Near-Infrared Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Novel Fluorescence Tissue Markers
Abstract
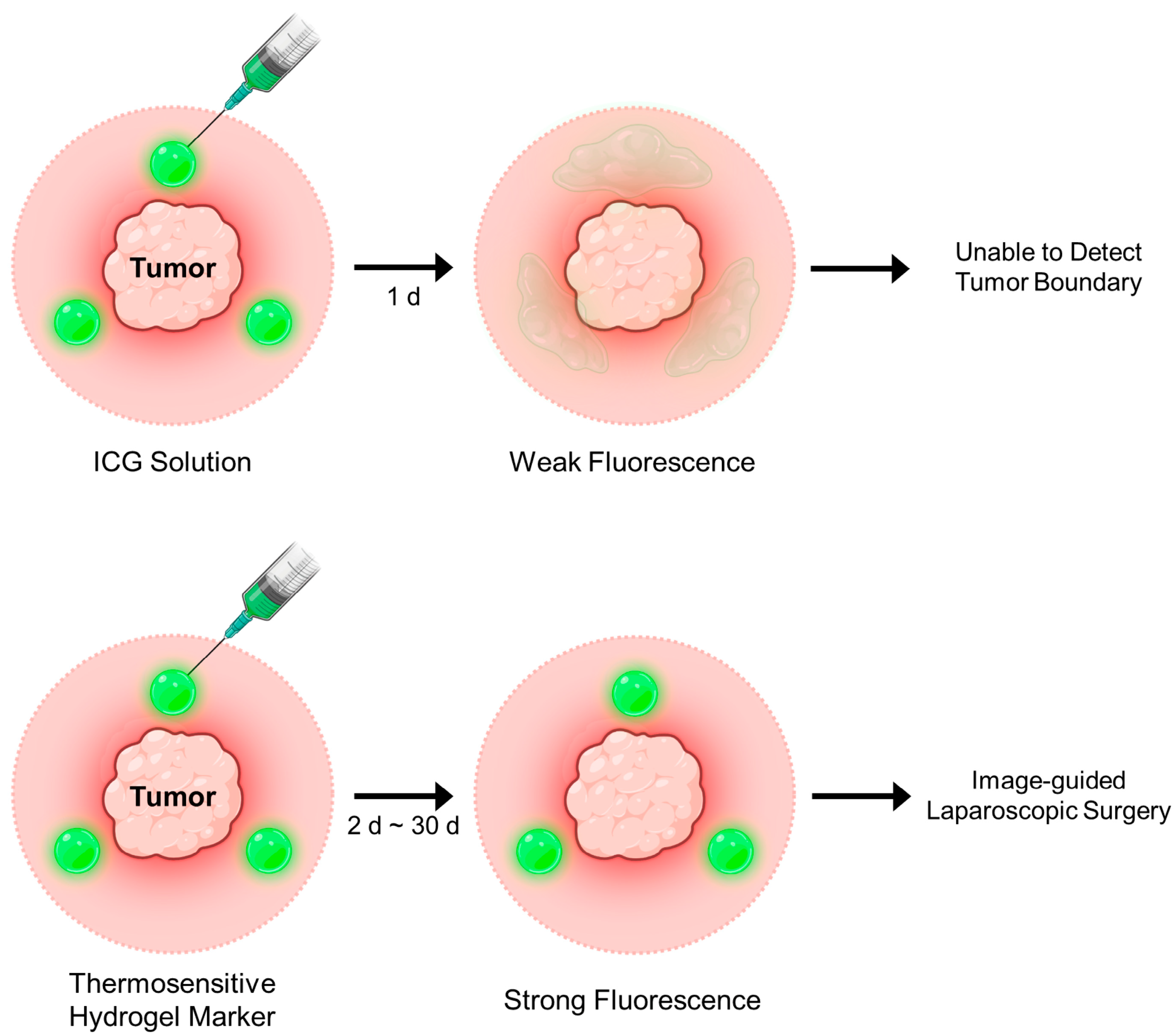
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of the Thermogelling Properties and Dye Retention of the HGC Hydrogel
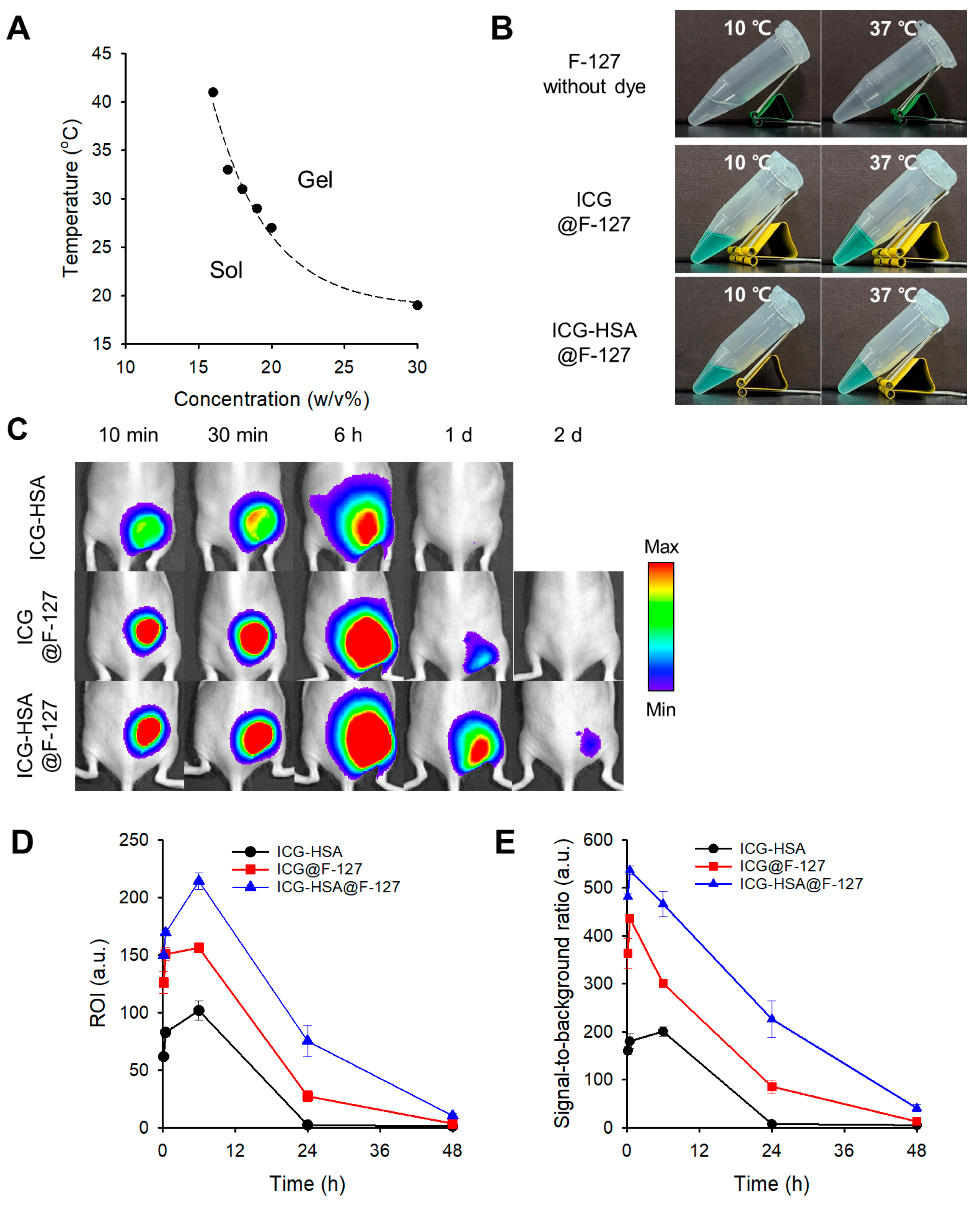
2.2. Evaluation of the Thermogelling Properties and Dye Retention of the F-127 Hydrogel
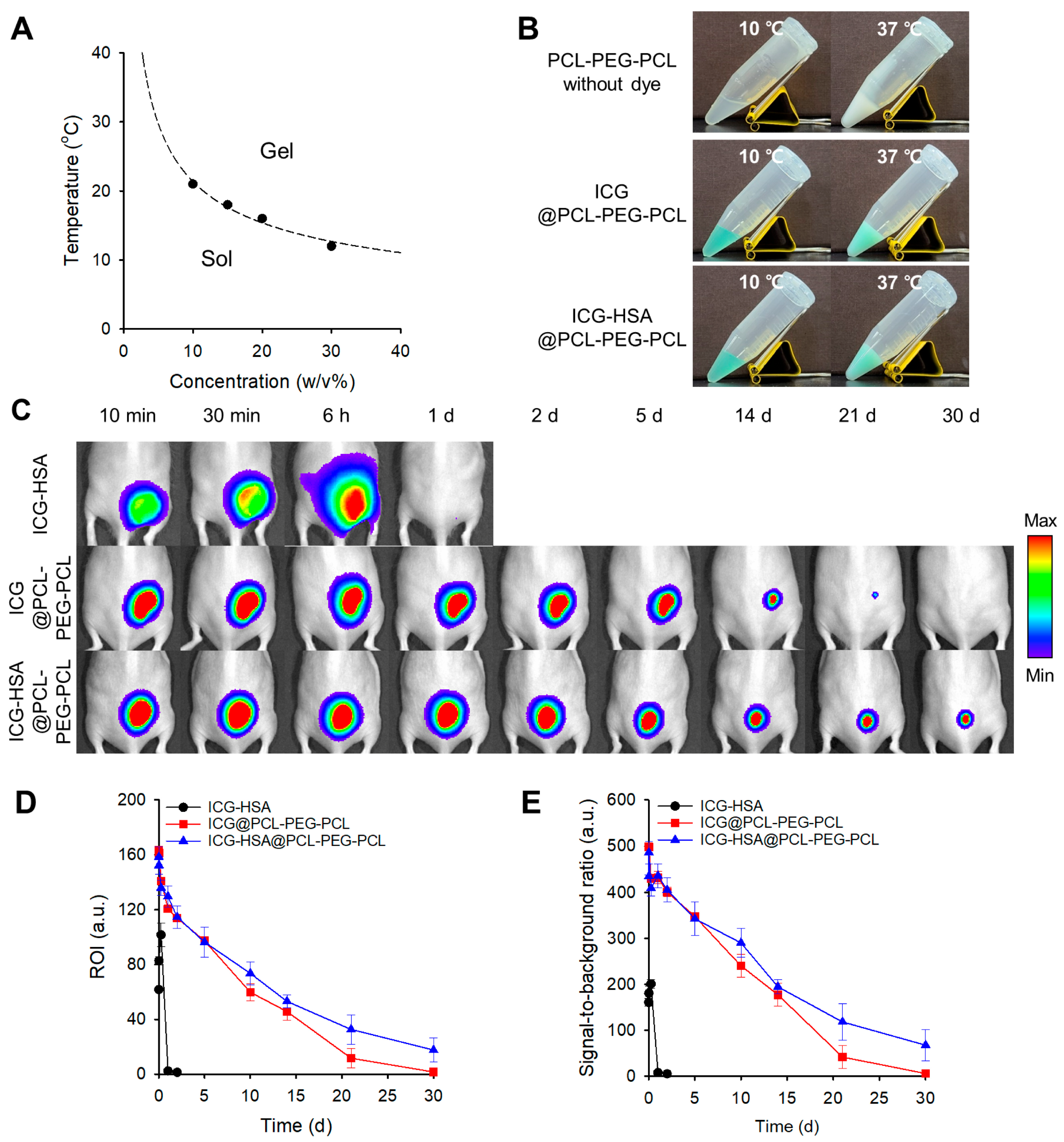
2.3. Evaluation of the Thermogelling Properties and Dye Retention of the PCL-PEG-PCL and PLA-PEG-PLA Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Phase Diagram of Thermosensitive Hydrogels
4.3. Gelation Behavior with Fluorescent Dyes
4.4. In Vivo Evaluation of Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogel Markers in a Mouse Model
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| F-127 | Pluronic F-127 |
| HGC | Hexanoyl glycol chitosan |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| ICG | Indocyanine green |
| LCST | Lower critical solution temperature |
| NAC | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| PCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| PGA | Poly(glycolide) |
| PLA | Poly(D,L-lactide) |
| PPO | Poly(propylene oxide) |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SBR | Signal-to-background ratio |
References
- Madhok, B.; Nanayakkara, K.; Mahawar, K. Safety considerations in laparoscopic surgery: A narrative review. World J. Gastrointest. Endosec. 2022, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.W.; Crowe, P. Visualisation ergonomics and robotic surgery. J. Rob. Surg. 2023, 17, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, N.; Dziedzic, J.; Nurczyk, K.; Zakościelny, A.; Bury, P.; Zgodziński, W.; Zinkiewicz, K. Application of endoscopic tattooing in intraoperative localization of colon tumours and sentinel lymph nodes. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2020, 14, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Moon, H.S.; Sul, J.Y.; Kwon, I.S.; Yun, G.