Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Gel Nanoparticles Loaded with a Pyrimidine-Based Drug for Potent Anticancer Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Drug-Loaded Albumin-Based Gel Nanoformulations Are Monodisperse and Exhibit Long Term Stability
2.2. Albumin-Based NPs Allow High Encapsulation Efficiencies and Sustained Drug Release
2.3. PP-Loaded BSA/HA Gel Nanoparticles Exhibit Potent Anticancer Activity in Colorectal and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
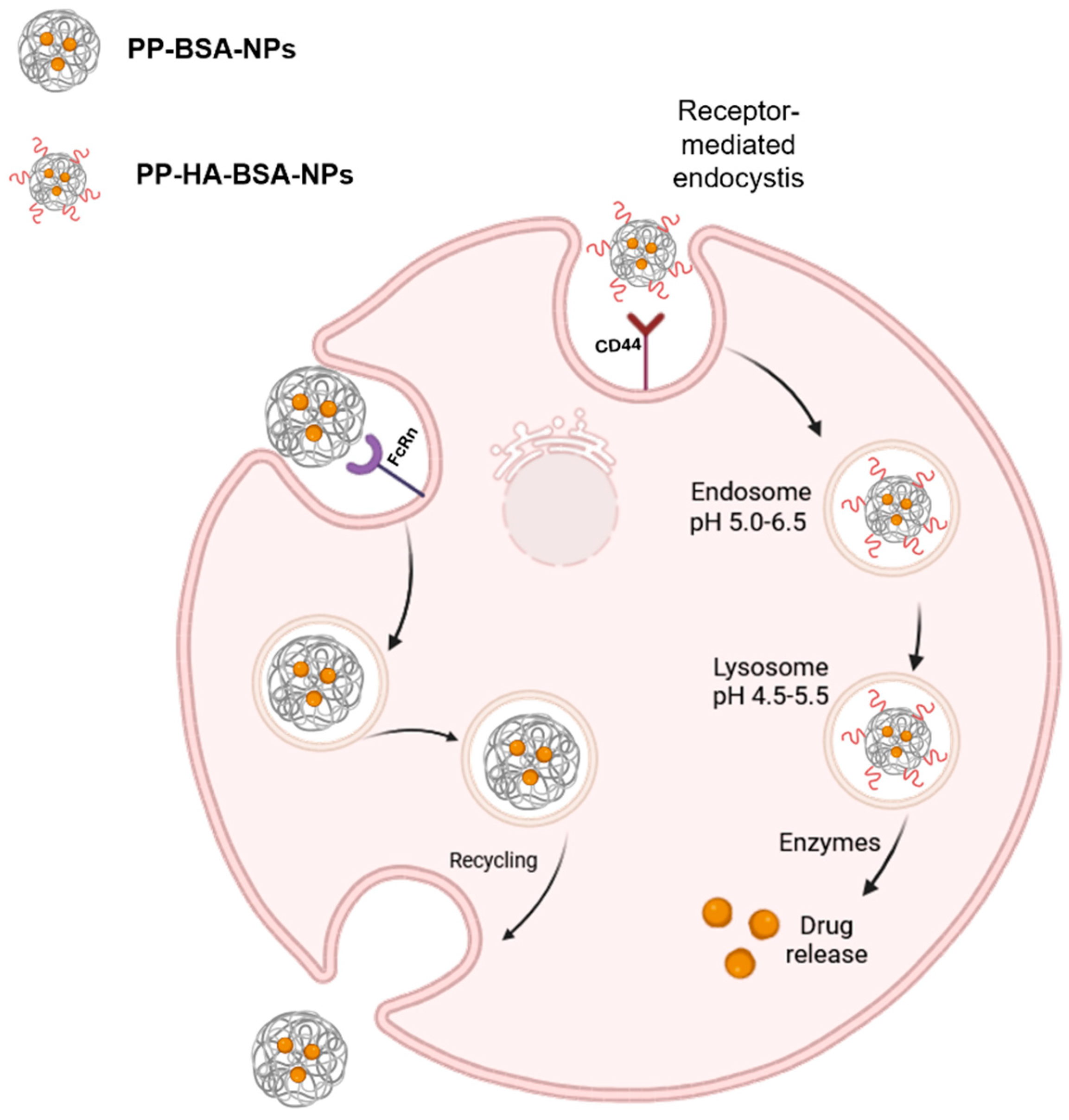
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Albumin-Based Gel Nanoformulations
4.2. Characterization of Albumin-Based Gel Nanoformulations
4.3. Characterization of Drug-Loaded Albumin-Based Gel Nanoformulations
4.3.1. Equipment
4.3.2. Drug Encapsulation Efficiency and Release Assays
4.4. Anticancer Activity
4.4.1. Cell Culture and Solutions
4.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PP | Pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine compound |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| EDC | N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| PDI | Polydispersity |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| STEM | Scanning electron microscopy in transmission mode |
References
- World Health Organization—Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Dey, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Sanyal, R.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, D.K.; De Falco, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status, drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted therapeutics. Genes Dis. 2023, 10, 1367–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zheng, S.; Liu, X.; Kamei, K.-I. Tumor-on-a-chip model for advancement of anti-cancer nano drug delivery system. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paresishvili, T.; Kakabadze, Z. Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Oncol. Rev. 2023, 17, 10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, U.; Sattar, A.; Rasheed, M.A.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Abbas, M. Preparation, characterization and toxicological evaluation of azithromycin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles alone and in combination with cetirizine dihydrochloride. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2025, 2025, 2024178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suardana, I.W.; Wihadmadyatami, H.; Widiasih, D.A. Anticancer Activity of the 28.4 kDa Protein from Pediococcus pentosaceus SR6 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 13, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.; Rasool, M.H.; Khurshid, M.; Aslam, B. Biogenic synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles: Exploring antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory activities and assessing antimicrobial potential against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, F.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Han, J.; Cao, C.; et al. A Review on Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 735446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, N.; Song, K.; Ji, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Lee, R.; Teng, L. Albumin Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 6945–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanjung, Y.; Dewi, M.; Gatera, V.; Barliana, M.; Joni, I.M.; Chaerunisaa, A. Factors Affecting the Synthesis of Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Using the Desolvation Method. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2024, 17, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.L.; Ho, H.K. Navigating albumin-based nanoparticles through various drug delivery routes. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R.; Garcia-Garrido, E.; Somoza, Á. Albumin-Based Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Doxorubicin in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketrat, S.; Japrung, D.; Pongprayoon, P. Exploring how structural and dynamic properties of bovine and canine serum albumins differ from human serum albumin. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 98, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jiang, G.; Yu, H.; Liu, S. Preparation of Metformin/Doxorubicin-Bovine Serum Albumin-Hyaluronic Acid-Carbon Dots Nanoparticles and Their Application in Treating Polycystic Ovary Syndrome on Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor of Patient Combine with Me. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismara, E.; Bongio, C.; Coletti, A.; Edelman, R.; Serafini, A.; Mauri, M.; Simonutti, R.; Bertini, S.; Urso, E.; Assaraf, Y.; et al. Albumin and Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Paclitaxel for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, A.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Vasheghani Farahani, E. 5-Fluorouracil-Loaded BSA Nanoparticles: Formulation Optimization and In Vitro Release Study. AAPS Pharmscitech 2008, 9, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincu Iurciuc, C.-E.; Andrițoiu, C.V.; Popa, M.; Ochiuz, L. Recent Advancements and Strategies for Overcoming the Blood–Brain Barrier Using Albumin-Based Drug Delivery Systems to Treat Brain Cancer, with a Focus on Glioblastoma. Polymers 2023, 15, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Liu, X.-R.; Chen, Q.-B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.-L.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Zou, T. Hyaluronic acid and albumin based nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Carvalho, M.A.