Process Variable Optimization in the Manufacture of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Gel Materials
Abstract
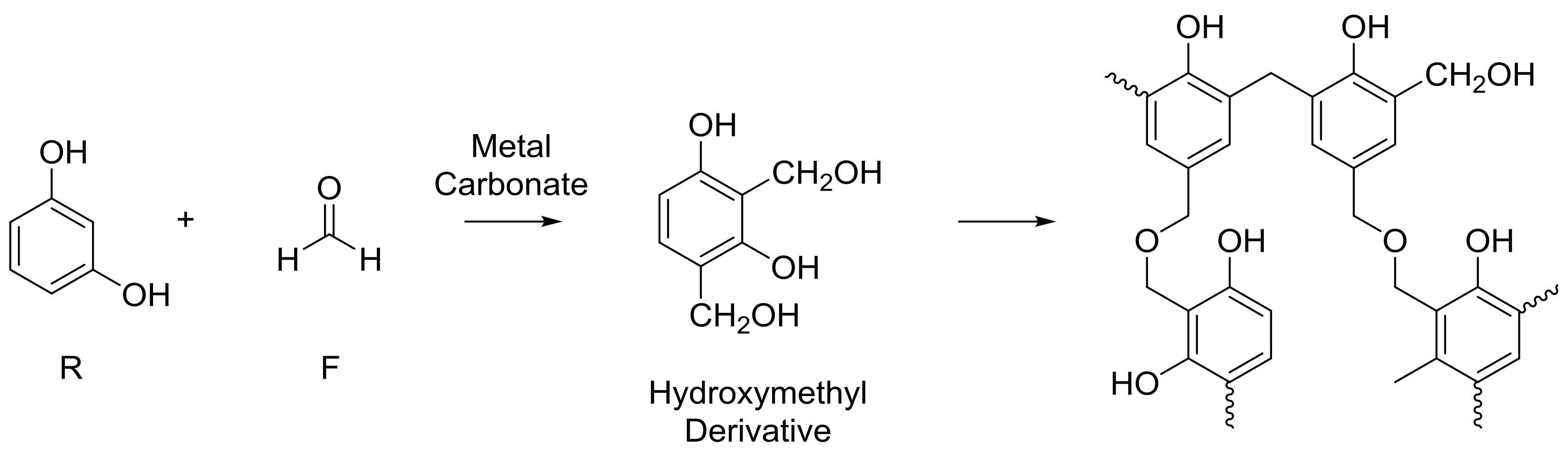
1. Introduction
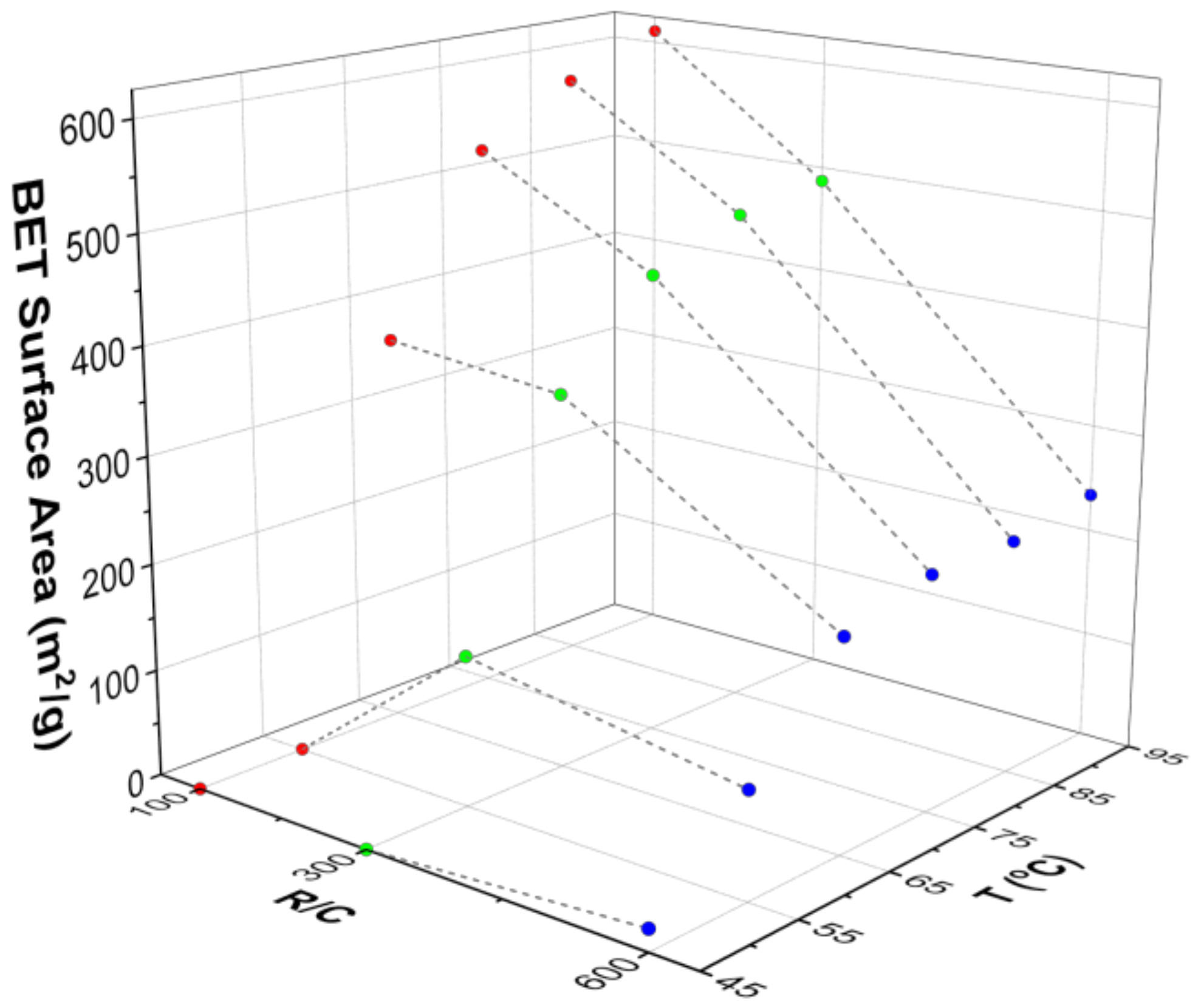
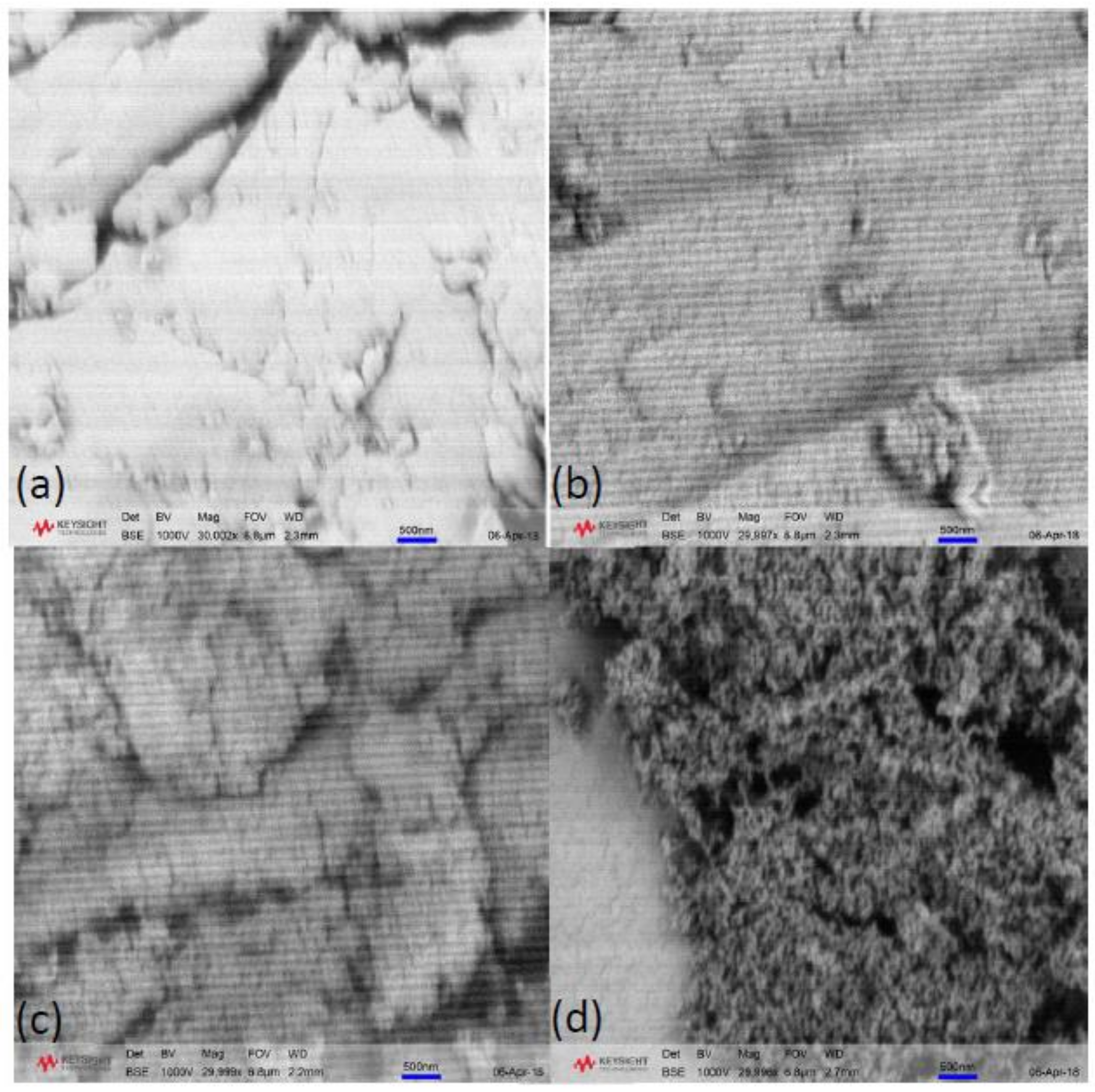
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Solvent Exchange Method
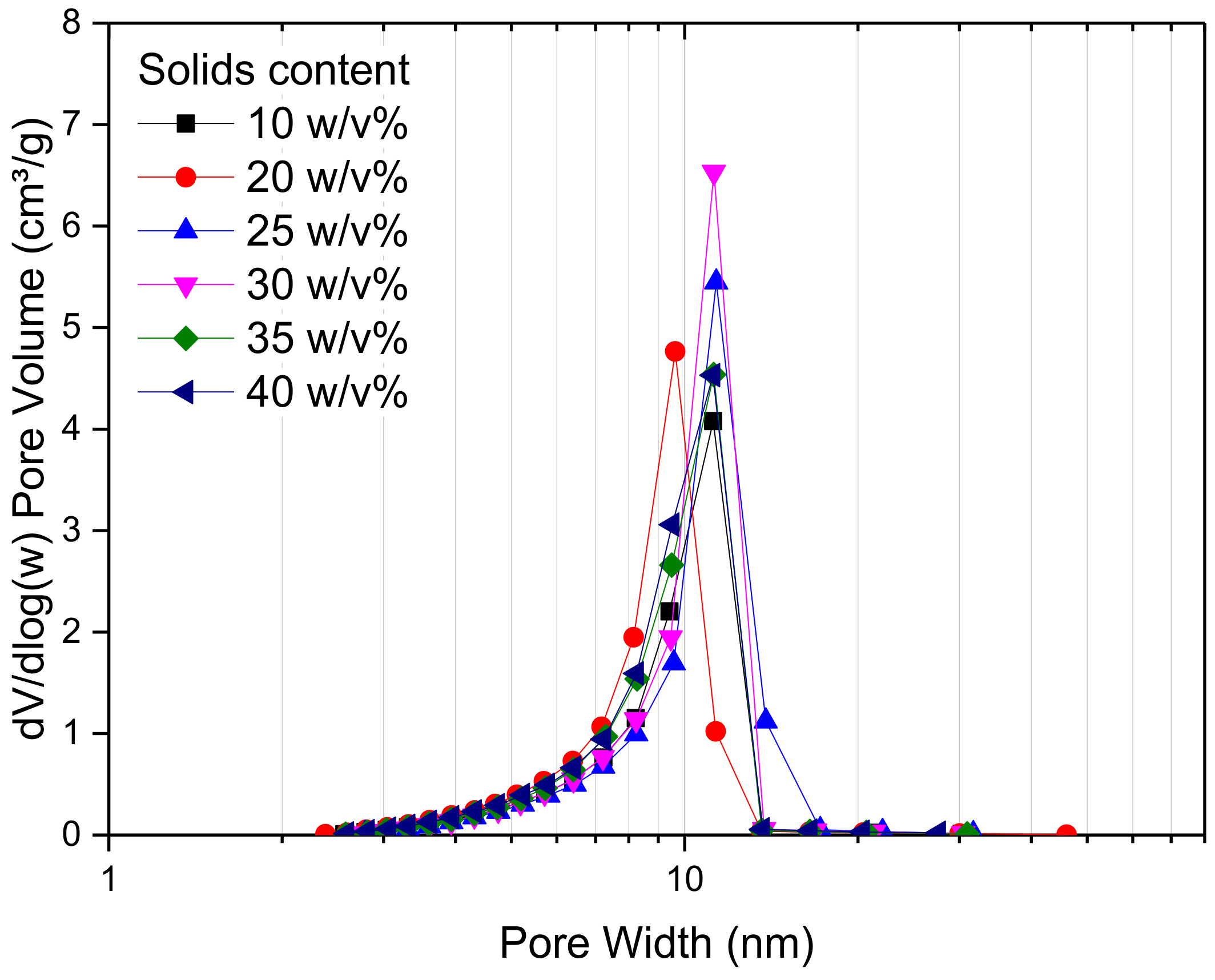
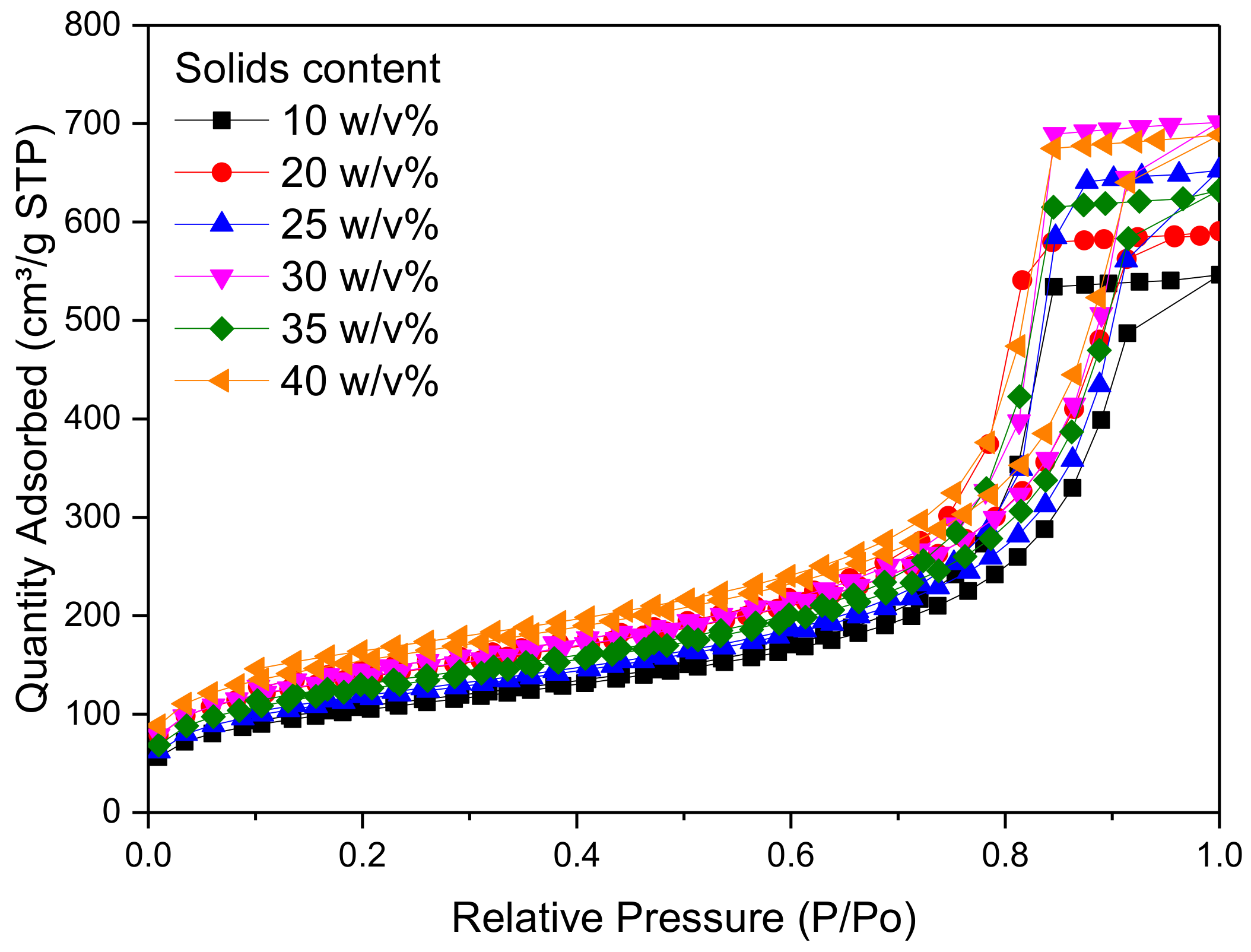
2.2. Effect of Changing Solids Content
2.3. Ambient Pressure vs. Vacuum Drying
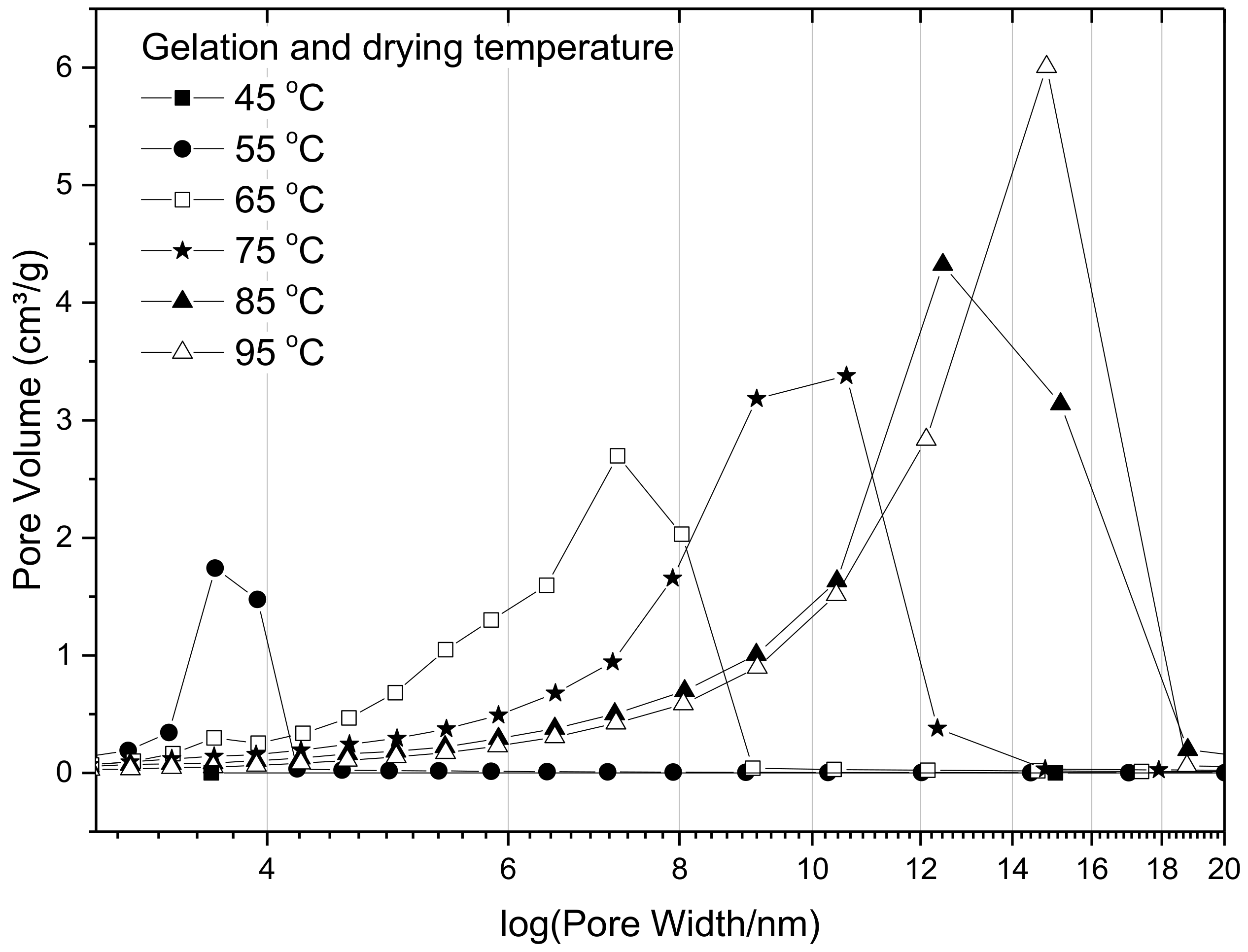
2.4. Influence of Synthetic and Processing Temperature
3. Conclusions
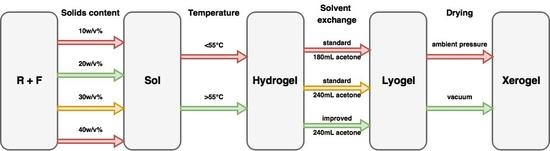
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Sample Characterisation
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pekala, R.W. Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, J.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Chatenet, M.; Chaînet, E.; Pirard, R.; Cornet, N.; Achard, P. Platinum supported on resorcinol–formaldehyde based carbon aerogels for PEMFC electrodes: Influence of the carbon support on electrocatalytic properties. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Marie, J.; Lambert, S.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Achard, P. Carbon xerogels as catalyst supports for PEM fuel cell cathode. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, A.; Dong, X.; Hara, H.; Vasiliev, A.; Sammes, N. Novel carbon aerogel-supported catalysts for PEM fuel cell application. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.; Mokaya, R. Microporous activated carbon aerogels via a simple subcritical drying route for CO2 capture and hydrogen storage. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.F.; Vajo, J.J.; Van Atta, S.L.; Olson, G.L. Enhanced hydrogen storage kinetics of LiBH4 in nanoporous carbon scaffolds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Endo, A.; Ohmori, T.; Nakaiwa, M. Porous properties of carbon gel microspheres as adsorbents for gas separation. Carbon 2004, 42, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-R.; Nakao, M.; Nishiyama, N.; Egashira, Y.; Ueyama, K. Gas permeation and pervaporation of water/alcohols through the microporous carbon membranes prepared from resorcinol/formaldehyde/quaternary ammonium compounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, R.; Lavela, P.; Ortiz, G.F.; Tirado, J.L. Carbon microspheres obtained from resorcinol-formaldehyde as high-capacity electrodes for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2005, 8, A222–A225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glora, M.; Wiener, M.; Petricevic, R.; Probstle, H.; Fricke, J. Integration of carbon aerogels in PEM fuel cells. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 285, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Arduini-Schuster, M.; Kuhn, J.; Nilsson, O.; Fricke, J.; Pekala, R. Thermal conductivity of monolithic organic aerogels. Science 1992, 255, 971–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, C.; Feng, J. Carbon fiber reinforced carbon aerogel composites for thermal insulation prepared by soft reinforcement. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.J.; Haw, M.D.; Sefcik, J.; Fletcher, A.J. Gelation mechanism of resorcinol-formaldehyde gels investigated by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10231–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.J.; Haw, M.D.; Sefcik, J.; Fletcher, A.J. Effects of secondary metal carbonate addition on the porous character of resorcinol–formaldehyde xerogels. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13571–13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Raap, N.; Angel Menéndez, J.; Arenillas, A. Simultaneous adjustment of the main chemical variables to fine-tune the porosity of carbon xerogels. Carbon 2014, 78, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Raap, N.; Angel Menéndez, J.; Arenillas, A. RF xerogels with tailored porosity over the entire nanoscale. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 195, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Gommes, C.J.; Pirard, R.; Pirard, J.-P. Effect of the counter-ion of the basification agent on the pore texture of organic and carbon xerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 4698–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairen-Jimenez, D.; Carrasco-Marin, F.; Moreno-Castilla, C. Porosity and surface area of monolithic carbon aerogels prepared using alkaline carbonates and organic acids as polymerization catalysts. Carbon 2006, 44, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, J.; Milow, B.; Ratke, L. Subcritically dried resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels from a base-acid catalyzed synthesis route. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and properties of resorcinol–formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. J. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khatat, A.M.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A. Advances in tailoring resorcinol-formaldehyde organic and carbon gels. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamon, H.; Ishizaka, H.; Mikami, M.; Okazaki, M. Porous structure of organic and carbon aerogels synthesized by sol-gel polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. Carbon 1997, 35, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaca, K.Z.; Parkinson, J.A.; Sefcik, J. Kinetics of early stages of resorcinol-formaldehyde polymerization investigated by solution-phase nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Polymer 2017, 110, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Herrera, J.; Lozano, P.C. Mitigation of anomalous expansion of carbon xerogels and controllability of mean-pore-size by changes in mold geometry. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 458, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C.; Pajonk, G.M. Chemistry of aerogels and their application. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4243–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2006; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, O.; Ehrburger-Dolle, F.; Rieker, T.P.; Pajonk, G.M.; Pinto, N.; Rao, A.V. Small-angle X-ray scattering of a new series of organic aerogels. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Aerogels (ISA-6), Albuquerque, NM, USA, 8–11 October 2000; pp. 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fricke, J.; Tillotson, T. Aerogels: Production, characterization, and applications. Thin Solid Films 1997, 297, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W.; Kong, F.M. A synthetic route to organic aerogels-mechanism, structure, and properties. J. Phys. Colloq. 1989, 50, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Pirard, R.; Marien, J.; Pirard, J.P. Porous carbon xerogels with texture tailored by pH control during sol-gel process. Carbon 2004, 42, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamon, H.; Ishizaka, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Suzuki, T. Preparation of mesoporous carbon by freeze drying. Carbon 1999, 37, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czakkel, O.; Marthi, K.; Geissler, E.; Laszlo, K. Influence of drying on the morphology of resorcinol-formaldehyde-based carbon gels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nishimura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tamon, H. Control of mesoporosity of carbon gels prepared by sol-gel polycondensation and freeze drying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 288, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Thery, A.; Pirard, R.; Marien, J.; Kocon, L.; Rouzaud, J.N.; Beguin, F.; Pirard, J.P. Carbon aerogels, cryogels and xerogels: Influence of the drying method on the textural properties of porous carbon materials. Carbon 2005, 43, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, N.; Mardan, A. Effect of water removal on the textural properties of resorcinol/formaldehyde gels by azeotropic distillation. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 5451–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertfeger, F.; Frank, D.; Schmidt, M. Hydrophobic waterglass based aerogels without solvent exchange or supercritical drying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 225, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargaftik, N.; Volkov, B.; Voljak, L. International tables of the surface tension of water. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1983, 12, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.R.; Tamitsuji, C.; Nishihara, H.; Tamon, H. Preparation of mesoporous carbon gels from an inexpensive combination of phenol and formaldehyde. Carbon 2005, 43, 2628–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, J.J. The surface tension of pure liquid compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1972, 1, 841–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanto, E.J.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Sol-gel-derived carbon aerogels and xerogels: Design of experiments approach to materials synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, S.; Barbieri, O.; Ehrburger-Dolle, F.; Geissler, E.; Achard, P.; Bley, F.; Hecht, A.