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, E.S.; et al. Role of preoperative endoscopic clipping in laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for early gastric cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoyoshi, T.; Okita, K.; Ishii, M.; Hamabe, A.; Usui, A.; Akizuki, E.; Okuya, K.; Nishidate, T.; Yamano, H.; Nakase, H.; et al. Timing of indocyanine green injection prior to laparoscopic colorectal surgery for tumor localization: A prospective case series. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haim Zada, M.; Gallimidi, Z.; Schlesinger Laufer, M.; Nyska, A.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable breast tissue marker clip. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7439–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, L.A.; Somerfield, M.R.; Carey, L.A.; Crews, J.R.; Denduluri, N.; Hwang, E.S.; Khan, S.A.; Loibl, S.; Morris, E.A.; Perez, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted therapy for breast cancer: ASCO guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1485–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, S.P.L.; Ong, B.H.; Chua, K.L.M.; Takano, A.; Tan, D.S.W. Revisiting neoadjuvant therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e510–e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Q.; Huang, S.T.; Yu, T.H.; Liu, H.L.; Zhao, L.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.Z.; Yang, K.; Hu, J.K.; et al. Optimal timing of surgery for gastric cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, R.; Chia, C.; Michael, M.; Heriot, A.G.; Warrier, S.K.; Kong, J.C. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced colon cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 36, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Mehta, A.K.; Talati, N.; Brem, R.; Margolies, L.R. Reprint of: Breast tissue markers: Why? What’s out there? How do I choose? Clin. Imaging 2019, 55, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Roy, S.; Muhammad, S.; Yu, C.; Huang, H.; Chen, D.; Long, H.; Yang, X.; Du, X.; Guo, B. Fluorescence imaging-guided surgery: Current status and future directions. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 3765–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, M.; Pizzicannella, M.; Spota, A.; Ashoka, A.H.; Agnus, V.; Al Taher, M.; Jansen-Winkeln, B.; Gockel, I.; Marescaux, J.; Swanström, L.; et al. Preoperative endoscopic marking of the gastrointestinal tract using fluorescence imaging: Submucosal indocyanine green tattooing versus a novel fluorescent over-the-scope clip in a survival experimental study. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 5115–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Kim, H.; Sohn, D.K.; Eom, J.B.; Seo, Y.S.; Yoon, H.M.; Choi, Y. Indocyanine green-loaded injectable alginate hydrogel as a marker for precision cancer surgery. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y. Indocyanine green-loaded microspheres as a near-infrared fluorescence marker for long-term localization of tumor sites. J. Pharm. Investig. 2024, 54, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Sohn, D.K.; Yoon, H.M.; Park, K.L.; Park, S.J.; Choi, Y. Multiporous PMMA microballs as a novel fluorescence tissue marker. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Sharma, S.; Jabin, S.; Jadoun, S. Chitosan nanocomposite for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Suh, E.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Le, T.P.; Kim, Y.; Shin, S.A.; Park, Y.H.; Huh, K.M. Injectable glycol chitosan thermogel formulation for efficient inner ear drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.S.; Park, C.G.; Huh, B.K.; Cho, M.O.; Khatun, Z.; Li, Z.; Kang, S.W.; Choy, Y.B.; Huh, K.M. Thermosensitive hexanoyl glycol chitosan-based ocular delivery system for glaucoma therapy. Acta Biomater. 2016, 39, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shim, H.; Cho, M.O.; Cho, I.