Gel-Based Self-Powered Nanogenerators: Materials, Mechanisms, and Emerging Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Working Principle
2.1. Overview
2.2. Working Modes
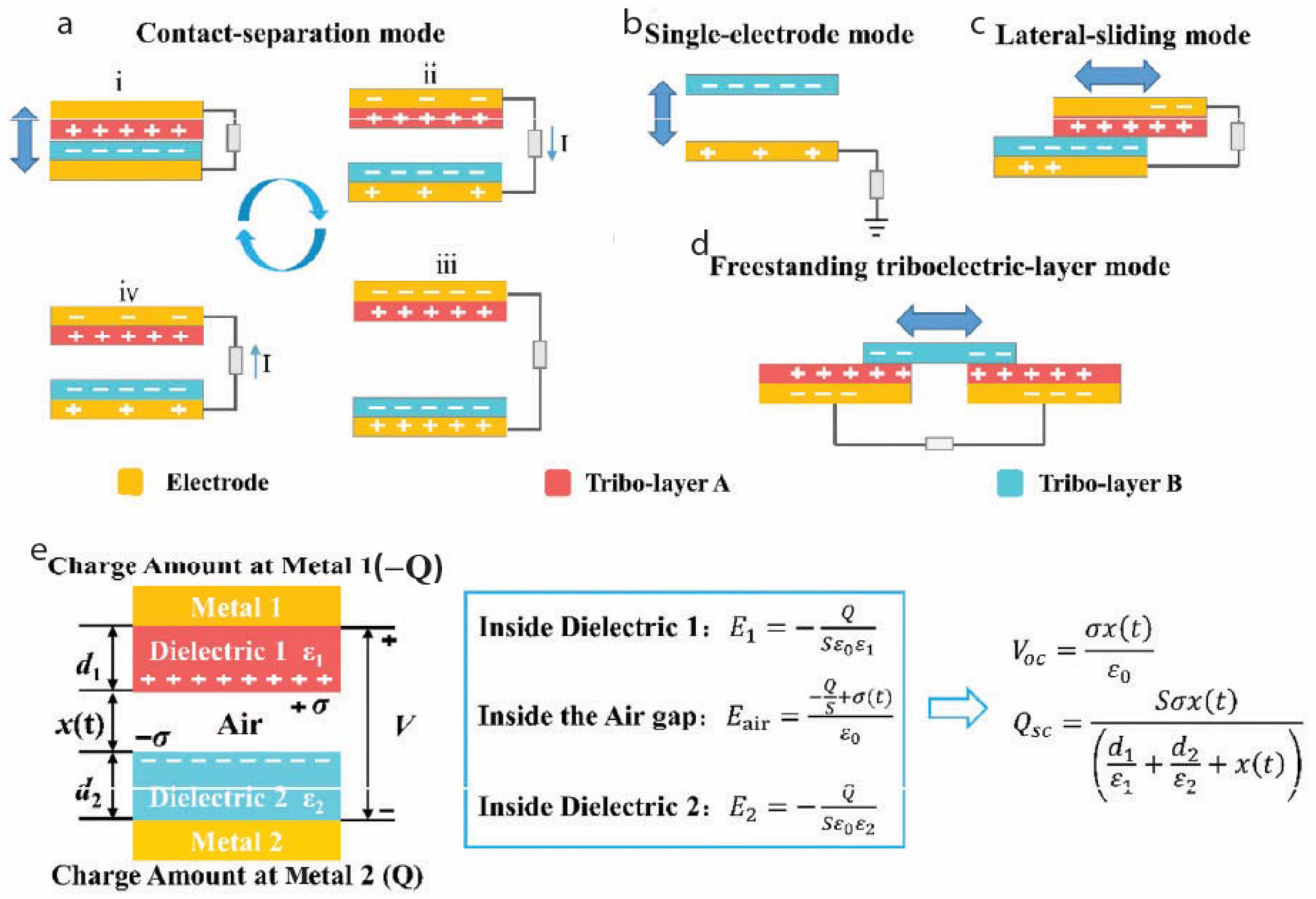
2.3. Performance Factors
2.3.1. Energy Conversion Efficiency
2.3.2. Piezo/Triboelectric Coefficient
Material Selection
Enhancing Coefficients
Application Implications
3. Materials-Based Strategies
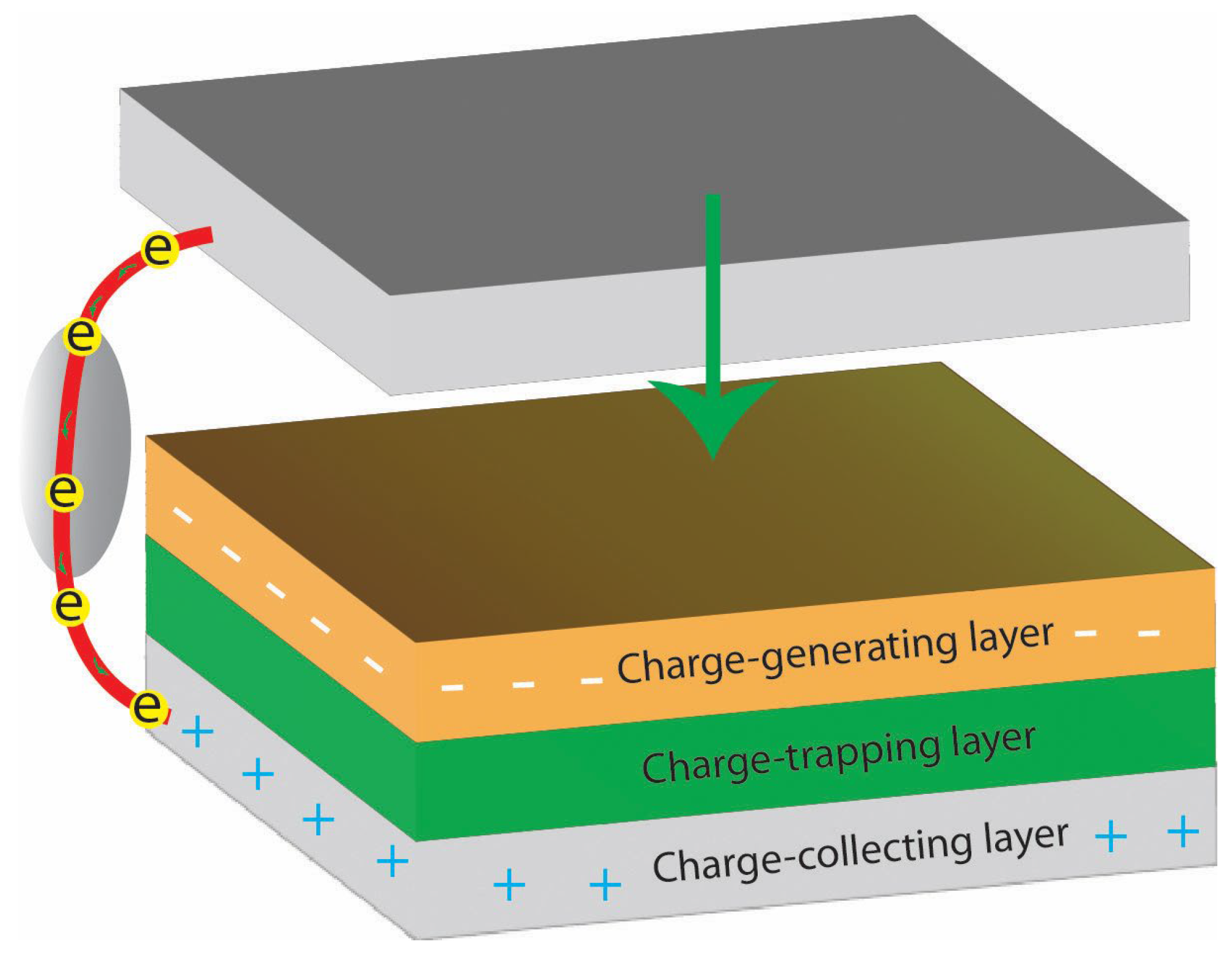
3.1. Fundamentals of Charge Generations in TENGs
3.2. Materials Perspective
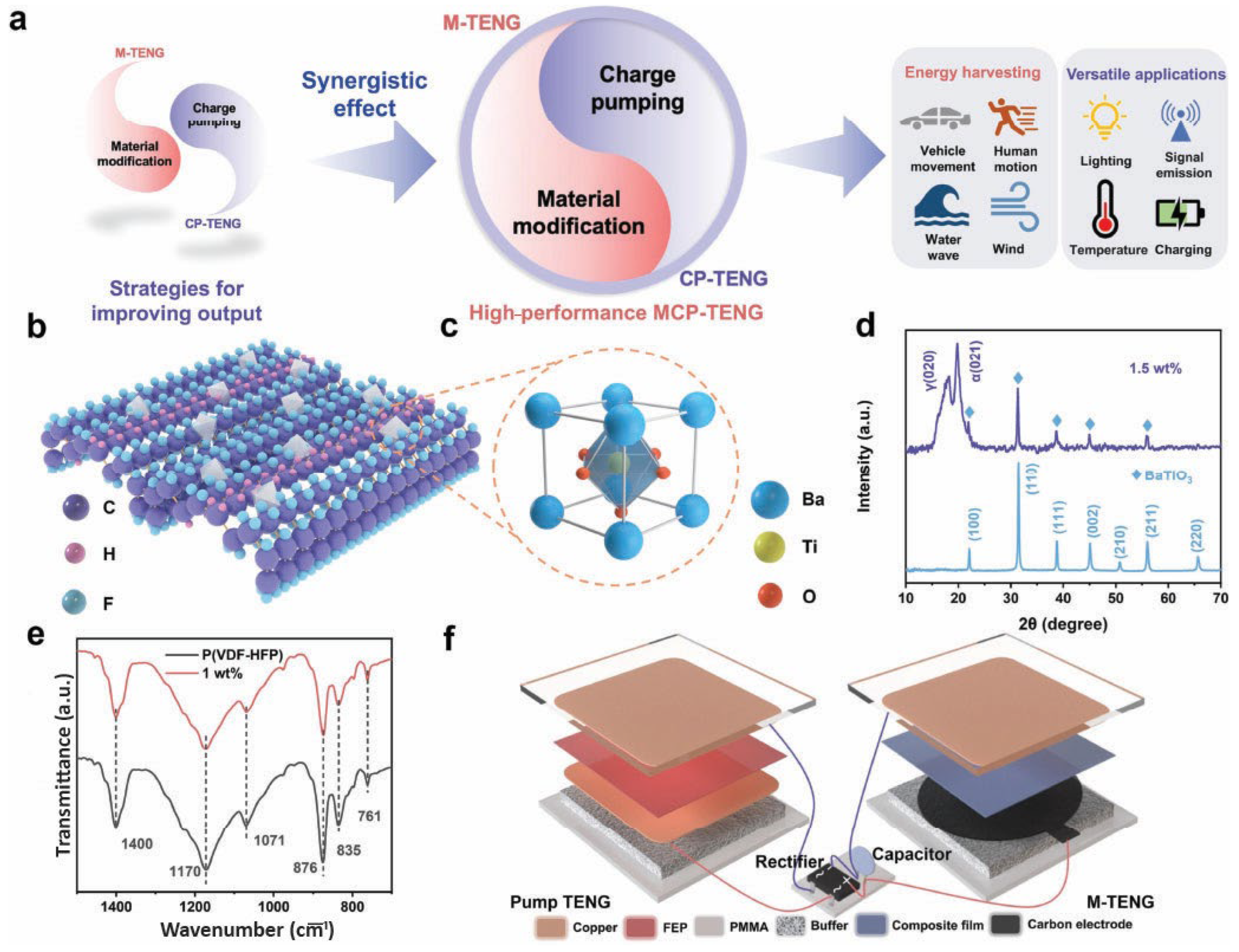
3.2.1. Gel-Based Polymer Composites
3.2.2. Scalable Fabrication Strategies for Gel-Based TENGs
3.3. Phosphorus-Containing Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials
3.4. Other Materials
3.5. Preventing Air Breakdown
4. Applications
4.1. TENGs as a Power Source
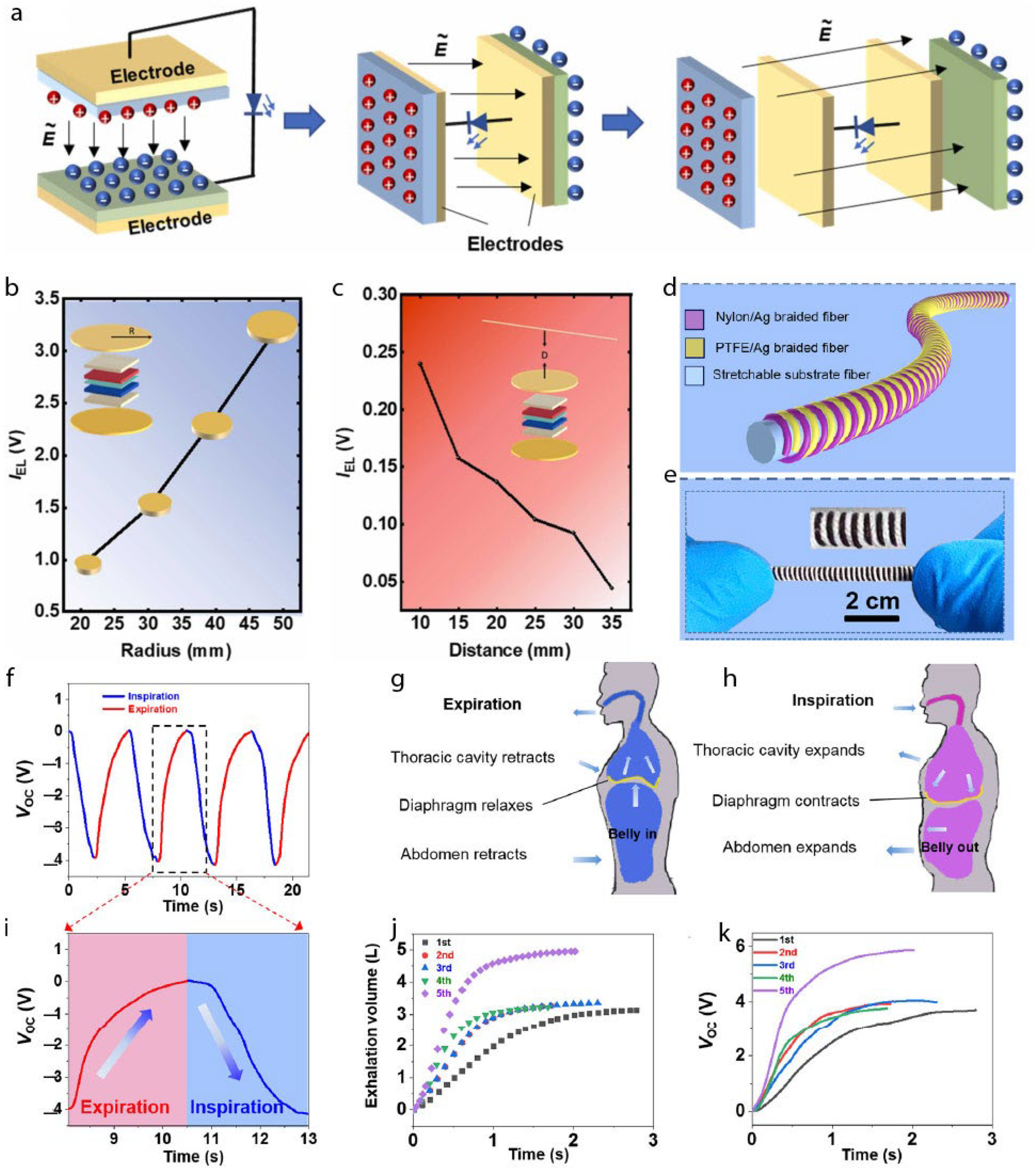
4.1.1. TENGs for Lighting and Power-Line Communication
4.1.2. TENGs for Wearable Respiratory Monitoring
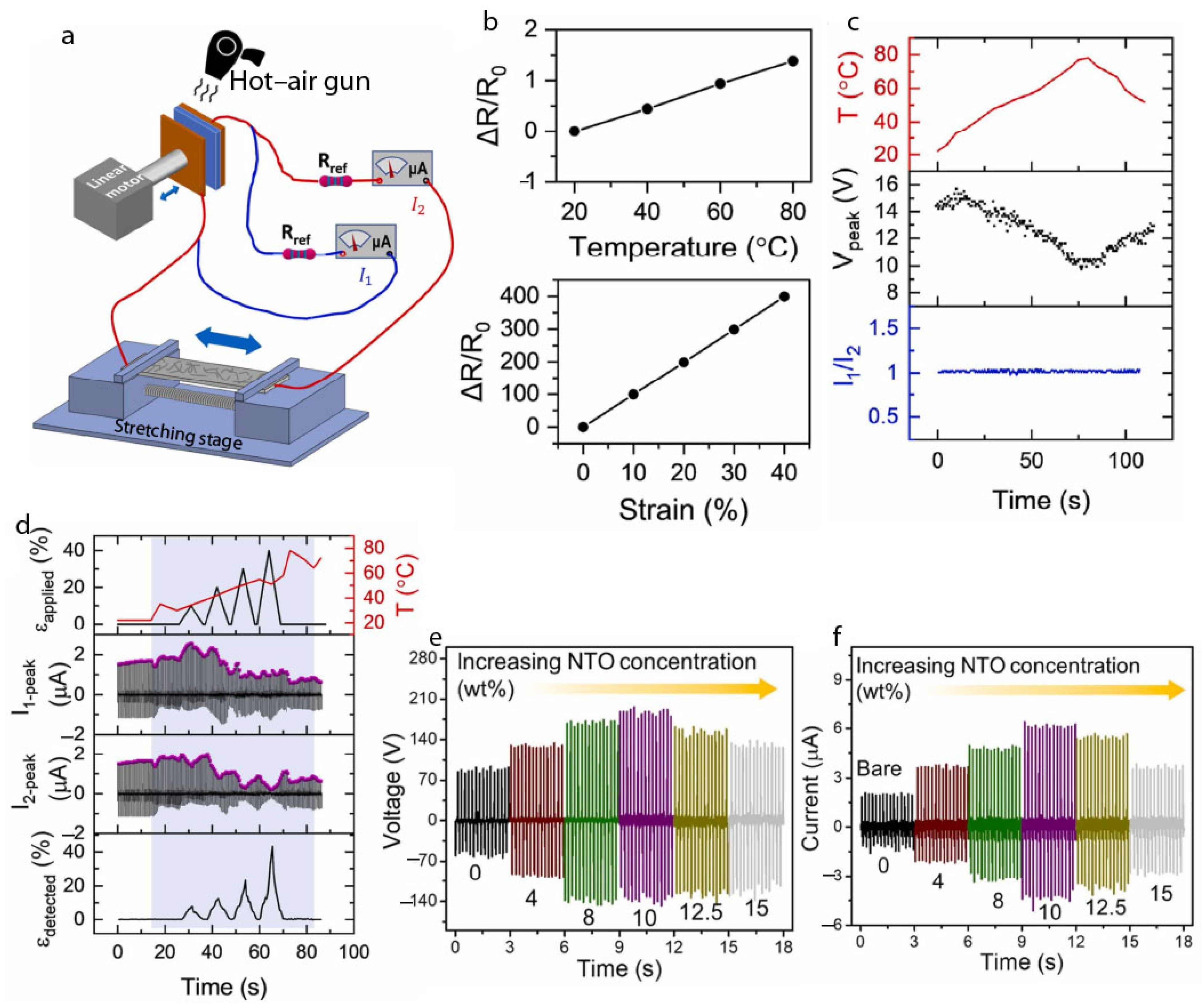
4.2. TENGs as Sensors
5. Problems to Be Discussed
5.1. Unclear Mechanisms of Contact Electrification
5.2. Material Durability and Surface Degradation
5.3. Environmental Stability and Packaging
5.4. Performance Enhancement Through Structure and Hybridization
| Energy-Harvesting Technology | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TENG | EMG | PENG | Solar Cell | TEG | PyNG | |
| Working mechanism | triboelectrification and electrostatic induction | electromagnetic induction | piezoelectric effect | photovoltaic effect | Seebeck effect | pyroelectric effect |
| Open-circuit voltage | high | low | medium | low | low | medium |
| Short-circuit current | low | high | low | high | medium | low |
| Output power | low | high | low | high | medium | low |
| Power characteristic | AC | AC | AC | DC | DC | AC |
| Internal impedance | MΩ | Ω | Ω | Ω | Ω | kΩ |
5.5. Scalability and Integration into Electronics
5.6. Opportunities in Bioengineering and Health Monitoring
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Buyya, R.; Kim, H. Securing Cloud-Based Internet of Things: Challenges and Mitigations. Sensors 2025, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Liao, X.; Guo, X.; Cai, C.; Liu, Y.; Chi, M.; Du, G.; Wei, Z.; Meng, X.; Nie, S. Gel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Flexible Sensing: Principles, Properties, and Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershad, F.; Patel, S.; Yu, C. Wearable bioelectronics fabricated in situ on skins. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, M.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Luo, L.; Chen, M. Large-scale ultra-robust MoS2 patterns directly synthesized on polymer substrate for flexible sensing electronics. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chhetry, A.; Zahed, M.A.; Sharma, S.; Park, C.; Yoon, S.; Park, J.Y. On-skin ultrathin and stretchable multifunctional sensor for smart healthcare wearables. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazoum, B.; Batoo, K.M.; Khan, M.A.A. Recent advances in flexible sensors and their applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kim, D.-H.; Lu, N. Introduction: Wearable Devices. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6145–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, N.; Wang, J.; Gao, W.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Dincer, C.; Ates, H.C.; Güder, F.; Olenik, S.; Schauwecker, I.; Schaffarczyk, D.; et al. Applied body-fluid analysis by wearable devices. Nature 2024, 636, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xie, J.; Nie, D.; Liu, T.; Luo, B.; Gao, C.; Luo, Y. Triboelectric negative air ion generators for efficient membrane fouling control. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Peng, W.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Meng, X.; Cai, C. Liquid metal-based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and emerging applications. Nano Energy 2024, 120, 109107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Cai, C.; Luo, B.; Liu, T.; Shao, Y.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Rational design of cellulosic triboelectric materials for self-powered wearable electronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Ji, G.; Zhou, H.; Fang, Z.; Gao, Z. TENG-based self-powered device-the heart of life. Nano Energy 2024, 119, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; Gomes, N.O.; Oliveira, T.V.d.; Fortes-Da-Silva, P.; Soares, N.d.F.F.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A. Review and Perspectives of sustainable, biodegradable, eco-friendly and flexible electronic devices and (Bio)sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 14, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Shi, S.; Wu, H.; Si, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lei, L.; Hu, J. Emerging Trends of Nanofibrous Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Applications: Mechanisms, Electroactive Materials, and Designed Architectures. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the first principle theory of nanogenerators from Maxwell’s equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Choi, I.Y.; Son, W.; Jung, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.S.; Pang, C.; Park, W.; Kim, J.K. High-Output and Bending-Tolerant Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on an Interlocked Array of Surface-Functionalized Indium Tin Oxide Nanohelixes. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.N.; Meena, A.; Nam, K.-W. Gels in Motion: Recent Advancements in Energy Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsarimanesh, N.; Nag, A.; e Alahi, M.E.; Sarkar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sabet, G.S.; Altinsoy, M.E. A critical review of the recent progress on carbon nanotubes-based nanogenerators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 344, 113743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, G.M.; Wu, C.-M.; Motora, K.G.; Umapathi, R.; Jose, C.R.M. Acoustic-electric conversion and triboelectric properties of nature-driven CF-CNT based triboelectric nanogenerator for mechanical and sound energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Sun, N.; Mi, Y.; Luo, X.; Dong, X.; Cai, J.; Jia, X.; Ramos, M.A.; Hu, T.S.; Xu, Q. Ultra-low CNTs filled high-performance fast self-healing triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable electronics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 208, 108733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, F.F.; Mohammad Haniff, M.A.S.; Mohamed, M.A. A review on applications of graphene in triboelectric nanogenerators. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 544–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, H.; Wu, S.; Cheng, L.; Feng, Z.; Sun, J. Scalable spinning, winding, and knitting graphene textile TENG for energy harvesting and human motion recognition. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Akram, W.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Fang, J. Comprehensive Insights on MXene-Based TENGs: From Structures, Functions to Applications. Small 2024, 20, 2404872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, R.; Ali, F. The future of energy harvesting: A brief review of MXenes-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 3193–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J.; Chi, M.; Meng, X.; Du, G.; Cai, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Cellulosic gel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and emerging applications. Nano Energy 2023, 106, 108079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, L.B.; Wong, M.C.; Chen, L.; Bai, G.; Hao, J. Environmentally friendly hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for versatile energy harvesting and self-powered sensors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Dudko, V.; Khoruzhenko, O.; Hong, X.; Lv, Z.-P.; Tunn, I.; Umer, M.; Timonen, J.V.I.; Linder, M.B.; Breu, J.; et al. Stiff and self-healing hydrogels by polymer entanglements in co-planar nanoconfinement. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y. Progress in the mechanical enhancement of hydrogels: Fabrication strategies and underlying mechanisms. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, U. Material aspects of triboelectric energy generation and sensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Enhancing performance of triboelectric nanogenerator by accelerating the charge transfer strategy. Nano Energy 2024, 121, 109194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Enhance Charge Transfer and Reduce Internal Resistance for Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Switching Charge Shuttling. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2405116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, Y.; Lin, Z.-H.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.; Ao, C.K.; Soh, S.; Sohn, C.; Jeong, C.K.; Lee, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Technological Progress to Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11087–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Ren, D.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Y. A review of material design for high performance triboelectric nanogenerators: Performance improvement based on charge generation and charge loss. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4522–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulathsinghala, R.L.; Ding, W.; Dharmasena, R.D.I.G. Triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable sensing applications: A system level analysis. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, W.; Qiao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Efficient energy transport from triboelectric nanogenerators to lithium-ion batteries via releasing electrostatic energy instantaneously. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Lu, H.; Khaladkar, S.; Wu, X.; Roy, S.; Ullah, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B. Recent advances in triboelectric nanogenerators: Mechanism, rational designing and applications. Mater. Today Energy 2024, 46, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Lu, X.; Qiao, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Mechanical Regulation Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Controllable Output Performance for Random Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shan, C.; Fu, S.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, H.; Hu, C. Efficient energy conversion mechanism and energy storage strategy for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Dual Effects in Mechanical-Energy Harvesting Using BaTiO3/Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34335–34341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Teng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Q. Wearing comfortable and high electrical output TENGs woven with PTFE core–shell nanofiber yarns. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasarn, H.; Ngennam, T.; Sumpao, T.; Thanachayanont, C.; Seetawan, T. The charging performance in contact electrification of fluorinated ethylene propylene surfaces by electrode bridge. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 346, 113881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okochi, K.; Oya, T. Unique Triboelectric Nanogenerator Using Carbon Nanotube Composite Papers. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborthy, A.; Nuthalapati, S.; Nag, A.; Altinsoy, M.E.; He, S. Graphene-based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy-harvesting applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 380, 116046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. Advanced Implantable Biomedical Devices Enabled by Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damte, J.Y.; Houska, J. Tribo-piezoelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting: A first-principles study. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2024, 8, 4213–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Studying of contact electrification and electron transfer at liquid-liquid interface. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Bu, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Tribovoltaic Effect on Metal–Semiconductor Interface for Direct-Current Low-Impedance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Fu, S.; Li, G.; Shan, C.; He, W.; Hu, C. Enhancement of output charge density of TENG in high humidity by water molecules induced self-polarization effect on dielectric polymers. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D. An Advanced Strategy to Enhance TENG Output: Reducing Triboelectric Charge Decay. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaty, C.; Rodrigues, C.; Ventura, J. Triboelectric nanogenerators in harsh conditions: A critical review. Nano Energy 2025, 135, 110661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Luo, J.; Qin, H.; Han, K.; Wang, Z.L. Charge Pumping Strategy for Rotation and Sliding Type Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, F.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y.-C. Hydrogel-based triboelectric devices for energy-harvesting and wearable sensing applications. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Chen, B.; Li, H.; Shen, A.; Mao, Y. Recent advances in stretchable hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for on-skin electronics. Mater. Chem. Front. 2024, 8, 4003–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, S.; Guo, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L.; Guan, Q.; You, Z. Ionogel-based, highly stretchable, transparent, durable triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and motion sensing over a wide temperature range. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, G.; Wu, M.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, D.; Wu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, L. Ionogel infiltrated paper as flexible electrode for wearable all-paper based sensors in active and passive modes. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Dickey, M.D. Tough Ionogels: Synthesis, Toughening Mechanisms, and Mechanical Properties—A Perspective. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2645–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, Y. Organogel electrode based continuous fiber with large-scale production for stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator textiles. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somton, S.; Wanwong, S.; Sangkhun, W.; Poolthong, N. Transparent perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane (PFDTES)/PDMS based water droplet-driven triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered energy devices. J. Power Sources 2025, 625, 235693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.H.; Lee, S.H.; Gao, J.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, K.J.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.-C.; Kim, Y.; Baik, J.M. Sustainable charged composites with amphiphobic surfaces for harsh environment–tolerant non-contact mode triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Pumping up the charge density of a triboelectric nanogenerator by charge-shuttling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Chi, M.; Miao, X.; Yang, H.; Cui, W.; Yu, A.; Zhai, J. Ultra-high output triboelectric nanogenerator based on synergies of material modification and charge pumping. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Dynamical charge transfer model for high surface charge density triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Shi, Y.; Tao, X.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Chen, X. Radical anion transfer during contact electrification and its compensation for charge loss in triboelectric nanogenerator. Matter 2023, 6, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Guan, S.; Huang, Z.; Pei, X.; Guan, Q. Wear-resistance triboelectric nanogenerator based on metal-organic framework modified short carbon fiber reinforced polyphenylene sulfide. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, L.; Gudla, S.; Shan, X.; Wang, Z.; Tay, F.E.H.; Heng, C.-H.; Lee, C. Large Scale Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Self-Powered Pressure Sensor Array Using Low Cost Roll-to-Roll UV Embossing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Machine learning-assisted triboelectric nanogenerator-based self-powered sensors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.N.; Islam, M.; Meena, A.; Faizan, M.; Han, D.; Bathula, C.; Hajibabaei, A.; Anand, R.; Nam, K.W. Unleashing the Potential of Sodium-Ion Batteries: Current State and Future Directions for Sustainable Energy Storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Mao, M.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Kong, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, Y. Application of self powered black phosphorus nanosheets-based hydrogel skin patch in wound healing of diabetes. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Advances in MXene-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2024, 125, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, K.; Xiao, C.; Yin, X.; Gui, X.; Song, Q.; Ye, F. Carbon nanotube-vertical edge rich graphene hybrid sponge as multifunctional reinforcements for high performance epoxy composites. Carbon 2023, 201, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Han, H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kang, S.; Jung, K.; Kim, Y.-K.; Song, T.; Mhin, S.; Kim, K.M. Laser-driven formation of ZnSnO3/CNT heterostructure and its critical role in boosting performance of the triboelectric nanogenerator. Carbon 2023, 212, 118120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, L.; Zienert, A.; Schuster, J.; Köhne, M.; Schulz, S.E. Electrical Conductivity Modeling of Graphene-based Conductor Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43088–43094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, X. Sustainable materials systems for triboelectric nanogenerator. SusMat 2024, 4, e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, F.F.; Mohammad Haniff, M.A.S.; Ambri Mohamed, M. Enhanced-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Polydimethylsiloxane/Barium Titanate/Graphene Quantum Dot Nanocomposites for Energy Harvesting. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5608–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayodhya, D. A review of recent progress in 2D MXenes: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 132, 109634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicklein, B.; Valurouthu, G.; Yoon, H.; Yoo, H.; Ponnan, S.; Mahato, M.; Kim, J.; Ali, S.S.; Park, J.Y.; Gogotsi, Y.; et al. Influence of MXene Composition on Triboelectricity of MXene-Alginate Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23948–23959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Tang, Q.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, C. Quantifying contact status and the air-breakdown model of charge-excitation triboelectric nanogenerators to maximize charge density. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Fan, F.R.; Pang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Realized by Air Breakdown Induced Ionized Air Channel. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Gao, F.; Zhao, B.; Ouyang, T.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Fingerprint-inspired electronic skin based on triboelectric nanogenerator for fine texture recognition. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kalra, A.; Lowe, A.; Yu, Y.; Anand, G. A Hydrogel-Based Electronic Skin for Touch Detection Using Electrical Impedance Tomography. Sensors 2023, 23, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, F.; Fang, C.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Cao, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. TENG-Bot: Triboelectric nanogenerator powered soft robot made of uni-directional dielectric elastomer. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as wearable power sources and self-powered sensors. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, N.; Wang, M.; et al. Self-Powered and Autonomous Vibrational Wake-Up System Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators and MEMS Switch. Sensors 2022, 22, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almardi, J.M.; Bo, X.; Shi, J.; Firdous, I.; Daoud, W.A. Drone rotational triboelectric nanogenerator for supplemental power generation and RPM sensing. Nano Energy 2025, 135, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Uy, C.; Xiao, X.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Self-powered environmental monitoring via a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Nanosensors and Nanosystems. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, C.; Park, J.H.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, T.; Kim, T.W. Triboelectric-nanogenerator-inspired light-emitting diode-in-capacitors for flexible operation in high-voltage and wireless drive modes. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Guo, T.; et al. TENG-inspired LED-in-capacitors for smart self-powered high-voltage monitoring and high-sensitivity demodulation of power-line communications. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Cheng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Sheng, F.; Yi, J.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. Helical Fiber Strain Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Human Respiratory Monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Gong, Q.; Xie, G.; Zhou, Y. Muscle fibers inspired high-performance piezoelectric textiles for wearable physiological monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, S.; Sha, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chu, D.; Wang, C.H.; Peng, S. A triboelectric nanogenerator powered piezoresistive strain sensing technique insensitive to output variations. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, M.V.; Manchi, P.; Kurakula, A.; Kavarthapu, V.S.; Lee, J.K.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S. Generalized utilization of energy harvesting ability of TENG for concurrent energy storage and motion sensing application with effective external circuitry. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Xi, G.; Mao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Luan, H. Ultrastretchable, Self-Healing Conductive Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Human–Computer Interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D. Highly Stretchable Conductive Hydrogel-Based Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Ultrasensitive Tactile Sensing. Polymers 2025, 17, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, F.; Guan, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. Mechanically and environmentally stable triboelectric nanogenerator based on high-strength and anti-compression self-healing ionogel. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fang, C.; Qin, B.; Yang, X.; Poechmueller, P. Conductive dual-network hydrogel-based multifunctional triboelectric nanogenerator for temperature and pressure distribution sensing. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors–Principles, problems and perspectives. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as flexible power sources. npj Flex. Electron. 2017, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, D.; Domingos, I.; Carvalho, N.; Pinho, P.; Alves, H. Harvesting circuits for triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable applications. iScience 2022, 25, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Kang, W.; Yang, G. An efficient charge extraction strategy for high-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators via a 3D nanostructured conductive network. Nano Energy 2025, 140, 111037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Derakhshani, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, C. Hybrid energy-harvesting systems based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Matter 2021, 4, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bick, M.; Xiao, X.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Chen, J. Leveraging triboelectric nanogenerators for bioengineering. Matter 2021, 4, 845–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburaj, A.; Banerjee, S.; Aliyana, A.K.; Shee, C.; Banakar, M.; Bairagi, S.; Naveen Kumar, S.K.; Ali, S.W.; Stylios, G.K. Biodegradable based TENGs for self-sustaining implantable medical devices. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.N.; Nam, K.-W. Gel-Based Self-Powered Nanogenerators: Materials, Mechanisms, and Emerging Opportunities. Gels 2025, 11, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060451
Singh AN, Nam K-W. Gel-Based Self-Powered Nanogenerators: Materials, Mechanisms, and Emerging Opportunities. Gels. 2025; 11(6):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060451
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Aditya Narayan, and Kyung-Wan Nam. 2025. "Gel-Based Self-Powered Nanogenerators: Materials, Mechanisms, and Emerging Opportunities" Gels 11, no. 6: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060451
APA StyleSingh, A. N., & Nam, K.-W. (2025). Gel-Based Self-Powered Nanogenerators: Materials, Mechanisms, and Emerging Opportunities. Gels, 11(6), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060451







