Cellulose-Based Pickering Emulsion-Templated Edible Oleofoam: A Novel Approach to Healthier Solid-Fat Replacers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
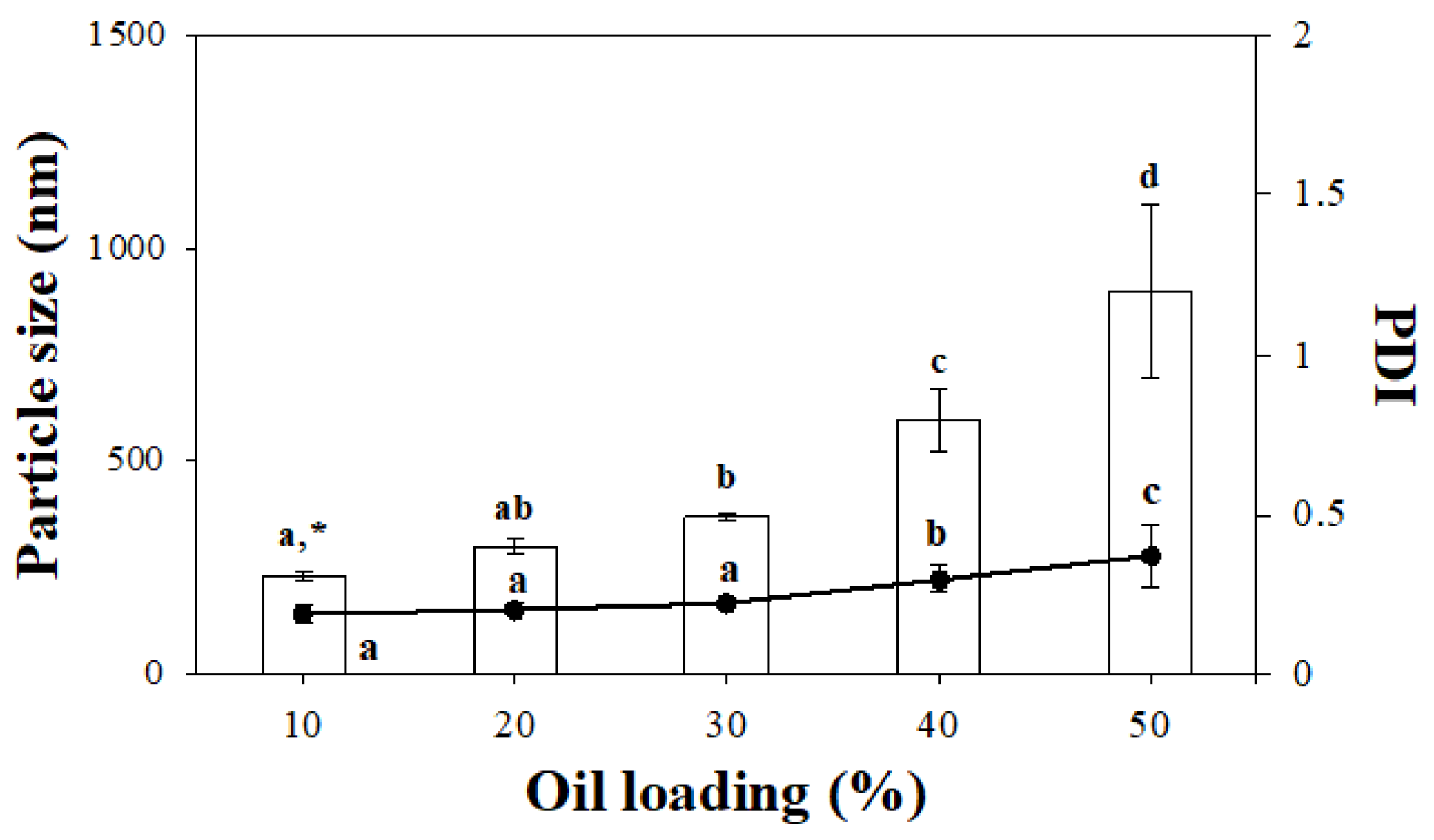
2.1. Mean Particle Diameter and Polydispersity Index (PDI) of the Cellulose Particle-Based Pickering Emulsions (CP-PEs)
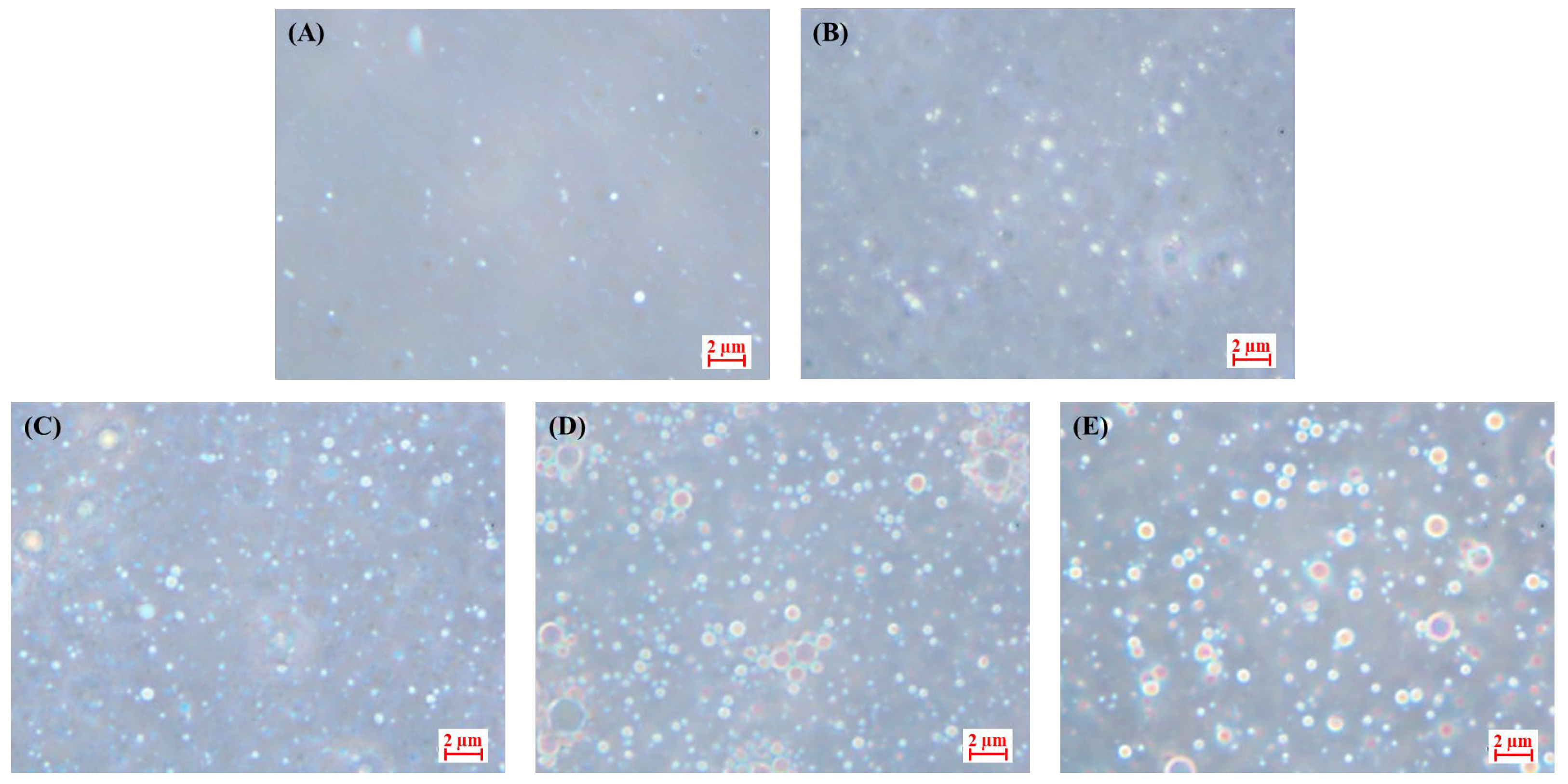
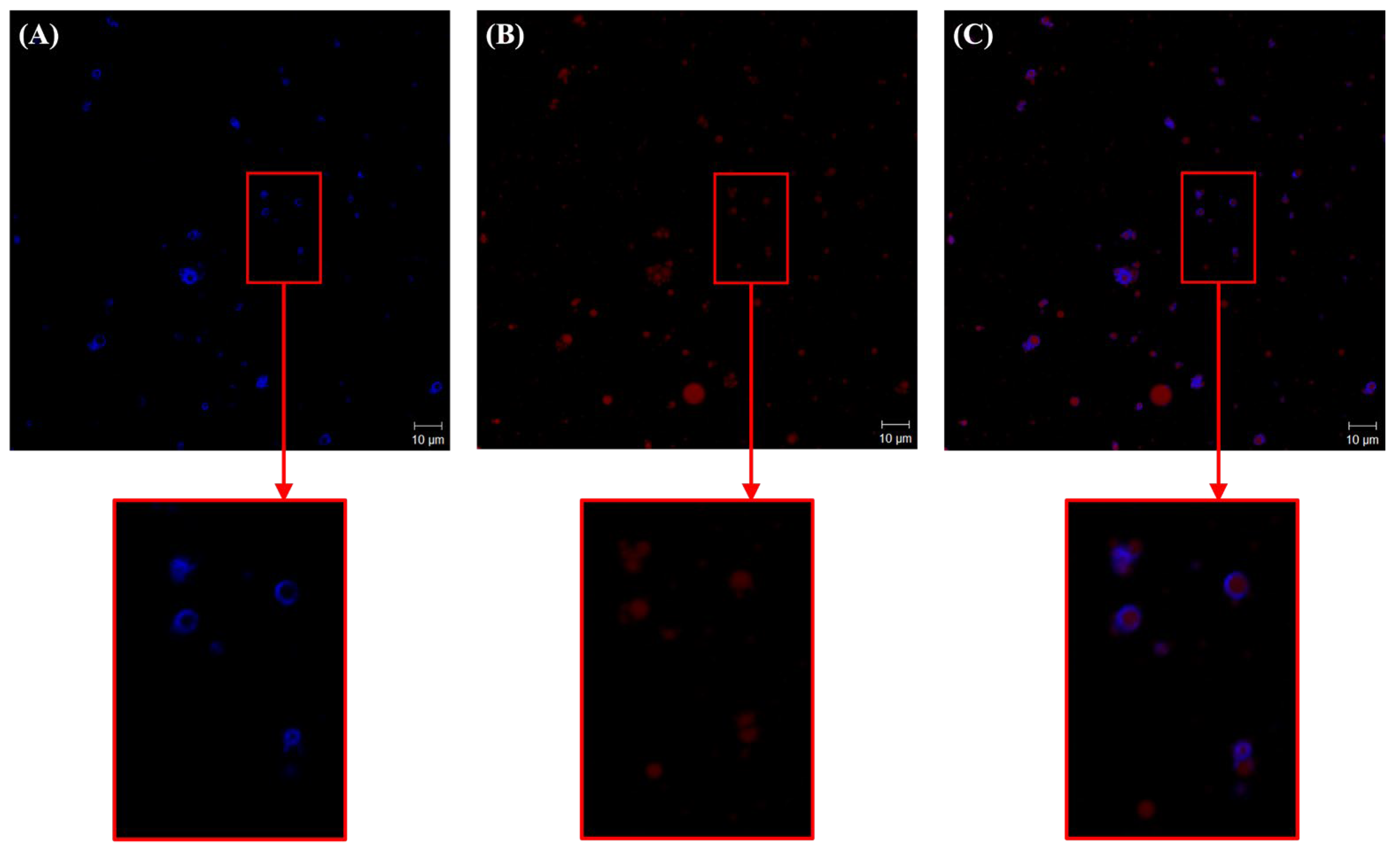
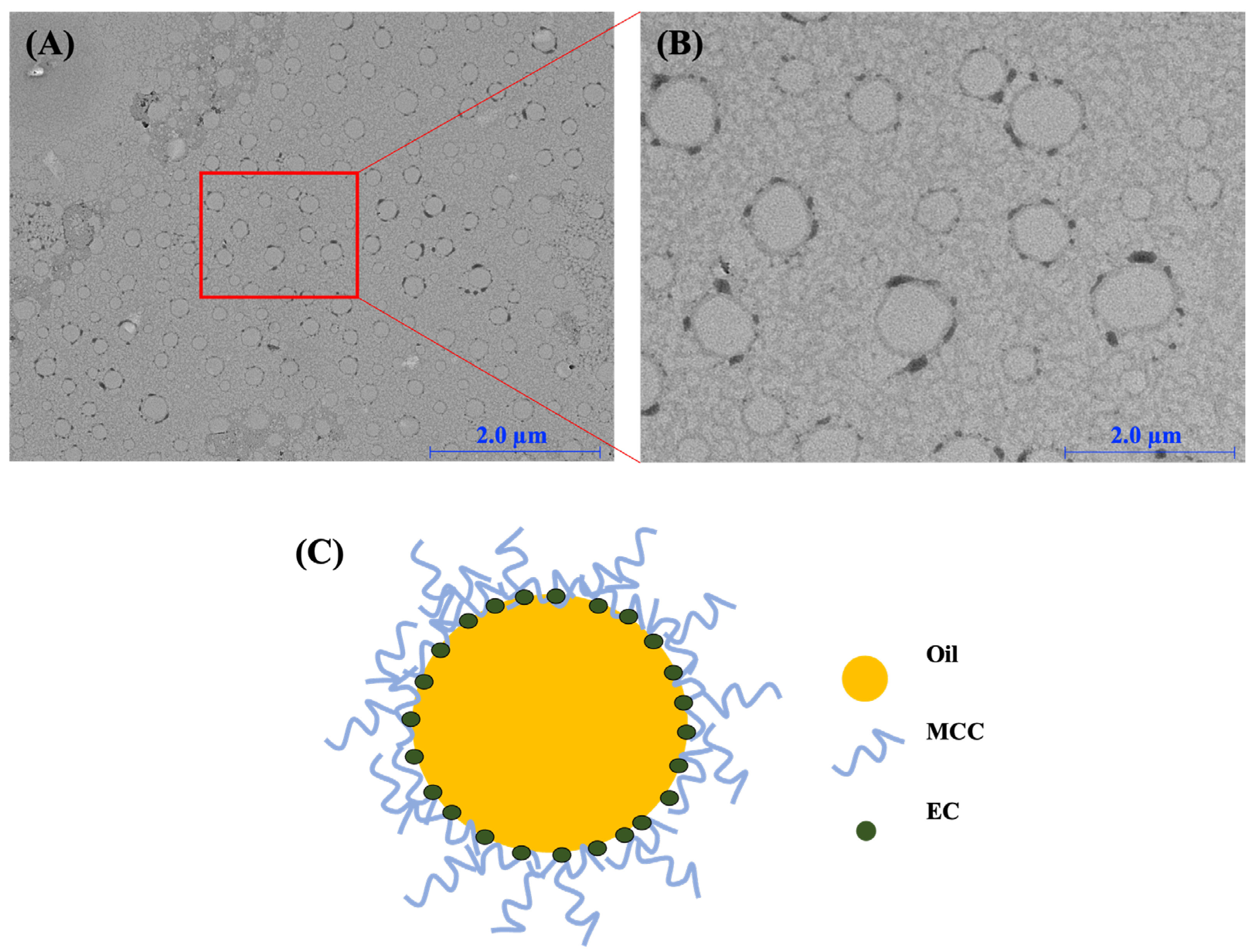
2.2. Morphological Characterization of the CP-PEs
2.2.1. Optical Images of the CP-PEs
2.2.2. Structure of Oil and Cellulose Particles in the CP-PEs
2.2.3. Structure of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) and Ethyl Cellulose (EC) in the CP-PEs
2.3. Characterization of the Cellulose Particle-Based Edible Oleofoams (CP-EOs)
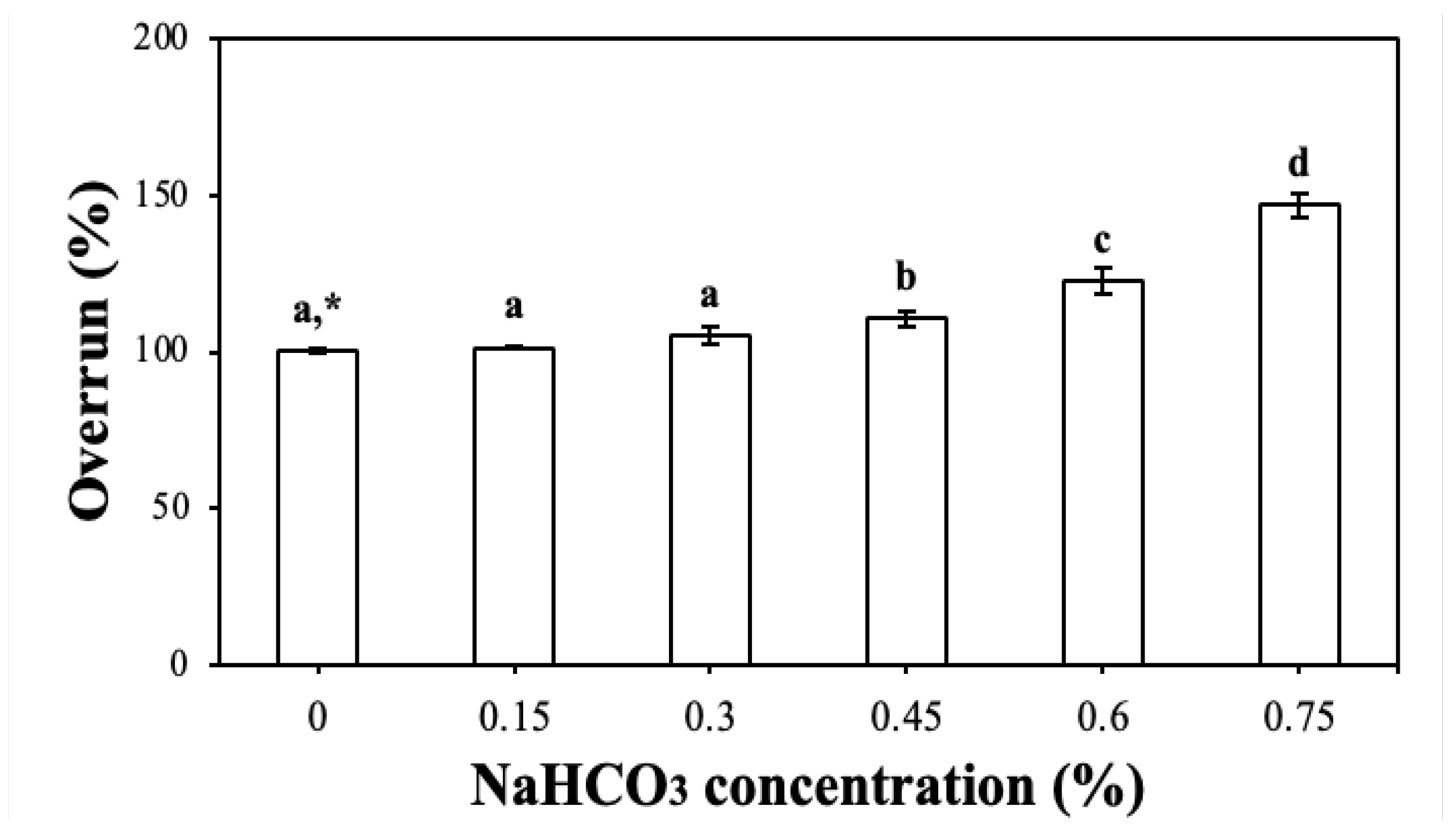
2.3.1. Overrun of the CP-EOs with Different Concentrations of NaHCO3
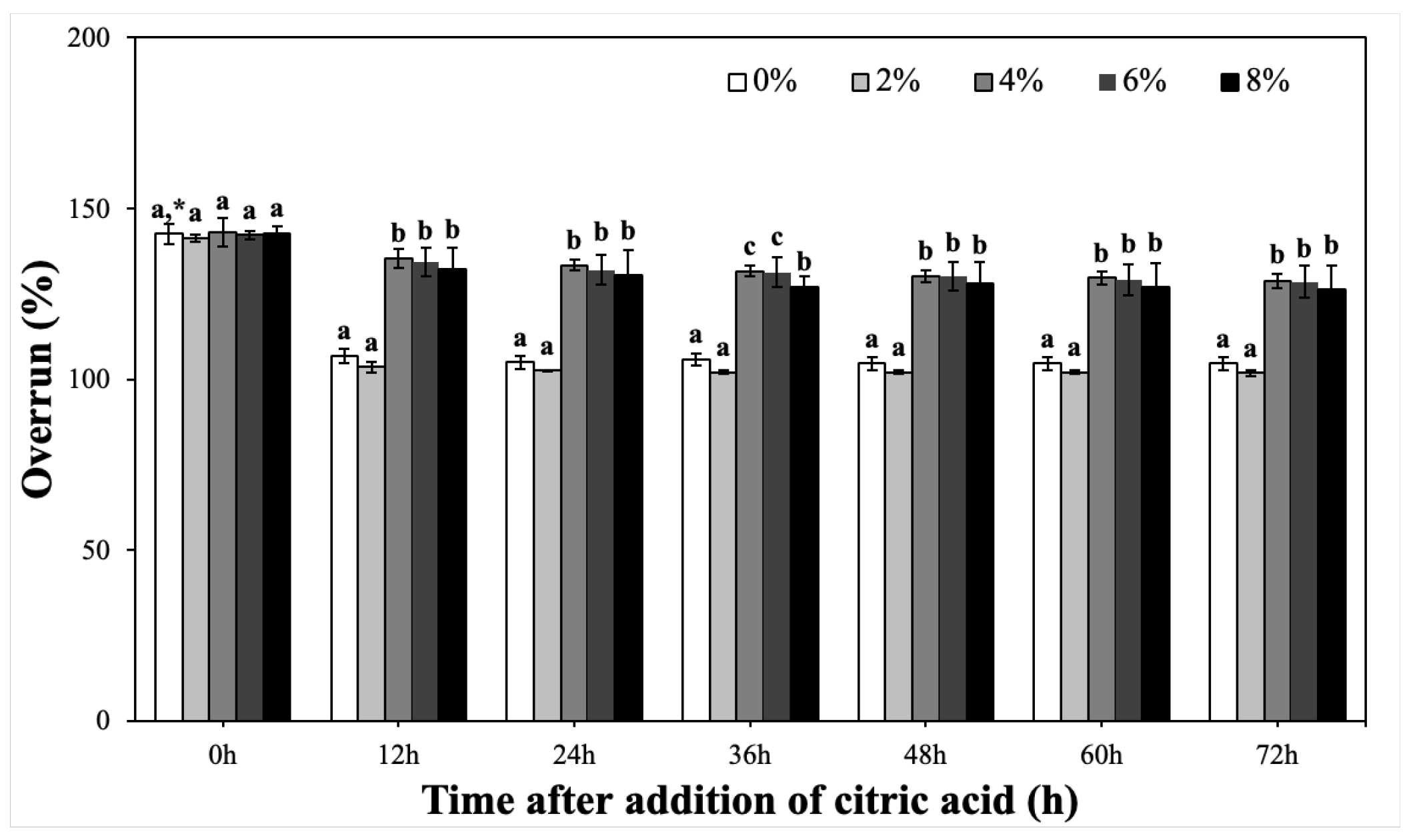
2.3.2. Overrun and Volumetric Stability of CP-EOs with Different Concentrations of Glyceryl Monostearate (GMS)
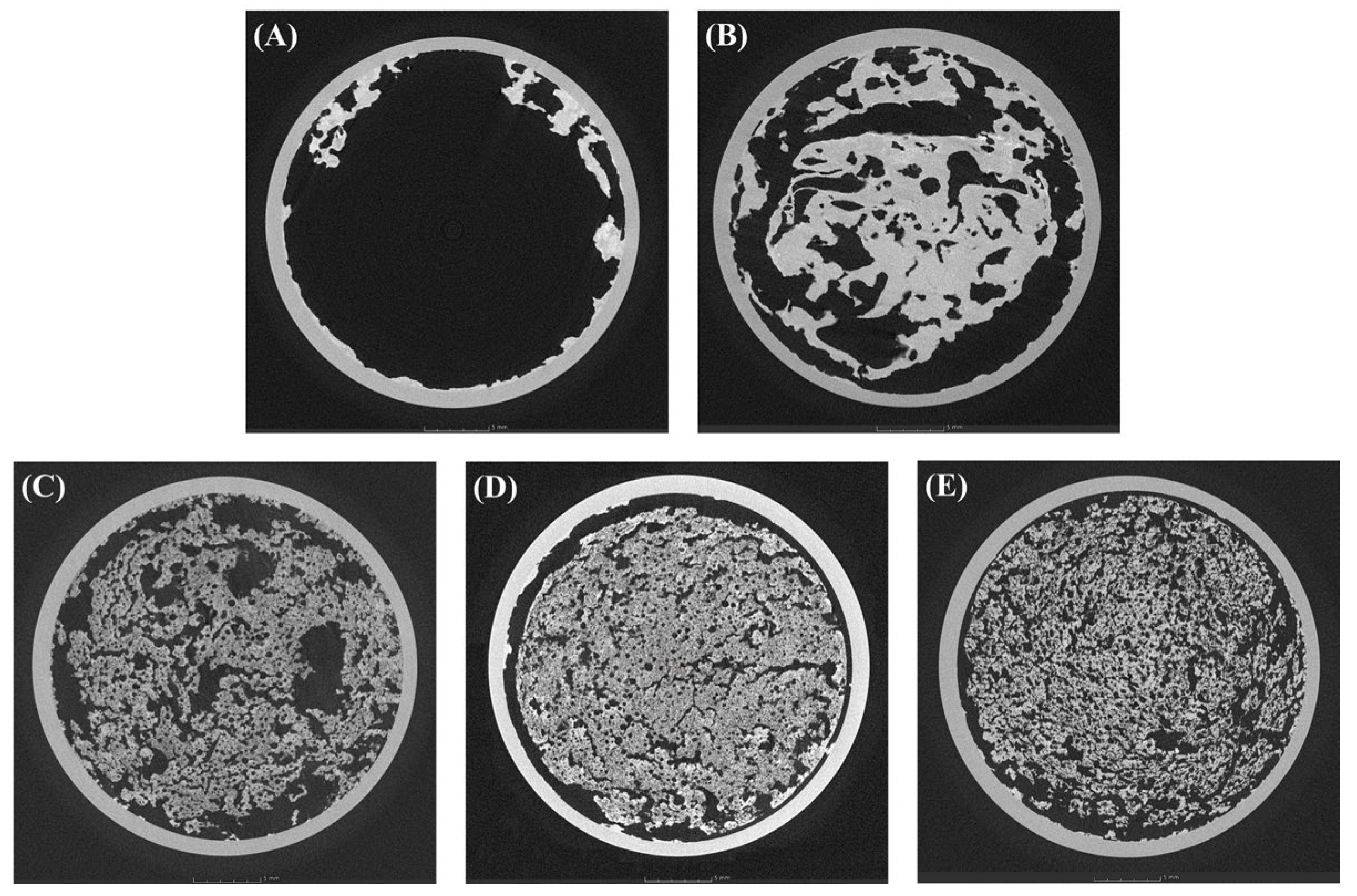
2.3.3. Microstructure of the CP-EOs
2.3.4. Rheological Properties of the CP-EOs
2.3.5. Melting Parameters of the CP-EOs
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of CP-PEs
4.3. Mean Droplet Size and PDI of the CP-PEs
4.4. Morphological Characterization of the CP-PEs
4.4.1. Optical Microscopy
4.4.2. Confocal Light Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
4.4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.5. Preparation of CP-EOs
4.6. Characterization of the CP-EOs
4.6.1. Overrun of the CP-EOs