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Functionalized Liposome and Albumin-Based Systems as Carriers for Poorly Water-Soluble Anticancer Drugs: An Updated Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassn Mesrati, M.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Syahir, A. CD44: A Multifunctional Mediator of Cancer Progression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadhan, A.; Hou, M.-F.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hu, S.C.-S.; Wang, Y.-M.; Cheng, T.-L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yuan, S.-S.F. CD44 Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis through AKT-Mediated Downregulation of Nuclear FOXA2. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xie, L.; Huang, A.; Xue, C.; Gu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zong, S. The Prognostic and Clinical Value of CD44 in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabil, G.; Alzhrani, R.; Alsaab, H.; Atef, M.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.; Banna, H. CD44 Targeted Nanomaterials for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.G.; Liu, S.L. Role of CD44high/CD133high HCT-116 cells in the tumorigenesis of colon cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7657–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, Q. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Ferreira, D.; Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Carvalho, M.A. Liposomal Formulations for Efficient Delivery of a Novel, Highly Potent Pyrimidine-Based Anticancer Drug. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters Jr., T. All About Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Dastmalchi, S.; Davaran, S. A simple improved desolvation method for the rapid preparation of albumin nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izci, M.; Maksoudian, C.; Manshian, B.B.; Soenen, S.J. The Use of Alternative Strategies for Enhanced Nanoparticle Delivery to Solid Tumors. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1746–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Prajapati, A. Albumin and functionalized albumin nanoparticles: Production strategies, characterization, and target indications. Asian Biomed. 2020, 14, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammady, M.; Mohammadi, Y.; Yousefi, G. Freeze-Drying of Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Nanoparticles: The Effects of Formulation and Technique Parameters on Nanoparticles Characteristics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 3235–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzini, V.; Landucci, E.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Tiozzo Fasiolo, L.; Cinci, L.; Colombo, G.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Bilia, A.R.; Luceri, C.; Bergonzi, M.C. Chitosan coated human serum albumin nanoparticles: A promising strategy for nose-to-brain drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhorn, M.G.; Mahler, H.C.; Langer, K. Freeze drying of human serum albumin (HSA) nanoparticles with different excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, A.A.; Whitney, W.R. The rate of solution of solid substances in their own solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1897, 19, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, V.; Kosmidis, K.; Vlachou, M.; Macheras, P. On the use of the Weibull function for the discernment of drug release mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, S.; Ming, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Luo, M.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Chen, J. Specific cancer stem cell-therapy by albumin nanoparticles functionalized with CD44-mediated targeting. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, C.; Li, F.; Maclean, J.L.; Chen, F.; Swami, A.; Qian, H.; Zhu, J.; Ge, L. The quantitative detection of the uptake and intracellular fate of albumin nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34956–34966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.T.; Mandrup, O.A.; Schelde, K.K.; Luo, Y.; Sørensen, K.D.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Cameron, J.; Stougaard, M.; Steiniche, T.; Howard, K.A. FcRn overexpression in human cancer drives albumin recycling and cell growth; a mechanistic basis for exploitation in targeted albumin-drug designs. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Howard, K.A. FcRn expression in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic opportunities. J. Control. Release 2021, 337, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Wang, W.; Sarkar, S.; Zhang, R. Oral delivery of anti-MDM2 inhibitor SP141-loaded FcRn-targeted nanoparticles to treat breast cancer and metastasis. J. Control. Release 2016, 237, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, R.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Levitzky, I.; Shahar, T.; Livney, Y.D. Hyaluronic acid-serum albumin conjugate-based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24337–24353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, W.; Chow, G.; Knudson, C.B. CD44-mediated uptake and degradation of hyaluronan. Matrix Biol. 2002, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Created with Biorender. Available online: https://biorender.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Solanki, R.; Saini, M.; Mochi, J.; Pappachan, A.; Patel, S. Synthesis, characterization, in-silico and in-vitro anticancer studies of Plumbagin encapsulated albumin nanoparticles for breast cancer treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senra, S.F.M.; Veloso, S.R.S.; Lira, M.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticle-Laden Contact Lenses for the Ocular Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2025, 113, e37839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
