Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Advanced Hydrogels as Tools for Gastrointestinal Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Current GI Diagnostics and Possibilities of Novel Tools’ Integration
3.1. Biomarkers
3.2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers In Vivo
4. Perspectives of MIP-Based Sensors
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | Alpha-Fetoprotein |
| ALT | Alanine Transaminase |
| ANCAs | Anti-neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies |
| ASCAs | Antifungal Brewer Yeast Antibodies |
| AST | Aspartate Transaminase |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ctDNA | Circulating Tumor DNA |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| FIT | Fecal Immunochemical Test |
| GC | Gastric Cancer |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-Gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LF | Lactoferrin |
| MIP | Molecularly Imprinted Polymer |
| miR | MicroRNA |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| Omp-C | Escherichia coli Outer Membrane Porin C |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate Kinase M2 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| Tregs | Regulatory T Cells |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| VOCs | Volatile Organic Compounds |
References
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chase, R.C.; Li, T.; Ramai, D.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Antwi, S.O.; Keaveny, A.P.; Pang, M. Global Burden of Digestive Diseases: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Diseases Study, 1990 to 2019. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 773–783.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Peptic Ulcer Disease Burden, Trends, and Inequalities in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Population-Based Study. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 17562848231210375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, F.; Wen, H. Global Incidence and Prevalence of Gastritis and Duodenitis from 1990 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, W.L.; Cai, M.H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Li, M.T.; Yan, X.L.; Xue, L.W.; Hong, L.; Tang, M.Y. Burden of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makharia, G.K.; Singh, P.; Catassi, C.; Sanders, D.S.; Leffler, D.; Ali, R.A.R.; Bai, J.C. The Global Burden of Coeliac Disease: Opportunities and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 313–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, C.; An, J.; Yang, Z.; Mo, X. The Global, Regional, and National Patterns of Change in the Burden of Non-Malignant Upper Gastrointestinal Diseases from 1990 to 2019 and the Forecast for the next Decade. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 111, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; Lund, J.L.; Dellon, E.S.; Williams, J.L.; Jensen, E.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Barritt, A.S.; Lieber, S.R.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2018. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 254–272.e11. [Google Scholar]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; Jensen, E.T.; Kim, H.P.; Egberg, M.D.; Lund, J.L.; Moon, A.M.; Pate, V.; Barnes, E.L.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2021. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 621–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Tackling the Burden of Digestive Disorders in Europe. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 95.
- Mathews, S.C.; Izmailyan, S.; Brito, F.A.; Yamal, J.M.; Mikhail, O.; Revere, F.L. Prevalence and Financial Burden of Digestive Diseases in a Commercially Insured Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1480–1487.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, A.; Silva, M.; Pereira, P.; Macedo, G. Biopsies in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: When and How. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 23, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.X.; Le Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, C.C. Appropriate Use of Endoscopy in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases: Up-to-Date Indications for Primary Care Providers. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2011, 53, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, D.L.; Culp, W.T.N. Chapter 136—Minimally Invasive Procedures. In Small Animal Critical Care Medicine, 2nd ed.; Silverstein, D.C., Hopper, K., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 715–721. ISBN 978-1-4557-0306-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, R.; Turnbull, D.; Haboubi, H.; Leeds, J.S.; Healey, C.; Hebbar, S.; Collins, P.; Jones, W.; Peerally, M.F.; Brogden, S.