Temperature-Mediated Gel Texture Transformation in Starch Noodles: In Respect of Glass Transition Temperature Tg’
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
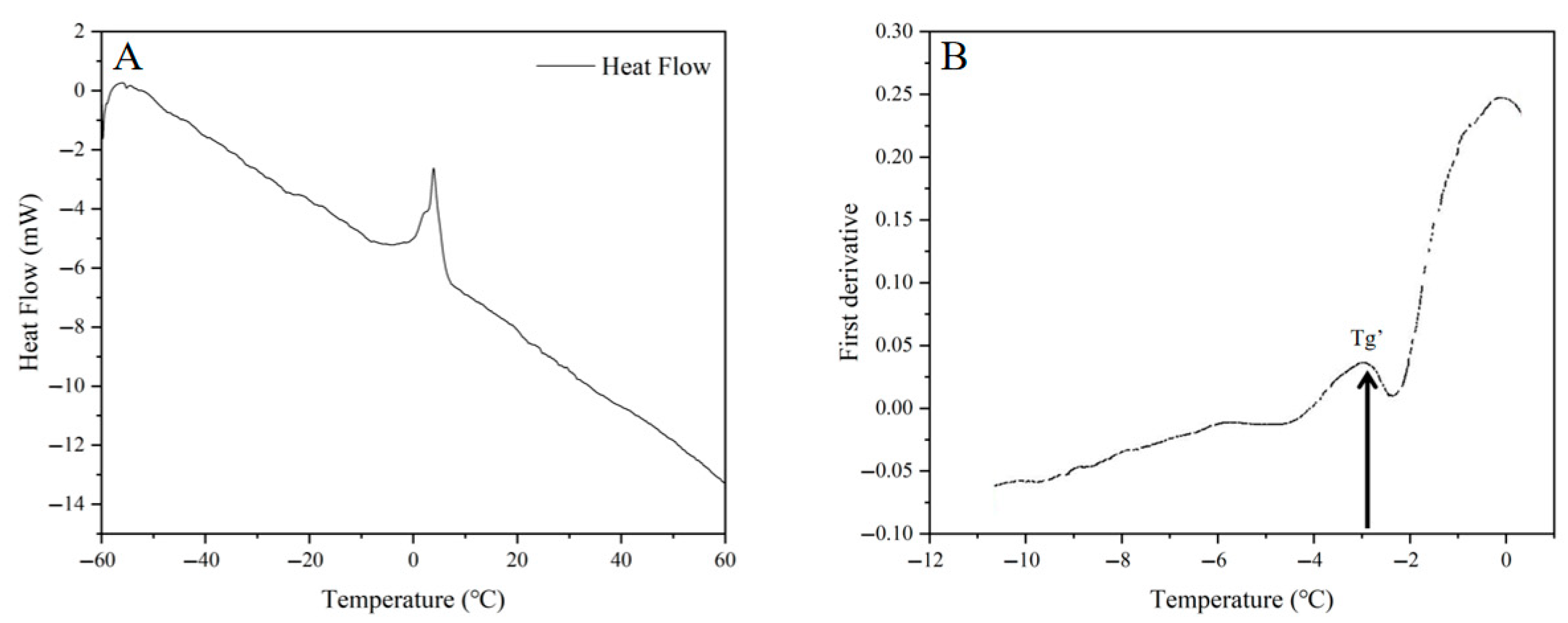
2.1. Determination of Freezing Curve and Glass Transition Temperature
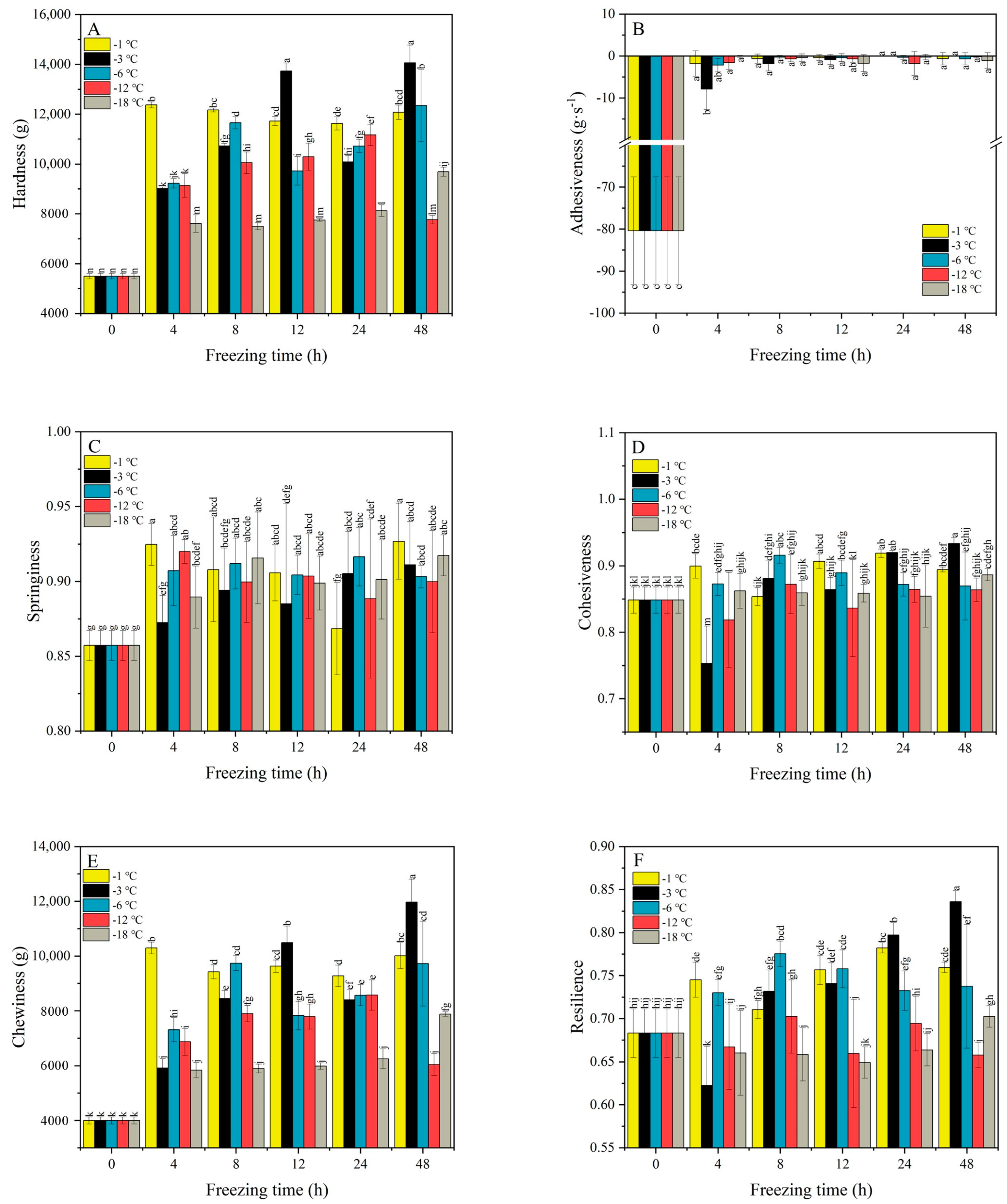
2.2. Texture Characteristics of PSN
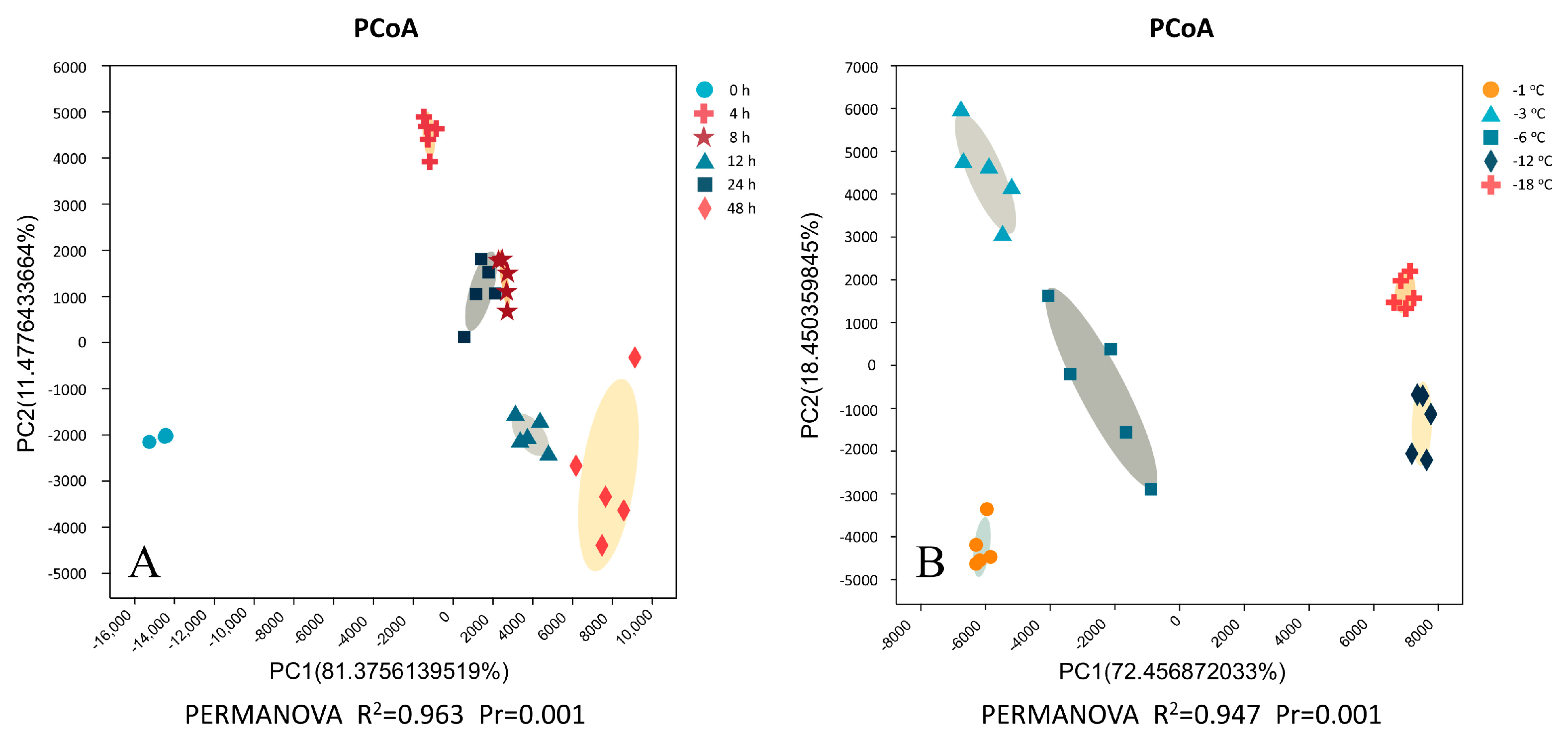
2.3. Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) and Cluster Analysis
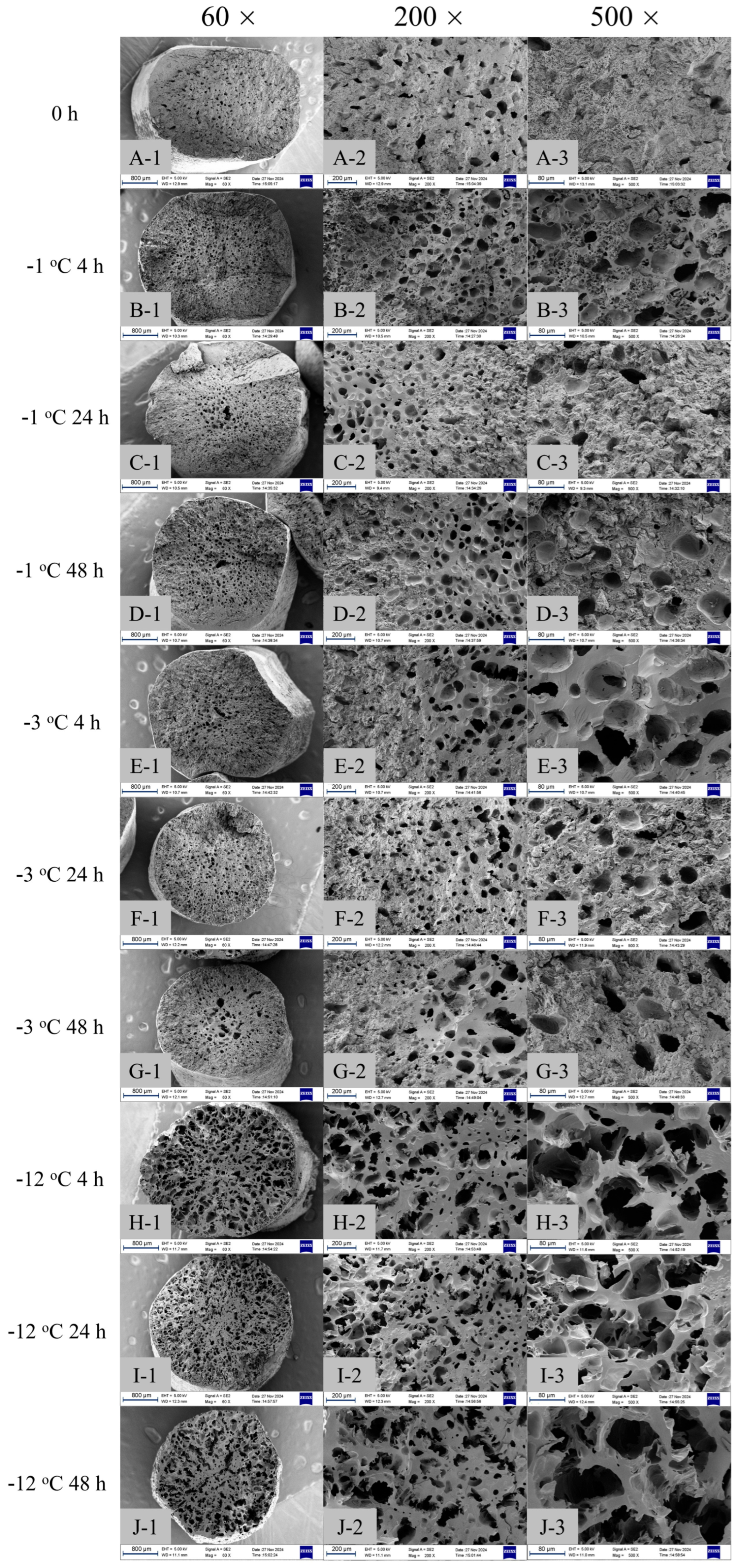
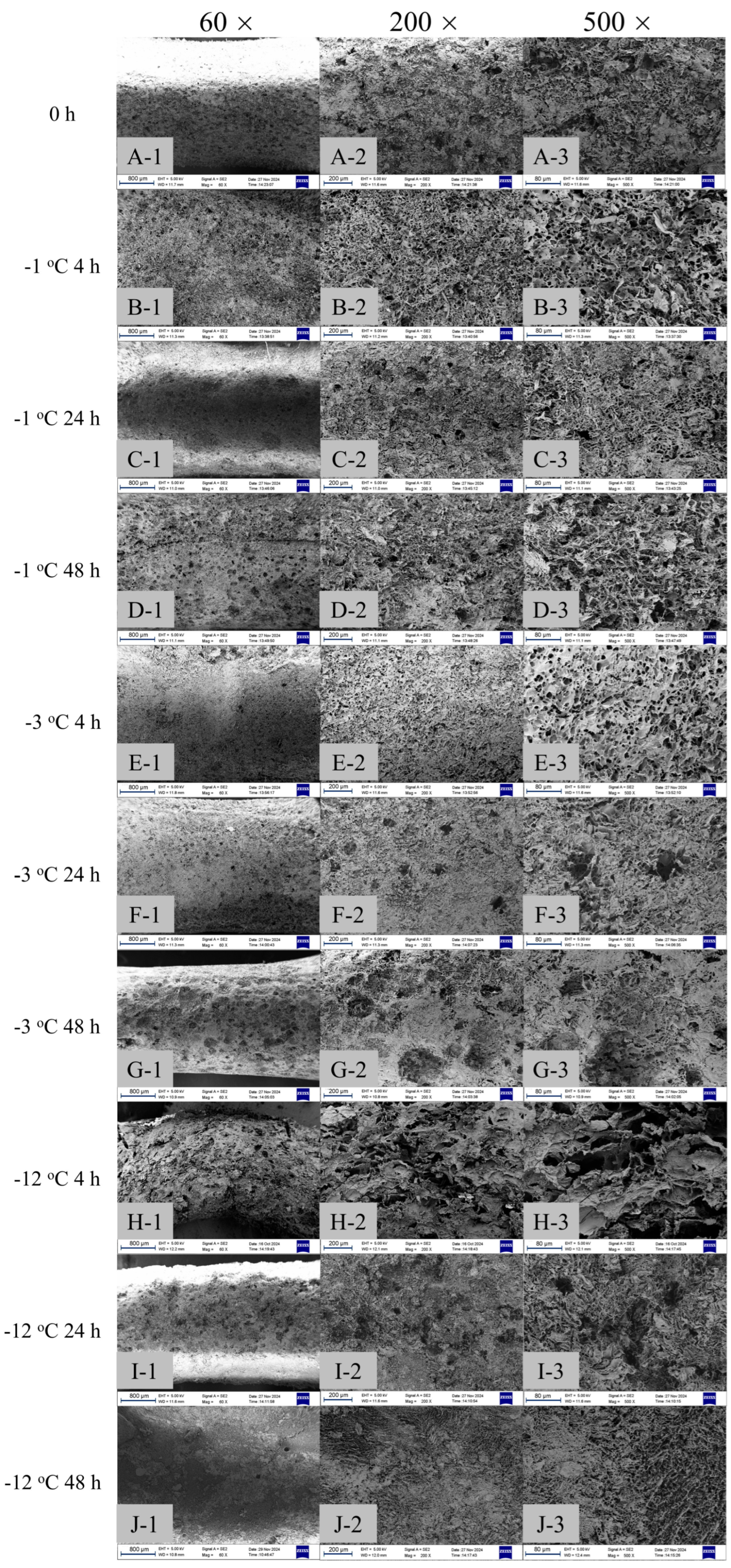
2.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis and SEM
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methodology
4.2.1. Preparation of PSN
4.2.2. Measurement of Freezing Point Temperature of PSN
4.2.3. Measurement of Glass Transition Temperature of PSN
4.3. Freezing of PSN
4.3.1. Textural Properties
4.3.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSN | Potato starch noodles |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
References
- Tan, H.; Li, Z.G.; Tan, B. Starch noodles: History, classification, materials, processing, structure, nutrition, quality evaluating and improving. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 551–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, G. Effects of the addition of starches in wheat flour on fried instant noodle quality. Food Sci. 2005, 11, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Ye, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, G. Performance and mechanism of an innovative humidity-controlled hot-air drying method for concentrated starch gels: A case of sweet potato starch noodles. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, D.-W. Regulating ice formation for enhancing frozen food quality: Materials, mechanisms and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Shan, C.; Chen, Z. Evaluation of cooking performance, structural properties, storage stability and shelf life prediction of high-moisture wet starch noodles. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Li, R.; Wang, N.; Yang, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, N.; Ai, Z. Effect of freezing process on the quality of sweet potato vermicelli without aluminum. Food Ferment. Ind. 2016, 42, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Mu, T.; Ma, M.; Chen, J. Processing technology optimization and physicochemical properties of alum-free fresh potato/cassava starch noodles. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Rumpagaporn, P.; Songsermpong, S. Investigation of freezing temperature and time to improve resistant starch content and quality of pure mung bean starch vermicelli. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2023, 17, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Jiang, J.; Gao, H.; Meng, K.; Song, M.; Li, G. Optimization of the Aging Process for Potato Vermicelli without Additives and Quality Changes during Storage. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.J.; Morris, V.J.; Orford, P.D.; Ring, S.G. The roles of amylose and amylopectin in the gelation and retrogradation of starch. Carbohydr. Res. 1985, 135, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keetels, C.J.A.M.; Vliet, T.v.; Walstra, P. Gelation and retrogradation of concentrated starch systems: 2. Retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 1996, 10, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Kowalski, S.; Tomasik, P.; Sady, M. Rheological and sensory properties of dessert sauces thickened by starch–xanthan gum combinations. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, S.G.; Colonna, P.; I’Anson, K.J.; Kalichevsky, M.T.; Miles, M.J.; Morris, V.J.; Orford, P.D. The gelation and crystallisation of amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 162, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burey, P.; Bhandari, B.R.; Howes, T.; Gidley, M.J. Hydrocolloid gel particles: Formation, characterization, and application. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Tan, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Wang, L. Insight of rheology, water distribution and in vitro digestive behavior of starch based-emulsion gel: Impact of potato starch concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetapan, N.; Limparyoon, N.; Gamonpilas, C.; Methacanon, P.; Fuongfuchat, A. Effect of cryogenic freezing on textural properties and microstructure of rice flour/tapioca starch blend gel. J. Food Eng. 2015, 151, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, Y.B.; Kwang, J.K.; Ki, C.C.; Yeon, C.H.; Wang, S.K. Recrystallization kinetics and glass transition of rice starch gel system. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tananuwong, K.; Reid, D.S. Differential scanning calorimetry study of glass transition in frozen starch gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4308–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominique, C.; Martine, L.M.; Denise, S. Towards an improved understanding of glass transition and relaxations in foods: Molecular mobility in the glass transition range. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenrein, S.; Preechathammawong, N. Undercooling associated with slow freezing and its influence on the microstructure and properties of rice starch gels. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ji, S.; Ren, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, K.; et al. Enhancing 3D printing accuracy of cassava starch gel through temperature-controlled freezing. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhan, J.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y. Amylose crystal seeds: Preparation and their effect on starch retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.M.R.; Okoniewska, M.; Martinez, M.M.; Zhao, B.; Hamaker, B.R. Investigating the potential of slow-retrograding starches to reduce staling in soft savory bread and sweet cake model systems. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, H. Effects of different freezing methods on the damage in potato tissues impregnated with trehalose. LWT 2024, 213, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zeng, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Su, T.; Xiang, F.; Li, G. Effect of low temperature on the aging characteristics of a potato starch gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, H.J. Effect of molecular structure on phase transition behavior of rice starch with different amylose contents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gao, H.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Su, T.; Li, G. Determination of subfreezing temperature and gel retrogradation characteristics of potato starch gel. LWT 2021, 149, 112037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sui, W.; Cui, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M. Glass transition features of frozen dough regulated by lentinan molecular weight and their correlation with dough structural and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.H.; Yoo, B.; Lim, S.T. Effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on thermal transition and cold stability of corn starch gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.-R.; Bae, J.-E.; An, H.W.; Yun, H.-J.; Retnoaji, B.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.G. Influence of potato starch on the 3D printing of senior-friendly foods enriched with oyster powder. LWT 2025, 224, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Pyun, Y.R. Effect of moisture level on the crystallinity of wheat starch aged at different temperatures. Starch-Stärke 2006, 49, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcenas, M.E.; Haros, M.; Benedito, C.; Rosell, C.M. Effect of freezing and frozen storage on the staling of part-baked bread. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetapan, N.; Limparyoon, N.; Fuongfuchat, A.; Gamonpilas, C.; Methacanon, P. Effect of freezing rate and starch granular morphology on ice formation and non-freezable water content of flour and starch gels. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 19, 1616–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, H.D. Low-temperature stability and the glassy state in frozen foods. Food Res. Int. 1992, 25, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Li, M.; Song, Q.; Guo, B.; Zhou, G.; Xie, F. Regulation of retrogradation and textural properties of mung bean starch gels during storage: Role of cooling rate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 366, 123915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuchajowska, Z.; Otto, T.; Paszczynska, B.; Baik, B.K. Composition, thermal behavior, and gel texture of prime and tailings starches from garbanzo beans and peas. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Peng, B. Freezing rate’s impact on starch retrogradation, ice recrystallization, and quality of water-added and water-free quick-frozen rice noodles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 134047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Park, J.-W. Assessing adhesiveness levels in a dysphagia diet for older adults. Geriatrics 2024, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, T.J.; Jaishankar, A.; McKinley, G.H. Describing the firmness, springiness and rubberiness of food gels using fractional calculus. Part I: Theoretical framework. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, A.-S.; Wolter, A.; Czerny, M.; Bez, J.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K.; Czerny, M. Investigation of product quality, sensory profile and ultrastructure of breads made from a range of commercial gluten-free flours compared to their wheat counterparts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadde, E.K.; Chen, J. Shear and extensional rheological characterization of thickened fluid for dysphagia management. J. Food Eng. 2019, 245, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, D.; Yan, X.; Zhao, S.; Jia, C.; Niu, M.; Xu, Y. Addition of κ-carrageenan increases the strength and chewiness of gelatin-based composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekuyt, H.A.; Dobson, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Lipid complexation improves the mechanical properties and functionality of legume starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Pi, X.; Zhang, B. Structural features of rice starch-protein system: Influence of retrogradation time and quick-freezing temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 133981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.Y.; Baik, B.-K.; Lim, S.-T. Influences of temperature-cycled storage on retrogradation and in vitro digestibility of waxy maize starch gel. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yang, J.; Qin, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X. Drying kinetics of soy protein isolate-corn starch film during preparation and its moisture adsorption characteristics during storage. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Mori, T.; Kitano, H.; Fukuda, M.; Mochizuki, A.; Tanaka, M. Fourier transform infrared study on the sorption of water to various kinds of polymer thin films. J. Polym. Sci. 2001, 39, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R. Composition, molecular structure, and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 45, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, H.; Qin, Z.; Che, P.; Yi, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Yao, F.; Li, J. Fully physically crosslinked pectin-based hydrogel with high stretchability and toughness for biomedical application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, S.J.; Mainwaring, D.E.; Cornell, H.J.; Rix, C.J. The role of hydrogen bonding in amylose gelation. Starch-Stärke 2004, 56, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, F.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, Q.; Rashed, M.M.A. Effect of pullulan on the short-term and long-term retrogradation of rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, C.; Zhu, H.; Bao, J.; Quan, K.; Yang, R. The texture of fresh rice noodles as affected by the physicochemical properties and starch fine structure of aged paddy. LWT 2020, 130, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Luo, S.; Huang, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, C. Chinese rice noodles form the viscoelastic texture by dual high-temperature retrogradation: An insight into the mechanism. LWT 2023, 189, 115496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S. Mechanistic studies of starch retrogradation and its effects on starch gel properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Huang, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, M.; Song, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guan, X. Influencing the retrogradation properties of potato mash through multi-scale structural modifications mediated by enzymatic hydrolysis forms. Food Chem. 2025, 485, 144467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Mechanistic insights into the enhanced texture of potato noodles by incorporation of small granule starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Dong, X. Temperature-Mediated Gel Texture Transformation in Starch Noodles: In Respect of Glass Transition Temperature Tg’. Gels 2025, 11, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080639
Liu H, Hu Q, Yang S, Liu L, Dong X. Temperature-Mediated Gel Texture Transformation in Starch Noodles: In Respect of Glass Transition Temperature Tg’. Gels. 2025; 11(8):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongxiao, Qing Hu, Sha Yang, Lina Liu, and Xuyan Dong. 2025. "Temperature-Mediated Gel Texture Transformation in Starch Noodles: In Respect of Glass Transition Temperature Tg’" Gels 11, no. 8: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080639
APA StyleLiu, H., Hu, Q., Yang, S., Liu, L., & Dong, X. (2025). Temperature-Mediated Gel Texture Transformation in Starch Noodles: In Respect of Glass Transition Temperature Tg’. Gels, 11(8), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080639