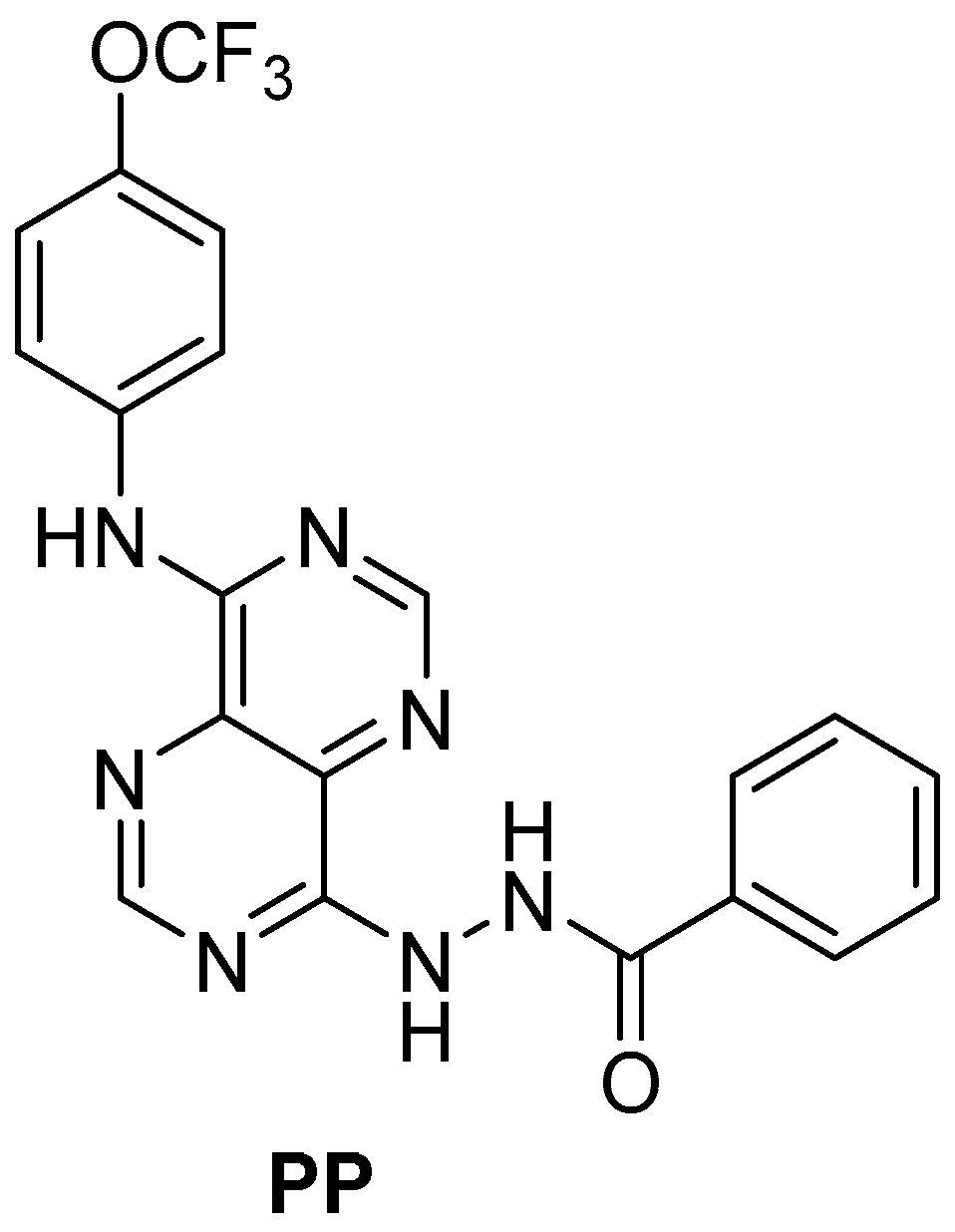
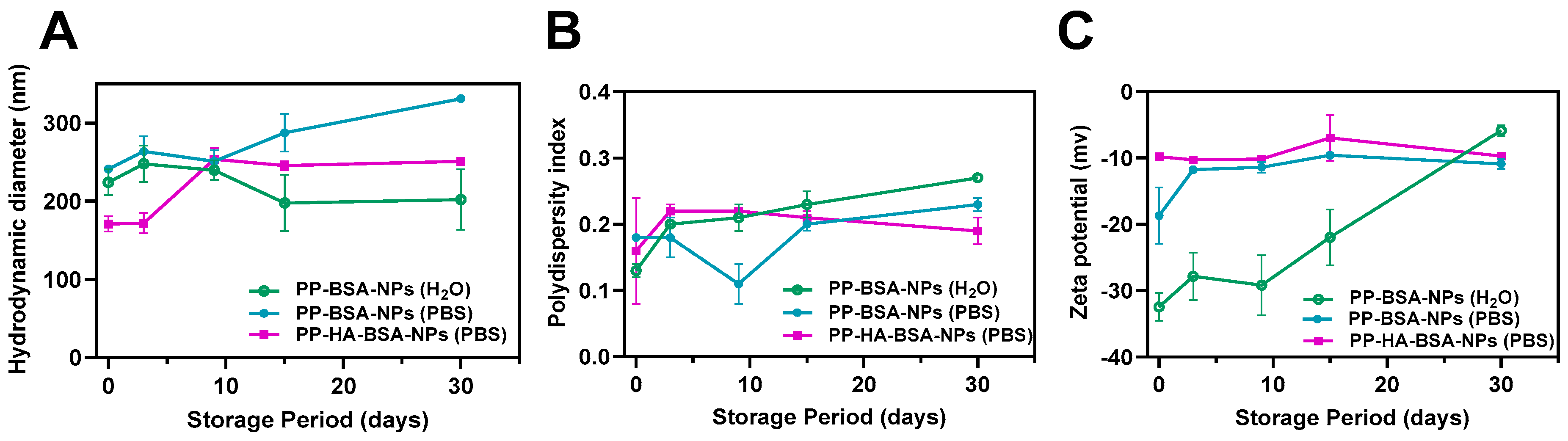
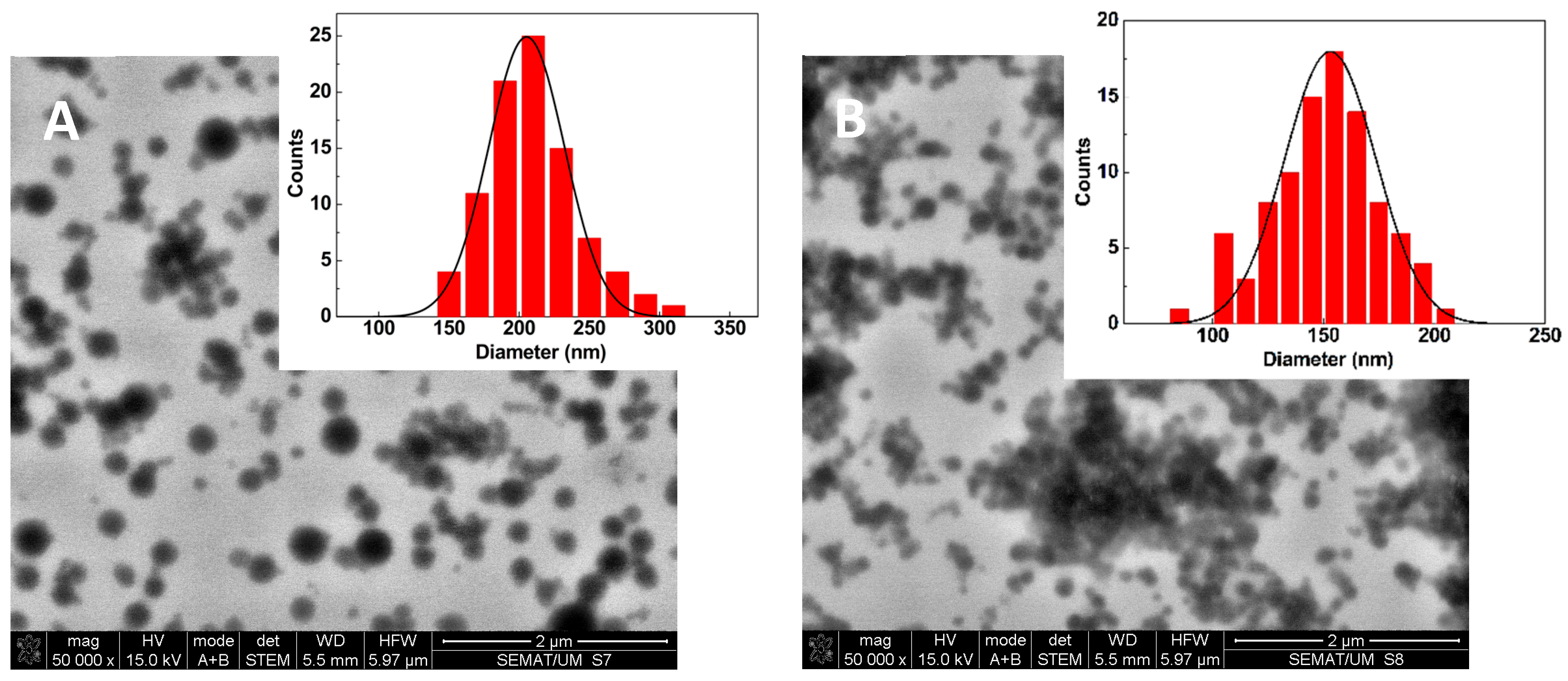
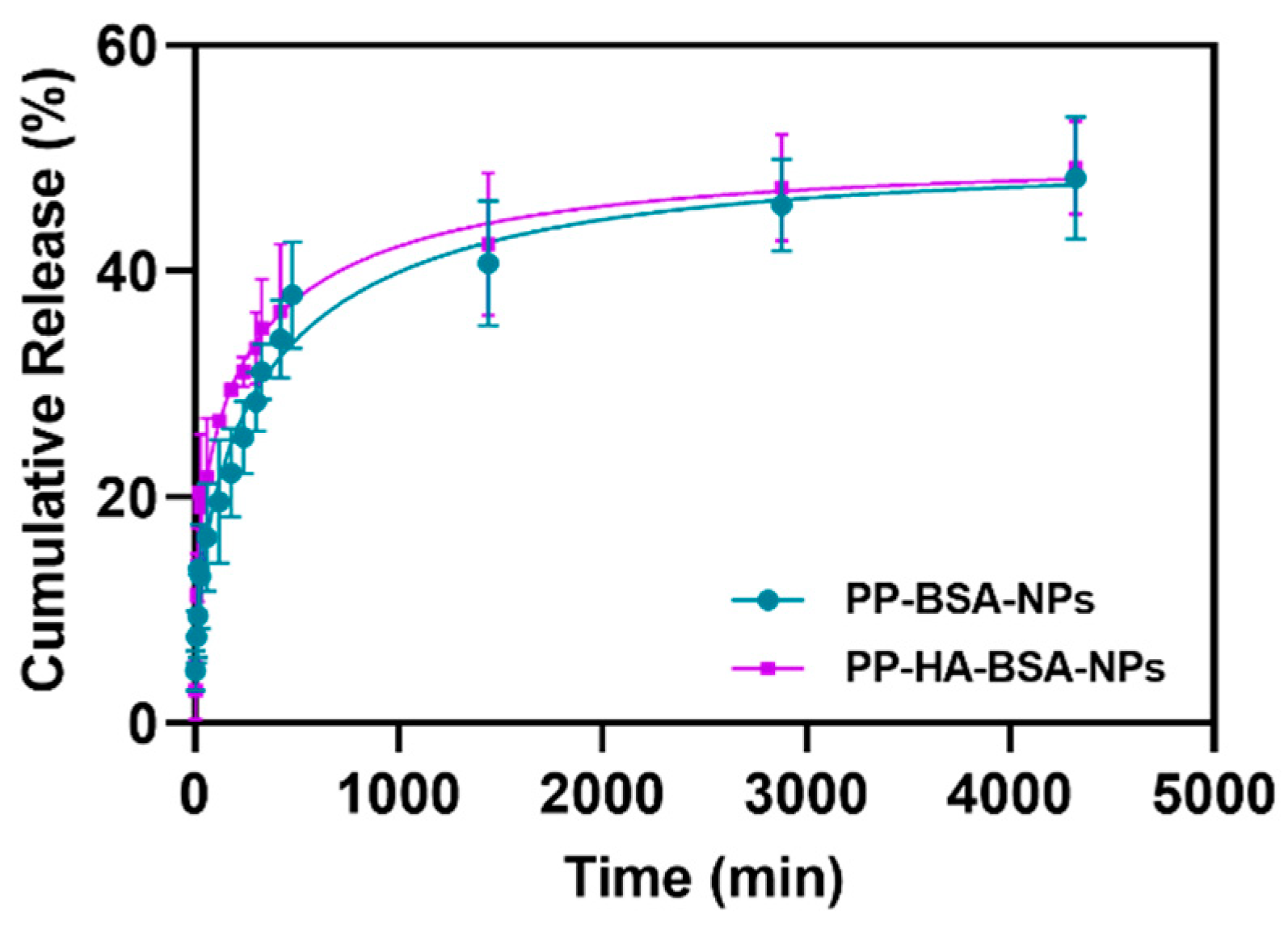
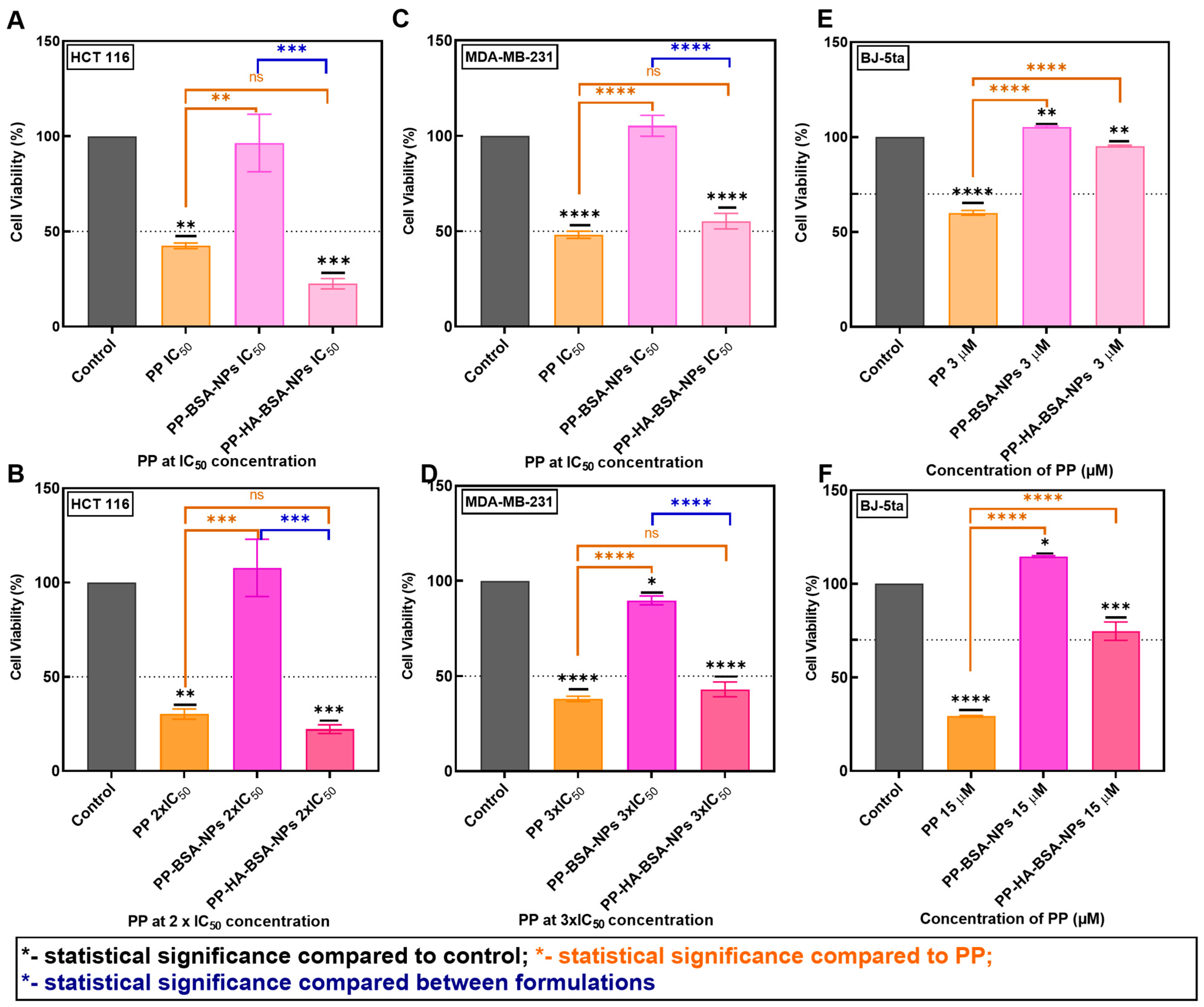
| Albumin Nanoformulations | Medium | Concentration of PP (µM) | Hydrodynamic Diameter ± SD 1 (nm) | PDI ± SD | Zeta Potential ± SD 1 (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSA-NPs | Water | - | 238 ± 2 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | −35.9 ± 0.9 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | Water | 16 | 224 ± 17 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | −32.4 ± 2 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | Phosphate buffer | 16 | 242 ± 3 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | −15.8 ± 5 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | Water | 32 | 208 ± 1 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | −28.4 ± 2 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | Water | 48 | 214 ± 10 | 0.20 ± 0.06 | −24.5 ± 5 |
| HA-BSA-NPs | Water | - | 192 ± 4 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | −26.6 ± 1 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs | Phosphate buffer | 16 | 205 ± 49 | 0.18 ± 0.07 | −9.0 ± 1 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs | Water | 48 | 245 ± 1 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | −26.1 ± 0.5 |
| Albumin Nanoformulations | Hydrodynamic Diameter ± SD 1 (nm) | PDI ± SD 1 |
|---|---|---|
| BSA-NPs | 238 ± 2 | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| BSA-NPs + 2% sucrose (w/v) | 266 ± 23 | 0.22 ± 0.02 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | 198 ± 3 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| PP-BSA-NPs + 2% sucrose (w/v) | 198 ± 1 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| HA-BSA-NPs | 192 ± 4 | 0.21 ± 0.02 |
