Physically Transient Gelatin-Based Memristors of Buildable Logic Gates
Abstract
1. Introduction
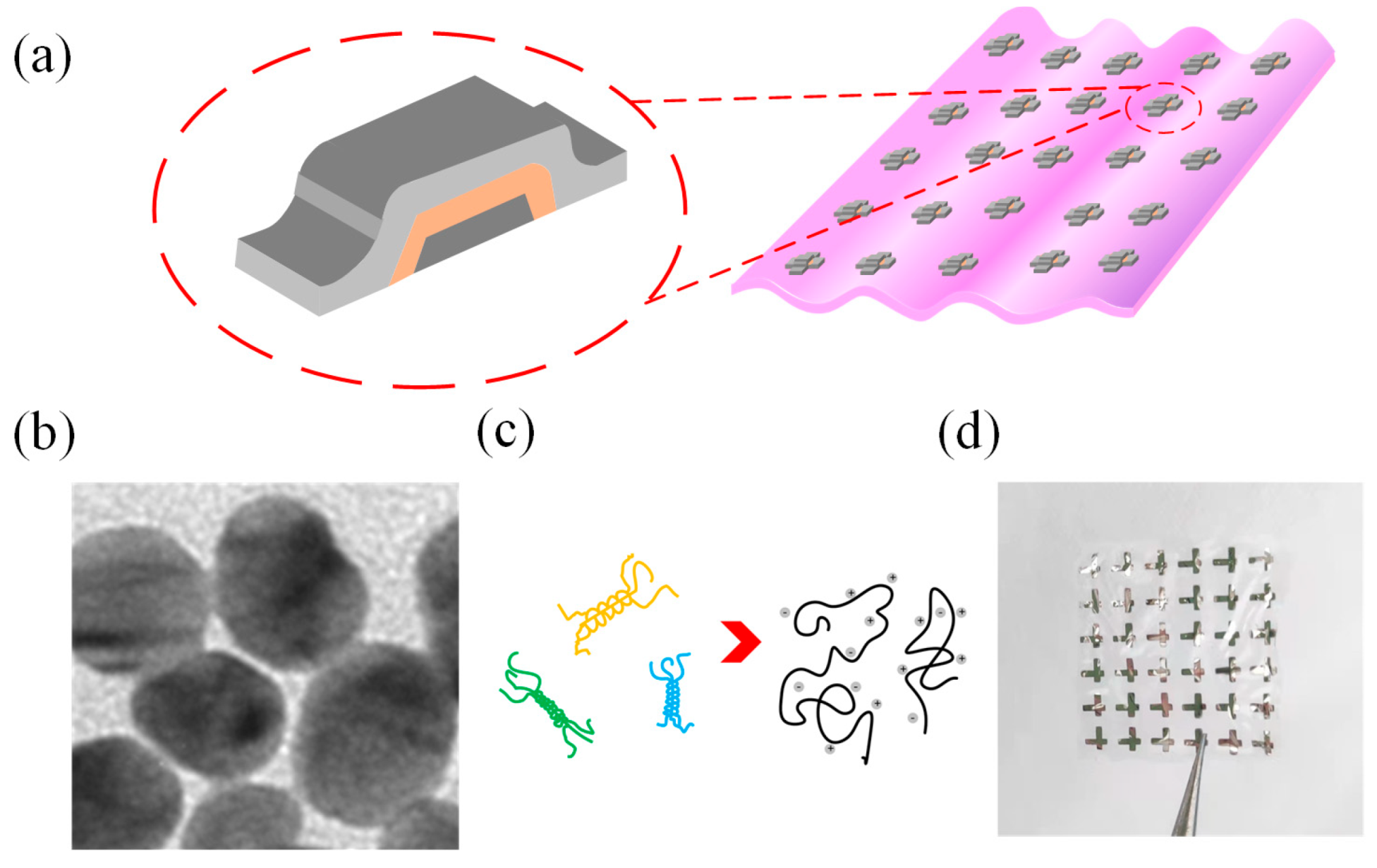
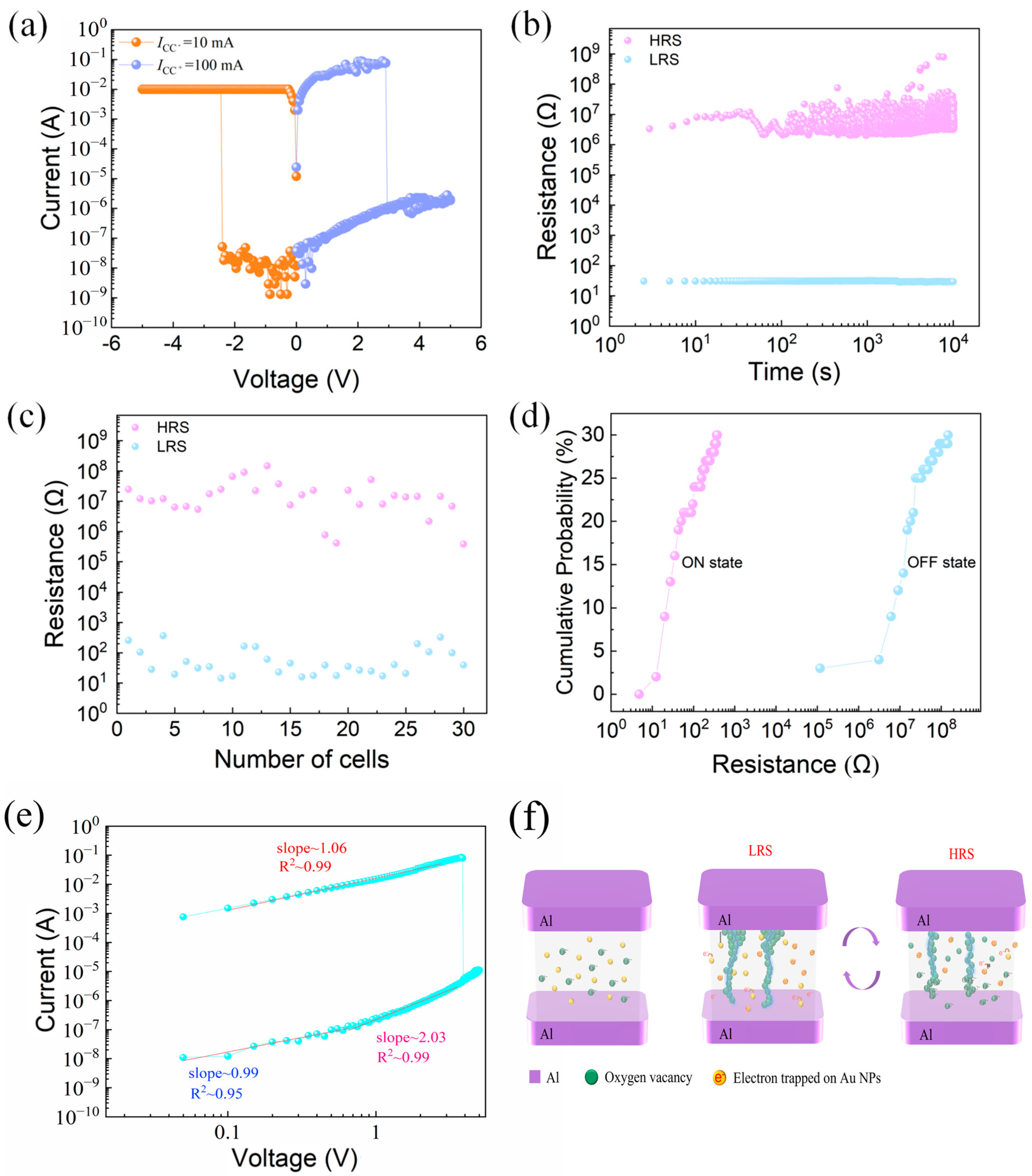
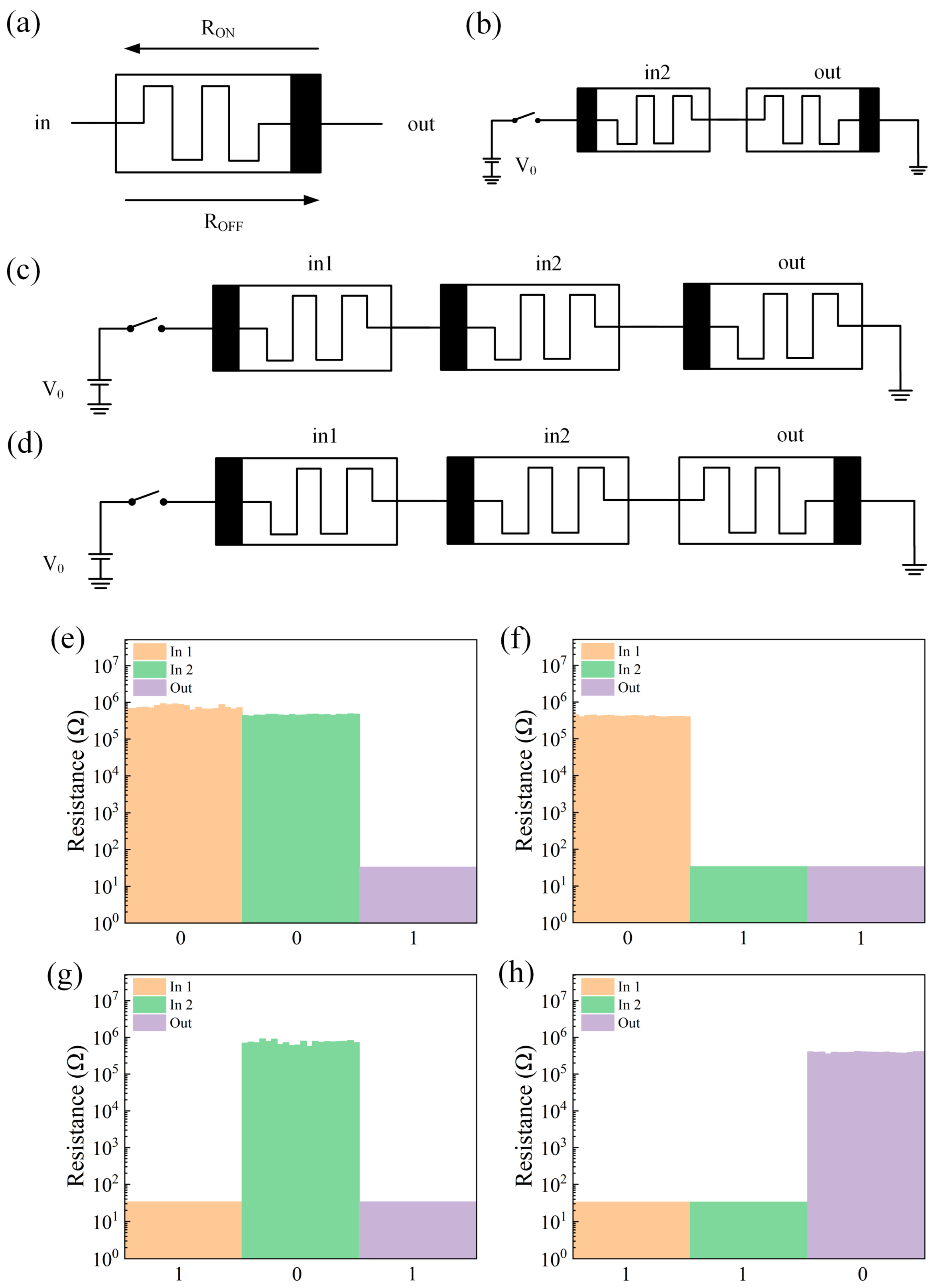
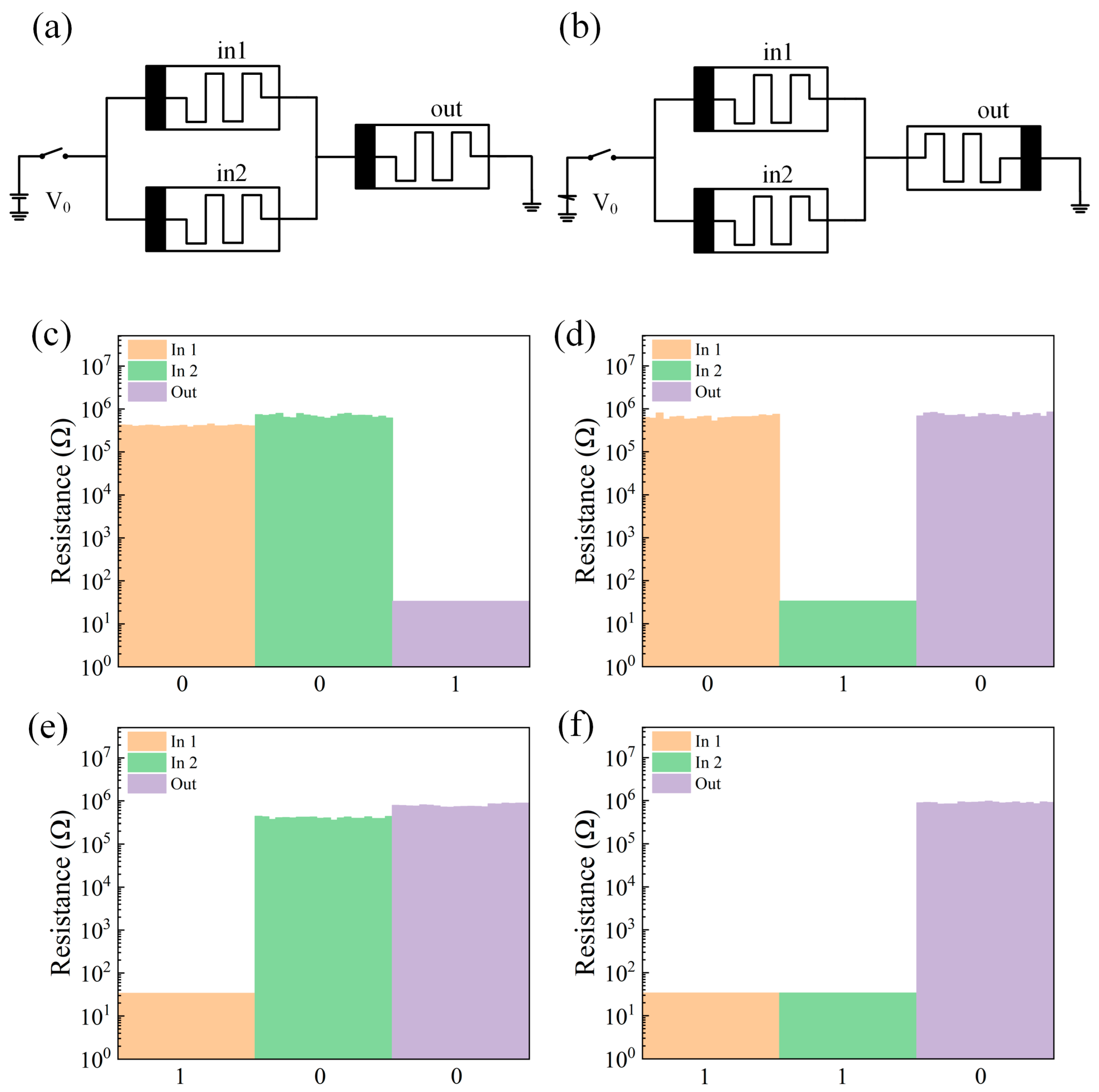
2. Results
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurshan, E.; Li, H.; Seok, M.; Xie, Y. A Case for 3D Integrated System Design for Neuromorphic Computing and AI Applications. Int. J. Semant. Comput. 2020, 14, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, J.; Pan, L.; Cao, D.; Ding, X. Artificial Intelligence Facilitates Drug Design in the Big Data Era. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 2019, 194, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; Qian, P.; Bi, D.; Ye, Z.W.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.H.; Su, L.; Li, S.L.; Zhu, Z.L. Application of AI and IoT in Clinical Medicine: Summary and Challenges. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagatheesaperumal, S.K.; Rahouti, M.; Ahmad, K.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Guizani, M. The Duo of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Industry 4.0: Applications, Techniques, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. IEEE Internet Things 2021, 9, 12861–12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Goshisht, M.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Arora, C. Applications of Artificial Intelligence to Drug Design and Discovery in the Big Data Era: A Comprehensive Review. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Zeng, S.; Huang, X.; Zhou, P. Versatile Logic and Nonvolatile Memory Based on a Van Der Waals Heterojunction. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 3079–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Tian, B.; Zhu, Q.; Dkhil, B.; Duan, C. Ferroelectric Polymers for Neuromorphic Computing. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 021309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, S.G.C.; Lugnan, A.; Gemo, E.; Bienstman, P.; Pernice, W.H.; Bhaskaran, H.; Wright, C.D. System-Level Simulation for Integrated Phase-Change Photonics. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 6392–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, D.; Liu, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.; Han, G.; Hao, Y. All-Optical Synapse with Directional Coupler Structure Based on Phase Change Material. IEEE Photonics J. 2021, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, C.; Lin, H.; Du, Q.; Hu, J.; Gong, Q. All-Optical Computing Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2021, 4, 200060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P. The Road for 2D Semiconductors in the Silicon Age. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluccio, A.; Casale, U.; Guastamacchia, A.; Turvani, G.; Vacca, M.; Roch, M.R.; Zamboni, M.; Graziano, M. Hybrid-SIMD: A Modular and Reconfigurable Approach to Beyond von Neumann Computing. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2021, 71, 2287–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Ganganaik, P.B.; Louis, J.; Chalamalasetty, H.; Rao, B.P. Memristors Enabled Computing Correlation Parameter In-Memory System: A Potential Alternative to von Neumann Architecture. IEEE Trans. VLSI. Syst. 2022, 30, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.Q.; Ding, S.J.; Zhang, D.W. Atomic Layer-Deposited HfAlOx-Based RRAM with Low Operating Voltage for Computing In-Memory Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.J.; Kang, I.S.; Lee, K.J. Unconventional Inorganic—Based Memristive Devices for Advanced Intelligent Systems. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Midya, R.; Xia, Q.; Yang, J.J. Review of Memristor Devices in Neuromorphic Computing: Materials Sciences and Device Challenges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 503002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, J.; Yan, X. The Future of Memristors: Materials Engineering and Neural Networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.F.; Kuo, W.C.; Bao, W.; Ho, C.H.; Huang, C.W.; Wu, W.W.; Chu, Y.H.; Juang, J.Y.; Tseng, S.H.; Hu, L. Self-Formed Conductive Nanofilaments in (Bi, Mn) Ox for Ultralow-Power Memory Devices. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Huang, R.; Cai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Record Low-Power Organic RRAM with Sub20-nA Reset Current. IEEE Electr. Device Lett. 2013, 34, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.E.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, D.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, D.S.; Chung, U.I. Investigation for Resistive Switching by Controlling Overflow Current in Resistance Change Nonvolatile Memory. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2012, 11, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.H.; Gao, B.; Deng, N.; Lu, Z.; Haukness, B.; Bronner, G.; Qian, H. Resistive Random Access Memory for Future Information Processing System. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1770–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotti, P.; Oukassi, S.; Molas, G.; Bernard, M.; Aussenac, F.; Pillonnet, G. In Memory Energy Application for Resistive Random Access Memory. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covi, E.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y.-H.; Farronato, M.; Ambrosi, E.; Ielmini, D. Switching Dynamics of Ag-Based Filamentary Volatile Re-Sistive Switching Devices—Part I: Experimental Characterization. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2021, 68, 4335–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Tian, H.; Zhao, H.M.; Zhang, T.Y.; Mao, W.Q.; Qiao, Y.C.; Pang, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.L. Interface Engineering with MoS2–Pd Nanoparticles Hybrid Structure for a Low Voltage Resistive Switching Memory. Small 2018, 14, 1702525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM Devices: Resistive Switching Mechanisms, Materials and Bionic Synaptic Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Wang, J.; Zhong, X. Electrically Controlled Nonlinear Switching and Multilevel Storage Characteristics in WOx Film-Based Memory Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 116, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, D. Flexible Nonvolatile Bioresistive Random Access Memory with an Adjustable Memory Mode Capable of Realizing Logic Functions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Peng, W.; Cao, Z.; Gao, K.