A Recent Insight into Research Pertaining to Collagen-Based Hydrogels as Dressings for Chronic Skin Wounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Skin and Wound Healing Process
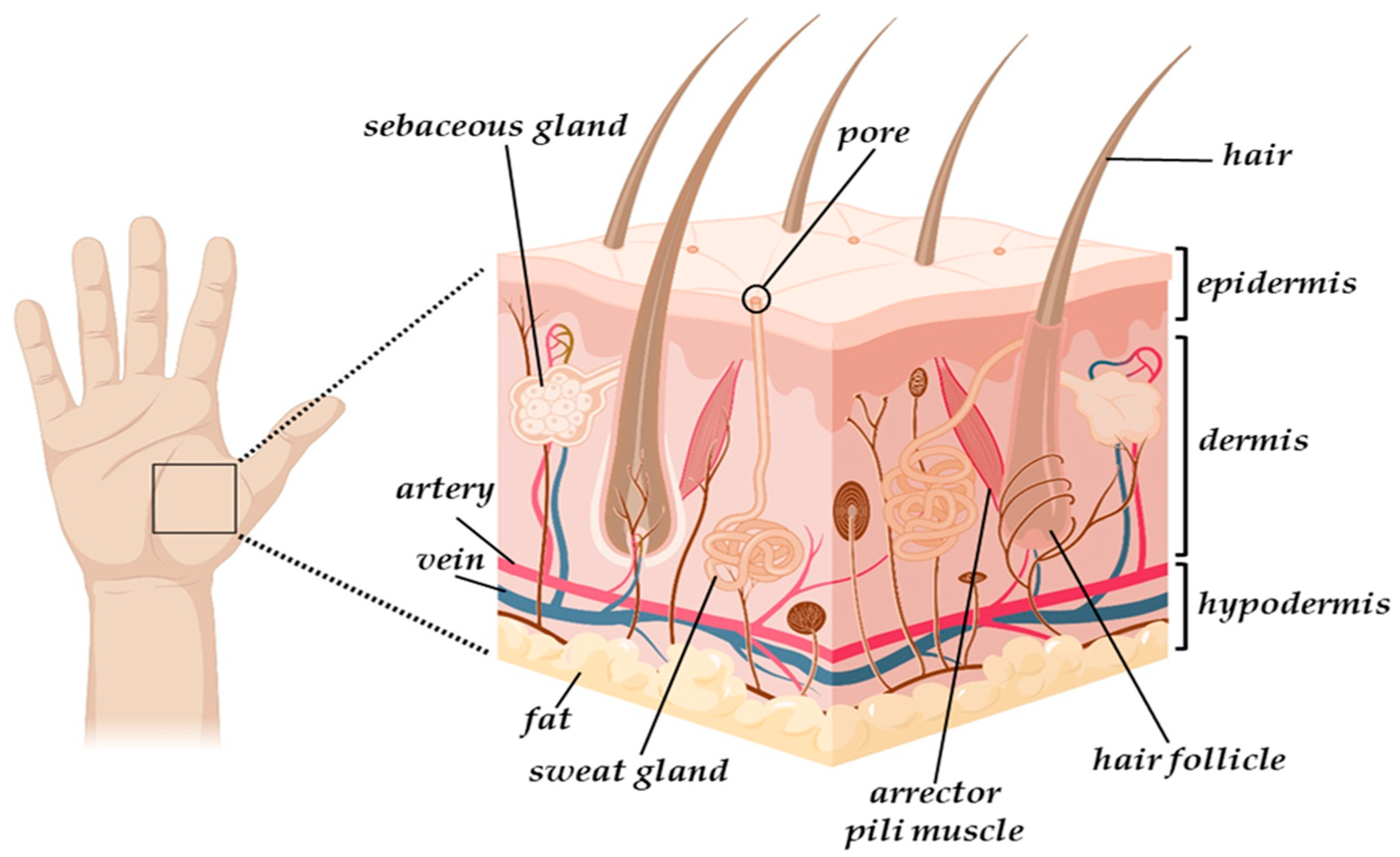
2.1. The Skin Structure
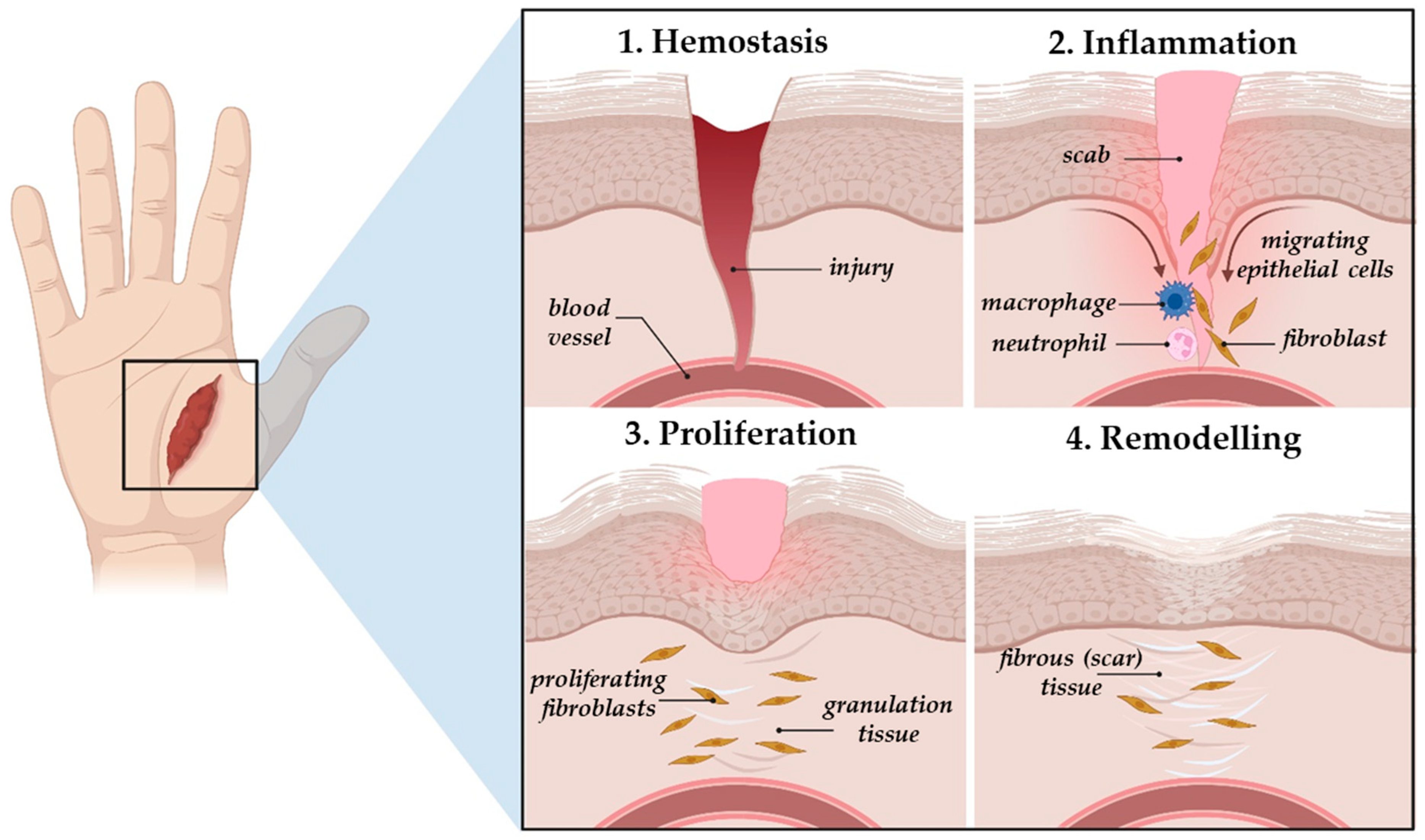
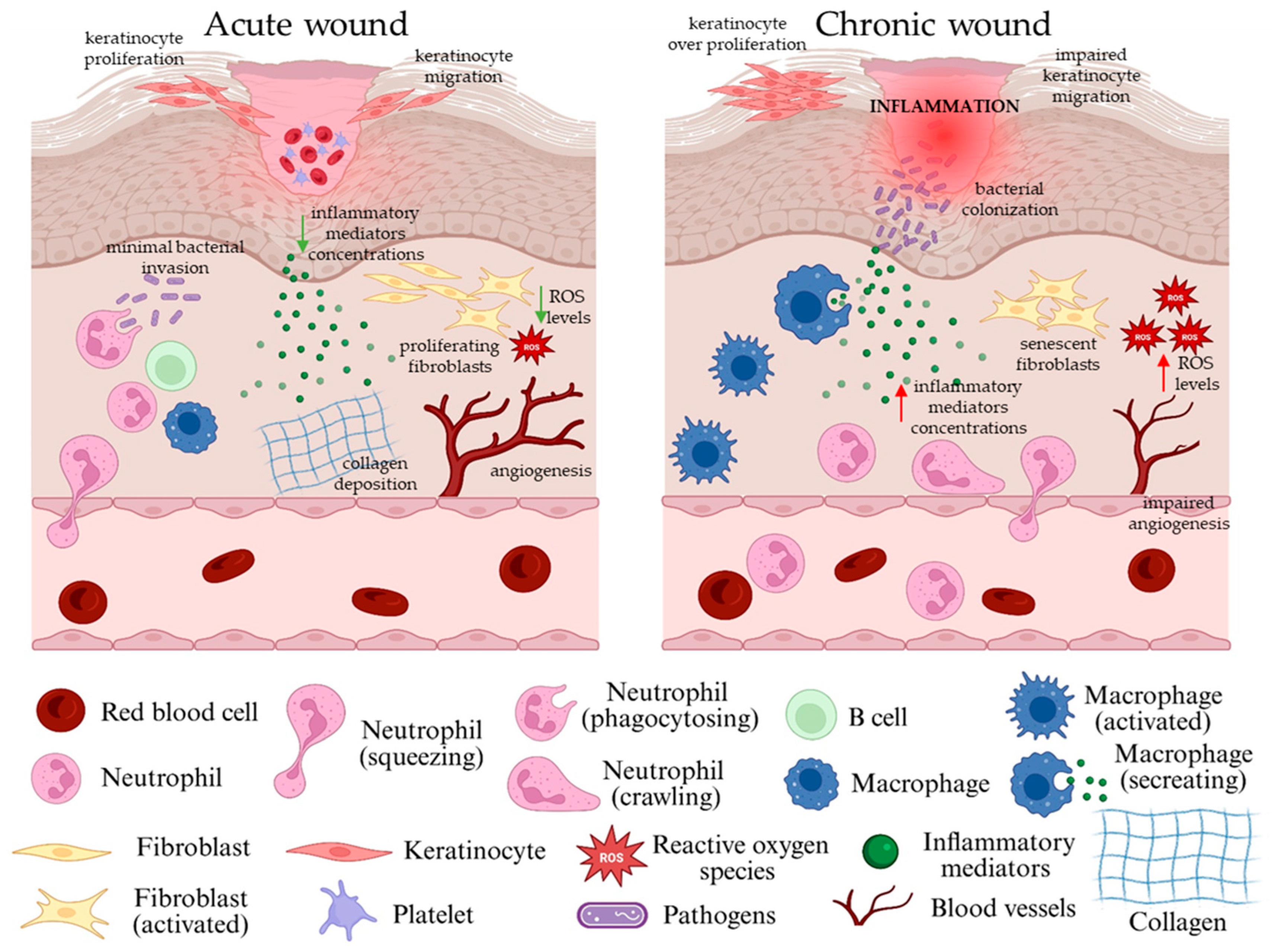
2.2. The Natural Wound Healing Process and Types of Skin Wounds
2.3. The Role of Endogenous Collagen in the Natural Skin Wound Healing
3. Collagen Structure and Sources
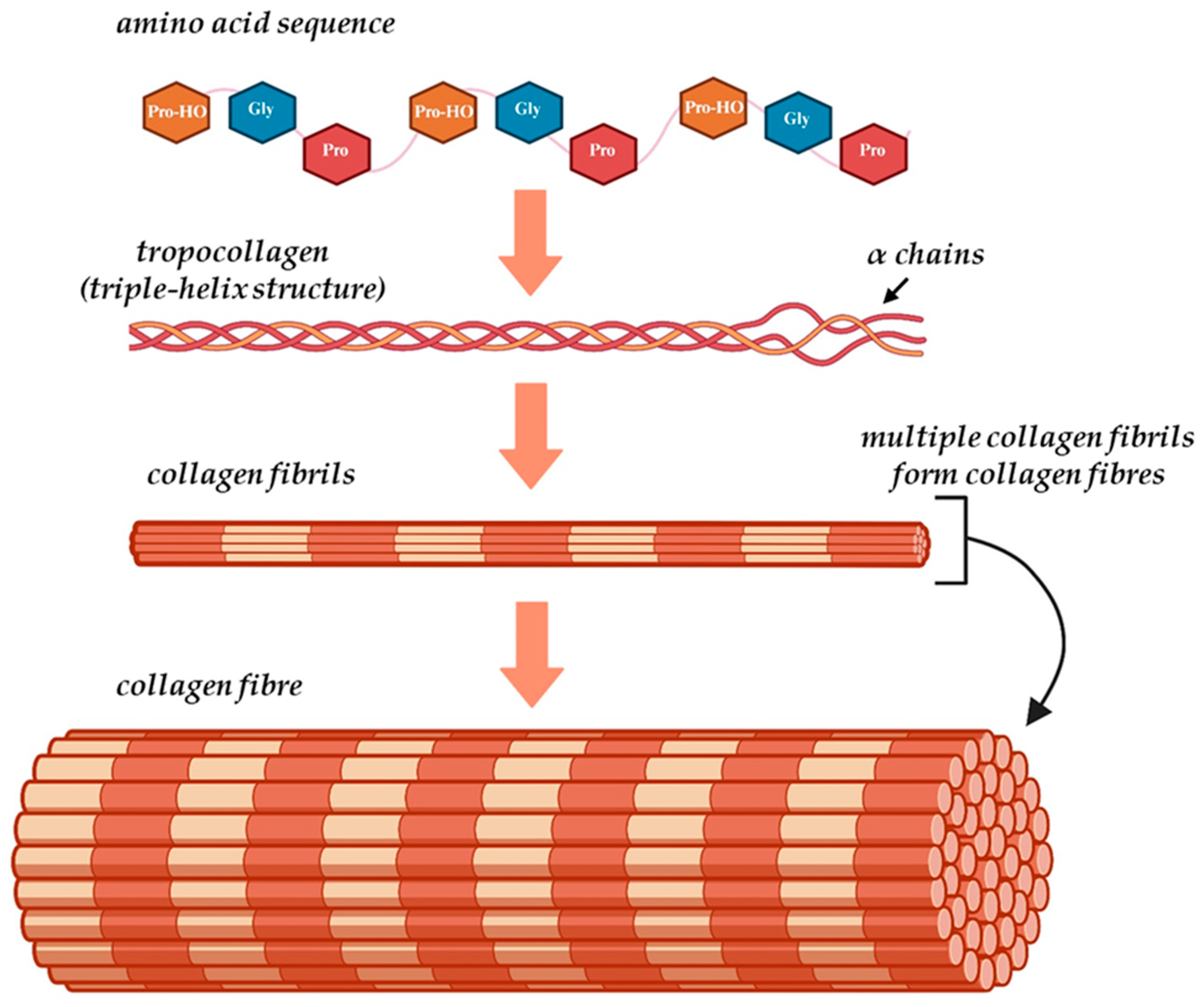
3.1. Collagen Structure
3.2. Collagen Sources for Hydrogel Manufacturing as Skin Wound Dressings
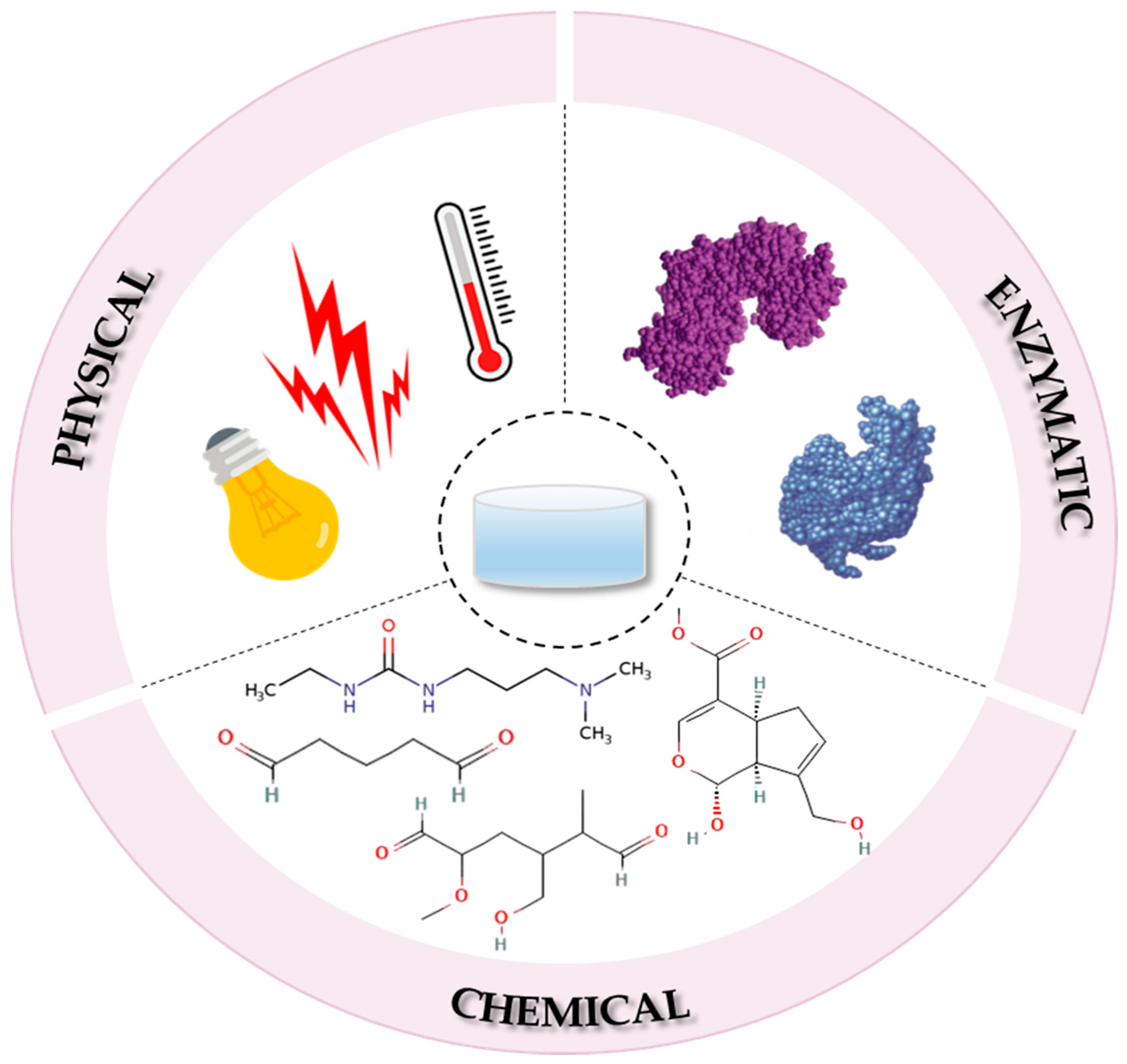
4. Fabrication Methods of Collagen-Based Hydrogels
4.1. The Physical Crosslinking Process
4.2. The Chemical Crosslinking Process
4.2.1. Glutaraldehyde
4.2.2. Dialdehyde Starch
4.2.3. Carbodiimides
4.2.4. Genipin
4.3. The Enzymatic Crosslinking Process
4.4. Emerging Cross-Linkers and Green Chemistry Approaches
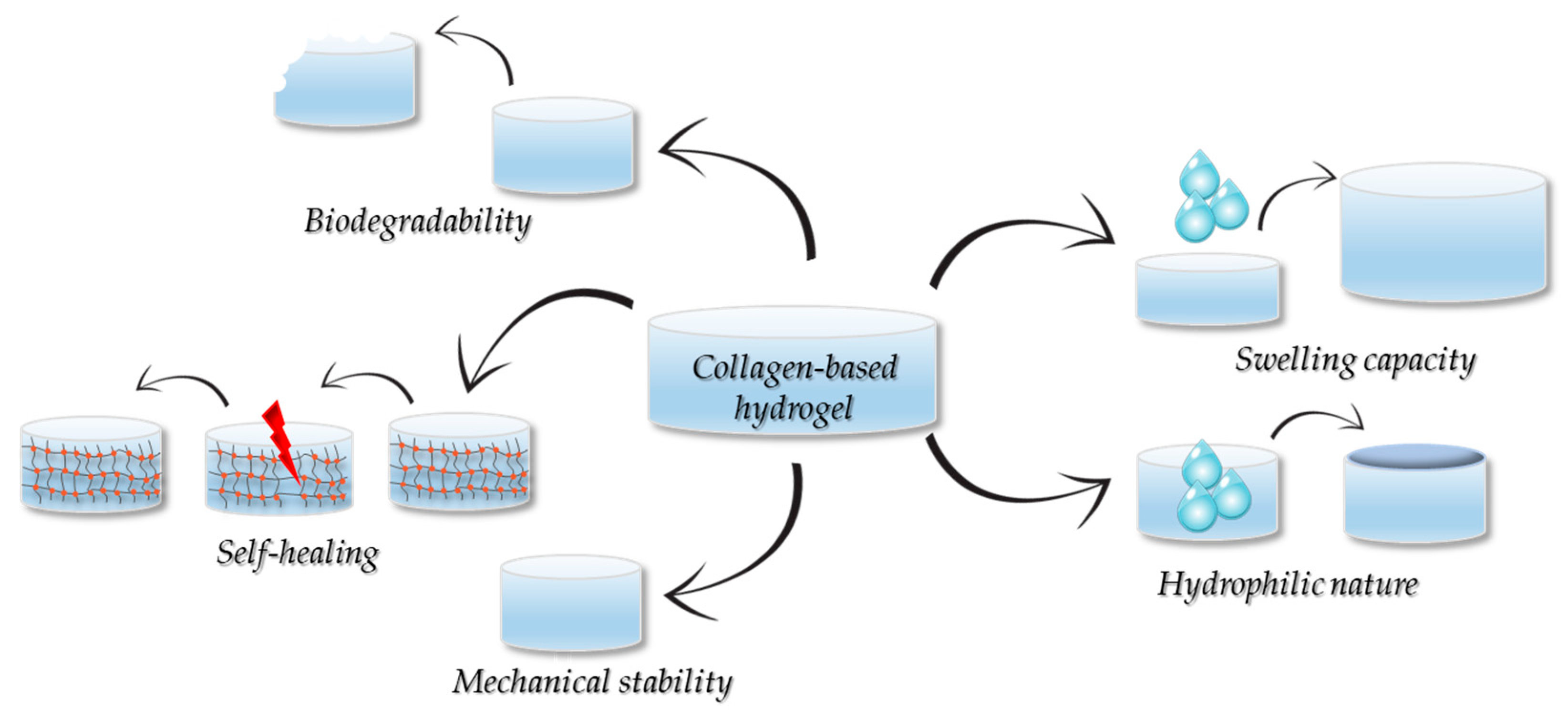
5. Properties of the Collagen-Based Hydrogels
5.1. Hydrophobicity and Moisturization
5.2. Mechanical Properties
5.3. Degradability
5.4. Swelling Properties
5.5. Self-Healing
6. Collagen-Based Hydrogels for Skin Wound Healing
6.1. Simple Collagen-Based Hydrogels for Chronic Skin Wounds
6.2. Collagen-Based Hydrogels Loaded with Bioactive Molecules for Chronic Skin Wounds
6.3. Composite Collagen/Polymer-Based Hydrogels for Chronic Skin Wounds
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Xing, F.; Yu, P.; Zhe, M.; Duan, X.; Liu, M.; Xiang, Z.; Ritz, U. A review of biomacromolecule-based 3D bioprinting strategies for structure-function integrated repair of skin tissues. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioce, A.; Cavani, A.; Cattani, C.; Scopelliti, F. Role of the Skin Immune System in Wound Healing. Cells 2024, 13, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olteanu, G.; Neacsu, S.M.; Joita, F.A.; Musuc, A.M.; Lupu, E.C.; Ionita-Mindrican, C.B.; Lupuliasa, D.; Mititelu, M. Advancements in Regenerative Hydrogels in Skin Wound Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vig, K.; Chaudhari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Dixit, S.; Sahu, R.; Pillai, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Advances in Skin Regeneration Using Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hong, Y.; Fu, X.; Sun, X. Advances and applications of biomimetic biomaterials for endogenous skin regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 39, 492–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.; Liu, P.Y.; Schultz, S.G.; Martins-Green, M.M.; Tanaka, R.; Weir, D.; Gould, L.J.; Armostrong, D.G.; Gibbons, G.W.; Wolcott, R.; et al. Chronic wounds: Treatment consensus. Wound Repair Regener. 2022, 30, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, A.; Bratu, A.G.; Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Collagen-Based Wound Dressings: Innovations, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jin, M.; Lin, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, K.; Zhang, T.; Tan, W. Application of Collagen-Based Hydrogel in Skin Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, D.; Dai, K.; Wang, Y.; Song, P.; Li, H.; Tang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Recent progress of collagen, chitosan, alginate and other hydrogels in skin repair and wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.E.; Anseth, K.S. Spatiotemporal hydrogel biomaterials for regenerative medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6532–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Optimization of Human-like Collagen Composite Polysaccharide Hydrogel Dressing Preparation Using Response Surface for Burn Repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 293, 116249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Mu, C.; Li, D.; Ge, L. Antibacterial Conductive Collagen-Based Hydrogels for Accelerated Full-Thickness Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 22817–22829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhong, S.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Recent advances in polysaccharide-based self-healing hy-drogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 283, 119161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, G.; Shalumon, K.T.; Chen, J.-P. Natural Polymers Based Hydrogels for Cell Culture Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2734–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, L.; Song, C.; Yao, L.; Xiao, J. Recent progresses of collagen dressings for chronic skin wound healing. Collagen Leather 2023, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Shahriar, S.M.S.; Yan, Z.; Xie, J. Recent Advances in functional Wound Dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2023, 12, 399–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheokand, B.; Vats, M.; Kumar, A.; Srivasta, C.M.; Bahadur, I.; Pathak, S. Natural polymers used in the dressing materials for wound healing: Past, present and future. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Developing natural polymers for skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 33, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberbigbe, B.A. Hybrid-Based Wound Dressings: A Combination of Synthetic and Biopolymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Darvishi, A. A review of the current state of natural biomaterials in wound healing applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1309541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorushanova, A.; Delgado, L.M.; Wu, Z.; Shologu, N.; Kshirsagar, A.; Raghunath, R.; Mullen, A.M.; Bayon, Y.; Pandit, A.; Raghunath, M.; et al. The Collagen Suprafamily: From Biosynthesis to Advanced Biomaterial Development. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1801651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taupin, P.; Gandhi, A.; Saini, S. Integra® Dermal Regeneration Template: From Design to Clinical Use. Cureus 2023, 15, e38608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, M.; Shafiee, M.; Afshari, F.; Mohammadi, H.; Ghasemi, Y. Collagen-Based Medical Devices for Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 169, 5563–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geanaliu-Nicole, R.E.; Andronescu, E. Blended Natural Support Materials-Collagen Based Hydrogels Used in Biomedicine. Materials 2020, 13, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noami, R.; Bahari, H.; Ridzuan, P.M.; Othman, F. Natural-based Biomterial for Skin Wound Healing (Gelatin vs. Collagen): Expert Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, C.A.; Simman, R. Modern Collagen Wound Dressings: Function and Purpose. J. Am. Coll. Or Certif. Wound Spec. 2010, 2, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Dawson, C.; Lamb, M.; Mueller, E.; Stefanek, E.; Akbari, M.; Hoare, T. Hydrogels for Tis-sue Engineering: Addressing Key Design Needs Towards Clinical translation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 849831. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.; Khoshfetrat, A.B.; Khatami, N.; Ahmadian, M.; Rahbarghazi, R. Comparative study of collagen and gelatin in chitosan-based hydrogels for effective wound dressing: Physical properties and fibroblastic cell behaviour. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2019, 518, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreazza, R.; Morales, A.; Pieniz, S.; Labidi, J. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Potential Biomaterials for Remediation. Polymers 2023, 15, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S. The skin. In Techniques in Small Animal Wound Management, 1st ed.; Buote, N.J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Balavigneswaran, C.K.; Selvaraj, S.; Vasudha, T.K.; Iniyan, S.; Muthuvijayan, V. Tissue engineered skin substitutes: A comprehensive review of basic design, fabrication using 3D printing, recent advances and challenges. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 153, 213570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, G.; Cai, X.; Dou, R.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. The potential of collagen-based materials for wound management. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 41, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound Healing: Cellular Mechanisms and Pathological Outcomes. Adv. Surg. Med. Spec. 2023, 10, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Monica, F.; Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Kirsner, R. Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonida, M.D.; Kumar, I. Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. In Bionanomaterials for Skin Regeneration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic wound healing: A review of current management and treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, F.; Luo, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, D. Inflammatory Microenvironment of Skin Wound. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 789274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Huang, B.S.; Horng, H.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, Y.J. Wound healing. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Repair in Acute and Chronic Wound Healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manon-Jensen, T.; Kjeld, N.G.; Karsdal, M.A. Collagen-mediated hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisling, A.; Lust, R.M.; Katwa, L.C. What is the role of peptide fragments of collagen I and IV in health and disease? Life Sci. 2019, 228, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosicka-Frackowiak, H.; Poniedzialek, K.; Wozny, S.; Kuprianowicz, M.; Nyga, M.; Jadach, B.; Milanowski, B. Collagen and Its Derivatives Serving Biomedical Purposes: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Raines, R.T. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Wound Healing. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouw, J.K.; Ou, G.; Weaver, V.M. Extracellular matrix assembly: A multiscale deconstruction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.K.; Hahn, R.A. Collagens. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison-Kotler, E.; Marshall, W.S.; Garcia-Gareta, E. Sources of collagen for biomaterial in skin wound healing. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.S.; Kumar, K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.D.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Collagen: Animal Sources and Biomedical Ap-plication. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Simoes, M.; Vitorino, C.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F. Hydrogels in Cutaneous Wound Healing: Insights into Characterization, Properties, Formulation and Therapeutic Potential. Gels 2024, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yue, O.; Bai, Z.; Cui, B.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X. A Review of Recent Progress on Collagen-Based Biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Liu, J.-X.; Cheng, J.-S.-Y.; Qi, X.-Y.; Ye, S.-J.; Gong, H.-L.; Zhao, X.-H.; Yu, J.; Xu, G.; et al. Marine Derived Collagen as Biomaterials for Human Health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702108. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine origin collagens and its potential applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jin, S.; Tang, Y. Marine Collagen Peptides Promote Cell Proliferation of NIH-3T3 Fibroblasts via NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Ding, N.; Ge, B. Self-assembly and cross-linking preparation of tilapia-skin-derived collagen/alginate hydrogels for efficient wound repair. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 1901–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, R.; Hossain, L.; Al-Arafat, T.; Karmakar, P.C.; Adnan, H.; Diba, F.; Karim, N.; Aktar, N.; Asaduzzaman, S.M. A comparative study of human amniotic membrane, tilapia skin collagen, and Centella asiatica derived gen to treat burn wound in rat model. Cell Tissue Bank. 2025, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydogan, B.; Kucuk, A.; Kozan, B.; Erdal, M.; Abas, B.I.; Cevik, O. Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment. BioChem 2025, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Sheng, W.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; et al. Injectable and self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose/marine snail peptide hydrogel for infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 288, 138784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, Z.; Qin, S. Preparation and characterization of novel poly (vinyl alcohol)/collagen double-network hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Liu, N.; Liang, F.; Zhao, X.; Long, J.; Yuan, F.; Yun, S.; Sun, Y.; Xi, Y. Molecular assembly of recombinant chicken type II collagen in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Kan, M.; et al. Advances in preparation and application of antibacterial hydrogels. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Desai, N.; Salave, S.; Karunakaran, B.; Giri, J.; Benival, D.; Gorantla, S.; Kommieni, N. Collagen-Based Hydrogels for the Eye: A Comprehensive Review. Gels 2023, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, S.; Ullah, I.; Xie, H.; Tao, X.D.; Xu, H.T.; Shen, J. Self-healing hydrogels as injectable implants: Advances in transla-tional wound healing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 509, 215790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.S.; Premanand, R.; Ragupathi, I.; Bhaviripudi, V.R.; Aepuru, R.; Kannan, K.; Shanmugaraj, K. Comprenhensive Review of Hydrol Sythesis, Characterization and Emerging Applications. J. Comps. Sci. 2024, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, D.V.; Davidenko, N.; Hamaia, S.W.; Farndale, R.W.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Impact of UV- and carbodiimide-based crosslinking on the integrin-binding properties of collagen-based materials. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiak, K.; Sionkowska, A. Current methods of collagen cross-linking: Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sionkowska, A.; Lewandowska, K.; Adamiak, K. The Influence of UV Light on Rheological Properties of Collagen Extracted from Silver Carp Skin. Materials 2020, 13, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S. Preparation of Recombinant Human Collagen III Protein Hydrogels with Sustained Release of Extracellular Vesicles for Skin Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Sun, W.; Ouyang, L. Recombinant Human Collagen-Based Bioinks for the 3D Bioprinting of Full-thickness Human Skin Equivalent. Int. J. Bioprint. 