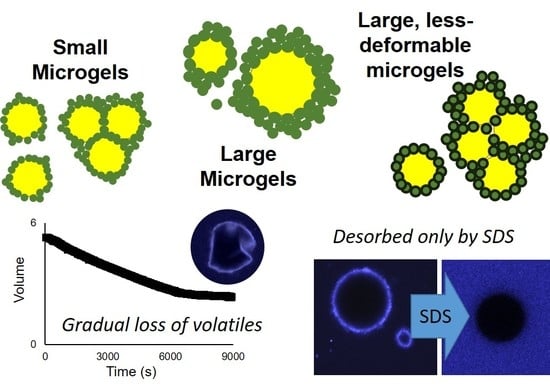
Impacts of Size and Deformability of β-Lactoglobulin Microgels on the Colloidal Stability and Volatile Flavor Release of Microgel-Stabilized Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Microgel Preparation
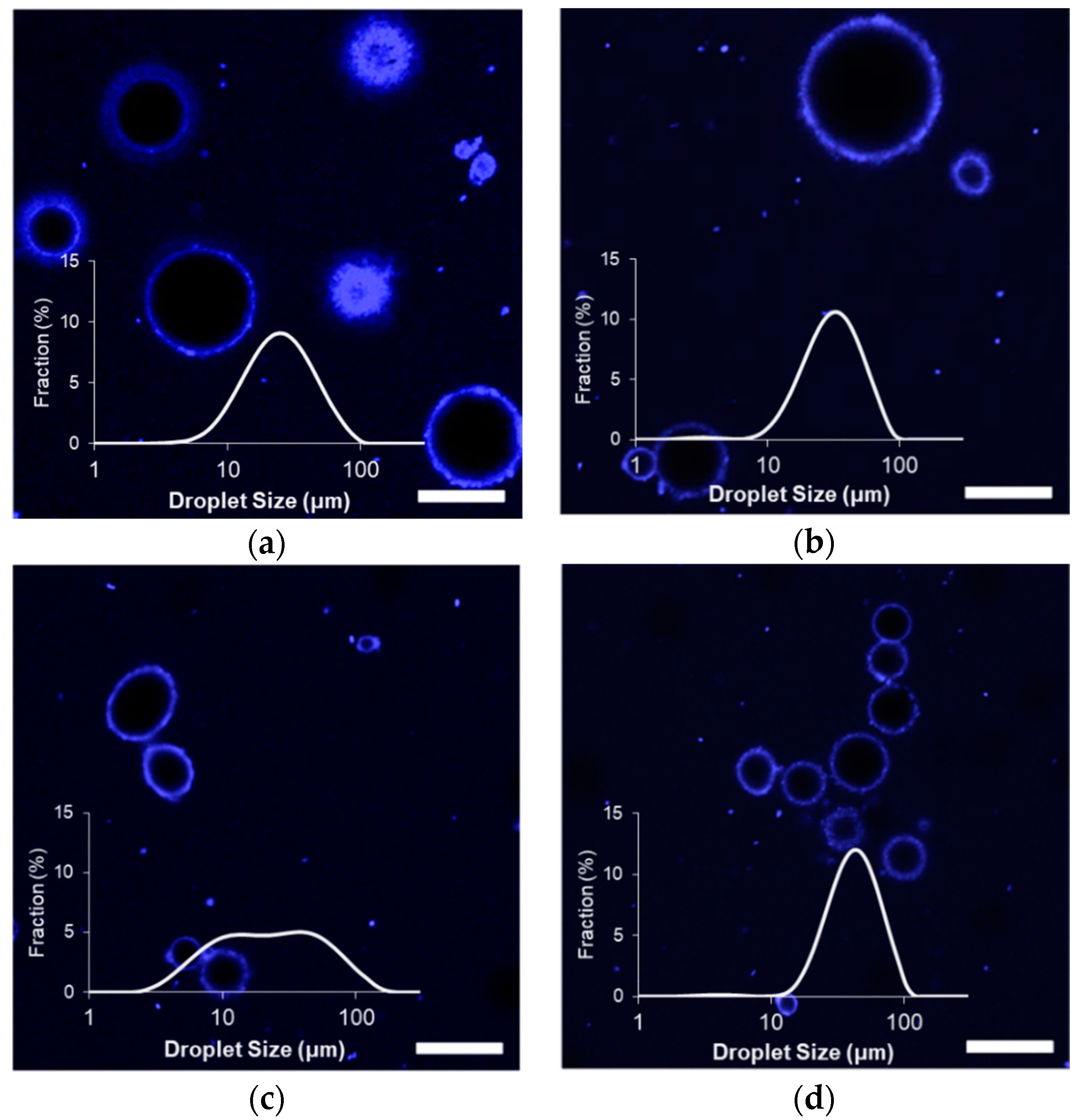
2.2. Emulsion Properties Following Homogenization
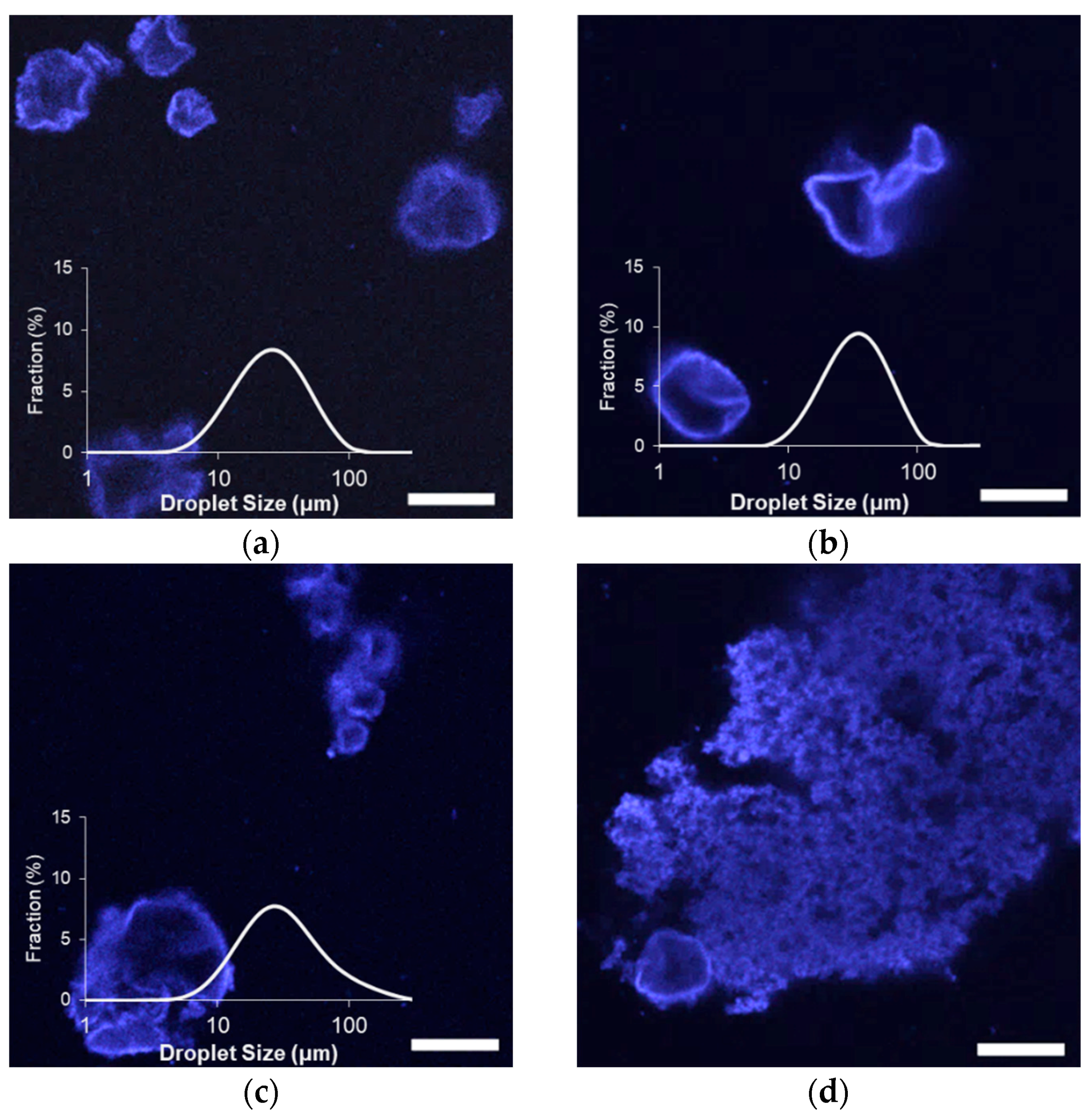
2.3. Effect of Storage on Emulsion Droplet Stability
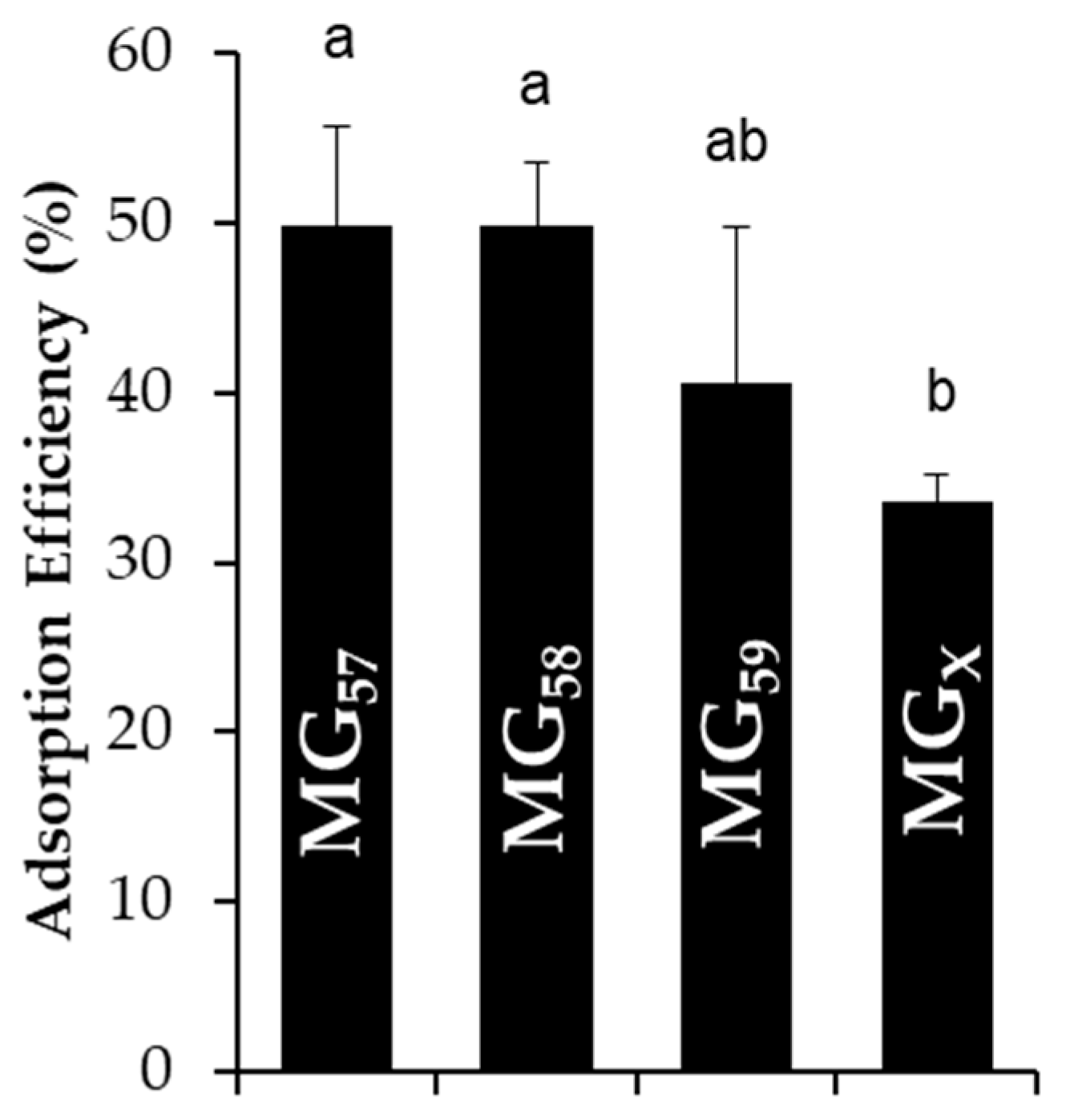
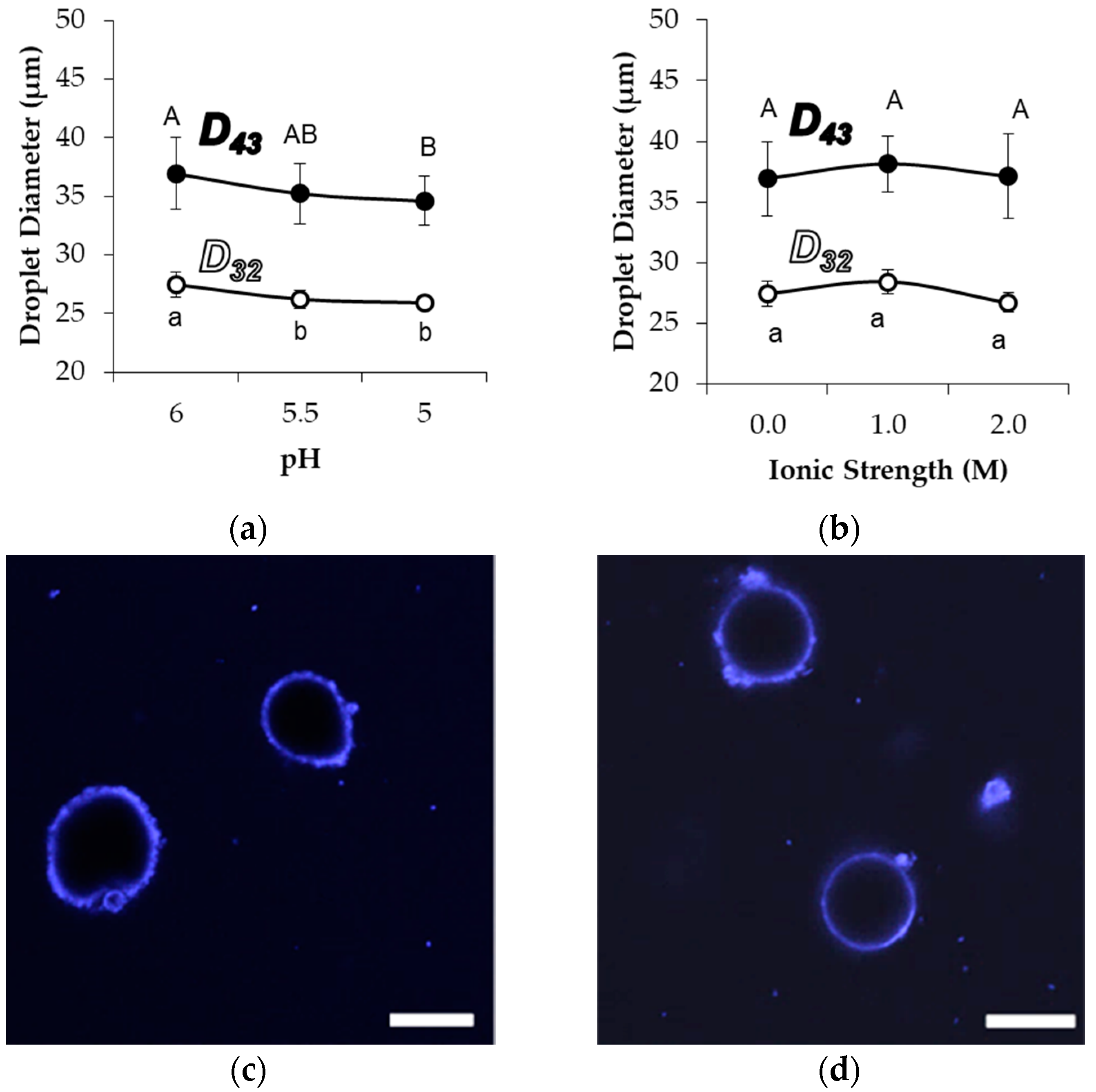
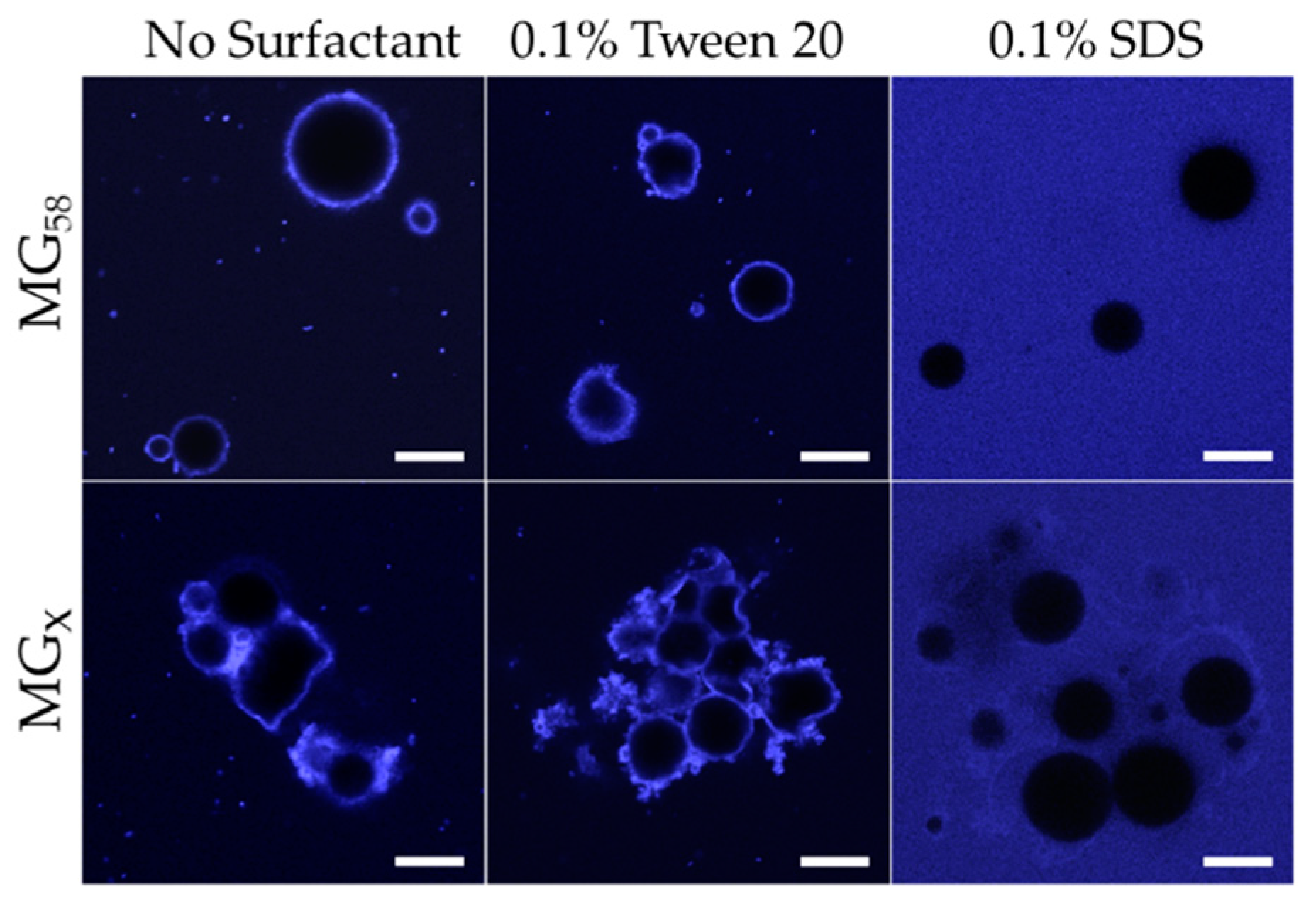
2.4. Effect of pH, Ionic Strength, and Surfactants on Initial Emulsion Droplet Stability
2.5. Flavor Release
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Microgel Preparation
4.3. Microgel Characterization
4.4. Emulsion Preparation
4.5. Emulsion Characterization
4.6. Adsorption Efficiency
4.7. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.8. Flavor Release
4.9. Statistical Treatment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pickering, S.U. Emulsion. J. Chem. Soc. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Use of nanoparticle and microparticles in the formation and stabilization of food emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, N.; Binks, B. Pickering emulsions stabilised by laponite clay