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.W.; Kwon, B.; Huh, K.M. Thermo-sensitive injectable glycol chitosan-based hydrogel for treatment of degenerative disc disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Costa, P.C.; Velho, S.; Amaral, M.H. Injectable poloxamer hydrogels for local cancer therapy. Gels 2023, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuszynska, M.; Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Bartniak, M.; Bajek, A. Conceptualization and preliminary characterization of poloxamer-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2025, 36, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, A.; Bercea, M.; Avadanei, M.; Gradinaru, L.M.; Nita, L.E.; Gradinaru, V.R. Temperature sensitive pluronic F127-based gels incorporating natural therapeutic agents. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2025, 310, 2400341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, N.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Sung, D.; Kim, H. Pluronic F-68 and F-127 based nanomedicines for advancing combination cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Spirito, N.A.; Grizzuti, N.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Urciuoli, G.; Auriemma, F.; Pasquino, R. Pluronic F68 micelles as carriers for an anti-inflammatory drug: A rheological and scattering investigation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, A.; Gradinaru, L.M.; Rusu, D.; Bercea, M. Self-healing of pluronic F127 hydrogels in the presence of various polysaccharides. Gels 2023, 9, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.E.; Jang, J.W.; Kim, C.; Yi, S. Enhancement of mechanical properties of PCL/PLA/DMSO2 composites for bone tissue engineering. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lim, J.Y.C.; Xue, K.; Chee, C.P.T.; Loh, X.J. Supramolecular thermogels from branched PCL-containing polyurethanes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 39109–39120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbaghi, A.; Ramazani, A.; Farshchi, N.; Rezaei, A.; Bodaghi, A.; Rezayati, S. Synthesis, physical and mechanical properties of amphiphilic hydrogels based on polycaprolactone and polyethylene glycol for bioapplications: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 101, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Shi, S.; Wu, L.; Gou, M.; Yin, Q.; Guo, Q.; Dong, P.; Zhang, F.