A Recyclable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Ionogel Based on Zinc–Halogen Coordination Anion Crosslinked Poly(ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Networks for High-Performance Microwave Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
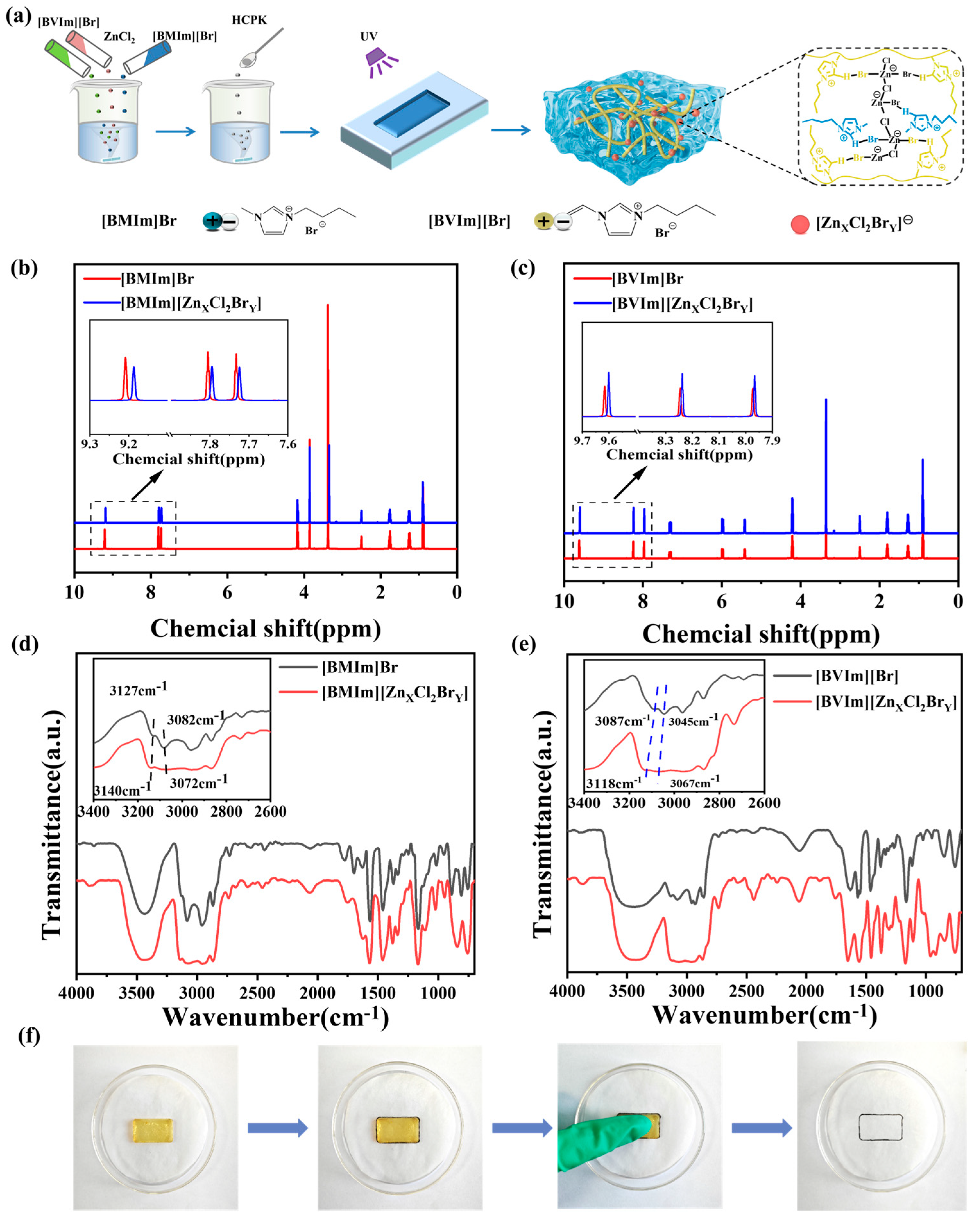
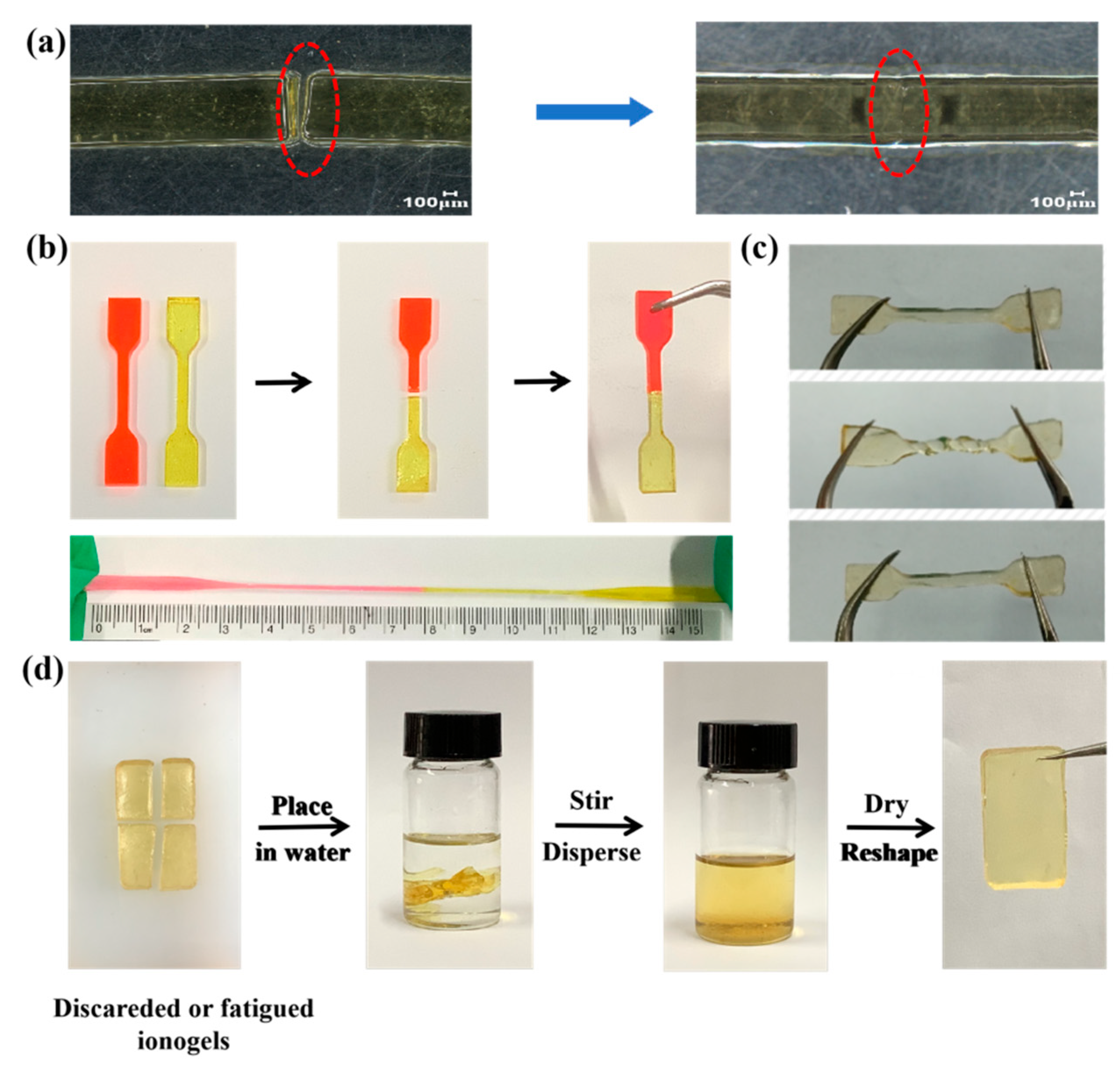
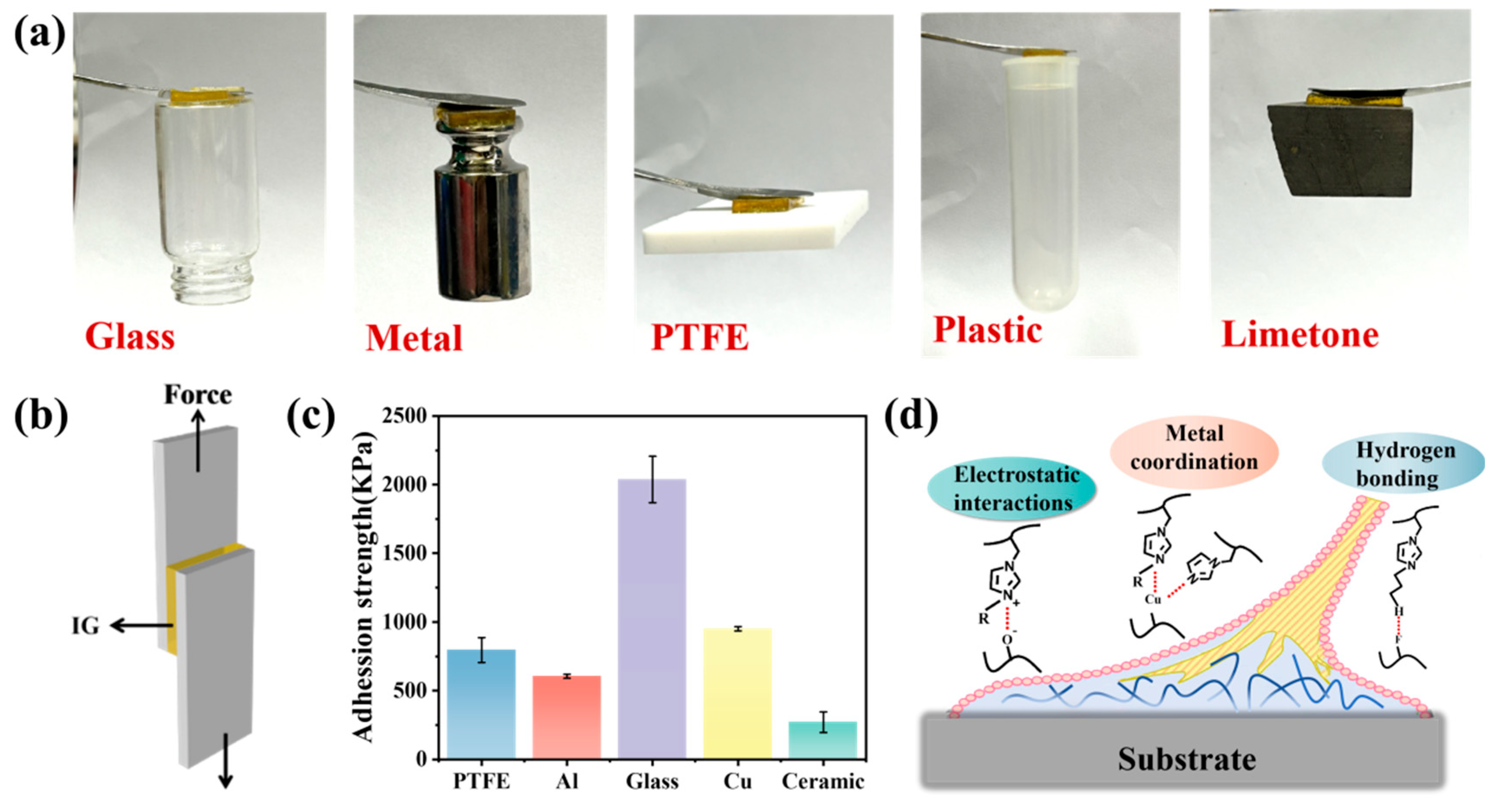
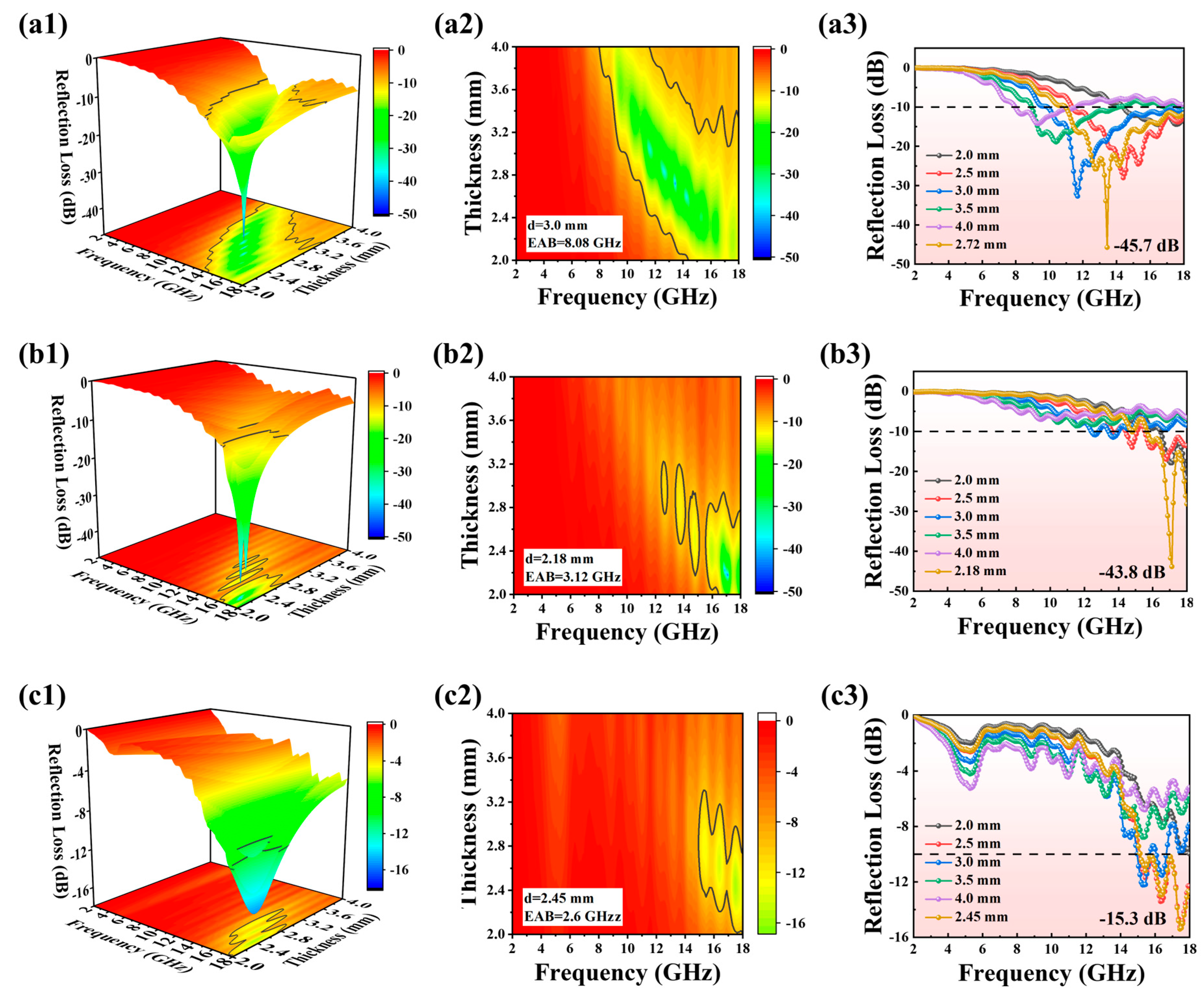
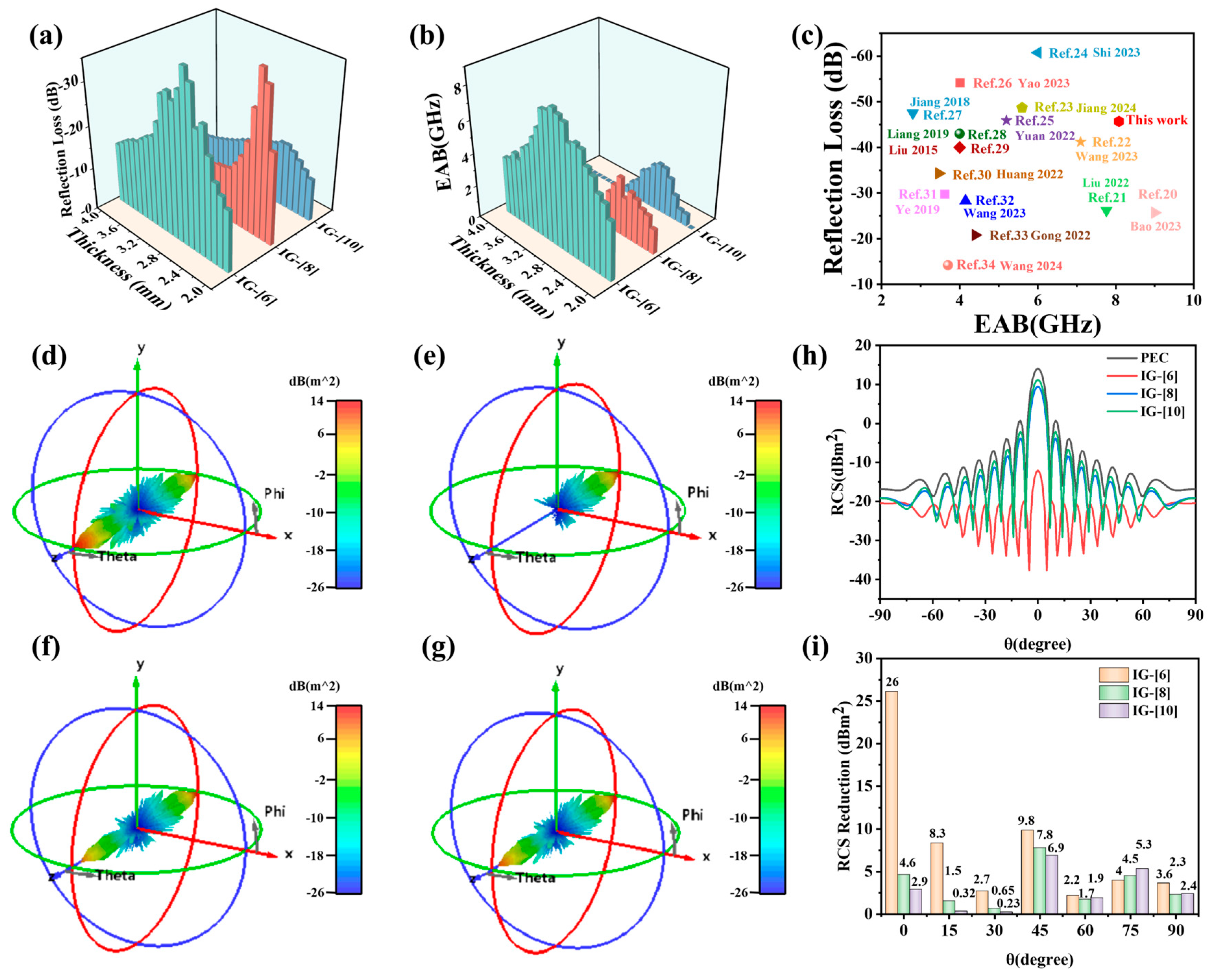
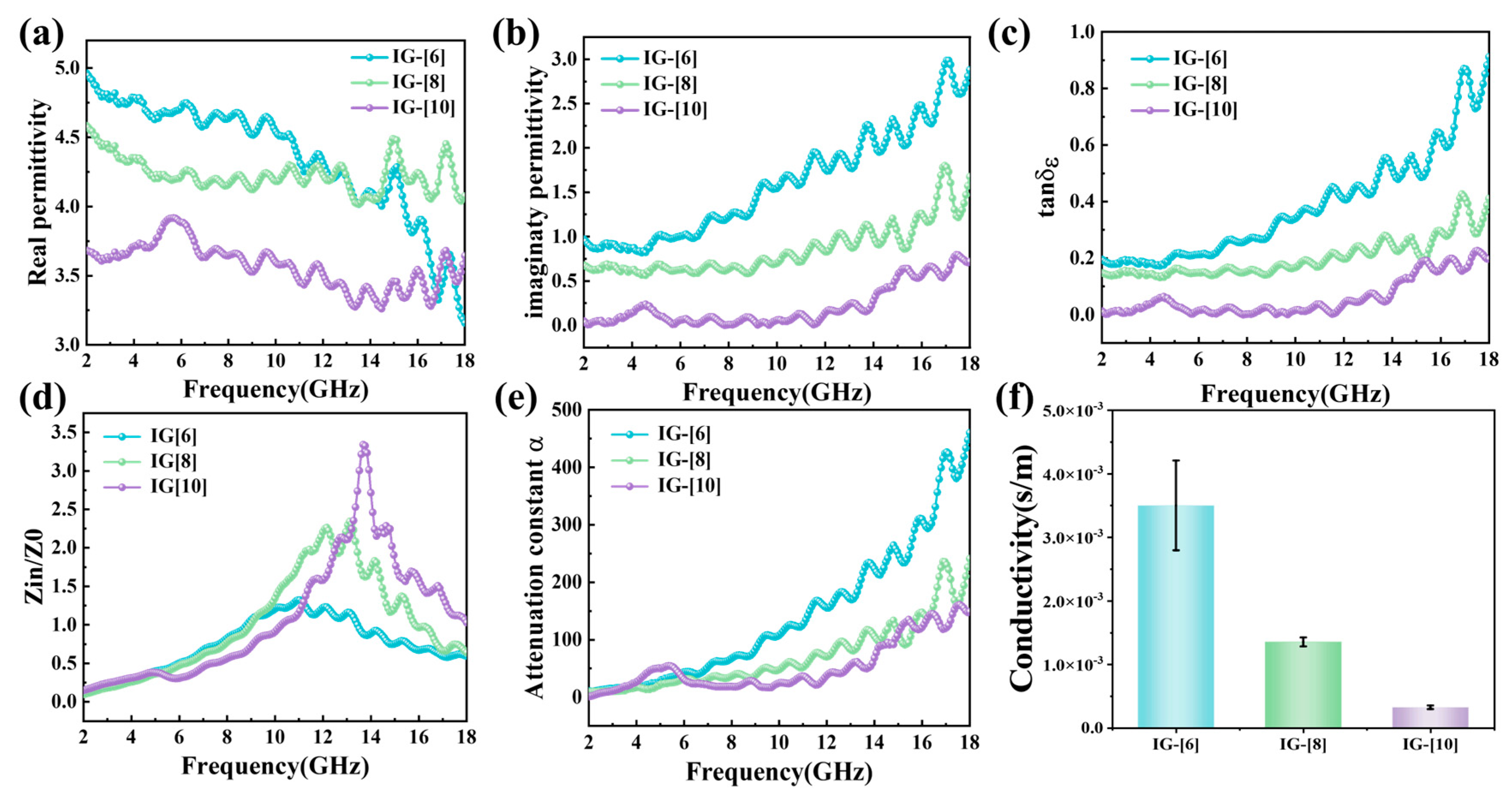
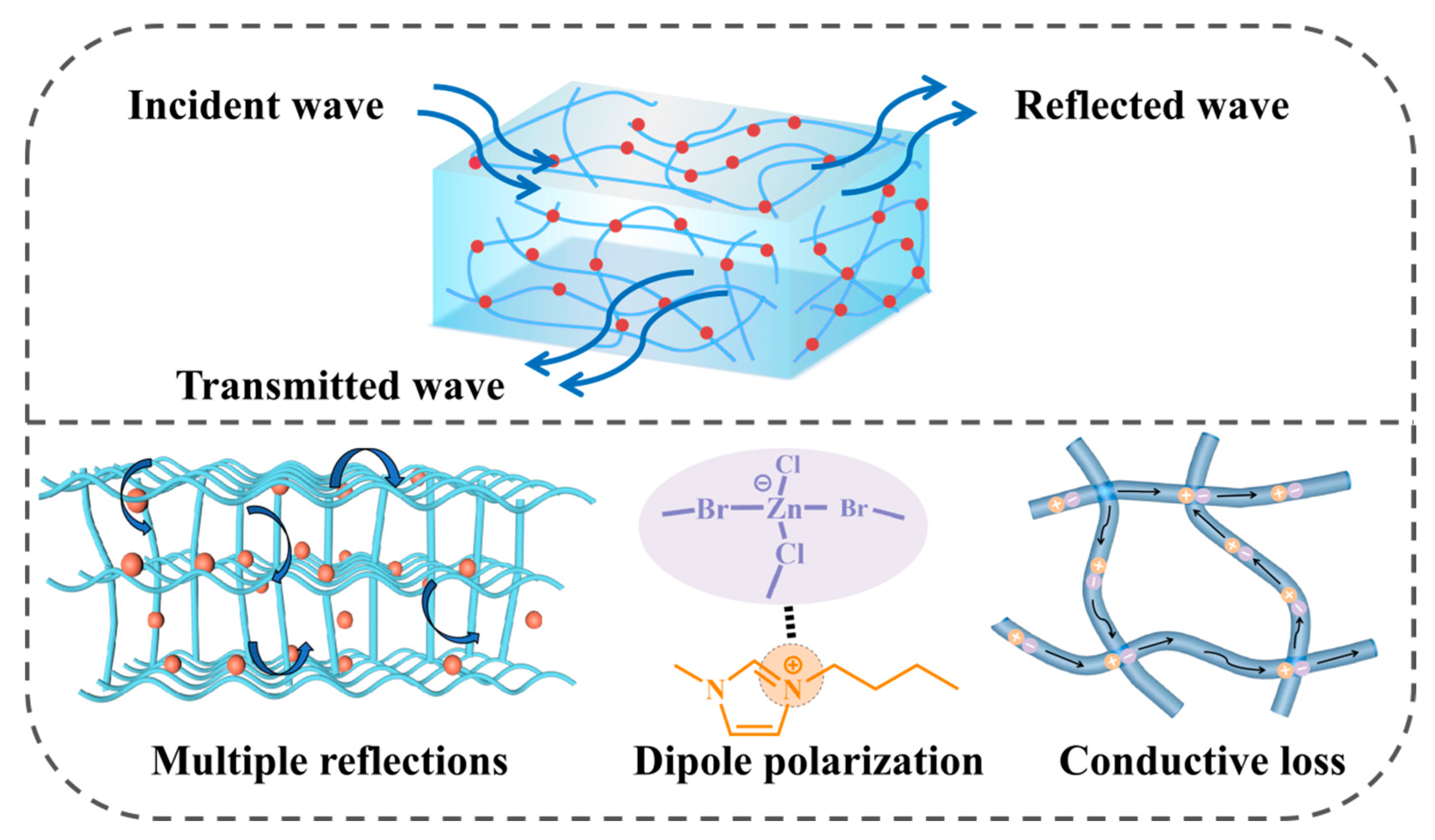
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Future Directions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Methods
5.3. Characterization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Liu, T.T.; Zhao, Q.L.; Li, C.S.; Cao, M.S. MXene Hybridized Polymer with Enhanced Electromagnetic Energy Harvest for Sensitized Microwave Actuation and Self-Powered Motion Sensing. Nano Micro Lett. 2025, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Ji, G.; Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; Du, Y. Rationally regulating complex dielectric parameters of mesoporous carbon hollow spheres to carry out efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2018, 127, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, A. Influence of Reduced Graphene Oxide Flakes Addition on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance of Silicon Carbide-Based Wave Absorber. JOM 2024, 76, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zong, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Luo, P.; Liu, S.; Ren, F.; Ren, P. Hetero-structured