-M.; Livet, F.; Pajonk, G.M.; Pinto, N. DLS and SAXS investigations of organic gels and aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 285, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (iupac technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Menéndez, J.; Arenillas, A. Influence of alkaline compounds on the porosity of resorcinol-formaldehyde xerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 452, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ritter, J.A. Effect of synthesis pH on the structure of carbon xerogels. Carbon 1997, 35, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamon, H.; Ishizaka, H. Influence of gelation temperature and catalysts on the mesoporous structure of resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 223, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GrenierLoustalot, M.F.; Larroque, S.; Grande, D.; Grenier, P.; Bedel, D. Phenolic resins: 2. Influence of catalyst type on reaction mechanisms and kinetics. Polymer 1996, 37, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Micropore analysis. In Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
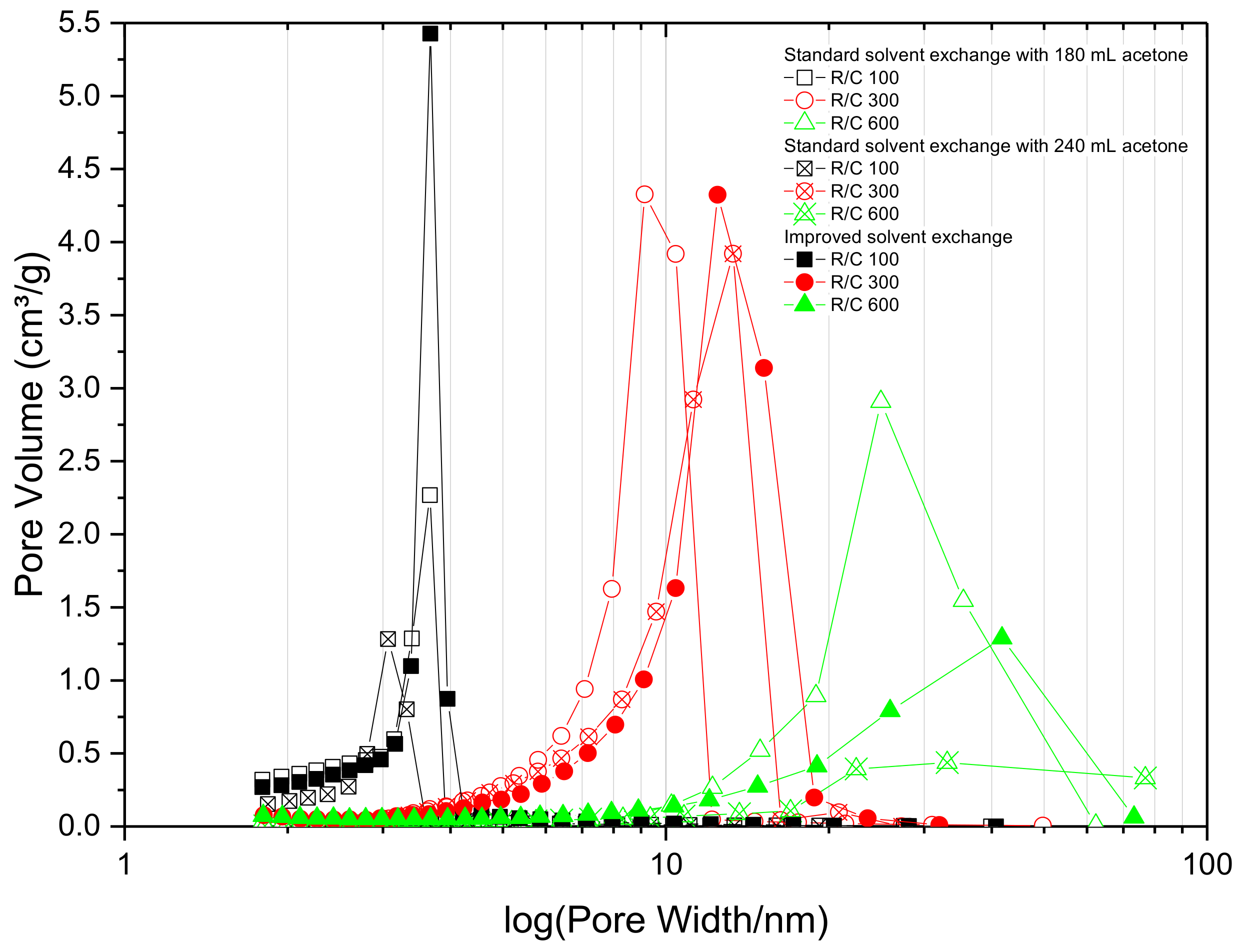
| R/C | SBET (m2/g) | VT (cm3/g) | Vµ (cm3/g) | (nm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetone Exchange Method | Acetone Exchange Method | Acetone Exchange Method | Acetone Exchange Method | |||||||||
| Standard | Improved | Standard | Improved | Standard | Improved | Standard | Improved | |||||
| 180 mL | 240 mL | 180 mL | 240 mL | 180 mL | 240 mL | 180 mL | 240 mL | |||||
| 100 | 480 | 470 | 580 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.052 | 0.046 | 0.059 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 200 | 470 | 530 | 500 | 0.54 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.040 | 0.056 | 0.052 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| 300 | 420 | 430 | 470 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 1.05 | 0.043 | 0.052 | 0.060 | 8 | 10 | 11 |
