Enhancement of Foaming Performance of Oat Globulin by Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Study from the Viewpoint of the Structural and Functional Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions
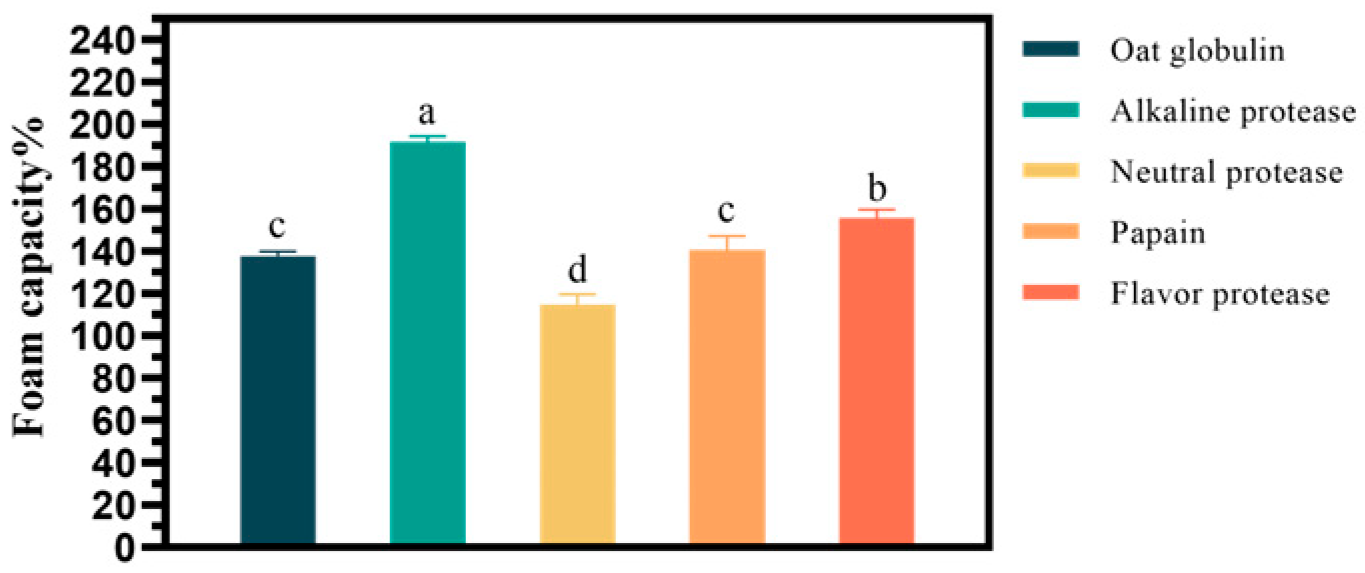
2.1.1. The Effect of Enzyme Types on the Foam Capacity of Oat Globulin Hydrolysates
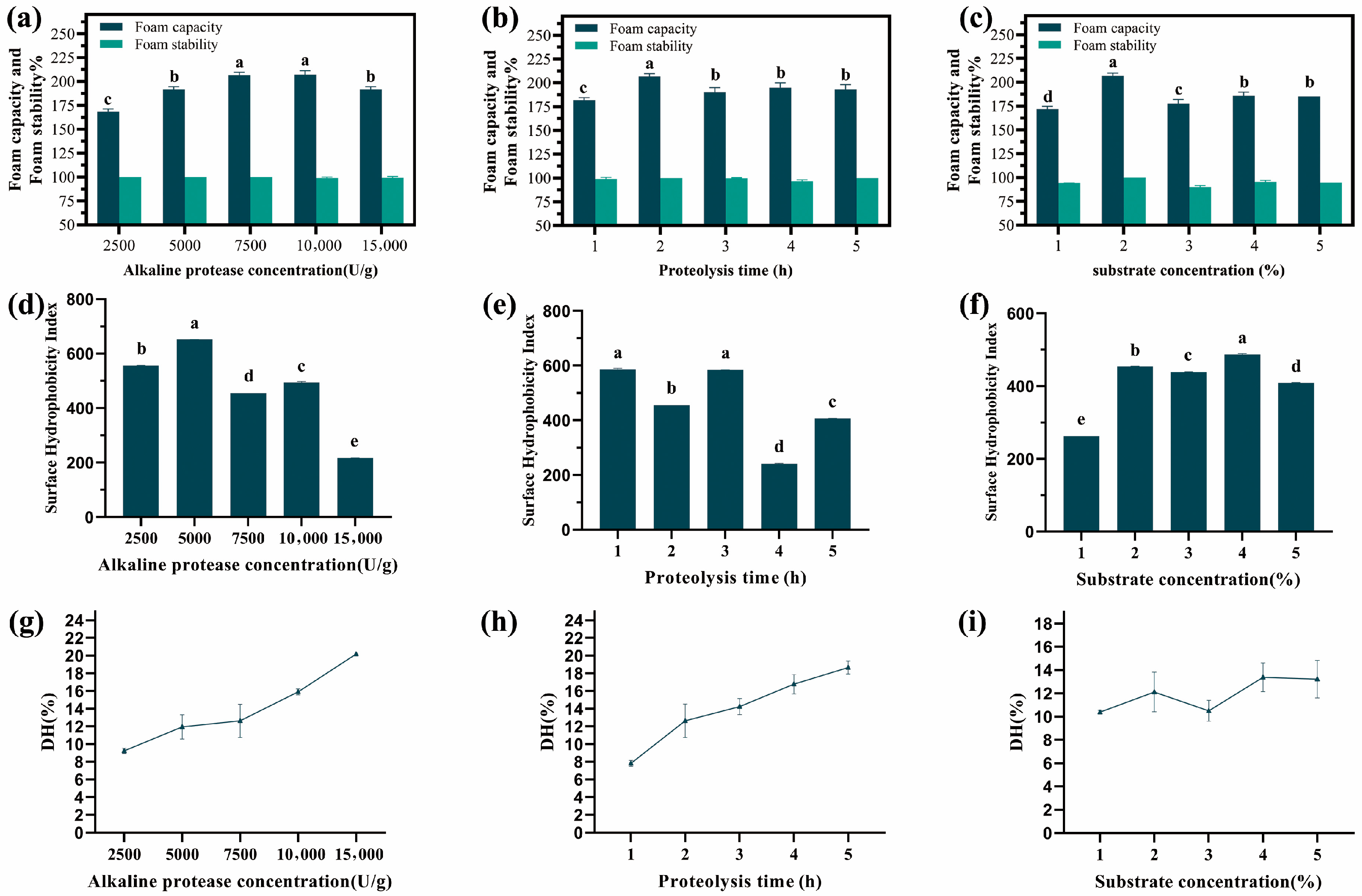
2.1.2. The Effect of Enzyme Dosage on the Foam Capacity of Oat Globulin Hydrolysates
2.1.3. The Effect of Proteolysis Time on the Foam Capacity of Oat Globulin Hydrolysates
2.1.4. The Effect of Substrate Concentration on the Foam Capacity of Oat Globulin Hydrolysates
2.1.5. Analysis of Orthogonal Experiment
2.1.6. Optimization of Process Amplification
2.2. The Surface Hydrophobicity Index of Oat Globulin Hydrolysate Under Different Factors
2.3. The Degree of Hydrolysis of Oat Globulin Hydrolysate Under Different Factors
2.4. Pearson Correlation Analysis
2.5. Functional Properties of the Optimal Foaming Oat Globulin Hydrolysate
2.5.1. Amino Acid Composition Analysis
2.5.2. Molecular Weight Distribution
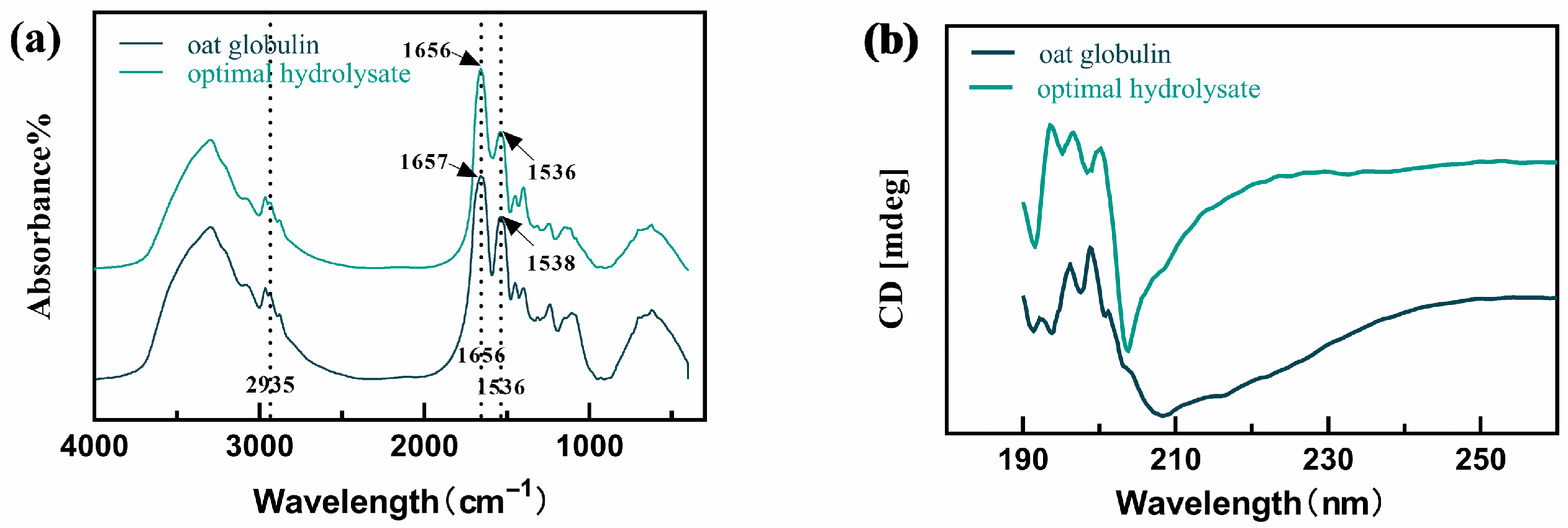
2.5.3. Secondary Structural Changes in Oat Globulin After Proteolysis Treatment
2.5.4. Surface Tension
2.5.5. Foams Microstructure
2.5.6. Strain Sweeps
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Oat Globulin
4.3. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions
4.3.1. Hydrolysis of Oat Globulin and Degree of Hydrolysis Determination
4.3.2. Single-Factor Tests
4.3.3. Orthogonal Test
4.4. Foaming Capacity (FC) and Foam Stability (FS)
4.5. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0) Determination
4.6. Amino Acid Composition
4.7. SDS-PAGE
4.8. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
4.9. Surface Tension Measurements
4.10. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra
4.11. CD Analysis
4.12. Microscopic Images of Bubbles
4.13. Rheological Measurements
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassity, J. The State of the Global Plant-Based Protein Market|Kerry. Available online: https://www.kerry.com/insights/kerrydigest/2019/the-state-of-the-global-plant-based-protein-market.html (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Murray, B.S. Recent Developments in Food Foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, H.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Alim, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Li, L.; Zou, L.; Hu, X. Dietary-Nutraceutical Properties of Oat Protein and Peptides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 950400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.L.; Clifton, P.M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Colonic Function: Roles of Resistant Starch and Nonstarch Polysaccharides. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1031–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Størsrud, S.; Hulthén, L.R.; Lenner, R.A. Beneficial Effects of Oats in the Gluten-Free Diet of Adults with Special Reference to Nutrient Status, Symptoms and Subjective Experiences. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T. Oats and the Gluten-Free Diet. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y. (Ed.) Oats Nutrition and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-35410-0. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, R.; Gonzalez, T.; Ferruzzi, M.; Jackson, E.; Winderl, D.; Watson, J. Oats—From Farm to Fork. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 77, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Tyagi, S.K.; Anurag, R.K. Plant-Based Milk Alternatives an Emerging Segment of Functional Beverages: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3408–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strategic Market Research Plant-Based Milk Market by Product (Pea Milk, Rice Milk, Almond Milk, Wheat Milk, Hemp Milk, Coconut Milk, Soy Milk, Others), by Formulation (Plain, Flavoured), by End Use (Food & Beverage Industry, Retail/Household, Foodservice Industry), by Application (Nutritional Application (Medical Nutrition, Sports Nutrition, Infant Nutrition), Snacks, Desert and Confectionary, Animal Feed, Bakery, Beverages, Dairy), Global Report by Size, Industry Analysis & Forecast, 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.strategicmarketresearch.com/market-report/plant-based-milk-market (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Damodaran, S. Protein Stabilization of Emulsions and Foams. J. Food Sci. 2006, 70, R54–R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.M.; Bhandari, B.R.; Bansal, N. Functionality of Bovine Milk Proteins and Other Factors in Foaming Properties of Milk: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4800–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T. Foaming Properties of Milk: A Review of the Influence of Composition and Processing. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakka, A.K.; Elias, M.; Jini, R.; Sakhare, P.Z.; Bhaskar, N. In-Vitro Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Fermentatively and Enzymatically Prepared Chicken Liver Protein Hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 8059–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, D.; Otter, D.E.; Gauthier, S.F.; Foegeding, E.A. Enzyme-Induced Gelation of Extensively Hydrolyzed Whey Proteins by Alcalase: Peptide Identification and Determination of Enzyme Specificity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6300–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Jyothirmayi, T.; Diwan, P.V.; Dinesh Kumar, B. Antioxidant Activity and Functional Properties of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates from Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) Roe (Egg). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5817–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, E.; Han, J.; Swallow, K.; Tian, Z.; Jarpa-Parra, M.; Chen, L. Effects of Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Ultrafiltration on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Faba Bean Protein. Cereal Chem. 2019, 96, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Martínez, M.; Moreno, F.J.; Villamiel, M.; Rodríguez Patino, J.M.; Carrera Sánchez, C. Effect of Glycation and Limited Hydrolysis on Interfacial and Foaming Properties of Bovine β-Lactoglobulin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jia, J.; Xiong, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. Effects of Short-Term Fermentation with Lactic Acid Bacteria on Egg White: Characterization, Rheological and Foaming Activities. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zou, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, M. Influence of High-Intensity Ultrasound on Foaming and Structural Properties of Egg White. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Roberts, R.; Felix, T.L.; Harte, F.M. Effect of High-Pressure-Jet Processing on the Viscosity and Foaming Properties of Pasteurized Whole Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3887–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-P.; Chen, X.-W.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.-M.; Yang, X.-Q. Stabilization of Foam and Emulsion by Subcritical Water-Treated Soy Protein: Effect of Aggregation State. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 87, S0268005X18307501-. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, F. Limited Hydrolysis of Dehulled Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Proteins Using Trypsin: Functional Properties and Structural Characteristics. LWT 2020, 133, 110035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Prakash, S.; Dai, X.; Meng, Y. Enzymolysis and Glycosylation Synergistic Modified Ovalbumin: Functional and Structural Characteristics. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Pan, F.; Zhang, T. Foaming Properties of Egg White Proteins Improved by Enzymatic Hydrolysis: The Changes in Structure and Physicochemical Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Yao, H.; Chen, Z.; Shan, L.; Zhang, M. Some Functional Properties of Oat Bran Protein Concentrate Modified by Trypsin. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B. Formation of Pea Protein Amyloid Fibrils to Stabilize High Internal Phase Emulsions for Encapsulation of Lutein. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, A.G.B.; Rombouts, I.; Fierens, E.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Relevance of the Functional Properties of Enzymatic Plant Protein Hydrolysates in Food Systems. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifard, N.; Murueta, J.H.C.; Abedian-Kenari, A.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Jamali, H. Comparison the Effect of Three Commercial Enzymes for Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Two Substrates (Rice Bran Protein Concentrate and Soy-Been Protein) with SDS-PAGE. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Combining Alcalase Hydrolysis and Transglutaminase-Cross-Linking Improved Bitterness and Techno-Functional Properties of Hypoallergenic Soybean Protein Hydrolysates through Structural Modifications. LWT 2021, 151, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Lian, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X. Effect of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Followed after Extrusion Pretreatment on the Structure and Emulsibility of Soybean Protein. Process Biochem. 2022, 116, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Tang, T.; Zhou, L.; Ling, Z.; Guo, S.; Jiang, A. Effects of Different Proteases on the Emulsifying Capacity, Rheological and Structure Characteristics of Preserved Egg White Hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarpa-Parra, M.; Bamdad, F.; Tian, Z.; Zeng, H.; Temelli, F.; Chen, L. Impact of pH on Molecular Structure and Surface Properties of Lentil Legumin-like Protein and Its Application as Foam Stabilizer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, E.A.; Luck, P.J.; Davis, J.P. Factors Determining the Physical Properties of Protein Foams. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, I.; Novales, B.; Boué, F.; Axelos, M.A.V. Foaming Properties of Protein/Pectin Electrostatic Complexes and Foam Structure at Nanoscale. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, P.J. Interfaces: Their Role in Foam and Emulsion Behaviour. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L. Characterization and Analysis of Protein Structures in Oat Bran. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C2337–C2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueckner-Guehmann, M.; Heiden-Hecht, T.; Sozer, N.; Drusch, S. Foaming Characteristics of Oat Protein and Modification by Partial Hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Grolle, K.; Bos, M.; Stuart, M.; Vanvliet, T. Network Forming Properties of Various Proteins Adsorbed at the Air/Water Interface in Relation to Foam Stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 254, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chi, Y.J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wei, X. Influence of Degree of Hydrolysis on Functional Properties, Antioxidant and ACE Inhibitory Activities of Egg White Protein Hydrolysate. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, J. Effects of Proteins on Emulsion Stability: The Role of Proteins at the Oil–Water Interface. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, D.W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. Principles and Applications of Spectroscopic Techniques for Evaluating Food Protein Conformational Changes: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z. Functional Properties and Structural Changes of Rice Proteins with Anthocyanins Complexation. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Madadlou, A. Characterization of Fibrillated Antioxidant Whey Protein Hydrolysate and Comparison with Fibrillated Protein Solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chi, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Physicochemical Properties, in Vitro Digestibility and Antioxidant Activity of Dry-Heated Egg White Protein. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, C.; Adamcik, J.; Jordens, S.; Mezzenga, R. General Self-Assembly Mechanism Converting Hydrolyzed Globular Proteins into Giant Multistranded Amyloid Ribbons. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezeshk, S.; Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, H.; Abdollahi, M. Impact of pH-Shift Processing Combined with Ultrasonication on Structural and Functional Properties of Proteins Isolated from Rainbow Trout by-Products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tao, H.; Wu, F.; Yang, N.; Chen, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of Frozen Storage on the Foaming Properties of Wheat Gliadin. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayas, J.F. Foaming Properties of Proteins. In Functionality of Proteins in Food; Zayas, J.F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 260–309. ISBN 978-3-642-59116-7. [Google Scholar]