| HA-BSA-NPs + 2% sucrose (w/v) | 225 ± 2 | 0.22 ± 0.03 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs | 245 ± 8 | 0.20 ± 0.03 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs + 2% sucrose (w/v) | 185 ± 1 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Nanoformulations | Final Concentration of Compound (µM) | EE(%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| PP-BSA-NPs | 16 | 94.8 ± 4 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | 32 | 96.1 ± 1 |
| PP-BSA-NPs | 48 | 98.2 ± 0.7 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs | 16 | 84.6 ± 6 |
| PP-HA-BSA-NPs | 48 | 98.5 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teixeira, S.; Ferreira, D.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Carvalho, M.A.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Gel Nanoparticles Loaded with a Pyrimidine-Based Drug for Potent Anticancer Activity. Gels 2025, 11, 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090759
Teixeira S, Ferreira D, Rodrigues LR, Carvalho MA, Castanheira EMS. Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Gel Nanoparticles Loaded with a Pyrimidine-Based Drug for Potent Anticancer Activity. Gels. 2025; 11(9):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090759
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeixeira, Sofia, Débora Ferreira, Ligia R. Rodrigues, M. Alice Carvalho, and Elisabete M. S. Castanheira. 2025. "Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Gel Nanoparticles Loaded with a Pyrimidine-Based Drug for Potent Anticancer Activity" Gels 11, no. 9: 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090759
APA StyleTeixeira, S., Ferreira, D., Rodrigues, L. R., Carvalho, M. A., & Castanheira, E. M. S. (2025). Albumin/Hyaluronic Acid Gel Nanoparticles Loaded with a Pyrimidine-Based Drug for Potent Anticancer Activity. Gels, 11(9), 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090759