| 400 | 370 | 300 | 220 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.046 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 12 | 14 | 24 |
| 500 | 300 | 220 | 230 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1.17 | 0.039 | 0.033 | 0.034 | 16 | 24 | 29 |
| 600 | 230 | 110 | 220 | 1.01 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.036 | 0.019 | 0.036 | 24 | 27 | 22 |
| w/v% Solids | SBET (m2/g) | VT (cm3/g) | Vµ (cm3/g) | (nm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | |||||||||
| 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | |
| 10 | 500 | 370 | - | 0.36 | 0.85 | - | 0.057 | 0.037 | - | 3 | 9 | - |
| 20 | 500 | 490 | 280 | 0.32 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.046 | 3 | 8 | 18 |
| 25 | 550 | 410 | 190 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 1.07 | 0.054 | 0.042 | 0.030 | 3 | 10 | 32 |
| 30 | 570 | 490 | 260 | 0.46 | 1.08 | 1.17 | 0.055 | 0.064 | 0.045 | 3 | 9 | 28 |
| 35 | 570 | 450 | 260 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 1.23 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.038 | 3 | 9 | 27 |
| 40 | 540 | 550 | 330 | 0.44 | 1.07 | 1.53 | 0.048 | 0.077 | 0.056 | 3 | 9 | 29 |
| R/C | SBET (m2/g) | VT (cm3/g) | Vµ (cm3/g) | (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Drying Method | Drying Method | Drying Method | |||||
| Ambient | Vacuum | Ambient | Vacuum | Ambient | Vacuum | Ambient | Vacuum | |
| 100 | 510 | 600 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.037 | 0.064 | 4 | 3 |
| 300 | 380 | 460 | 1.11 | 1.12 | 0.044 | 0.064 | 13 | 12 |
| 600 | 90 | 120 | 0.31 | 0.54 | 0.014 | 0.023 | 19 | 30 |