2022, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazobolis, V.; Labiris, G.; Gkika, M.; Sideroudi, H.; Kalaghianni, E.; Papadopoulou, D.; Toufexis, G. UV-A collagen cross-linking treatment of bullous keratopathy combined with corneal ulcer. Cornea 2010, 29, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richoz, O.; Hammer, A.; Tabibian, D.; Gatzioufas, Z.; Hafezi, F. The biochemical effect of corneal collagen crosslinking (CXL) with riboflavin and UV-A is oxygen dependent. Transl. Vis. Sci. Techn. 2013, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-O.; Jeong, S.I.; Park, J.-S.; Ju, Y.M.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, Y.-M. One step gamma-ray induced crosslinking and sterilization of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/collagen composite scaffolds. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ismal, M.; Hasan, K.; Nam, K.-W. A Comprehensive Review of Radiation-Induced Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Multidimensional Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, M.; Calina, I.; Scraisoreanu, A.; Micutz, M.; Kaya, M.A. Correlations on the Structure and Properties of Collagen Hydrogels produces by E-beam Crosslinking. Materials 2022, 15, 7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, S.; Hietschold, P.; Krömmelbein, C.; Kunschmann, T.; Konieczny, R.; Knolle, W.; Mierke, C.T.; Zink, M.; Mayr, S.G. Design of Biomimetic Collagen Matrices by Reagent-Free Electron Beam Induced Crosslinking: Structure-Property Relationships and Cellular Response. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Shinoda, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamane, H. Effect of the Application of a Dehydrothermal Treatment on the Structure and the Mechanical Properties of Collagen Film. Materials 2020, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzma, J.; Suchy, T.; Horny, L.; Supova, M.; Sucharda, Z. Comparative Study of the Dehydrothermal Crosslinking of Elec-trospun Collagen Nanaofibers: The Effects of Vacuum Conditions and Subsequent Chemical Crosslinking. Polymers 2024, 16, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Fu, C.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Yao, L.; Xiao, J. Biomimetic tri-layered artificial skin comprising silica gel-collagen membrane-collagen porous scaffold for enhanced full-thickness wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Shan, T.; Ma, Y.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L. Novel Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Collagen. Trend Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 464–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.P.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Masih, P.; Pandya, D.; Amara, S.; Collins, G.; Arinzeh, T.L. An investigation of common crosslinking agents on the stability of Electrospun collagen scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 103, 726–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wu, K.; Liu, W.; Shen, L.; Li, G. Two-dimensional infrared spectroscopic study on the thermally induced structural changes of glutaraldehyde-crosslinked collagen. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 140, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, D.M.; Yost, M.J.; Matthews, M.A. Eliminating glutaraldehyde from crosslinked collagen films using critical CO2. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Dialdehyde Starch by One-Step Acid Hydrolysis and Oxidation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabskaielinska, S. Cross-linking Agents in Three-component Materials Dedicated to Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2024, 6, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valipour, F.; Rahimabadi, E.Z.; Rostamzad, H. Preparation and characterization of wound healing hydrogel based on fish skin collagen and chitosan cross-linked by dialdehyde starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Zielinska, S.; Sinokowska, A.; Reczynska, K.; Pamula, E. Physico-chemical characterisation and biological tests of collagen/silk fibroin/chitosan scaffolds cross-linked by dialdehyde starch. Polymers 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queen, D.; Gaylor, J.D.S.; Evans, J.H. The preclinical evaluation of the water vapour transmission rate through burn wound dressing. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Mu, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Ge, L. Crosslinking effect of dialdehyde cholesterol modified starch nanoparticles on collagen hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 285, 119237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapach, L.A.; Vanderburgh, J.A.; Miller, J.P.