- Narsimhan, G.; Xiang, N. Role of Proteins on Formation, Drainage, and Stability of Liquid Food Foams. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Ren, J.; Zhao, M.; Luo, D.; Gu, L. Effects of Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Pepsin and High-Pressure Homogenization on the Functional Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nguyen, A.V.; Farrokhpay, S. A Critical Review of the Growth, Drainage and Collapse of Foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 228, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklehaimanot, W.H.; Emmambux, M.N. Foaming Properties of Total Zein, Total Kafirin and Pre-Gelatinized Maize Starch Blends at Alkaline pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, P.J. Foams, Conductivity of. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 2613–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, M.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Xie, J. Proteolysis Improves the Foaming Properties of Rice Protein Fibrils: Structure, Physicochemical Properties Changes, and Application in Angel Food Cake. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, J.C.; Sørensen, J.L.; Warming, A.S.; Clausen, M.P. Quantitative Image Analysis of Protein Foam Microstructure and Its Correlation with Rheological Properties: Egg White Foam. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Habibi, M.; Sagis, L.M.C. Interfacial and Foaming Properties of Soluble Lupin Protein Isolates: Effect of pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Rout, M.K.; Mock, W.-Y. Study of Oat Globulin Conformation by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3328–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tontisirin, K.; MacLean, W.C.; Warwick, P.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (Eds.) Food Energy: Methods of Analysis and Conversion Factors: Report of a Technical Workshop, Rome, 3-6 December 2002; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2003; ISBN 978-92-5-105014-9. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Zhou, F.; Yu, M.; Ge, R.; Fan, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Enhance the Resistance of Oat-Derived Peptides That Inhibit Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Enzymic Hydrolysis of Food Proteins; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hettiarachchi, C.A.; Corzo-Martínez, M.; Mohan, M.S.; Harte, F.M. Enhanced Foaming and Emulsifying Properties of High-Pressure-Jet-Processed Skim Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskard, C.A.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Hydrophobicity of Bovine Serum Albumin and Ovalbumin Determined Using Uncharged (PRODAN) and Anionic (ANS-) Fluorescent Probes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity Determined by a Fluorescence Probe Method and Its Correlation with Surface Properties of Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runyon, J.R.; Sunilkumar, B.A.; Nilsson, L.; Rascon, A.; Bergenståhl, B. The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Soluble Protein Content of Oats. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ma, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, L.; Lu, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J. Ultrasonic Structural Modification of Myofibrillar Proteins from Coregonus Peled Improves Emulsification Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Peng, J.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Landman, J. Air-Water Interface Properties and Foam Stabilization by Mildly Extracted Lentil Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, C.; Wang, T.; Michaelos, M.; Pachitariu, M. Cellpose: A Generalist Algorithm for Cellular Segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Level | A Dosage (U/g) | B Time (h) | C Substrate Concentration (%) | Null Column | Foam Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (5000) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (1.5) | 1 | 171.67 |
