Hydrogen Bond-Regulated Rapid Prototyping and Performance Optimization of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Tannic Acid Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
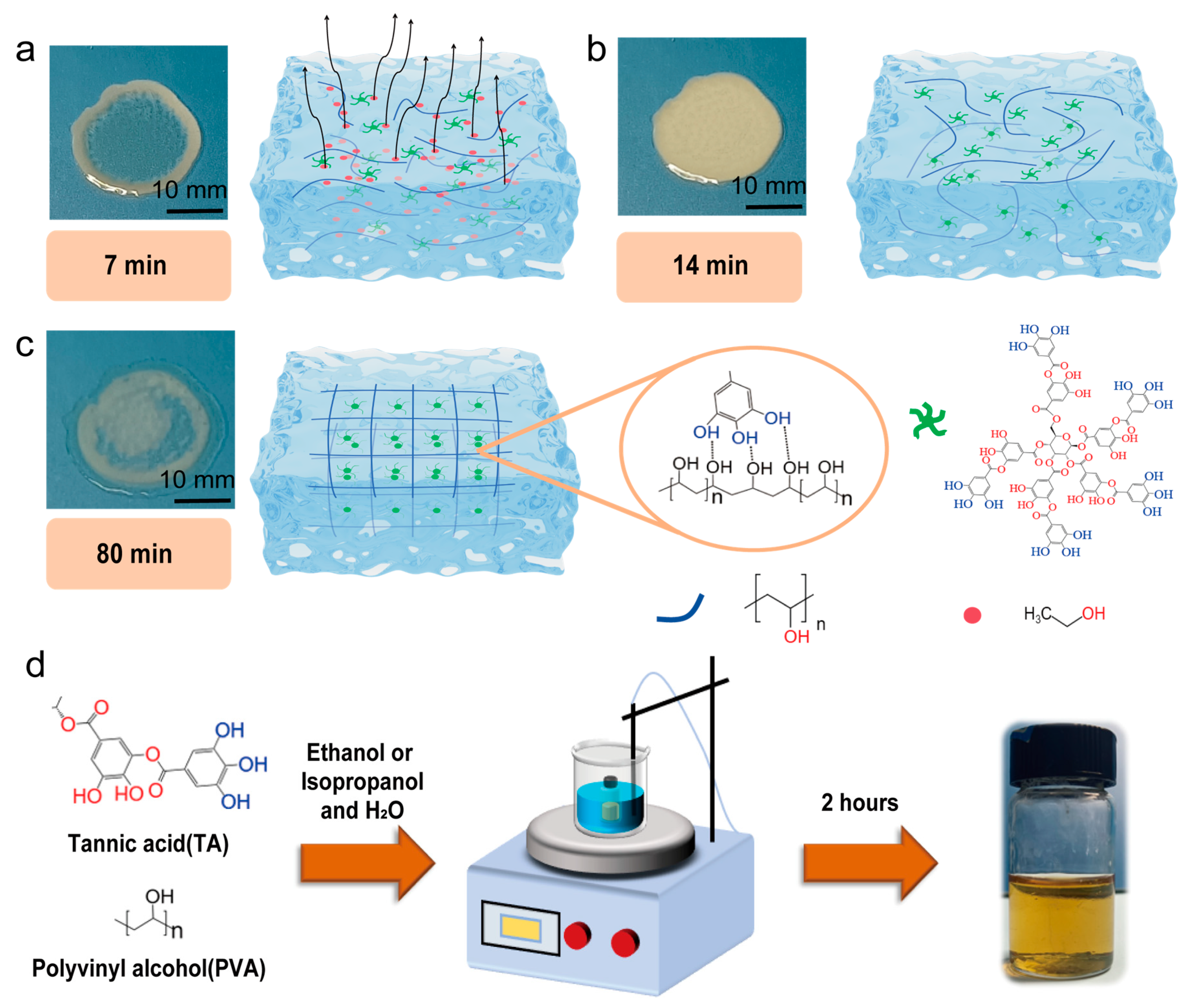
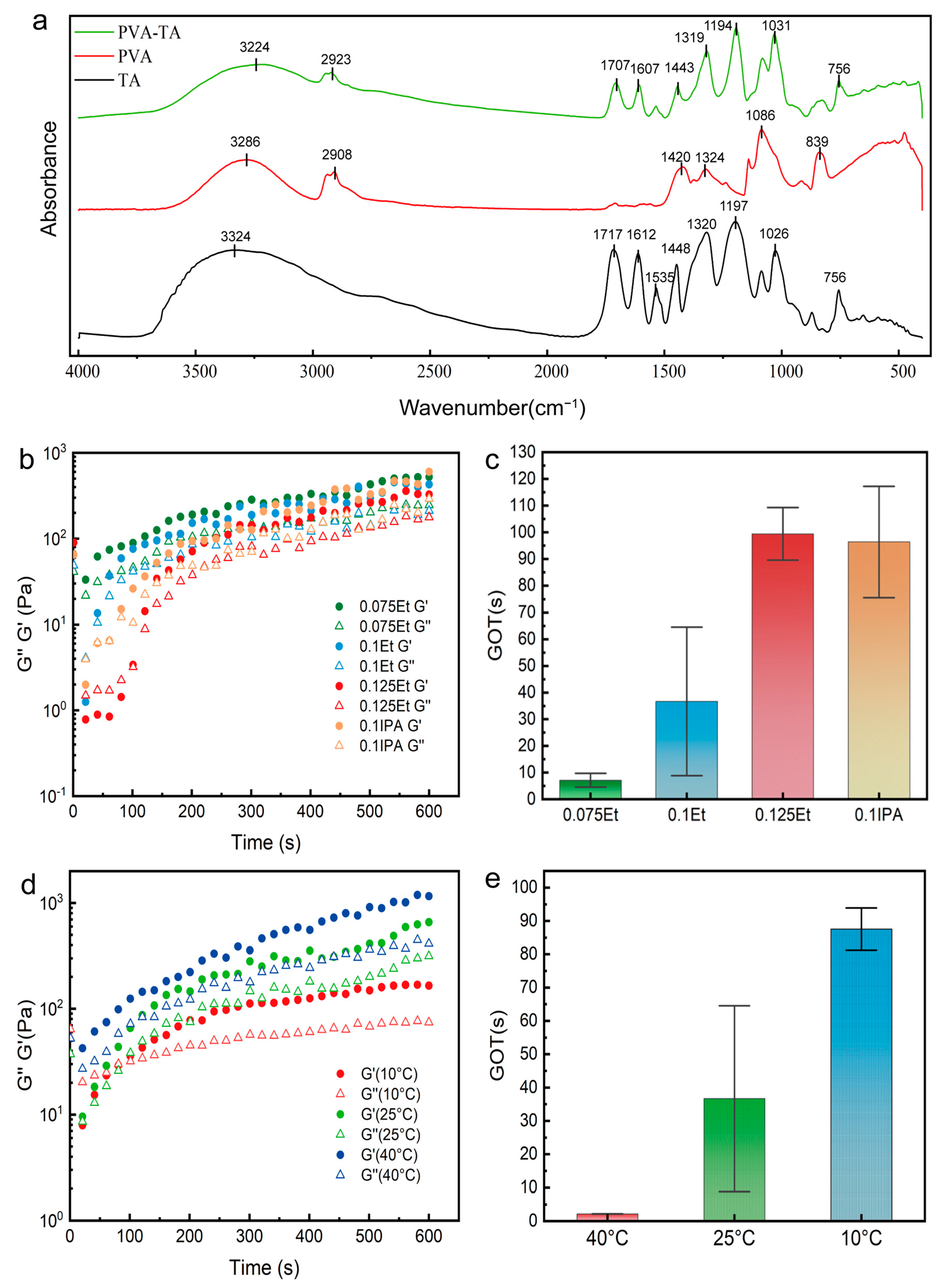
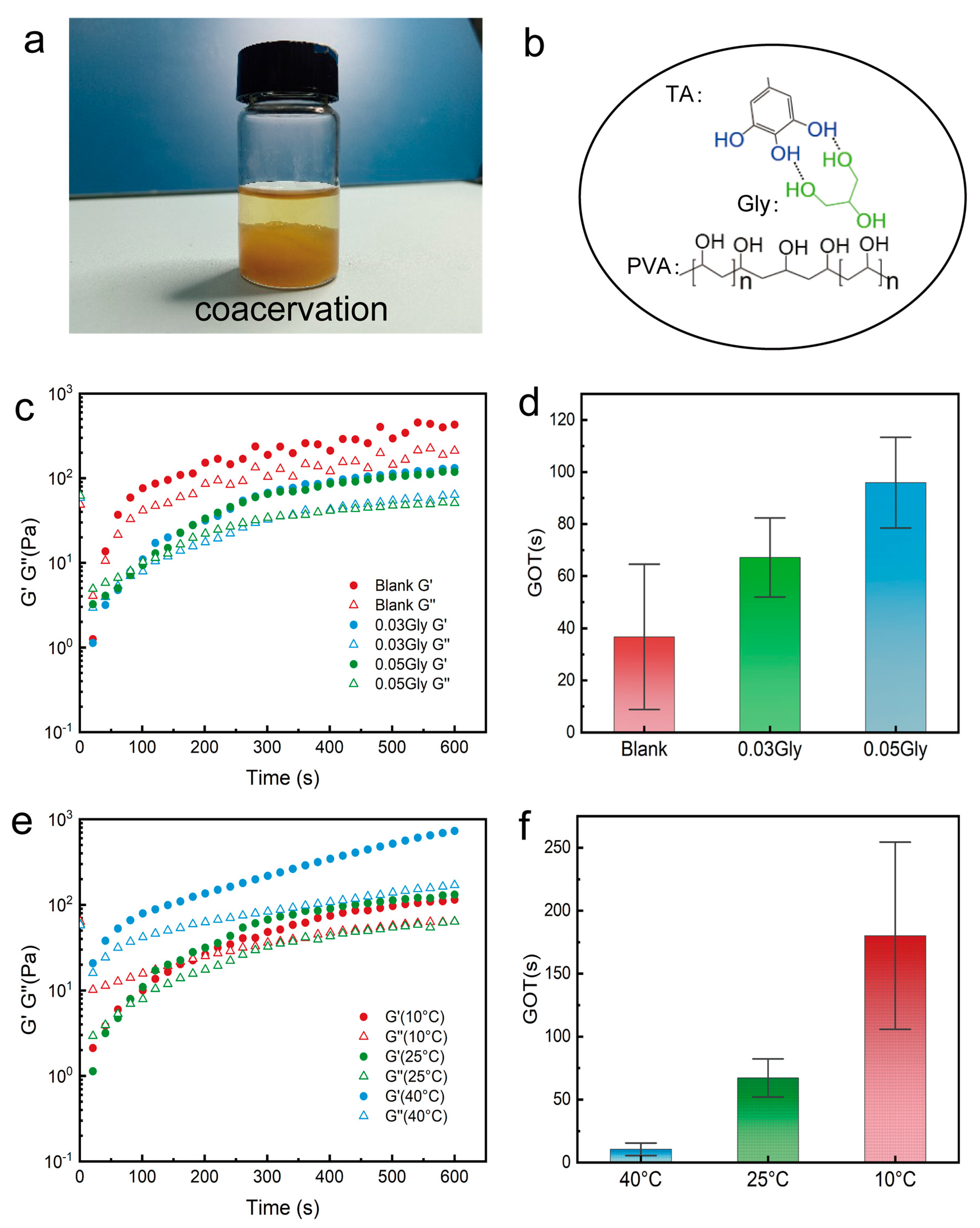
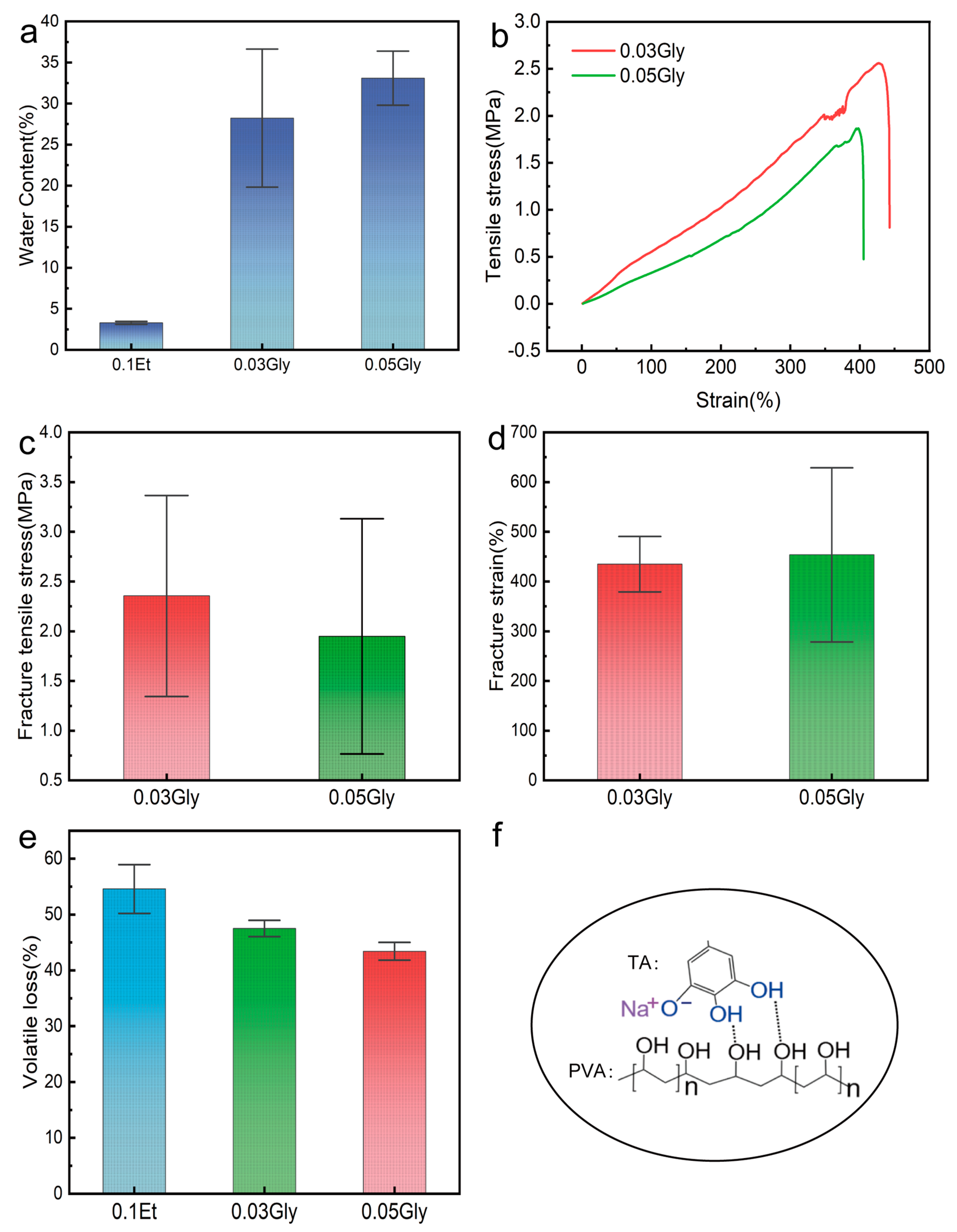
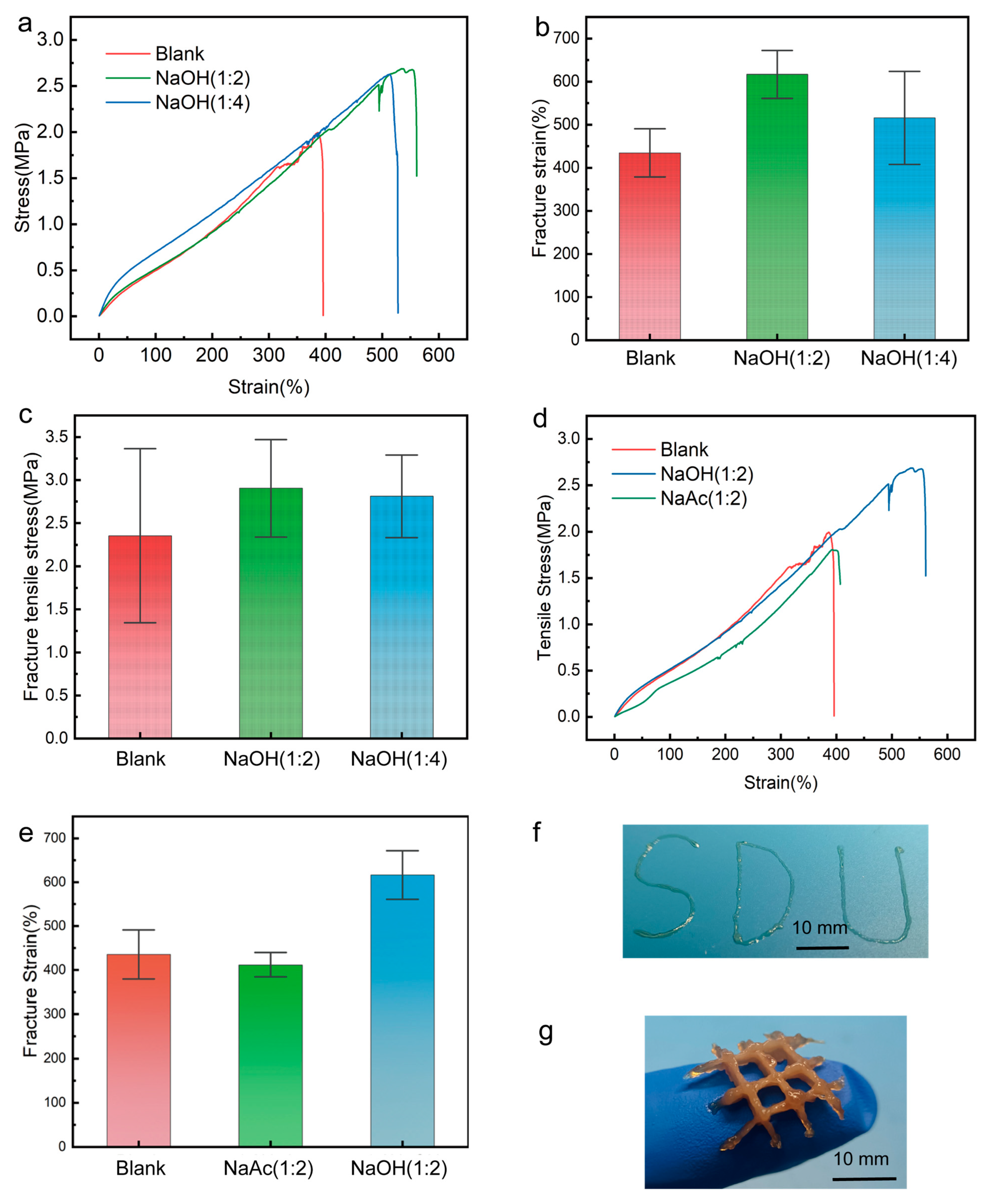
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the PVA-TA Hydrogels
4.3. Characterization of the Gelation Process at the Macroscopic Level
4.4. Characterization of Gelation Time
4.5. Mechanical Property Testing
4.6. Volatility and Water Retention Testing
4.7. FTIR Spectra Test
4.8. Preparation for 3D Printing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol | NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| TA | Tannic acid | NaAc | Sodium acetate |
| Et | Ethanol | G′ | Storage modulus |
| Gly | Glycerol | G” | Loss modulus |
| IPA | Isopropanol | GOT | Gelation onset time |
| Ratio Nomenclature In Sample | |||
| 0.075Et | n(Et):n(H2O) = 0.075:0.5 | 0.05Gly | n(Gly):n(H2O) = 0.05:0.5 |
| 0.1Et | n(Et):n(H2O) = 0.1:0.5 | NaOH(1:2) | n(TA):n(NaOH) = 1:2 |
| 0.125Et | n(Et):n(H2O) = 0.125:0.5 | NaOH(1:4) | n(TA):n(NaOH) = 1:4 |
| 0.1IPA | n(IPA):n(H2O) = 0.1:0.5 | NaAc(1:2) | n(TA):n(NaAc) = 1:2 |
| 0.03Gly | n(Gly):n(H2O) = 0.03:0.5 | ||
References
- Jung, D.Y.; Kwon, M.; Kim, K.S. Recent research trends in gradient hydrogels for various biomedical applications. Macromol. Res. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Zhu, P.; Mao, Y. Recent progress of nanomaterials-based composite hydrogel sensors for human–machine interactions. Discov. Nano 2025, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Kanti Mondal, A. Anti-swellable, stretchable, self-healable, shape-memory and supramolecular conductive TA-based hydrogels for amphibious motion sensors. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 211, 113034–113043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, X. Multiple hydrogen bonds enable high strength and anti-swelling cellulose-based ionic conductive hydrogels for flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148318–148327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Kim, D.Y.; Lim, S.I.; Lim, H.-R. Hydrogel-Based Biointerfaces: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions in Human–Machine Integration. Gels 2025, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Duan, Z.; Fu, R.; Fan, D. Tannic acid-Fe3+ dual catalysis induced rapid polymerization of injectable poly(lysine) hydrogel for infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 125911–125922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaheri, H.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Keshtkar Vanashi, A. Double network hydrogel based on PVA and CMC: Synthesis and its potential application in local drug delivery. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2025, 303, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Chen, W.; Liao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, C.; Chen, T.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Huang, R.; Liu, T.; et al. Reinforcing Gelatin Hydrogels via In Situ Phase Separation and Enhanced Interphase Bonding for Advanced 3D Fabrication. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2416432–2416444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Wan, R.; Yao, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, B. All 3D-printed high-sensitivity adaptive hydrogel strain sensor for accurate plant growth monitoring. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliaraj, G.S.; Shanmugam, D.K.; Dasan, A.; Mosas, K.K.A. Hydrogels—A Promising Materials for 3D Printing Technology. Gels 2023, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Zhang, P.; Xu, S.; Kong, L.; Liang, X.; Li, C.