Fe3+-Modulated In Situ Formation of Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties
Abstract
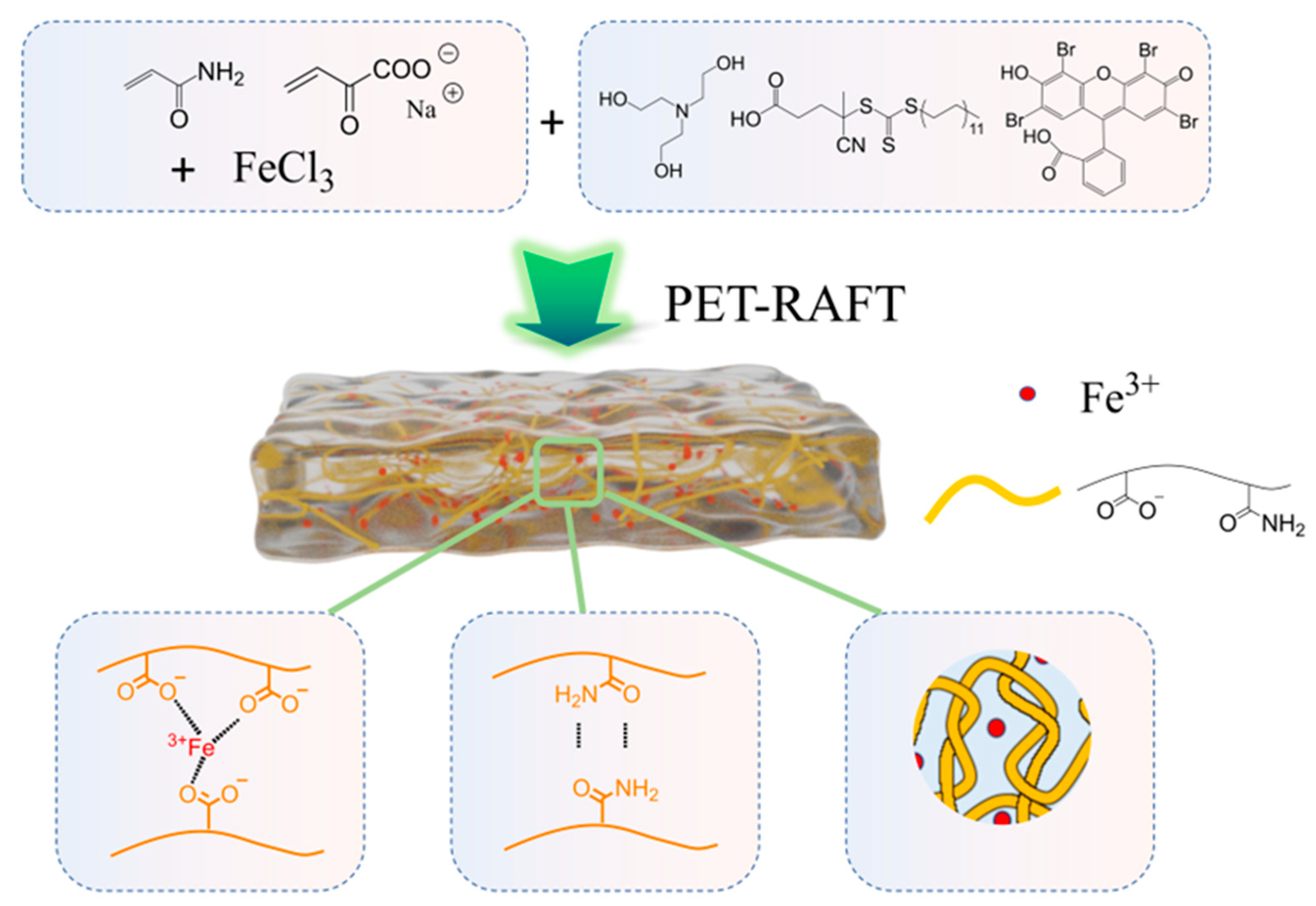
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hydrogel Preparation
2.2. Tensile Tests
2.3. Compressive Tests
2.4. Cyclic Load–Unload Tests
2.5. Degree of Swelling
2.6. Self-Adhesive, Ionic Conductivity, and Sensory Applications
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Fe3+ Modulated In Situ Formation of PAM-SA Hydrogels
4.3. Tensile Tests
4.4. Compressive Tests
4.5. Load–Unload Cycles
4.6. Swelling Tests
4.7. Sensing Finger and Elbow Bending
4.8. Ionic Conductivity
4.9. Gauge Factor (GF) Tests
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Kim, D.-H.; Lu, N. Introduction: Wearable Devices. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6145–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknejad, N.; Ismail, W.B.; Mardani, A.; Liao, H.; Ghani, I. A comprehensive overview of smart wearables: The state of the art literature, recent advances, and future challenges. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 90, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, H.C.; Nguyen, P.Q.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Güder, F.; Collins, J.J.; Dincer, C. End-to-end design of wearable sensors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Sharma, M.; Devi, M. Hydrogels: An overview of its classifications, properties, and applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 147, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, P.; Shojaei, A. A review on the features, performance and potential applications of hydrogel-based wearable strain/pressure sensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 298, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of Conductive Hydrogels for Fabricating Flexible Strain Sensors. Small 2022, 18, 2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, D.; George Thuruthel, T.; Iida, F. Self-healing ionic gelatin/glycerol hydrogels for strain sensing applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, M.; Yan, X.; Li, Y. Functional Hydrogel Strain Sensors for Smart Electronic Devices: Strategies and Recent Progress. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 5402–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhong, J.; Sun, F.; Liu, B.; Peng, Z.; Lian, J.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Hao, M.; Zhang, T. Hydrogel sensors for biomedical electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Hydrogels and Their Role in Biosensing Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Hydrogel Based Sensors for Biomedical Applications: An Updated Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, N.; Sun, S.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, L. Recent progress of hydrogel-based bioelectronics for mechanophysiological signal sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2025, 162, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Su, M.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L. Hydrogel-Based Bioelectronics and Their Applications in Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Bai, Y.; Ma, G. Metal Ion-Containing Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications in Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 3217–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janarthanan, G.; Noh, I. Recent trends in metal ion based hydrogel biomaterials for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z. Metal ion mediated conductive hydrogels with low hysteresis and high resilience. Mater. Today Phys. 2025, 51, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, B.; Peng, Y.; Ran, R. Fe3+-citric acid/sodium alginate hydrogel: A photo-responsive platform for rapid water purification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Debnath, A.; Tasnim, K.T.; Sarker, S.S.; Uddin, M.T.; Kamruzzaman, S.; Chowdhury, I.F.; Shawon, M.T.A.; Tang, Z.; Mondal, A.K. Facile strategy of Fe3+ rich collagen-based composite hydrogel for antibacterial, electricity harvesting and sensing applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Zeng, R.