particles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 5640–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.; Fletcher, P.; Holt, B.; Beaussoubre, P.; Wong, K. Selective retardation of perfume oil evaporation from oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by either surfactant or nanoparticles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18024–18030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aveyard, R.; Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Emulsions stabilized solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 503–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Velikov, K.P.; Velev, O.D. Pickering stabilization of foams and emulsions with particles of biological origin. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brom, F.W. Food, consumer concerns, and trust: Food ethics for a globalizing market. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2000, 12, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, S.; Bear, C.; Walker, G. The sceptical consumer? Exploring views about food assurance. Food Policy 2008, 33, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Lee, D.I.; Park, J.M. Biopolymer-based microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1261–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destribates, M.; Eyharts, M.; Lapeyre, V.; Sellier, E.; Varga, I.; Ravaine, V.; Schmitt, V. Impact of PNIPAM microgel size on its ability to stabilize pickering emulsions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, L.; Schmitt, C.; Bovetto, L.; Rouvet, M. Mechanism of formation of stable heat-induced beta-lactoglobulin microgels. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 9, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Savin, G.; Pouzot, M.; Schmitt, C.; Mezzenga, R. Structure of heat-induced beta-lactoglobulin aggregates and their complexes with sodium-dodecyl sulfate. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.; Cho, Y.; Farkas, B.; Jones, O. Control of thermal fabrication and size of b-lactoglobulin-based microgels and their potential applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Moitzi, C.; Bovay, C.; Rouvet, M.; Bovetto, L.; Donato, L.; Leser, M.E.; Schurtenberger, P.; Stradner, A. Internal structure and colloidal behaviour of covalent whey protein microgels obtained by heat treatment. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4876–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerer, L.; Jones, O. Emulsification capacity of microgels assembled from β-lactoglobulin and pectin. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.; Farkas, B.; Jones, O. Dynamic and viscoelastic behavior of β-lactoglobulin microgels of varying sizes at fluid interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.; Farkas, B.; Jones, O. Effect of crosslinking on the physical and chemical properties of β-lactoglobulin (BLG) microgels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Murray, B.; Holmes, M.; Ettelaie, R.; Abdalla, A.; Yang, X. In vitro digestion of pickering emulsions stabilized by soft whey protein microgel particles: Influence of thermal treatment. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 3558–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horozov, T.S.; Binks, B.P. Particle-stabilized emulsions: A bilayer or a bridging monolayer? Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignati, E.; Piazza, R.; Lockhart, T.P. Pickering emulsions: Interfacial tension, colloidal layer morphology, and trapped-particle motion. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6650–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destribates, M.; Rouvet, M.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Schmitt, C.; Binks, B. Emulsions stabilized by whey protein microgel particles: Towards food-grade pickering emulsions. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6941–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinska, K.; Campbell, R.A.; Zarbakhsh, A.; Resmini, M. Adsorption versus aggregation of nipam nanogels: New insight into their behaviour at the air/water interface as a function of concentration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 17173–17179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copolovici, L.O.; Niinemets, Ü. Temperature dependencies of henry’s law constants and octanol/water partition coefficients for key plant volatile monoterpenoids. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, A.; Caggioni, M.; Ergun, R.; Hartel, R.; Spicer, P. Arrested coalescence in pickering emulsions. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchcic, C.; Tromp, R.; Meinders, M.; Stuart, M. Harnessing the advantages of hard and soft colloids by the use of core–shell particles as interfacial stabilizers. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erni, P.; Jerri, H.A.; Wong, K.; Parker, A. Interfacial viscoelasticity controls buckling, wrinkling and arrest in emulsion drops undergoing mass transfer. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6958–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.G.