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Manipulation of in Vitro Collagen Matrix Architecture for Scaffolds of Improved Physiological Relevance. Phys. Biol. 2015, 12, 61002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Yang, J. Preparation of aminated fish scale collagen and oxidized sodium alginate hybrid hydrogel for enhanced full-thickness wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, T.; Feng, Y.; Xu, T.; Pan, S.; Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, S.; et al. Synthesis of collagen-grafted polyacrylamide hydrogel for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 212, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Kulka-Kaminska, K.; Brudzynska, P.; Lewandowska, K.; Piwowarski, L. The Influence of Various Crosslinking Conditions of EDC/NSH on the Properties of Fish Collagen Film. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Gilarska, A.; Buła, A.; Horak, W.; Łatkiewicz, A.; Nowakowska, M. Genipin crosslinked bioac-tive collagen/chitosan/hyaluronic acid injectable hydrogels structurally amended via covalent attachment of surface-modified silica particles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, C.; Zheng, X.; Qi, X.; Bi, J.; Wang, H.; Cao, J. Collagen/chitosan/genipin hydrogel loaded with phycocyanin nanoparticles and ND-336 for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Hou, J.; Xheng, N.; Huang, M.; Luo, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Recombinant human collagen I/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel loaded with long-term released huCMSCs derived exosomes promoted skin wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagdarova, B.; Konovalova, M.; Zhuikova, Y.; Lunkov, A.; Zhuikov, V.; Khaydapova, D.; Il’ina, A.; Svirshchevskaya, E.; Varlamov, V. Collegn/Chitosan Gels Cross-Linked with Genupin for Wound Healing in Mice with Induced Diabetes. Materials 2022, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Hao, J. Enzyme-regulated healable polymeric hydrogels. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1507–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayssinet, A.; Petta, D.; Illoul, C.; Haye, B.; Markitantova, A.; Eglin, D.; Mosser, G.; D’Este, M.; Hélary, C. Extracellular ma-trix-mimetic composite hydrogels of cross-linked hyaluronan and fibrillar collagen with tunable properties and ultrastructure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Double crosslinked HLC-CCS hydrogel tissue engineering scaffold for skin wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapula, P.; Bilik-Was, K.; Malarz, K. Are Natural Compounds a Promising Alternative to Synthetic Cross-Linking in the preparation of Hydrogels? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cmaci, Y.; Turk, S.; Ozacar, M. An innovative approach to wound dressings: Citric acid cross-linked carbotmethylcellulose-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with variable pore size. Nanomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 7, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Di Francesco, S.; Petralito, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Ceseracciu, L.; Palocci, C. Natural Compounds and Biopolymers-Based Hydrogels Join Forces to Promote Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishalska-Sionkowska, M.; Warzynska, O.; Kaczmarek-Szczpanska, B.; Lukowicz, K.; Osyczka, A.M.; Walczak, M. Charcterization of Caollegn/Beta Glucan Hydrogels Crosslinked with Tannic Acid. Polymers 2021, 13, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacmarek-Szczepanska, B.; Wekwejt, M.; Palubicka, A.; Michno, A.; Zasada, L.; Alsharabasy, A.M. Cold plasma treatment of tannic acid as a green technology for the fabrication of advanced cross-linkers for bioactive collagen/gelatin hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258 Pt 1, 128870. [Google Scholar]
- Maikovych, O.; Nosova, N.; Bukartyk, N.; Fihurka, N.; Ostapiv, D.; Samaryk, V.; Pasetto, P.; Varvarenko, S. Gelatin-based hydrogel with antiseptic properties: Synthesis and properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 7611–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Dan, N.; Chen, Y. Utilizing epoxy Bletilla striata polysaccharide collagen sponge for hemostatic care and wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 128389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, J.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Lv, S.; Tong, J.; Liu, L.; He, T.; Wang, J.; Wei, D. Recent advances in collagen-based hydrogels: Materials, preparation and applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 207, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrigiaddidis, S.O.; Rey, J.M.; Dobre, O.; Gonzales-Gracia, C.; Dlby, M.J.