Topical Delivery of Terbinafine HCL Using Nanogels: A New Approach to Superficial Fungal Infection Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
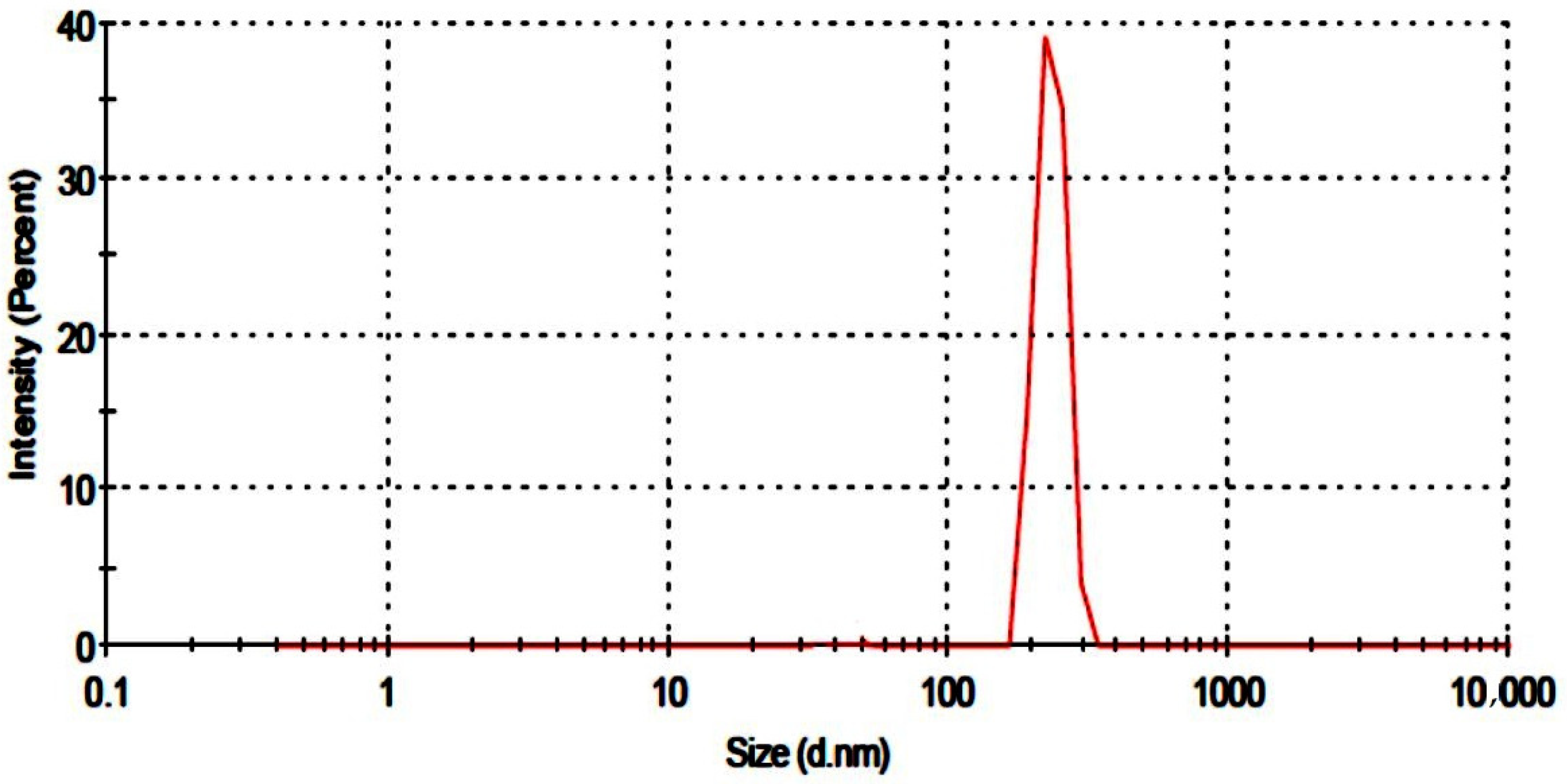
2.1. Particle Size Analysis
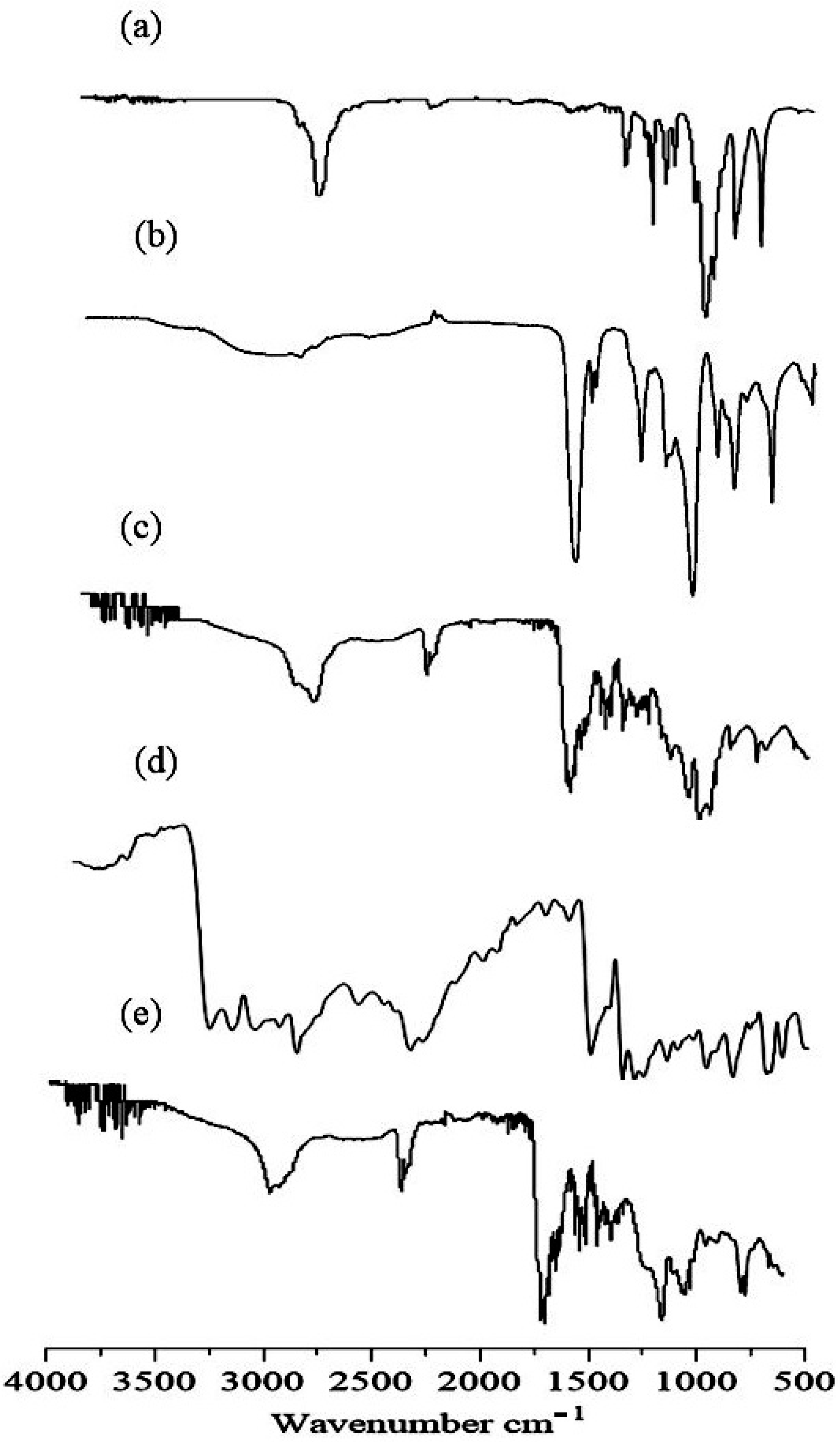
2.2. FTIR
2.3. TGA
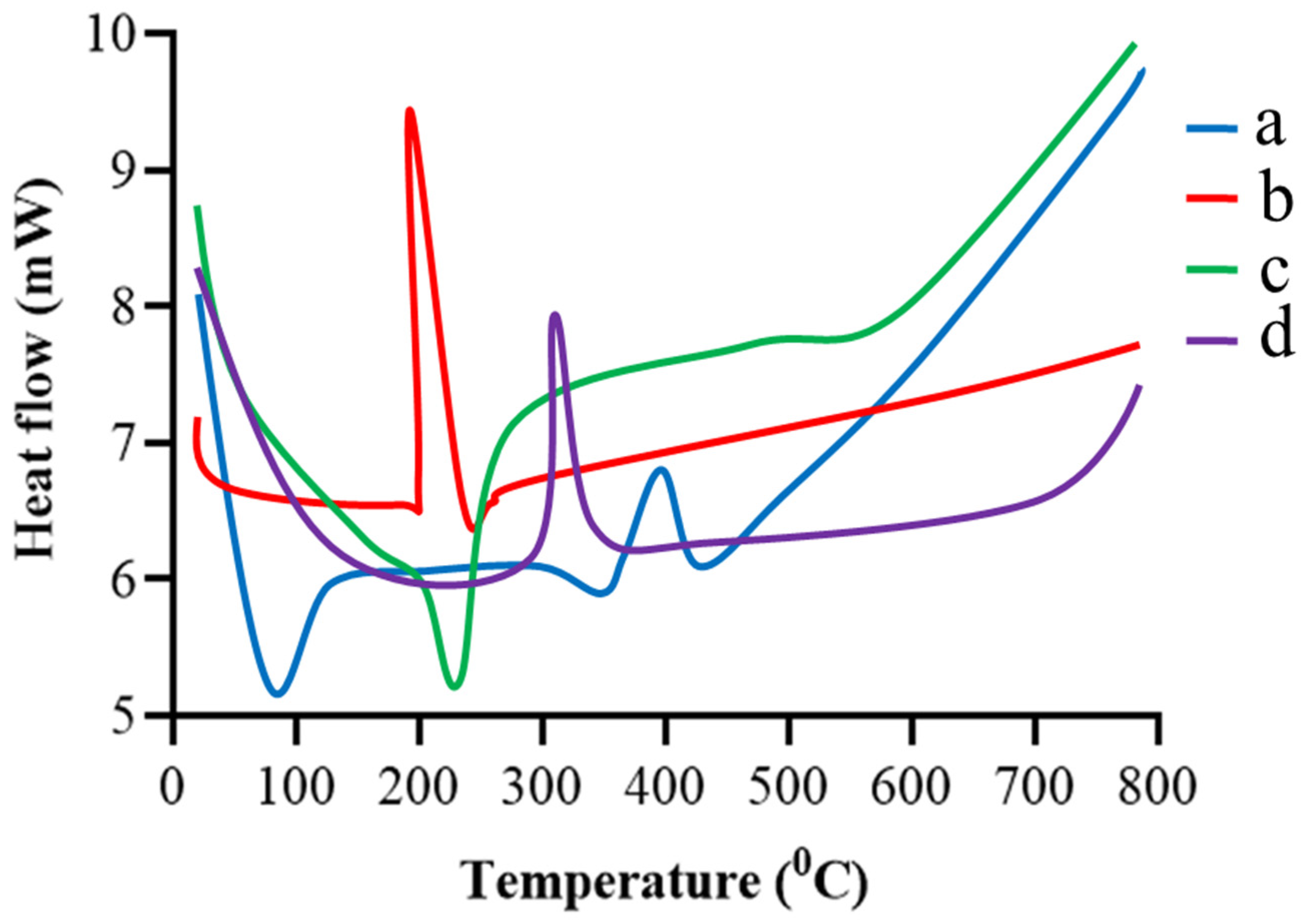
2.4. DSC
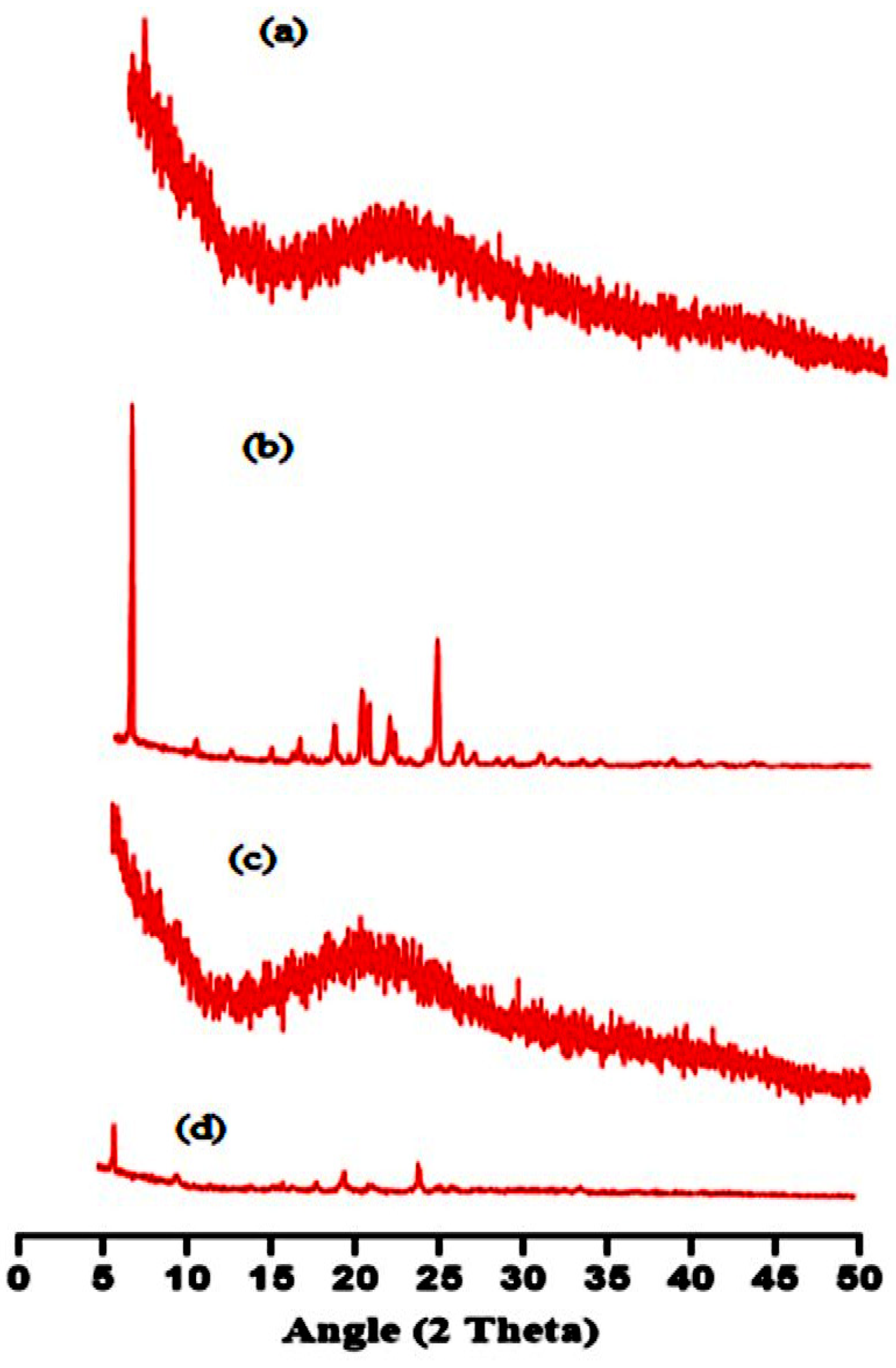
2.5. XRD
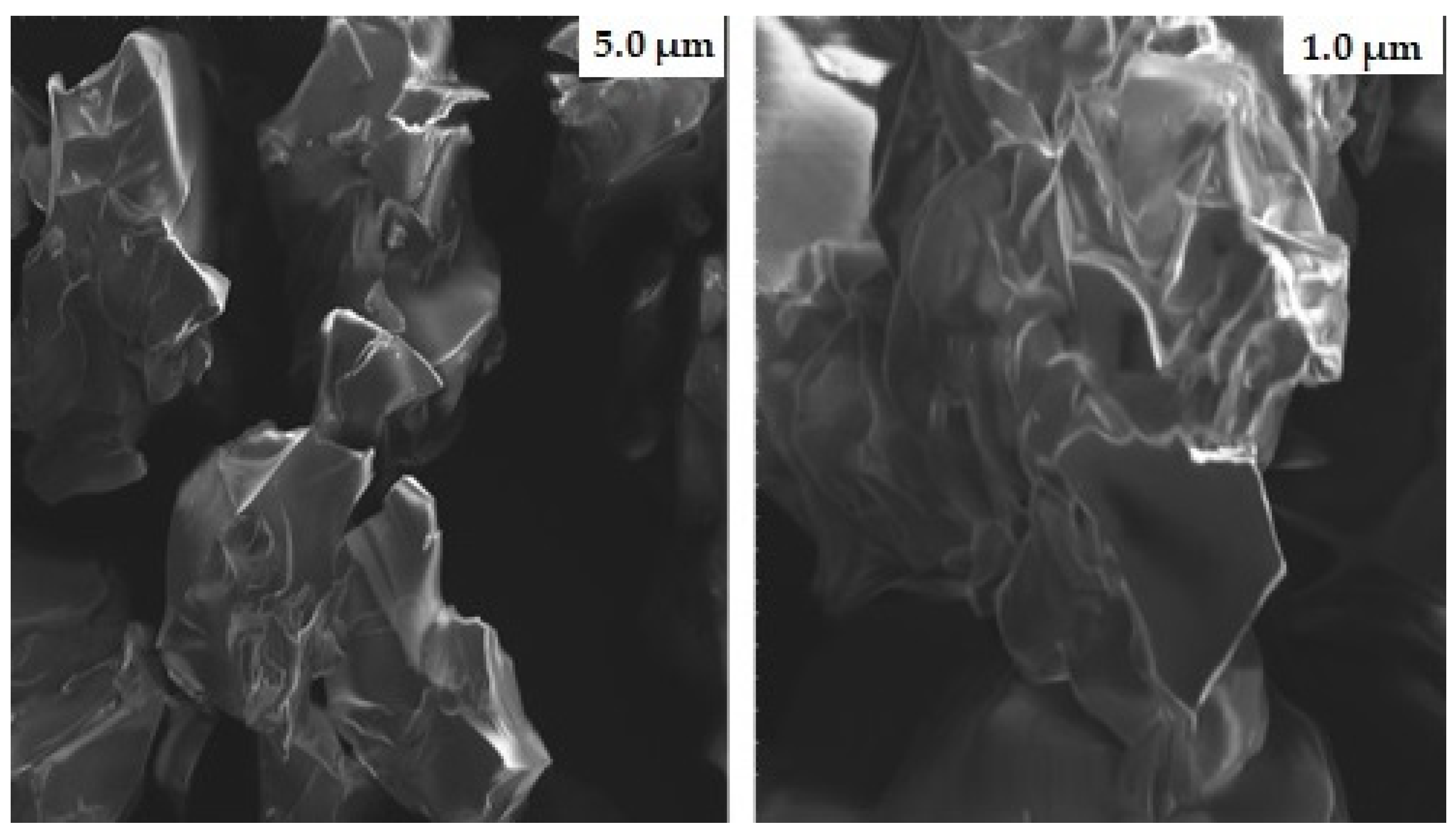
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
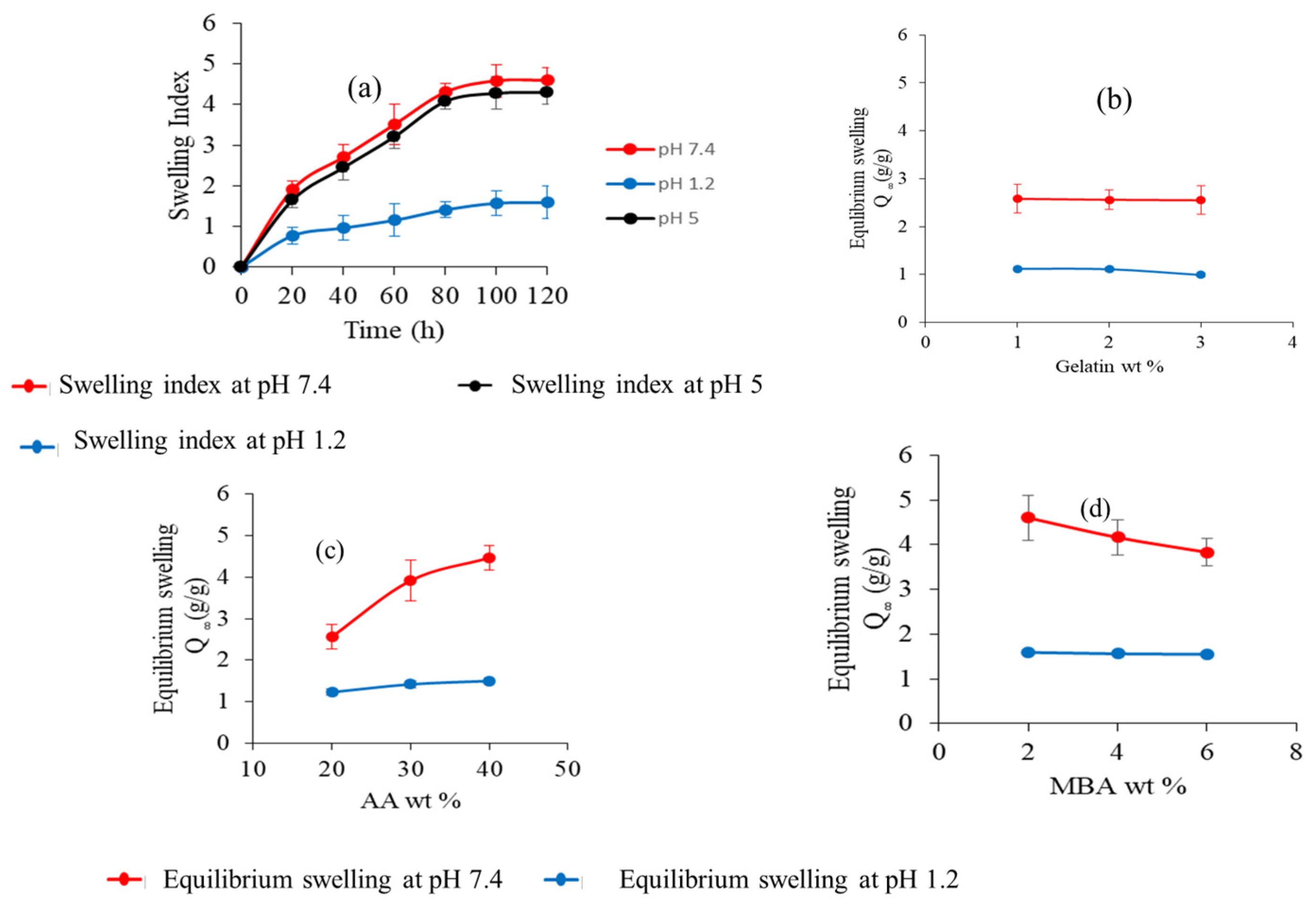
2.7. Swelling Studies
2.8. DEE
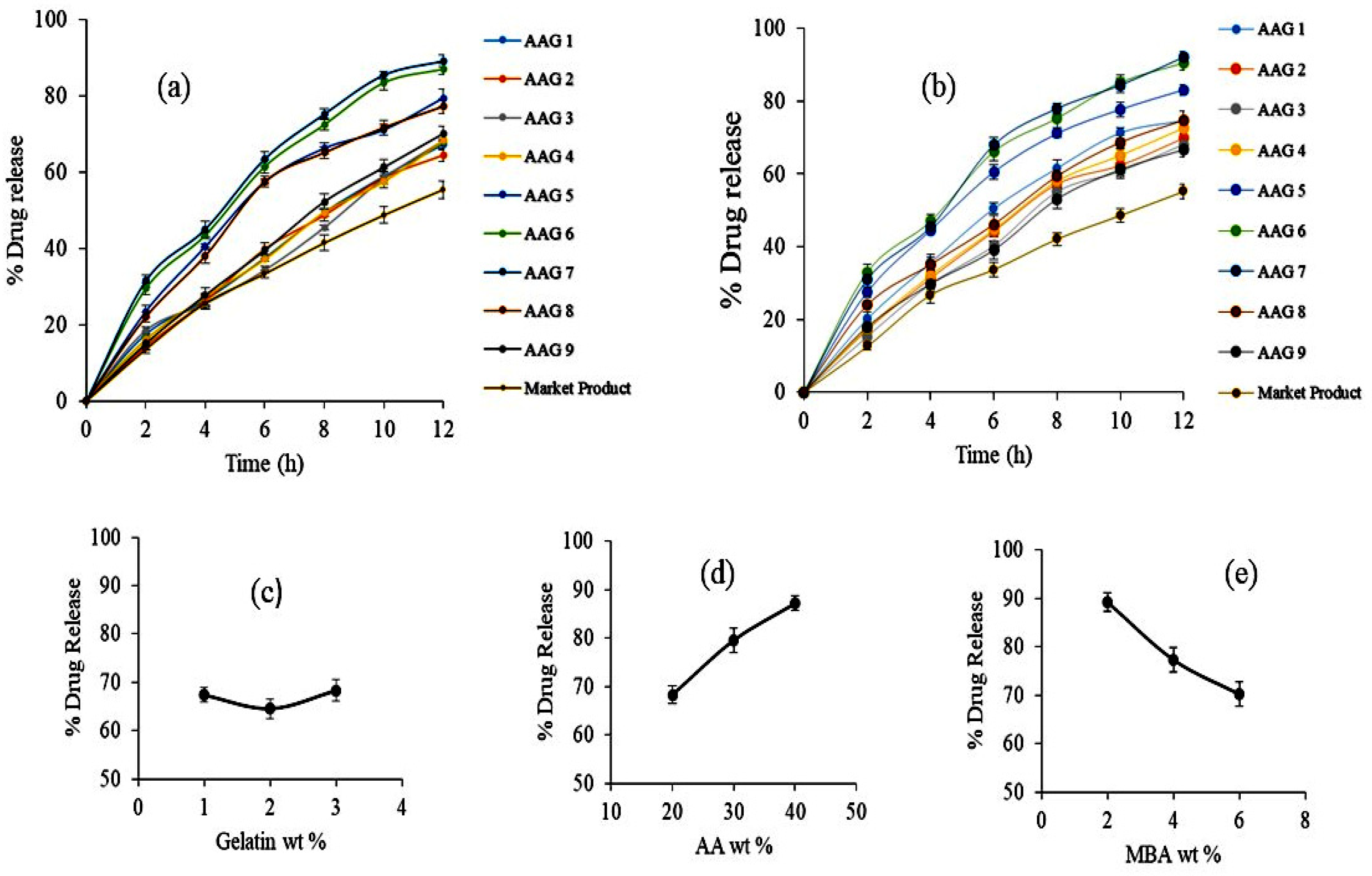
2.9. Drug Release Studies and Kinetics
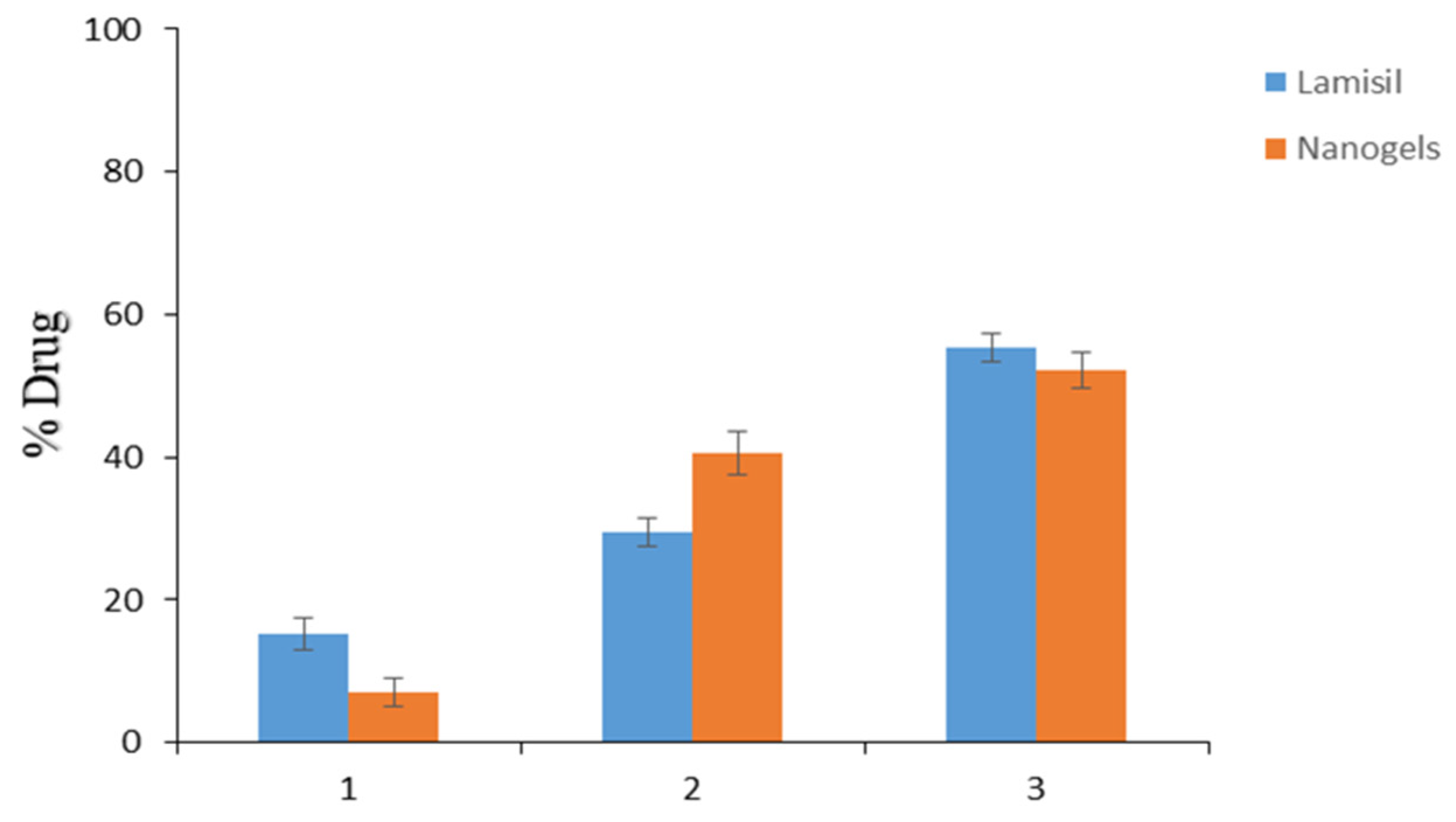
2.10. TBH Skin Penetration and Retention Studies
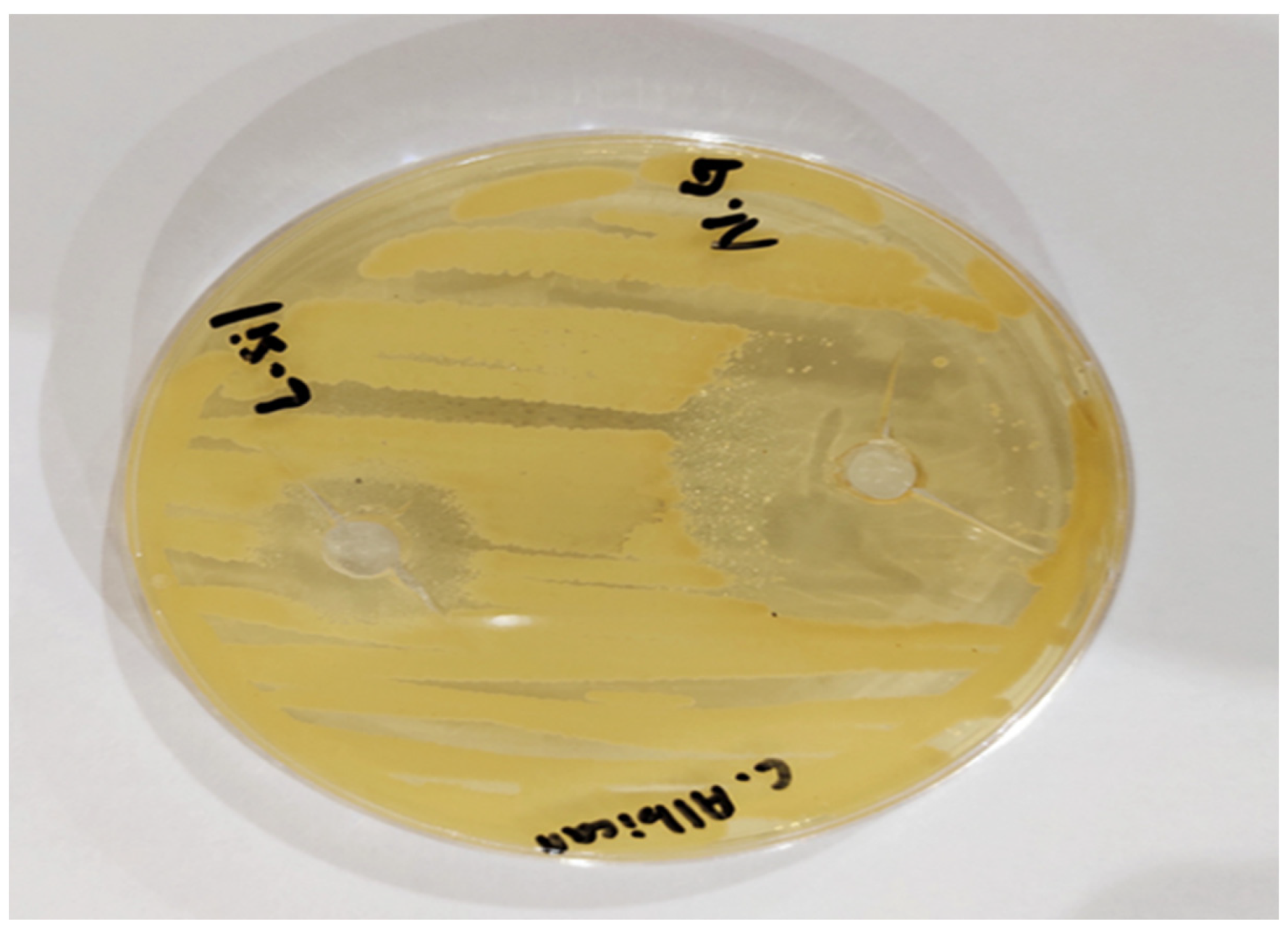
2.11. Antifungal Activity Study
2.12. Skin Irritancy Studies
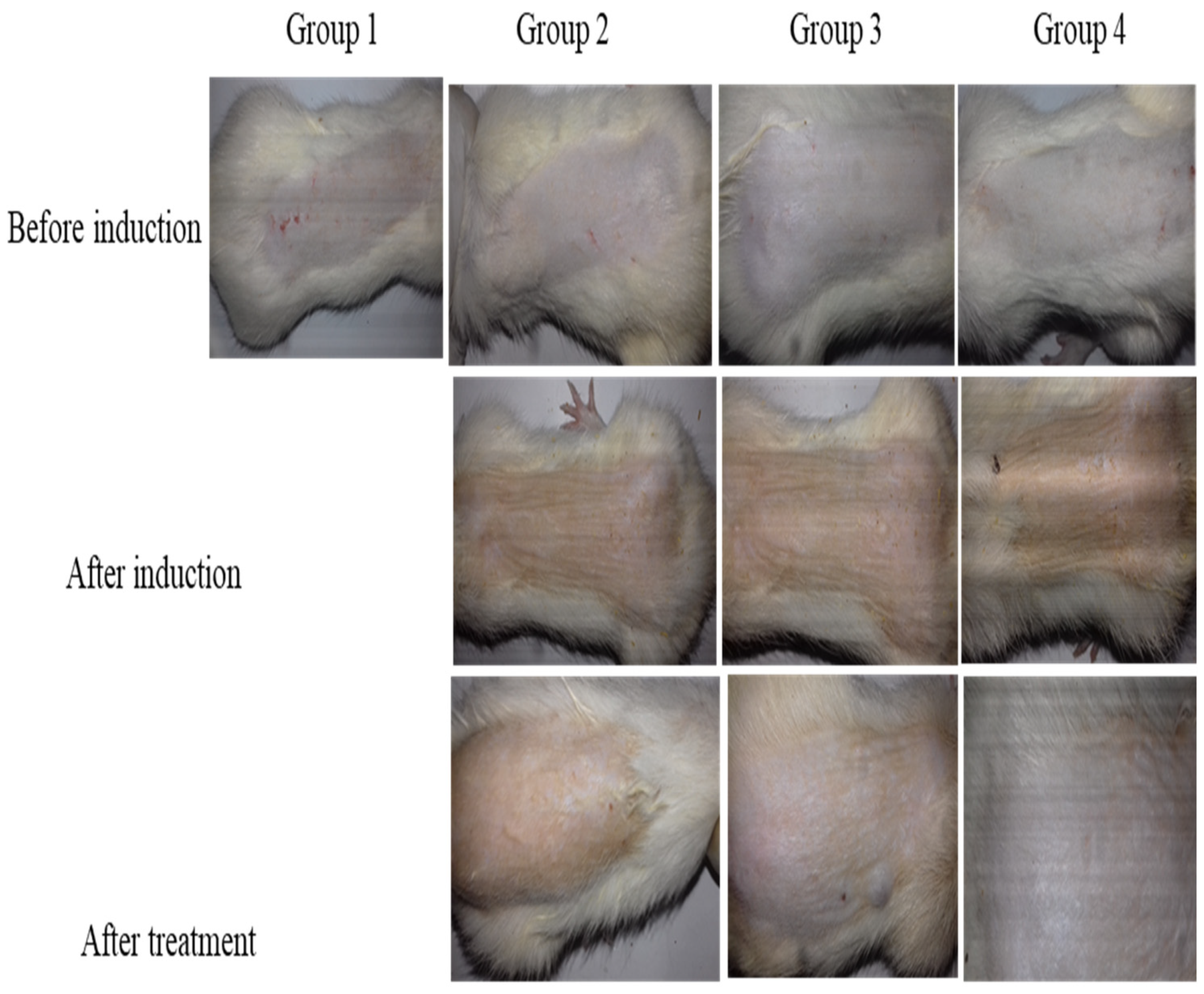
2.13. In Vivo Antifungal Study
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
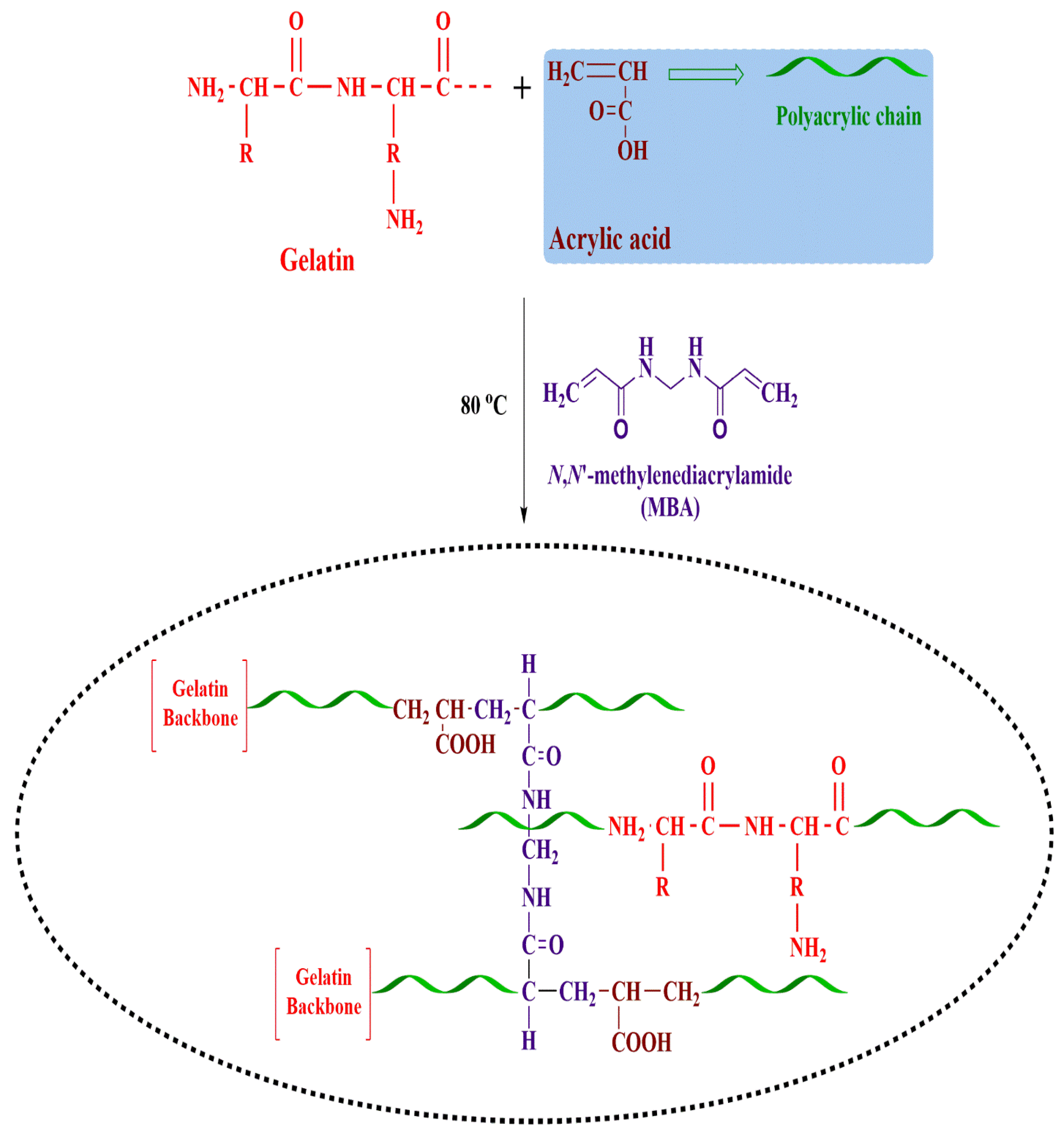
4.2. Synthesis of Gelatin-g-Poly-(Acrylic Acid) Nanogels
4.3. Characterization
4.3.1. Particle Size Analysis
4.3.2. FTIR
4.3.3. Thermal Stability
4.3.4. XRD
4.3.5. SEM
4.3.6. Swelling Study
4.3.7. Drug Loading and DEE
4.3.8. Drug Release Studies and Kinetics
4.3.9. Preparation of HPMC Gel-Containing TBH-Loaded Nanogels
4.3.10. TBH Skin Penetration and Retention Studies
4.3.11. Antifungal Activity Studies
4.3.12. Skin Irritation Studies
4.3.13. In Vivo Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—Estimate precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, K.; Chu, S.; Scheufele, C.; Giesey, R.L.; Mehrmal, S.; Uppal, P.; Delost, G.R. The global, regional, and national burden of fungal skin diseases in 195 countries and territories: A cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. JAAD Int. 2021, 2, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, S.; Haroon, T.; Hussain, I.; Bokhari, M.; Khurshid, K. Tinea unguium in Lahore, Pakistan. Med. Mycol. 2001, 39, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, S.; Tesfaye, B.; Fente, D. Epidemiology of dermatophyte and non-dermatophyte fungi infection in Ethiopia. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.; Whitham, H.K.; Jackson, B.R. Economic Burden of Fungal Diseases in the United States. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; p. ofac097. [Google Scholar]
- Drgona, L.; Khachatryan, A.; Stephens, J.; Charbonneau, C.; Kantecki, M.; Haider, S.; Barnes, R. Clinical and economic burden of invasive fungal diseases in Europe: Focus on pre-emptive and empirical treatment of Aspergillus and Candida species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Sharma, G.S.; Goyal, A.K.; Ghosh, G.; Si, S.C.; Rath, G. Recent advances in topical carriers of anti-fungal agents. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, D.; Zu, G.; Forson, A.M.; Tromp, L.; Sjollema, J.; van Rijn, P. Nanogels: A novel approach in antimicrobial delivery systems and antimicrobial coatings. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3634–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Rangaraj, N.; Laxmikeshav, K.; Sampathi, S. Nanogels as drug carriers–Introduction, chemical aspects, release mechanisms and potential applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sennakesavan, G.; Mostakhdemin, M.; Dkhar, L.; Seyfoddin, A.; Fatihhi, S. Acrylic acid/acrylamide based hydrogels and its properties-A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 180, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkes, M.J.; Scott, L.J.; Goa, K.L. Terbinafine. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karri, V.; Raman, S.K.; Kuppusamy, G.; Mulukutla, S.; Ramaswamy, S.; Malayandi, R. Terbinafine hydrochloride loaded nanoemulsion based gel for topical application. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 45, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, V.; Mohamed, R.; Kuckling, D.; Adler, H.-J.P.; Choudhary, V. Interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) nanogels based on gelatin and poly (acrylic acid) by inverse miniemulsion technique: Synthesis and characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaz, N.; Khan, I.U.; Khalid, I.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, H.A.; Asghar, S.; Khalid, S.H.; Shahzad, Y.; Yousaf, A.M.; Hussain, T. In vitro and toxicological assessment of dexamethasone sodium phosphate loaded pH sensitive Pectin-g-poly (AA)/PVP semi interpenetrating network. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.S.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U. Cross-linked β-cyclodextrin and carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels for controlled drug delivery of acyclovir. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuminek, G.; Rauber, G.S.; Riekes, M.K.; de Campos, C.E.M.; Monti, G.A.; Bortoluzzi, A.J.; Cuffini, S.L.; Cardoso, S.G. Single crystal structure, solid state characterization and dissolution rate of terbinafine hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 78, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Vora, Z.M. Formulation development and optimization of transungual drug delivery system of terbinafine hydrochloride for the treatment of onychomycosis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Heidari, B. Crosslinked graft copolymer of methacrylic acid and gelatin as a novel hydrogel with pH-responsiveness properties. Materials 2011, 4, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.P.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.L.; Yao, K.D. Gelatin/montmorillonite hybrid nanocomposite. I. Preparation and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, N.; Chu, X.; Yuan, P.; Chi, C.; Wu, F.; Shen, J. Study on montmorillonite–chlorhexidine acetate–terbinafine hydrochloride intercalation composites as drug release systems. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21369–21377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta-Taboada, O.; Sobral, P.J.d.A.; Carvalho, R.A.; Habitante, A.M.B. Thermomechanical properties of biodegradable films based on blends of gelatin and poly (vinyl alcohol). Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, N.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F.; Malik, N.S.; Khan, K.U. Designing gelatin-based swellable hydrogels system for controlled delivery of salbutamol sulphate: Characterization and toxicity evaluation. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 4535–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.M.A.; Sil, B.C.; Iliopoulos, F.; Lever, R.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Preparation, characterisation, and topical delivery of terbinafine. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šnejdrová, E.; Martiška, J.; Loskot, J.; Paraskevopoulos, G.; Kováčik, A.; Regdon Jr, G.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Palát, K.; Konečná, K. PLGA based film forming systems for superficial fungal infections treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 163, 105855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radev, L.; Fernandes, M.; Salvado, I.; Kovacheva, D. Organic/Inorganic bioactive materials Part III: In vitro bioactivity of gelatin/silicocarnotite hybrids. Open Chem. 2009, 7, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajare, A.; Dol, H.; Patil, K. Design and development of terbinafine hydrochloride ethosomal gel for enhancement of transdermal delivery: In vitro, in vivo, molecular docking, and stability study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mohan, C.; Shankar, M.K.U.; Gulati, M. Physiochemical characterization and release rate studies of soliddispersions of ketoconazole with pluronic f127 and pvp k-30. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2011, 10, 685. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukat, H.; Pervaiz, F.; Khan, M.; Rehman, S.; Akram, F.; Abid, U.; Noreen, S.; Nadeem, M.; Qaiser, R.; Ahmad, R. Development of β-cyclodextrin/polyvinypyrrolidone-co-poly (2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulphonic acid) hybrid nanogels as nano-drug delivery carriers to enhance the solubility of Rosuvastatin: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.M.H.; Khan, S.; Rehanullah, M.; Ranjha, N.M. Synthesis and characterization of chemically cross-linked acrylic acid/gelatin hydrogels: Effect of pH and composition on swelling and drug release. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 187961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Pervaiz, F.; Shoukat, H.; Shabbir, K.; Noreen, S.; Anwar, M. Fabrication and evaluation of pH sensitive chemically cross-linked interpenetrating network [Gelatin/Polyvinylpyrrolidone-co-poly (acrylic acid)] for targeted release of 5-fluorouracil. Polym. Bull. 2020, 79, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, B. Mucoadhesive and pH-responsive behavior of gelatin containing hydrogels for protein drug delivery applications. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2020, 32, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rehim, H.A.; Hegazy, E.-S.A.; Hamed, A.A.; Swilem, A.E. Controlling the size and swellability of stimuli-responsive polyvinylpyrrolidone–poly (acrylic acid) nanogels synthesized by gamma radiation-induced template polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qian, H.; Mao, Z.; Ding, D.; Jiang, X. Hollow core–porous shell structure poly (acrylic acid) nanogels with a superhigh capacity of drug loading. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3532–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackiewicz, M.; Stojek, Z.; Karbarz, M. Synthesis of cross-linked poly (acrylic acid) nanogels in an aqueous environment using precipitation polymerization: Unusually high volume change. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashri, A.; Lazim, A. A study on the effect of the concentration of N,N-methylenebisacrylamide and acrylic acid toward the properties of Dioscorea hispida-starch-based hydrogel. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1614, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadani, R.; Mitra, U.K. Synthesis and studies on water swelling behaviour of polyacrylamide hydrogels. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 369, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Ahmad, M.; Aamir, M.N.; Minhas, M.U.; Shah, H.H.; Shah, M.A. Cross-linked pH-sensitive pectin and acrylic acid based hydrogels for controlled delivery of metformin. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mackiewicz, M.; Dagdelen, S.; Marcisz, K.; Waleka-Bargiel, E.; Stojek, Z.; Karbarz, M. Redox-degradable microgel based on poly (acrylic acid) as drug-carrier with very high drug-loading capacity and decreased toxicity against healthy cells. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 190, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Naz, F.; Dinda, A.K.; Koul, V. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of doxorubicin loaded biodegradable semi-interpenetrating hydrogel implants of poly (acrylic acid)/gelatin for post surgical tumor treatment. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, A.I. Gelatin based pH-sensitive hydrogels for colon-specific oral drug delivery: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro release study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Omidian, H.; Hashemi, S.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M. Synthesis of fast-swelling superabsorbent hydrogels: Effect of crosslinker type and concentration on porosity and absorption rate. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avasatthi, V.; Pawar, H.; Dora, C.P.; Bansod, P.; Gill, M.S.; Suresh, S. A novel nanogel formulation of methotrexate for topical treatment of psoriasis: Optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, N.; Rejinold, N.S.; Mangalathillam, S.; Biswas, R.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Fluconazole loaded chitin nanogels as a topical ocular drug delivery agent for corneal fungal infections. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datt, N.; Poonuru, R.R.; Yadav, P.K. Development and Characterization of Griseofulvin Loaded nanostructured lipid carrier gel for Treating Dermatophytosis. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2022, 2, 100074. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, U.; Rasul, A.; Sher, M.; Qadir, M.I.; Nazir, I.; Mehmood, Y.; Riaz, H.; Shah, P.A.; Jamil, Q.A.; Khan, B.A. Development, characterization and evaluation of anti-fungal activity of miconazole based nanogel prepared from biodegradable polymer. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Giulbudagian, M.; Yealland, G.; Hönzke, S.; Edlich, A.; Geisendörfer, B.; Kleuser, B.; Hedtrich, S.; Calderón, M. Breaking the barrier-potent anti-inflammatory activity following efficient topical delivery of etanercept using thermoresponsive nanogels. Theranostics 2018, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, S.Y.B.; Almeida, R.R.; Pinto, N.A.R.; de Mayrinck, C.; Vieira, S.S.; Haddad, J.F.; Leitao, A.A.; Guimaraes, L.G.d.L. Encapsulation of essential oils using cinnamic acid grafted chitosan nanogel: Preparation, characterization and antifungal activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 902–912. [Google Scholar]
- Elnaggar, Y.S.; Talaat, S.M.; Bahey-El-Din, M.; Abdallah, O.Y. Novel lecithin-integrated liquid crystalline nanogels for enhanced cutaneous targeting of terconazole: Development, in vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, G.; Panonnummal, R.; Gupta, S.; Jayakumar, R.; Sabitha, M. Acitretin and aloe-emodin loaded chitin nanogel for the treatment of psoriasis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Elkomy, M.H.; Elmenshawe, S.F.; Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.M. Topical ketoprofen nanogel: Artificial neural network optimization, clustered bootstrap validation, and in vivo activity evaluation based on longitudinal dose response modeling. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3294–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.; Zhaveh, S.; Khalili, S.T.; Rahmani-Cherati, T.; Abollahi, A.; Bayat, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Mohsenifar, A. Encapsulation of Mentha piperita essential oils in chitosan–cinnamic acid nanogel with enhanced antimicrobial activity against Aspergillus flavus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 54, 310–319. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.M.; Patel, P.; Sheth, N.R.; Rathod, L.V.; Ashara, K.C. Fabrication and characterization of film-forming voriconazole transdermal spray for the treatment of fungal infection. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2017, 55, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Somagoni, J.; Boakye, C.H.; Godugu, C.; Patel, A.R.; Mendonca Faria, H.A.; Zucolotto, V.; Singh, M. Nanomiemgel-a novel drug delivery system for topical application-in vitro and in vivo evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115952. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, Q.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Batool, F.; Malik, N.S.; Rehman, M. Novel β-cyclodextrin nanosponges by chain growth condensation for solubility enhancement of dexibuprofen: Characterization and acute oral toxicity studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102089. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Khan, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Akram, M.R.; Minhas, M.U.; Qaisar, M.N.; Ali, M.R.; Ahmad, H.; Zaman, M. Synthesis of co-polymeric network of carbopol-g-methacrylic acid nanogels drug carrier system for gastro-protective delivery of ketoprofen and its evaluation. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Feky, G.S.; El-Banna, S.T.; El-Bahy, G.; Abdelrazek, E.; Kamal, M. Alginate coated chitosan nanogel for the controlled topical delivery of Silver sulfadiazine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.; Kashaw, S.K.; Sau, S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S.; Agrawal, R.K.; Iyer, A.K. pH responsive 5-fluorouracil loaded biocompatible nanogels for topical chemotherapy of aggressive melanoma. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 232–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Sarfraz, M.; Sohail, M.; Khan, K.U.; Tanveer, S.; Ijaz, S. Synthesis and Evaluation of Finasteride-Loaded HPMC-Based Nanogels for Transdermal Delivery: A Versatile Nanoscopic Platform. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2426960. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.M.; Mallikarjuna, B.; Rao, K.K.; Siraj, S.; Rao, K.C.; Subha, M. Novel thermo/pH sensitive nanogels composed from poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) for controlled release of an anticancer drug. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 891–897. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, P.; Kashaw, S.K.; Kashaw, V.; Shabaaz, J.; Dahiya, R. Synthesis and ex vivo evaluation of PLGA chitosan surface modulated double walled transdermal Pluronic nanogel for the controlled delivery of Temozolomide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 742–754. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, R.L.; Narkhede, J.S.; Mujumdar, A.; Naik, J.B. Synthesis and evaluation of luliconazole loaded biodegradable nanogels prepared by pH-responsive Poly (acrylic acid) grafted Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose using amine based cross linker for topical targeting: In vitro and Ex vivo assessment. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.G.; Ayoub, B.M. DOE optimization of nano-based carrier of pregabalin as hydrogel: New therapeutic & chemometric approaches for controlled drug delivery systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41503. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.J.; Mesquida, P.; Jones, S.A. Investigating the ability of nanoparticle-loaded hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and xanthan gum gels to enhance drug penetration into the skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, D.-Z.; Liu, J.-J.; Chang, T.-W.; Ho, H.-O.; Sheu, M.-T. Development of terbinafine solid lipid nanoparticles as a topical delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4409. [Google Scholar]
- Vaghasiya, H.; Kumar, A.; Sawant, K. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles based controlled release system for topical delivery of terbinafine hydrochloride. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Rashidipour, M.; Khosravi, P.; Shahryarhesami, S.; Ashrafi, B.; Kaviani, M.; Sarabi, M.M. Biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial and epigenetic effects of novel chitosan-based quercetin nanohydrogel in human cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5963. [Google Scholar]
- Wavikar, P.; Vavia, P. Nanolipidgel for enhanced skin deposition and improved antifungal activity. AAPS Pharmscitech 2013, 14, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A.; Nabi, B.; Rehman, S.; Md, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Ahmad, O.A.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Development and Evaluation of Polymeric Nanosponge Hydrogel for Terbinafine Hydrochloride: Statistical Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Polymers 2020, 12, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morteza-Semnani, K.; Saeedi, M.; Akbari, J.; Hedayati, S.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Rahimnia, S.M.; Babaei, A.; Ghazanfari, M.; Haghani, I.; Hedayati, M.T. Green Formulation, characterization, antifungal and biological safety evaluation of Terbinafine HCl niosomes and niosomal gels manufactured by eco-friendly green method. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 2325–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Rarokar, N.R.; Menghani, S.S.; Kerzare, D.R.; Khedekar, P.B.; Bharne, A.P.; Alamri, A.S.; Alsanie, W.F.; Alhomrani, M.; Sreeharsha, N.; Asdaq, S.M.B. Preparation of Terbinafin-Encapsulated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Antifungal Carbopol® Hydrogel with Improved Efficacy: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Formulation Code | pH | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi Model | Korsmeyer–Peppas Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | n | ||