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Phospholipid reinforced P(AAm-co-AAc)/Fe3+ hydrogel with ultrahigh strength and superior tribological performance. Tribol. Int. 2022, 168, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.K.; Xu, D.; Wu, S.; Zou, Q.; Huang, F.; Ni, Y. Design of Fe3+-Rich, High-Conductivity Lignin Hydrogels for Supercapacitor and Sensor Applications. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J. Fe3+-Coordination mediated synergistic dual-network conductive hydrogel as a sensitive and highly-stretchable strain sensor with adjustable mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, X. Engineering hydrogels by soaking: From mechanical strengthening to environmental adaptation. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 13731–13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, X.; Lin, C.; Ma, X.; Cao, S.; Ni, Y. Ultrafast gelling using sulfonated lignin-Fe3+ chelates to produce dynamic crosslinked hydrogel/coating with charming stretchable, conductive, self-healing, and ultraviolet-blocking properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wan, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Tongue-inspired gelatin/poly(acrylate-co-acrylamide)-Fe3+ organic hydrogel with tunable mechanical, electrical, and sensory properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 210, 112992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi-Silab, S.; Pan, X.; Matyjaszewski, K. Photoinduced Iron-Catalyzed Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization with ppm Levels of Iron Catalyst under Blue Light Irradiation. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7967–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, N.; Yang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Zhu, X. Zero-valent Iron/RAFT Agent-Mediated Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate at Ambient Temperature. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7979–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, J.P. Design principles for strong and tough hydrogels. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2024, 9, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, Y.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Dhiman, P.; Si, C.; Stadler, F.J. Synthesizing pectin-crosslinked gum ghatti hydrogel for efficient adsorptive removal of malachite green. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lan, J.; Hua, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, S.; Ni, Y. An oriented Fe3+-regulated lignin-based hydrogel with desired softness, conductivity, stretchability, and asymmetric adhesiveness towards anti-interference pressure sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordi, F.; Colby, R.H.; Cametti, C.; De Lorenzo, L.; Gili, T. Electrical Conductivity of Polyelectrolyte Solutions in the Semidilute and Concentrated Regime: The Role of Counterion Condensation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 6887–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Qin, Y. Ultrastretchable, Ultralow Hysteresis, High-Toughness Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Pressure Recognition with Deep Learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 49834–49844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, T.; Wu, H.; Ye, M.; Yuan, G.; Jia, H. Tannic acid-Fe3+ activated rapid polymerization of ionic conductive hydrogels with high mechanical properties, self-healing, and self-adhesion for flexible wearable sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Fang, X.; Lin, B.