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines on Sedation in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gut 2023, 73, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D. The Utility of Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1817–1826.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskandar, H.N.; Ciorba, M.A. Biomarkers in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Practices and Recent Advances. Transl. Res. 2012, 159, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, G.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. Serum Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Colorectal Cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and Mortality Estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, J.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Cotillard, A.; Pichaud, M.; McDonald, D.; Song, S.J.; Knight, R.; Veiga, P.; Derrien, M. Global Branches and Local States of the Human Gut Microbiome Define Associations with Environmental and Intrinsic Factors. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, K.; Ma, W.; Li, D.; Mo, T.; Liu, Q. The Gut Microbiome in Human Health and Disease—Where Are We and Where Are We Going? A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1018594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvenyte, G.; Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Plausinaitis, D.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Recognition of Biomarkers of Certain Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 228, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel-Fiuza, M.F.; Muller, G.C.; Campos, D.M.S.; do Socorro Silva Costa, P.; Peruzzo, J.; Bonamigo, R.R.; Veit, T.; Vianna, F.S.L. Role of Gut Microbiota in Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1098386. [Google Scholar]
- Novis, C.L.; Wahl, E.; Camacho, E.; Aure, M.A.; Mahler, M.; Nandakumar, V. Performance Assessment of a Novel Multianalyte Methodology for Celiac Disease Biomarker Detection and Evaluation of the Serology-Alone Criteria for Biopsy-Free Diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2023, 147, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Conducting Polymers in the Design of Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications (Review). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 215, 114739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Development of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Phase Boundaries for Sensors Design (Review). Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 305, 102693. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole-Based Synthetic Receptor for Direct Detection of Bovine Leukemia Virus Glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based Affinity Sensors (Review). Polymers 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimer, S.A.; Booij, B.B.; Tobert, G.; Hebbeler, A.; Oloo, P.; Brangel, P.; L’Azou Jackson, M.; Jarman, R.; Craig, D.; Avumegah, M.S.; et al. Rapid Diagnostic Test: A Critical Need for Outbreak Preparedness and Response for High Priority Pathogens. BMJ Glob. Health 2024, 9, e014386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Chen, C.F.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanavicius, A. Biosensors for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Brazys, E.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ciplys, E.; Juozapaitis, M.; Slibinskas, R.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole Based Sensor for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 403, 139581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobysh, M.; Ratautaite, V.; Brazys, E.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly Imprinted Composite-Based Biosensor for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 251, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvenyte, G.; Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Ramanavicius, A.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Determination of Cancer Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liustrovaite, V.; Pogorielov, M.; Boguzaite, R.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Pilvenyte, G.; Holubnycha, V.; Korniienko, V.; Diedkova, K.; Viter, R.; et al. Towards Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole for the Detection of Bacteria—Listeria Monocytogenes. Polymers 2023, 15, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, A. Affinity Sensors for the Diagnosis of Covid-19. Micromachines 2021, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Tsujinaka, S.; Miura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Shibata, C. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, Surveillance, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chauhan, A.; Ranjan, A.; Mathkor, D.M.; Haque, S.; Ramniwas, S.; Tuli, H.S.; Jindal, T.; Yadav, V. Emerging Challenges in Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications for Pathogenic Microorganisms, Novel Antibiotics, and Their Impact on Sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1403168. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J.C.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Gastrointestinal Disease. In Pathophysiology of Disease: An Introduction to Clinical Medicine, 7th ed.; Hammer, G.D., McPhee, S.J., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, K.M.; Kim, J.; Bahnsen, K.; Heuckeroth, R.O.; Thaiss, C.A. Environmental Perception and Control of Gastrointestinal Immunity by the Enteric Nervous System. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, C.; Pande, B.; Sahu, T.; Sahithi, L.S.; Verma, H.K. Revolutionizing Gastrointestinal Disorder Management: Cutting-Edge Advances and Future Prospects. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, L. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Evidence-Based Medicine. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6759–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuy, D.S.; Wi, R.S.; Tadros, M. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Current Landscape of Diagnostic Guidelines and Therapeutic Strategies. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 786–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Epitope-Imprinted Biomaterials with Tailor-Made Molecular Targeting for Biomedical Applications. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 45, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabaleiro-Lago, C.; Hasterok, S.; Gjörloff Wingren, A.; Tassidis, H. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Disease-Related Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, K.; Murti, B.T.; Yang, P.K.; Malhotra, B.D.; Chauhan, N.; Jain, U. Fabrication of a Molecularly Imprinted Nano-Interface-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of CagA Virulence Factors of H. Pylori. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, K.; Chauhan, N.; Malhotra, B.D.; Jain, U. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Detection of VacA Virulence Factor of H. Pylori Causing Gastric Cancer. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, N.E.; Theethira, T.G.; Leffler, D.A. The Present and the Future in the Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 3, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.P. Review Article: Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease: A Perspective on Current and Future Approaches. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, S18–S37. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.P.; Verma, R.; Schumann, M. A Look Into the Future: Are We Ready for an Approved Therapy in Celiac Disease? Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi, A.; Fattahi, N.; Ramazani, A. Biomarkers: Promising and Valuable Tools towards Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Covid-19 and Other Diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonaitis, P.; Kiudelis, V.; Streleckiene, G.; Gedgaudas, R.; Skieceviciene, J.; Kupcinskas, J. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Gastrointestinal Diseases. Dig. Dis. 2021, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Ghasemian, M.; Maniati, M.; Khatami, S.H.; Jamali, N.; Taheri-Anganeh, M. Gastrointestinal Disorder Biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 530, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.J.; Mitchell, E.P. Carcinoembryonic Antigen in the Staging and Follow-up of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2005, 23, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, W.; Lv, Y.; Shan, L.; Xu, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qi, H. Postoperative Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Levels Predict Outcomes after Resection of Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Normal Preoperative CEA Levels. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiernan, J.P.; Perry, S.L.; Verghese, E.T.; West, N.P.; Yeluri, S.; Jayne, D.G.; Hughes, T.A. Carcinoembryonic Antigen Is the Preferred Biomarker for in Vivo Colorectal Cancer Targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Foerster, F.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Llovet, J.M.; Qin, S.; Schelman, W.R.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Abada, P.B.; Sherman, M.; et al. Biology and Significance of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, H.; Ali, M.J.; Khan, I.W.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Tan-Yeung Lau, D.; Susheela, A.T. Update on the Applications and Limitations of Alpha-Fetoprotein for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, B.K.; Seo, J.H.; Choi, J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, C.K.; Chung, J.B.