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J.; Cui, X. Fundamental, mechanism and development of hydration lubrication: From bio-inspiration to artificial manufacturing. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 327, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Q.; Ouyang, W.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Chen, B. Triboelectric Sensor Based on NaCl/agar Hydrogel as Portable Implicit Alarm Cipher System. J. Electron. Mater. 2025, 54, 4388–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Zang, D.; Long, H.; Weng, L.; Guo, N.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.B. A wearable ionic hydrogel strain sensor with double cross-linked network for human–machine interface. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Song, M.; Cui, J.; Wei, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J. Kneading-Dough-Inspired Quickly Dispersing of Hydrophobic Particles into Aqueous Solutions for Designing Functional Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Yan, H.; Tan, H.; Esmaeely Neisiany, R.; Sun, W.; You, Z. Readily recyclable, degradable, stretchable, highly conductive, anti-freezing and anti-drying glycerohydrogel for triboelectric nanogenerator. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qiu, X.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X.; Gai, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, J. A sprayable and rapidly cross-linked hydrogel membrane for fruit preservation. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 46, 101400–101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Yang, Z.; Liang, J.; Xie, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X. Recyclable, high strength and electrical-mechanical self-healing wearable ionic hydrogel sensor. Polymer 2024, 315, 127826–127836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunan, E.; Desiraju, G.R.; Klein, R.A.; Sadlej, J.; Scheiner, S.; Alkorta, I.; Clary, D.C.; Crabtree, R.H.; Dannenberg, J.J.; Hobza, P.; et al. Defining the hydrogen bond: An account (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, R.; Mompeán, M.; Laurents, D.V. Orientation affects hydrogen bonding cooperativity in polyproline II helical bundles. Commun. Chem. 2025, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yang, W.; Yan, S.; Yan, J. Sealing the Pandora’s vase of pancreatic fistula through entrapping the digestive enzymes within a dextrorotary (D)-peptide hydrogel. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Pan, F. Proton storage and transfer in aqueous batteries. Matter 2025, 8, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Das, K.; Sen, S.; Halder, S. Amino Acid Derived Hydrogen Bond Donor (HBD) Catalyst for the Synthesis of Cyclic Carbonates and Cyclic Dithiocarbonates: Experimental and Computational Studies **Supratim Halder and Koushik Das contribute equally to this work. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2025, e00244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Shi, N.; Dang, M.; Ji, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Hu, Z. Tailor-made high elasticity and low-hysteresis hydrogels based on asymmetric H-bonding crosslinking for wearable applications. Sci. China Chem. 2025, 68, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, C. Fabrication of temperature and pH dual-sensitive semi-interpenetrating network hydrogel with enhanced adhesion and antibacterial properties. Polymer 2025, 326, 128343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelnia, H.; Ensandoost, R.; Shebbrin Moonshi, S.; Gavgani, J.N.; Vasafi, E.I.; Ta, H.T. Freeze/thawed polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels: Present, past and future. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 164, 110974–110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A. Turbidimetric studies of aqueous poly(vinyl alcohol) solutions. Makromol. Chem. 1975, 176, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chowdhury, I.F.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Mondal, A.K.; Wu, H. Recent advances in tannic acid-based gels: Design, properties, and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 339, 103425–103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Peng, X.; Xi, L.; Wan, C.; Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. An agar–polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel loaded with tannic acid with efficient hemostatic and antibacterial capacity for wound dressing. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9622–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Liang, T.; Cao, J.; De Hoop, C.F.; Peng, X.; et al. High-Performance Biocomposite Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Films Modified with Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs), Tannic Acid (TA), and Chitosan (CS) for Food Packaging. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 4821717–4821725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W. Biocompatible autonomous self-healing PVA-CS/TA hydrogels based on hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Peng, W.; Chen, J.; Yu, C.; Bo, R.; Liu, M.; Li, J. Multifunctional hydrogel based on polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/metal polyphenols for facilitating acute and infected wound healing. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101315–101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuş, N.R.; Türk, S.; Guney Eskiler, G.; Syzdykbayev, M.; Appazov, N.O.; Özacar, M. Investigation of Tannic Acid Crosslinked PVA/PEI-Based Hydrogels as Potential Wound Dressings with Self-Healing and High Antibacterial Properties. Gels 2024, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1997, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Han, Y.; Kumar, R.; He, Y.; Hong, K.; Bonnesen, P.V.; Sumpter, B.G.; Smith, S.C.; Smith, G.S.; Ivanov, I.N.; et al. Controlling molecular ordering in solution-state conjugated polymers. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15134–15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Gao, T.; Dong, K.; Wei, G.; Yao, J. Facile Preparation of Tannic Acid–Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Beads for Methylene Blue Removal from Simulated Solution. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7523–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, S.; Lin, D.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, G. Research progress on antimicrobial hydrogel dressing for wound repair. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 197, 112372–112387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, B. Chitosan-Based Hydrogel-Incorporated Trp-CDs with Antibacterial Properties and pH-Mediated Fluorescence Response as a Smart Food Preservation Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 44097–44108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z. Janus Membrane with Hydrogel-like Coating for Robust Fouling and Wetting Resistance in Membrane Distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 19504–19513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawde, S.; Deshmukh, K. Characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin blend hydrogel films for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Ding, S.; Zhang, W. Biocompatible Autonomic Self-healing PVA-TA Hydrogel with High Mechanical Strength. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, C.; Chang, B.; Zhang, B.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Hou, C. On-Skin Paintable Water-Resistant Biohydrogel for Wearable Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400884–2400893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Gong, L.; Peng, X.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Wu, F.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Coacervation-driven instant paintable underwater adhesives with tunable optical and electrochromic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 12988–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, C.E.; Perry, S.L. Recent progress in the science of complex coacervation. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2885–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Ren, X.; Long, Y.; Fang, L.; Ou, R.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q. Highly compressible hydrogel sensors with synergistic long-lasting moisture, extreme temperature tolerance and strain-sensitivity properties. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulogne, F.; Restagno, F.; Rio, E. Measurement of the Temperature Decrease in Evaporating Soap Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 268001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Multi-scale multi-mechanism design of tough hydrogels: Building dissipation into stretchy networks. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 672–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.Z.; Yao, Y.; Halada, G.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, T. Impact of NaOH Concentration on Deweaving of Cotton Fabric in Aqueous Solutions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordi, S.S.; Noor, E.E.M.; Kok, C.K.; Julkapli, N.M.; Baig, M.F. Phase, Chemical, Thermal, and Morphological Analyses of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Nanocomposites Reinforced with Jute Cellulose Nanofibers (CNFs). Polymers 2025, 17, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhan, W.; Zuo, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Cai, G.; Tian, Y. Elastic, tough and switchable