construction of RGO nanosheets decorated by flower-like MoS2 toward the regulation of electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Mater. Today Phys. 2024, 50, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aka, C.; Kıvrak, B.; Tekşen, F.A. Phase (1T/2H) dependent electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of flower-like MoS2 nanosheet. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z.; Wei, W.; Lin, Z.; Yuan, R.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chang, J.; Hao, Y. Arginine-inspired Ti3C2Tx MXenes with antioxidation function for highly air-stable electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater. Today Nano 2025, 29, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhu, R.; Qiu, Z.; Yan, Y. Fully physically crosslinked PNIPAM ionogels with high mechanical properties and temperature-managed adhesion achieved by H2O/ionic liquid binary solvents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, R.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Nucleobase-driven wearable ionogel electronics for long-term human motion detection and electrophysiological signal monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2412244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Hydro/organo/ionogels: “Controllable” electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2205376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, K.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Y.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.; Ma, W.; Gong, F.; Liu, C.; Pan, J. Highly efficient and selective removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using polyacrylamide/peach gum polysaccharide/attapulgite composite hydrogels with positively charged hybrid network. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zeb, A.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Poly (ionic liquid) s-based ionogels for sensor applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 14260–14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, F.C.; Cholant, C.M.; Kohlrausch, E.C. Ionic liquid boosted conductivity of biopolymer gel electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 084501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftelchari, A.; Saito, T. Synthesis and properties of polymerized ionic liquids. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 90, 245–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Zheng, S.; Zou, X.; Xiong, J.; Li, W.; Yan, F. High-toughness and high-strength solvent-free linear poly (ionic liquid) elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Z.H.; Yue, K. Recent progresses in liquid-free soft ionic conductive elastomers. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 835–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Fu, M.; Ou, W.; Huang, T.; Yue, K. A fully self-healing and highly stretchable liquid-free ionic conductive elastomer for soft ionotronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedano-Serrano, F.J.; Sidoli, U.; Synytska, A.; Tran, Y.; Hourdet, D.; Creton, C. From molecular electrostatic interactions and hydrogel architecture to macroscopic underwater adherence. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3852–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Poseu, J.; Mancebo-Aracil, J.; Nador, F.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. The chemistry behind catechol-based adhesion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 696–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deptula, A.; Rangel-Galera, J.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M. Control of Surface Morphology, Adhesion and Friction of Colloidal Gels with Lamellar Surface Interactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, Z. Thermal energy compensation strategy to achieve rambutan-like CoFe@ C-CNTs composites with controllable cross-linked networks for broadband microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 215, 118413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; An, Z.; Liao, B.; Zhang, J. FeNi alloy and nickel ferrite codoped carbon hollow microspheres for high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 6085–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Q.; Gao, J.; He, Y. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of Fe3O4@MnO2@Ni–Co/C composites derived from Prussian blue analogues. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 8255–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Shang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yue, X. Highly flexible hydrogels with readily adjustable electromagnetic parameter for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 16488–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Hu, Z. 3D lamellar skeletal network of porous carbon derived from hull of water chestnut with excellent microwave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 641, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, F.; Xue, T.; Shu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Transparent organogel based on photopolymerizable magnetic cationic monomer for electromagnetic wave absorbing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Rong, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, H.; Kang, S. CuCo nanocube/N-doped carbon nanotube composites for microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Sui, G.X. Lightweight spongy bone-like graphene@ SiC aerogel composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, Z. Eggplant-derived SiC aerogels with high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal insulation properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Ye, F.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L. The microstructure of SiCN ceramics and their excellent electromagnetic wave absorbing properties. Ceram Int. 2015, 41, 11372–11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, X.; Chai, C. Variety of ZIF-8/MXene-based lightweight microwave-absorbing materials: Preparation and performances of ZnO/MXene nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 13847–13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Ai, S.; Hou, B.