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; et al. Biodegradable in situ gel-forming controlled drug delivery system based on thermosensitive PCL-PEG-PCL hydrogel. Part 2: Sol-gel-sol transition and drug delivery behavior. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 3358–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, C.T.; Nguyen, K.; Lee, D.S. Injectable block copolymer hydrogels: Achievements and future challenges for biomedical applications. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6629–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, D.; Dube, K.; Damodaran, V.B.; Subramanian, G.; Aston, K.; Halperin, F.; Mao, M.; Pricer, K.; Murthy, N.S.; Kohn, J. Effects of terminal sterilization on PEG-based bioresorbable polymers used in biomedical applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UltraCor™ Twirl™ Breast Tissue Marker. Available online: https://www.bd.com/en-us/products-and-solutions/products/product-families/ultracor-twirl-breast-tissue-marker (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Clear-Jet Injection Catheter. Available online: https://finemedix.com/en/clear-jet-injection-catheter/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.S.; Choi, Y. Near-Infrared Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Novel Fluorescence Tissue Markers. Gels 2025, 11, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080649
Lee SS, Choi Y. Near-Infrared Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Novel Fluorescence Tissue Markers. Gels. 2025; 11(8):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seon Sook, and Yongdoo Choi. 2025. "Near-Infrared Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Novel Fluorescence Tissue Markers" Gels 11, no. 8: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080649
APA StyleLee, S. S., & Choi, Y. (2025). Near-Infrared Dye-Loaded Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Novel Fluorescence Tissue Markers. Gels, 11(8), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080649