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M. A tough act to follow: Collagen hydrogel modifications to improve mechanical and growth factor loading capabilities. Mater. Today Bio. 2021, 10, 100098. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, W.; Gao, Y.; Dong, L.; Jia, H.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. The synergistic regulation of chondrogenesis by collagen-based hydrogels and cell co-culture. Acta Biomater. 2022, 154, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Ruan, D.; Huang, M.; Tian, M.; Zhu, K.; Gan, Z.; Xiao, Z. Harnessing the potential oh hydrogels for advanced thera-peutic applications: Current achievements and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Lian, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Reis, R.L.; Oliviera, J.M. Properties of Collagen/Sodium Alginate Hydrogels for Bioprinting of Skin Models. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 20, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.I.E.; Mollari, K.G.; Komvopoulos, K. Design Challenges in Polymeric Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 617141. [Google Scholar]
- Rahvar, P.T.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Jooybar, E.; Gantenbein, B. An enzymatically crosslinked collagen type II/hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogel: A biomimetic cell delivery system for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 134614. [Google Scholar]
- Dinescu, S.; Albu Kaya, M.; Chiroiu, L.; Ignat, S.; Kaya, D.A.; Costache, M. Collagen-Based Hydrogels and Their Applications for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Mondal, M., Ed.; Polymers and Polymeric Compoistes: A Reference Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.E.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound Healing Dressings and Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajvazi, N.; Milošev, I.; Čelan Korošin, N.; Rodič, P.; Božić, B. Enhancing Cross-Linking Efficiency in Gelatin-Based Hydrogels via Incorporation of Tannic Acid, Pluronic F-127, and Phytic Acid. Polymers 2025, 17, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek-Szczepańska, B.; D’Amora, U.; Zasada, L.; Michalska-Sionkowska, M.; Miłek, O.; Łukowicz, K.; Osyczka, A.M. Enhancing Thin Film Properties of Chitosan–Collagen Biocomposites through Potassium Silicate and Tannic Acid Integration. Polymers 2025, 17, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brăzdaru, L.; Staicu, T.; Albu Kaya, M.G.; Chelaru, C.; Ghica, C.; Cîrcu, V.; Leca, M.; Ghica, M.V.; Micutz, M. 3D Porous Collagen Matrices—A Reservoir for In Vitro Simultaneous Release of Tannic Acid and Chlorhexidine. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.A.; Maarof, M.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Hao, D.L.Q.; Tabata, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliari, S.R.; Burdick, J.A. A practical guide to hydrogels for cell culture. Nature Methods 2016, 13, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Neisiany, R.E.; Gu, S.; You, Z. Mechanically robust and room temperature self-healing Ionogel based on ionic liquid inhibited reversible reaction of disulfide bonds. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Oh, D.X.; Park, J. Recent progress in self-healing polymers and hydrogels based on reversible dynamic B-O bonds: Boronic/boronate esters, borax, and benzoxaborole. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Wei, Q. Collagen-based injectable and-self healing hydrogel with multifunction for regenerative repair-men of infected wounds. Regen. Biomater. 2023, 10, rbad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Mooney, D.J. Tissue-engineered wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcers. In The Diabetic Foot; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 12, pp. 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Khampieng, T.; Wongkittithavorn, S.; Chaiarwut, S.; Ekabutr, P.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Silver nanoparticles-based hy-drogel: Characterization of material parameters for pressure ulcer dressing applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrowicz, H.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Placek, W. Venous leg ulcers: Advanced therapies and new technologies. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizanova, O.; Penesova, A.; Hokynkova, A.; Pokorna, A.; Samadian, A.; Babula, P. Chronic venous insufficiency and ve-nous leg ulcers: Aetiology, on the pathophysiology-based treatment. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, T.V.; Longaker, M.T.; Yang, G.P. Review of the current management of pressure ulcers. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, Y.N.; Xu, J.P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yang, H.R.; Che, H.J.; Liu, C.K.; Qu, J.B. An injectable collagen peptide-based hydrogel with desirable antibacterial, self-healing and wound healing properties based on multiple-dynamic crosslinking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.F.; Zheng, B.D.; Xu, Y.L.; Li, B.Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.T. Multifunctional fish-skin collagen-based hydrogel sealant with dual-dynamic-bond cross-linked for rapid hemostasis and accelerated wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Hu, X.; Shi, X.; Li, T.; Yang, H. Exploration on the multifunctional hydrogel dressings based on collagen and oxidized sodium: A novel approach for dynamic wound treatment and monitoring. J. Mol. Liquids 2024, 409, 125478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Morales, H.; Cobos-Puc, L.E.; Lopez-Badillo, C.M.; Oyervides-Munoz, E.; Ramirez-Garcia, G.; Claudio-Rizo, J.A. Collagen-polyurethane-dextran hydrogels enhace wound healing by inhibiting inflammation and promoting collagen fibrillogenesis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2024, 112, 1760–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Z.; Ji, S.; Xiao, S.; Gao, J. Metal nanoparticles hybrid hydrogels: The state-of-the-art of combining hard and soft materials to promote wound healing. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1534–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Qi, X.; Shi, G.; Zhang, M.; Haick, H. Wound Dressing: From Nanomaterials to Diagnostic Dressings and Healing Evaluations. ACS Nano. 2022, 16, 1708–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzulkharnien, N.S.F.; Rohani, R. A Review on Current Designation of Metallic Nanocomposite Hydrogel in Biomedical Ap-plications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, K.; Mostafavi, E.; Afifi, A.M. Wound dressings functionalized with silver nanoparticles: Promises and pitfalls. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2268–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Long, L.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Microenvironment-responsive multifunctional hydrogels with spatiotemporal sequential release of tailored recombinant human collagen type III for the rapid repair of infected chronic diabetic wounds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9684–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Song, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X. A chitosan-based multifunctional hydrogel containing in situ rapidly bioreduced silver nanoparticles for accelerating infected wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Fan, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Ma, J.; Xiao, J. One-step fabrication of an injectable antibacterial collagen hydrogel with in situ synthesized silver nanoparticles for accelerated diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birca, A.C.; Minculescu, M.A.; Niculescu, A.G.; Hudita, A.; Holban, A.M.; Alberts, A.; Grumezescu, A.M. Nanoparticles-Enhanced Collagen Hydrogels for Chronic Wound Management. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino-Sanz, I.M.; Lopez-Franco, M.D.; Castro, B.; Pancorbo-Hidalgo, P.L. The Role of Antioxidants on Wound Healing: A Review of the Current Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazarlu, O.; Iranshahi, M.; Kashani, H.R.K.; Reshadat, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Iranshahy, M.; Hasanpour, M. Perspective on the application of medicinal plants and natural products in wound healing: A mechanistic review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Fan, D.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J. An ultrasmall infinite coordination polymer nanomedicine-composited biomimetic hydrogel for programmed dressing-chemo-low level laser combination therapy of burn wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 1306106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Nqoro, X.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Polymer-Based Materials Loaded with Curcumin for Wound Healing Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Peng, W.; Lu, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Wang, H. Collagen-based hydrogel derived from amniotic membrane loaded with quercetin accelerates wound healing by improving sterelogical parameters and reducing inflammation in a diabetic rat model. Tissue Cell 2025, 93, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceituno-Medina, M.; Mendoza, S.; Rodríguez, B.A.; Lagaron, J.M.; López-Rubio, A. Improved antioxidant capacity of quercetin and ferulic acid during in-vitro digestion through encapsulation within food-grade electrospun fibers. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, C.Y.; Kenar, H.; Uzuner, H.; Karadenizli, A. Atelocollagen-based hydrogel loaded with Crotinus coggygria extract for treatment of type 2 diabetic wounds. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 20, 025009. [Google Scholar]