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.W. Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Elevation without Evidence of Malignant or Pancreatobiliary Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsen, A.; Barbara, M.; Rosenkranz, L. Dilemma of Elevated CA 19-9 in Biliary Pathology. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 862–867. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.R.; Machado, M.V. New Insights about Albumin and Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2012; Vincent, J.-L., Ed.; Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 2012, ISBN 978-3-642-25715-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jagdish, R.K.; Singh Maras, J.; Sarin, S.K. Albumin in Advanced Liver Diseases: The Good and Bad of a Drug! Hepatology 2021, 74, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, N.; Higuchi, T.; Miyazu, T.; Tamura, S.; Tani, S.; Yamade, M.; Iwaizumi, M.; Hamaya, Y.; Osawa, S.; Furuta, T.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Is Superior to Fecal Biomarkers for Evaluating Colon-Wide Active Inflammation in Ulcerative Colitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, O.Z.; Bhayana, V. Lipase or Amylase for the Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis? Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-J.; Choi, Y.-K.; Im, H.-S.; Yarimaga, O.; Yoon, E.; Kim, H.-S. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) Detection Techniques. Sensors 2006, 6, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; Pine, S.R.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Caporaso, N.; Harris, C.C. A Combined Prognostic Serum Interleukin-8 and Interleukin-6 Classifier for Stage 1 Lung Cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and Tumor Progression: Signaling Pathways and Targeted Intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pastrez, P.R.A.; Barbosa, A.M.; Mariano, V.S.; Causin, R.L.; Castro, A.G.; Torrado, E.; Longatto-Filho, A. Interleukin-8 and Interleukin-6 Are Biomarkers of Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; Niu, P.Q.; Li, X.F.; Sun, M.M.; Wei, W.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zheng, J.Y. Differential cytokine expression in gastric tissues highlights helicobacter pylori’s role in gastritis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, B.W.; Bickston, S.J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Antibody for Maintenace of Remission in Crohn’s Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnini, C.; Cominelli, F. Tumor Necrosis Factor’s Pathway in Crohn’s Disease: Potential for Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farasati Far, B.; Vakili, K.; Fathi, M.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Bhia, M.; Naimi- Jamal, M.R. The Role of MicroRNA-21 (MiR-21) in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Prognosis of Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Review. Life Sci. 2023, 316, 121340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalajahi, H.G.; Yari, A.H.; Amini, M.; Catal, T.; Ahmadpour Youshanlui, M.; Pourbagherian, O.; Zhmurov, C.S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Therapeutic Effect of MicroRNA-21 on Differentially Expressed Hub Genes in Gastric Cancer Based on Systems Biology. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kacimi, S.E.O.; Nguyen, T.L.; Suman, K.H.; Lemus-Martin, R.; Saleem, H.; Do, D.N. MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker. Biology 2021, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhu, A.; Wang, X.W. MicroRNAs and Gastroenterological Cancers. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2011, 8, e95–e102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerke, M.B.; Jansen, C.S.; Bilen, M.A. Circulating Tumor DNA in Genitourinary Cancers: Detection, Prognostics, and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2024, 16, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alese, O.B.; Cook, N.; Ortega-Franco, A.; Ulanja, M.B.; Tan, L.; Tie, J. Circulating Tumor DNA: An Emerging Tool in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moati, E.; Taly, V.; Garinet, S.; Didelot, A.; Taieb, J.; Laurent-puig, P.; Zaanan, A. Role of Circulating Tumor Dna in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Zhang, L. The Emerging Role of Lactate in Tumor Microenvironment and Its Clinical Relevance. Cancer Lett. 2024, 590, 216837. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Tomás, R.; Pérez-Guillén, I. Lactate in the Tumor Microenvironment: An Essential Molecule in Cancer Progression and Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz-López, K.G.; Castro-Muñoz, L.J.; Reyes-Hernández, D.O.; García-Carrancá, A.; Manzo-Merino, J. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra Ruiz, A.R.; Crespo, J.; López Martínez, R.M.; Iruzubieta, P.; Casals Mercadal, G.; Lalana Garcés, M.; Lavin, B.; Morales Ruiz, M. Measurement and Clinical Usefulness of Bilirubin in Liver Disease. Adv. Lab. Med. 2021, 2, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.A.; Nisar, S.; Maacha, S.; Carneiro-Lobo, T.C.; Akhtar, S.; Siveen, K.S.; Wani, N.A.; Rizwan, A.; Bagga, P.; Singh, M.; et al. Cytokine-Chemokine Network Driven Metastasis in Esophageal Cancer; Promising Avenue for Targeted Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diesch, T.; Filippi, C.; Fritschi, N.; Filippi, A.; Ritz, N. Cytokines in Saliva as Biomarkers of Oral and Systemic Oncological or Infectious Diseases: A Systematic Review. Cytokine 2021, 143, 155506. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, K.; Higuchi, R.; Iwane, T.; Iida, A. The Association of Low Serum Salivary and Pancreatic Amylases with the Increased Use of Lipids as an Energy Source in Non-Obese Healthy Women. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, K.R.; Junjappa, R.; Handigund, M.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. The Imprint of Salivary Secretion in Autoimmune Disorders and Related Pathological Conditions. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 376–390. [Google Scholar]
- Peyrot des Gachons, C.; Breslin, P.A.S. Salivary Amylase: Digestion and Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.; Sekar, R.; Priya, M.D.L.; Varma, S.R.; Karobari, M.I. A New Perspective on Diagnostic Strategies Concerning the Potential of Saliva-Based MiRNA Signatures in Oral Cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 19, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Săsăran, M.O.; Bănescu, C. Role of Salivary MiRNAs in the Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Mini-Review of Available Evidence. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1228482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga Pathirana, W.W.; Paul Chubb, S.; Gillett, M.J.; Vasikaran, S.D. Faecal Calprotectin. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2018, 39, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bayo Calero, J.; Castaño López, M.A.; Casado Monge, P.G.; Díaz Portillo, J.; Bejarano García, A.; Navarro Roldán, F. Analysis of Blood Markers for Early Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Selby, K. Fecal Immunochemical Test: The World’s Colorectal Cancer Screening Test. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 30, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syrjänen, K.; Eskelinen, M.; Meklin, J.; Hendolin, P.; Eskelinen, M.; Suovaniemi, O. Colorectal Cancer Screening by Fecal Immunochemical Tests (FIT): Considerations on Sampling and Markers (Hb and Hb/Hp Complex) of Fecal Occult Blood (FOB). Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Molina, R.; Suárez, M.; Martínez, R.; Chilet, M.; Bauça, J.M.; Mateo, J. Utility of Stool-Based Tests for Colorectal Cancer Detection: A Comprehensive Review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi Abdolmaleky, H.; Zhou, J.R. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Anjankar, A. Alterations of Gastrointestinal Microbe Composition in Various Human Diseases and Its Significance in the Early Diagnosis of Diseases. Cureus 2024, 16, e52435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ming, H.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, H. DNA Methylation Analysis of the SDC2, SEPT9 and VIM Genes in Fecal DNA for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Miao, J.; Xiong, S.; Fei, S.; et al. Aberrant DNA Methylation of SEPT9 and SDC2 in Stool Specimens as an Integrated Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer Early Detection. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Tang, W.; Zhou, L.; Xie, X.; Qu, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, T.; Dai, Y.; et al. DNA Methylation Biomarkers in Stool for Early Screening of Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5264–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Sumii, K.; Kawano, M.; Kido, T.; Nojima, K.; Sumii, M.; Haruma, K.; Yoshihara, M.; Chayama, K. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Increases Serum Nitrate and Nitrite More Prominently than Serum Pepsinogens. Helicobacter 2002, 7, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayiannis, I.; Martinez-Gonzalez, B.; Kontizas, E.; Kokkota, A.V.; Petraki, K.; Mentis, A.; Kollia, P.; Sgouras, D.N. Induction of MMP-3 and MMP-9 Expression during Helicobacter Pylori Infection via MAPK Signaling Pathways. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, T.; Dagher, A.; Sachdev, M.; Ebi, M.; Yamada, T.; Yamada, T.; Joh, T.; Moses, M.A. Urinary ADAM12 and MMP-9/NGAL Complex Detect the Presence of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, A.; Chandrapalan, S.; Ahmed, M.; Arasaradnam, R.P. The Diagnostic Utility of Volatile Organic Compounds in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2024, 18, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Liere, E.L.S.A.; van Dijk, L.J.; Bosch, S.; Vermeulen, L.; Heymans, M.W.; Burchell, G.L.; de Meij, T.G.J.; Ramsoekh, D.; de Boer, N.K.H. Urinary Volatile Organic Compounds for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 186, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernia, F.; Valvano, M.; Fabiani, S.; Stefanelli, G.; Longo, S.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Are Volatile Organic Compounds Accurate Markers in the Assessment of Colorectal Cancer and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? A Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.A.R.; Gaiteiro, C.; Santos, M.; Santos, L.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Lima, L. MicroRNA Biomarkers as Promising Tools for Early Colorectal Cancer Screening—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ždralević, M.; Radović, A.; Raonić, J.; Popovic, N.; Klisic, A.; Vučković, L. Advances in MicroRNAs as Emerging Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, A.I.; Batool, W.; Ahmed, A.; Zafar, S.; Patel, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Zia, U.; Aminpoor, H.; Kumar, V.; Tejwaney, U. Role of MicroRNA in Colorectal Carcinoma (CRC): A Narrative Review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Fleshman, J.; Richard Boland, C.; Goel, A. MicroRNAs as Potential Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, D.D.R.; Ferreira, W.A.S.; Barros, M.B.L.; Araújo, M.D.; Rodrigues-Antunes, S.; Borges, B.D.N. Perspectives on New Biomarkers in Gastric Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Applications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11574–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Jin, H.; Song, B.; Jing, T.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, Y.I.; Mei, S. Fabrication of a Selective and Sensitive Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer/Acetylene Black for the Determination of Azithromycin in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Samples. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Food Contaminants Determination. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116830. [Google Scholar]
- Ryma, M.; Tylek, T.; Liebscher, J.; Blum, C.; Fernandez, R.; Böhm, C.; Kastenmüller, W.; Gasteiger, G.; Groll, J. Translation of Collagen Ultrastructure to Biomaterial Fabrication for Material-Independent but Highly Efficient Topographic Immunomodulation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mei, R.; Fu, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, L. Label-Free SERS Detection of Raman-Inactive Protein Biomarkers by Raman Reporter Indicator: Toward Ultrasensitivity and Universality. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, Y.; Mei, R.; Fu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Chiral Molecular Imprinting-Based SERS Detection Strategy for Absolute Enantiomeric Discrimination. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, S.; Piletsky, S.S.; Yesilkaya, H.; Gazioglu, O.; Habtom, M.; Canfarotta, F.; Piletska, E.; Spivey, A.C.; Aboagye, E.O.; Piletsky, S.A. Assessing the In Vivo Biocompatibility of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Shanan, N.; Eissa, G.; Mizaikoff, B.; Gohary, N.A. El In Vivo Application of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in Rheumatoid Arthritis Rat Model. J. Drug Target. 2023, 31, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kiguchi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Hayashi, S.; Akasaka, H.; Igarashi, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sasaki, R.; et al. In Vivo Stealthified Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels Incorporated with Gold Nanoparticles for Radiation Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6784–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz Hemed, N.; Leal-Ortiz, S.; Zhao, E.T.; Melosh, N.A. On-Demand, Reversible, Ultrasensitive Polymer Membrane Based on Molecular Imprinting Polymer. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 5632–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackers, G.; Putzeys, T.; Peeters, M.; Van de Cauter, L.; Cornelis, P.; Wübbenhorst, M.; Tack, J.; Troost, F.; Verhaert, N.; Doll, T.; et al. Towards a Catheter-Based Impedimetric Sensor for the Assessment of Intestinal Histamine Levels in IBS Patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158, 112152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Tan, L.; Yuan, J.B.; Qiao, R.F.; Wang, C.Z.; Yang, F.Q.; Zhou, L.D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Xia, Z.N.; Yuan, C.S. Extraction of Activated Epimedium Glycosides in Vivo and in Vitro by Using Bifunctional-Monomer Chitosan Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Identification by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Talanta 2020, 219, 121350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y. A High-Throughput Screening Strategy for Synthesizing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles Selectively Targeting Tumors. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2400290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, X.E.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Synchronous Measuring of Triptolide Changes in Rat Brain and Blood and Its Application to a Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in Normal and Alzheimer’s Disease Rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Song, H.; Tang, X.; Hao, Y.; Guan, Y.; Chong, T.; Hussain, S.; Gao, R. Unveiling a PH-Responsive Dual-Androgen-Blocking Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Enhanced Synergistic Therapy of Prostate Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 4348–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawad, D.; Stewart, E.; Officer, D.L.; Romeo, T.; Wagner, P.; Wagner, K.; Wallace, G.G. A Single Component Conducting Polymer Hydrogel as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Yang, D.; Chen, C.-R.; Tian, G.-Z.; Kim, D.-H. In Situ Polymerization of Conducting Polymers around Living Neural Cells: Cellular Effect Study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 213, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, C.; Zou, K.; Tu, L.; Yan, W.; Hou, X. Comparison of Non-Invasive Biomarkers Faecal BAFF, Calprotectin and FOBT in Discriminating IBS from IBD and Evaluation of Intestinal Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, E.; Corrigan, D.T.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Kim, R.S.; Song, L.; Rutledge, T.M.; Magee, D.M.; LaBaer, J.; Lowary, T.L.; et al. Mucosal and Systemic Antigen-Specific Antibody Responses Correlate with Protection against Active Tuberculosis in Nonhuman Primates. eBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, J.; Paulo-Mirasol, S.; Estrany, F.; Torras, J. Recent Progress in Biomedical Sensors Based on Conducting Polymer Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 1720–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y. Self-Assembled Polymers for Gastrointestinal Tract Targeted Delivery through the Oral Route: An Update. Polymers 2023, 15, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, G.B.V.S.; Yadav, A.K.; Mehlawat, N.; Jalandra, R.; Solanki, P.R.; Kumar, A. Gut Microbiota Derived Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Detection through Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kumar, N.; Chattopadhyay, S. ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTIVE “SMART” HYDROGELS FOR ON-DEMAND DRUG DELIVERY. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.W.; Chen, C.; Duan, S.; Yan, Y.; He, P.; He, X. Hydrogel-Based Soft Bioelectronics for Personalized Healthcare. Med-X 2024, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. A Nanostructured Conductive Hydrogels-Based Biosensor Platform for Human Metabolite Detection. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huyan, C.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Torun, H.; Mulvihill, D.; Xu, B.B.; Chen, F. Conductive Polymer Based Hydrogels and Their Application in Wearable Sensors: A Review. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2800–2823. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.B.; Yin, G.F.; Liao, X.M.; Gu, J.W. Conducting Polypyrrole in Tissue Engineering Applications. Front. Mater. Sci. 2014, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Oztekin, Y.; Ramanaviciene, A. Electrochemical Formation of Polypyrrole-Based Layer for Immunosensor Design. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, T.J.; Hudson, T.W.; Schmidt, C.E. Synthesis of a Novel, Biodegradable Electrically Conducting Polymer for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, Z.; Duffy, F.; Gomez, J.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Gastroparesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Conducting Polymers for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Charge Transfer and Biocompatibility Aspects in Conducting Polymer-Based Enzymatic Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubur Rahman, M.; Li, X.B.; Lopa, N.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.J. Electrochemical DNA Hybridization Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2015, 15, 3801–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A Brief Overview of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Highlighting Computational Design, Nano and Photo-Responsive Imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Petrov, P.D. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, G.; Sun, S.; Xu, P. Medical Applications and Prospects of Polylactic Acid Materials. iScience 2024, 27, 111512. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.R.G.; Conde, G.; Antonioli, M.L.; Dias, P.P.; Vasconcelos, R.O.; Taboga, S.R.; Canola, P.A.; Chinelatto, M.A.; Pereira, G.T.; Ferraz, G.C. Biocompatibility and Biodegradation of Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) and an Immiscible PLA/Poly(ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) Blend Compatibilized by Poly(ε-Caprolactone-b-Tetrahydrofuran) Implanted in Horses. Polym. J. 2020, 52, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Allahou, L.W.; Chang, J.; Williams, G.; Knowles, J.C.; Poma, A. Nanotechnology in Healthcare, and Its Safety and Environmental Risks. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
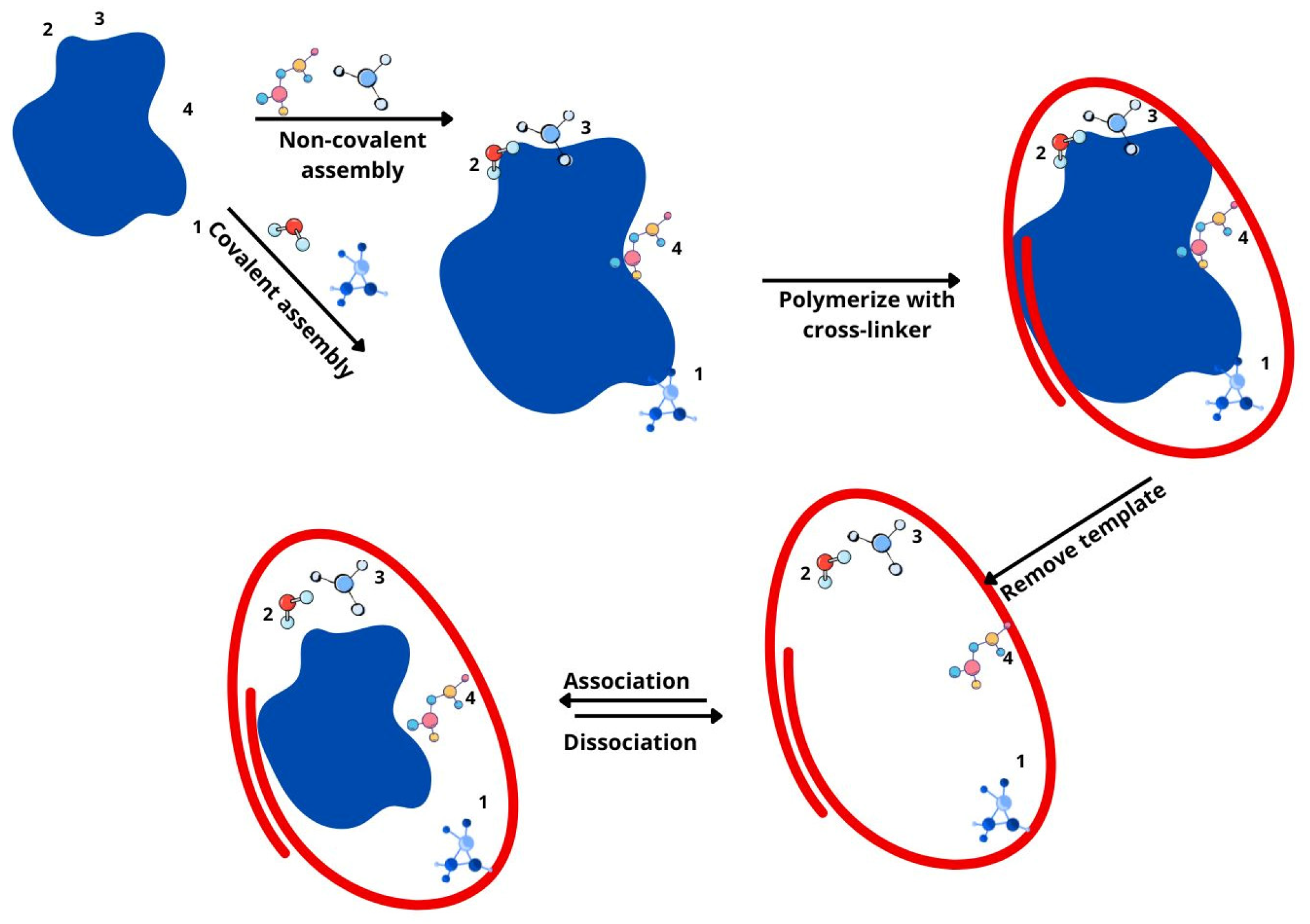
- Bărăian, A.I.; Iacob, B.C.; Bodoki, A.E.; Bodoki, E. In Vivo Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Drug Delivery: A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fluid | Biomolecules | Biomarkers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood-Based Biomarkers | Proteins | Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA): Commonly elevated in colorectal cancer. CA 19-9: Associated with pancreatic and biliary cancers. Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP): Used in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. C-Reactive Protein (CRP): Indicates inflammation in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Serum Albumin: Lower levels are often linked to liver disease. | [17,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] |
| Enzymes | Amylase and Lipase: Indicators of pancreatic inflammation (e.g., pancreatitis). Aspartate Transaminase (AST) and Alanine Transaminase (ALT): Reflect liver function. | [66,67] | |
| Cytokines | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α): Elevated in IBD and Crohn’s disease. Interleukins (e.g., IL-6, IL-8): Markers of inflammation and cancer progression. | [68,69,70,71,72,73] | |
| Nucleic Acids | Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA): Useful for detecting genetic mutations in GI cancers. MicroRNAs (e.g., miR-21): Associated with gastric and colorectal cancers. | [74,75,76,77,78,79,80] | |
| Metabolites | Bilirubin: Indicates liver function or obstruction in bile ducts. Lactate: Can reflect hypoxia or tumor metabolism in cancers. | [81,82,83,84] | |
| Saliva-Based Biomarkers | Proteins | Cytokines (e.g., IL-8): Indicators of oral and esophageal cancers or systemic inflammation. Amylase: Reflects salivary gland or pancreatic function. | [85,86,87,88,89] |
| DNA/RNA | MicroRNAs (e.g., miR-21): Associated with GI cancer detection. | [90,91] | |
| Stool-Based Biomarkers | Proteins | Fecal Calprotectin: A marker for IBD and colorectal cancer. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): Detects occult blood in stool, used in colorectal cancer screening. | [92,93,94,95,96] |
| DNA/RNA | Methylated DNA (e.g., SEPT9): Found in stool for colorectal cancer screening. Microbial DNA (e.g., alterations in gut microbiome composition): Associated with various GI diseases. | [22,97,98,99,100,101] | |
| Urine-Based Biomarkers | Proteins | Urinary Peptides (e.g., MMP-9): Linked to gastric cancer. Nitrites: May indicate infection (e.g., Helicobacter pylori). | [102,103,104,105] |
| Metabolites | Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Associated with colorectal cancer and GI inflammation. | [106,107,108] | |
| Genetic Material | Urinary MicroRNAs (e.g., miR-92a): Indicators of colorectal cancer. | [109,110,111,112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivaskiene, T.; Kaspute, G.; Ramanavicius, A.; Prentice, U. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Advanced Hydrogels as Tools for Gastrointestinal Diagnostics. Gels 2025, 11, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040269
Ivaskiene T, Kaspute G, Ramanavicius A, Prentice U. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Advanced Hydrogels as Tools for Gastrointestinal Diagnostics. Gels. 2025; 11(4):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040269
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvaskiene, Tatjana, Greta Kaspute, Arunas Ramanavicius, and Urte Prentice. 2025. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Advanced Hydrogels as Tools for Gastrointestinal Diagnostics" Gels 11, no. 4: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040269
APA StyleIvaskiene, T., Kaspute, G., Ramanavicius, A., & Prentice, U. (2025). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Advanced Hydrogels as Tools for Gastrointestinal Diagnostics. Gels, 11(4), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040269