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, H.; Cui, S. Effects of SiC coating on microwave absorption of novel three-dimensional reticulated SiC/porous carbon foam. Ceram Int. 2019, 45, 8660–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, J.; Zhou, J.; Van Zalinge, H.; Yao, Z.; Yang, L. Synthesis mechanism of different morphological SiC and its electromagnetic absorption performance. Mater. Charact. 2023, 205, 113328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Liang, S.; Lu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Compounds, Wave-absorbing properties of Ni-Zn ferrites loaded on coal-based, densely porous light carbon functional materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 900, 163485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, S.; Peng, G.; Tao, J.; Yao, J.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J. Interfaces, intelligent tunable wave-absorbing CNTs/VO2/ANF composite aerogels based on temperature-driving. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32773–32783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; He, Z.L.; Zhang, Y. Trimetallic FeCoNi@C nanocomposite hollow spheres derived from metal–organic frameworks with superior electromagnetic wave absorption ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39304–39314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Zade, R.A. Study of Nanocomposite Permittivity on the Basis of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4) and Polymeric Matrix: Polyethylene and Polystyrene in Electromagnetic Field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.L.; Jiang, P.; Hou, X.; Xiao, T.; Zheng, Q.F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.X.; Cao, W.B. Dielectric permittivity and microwave absorption properties of SiC nanowires with different lengths. Solid State Sci. 2019, 91, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Aslam, M.A.; Bilal, M. Modulating dielectric loss of MoS2@ Ti3C2Tx nanoarchitectures for electromagnetic wave absorption with radar cross section reduction performance verified through simulations. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20706–20716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, R.; Kim, J.M.; Aiton, S. Guided waves based damage localization using acoustically coupled optical fibers and a single fiber Bragg grating sensor. Measurement 2022, 203, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Deng, L.C.; Luo, B.C.; Zhang, L.M.; Tao, K.; Li, X.X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H.J. Flexible, large area preparable phase change PVA/P(ILs-AM)/SSD films for electromagnetic wave absorption and infrared stealth. iScience 2025, 28, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.K.; Tang, Q.; Xie, J.L.; Fei, Y.; Wan, H.J.; Zhao, T.; Ding, T.P.; Xiao, X.; Wen, Q.Y. Organohydrogel-based transparent terahertz absorber via ionic conduction loss. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Akhtar, M.J.; Kar, K.K. Hierarchical carbon nanotube-coated carbon fiber: Ultra lightweight, thin, and highly efficient microwave absorber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24816–24828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zong, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. A Recyclable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Ionogel Based on Zinc–Halogen Coordination Anion Crosslinked Poly(ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Networks for High-Performance Microwave Absorption. Gels 2025, 11, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060436
Wang L, Liu J, Zong M, Liu Y, Zhu J. A Recyclable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Ionogel Based on Zinc–Halogen Coordination Anion Crosslinked Poly(ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Networks for High-Performance Microwave Absorption. Gels. 2025; 11(6):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060436
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Jie Liu, Meng Zong, Yi Liu, and Jianfeng Zhu. 2025. "A Recyclable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Ionogel Based on Zinc–Halogen Coordination Anion Crosslinked Poly(ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Networks for High-Performance Microwave Absorption" Gels 11, no. 6: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060436
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, J., Zong, M., Liu, Y., & Zhu, J. (2025). A Recyclable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Ionogel Based on Zinc–Halogen Coordination Anion Crosslinked Poly(ionic Liquid)/Ionic Liquid Networks for High-Performance Microwave Absorption. Gels, 11(6), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060436