4.6.2. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Analysis
4.6.3. Rheological Property of the CP-EOs
4.6.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
4.7. SPSS Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.J.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Fabrication and Application of Turmeric Extract-Incorporated Oleogels Structured with Xanthan Gum and Soy Lecithin by Emulsion Template. Gels 2024, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yi, B.R.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H. Oxidative Stability of Solid Fats Containing Ethylcellulose Determined Based on the Headspace Oxygen Content. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Vitamin E-Fortified Emulsion-Templated Oleogels Structured with Xanthan Gum and Soybean Lecithin and Their Application in Pound Cakes. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Krauss, R.M. Public Health Guidelines Should Recommend Reducing Saturated Fat Consumption as Much as Possible: YES. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A. Mixing Bubbles and Drops to Make Foamed Emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, C.; Emond, E.; Schneider, S.; Dalmazzone, C.; Bergeron, V. Non-Aqueous and Crude Oil Foams. Oil Gas Sci. 2014, 69, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Recent Developments in Food Foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, K.P.; Frank, S.G. Microcrystalline Cellulose Stabilized Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1986, 7, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ao, F.; Ge, X.; Shen, W. Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions: Preparation, Stabilization and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsor-Atindana, J.; Chen, M.; Goff, H.D.; Zhong, F.; Sharif, H.R.; Li, Y. Functionality and Nutritional Aspects of Microcrystalline Cellulose in Food. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Ye, Y.; Abid, M.; Jabbar, S.; Wang, P.; Zeng, X.; Wu, T. Rheological Properties of an Amorphous Cellulose Suspension. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, K.; Winnicka, K. Ethylcellulose-a Pharmaceutical Excipient with Multidirectional Application in Drug Dosage Forms Development. Materials 2019, 12, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.d.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Kos Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; Marcon, F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Ethyl Cellulose for All Animal Species. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6210. [Google Scholar]
- Nurhadi, B.; Sulaeman, M.Y. Mahani Antioxidant Stability of Vitamin C in Double Pickering Emulsion W/O/W with Microcrystalline Cellulose. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Marangoni, A.G.; Davidovich-pinhas, M. Ethylcellulose Oleogels; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780128142707. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. Improving Emulsion Formation, Stability and Performance Using Mixed Emulsifiers: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 251, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Garcia, C.V.