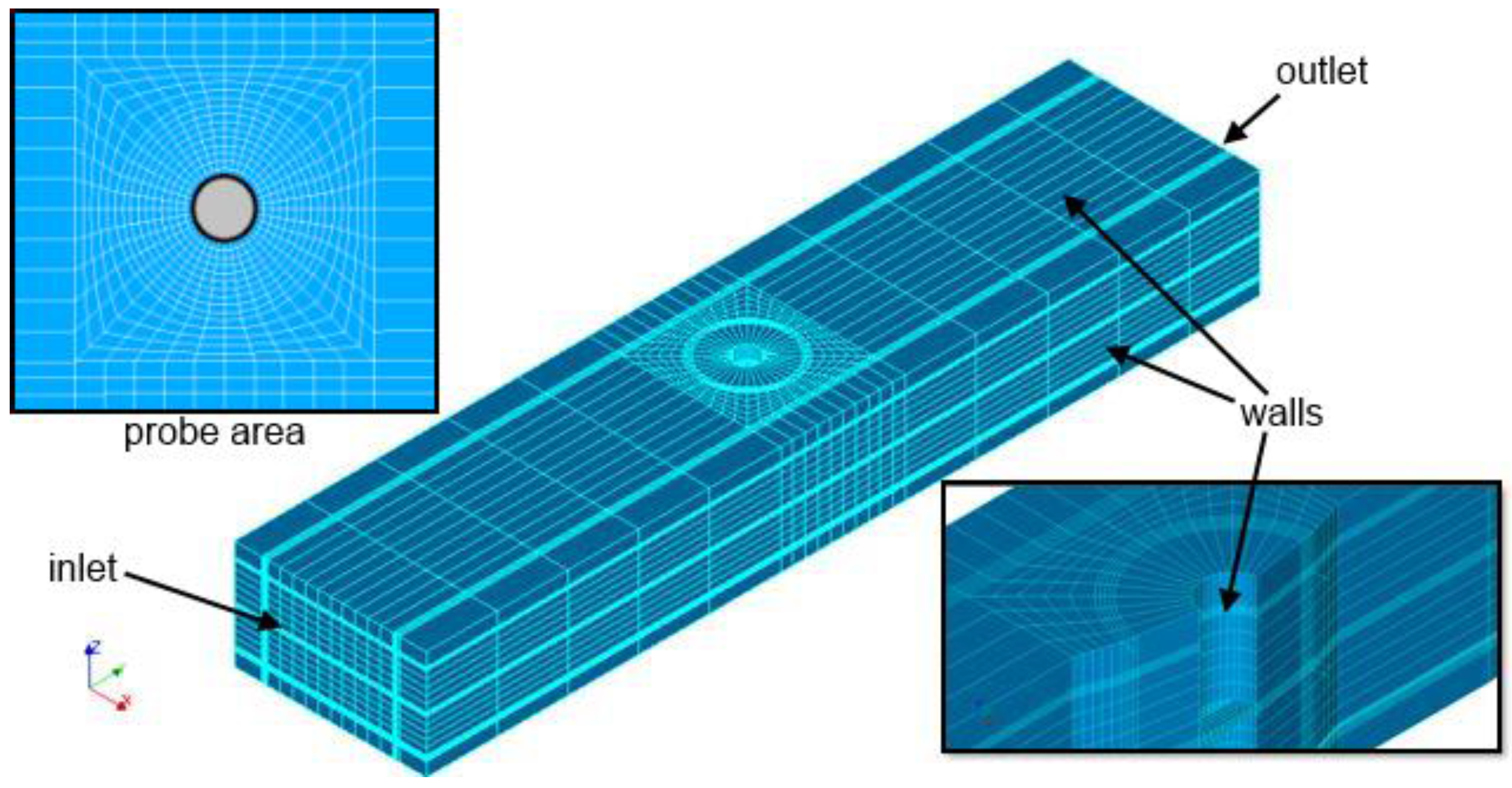
2.2. Numerical Model of Multiphase Flow
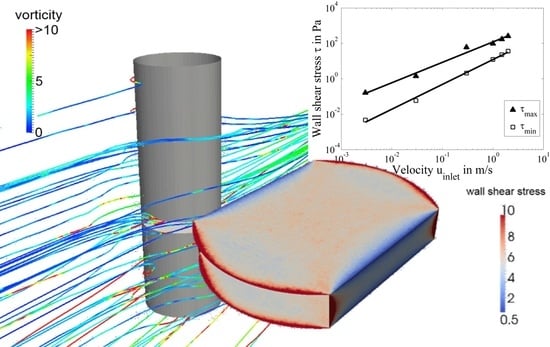
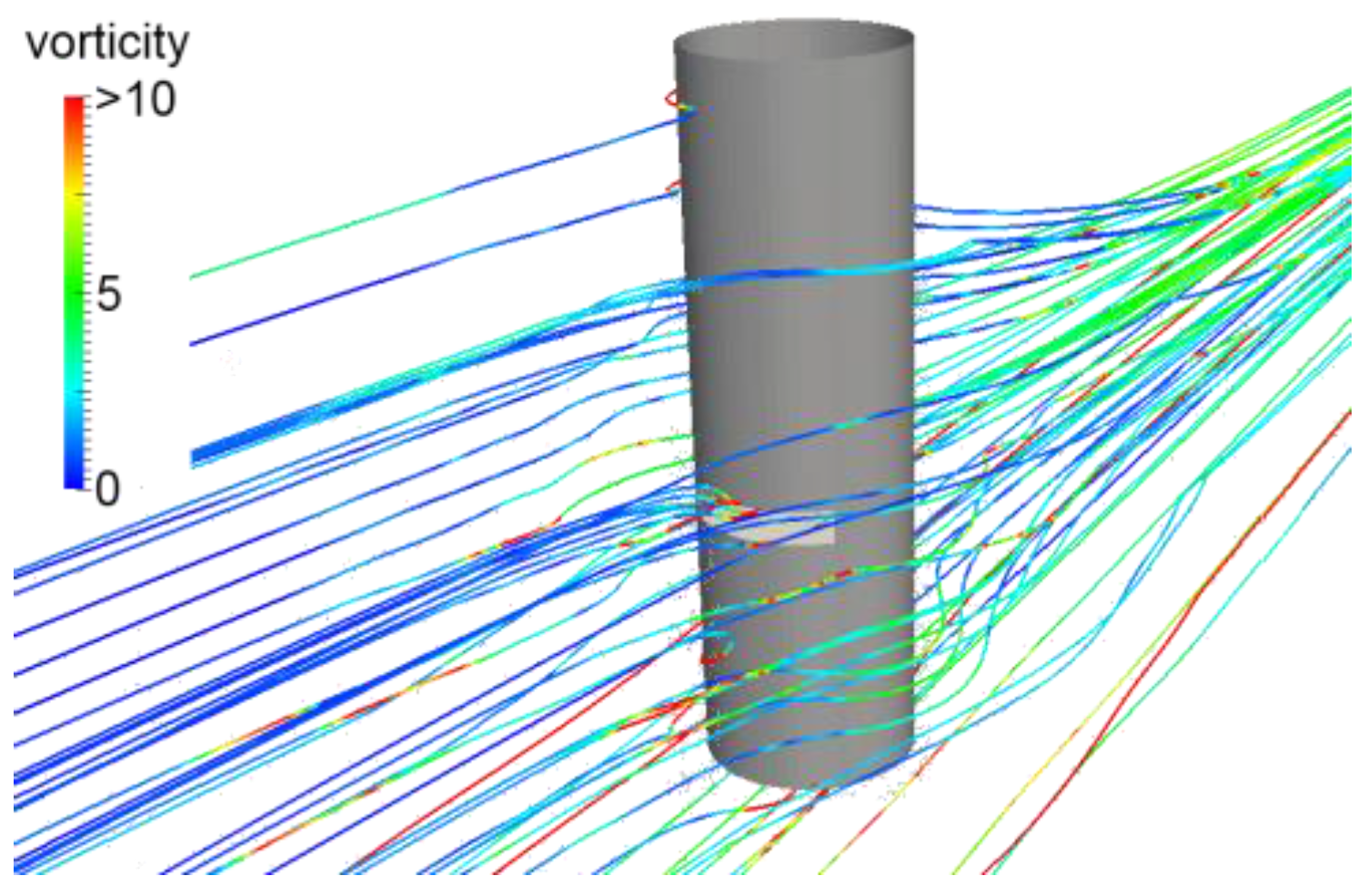
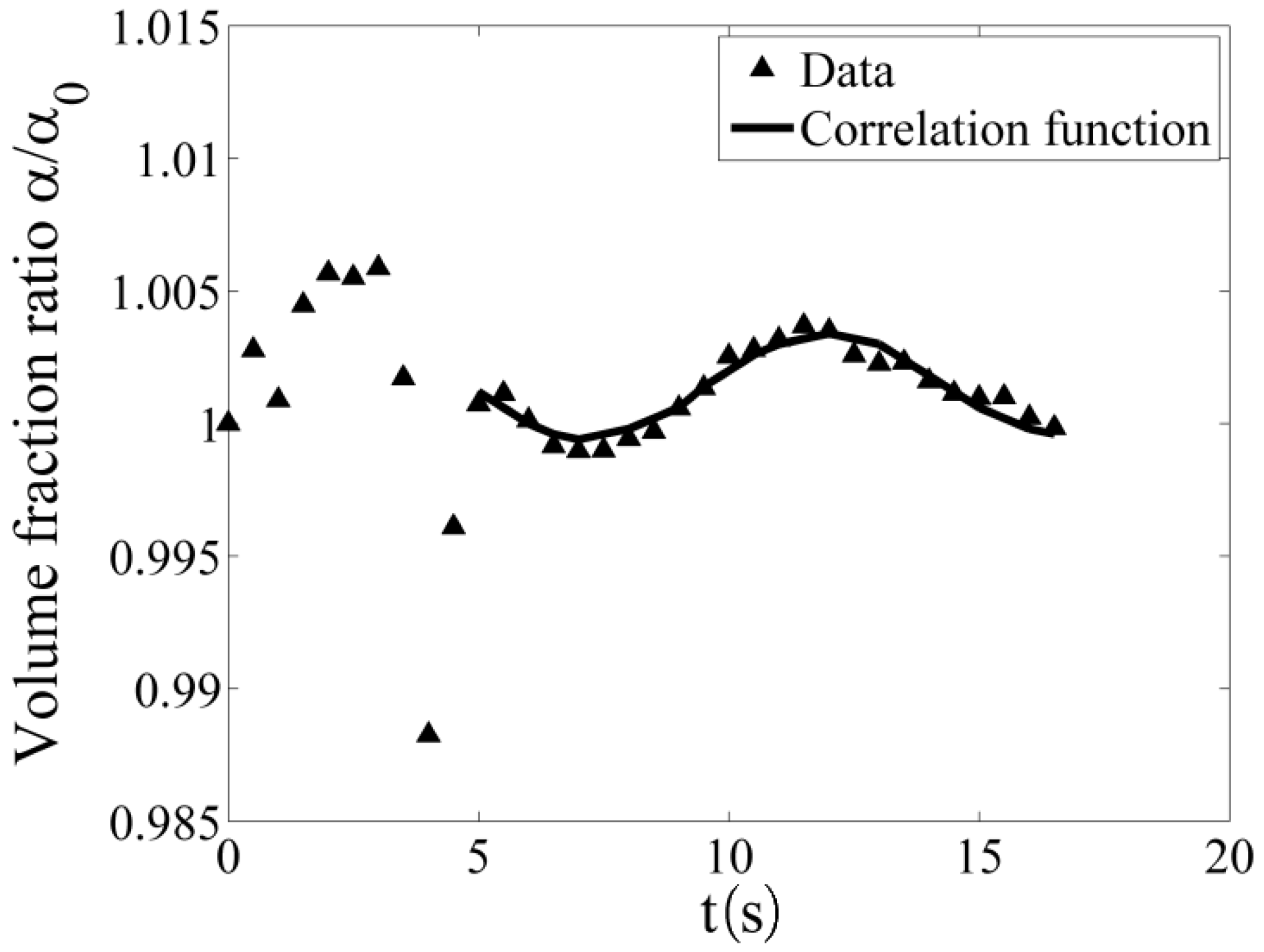
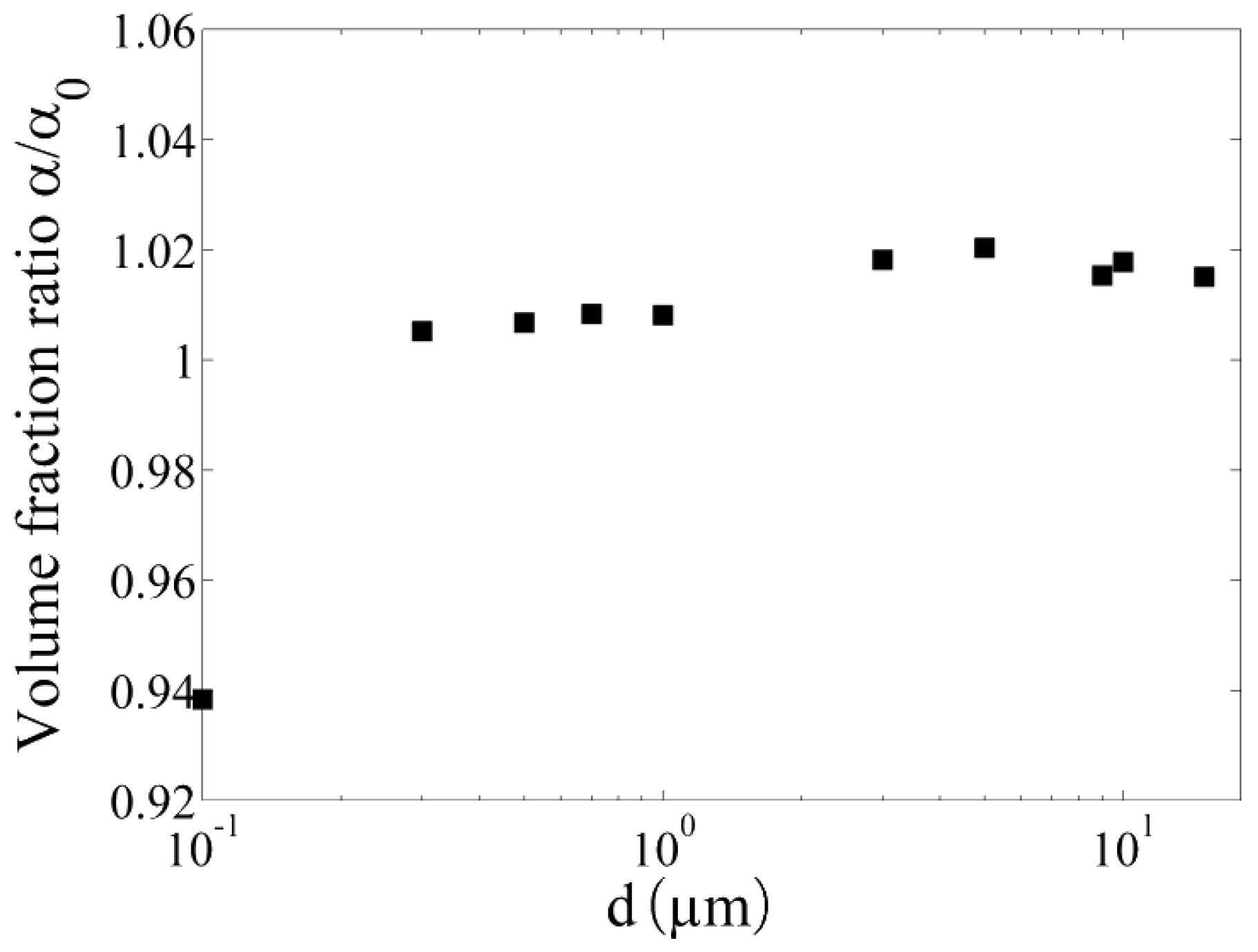
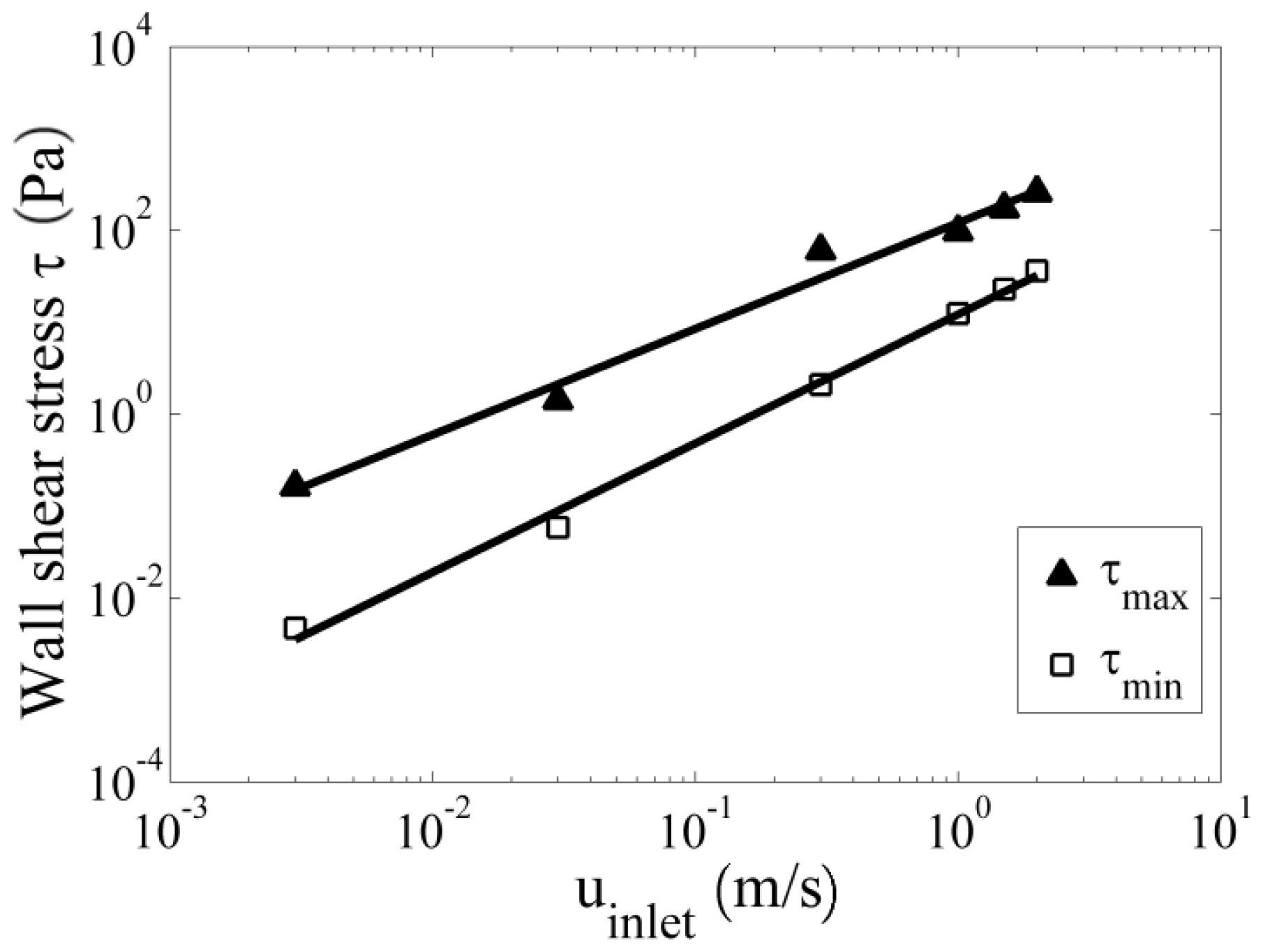
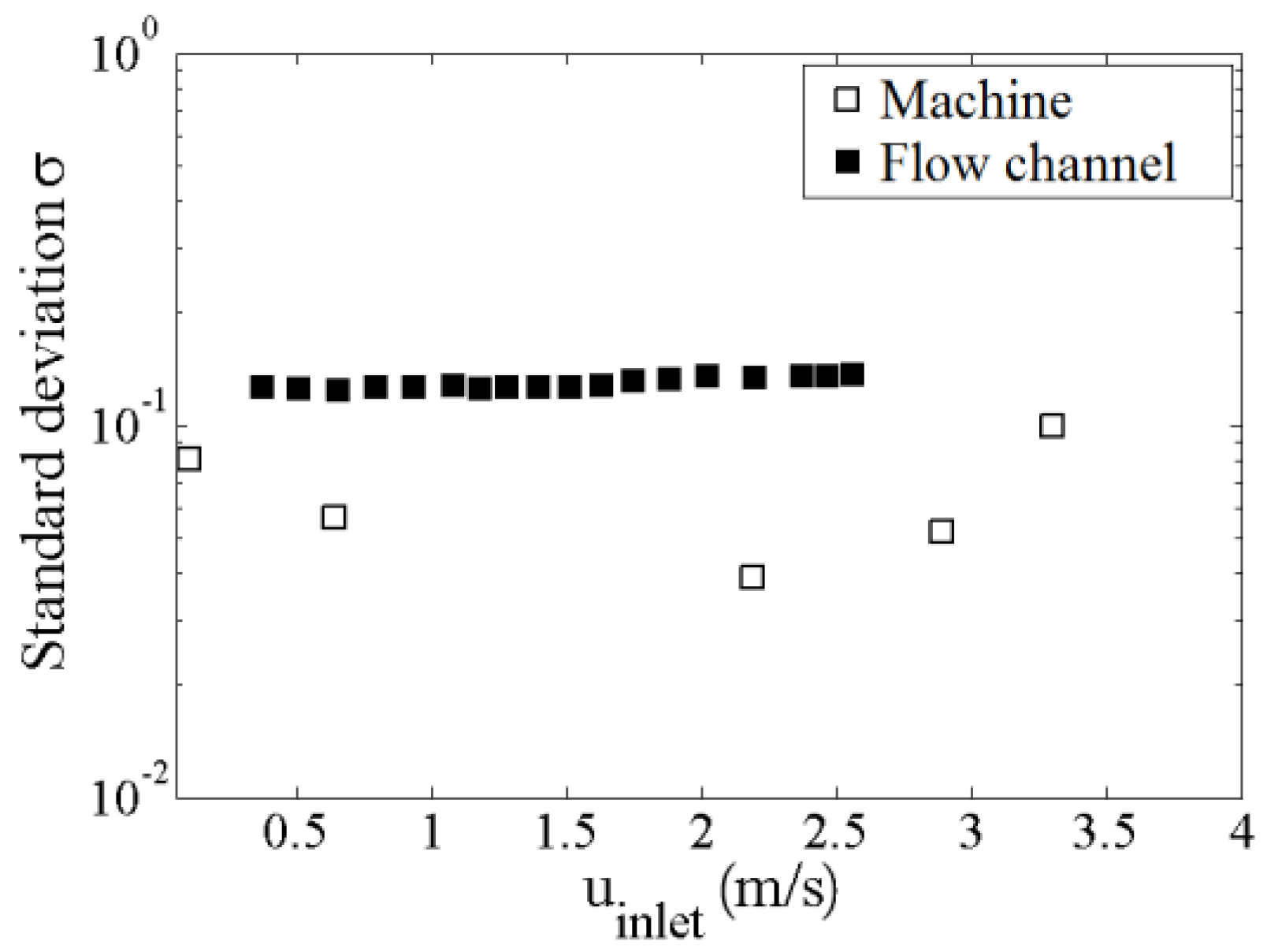
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| C | coefficient |
| D | diameter (m) |
| d | droplet size diameter (nm) |
| f | frequency (s−1) |
| F | force (N) |
| g | gravitational constant (m·s−1) |
| I | intensity |
| k | turbulent kinetic energy (m2·s−2) |
| L | length (cm) |
| m | number of τ(λ = i) in one spectrum |
| n | refractive index |
| P | pressure (N·m−2) |
| R | Reynolds stress |
| S | source (N) |
| t | time (s) |
| u | velocity (m·s−1) |
| V | volume (m3) |
| x | coordinate length (m) |
Greek letters
| α | volume fraction |
| α* | closure coefficient |
| β | closure coefficient |
| β* | closure coefficient |
| ε | turbulent dissipation rate (m2·s−2) |
| λ | wavelength (nm) |