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of protein–polysaccharide nanoparticle fabrication methods: Impact of biopolymer complexation before or after particle formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, A.R.; Parker, R.M.; Groombridge, A.S.; Maestro, A.; Coulston, R.J.; Hegemann, J.; Kierfeld, J.; Scherman, O.A.; Abell, C. Microcapsule buckling triggered by compression-induced interfacial phase change. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10987–10994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, S.; Jones, O.G. Effects of chloride, thiocyanate and sulphate salts on β-lactoglobulin–pectin associative complexes. Intl. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, M.; Wei, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Norde, W.; Li, Y. Pickering emulsions stabilized by whey protein nanoparticles prepared by thermal cross-linking. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 127, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Microgel | 1 Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| MG57 | 266 ± 7.91 a | 0.0368 |
| MG58 | 231 ± 7.11 b | 0.0195 |
| MG59 | 150 ± 2.47 c | 0.0327 |
| MGX | 228 ± 12.0 b | 0.0233 |
| Microgel Used | D32 (μm) 1 | D43 (μm) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Weeks | Six Weeks | Zero Weeks | Six Weeks | |
| MG57 | 21.8 ± 1.52 cd | 21.9 ± 2.37 cd | 30.4 ± 3.27 d | 32.0 ± 5.05 cd |
| MG58 | 27.6 ± 2.19 bc | 30.5 ± 2.50 b | 36.8 ± 3.97 bcd | 41.7 ± 4.14 abc |