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Improvement of Curcuminoid Bioaccessibility from Turmeric by a Nanostructured Lipid Carrier System. Food Chem. 2018, 251, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Calderon, F.; Thivilliers, F.; Schmitt, V. Structured Emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 12, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, R.; Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Emulsions Stabilised Solely by Colloidal Particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 503–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Hong, S.J.; Garcia, C.V.; Lee, S.B.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Stability Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Nanoemulsion Powder after Application in Milk as a Food Model. J. Food Eng. 2019, 259, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; McClements, D.J. Impact of Electrostatic Interactions on Lecithin-Stabilized Model O/W Emulsions. Food Biophys. 2018, 13, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Dai, H.; Ma, L.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Properties of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Food-Grade Gelatin Nanoparticles: Influence of the Nanoparticles Concentration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, K.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, P. Fabrication of Starch-Based Nanospheres to Stabilize Pickering Emulsion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkuratipakorn, T.; Sriprai, A.; Tantrawong, S.; Chaiyasit, W.; Singkhonrat, J. Fabrication and Characterization of Rice Bran Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Cellulose Nanocrystals. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, F.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Li, D.; Huang, Q. Exploiting the Robust Network Structure of Zein/Low-Acyl Gellan Gum Nanocomplexes to Create Pickering Emulsion Gels with Favorable Properties. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Lv, S.; Xiang, W.; Huan, S.; McClements, D.J.; Rojas, O.J. Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsions via Microfluidization with Cellulose Nanocrystals: 1. Formation and Stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naduparambath, S.; Jinitha, T.V.; Shaniba, V.; Sreejith, M.P.; Balan, A.K.; Purushothaman, E. Isolation and Characterisation of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Sago Seed Shells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Z. Ethyl Cellulose Nanodispersions as Stabilizers for Oil in Water Pickering Emulsions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Tan, Y.; Meng, Z. Microstructure Evolution and Partial Coalescence in the Whipping Process of Oleofoams Stabilized by Monoglycerides. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, D.Z.; Murith, M.; Godefroid, J.; Pelloux, C.; Deyber, H.; Schafer, O.; Breton, O. Oleofoams: Properties of Crystal-Coated Bubbles from Whipped Oleogels-Evidence for Pickering Stabilization. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Garvey, E.J.; Vieira, J. Whipped Oil Stabilised by Surfactant Crystals. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2621–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.M.; Mougeot, E. Creation and Characterisation of Aerated Food Products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B. Effects of Crystallisation of Native Phytosterols and Monoacylglycerols on Foaming Properties of Whipped Oleogels. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puşcaş, A.; Mureşan, V. The Feasibility of Shellac Wax Emulsion Oleogels as Low-Fat Spreads Analyzed by Means of Multidimensional Statistical Analysis. Gels 2022, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metilli, L.; Lazidis, A.; Francis, M.; Marty-Terrade, S.; Ray, J.; Simone, E. The Effect of Crystallization Conditions on the Structural Properties of Oleofoams Made of Cocoa Butter Crystals and High Oleic Sunflower Oil. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 1562–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Erazo, E.M.; Bosqui, K.; Rabelo, R.S.; Kurozawa, L.E.; Hubinger, M.D. High Internal Phase Emulsions (HIPE) Using Pea Protein and Different Polysaccharides as Stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf, M.; Naji-Tabasi, S.; Beig-Babaei, A.; Moros, J.E.; Carrillo, M.C.S.; Tenorio-Alfonso, A. Developing edible oleogels structure prepared with emulsion-template approach based on soluble biopolymer complex. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.Y.; Ahn, J.; Kwak, H.S. Functional Properties of Cholesterol-Removed Compound Whipping Cream by Palm Oil. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 17, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Santana, M.; Cagampang, G.B.; Nieves, C.; Cedeño, V.; MacIntosh, A.J. Use of High Oleic Palm Oils in Fluid Shortenings and Effect on Physical Properties of Cookies. Foods 2022, 11, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample (GMS Concentrations) | Tm (°C) | Onset Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsalted butter | 14.07 ± 0.06 a,* | 10.18 ± 0.01 a | 10.10 ± 0.87 d |
| CP-EOs (0%) | ND ** | ND | ND |
| CP-EOs (2%) | 43.40 ± 0.32 b | 39.96 ± 0.72 b | 1.32 ± 0.27 a |
| CP-EOs (4%) | 47.37 ± 0.01 c | 40.54 ± 0.12 b | 5.43 ± 0.58 b |
| CP-EOs (6%) | 48.02 ± 0.11 d | 40.02 ± 0.20 b | 8.44 ± 0.26 c |
| CP-EOs (8%) | 48.90 ± 0.11 e | 40.09 ± 0.20 b | 12.71 ± 0.54 e |
| Sample (Oil Concentrations) | Oil Phase | Aqueous Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSO (g) | MCC (g) | EC (g) | DW (g) | PetOH (g) | |
| CP-PEs (10%) | 3 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 12.96 | 12.96 |
| CP-PEs (20%) | 6 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 11.52 | 11.52 |
| CP-PEs (30%) | 9 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 10.08 | 10.08 |
| CP-PEs (40%) | 12 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 8.64 | 8.64 |
| CP-PEs (50%) | 15 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 7.20 | 7.20 |
| Sample (NaCO3 Concentrations) | Oil Phase | Aqueous Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSO (g) | GMS (g) | MCC (g) | EC (g) | DW (g) | PetOH (g) | NaHCO3 (g) | |
| CP-EOs (0.00%) | 10.2 | 1.8 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 8.640 | 8.640 | 0.000 |
| CP-EOs (0.15%) | 8.595 | 0.045 | |||||