| μ | dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| ν | kinematic viscosity (m2·s−1) |
| ρ | density (kg·m−3) |
| σ | standard deviation |
| σ* | closure coefficient |
| τ | shear stress (Pa) |
| τ(λ) | turbidity (A.U.) |
| ω | specific dissipation rate (s−1) |
Subscripts
| 0 | initial |
| c | continuous |
| cyl | cylinder |
| d | drag |
| eff | effective |
| i | direction 1 |
| inlet | inlet |
| j | direction 2 |
| l | lift |
| max | maximal |
| mean | mean |
| min | minimal |
| p | particulate |
| t | turbulent |
| vm | virtual mass |
| wall | wall |
References
- Brinksmeier, E.; Garbrecht, M.; Heinzel, C.; Koch, T.; Eckebrecht, J. Current approaches in design and supply of metalworking fluids. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 52, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Sharma, G.; Shishodia, K.; Sekhon, G. Study on the performance of oil-in-water emulsions during cold rolling of steel strip. Tribol. Trans. 2005, 48, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, J.P. Metalworking Fluids, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- De Paula Dias, A.M. Ressourcenschonender Einsatz von Kühlschmierstoffen; University of Bremen: Bremen, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Celis, M.T.; Garcia-Rubio, L.H. Stability of emulsions from multiwavelength transmission measurements. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluhery, J.; Rajagopalan, N. A turbidimetric method for the rapid evaluation of MWF emulsion stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 256, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasse, B.; Assenhaimer, C.; Guardani, R.; Fritsching, U. Turbidimetry for the stability evaluation of emulsions used in machining industry. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 92, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alupoaei, C.E.; Olivares, J.A.; Garcı́a-Rubio, L.H. Quantitative spectroscopy analysis of prokaryotic cells: Vegetative cells and spores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VDI3397. Maintenance