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J. Highly sensitive and multifunctional Fe3+ enhanced PVA/gelatin multi-network hydrogels with wide temperature range environmental stability for wearable sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, F. A highly stretchable and self-adhesive cellulose complex hydrogels based on PDA@Fe3+ mediated redox reaction for strain sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qin, L.; Yang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Gao, P.; Yu, J.; Cai, K. A Conductive Hydrogel Based on GaIn and PVA/PAA/Fe3+ for Strain Sensor and Physiological Signal Detection. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5268–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, T.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Que, X.; Sheng, L.; Hu, Y.; Peng, J.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; et al. Polyacrylamide/Copper-Alginate Double Network Hydrogel Electrolyte with Excellent Mechanical Properties and Strain-Sensitivity. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Ahommed, M.S.; Wang, C.; Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Ni, Y.; Lyu, G. Zinc-ion engineered Plant-based multifunctional hydrogels for flexible wearable strain Sensors, Bio-electrodes and Zinc-ion hybrid capacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample (PxMyFez) | AM (g) | SA (g) | MBAA (mg) | FeCl3 (mg) | EY (mg) | TEOH (mg) | CDTPA (mg) | Water (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1M0.5Fe0 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M0.5Fe1 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M0.5Fe2 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M0.5Fe3 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.5 | 3 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P0.3M0.5Fe1 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P0.5M0.5Fe1 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P2M0.5Fe1 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P3M0.5Fe1 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M1Fe1 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M2Fe1 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| P1M3Fe1 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 3 | 1 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 |
| p value (x): | Adjusting AM:SA ratio | |||||||
| M value (y): | Adjusting crosslinker (MBAA) amount | |||||||
| Fe value (z): | Adjusting Fe3+ amount | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, L.; Guan, T.; Fan, X.; Zhi, W.; Zhou, R.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. Fe3+-Modulated In Situ Formation of Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties. Gels 2025, 11, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080586
Rong L, Guan T, Fan X, Zhi W, Zhou R, Li F, Liu Y. Fe3+-Modulated In Situ Formation of Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties. Gels. 2025; 11(8):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080586
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Lihan, Tianqi Guan, Xinyi Fan, Wenjie Zhi, Rui Zhou, Feng Li, and Yuyan Liu. 2025. "Fe3+-Modulated In Situ Formation of Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties" Gels 11, no. 8: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080586
APA StyleRong, L., Guan, T., Fan, X., Zhi, W., Zhou, R., Li, F., & Liu, Y. (2025). Fe3+-Modulated In Situ Formation of Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties. Gels, 11(8), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080586