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, Q.; et al. Data encryption/decryption and medical image reconstruction based on a sustainable biomemristor designed logic gate circuit. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Niu, Q.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.P. Intrinsically ionic conductive nanofibrils for ultrathin biomemristor with low operating voltage. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 3096–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Li, F.F.; Wu, M.Q.; Liang, K.; Ren, H.H.; Zheng, X.R.; Guo, C.C.; et al. Silk protein based volatile threshold switching memristors for neuromorphic computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.H.; Zhang, M.C.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Saadi, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y.R.; He, N.; Hu, E. Demonstration of electronic synapses using a sericin-based biomemristor. Appl. Phys. Express 2023, 16, 031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungkavet, T.; Pattavarakorn, D.; Sirivat, A. Biocompatible Gelatins (Ala-Gly-Pro-Arg-Gly-Glu-4Hyp-Gly-Pro-) and Electro-Mechanical Properties: Effects of Temperature and Electric Field. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Wald, N.; Satat, G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C.; Friedman, E.G. MRL—Memristor Ratioed Logic. In Proceedings of the 2012 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and Their Applications, Turin, Italy, 29–31 August 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]

| Device Structure | Switching Current Ratio | Retention Time (s) | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al/gelatin:Au NPs/ITO | ~7.68 × 106 | 104 | NAND and NOR | This paper |
| Al/tussah hemolymph/ITO | ~102 | 104 | AND and OR | [27] |
| Ag/mugwort:PVDF/ITO | ~3.6 | 105 | AND/OR/NAND/NOR/XOR | [28] |
| Ag/silk nanofibrils/ITO | 102 | 105 | AND and OR | [29] |
| Au/silk:AgNO3/Ag | 3 × 106 | 103 | short-term plasticity and paired-pulse facilitation | [30] |
| Ag/sericin/W | 100 | / | spiking rate-dependent plasticity and spiking time-dependent plasticity | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Han, Y.; Wen, D. Physically Transient Gelatin-Based Memristors of Buildable Logic Gates. Gels 2025, 11, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060428
Wang L, Wang Y, Li W, Gao Z, Han Y, Wen D. Physically Transient Gelatin-Based Memristors of Buildable Logic Gates. Gels. 2025; 11(6):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060428
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Yuting Wang, Wenhao Li, Zhiqiang Gao, Yutong Han, and Dianzhong Wen. 2025. "Physically Transient Gelatin-Based Memristors of Buildable Logic Gates" Gels 11, no. 6: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060428
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, Y., Li, W., Gao, Z., Han, Y., & Wen, D. (2025). Physically Transient Gelatin-Based Memristors of Buildable Logic Gates. Gels, 11(6), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060428