swelling hydrogels with high entanglements and low crosslinks for water remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138417–138425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, D.; George Thuruthel, T.; Iida, F. Self-healing ionic gelatin/glycerol hydrogels for strain sensing applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ouyang, F.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Wen, M.; Zha, G.; Yang, X. Tannic acid modified keratin/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan biocomposite hydrogels with good mechanical properties and swelling behavior. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruksawan, S.; Loh, J.E.T.; Chong, K.H.Z.; Chua, Z.A.; Chong, Y.T.; Chia, Z.Y.; Yew, K.S.A.; Wang, F. Tough, self-healing and weldable hydrogel via thermal engineering optimized multi-scale structures. Commun. Mater. 2025, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, X.; Huang, J. Hydrogen Bond-Regulated Rapid Prototyping and Performance Optimization of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Tannic Acid Hydrogels. Gels 2025, 11, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080602
Zou X, Huang J. Hydrogen Bond-Regulated Rapid Prototyping and Performance Optimization of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Tannic Acid Hydrogels. Gels. 2025; 11(8):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Xiangyu, and Jun Huang. 2025. "Hydrogen Bond-Regulated Rapid Prototyping and Performance Optimization of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Tannic Acid Hydrogels" Gels 11, no. 8: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080602
APA StyleZou, X., & Huang, J. (2025). Hydrogen Bond-Regulated Rapid Prototyping and Performance Optimization of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Tannic Acid Hydrogels. Gels, 11(8), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080602







