Rat Islet pECM Hydrogel-Based Microencapsulation: A Protective Niche for Xenotransplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
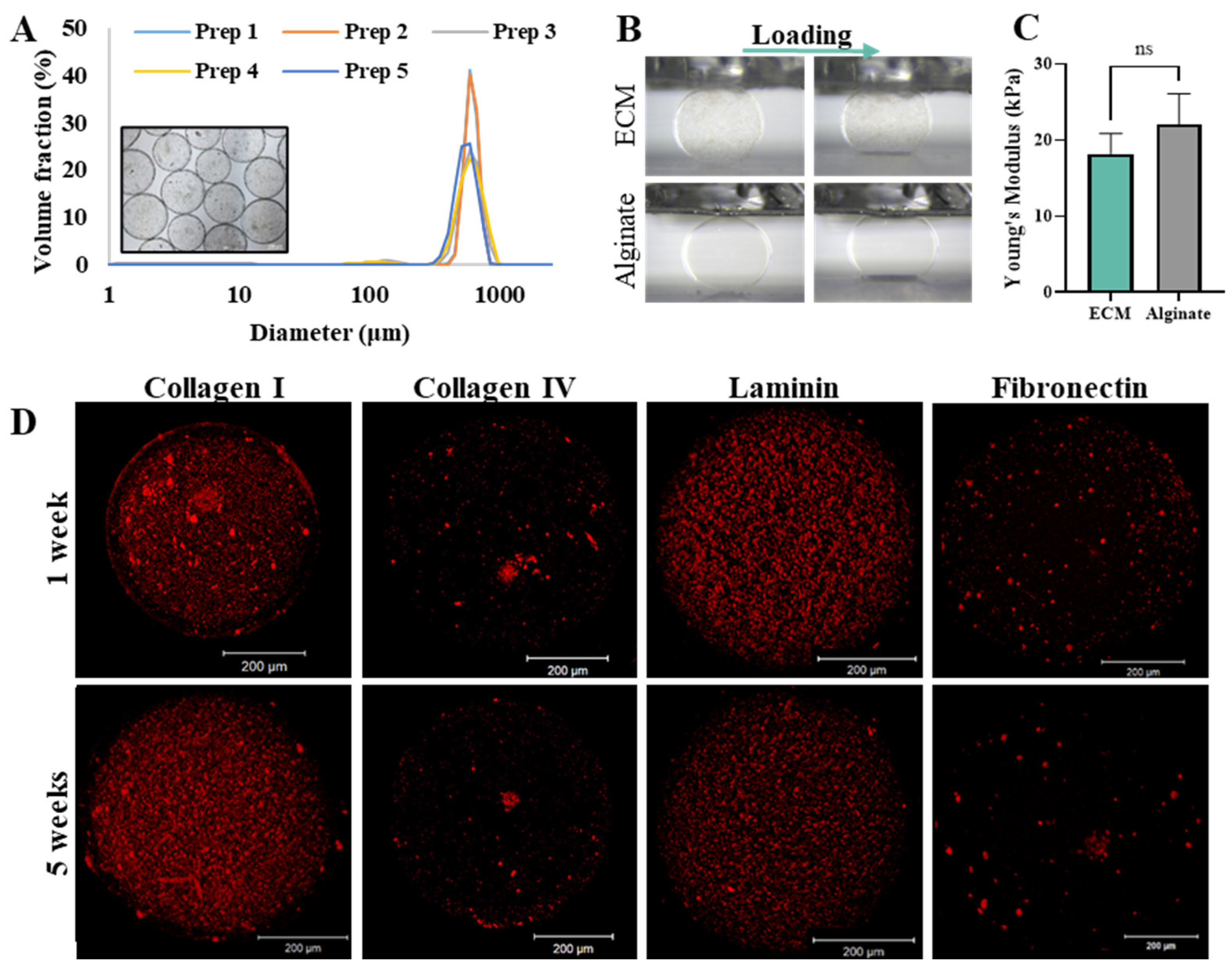
2.1.1. Microcapsules Characterization
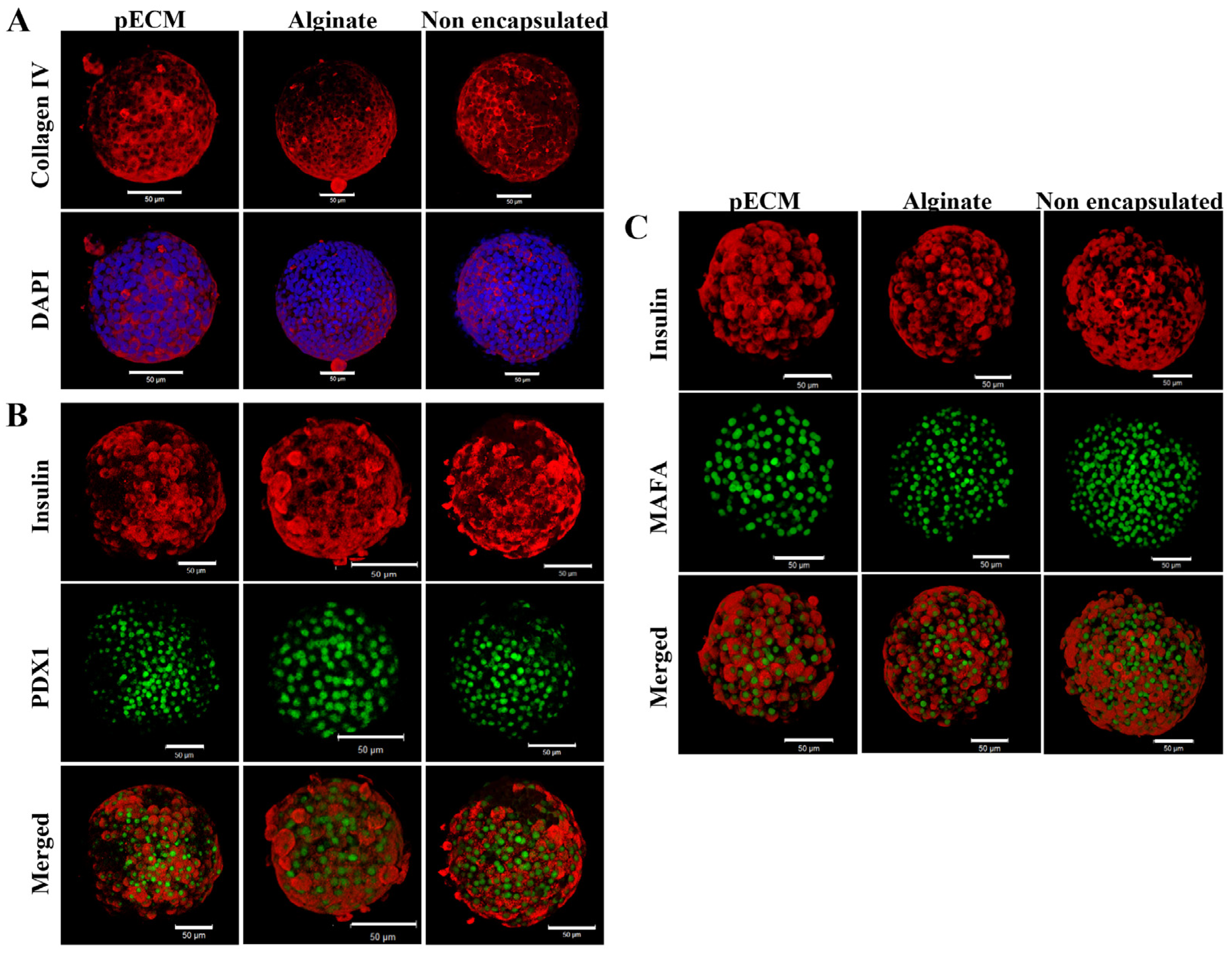
2.1.2. Encapsulated Islet Characterization
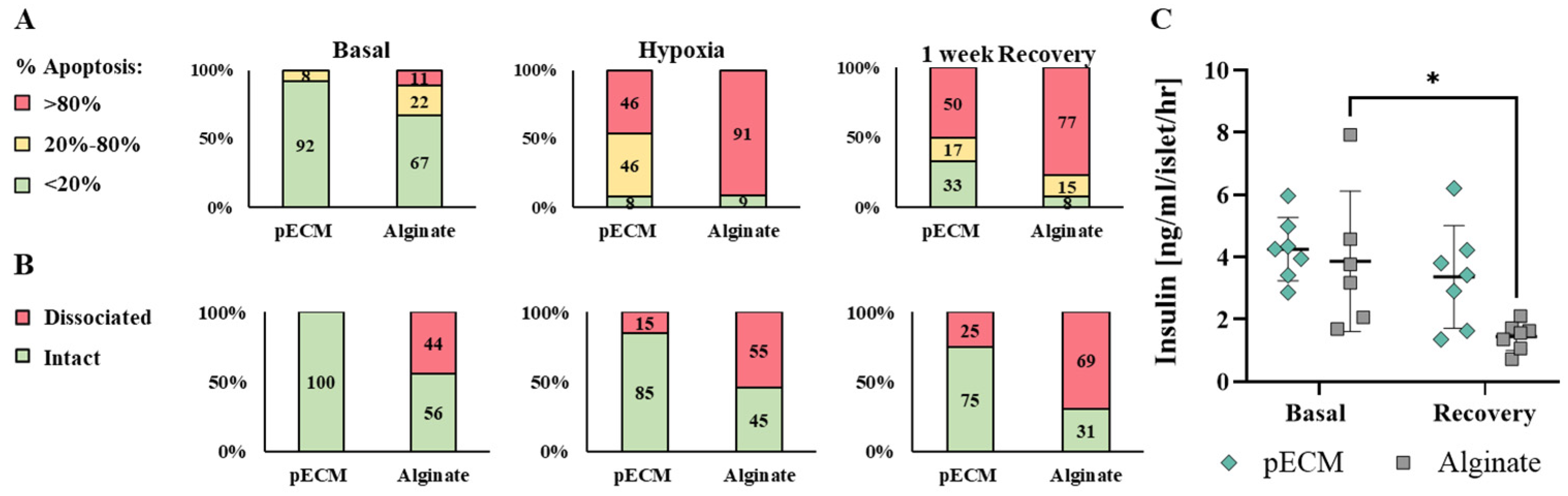
2.1.3. pECM Microcapsules Protect the Islets from Hypoxia Damage
2.1.4. Biocompatibility of pECM Microcapsules
2.2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rat Islet Isolation
4.2. Preparation of pECM Biomaterial
4.3. Microencapsulation of Islets
4.4. Microcapsules Characterization
4.4.1. Size Distribution Analysis
4.4.2. Mechanical Properties
4.4.3. Immunostaining Microcapsules and Encapsulated Islets
4.5. Islet Viability
4.6. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Analysis
4.7. Effect of Hypoxia on Islet Survival and Function
4.8. Biocompatibility pECM-Encapsulated Islets
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
AI Usage Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, A. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendez-Ramirez, L.Y.; Richards, R.J.; Cefalu, W.T. Complications of Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2010, 39, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscari, F.; Avogaro, A. Current Treatment Options and Challenges in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: Pharmacological, Technical Advances and Future Perspectives. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon Martinez, E.; Castillo, J.L.; Zachariah Saji, S.; Stein, D.; Khan, T.J.; Guardado Williams, R.F.; Munguía, I.D.; Arruarana, V.S.; Velasquez, K. Insulin Pump Therapy vs Multiple Daily Insulin Injections for Glycemic Control in Children With Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, r154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantyghem, M.C.; de Koning, E.J.P.; Pattou, F.; Rickels, M.R. Advances in β-Cell Replacement Therapy for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Lancet 2019, 394, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.D.; Lillehei, R.C.; Merkel, F.K.; Idezuki, Y.; Goetz, F.C. Allotransplantation of the Pancreas and Duodenum along with the Kidney in Diabetic Nephropathy. Surgery 1967, 61, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtusciszyn, A.; Branchereau, J.; Esposito, L.; Badet, L.; Buron, F.; Chetboun, M.; Kessler, L.; Morelon, E.; Berney, T.; Pattou, F.; et al. Indications for Islet or Pancreatic Transplantation. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Lakey, J.R.; Ryan, E.A.; Korbutt, G.S.; Toth, E.; Warnock, G.L.; Kneteman, N.M.; Rajotte, R.V. Islet Transplantation in Seven Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using a Glucocorticoid-Free Immunosuppressive Regimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Abalovich, A.; Wechsler, C.; Wynyard, S.; Elliott, R.B. Clinical Benefit of Islet Xenotransplantation for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Bottino, R.; Hawthorne, W.J. Current Status of Islet Xenotransplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 23, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opara, E.C. (Ed.) Cell Microencapsulation: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781493963621. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, N. Encapsulated Islets Transplantation: Past, Present and Future. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2012, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.I.; Norton De Matos, A.; Brons, I.G.; Mateus, M. An Overview on the Development of a Bio-Artificial Pancreas as a Treatment of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 181–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, G.; Zou, H.; Zhong, Y. A Novel Pulsed Drug-Delivery System: Polyelectrolyte Layer-by-Layer Coating of Chitosan-Alginate Microgels. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Li, Y.; Geng, Z.; Gerber-Lemaire, S.; Wang, Y.; Buhler, L. Islet Encapsulation: New Developments for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H. Materials for Immunoisolated Cell Transplantation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 33, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.L.; Coron, A.E.; Skjak-Braek, G. Current and Future Perspectives on Alginate Encapsulated Pancreatic Islet. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Akbari, E.; Imani, R. An Overview of Engineered Hydrogel-Based Biomaterials for Improved β-Cell Survival and Insulin Secretion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 662084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, F.T.; Stamenkovic, I. Functional Structure and Composition of the Extracellular Matrix. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kular, J.K.; Basu, S.; Sharma, R.I. The Extracellular Matrix: Structure, Composition, Age-Related Differences, Tools for Analysis and Applications for Tissue Engineering. J. Tissue Eng. 2014, 5, 2041731414557112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishtul, S.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Processed Tissue–Derived Extracellular Matrices: Tailored Platforms Empowering Diverse Therapeutic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1900386, 1900386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, H.; Krishtul, S.; Brandhorst, D.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M.; Johnson, P.R. Solubilized Pancreatic Extracellular Matrix from Juvenile Pigs Protects Isolated Human Islets from Hypoxia-Induced Damage: A Viable Option for Clinical Islet Transplantation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 2023, 7452682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stendahl, J.C.; Kaufman, D.B.; Stupp, S.I. Extracellular Matrix in Pancreatic Islets: Relevance to Scaffold Design and Transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2009, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, S.E.; Gannon, M. Extracellular Matrix-Associated Factors Play Critical Roles in Regulating Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation and Survival. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llacua, L.A.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Extracellular Matrix Molecules and Their Potential Contribution to the Function of Transplanted Pancreatic Islets. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llacua, A.; De Haan, B.J.; Smink, S.A.; De Vos, P. Extracellular Matrix Components Supporting Human Islet Function in Alginate-Based Immunoprotective Microcapsules for Treatment of Diabetes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Jung, G.S.; Jeon, W.B.; Lee, K.M. Arg-Gly-Asp-Modified Elastin-like Polypeptide Regulates Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Proteins via the Phosphorylation of Erk and Akt in Pancreatic β-Cell. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Jung, G.S.; Park, J.K.; Choi, S.K.; Jeon, W.B. Effects of Arg-Gly-Asp-Modified Elastin-like Polypeptide on Pseudoislet Formation via up-Regulation of Cell Adhesion Molecules and Extracellular Matrix Proteins. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5600–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackett, S.D.; Tremmel, D.M.; Ma, F.; Feeney, A.K.; Maguire, R.M.; Brown, M.E.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; O’Brien, C.; Li, L.; et al. Extracellular Matrix Scaffold and Hydrogel Derived from Decellularized and Delipidized Human Pancreas. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Qiang, M.; Luo, Y. A Bilaminated Decellularized Scaffold for Islet Transplantation: Structure, Properties and Functions in Diabetic Mice. Biomaterials 2017, 138, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaido, T.; Yebra, M.; Cirulli, V.; Montgomery, A.M. Regulation of Human β-Cell Adhesion, Motility, and Insulin Secretion by Collagen IV and Its Receptor A1β1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53762–53769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, N.; Shakirova, K.; Dashinimaev, E. PDX1 Is the Cornerstone of Pancreatic β-Cell Functions and Identity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1091757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Brun, T.; Kataoka, K.; Sharma, A.J.; Wollheim, C.B. MAFA Controls Genes Implicated in Insulin Biosynthesis and Secretion. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orive, G.; Emerich, D.; Khademhosseini, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Hernández, R.M.; Pedraz, J.L.; Desai, T.; Calafiore, R.; de Vos, P. Engineering a Clinically Translatable Bioartificial Pancreas to Treat Type I Diabetes. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Paredes-Juarez, G.A.; Niclou, S.P.; de Vos, P. Factors Influencing the Mechanical Stability of Alginate Beads Applicable for Immunoisolation of Mammalian Cells. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiseh, O.; Doloff, J.C.; Ma, M.; Vegas, A.J.; Tam, H.H.; Bader, A.R.; Li, J.; Langan, E.; Wyckoff, J.; Loo, W.S.; et al. Size- and Shape-Dependent Foreign Body Immune Response to Materials Implanted in Rodents and Non-Human Primates. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, P.; Bučko, M.; Gemeiner, P.; Navrátil, M.; Švitel, J.; Faas, M.; Strand, B.L.; Skjak-Braek, G.; Morch, Y.A.; Vikartovská, A.; et al. Multiscale Requirements for Bioencapsulation in Medicine and Biotechnology. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Mechanical Characterization of Biocompatible Microspheres and Microcapsules by Direct Compression. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2004, 32, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanos, C.G.; Bintz, B.E.; Emerich, D.F. Stability of Alginate-Polyornithine Microcapsules Is Profoundly Dependent on the Site of Transplantation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 81A, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.L.; Najia, M.A.; Saeed, R.; McDevitt, T.C. Alginate Encapsulation Parameters Influence the Differentiation of Microencapsulated Embryonic Stem Cell Aggregates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, S.H.; Dufresne, M.; Rechel, M.; Fleury, M.J.; Salsac, A.V.; Paullier, P.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; Legallais, C. Impact of Alginate Composition: From Bead Mechanical Properties to Encapsulated HepG2/C3A Cell Activities for In Vivo Implantation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.R.; Rodriguez, S.M.; Luong, J.C.; Li, S.; Cao, R.; Alshetaiwi, H.; Lau, H.; Davtyan, H.; Jones, M.B.; Jafari, M.; et al. Exosome Loaded Immunomodulatory Biomaterials Alleviate Local Immune Response in Immunocompetent Diabetic Mice Post Islet Xenotransplantation. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthew Riopel, R.W. Collagen Matrix Support of Pancreatic Islet Survival and Function. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöschl, E.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Brachvogel, B.; Saito, K.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mayer, U. Collagen IV Is Essential for Basement Membrane Stability but Dispensable for Initiation of Its Assembly during Early Development. Development 2004, 131, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, K.; Kenneth, S. Polonsky Pdx1 and Other Factors That Regulate Pancreatic β-Cell Survival. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 11, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Stein, R. MafA and MafB Activity in Pancreatic β Cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, D.K.; Hays, L.B.; Parazzoli, S.D.; Poitout, V. Palmitate Inhibits Insulin Gene Expression by Altering PDX-1 Nuclear Localization and Reducing MafA Expression in Isolated Rat Islets of Langerhans. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32413–32418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, J.S.; Stein, R.; Robertson, R.P. Oxidative Stress-Mediated, Post-Translational Loss of MafA Protein as a Contributing Mechanism to Loss of Insulin Gene Expression in Glucotoxic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11107–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, A.; Larkin, E.J.; Fontaine, M.J. Co-Encapsulation of ECM Proteins to Enhance Pancreatic Islet Cell Function; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 2, ISBN 9780128148310. [Google Scholar]
- Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; Lee Layland, S.; Acreman, S.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Johnson, P.R.V. Basement Membrane Proteins Improve Human Islet Survival in Hypoxia: Implications for Islet Inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 137, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.D.; Alexander, M.; Hunckler, M.D.; Fernández-Yagüe, M.A.; Coronel, M.M.; Smink, A.M.; Lakey, J.R.; de Vos, P.; García, A.J. Functionalization of Alginate with Extracellular Matrix Peptides Enhances Viability and Function of Encapsulated Porcine Islets. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaido, T.; Yebra, M.; Cirulli, V.; Rhodes, C.; Diaferia, G.; Montgomery, A.M. Impact of Defined Matrix Interactions on Insulin Production by Cultured Human β-Cells: Effect on Insulin Content, Secretion, and Gene Transcription. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, S.E.; Vaughan, R.H.; Willcox, A.J.; McBride, A.J.; Abraham, A.A.; Han, B.; Johnson, J.D.; Maillard, E.; Bateman, P.A.; Ramracheya, R.D.; et al. Key Matrix Proteins Within the Pancreatic Islet Basement Membrane Are Differentially Digested During Human Islet Isolation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, P.; De Haan, B.J.; De Haan, A.; Van Zanten, J.; Faas, M.M. Factors Influencing Functional Survival of Microencapsulated Islet Grafts. Cell Transplant. 2004, 13, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbinden, A.; Urbanczyk, M.; Layland, S.L.; Becker, L.; Marzi, J.; Bosch, M.; Loskill, P.; Duffy, G.P.; Schenke-Layland, K. Collagen and Endothelial Cell Coculture Improves β-Cell Functionality and Rescues Pancreatic Extracellular Matrix. Tissue Eng. Part A 2020, 27, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Lu, C.; Jiang, X.; Yao, Q.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, L.; Fu, H.; Zhao, Y. Using Recombinant Human Collagen with Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor to Provide a Simulated Extracellular Matrix Microenvironment for the Revascularization and Attachment of Islets to the Transplantation Region. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmasekar, M.; Lingwal, N.; Samikannu, B.; Chen, C.; Sauer, H.; Linn, T. Exendin-4 Protects Hypoxic Islets from Oxidative Stress and Improves Islet Transplantation Outcome. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden, A.; Layland, S.L.; Urbanczyk, M.; Carvajal Berrio, D.A.; Marzi, J.; Zauner, M.; Hammerschmidt, A.; Brauchle, E.M.; Sudrow, K.; Fink, S.; et al. Nidogen-1 Mitigates Ischemia and Promotes Tissue Survival and Regeneration. Advanced Science 2020, 8, 2002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishtul, S.; Skitel Moshe, M.; Kovrigina, I.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. ECM-Based Bioactive Microencapsulation Significantly Improves Islet Function and Graft Performance. Acta Biomater. 2023, 171, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.J.; Andrews, G.K.; Bittel, D.; Discher, D.J.; McCue, J.; Green, C.J.; Yanovsky, M.; Giaccia, A.; Sutherland, R.M.; Laderoute, K.R.; et al. Activation of Metallothionein Gene Expression by Hypoxia Involves Metal Response Elements and Metal Transcription Factor-1. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Atilano, S.; Lee, D.; Fukuhara, P.; Chwa, M.; Nesburn, A.; Udar, N.; Kenney, C. Corneal Oxidative Damage in Keratoconus Cells Due to Decreased Oxidant Elimination from Modified Expression Levels of SOD Enzymes, PRDX6, SCARA3, CPSF3, and FOXM1. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2019, 14, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokstad, A.M.A.; Lacík, I.; de Vos, P.; Strand, B.L. Advances in Biocompatibility and Physico-Chemical Characterization of Microspheres for Cell Encapsulation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 67–68, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimov, D.; Baruch, L.; Krishtul, S.; Meivar-levy, I.; Ferber, S.; Machluf, M. Innovative Encapsulation Platform Based on Pancreatic Extracellular Matrix Achieve Substantial Insulin Delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 257, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babensee, J.E.; Anderson, J.M.; McIntire, L.V.; Mikos, A.G. Host Response to Tissue Engineered Devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 33, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, P. Bioartificial Pancreas: Challenges and Progress. In Principles of Tissue Engineering, 5th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9780128184226. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.E.; Johnson, R.C.; Papas, K.K. Update on Cellular Encapsulation. Xenotransplantation 2018, 25, e12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyland, J.; Lipiński, D.; Słomski, R. The Current State of Xenotransplantation. J. Appl. Genet. 2015, 56, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishtul, S.; Davidov, T.; Efraim, Y.; Skitel-Moshe, M.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Development of a Bioactive Microencapsulation Platform Incorporating Decellularized Extracellular Matrix to Entrap Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Versatile Biomedical Applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 3842–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skitel Moshe, M.; Krishtul, S.; Brandis, A.; Hayam, R.; Hamias, S.; Faraj, M.; Davidov, T.; Kovrigina, I.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Rat Islet pECM Hydrogel-Based Microencapsulation: A Protective Niche for Xenotransplantation. Gels 2025, 11, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070517
Skitel Moshe M, Krishtul S, Brandis A, Hayam R, Hamias S, Faraj M, Davidov T, Kovrigina I, Baruch L, Machluf M. Rat Islet pECM Hydrogel-Based Microencapsulation: A Protective Niche for Xenotransplantation. Gels. 2025; 11(7):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070517
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkitel Moshe, Michal, Stasia Krishtul, Anastasia Brandis, Rotem Hayam, Shani Hamias, Mazal Faraj, Tzila Davidov, Inna Kovrigina, Limor Baruch, and Marcelle Machluf. 2025. "Rat Islet pECM Hydrogel-Based Microencapsulation: A Protective Niche for Xenotransplantation" Gels 11, no. 7: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070517
APA StyleSkitel Moshe, M., Krishtul, S., Brandis, A., Hayam, R., Hamias, S., Faraj, M., Davidov, T., Kovrigina, I., Baruch, L., & Machluf, M. (2025). Rat Islet pECM Hydrogel-Based Microencapsulation: A Protective Niche for Xenotransplantation. Gels, 11(7), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070517