of Metalworking Fluids—Measures for Maintaining Quality, and for Reducing Solid and Liquid Waste; Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, B.B.B.; Friis, A. Critical wall shear stress for the ehedg test method. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C. Microbial adhesion in flow displacement systems. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemot, G.; Vaca-Medina, G.; Martin-Yken, H.; Vernhet, A.; Schmitz, P.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Shear-flow induced detachment of saccharomyces cerevisiae from stainless steel: Influence of yeast and solid surface properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 49, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgoren, M.; Pinar, E.; Sahin, B.; Akilli, H. Comparison of flow structures in the downstream region of a cylinder and sphere. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Jakirlić, S.; Tropea, C.; Obi, S. Shearless and sheared flow past a circular cylinder: Comparative analysis by means of les. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H. Emulgiertechnik—Grundlagen, Verfahren und Anwendungen; Behr’s Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.H.K. Vortex dynamics in the cylinder wake. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1996, 28, 477–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Fan, J.; Li, W.; Cen, K. Transient, three-dimensional simulation of particle dispersion in flows around a circular cylinder Re = 140–260. Fuel 2009, 88, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenhaimer, C.; Machado, L.J.; Glasse, B.; Fritsching, U.; Guardani, R. Use of a spectroscopic sensor to monitor droplet size distribution in emulsions using neural networks. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 92, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusche, H. Computational Fluid Dynamics of Dispersed Two-Phase Flows at High Phase Fractions; University of London: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gosman, A.D.; Lekakou, C.; Politis, S.; Issa, R.I.; Looney, M.K. Multidimensional modeling of turbulent two-phase flows in stirred vessels. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. J. 1992, 38, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D. The Computer Simulation of Dispersed Two-Phase Flows; University of London: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R. Modeling the viscosity of concentrated nanoemulsions and nanosuspensions. Fluids 2016, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, S. Prediction of Two-Phase Solid-Liquid Turbulent Flow in Stirred Vessels; University of London: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Auton, T.R.; Hunt, J.C.R.; Prud’Homme, M. The force exerted on a body in inviscid unsteady non-uniform rotational flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 197, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.; Naumann, A. A drag coefficient correlation. Zeitschrift des Vereins Deutscher Ingenieure 1935, 77, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, R.; Grace, J.R.; Weber, M.E. Bubbles, Drops, and Particles; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Weller, H.G.; Tabor, G.; Jasak, H.; Fureby, C. A tensorial approach to computational continuum mechanics using object-oriented techniques. Comput. Phys. 1998, 12, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalitzin, G.; Medic, G.; Iaccarino, G.; Durbin, P. Near-wall behavior of rans turbulence models and implications for wall functions. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 204, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Teoh, B.C.; Clements, L.D. Densities of vegetable oils and fatty acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, A.; Koch, T.; Remesch, M.; Brinksmeier, E.; Kuever, J. Microbial degradation of water miscible metal working fluids. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuyer, S.; Rusconi, R.; Shen, Y.; Forsyth, A.; Vlamakis, H.; Kolter, R.; Stone, H. Shear stress increases the residence time of adhesion of pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sander, S.; Glasse, B.; Grosche, L.; De Paiva, J.L.; Guardani, R.; Fritsching, U. Emulsion Flow Analysis of a Sensor Probe for Sustainable Machine Operation. Fluids 2017, 2, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2010009
Sander S, Glasse B, Grosche L, De Paiva JL, Guardani R, Fritsching U. Emulsion Flow Analysis of a Sensor Probe for Sustainable Machine Operation. Fluids. 2017; 2(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSander, Sören, Benjamin Glasse, Lucas Grosche, Jose Luis De Paiva, Roberto Guardani, and Udo Fritsching. 2017. "Emulsion Flow Analysis of a Sensor Probe for Sustainable Machine Operation" Fluids 2, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2010009
APA StyleSander, S., Glasse, B., Grosche, L., De Paiva, J. L., Guardani, R., & Fritsching, U. (2017). Emulsion Flow Analysis of a Sensor Probe for Sustainable Machine Operation. Fluids, 2(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2010009