| F1 | 5 | 0.9656 | 0.9849 | 0.8862 | 0.9955 | 0.808 |
| 7.4 | 0.8753 | 0.9954 | 0.9267 | 0.9802 | 0.691 | |
| F2 | 5 | 0.9599 | 0.9944 | 0.8853 | 0.9917 | 0.802 |
| 7.4 | 0.9138 | 0.9953 | 0.9117 | 0.9843 | 0.731 | |
| F3 | 5 | 0.9694 | 0.9556 | 0.8535 | 0.9794 | 0.860 |
| 7.4 | 0.9436 | 0.9908 | 0.8908 | 0.9848 | 0.779 | |
| F4 | 5 | 0.9736 | 0.9850 | 0.8803 | 0.9977 | 0.825 |
| 7.4 | 0.9313 | 0.9946 | 0.9083 | 0.9906 | 0.750 | |
| F5 | 5 | 0.7687 | 0.9938 | 0.9524 | 0.9732 | 0.615 |
| 7.4 | 0.7050 | 0.9980 | 0.9693 | 0.9800 | 0.581 | |
| F6 | 5 | 0.7683 | 0.9868 | 0.9618 | 0.9833 | 0.611 |
| 7.4 | 0.6756 | 0.9862 | 0.9776 | 0.9852 | 0.567 | |
| F7 | 5 | 0.7341 | 0.9834 | 0.9668 | 0.9819 | 0.594 |
| 7.4 | 0.7284 | 0.9802 | 0.9582 | 0.9713 | 0.594 | |
| F8 | 5 | 0.7910 | 0.9903 | 0.9364 | 0.9618 | 0.634 |
| 7.4 | 0.8646 | 0.9865 | 0.9451 | 0.9928 | 0.671 | |
| F9 | 5 | 0.9782 | 0.9849 | 0.8722 | 0.9973 | 0.841 |
| 7.4 | 0.9277 | 0.9915 | 0.9101 | 0.9898 | 0.745 | |
| Groups | Score ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (No application) | Erythema | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Edema | 0.00 ± 0.00 | |
| Group 2 (Formalin) | Erythema | 2.66 ± 0.57 |
| Edema | 2.33 ± 0.57 | |
| Group 3 (nanogels) | Erythema | 0.66 ± 0.57 |
| Edema | 0.33 ± 0.57 | |
| Code | Gelatin (%w/w) | A.A (%w/w) | APS (%w/w) | MBA (%w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAG 1 | 1 | 20 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 2 | 2 | 20 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 3 | 3 | 20 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 4 | 2 | 20 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 5 | 2 | 30 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 6 | 2 | 40 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 7 | 2 | 40 | 0.40 | 2 |
| AAG 8 | 2 | 40 | 0.40 | 4 |
| AAG 9 | 2 | 40 | 0.40 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, S.u.; Khalid, I.; Hussain, L.; Imam, M.T.; Shahid, I. Topical Delivery of Terbinafine HCL Using Nanogels: A New Approach to Superficial Fungal Infection Treatment. Gels 2023, 9, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110841
Hassan Su, Khalid I, Hussain L, Imam MT, Shahid I. Topical Delivery of Terbinafine HCL Using Nanogels: A New Approach to Superficial Fungal Infection Treatment. Gels. 2023; 9(11):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Shams ul, Ikrima Khalid, Liaqat Hussain, Mohammad T. Imam, and Imran Shahid. 2023. "Topical Delivery of Terbinafine HCL Using Nanogels: A New Approach to Superficial Fungal Infection Treatment" Gels 9, no. 11: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9110841