| 2 | 1 (5000) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 | 176.67 |
| 3 | 1 (5000) | 3 (2.5) | 3 (2.5) | 3 | 175 |
| 4 | 2 (7500) | 1 (1.5) | 2 (2) | 3 | 211.67 |
| 5 | 2 (7500) | 2 (2) | 3 (2.5) | 1 | 196.67 |
| 6 | 2 (7500) | 3 (2.5) | 1 (1.5) | 2 | 194.17 |
| 7 | 3 (10,000) | 1 (1.5) | 3 (2.5) | 2 | 205 |
| 8 | 3 (10,000) | 2 (2) | 1 (1.5) | 3 | 210 |
| 9 | 3 (10,000) | 3 (2.5) | 2 (2) | 1 | 211.67 |
| K1 | 174.45 | 196.11 | 191.95 | 193.34 | |
| K2 | 200.84 | 194.45 | 200.00 | 191.95 | |
| K3 | 208.89 | 193.61 | 192.22 | 198.89 | |
| R | 34.44 | 1.67 | 8.06 | 6.94 | |
| Sum of Squares | 395.8203 | 69.5911 | 68.0703 | 20.6224 | |
| Freedom | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| F | 24.040 | 0.120 | 1.549 | ||
| Conspicuousness | * | - | - |
| Degree of Hydrolysis | Surface Hydrophobicity Index | Foam Stability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam capacity | Pearson correlation | 0.711 * | −0.704 * | −0.478 |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.162 | |
| sample number | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| Item | Oat Globulin % | Optimal Combination of Hydrolysates % |
|---|---|---|
| Nonpolar amino acid | 17.08 | 19.13 |
| Polar neutral amino acids | 32.74 | 32.96 |
| Acidic amino acid | 36.69 | 32.75 |
| Basic amino acid | 13.49 | 15.16 |
| Samples | Functional Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-H | C=O | C-H | C-N | |
| oat globulin | 3296.65; 1536.77 | 3082.55; 1657.38 | 2962.26; 2934.15 | 1311.86; 1237.84 |
| optimal hydrolysate | 3296.12; 1538.36 | 3084.45; 1656.15 | 2962.56; 2933.16 | 1315.81; 1243.5 |
| Samples | Secondary Structures (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Unordered | |
| oat globulin | 15.0% | 31.2% | 12.8% | 41.0% |
| optimal hydrolysate | 12.8% | 28.8% | 13.7% | 44.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, H. Enhancement of Foaming Performance of Oat Globulin by Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Study from the Viewpoint of the Structural and Functional Properties. Gels 2025, 11, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080615
Zhu Y, Zhang J, Gu X, Wang P, Liu Y, Jiao Y, Yang L, Chen H. Enhancement of Foaming Performance of Oat Globulin by Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Study from the Viewpoint of the Structural and Functional Properties. Gels. 2025; 11(8):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080615
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yahui, Junlong Zhang, Xuedong Gu, Pengjie Wang, Yang Liu, Yingze Jiao, Lin Yang, and Han Chen. 2025. "Enhancement of Foaming Performance of Oat Globulin by Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Study from the Viewpoint of the Structural and Functional Properties" Gels 11, no. 8: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080615
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, J., Gu, X., Wang, P., Liu, Y., Jiao, Y., Yang, L., & Chen, H. (2025). Enhancement of Foaming Performance of Oat Globulin by Limited Enzymatic Hydrolysis: A Study from the Viewpoint of the Structural and Functional Properties. Gels, 11(8), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080615