| MG59 | 16.0 ± 2.32 d | 25.9 ± 2.05 bc | 34.4 ± 1.62 cd | 44.7 ± 2.60 ab |
| MGX | 38.7 ± 5.58 a | N/A 2 | 48.2 ± 2.99 a | N/A 2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murphy, R.W.; Zhu, L.; Narsimhan, G.; Jones, O.G. Impacts of Size and Deformability of β-Lactoglobulin Microgels on the Colloidal Stability and Volatile Flavor Release of Microgel-Stabilized Emulsions. Gels 2018, 4, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030079
Murphy RW, Zhu L, Narsimhan G, Jones OG. Impacts of Size and Deformability of β-Lactoglobulin Microgels on the Colloidal Stability and Volatile Flavor Release of Microgel-Stabilized Emulsions. Gels. 2018; 4(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurphy, Ryan W., Lijie Zhu, Ganesan Narsimhan, and Owen Griffith Jones. 2018. "Impacts of Size and Deformability of β-Lactoglobulin Microgels on the Colloidal Stability and Volatile Flavor Release of Microgel-Stabilized Emulsions" Gels 4, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030079
APA StyleMurphy, R. W., Zhu, L., Narsimhan, G., & Jones, O. G. (2018). Impacts of Size and Deformability of β-Lactoglobulin Microgels on the Colloidal Stability and Volatile Flavor Release of Microgel-Stabilized Emulsions. Gels, 4(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030079