Development and Interfacial Mechanism of Epoxy Soybean Oil-Based Semi-Liquid Gel Materials for Wellbore Sealing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Liquid Rubber Plug
2.2. Rheology
2.3. Compressive Strength Regulation Mechanism
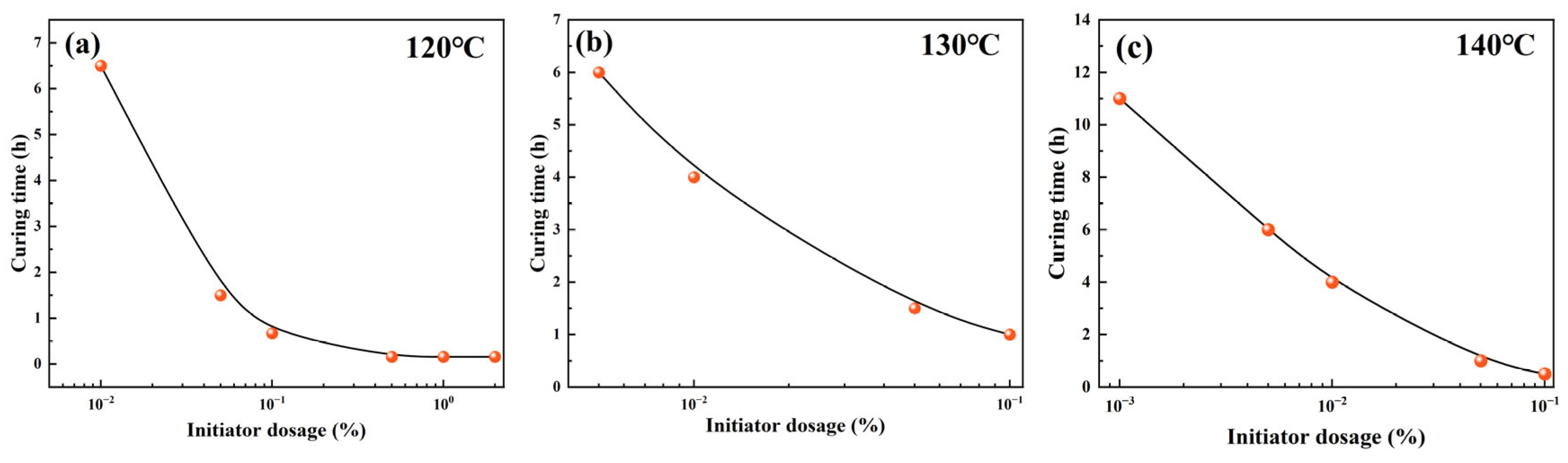
2.4. Curing Time Regulation Mechanism
2.5. Interfacial Adhesive Performance and Mechanism
2.6. Plugging Property and Degradation Performance
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of Liquid Rubber Plug
4.2.2. Characterization
4.2.3. Compressive Strength
4.2.4. Determination of Curing Time
4.2.5. Rheological Characterization Method
4.2.6. Interfacial Adhesive Strength Measurement
4.2.7. Plugging Property Experiment
4.2.8. Degradation Performance Test
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Li, F.; Ji, R.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Su, G. Self-Degradable Rubber Plug for Temporary Plugging and Its Degradation Mechanism. Gels 2024, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, P.; Du, J.; Liang, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, D.; Liu, F. A critical review of key points in temporary plugging fracturing: Materials, injection, temporary plugging, and design. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 240, 212981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anya, A.; Emadi, H.; Watson, M. A novel apparatus and method for lab-scale study of wellbore integrity using CT imaging and analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220 Pt B, 111209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liao, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. Study of adhesive self-degrading gel for wellbore sealing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klishin, S.V.; Klishin, V.I. Packer Sealing–Wellbore Interaction in Hydraulic Fracturing in Coal Seams. J. Min. Sci. 2020, 56, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lv, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Kang, W. Laboratory evaluation of a controllable self-degradable temporary plugging agent in fractured reservoir. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 083314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, N.; Liang, H.; Wei, M.; Ma, B.; Qiu, D. The Wellbore Temperature and Pressure Behavior during the Flow Testing of Ultra-Deepwater Gas Wells. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2024, 20, 2523–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Pu, W.; Jin, X.; Shen, C.; Ren, H. Review of the micro and Macro mechanisms of gel-based plugging agents for enhancing oil recovery of unconventional water flooding oil reservoirs. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wei, C. Urea formaldehyde resin used as plugging agent in fractured and caved reservoirs: Preparation, optimization and modification. Polymer 2025, 317, 127901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, C.; Taleghani, A.D. An evaluation of fiber-based lost circulation material for fracture plugging using simulations. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 229, 212144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-Y.; Fang, X.-Y.; Sun, R.-X.; Xu, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.-Y. Development of degradable pre-formed particle gel (DPPG) as temporary plugging agent for petroleum drilling and production. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-D.; Pu, W.-F.; Jin, F.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Jia, H.; Zhao, T.-H. Performance of Oil-Based Cement Slurry as a Selective Water-Plugging Agent in High-Temperature and High-Salinity Cave-Fractured Carbonate Reservoirs. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6137–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Zhao, J.-Z. Development of a Novel In-Situ-Generated Foamed Gel as Temporary Plugging Agent Used for Well Workover: Affecting Factors and Working Performance. SPE J. 2019, 24, 1757–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Song, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, K. A review on mechanism and adaptive materials of temporary plugging agent for chemical diverting fracturing. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, K.; Yao, H.; Zhao, W.; Qin, H.; Wu, Z.; Wei, G. A novel dynamic filling material for plugging fractures around underground gas extraction boreholes: Experimental and engineering performances. Energy 2025, 314, 134202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Qi, N.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Chen, S. Flow and plugging behavior of foams in fractures of fractured reservoirs. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 679 (Suppl. SC), 132577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-B.; Bai, Y.-R.; Sun, J.-S.; Lv, K.-H. Curing kinetics and plugging mechanism of high strength curable resin plugging material. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 3446–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wu, R.; Xu, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, H.; Jin, B.; Wu, W.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J. Mechanically robust and rapidly degradable hydrogels for temporary water plugging in oilfields. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, N.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Tang, L. Establishment of temperature-strength response prediction model of supramolecular gel temporary plugging agent by response surface method analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.-Y.; Yan, W.; Ye, H.-M.; Yao, E.-D.; Duan, J.-B.; Xu, Z.-X.; Li, K.-P.; Zhang, J.-R.; Li, Z. Evaluation of the injection and plugging ability of a novel epoxy resin in cement cracks. Pet. Sci. 2023, 21, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ye, J.; Jiang, Y. Preparation of Low-Viscosity Epoxy Resin Sealing Agent and Evaluation of Injection, Plugging, and Degradation Properties. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 19992–20002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Urushisaki, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Kawabe, K. Novel degradable acetal-linkage-containing epoxy resins with high thermal stability: Synthesis and application in carbon fiber-reinforced plastics. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Long, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Recovery of epoxy thermosets and their composites. Mater. Today 2023, 64 (Suppl. SC), 72–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Choudhary, P.; Krishnan, V.; Zafar, S. A review on recycling and reuse methods for carbon fiber/glass fiber composites waste from wind turbine blades. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215 (Suppl. SC), 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Herrador, F.; Eschenbacher, A.; Blondeau, J.; Magin, T.E.; Geem, K.M.V. Study of the degradation of epoxy resins used in spacecraft components by thermogravimetry and fast pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandro Dattilo, G.C. Paolo Maria Riccobene, Concetto Puglisi, Lorena Saitta, Full Recycling and Re-Use of Bio-Based Epoxy Thermosets: Chemical and Thermomechanical Characterization of the Recycled Matrices. Polymers 2022, 14, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero-Hernanz, R.; Dodds, C.; Hyde, J.; García-Serna, J.; Poliakoff, M.; Lester, E.; Cocero, M.J.; Kingman, S.; Pickering, S.; Wong, K.H. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced composites in nearcritical and supercritical water. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.N.; Kim, Y.-O.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.; Yang, B.; Kim, J.; Jung, Y.C. Application of supercritical water for green recycling of epoxy-based carbon fiber reinforced plastic. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 173, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, X.; van Kasteren, J.; Wang, Y. Highly efficient solvolysis of epoxy resin using poly(ethylene glycol)/NaOH systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, X.; Zhao, T.; Yuan, L.; Qi, Y.; Hou, X.; Jin, H.; Deng, T. Efficient catalytic degradation of anhydride-cured epoxy resin by amphiphilic molecule catalysts. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Ru, M.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, S.; Fu, F.; Diao, H.; Liu, X. A fully degradable epoxy resin based on a nontoxic triphenol derived from diphenolic acid and eugenol. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X. An anhydride-cured degradable epoxy insulating material exhibiting recyclability, reusability, and excellent electrical performance. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Sun, J.; Tian, P.; Liu, H.; Mao, Z.; Kan, S.; Yu, X. Curing characteristics and performance of a bio-based polyurethane engineered sealant with high bonding strength: Effect of R value and chain extender content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ban, X.; Ji, J.; Tian, P.; Yang, Y. The influence of filler types and content on the curing behavior and properties of a bio-based polyurethane engineered sealant. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2025, 136, 103866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.; Ponrathnam, S.; Chavan, N. Role of interfacial tension of solvating diluents and hydrophilic–hydrophobic cross-Linkers in hyper-cross-linked solid supports. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6893–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Douglas, J.F.; Xia, W. Competing effects of molecular additives and cross-link density on the segmental dynamics and mechanical properties of cross-linked polymers. ACS Eng. Au 2023, 3, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yang, W.; Yan, S.; Yan, J. Sealing the Pandora’s vase of pancreatic fistula through entrapping the digestive enzymes within a dextrorotary (D)-peptide hydrogel. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Ren, F.; Wang, B.; Hou, J.; Wiercigroch, M. Multi-scale mechanics of submerged particle impact drilling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 285, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Taleghani, A.D.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, Q. Modeling thermal-induced wellhead growth through the lifecycle of a well. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 241, 213098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Diluent Dosage | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial state |  |  |  |  |  |
| Repture state |  |  |  |  |  |
| Diluent Dosage | 0 | 0.25% | 0.5% | 0.75% | 1% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial state |  |  |  |  |  |
| Injection Volume (PV) | Breakthrough Pressure Gradient (MPa/m) | Calculated Post-Plugging Permeability (mD) | Permeability Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 PV | 19.11 | 19.04 | 85.6% |
| 0.5 PV | 24.50 | 24.51 | 81.5% |
| 0.7 PV | 34.38 | 34.32 | 74.1% |
| 0.9 PV | 50.59 | 50.47 | 61.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, J. Development and Interfacial Mechanism of Epoxy Soybean Oil-Based Semi-Liquid Gel Materials for Wellbore Sealing Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070482
Tian Y, Liu Y, Dong H, Liu X, Huang J. Development and Interfacial Mechanism of Epoxy Soybean Oil-Based Semi-Liquid Gel Materials for Wellbore Sealing Applications. Gels. 2025; 11(7):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070482
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuexin, Yintao Liu, Haifeng Dong, Xiangjun Liu, and Jinjun Huang. 2025. "Development and Interfacial Mechanism of Epoxy Soybean Oil-Based Semi-Liquid Gel Materials for Wellbore Sealing Applications" Gels 11, no. 7: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070482
APA StyleTian, Y., Liu, Y., Dong, H., Liu, X., & Huang, J. (2025). Development and Interfacial Mechanism of Epoxy Soybean Oil-Based Semi-Liquid Gel Materials for Wellbore Sealing Applications. Gels, 11(7), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070482






