Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Reveals the Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by Orbital Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Hyaluronan Production of Orbital Fibroblasts Increases Under Adipogenic Stimuli
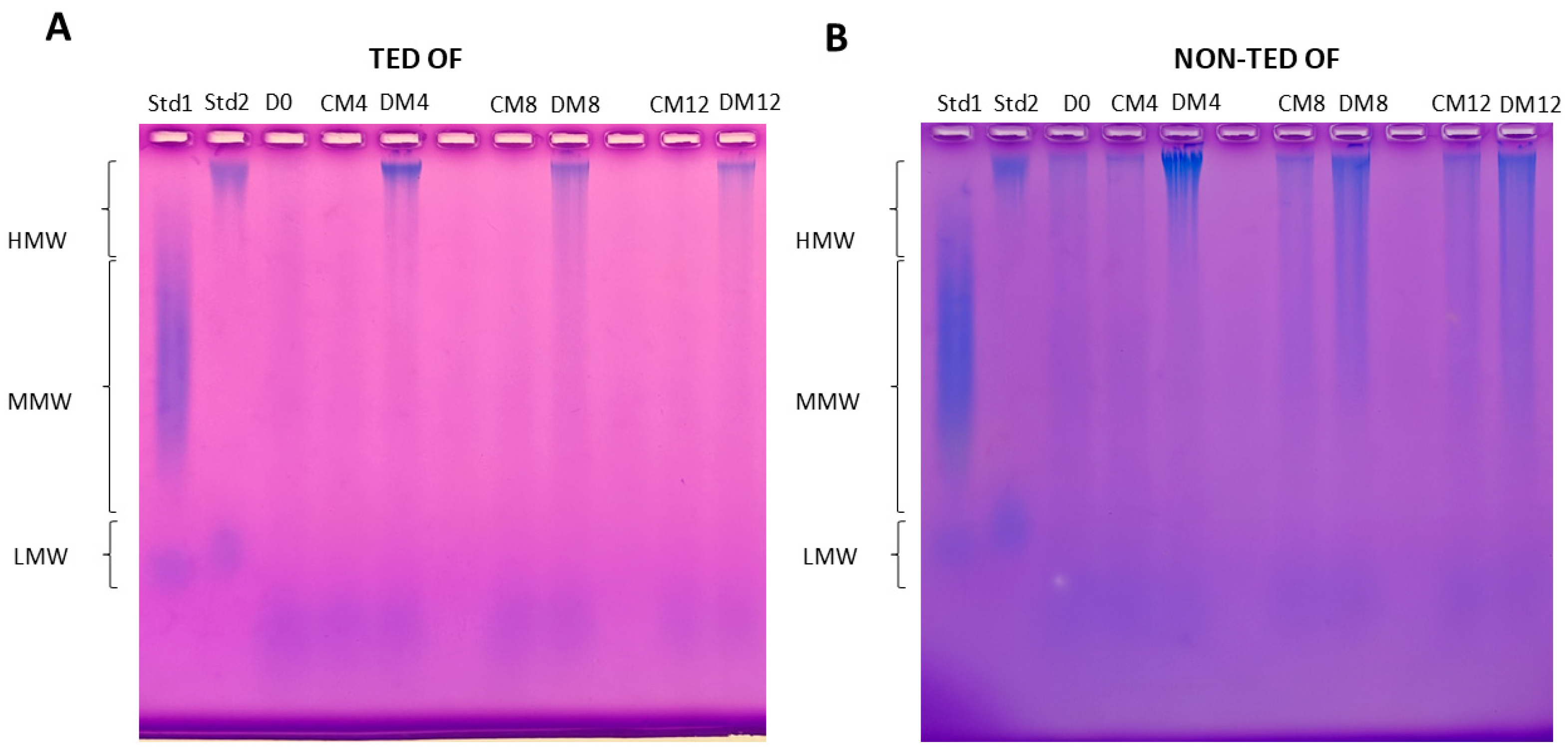
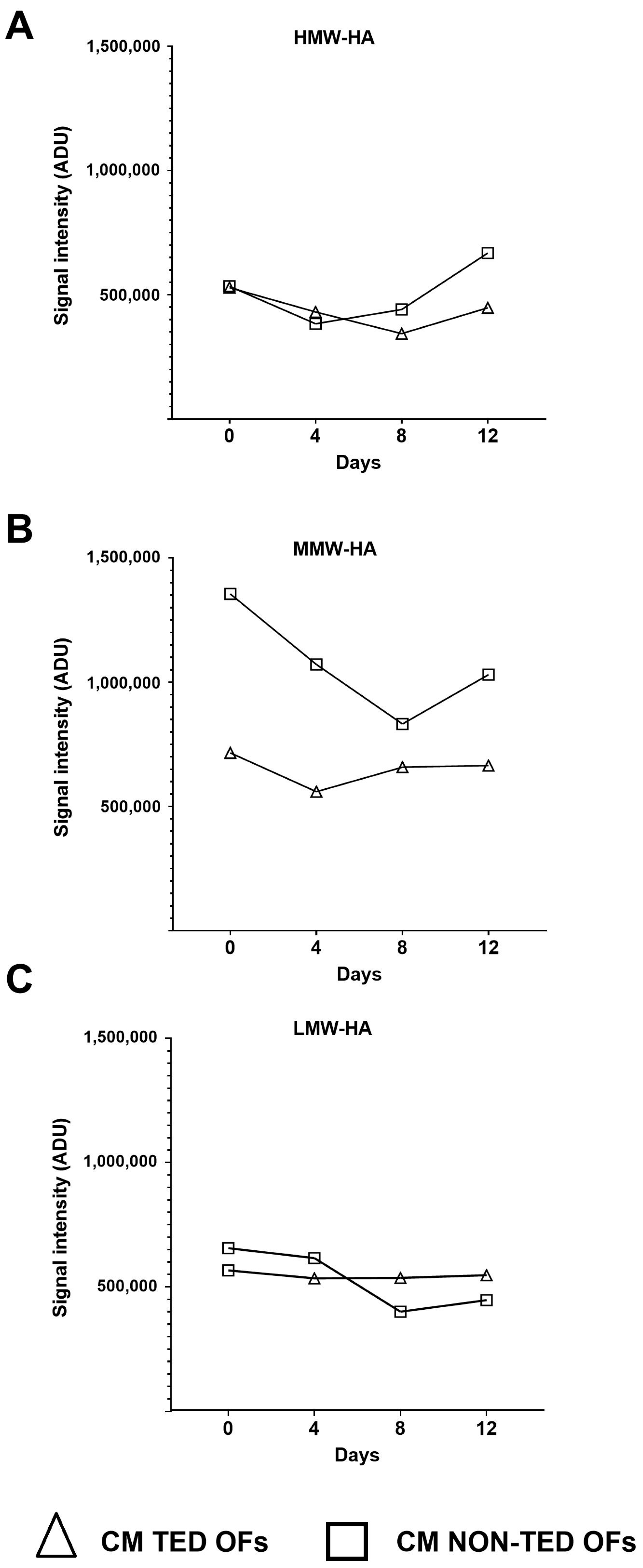
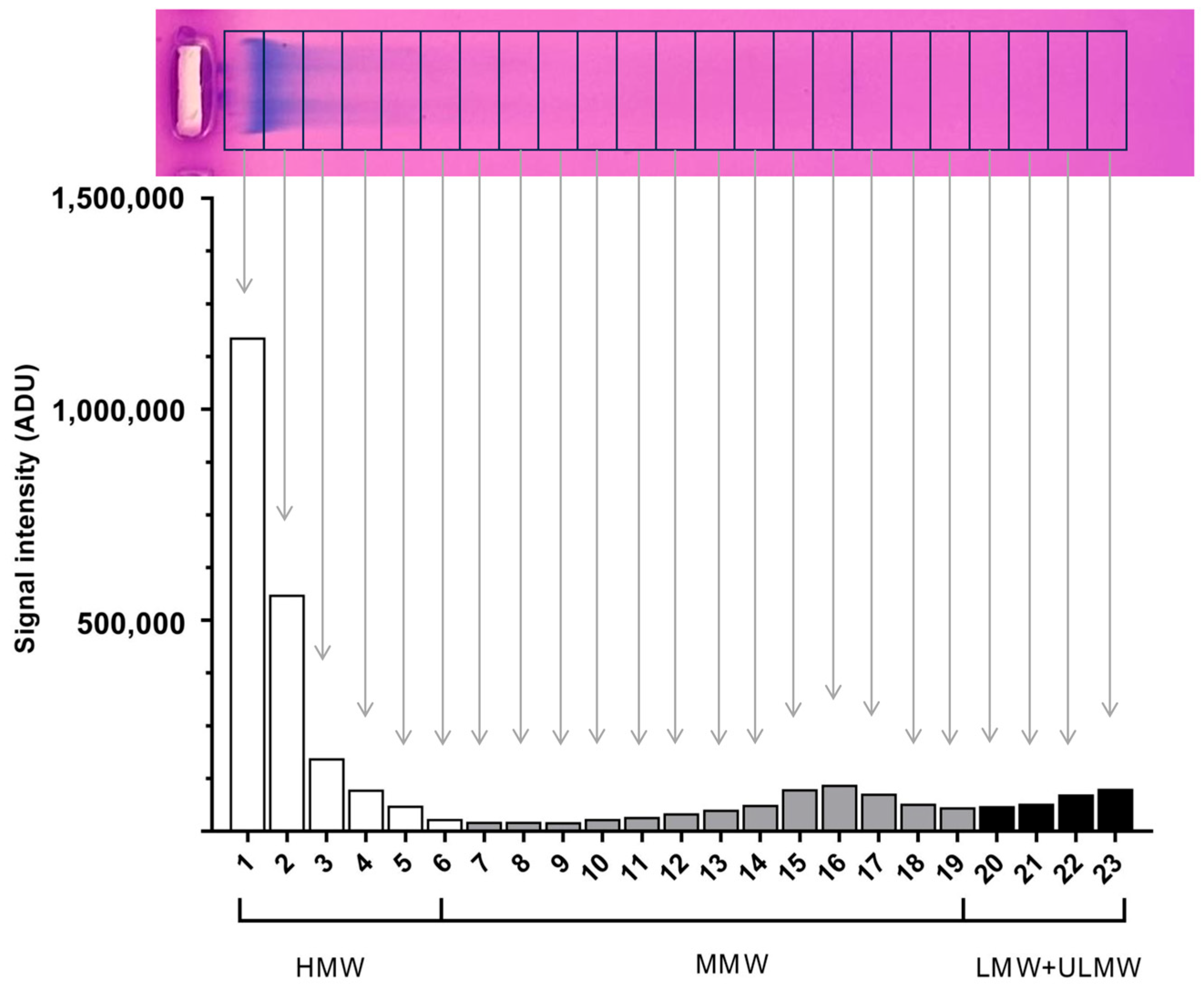
2.2. The Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by TED and Non-TED OFs Shows Different Patterns
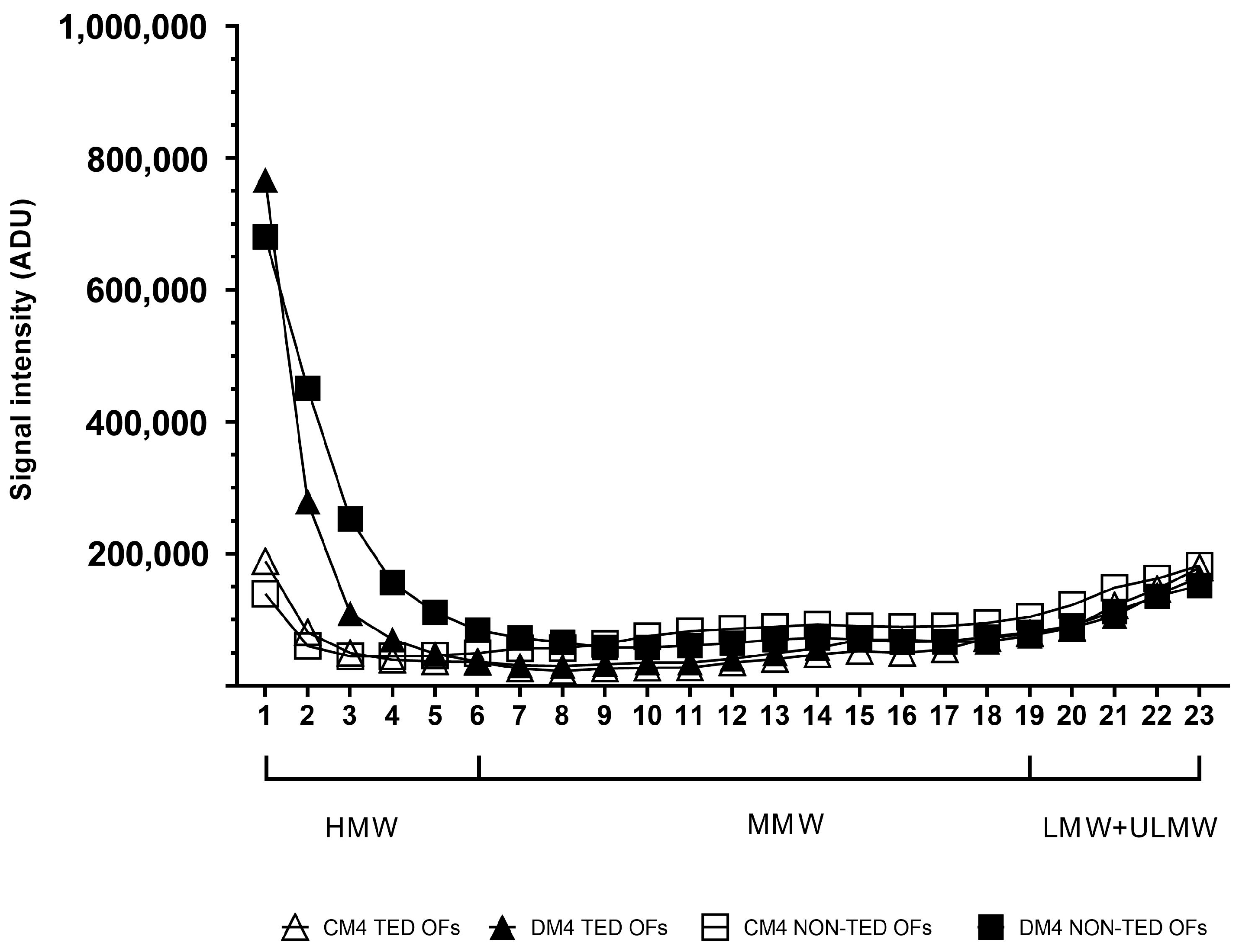
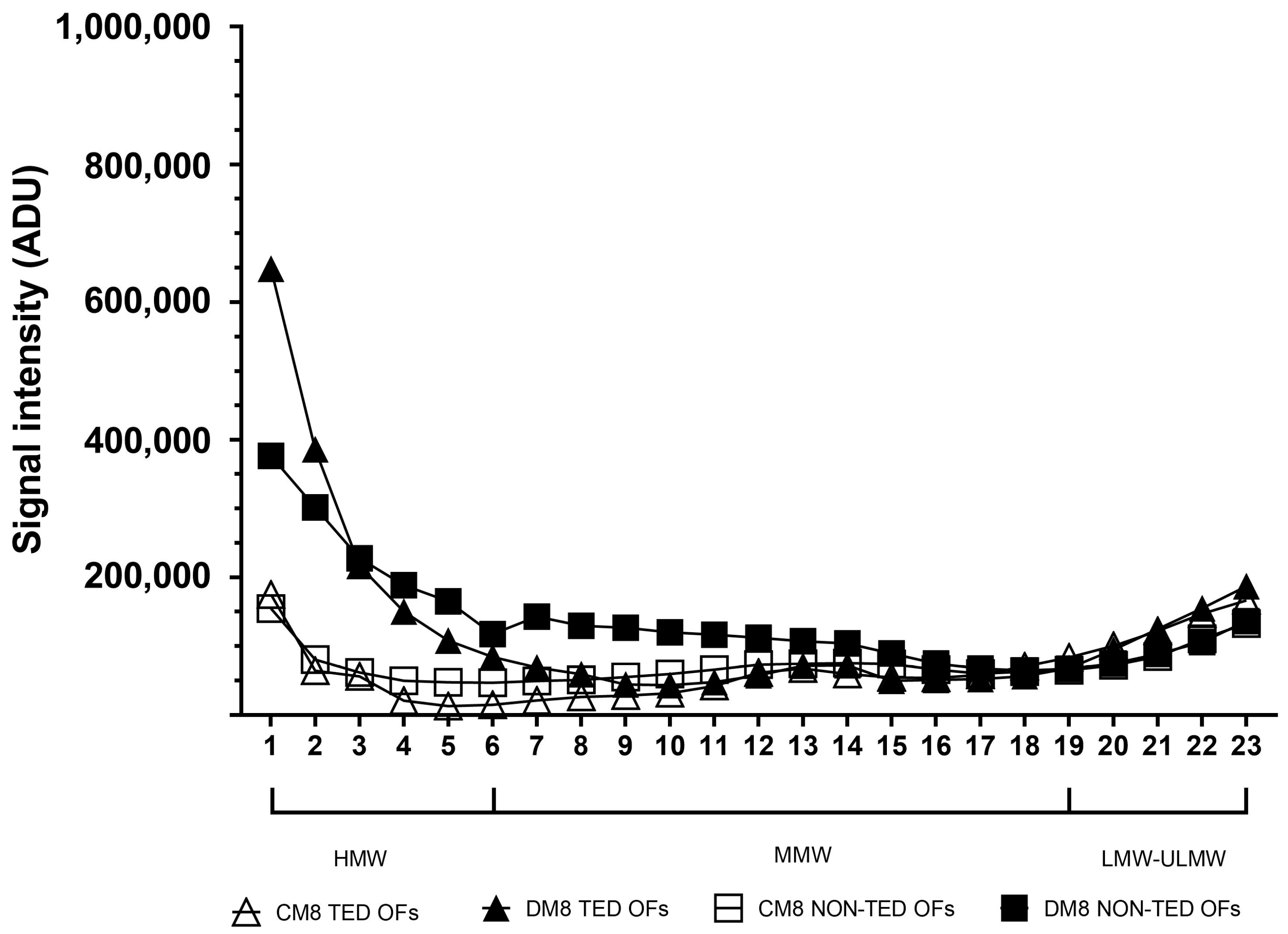
2.3. The Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced Under Adipogenic Stimuli
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Tissues and Cell Cultures
4.3. HA Measurement
4.4. HA Isolation from Cell Culture Media
4.5. HA Separation by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
4.6. Evaluation of Molecular Weight Distribution
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z. Novel perspectives on the pharmacological treatment of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1469268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Hegedus, L. Graves’ Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, R.S. Graves’ ophthalmopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Grennan-Jones, F.; Lane, C.; Rees, D.A.; Dayan, C.M.; Ludgate, M. Adipose tissue depot-specific differences in the regulation of hyaluronan production of relevance to Graves’ orbitopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chanmee, T.; Itano, N. Hyaluronan: Metabolism and Function. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandalis, S.S.; Karalis, T.; Heldin, P. Intracellular hyaluronan: Importance for cellular functions. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020, 62, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, N.; Kimata, K. Mammalian hyaluronan synthases. IUBMB Life 2002, 54, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monslow, J.; Govindaraju, P.; Puré, E. Hyaluronan—A functional and structural sweet spot in the tissue microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiprich, S.; Hofbauer, E.; Kiderlen, S.; Clausen-Schaumann, H.; Böcker, W.; Aszódi, A.; Schönitzer, V. Adhesive Properties of the Hyaluronan Pericellular Coat in Hyaluronan Synthases Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, P.; Lin, C.Y.; Kolliopoulos, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Skandalis, S.S. Regulation of hyaluronan biosynthesis and clinical impact of excessive hyaluronan production. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousou, E.; D’Angelo, M.L.; Kouvidi, K.; Vigetti, D.; Viola, M.; Nikitovic, D.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. Collagen VI and hyaluronan: The common role in breast cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 606458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, P.A.; Mirzapoiazova, T.; Guo, Y.; Sammani, S.; Mambetsariev, N.; Lennon, F.E.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Garcia, J.G.N. High-molecular-weight hyaluronan is a novel inhibitor of pulmonary vascular leakiness. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L639–L651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, C.M.; Penno, M.B.; Cowman, M.; Burdick, M.D.; Strieter, R.M.; Bao, C.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan (HA) fragments induce chemokine gene expression in alveolar macrophages. The role of HA size and CD44. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Han, W. Effects of molecular weights on the bioactivity of hyaluronic acid: A review. Carbohydr Res. 2025, 552, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, C.; Stellavato, A.; d’Agostino, M.; D’Agostino, A.; Schiraldi, C.; La Gatta, A. Hyaluronan size and concentration: Effect on key biophysical and biochemical features. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282 Pt 5, 137125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Black, K.E.; Chan-Li, Y.; Ahn, Y.H.; Cole, P.A.; Powell, J.D.; Horton, M.R. Hyaluronan fragments promote inflammation by down-regulating the anti-inflammatory A2a receptor. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargittai, I.; Hargittai, M. Molecular structure of hyaluronan: An introduction. Struct. Chem. 2008, 19, 697–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, A.; Martinussen, H.J.; Gerdin, B.; Hällgren, R. Accumulation of hyaluronan and tissue edema in experimental myocardial infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Bahn, R.S.; Gorman, C.A. Connective tissue, glycosaminoglycans, and diseases of the thyroid. Endocr. Rev. 1989, 10, 366–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, J.C.; Spaugh, B.I.; Vanderburg, J.A. Functional aspects of fibroblasts derived from the retrobulbar tissue of man. Exp. Eye Res. 1970, 10, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, C.C.; Gershengorn, M.C. A modified ELISA accurately measures secretion of high molecular weight hyaluronan (HA) by Graves’ disease orbital cells. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgoczi, E.; Orsos, I.; Molnar, Z.; Ujhelyi, B.; Steiber, Z.; Szabo, L.; Dienes, B.; Csernoch, L.; Nagy, E.V.; Katko, M. Stimulation of Piezo1 mechanosensitive channels inhibits adipogenesis in thyroid eye disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Dik, W.A.; Virakul, S.; van Steensel, L. Current perspectives on the role of orbital fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 142, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, F.R.; Katko, M.; Csiki, R.; Galgoczi, E.; Molnar, Z.; Erdei, A.; Bodor, M.; Steiber, Z.; Ujhelyi, B.; Nagy, E.V. Characteristics of Hyaluronan Metabolism During Myofibroblast Differentiation in Orbital Fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, J.; Bernecker, A.; Bakker, H.J.; Bonn, M.; Richter, R.P. Hydration dynamics of hyaluronan and dextran. Biophy.s J. 2012, 103, L10–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdin, B.; Hällgren, R. Dynamic role of hyaluronan (HYA) in connective tissue activation and inflammation. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Roh, K.; Park, J.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, M.; Kil, E.J.; Cho, M.-J.; Oh, J.S.; Byun, H.-S.; Cho, S.H. Hydrolysis of Hyaluronic Acid in Lymphedematous Tissue Alleviates Fibrogenesis via T(H)1 Cell-Mediated Cytokine Expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufveson, G.; Gerdin, B.; Larsson, E.; Laurent, T.; Wallander, J.; Wells, A.; Hällgren, R. Hyaluronic acid accumulation; the mechanism behind graft rejection edema. Transpl. Int. 1992, 5 (Suppl. 1), S688–S689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaichi, Y.; Tanitame, K.; Terada, H.; Itakura, H.; Ohno, H.; Yoneda, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Awai, K. Thyroid-associated Orbitopathy: Quantitative Evaluation of the Orbital Fat Volume and Edema Using IDEAL-FSE. Eur. J. Radiol. Open. 2019, 6, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.C.; Kabala, J.; Laitt, R.; Goddard, P.; Hoh, H.B.; Potts, M.J.; Lee, R. Magnetic resonance