| T (°C) | SBET (m2/g) | VT (cm3/g) | Vµ (cm3/g) | (nm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | R/C Ratio | |||||||||
| 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | 100 | 300 | 600 | |
| 45 | - | <1 | 20 | - | - | 0.07 | - | - | 0.002 | - | - | 9 |
| 55 | <1 | 140 | 100 | - | 0.14 | 0.48 | - | 0.010 | 0.011 | - | 4 | 22 |
| 65 | 370 | 350 | 200 | 0.22 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.054 | 0.036 | 0.027 | 3 | 6 | 20 |
| 75 | 530 | 440 | 220 | 0.37 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.064 | 0.052 | 0.030 | 3 | 8 | 21 |
| 85 | 580 | 470 | 220 | 0.46 | 1.05 | 0.81 | 0.059 | 0.060 | 0.036 | 3 | 11 | 22 |
| 95 | 610 | 490 | 230 | 0.52 | 1.18 | 0.92 | 0.057 | 0.064 | 0.038 | 4 | 12 | 24 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prostredný, M.; Abduljalil, M.G.M.; Mulheran, P.A.; Fletcher, A.J. Process Variable Optimization in the Manufacture of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Gel Materials. Gels 2018, 4, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020036
Prostredný M, Abduljalil MGM, Mulheran PA, Fletcher AJ. Process Variable Optimization in the Manufacture of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Gel Materials. Gels. 2018; 4(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleProstredný, Martin, Mohammed G. M. Abduljalil, Paul A. Mulheran, and Ashleigh J. Fletcher. 2018. "Process Variable Optimization in the Manufacture of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Gel Materials" Gels 4, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020036
APA StyleProstredný, M., Abduljalil, M. G. M., Mulheran, P. A., & Fletcher, A. J. (2018). Process Variable Optimization in the Manufacture of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Gel Materials. Gels, 4(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020036