- Olivetti, C.E.; Alvarez Echazú, M.I.; Perna, O.; Perez, C.J.; Mitarotonda, R.; De Marzi, M.; Desimone, M.F.; Alvarez, G.S. Dodecenylsuccinic anhydride modified collagen hydrogels loaded with simvastatin as skin wound dressings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Lin, C.; Tao, B.; Deng, Z.; Gao, P.; Yang, Y.; Cai, K. A pH-responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel for regulating the inflammation and remodeling of the ECM in diabetic wounds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Su, D.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Injectable, self-healing and pH responsive stem cell factor loaded collagen hydrogel as a dynamic bioadhesive dressing for diabetic wound repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5887–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, M.; Alissa, M.; Alghamadi, A. Collagen-based hydrogel encapsulated with SDF-1α microspheres accelerate diabetic wound healing in rats. Tissue Cell 2025, 95, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tai, Y.F.; Liu, X.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Dong, Y.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, C.; Kong, D.L.; Qi, C.X.; Wang, S.F.; et al. Natural polymeric and peptide-loaded composite wound dressings for scar prevention. Appl. Mater Today 2021, 25, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Zhao, W.Y.; Fang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Shi, B.H.; Zheng, B.; Wang, S.J.; Tan, W.Q.; Wu, L.H. Effects of chitosan-collagen dressings on wound healing in vitro and in vivo assays. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2021, 19, 2280800021989698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Yin, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.Y.; Fan, Z. A Facile and large-scale synthesis of PVA/Chitosan/Collagen hydrogel for wound healing. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20776–20784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, M.; Negrescu, A.M.; Ion, C.; Scariosreanu, A.; Albu Kaya, M.; Micutz, M.; Dumitru, M.; Cimpean, A. Synthesis, Physicochemical Characteristics, and Biocompatibility of Multi-Component Collagen-Based Hydrogels Developed by E-Beam Irradiation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, H.S.; Saleh, S.; Omar, A.E.; Saleh, A.K.; Salama, A.; Tolba, E. Development of collagen-chitosan dressing gel func-tionalized with propolis-zinc oxide nanoarhitectonics to accelerate wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindi, B.; Perioli, A.; Melo, P.; Mattu, C.; Ferreira, A.M. Bioinspired Collagen/Hyaluronic Acid/Fibrin-Based Hydrogels for Soft Tissue Engineering: Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Characterization. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, K.J.; Kumar, S. Hyaluronic acid: Incorporating the bio into the material. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 8, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burla, F.; Tauber, J.; Dussi, S.; van der Gucht, J.; Koenderink, G.H. Stress management in composite biopolymer networks. Nat. Phys. 2018, 15, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Dong, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Wei, C.; Mi, S.; Sun, W. Collagen-Hyaluronic Acid Composite Hydrogels with Applications for Chronic Diabetic Wound Repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5376–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, P.; Zheng, T.; Ran, R.; Li, G. An injectable, self-healing, and antioxidant collagen- and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel mediated with gallic acid and dopamine for wound repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negrescu, A.M.; Cimpean, A. A Recent Insight into Research Pertaining to Collagen-Based Hydrogels as Dressings for Chronic Skin Wounds. Gels 2025, 11, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070527
Negrescu AM, Cimpean A. A Recent Insight into Research Pertaining to Collagen-Based Hydrogels as Dressings for Chronic Skin Wounds. Gels. 2025; 11(7):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070527
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegrescu, Andreea Mariana, and Anisoara Cimpean. 2025. "A Recent Insight into Research Pertaining to Collagen-Based Hydrogels as Dressings for Chronic Skin Wounds" Gels 11, no. 7: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070527
APA StyleNegrescu, A. M., & Cimpean, A. (2025). A Recent Insight into Research Pertaining to Collagen-Based Hydrogels as Dressings for Chronic Skin Wounds. Gels, 11(7), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070527