| CP-EOs (0.30%) | 8.550 | 0.090 | |||||
| CP-EOs (0.45%) | 8.505 | 0.135 | |||||
| CP-EOs (0.60%) | 8.460 | 0.180 | |||||
| CP-EOs (0.75%) | 8.415 | 0.225 | |||||
| Sample (GMS Concentrations) | Oil Phase | Aqueous Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSO (g) | GMS (g) | MCC (g) | EC (g) | DW (g) | PetOH (g) | NaHCO3 (g) | |
| CP-EOs (0%) | 12.0 | 0.0 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 8.415 | 8.640 | 0.225 |
| CP-EOs (2%) | 11.4 | 0.6 | |||||
| CP-EOs (4%) | 10.8 | 1.2 | |||||
| CP-EOs (6%) | 10.2 | 1.8 | |||||
| CP-EOs (8%) | 9.6 | 2.4 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.M.; Hong, S.J.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Cellulose-Based Pickering Emulsion-Templated Edible Oleofoam: A Novel Approach to Healthier Solid-Fat Replacers. Gels 2025, 11, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060403
Lee SM, Hong SJ, Shin GH, Kim JT. Cellulose-Based Pickering Emulsion-Templated Edible Oleofoam: A Novel Approach to Healthier Solid-Fat Replacers. Gels. 2025; 11(6):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sang Min, Su Jung Hong, Gye Hwa Shin, and Jun Tae Kim. 2025. "Cellulose-Based Pickering Emulsion-Templated Edible Oleofoam: A Novel Approach to Healthier Solid-Fat Replacers" Gels 11, no. 6: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060403
APA StyleLee, S. M., Hong, S. J., Shin, G. H., & Kim, J. T. (2025). Cellulose-Based Pickering Emulsion-Templated Edible Oleofoam: A Novel Approach to Healthier Solid-Fat Replacers. Gels, 11(6), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060403