imaging in thyroid eye disease. Eye 1996, 10 Pt 5, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.J.; Fox, D.L.; Herdman, G.; Hsuan, J.; Kabala, J.; Goddard, P.; Potts, M.; Lee, R. Signal intensity, clinical activity and cross-sectional areas on MRI scans in thyroid eye disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2005, 56, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdei, A.; Gazdag, A.; Ujhelyi, B.; Nagy, E.B.; Berenyi, E.; Berta, E.; Steiber, Z.; Barna, S.; Mezosi, E.; Bodor, M.; et al. Non-surgical orbital decompression using diuresis in dysthyroid optic neuropathy: A case report. Eur. Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e220078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, H.; Fitchett, C.; Kozdon, K.; Jayaram, H.; Rose, G.E.; Bailly, M.; Ezra, D.G. Independent adipogenic and contractile properties of fibroblasts in Graves’ orbitopathy: An in vitro model for the evaluation of treatments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 221–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Fan, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, Y.; Prestwich, G.D.; Mascarenhas, M.M.; Garg, H.G.; Quinn, D.A.; et al. Regulation of lung injury and repair by Toll-like receptors and hyaluronan. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salagean, A.A.; Moldovan, C.A.; Slevin, M. Utilisation of High Molecular Weight and Ultra-High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan in Management of Glioblastoma. Gels 2025, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelink, T.J.; Wang, G.; van der Vlag, J.; van den Berg, B.M. The roles of hyaluronan in kidney development, physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xiao, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Yin, G.; Xu, W.; Cheng, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Kang, Z. Regulating cellular metabolism and morphology to achieve high-yield synthesis of hyaluronan with controllable molecular weights. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertli, B.; Beck-Schimmer, B.; Fan, X.; Wüthrich, R.P. Mechanisms of hyaluronan-induced up-regulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression by murine kidney tubular epithelial cells: Hyaluronan triggers cell adhesion molecule expression through a mechanism involving activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and activating protein-1. J Immunol. 1998, 161, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan: From extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.G.; Lee, C.W.; Park, J.W.; Cui, Y.; Park, Y.S.; Shin, W.S. Enzymatic fragments of hyaluronan inhibit adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Hernández, L.A.; Camacho-Ruíz, R.M.; Arriola-Guevara, E.; Padilla-Camberos, E.; Kirchmayr, M.R.; Corona-González, R.I.; Guatemala-Morales, G.M. Validation of an Analytical Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Hyaluronic Acid Concentration and Molecular Weight by Size-Exclusion Chromatography. Molecules 2021, 26, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, P.S.; Maziarz, E.P.; Liu, X.M. Detailed characterization of hyaluronan using aqueous size exclusion chromatography with triple detection and multiangle light scattering detection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K.; Chen, C.C.; Pandya, M.; Yuan, H.; Ramkishun, D.; LoBello, J.; Bhilocha, S.; Russell-Puleri, S.; Skendaj, E.; Mijovic, J.; et al. Improved agarose gel electrophoresis method and molecular mass calculation for high molecular mass hyaluronan. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, M.K.; Lee, H.G.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; McCarthy, J.B.; Turley, E.A. The Content and Size of Hyaluronan in Biological Fluids and Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K. Methods for Hyaluronan Molecular Mass Determination by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1952, 91–102. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galgoczi, E.; Katko, M.; Borbely, S.; Orsos, I.; Molnar, Z.; Ujhelyi, B.; Steiber, Z.; Nagy, E.V. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Reveals the Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by Orbital Fibroblasts. Gels 2025, 11, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060406
Galgoczi E, Katko M, Borbely S, Orsos I, Molnar Z, Ujhelyi B, Steiber Z, Nagy EV. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Reveals the Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by Orbital Fibroblasts. Gels. 2025; 11(6):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060406
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalgoczi, Erika, Monika Katko, Sara Borbely, Istvan Orsos, Zsanett Molnar, Bernadett Ujhelyi, Zita Steiber, and Endre V. Nagy. 2025. "Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Reveals the Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by Orbital Fibroblasts" Gels 11, no. 6: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060406
APA StyleGalgoczi, E., Katko, M., Borbely, S., Orsos, I., Molnar, Z., Ujhelyi, B., Steiber, Z., & Nagy, E. V. (2025). Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Reveals the Molecular Weight Distribution of Hyaluronan Produced by Orbital Fibroblasts. Gels, 11(6), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060406







